Latest Articles
Articles in press have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes/issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250164
Abstract:
The rapid expansion of rubber plantations has triggered multiple ecological and environmental effects, leading to surface warming through alterations in land surface energy balance and vegetation–atmosphere interactions. Based on multi-source satellite observations, a temperature response model, and the two-resistance mechanism (TRM) framework, the differences in land surface temperature (LST) between natural forests and rubber plantations in the Southeast Asia countries were systematically attributed. The results show that, compared with adjacent natural forests, rubber plantations exhibit an annual mean LST increase of approximately 0.63°C, presenting a consistently “warmer” signal throughout the year. The warming peaks in June and reaches its minimum in July. Mechanistic diagnosis indicates that the increase in aerodynamic resistance (ra) is the dominant driver of surface warming, accounting for more than 60% of the total contribution, which is substantially higher than that of radiative factors such as albedo (α), downward shortwave radiation (S), and downward longwave radiation (L↓). By suppressing latent heat flux and enhancing sensible heat transfer, increased ra elevates surface temperature. In contrast, L↓ exhibits a cooling effect in the attribution framework and jointly regulates surface temperature together with downward shortwave radiation and albedo. Furthermore, under dry and normal moisture conditions, temperature regulation is primarily controlled by ra, whereas under wet conditions, the influence of L↓ becomes more pronounced. These findings reveal the coupled feedback mechanisms among land-use practices, vegetation structure, and regional climate across multiple spatial scales and seasons. The redistribution of radiative and non-radiative fluxes alters surface energy balance and temperature differentials, providing methodological support and a scientific basis for developing region-specific, scenario-sensitive sustainable agricultural policies and land-based climate change mitigation strategies.
The rapid expansion of rubber plantations has triggered multiple ecological and environmental effects, leading to surface warming through alterations in land surface energy balance and vegetation–atmosphere interactions. Based on multi-source satellite observations, a temperature response model, and the two-resistance mechanism (TRM) framework, the differences in land surface temperature (LST) between natural forests and rubber plantations in the Southeast Asia countries were systematically attributed. The results show that, compared with adjacent natural forests, rubber plantations exhibit an annual mean LST increase of approximately 0.63°C, presenting a consistently “warmer” signal throughout the year. The warming peaks in June and reaches its minimum in July. Mechanistic diagnosis indicates that the increase in aerodynamic resistance (ra) is the dominant driver of surface warming, accounting for more than 60% of the total contribution, which is substantially higher than that of radiative factors such as albedo (α), downward shortwave radiation (S), and downward longwave radiation (L↓). By suppressing latent heat flux and enhancing sensible heat transfer, increased ra elevates surface temperature. In contrast, L↓ exhibits a cooling effect in the attribution framework and jointly regulates surface temperature together with downward shortwave radiation and albedo. Furthermore, under dry and normal moisture conditions, temperature regulation is primarily controlled by ra, whereas under wet conditions, the influence of L↓ becomes more pronounced. These findings reveal the coupled feedback mechanisms among land-use practices, vegetation structure, and regional climate across multiple spatial scales and seasons. The redistribution of radiative and non-radiative fluxes alters surface energy balance and temperature differentials, providing methodological support and a scientific basis for developing region-specific, scenario-sensitive sustainable agricultural policies and land-based climate change mitigation strategies.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250122
Abstract:
In recent years, due to the impact of human activities such as large-scale logging and slash-and-burn cultivation, the area of tropical primeval forests has continued to decrease, gradually forming a series of tropical secondary forests at different stages of recovery. However, there is still a lack of clear understanding of the evolution of soil water holding capacity of secondary forests and its dominant regulatory factors at different recovery stages. In this context, soil physical and chemical properties and water-holding performance of tropical secondary forests at three restoration stages (early, middle and late) in Hainan were determined to systematically analyze the effects of different restoration stages on soil water-holding capacity and its internal regulatory mechanism. The results showed that with the progress of restoration, the soil water holding capacity of the (0~60 cm) soil layer increased significantly, and that the natural water content, saturated water holding capacity, capillary water holding capacity and field water holding capacity of the (0~10 cm) soil layer gave a gradual upward trend. At the same time, the total porosity and capillary porosity of the (0~10 cm) soil layer at the late stage of restoration were significantly higher than those at the early and middle stages (P<0.05), while the soil bulk density of the (0~60 cm) soil layer decreased significantly at the late stage of restoration. Soil water holding capacity was positively correlated with total porosity, capillary porosity, non-capillary porosity and organic matter content, and negatively correlated with bulk density. The influence of total porosity was the most significant, with a contribution rate of 26.95%, followed by capillary porosity (23.02%) and bulk density (21.39%). Non-capillary porosity and organic matter also had a certain effect, while the influence of soil particle composition was relatively weak. In conclusion, the restoration of secondary forests significantly enhanced the soil water-holding capacity by improving the pore structure and increasing the content of organic matter, and the effect was most significant at the late stage of restoration.
In recent years, due to the impact of human activities such as large-scale logging and slash-and-burn cultivation, the area of tropical primeval forests has continued to decrease, gradually forming a series of tropical secondary forests at different stages of recovery. However, there is still a lack of clear understanding of the evolution of soil water holding capacity of secondary forests and its dominant regulatory factors at different recovery stages. In this context, soil physical and chemical properties and water-holding performance of tropical secondary forests at three restoration stages (early, middle and late) in Hainan were determined to systematically analyze the effects of different restoration stages on soil water-holding capacity and its internal regulatory mechanism. The results showed that with the progress of restoration, the soil water holding capacity of the (0~60 cm) soil layer increased significantly, and that the natural water content, saturated water holding capacity, capillary water holding capacity and field water holding capacity of the (0~10 cm) soil layer gave a gradual upward trend. At the same time, the total porosity and capillary porosity of the (0~10 cm) soil layer at the late stage of restoration were significantly higher than those at the early and middle stages (P<0.05), while the soil bulk density of the (0~60 cm) soil layer decreased significantly at the late stage of restoration. Soil water holding capacity was positively correlated with total porosity, capillary porosity, non-capillary porosity and organic matter content, and negatively correlated with bulk density. The influence of total porosity was the most significant, with a contribution rate of 26.95%, followed by capillary porosity (23.02%) and bulk density (21.39%). Non-capillary porosity and organic matter also had a certain effect, while the influence of soil particle composition was relatively weak. In conclusion, the restoration of secondary forests significantly enhanced the soil water-holding capacity by improving the pore structure and increasing the content of organic matter, and the effect was most significant at the late stage of restoration.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250121
Abstract:
To address the issue of "white pollution" caused by conventional polyethylene mulch films in open-field watermelon production in tropical regions, fully biodegradable mulch films capable of replacing PE films were screened. Nine biodegradable mulch films made from polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate (PBAT), lignin, polylactic acid (PLA), polypropylene carbonate (PPC) were employed to mulch the watermelon open fields with conventional PE film as the control (CK) to investigate their application effects on soil water-heat effects, watermelon growth and yield quality, and film biodegradation characteristics. The results indicated that the tested biodegradable films showed no significant difference from CK in terms of heat retention, soil moisture conservation, and promotion of watermelon growth. Of the treatments, Treatment F6 (PBAT + PPC, 0.012 mm) demonstrated the highest fruit edge sugar content (9.53%). Treatment F9 (PBAT+PLA, 0.012 mm) exhibited stable individual melon weight (6.80 kg) and yield per unit area (136.04 t·hm−2), slightly outperforming the CK. Mulch degradation observations revealed that among all the fully biodegradable films, Treatment F9 exhibited the slowest degradation rate, second only to the CK. Regarding costs, the total cost per mu for Treatments F6 and F9 (approximately ¥275) increased by about 4.6% compared to CK (approximately ¥263). In summary, the 0.012 mm thick films in Treatments F6 and F9 demonstrate promising potential for replacing conventional PE films in open-field watermelon production in tropical regions. Their degradation cycles align well with the watermelon growth period, maintaining stable soil conditions at the critical growth stages.
To address the issue of "white pollution" caused by conventional polyethylene mulch films in open-field watermelon production in tropical regions, fully biodegradable mulch films capable of replacing PE films were screened. Nine biodegradable mulch films made from polybutylene adipate-co-terephthalate (PBAT), lignin, polylactic acid (PLA), polypropylene carbonate (PPC) were employed to mulch the watermelon open fields with conventional PE film as the control (CK) to investigate their application effects on soil water-heat effects, watermelon growth and yield quality, and film biodegradation characteristics. The results indicated that the tested biodegradable films showed no significant difference from CK in terms of heat retention, soil moisture conservation, and promotion of watermelon growth. Of the treatments, Treatment F6 (PBAT + PPC, 0.012 mm) demonstrated the highest fruit edge sugar content (9.53%). Treatment F9 (PBAT+PLA, 0.012 mm) exhibited stable individual melon weight (6.80 kg) and yield per unit area (136.04 t·hm−2), slightly outperforming the CK. Mulch degradation observations revealed that among all the fully biodegradable films, Treatment F9 exhibited the slowest degradation rate, second only to the CK. Regarding costs, the total cost per mu for Treatments F6 and F9 (approximately ¥275) increased by about 4.6% compared to CK (approximately ¥263). In summary, the 0.012 mm thick films in Treatments F6 and F9 demonstrate promising potential for replacing conventional PE films in open-field watermelon production in tropical regions. Their degradation cycles align well with the watermelon growth period, maintaining stable soil conditions at the critical growth stages.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250135
Abstract:
As the dominant groups in saline ecosystems,halophytes have been systematically studied in their salt tolerance mechanisms at the physiological, biochemical, molecular and metabolomic levels. In recent years, the issue of combined soil heavy metal-saline-alkali pollution has become increasingly severe, drawing significant attention to halophytes due to their cross-tolerance to multiple stresses. Research indicates that halophytes precisely regulate heavy metal uptake, compartmentalization, and efflux through specific ion transport systems such as HMA. They achieve synergistic detoxification via antioxidant defenses and chelation mechanisms (e.g., plant chelating peptides, metallothionein). It is interesting to note that salinity and heavy metal stresses share epigenetic regulatory mechanisms—including MAPK signaling cascades, ABA/JA hormone pathways, thereby establishing the molecular basis for cross-tolerance. Therefore, halophytes are not only adapted to high-salinity environments but also possess the capacity to accumulate or stabilise heavy metals in soil, presenting a green solution for concurrently addressing salinisation and heavy metal contamination. This paper systematically reviews the mechanisms underlying the cross-tolerance traits of halophytes. Drawing upon representative case studies, it examines their remediation potential from multiple perspectives, including restoration principles and molecular breeding improvement strategies, aiming to provide theoretical foundations for the green and sustainable management of combined saline-alkali and heavy metal pollution.
As the dominant groups in saline ecosystems,halophytes have been systematically studied in their salt tolerance mechanisms at the physiological, biochemical, molecular and metabolomic levels. In recent years, the issue of combined soil heavy metal-saline-alkali pollution has become increasingly severe, drawing significant attention to halophytes due to their cross-tolerance to multiple stresses. Research indicates that halophytes precisely regulate heavy metal uptake, compartmentalization, and efflux through specific ion transport systems such as HMA. They achieve synergistic detoxification via antioxidant defenses and chelation mechanisms (e.g., plant chelating peptides, metallothionein). It is interesting to note that salinity and heavy metal stresses share epigenetic regulatory mechanisms—including MAPK signaling cascades, ABA/JA hormone pathways, thereby establishing the molecular basis for cross-tolerance. Therefore, halophytes are not only adapted to high-salinity environments but also possess the capacity to accumulate or stabilise heavy metals in soil, presenting a green solution for concurrently addressing salinisation and heavy metal contamination. This paper systematically reviews the mechanisms underlying the cross-tolerance traits of halophytes. Drawing upon representative case studies, it examines their remediation potential from multiple perspectives, including restoration principles and molecular breeding improvement strategies, aiming to provide theoretical foundations for the green and sustainable management of combined saline-alkali and heavy metal pollution.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20260028
Abstract:
To establish an accurate identification and evaluation system for bitter melon peel color based on image analysis and deep learning, peel color was used as a typical continuous phenotypic trait to develop an integrated system combining color standardization and sequential deep learning. A traditional machine learning model was constructed using Lab color mean features, yielding a baseline classification accuracy of 73.68%. By optimizing the classification criteria through K-means clustering and CIE1976 ΔE color difference quantification, the accuracy was improved to 76.09%. Furthermore, a color sequence dataset was established, and convolutional neural network (CNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) models were compared. The results demonstrated that the LSTM model effectively captured the dependencies in color sequences, achieving a maximum classification accuracy of 82.11% and a macro-average AUC of 0.9645. These results indicate that the combination of color standardization and sequential deep learning can effectively address the classification challenges caused by continuous color phenotypes. The proposed method provides a reliable theoretical basis and technical reference for high-throughput and accurate identification of peel color in crop germplasm resources.
To establish an accurate identification and evaluation system for bitter melon peel color based on image analysis and deep learning, peel color was used as a typical continuous phenotypic trait to develop an integrated system combining color standardization and sequential deep learning. A traditional machine learning model was constructed using Lab color mean features, yielding a baseline classification accuracy of 73.68%. By optimizing the classification criteria through K-means clustering and CIE1976 ΔE color difference quantification, the accuracy was improved to 76.09%. Furthermore, a color sequence dataset was established, and convolutional neural network (CNN) and long short-term memory (LSTM) models were compared. The results demonstrated that the LSTM model effectively captured the dependencies in color sequences, achieving a maximum classification accuracy of 82.11% and a macro-average AUC of 0.9645. These results indicate that the combination of color standardization and sequential deep learning can effectively address the classification challenges caused by continuous color phenotypes. The proposed method provides a reliable theoretical basis and technical reference for high-throughput and accurate identification of peel color in crop germplasm resources.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250207
Abstract:
A method based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS was established for the systematic characterization and comparison of metabolic profiles and in vitro antioxidant activities in the aerial parts of Houttuynia cordata under different harvest methods (first and second crops in July, and first crop in October). Untargeted metabolomics integrated with multivariate statistical analysis was employed to deeply investigate the dynamic regulatory influence of harvesting approaches on the accumulation of secondary metabolites. Moreover, the ABTS radical scavenging assay was applied to validate antioxidant capacity and to explore its correlation with compositional characteristics. The results showed that 23 differential metabolites were identified in the samples collected by different harvest methods. Among all the harvest methods, Method 1 yielded the highest number of identified metabolites (53), followed by Method 2 (51) and Method 3 (49), respectively. More importantly, Houttuynoside A, Houttuynoid C, Afzelin, Vitexin and Quercetin were identified as key biomarkers associated with antioxidant capacity, among which Quercetin had the highest correlation with antioxidant capacity.
A method based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS was established for the systematic characterization and comparison of metabolic profiles and in vitro antioxidant activities in the aerial parts of Houttuynia cordata under different harvest methods (first and second crops in July, and first crop in October). Untargeted metabolomics integrated with multivariate statistical analysis was employed to deeply investigate the dynamic regulatory influence of harvesting approaches on the accumulation of secondary metabolites. Moreover, the ABTS radical scavenging assay was applied to validate antioxidant capacity and to explore its correlation with compositional characteristics. The results showed that 23 differential metabolites were identified in the samples collected by different harvest methods. Among all the harvest methods, Method 1 yielded the highest number of identified metabolites (53), followed by Method 2 (51) and Method 3 (49), respectively. More importantly, Houttuynoside A, Houttuynoid C, Afzelin, Vitexin and Quercetin were identified as key biomarkers associated with antioxidant capacity, among which Quercetin had the highest correlation with antioxidant capacity.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240134
Abstract:
In order to explore the effect of mineral nutrient elements on fruit quality and screen the main mineral element factors affecting fruit quality, fruit of durian (Durio zibethinus Murr) Jinzhen planted in Hainan Province were selected for correlation and path coefficient analysis of the external morphology and internal quality indexes of the fruit as well as 11 mineral elements. The correlation analysis showed that there was a significantly negative correlation between soluble solids content and sulfur (S) content. The total acid content was significantly positively correlated with calcium (C) and boron (B) contents. There was a significantly positive correlation between vitamin C content and magnesium (Mg) and S contents. There was a significantly negative correlation between sugar-acid ratio and B content. The solid-acid ratio was significantly negatively correlated with Ca and B contents. The path analysis showed that there were some differences in the effects of mineral elements on fruit quality indexes. The main elements influencing soluble solids content were nitrogen (N), Mg, zinc (Zn) and manganese (Mn). The main factors influencing soluble sugar content were B, Mn, Zn and N, and the main elements affecting the total acid content of the fruit were potassium (K), N, Mg and Zn. The main elements affecting the content of vitamin C were S, iron (Fe), Mg and Zn. The main elements affecting the ratio of sugar to acid are K, Zn, Mn and B, and the main elements influencing solid acid ratio were Mg, Zn, Fe and Mn. In summary, K, N, Ca, Mg, Zn and B are the main elements affecting the quality of the durian fruit, and are the comprehensive results of the synergistic regulation of various mineral elements. Considering the local soil and fruit nutrient content in Hainan, the fruit yield and quality can be improved through application of K, Mg, Zn and B fertilizers at a slightly higher rate and a coordinated ratio.
In order to explore the effect of mineral nutrient elements on fruit quality and screen the main mineral element factors affecting fruit quality, fruit of durian (Durio zibethinus Murr) Jinzhen planted in Hainan Province were selected for correlation and path coefficient analysis of the external morphology and internal quality indexes of the fruit as well as 11 mineral elements. The correlation analysis showed that there was a significantly negative correlation between soluble solids content and sulfur (S) content. The total acid content was significantly positively correlated with calcium (C) and boron (B) contents. There was a significantly positive correlation between vitamin C content and magnesium (Mg) and S contents. There was a significantly negative correlation between sugar-acid ratio and B content. The solid-acid ratio was significantly negatively correlated with Ca and B contents. The path analysis showed that there were some differences in the effects of mineral elements on fruit quality indexes. The main elements influencing soluble solids content were nitrogen (N), Mg, zinc (Zn) and manganese (Mn). The main factors influencing soluble sugar content were B, Mn, Zn and N, and the main elements affecting the total acid content of the fruit were potassium (K), N, Mg and Zn. The main elements affecting the content of vitamin C were S, iron (Fe), Mg and Zn. The main elements affecting the ratio of sugar to acid are K, Zn, Mn and B, and the main elements influencing solid acid ratio were Mg, Zn, Fe and Mn. In summary, K, N, Ca, Mg, Zn and B are the main elements affecting the quality of the durian fruit, and are the comprehensive results of the synergistic regulation of various mineral elements. Considering the local soil and fruit nutrient content in Hainan, the fruit yield and quality can be improved through application of K, Mg, Zn and B fertilizers at a slightly higher rate and a coordinated ratio.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240140
Abstract:
Solanum lycopersicum is a model plant for research in genetics and molecular biology. Recently selection of tomato internal reference genes has been reported but with less types of exogenous hormones used for treatment. An attempt was hence made to select internal reference genes with stable expression in different tissues of tomato and under treatment with plant hormones. DANJ, EF-1α, ACT, UBI, APT, CAC, TIP41 and RPL8 were used as candidate internal reference genes, and selected under the 8 experimental conditions: exogenous hormone treatment with auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, cytokinin, salicylic acid, brassinolide and ethylene and various plant parts. The stability of the candidate reference genes was comprehensively evaluated using algorithms such as geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper, Delta CT and RefFinder. The stability of the reference genes was validated using the auxin-responsive gene SlGH3.4. The results showed that APT is the most stable reference gene expressed in auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, brassinosteroid treatment and various plant parts, that UBI is the most stable reference gene expressed in all samples under cytokinin and salicylic acid treatment, and that TIP41 is the most stable reference gene expressed under ethylene treatment. Finally, when APT, which has a relatively stable comprehensive ranking, was used as an internal reference gene, it was found that the expression level of SlGH3.4 gene showed a similar trend under IAA treatment conditions, while the less stable RPL8 gene failed to accurately correct the expression level of the target gene. All these results may provide theoretical support for the analysis of gene expression networks and molecular regulatory mechanisms in the response of tomato to exogenous hormone treatment.
Solanum lycopersicum is a model plant for research in genetics and molecular biology. Recently selection of tomato internal reference genes has been reported but with less types of exogenous hormones used for treatment. An attempt was hence made to select internal reference genes with stable expression in different tissues of tomato and under treatment with plant hormones. DANJ, EF-1α, ACT, UBI, APT, CAC, TIP41 and RPL8 were used as candidate internal reference genes, and selected under the 8 experimental conditions: exogenous hormone treatment with auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, cytokinin, salicylic acid, brassinolide and ethylene and various plant parts. The stability of the candidate reference genes was comprehensively evaluated using algorithms such as geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper, Delta CT and RefFinder. The stability of the reference genes was validated using the auxin-responsive gene SlGH3.4. The results showed that APT is the most stable reference gene expressed in auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, brassinosteroid treatment and various plant parts, that UBI is the most stable reference gene expressed in all samples under cytokinin and salicylic acid treatment, and that TIP41 is the most stable reference gene expressed under ethylene treatment. Finally, when APT, which has a relatively stable comprehensive ranking, was used as an internal reference gene, it was found that the expression level of SlGH3.4 gene showed a similar trend under IAA treatment conditions, while the less stable RPL8 gene failed to accurately correct the expression level of the target gene. All these results may provide theoretical support for the analysis of gene expression networks and molecular regulatory mechanisms in the response of tomato to exogenous hormone treatment.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250199
Abstract:
Abiu (Pouteria caimito), an evergreen tree belonging to the genus Pouteria of the Sapotaceae family, boasts high cultivation benefits. However, severe fruit drop under natural conditions significantly undermines its economic value. This study investigated the fruit set characteristics of Abiu cultivars including ‘BaJin’, ‘ShengDa 1’,‘XiongZan’, ‘JiuDa’and ‘DongMi’. The results showed that the mature fruits were mostly borne on the middle and basal parts of the branches, with 1–2 mature fruits per branch on average. Based on these fruit set characteristics, thinning treatments were conducted on the "BaiJin" and "DongMi" cultivars, setting three fruit retention groups: 3 fruits per branch (T3), 2 fruits per branch (T2), and 1 fruit per branch (T1). The effects of fruit thinning on fruit set, fruit development and quality were comprehensively evaluated by determining indicators such as fruit-bearing branch rate, number of mature fruits, fruit transverse and longitudinal diameters, fruit shape index, single fruit weight and fruit quality in different groups. The results indicated that fruit thinning could effectively reduce fruit drop in Abiu. Moreover, the fruit-bearing branch rate and number of mature fruits in the T1 group were significantly higher than those in the T2 and T3 groups. Dynamic measurements of fruit transverse and longitudinal diameters revealed that fruit thinning promoted fruit development; the single fruit weights of "BaiJin" and "DongMi" in the T2 and T1 groups were significantly higher than those in the T3 group. In addition, compared with the T3 group, the soluble solids content and sugar-acid ratio of "BaiJin" increased by 2.99% and 2.7%, respectively, while those of ‘DongMi’ increased by 2.36% and 3.35, respectively, in the T2 group. In conclusion, retaining 1 fruit per branch (T1) through thinning can significantly increase the fruit-bearing branch rate and number of mature fruits, reduce fruit drop, effectively promote fruit development and improve fruit quality, which has important application value in the production of Abiu.
Abiu (Pouteria caimito), an evergreen tree belonging to the genus Pouteria of the Sapotaceae family, boasts high cultivation benefits. However, severe fruit drop under natural conditions significantly undermines its economic value. This study investigated the fruit set characteristics of Abiu cultivars including ‘BaJin’, ‘ShengDa 1’,‘XiongZan’, ‘JiuDa’and ‘DongMi’. The results showed that the mature fruits were mostly borne on the middle and basal parts of the branches, with 1–2 mature fruits per branch on average. Based on these fruit set characteristics, thinning treatments were conducted on the "BaiJin" and "DongMi" cultivars, setting three fruit retention groups: 3 fruits per branch (T3), 2 fruits per branch (T2), and 1 fruit per branch (T1). The effects of fruit thinning on fruit set, fruit development and quality were comprehensively evaluated by determining indicators such as fruit-bearing branch rate, number of mature fruits, fruit transverse and longitudinal diameters, fruit shape index, single fruit weight and fruit quality in different groups. The results indicated that fruit thinning could effectively reduce fruit drop in Abiu. Moreover, the fruit-bearing branch rate and number of mature fruits in the T1 group were significantly higher than those in the T2 and T3 groups. Dynamic measurements of fruit transverse and longitudinal diameters revealed that fruit thinning promoted fruit development; the single fruit weights of "BaiJin" and "DongMi" in the T2 and T1 groups were significantly higher than those in the T3 group. In addition, compared with the T3 group, the soluble solids content and sugar-acid ratio of "BaiJin" increased by 2.99% and 2.7%, respectively, while those of ‘DongMi’ increased by 2.36% and 3.35, respectively, in the T2 group. In conclusion, retaining 1 fruit per branch (T1) through thinning can significantly increase the fruit-bearing branch rate and number of mature fruits, reduce fruit drop, effectively promote fruit development and improve fruit quality, which has important application value in the production of Abiu.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240185
Abstract:
To clarify the effects of aluminum stress on latex yield, physiological parameters and tapping panel dryness (TPD) of mature rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), rubber trees of clone Reyan7-33-97 tapped for eight-years were treated with AlCl3 solution at different concentrations. Two control solutions with different pH values (T0 was treated with ultrapure water of pH7.0 and T1 was treated with ultrapure water solution of pH adjusted to 4.2 by hydrochloric acid) and four concentrations (i.e. 50, 100, 200 and 400 mmol·L−1) of AlCl3 solutions with pH4.2 were applied just above the tapping cut. The rubber trees were tapped regularly and the latex volume, dry rubber yield, latex physiological parameters, TPD incidence and grade were observed in the early, middle and late stage of the treatment. The results showed that the harvested latex volume and dry rubber yield increased in the early stage of aluminum treatment, decreased to the same level as the control in the middle stage, and was lower than the control in the late stage, while the total latex volume and dry rubber yield of the 10 tappings after Al treatment were not significantly different from those of the control. Aluminum treatment increased dry rubber content, lutoid bursting index of the early latex and thiols content of late latex, indicating that aluminum treatment led to the decrease of latex flow capacity. Meanwhile aluminum treatment decreased latex sucrose content, and Mg2+ content of latex at the middle and late stages, and increased the inorganic phosphor content of latex at the late stage, which indicates that aluminum treatment also led to the decrease of rubber regeneration ability. High concentration aluminum treatment increased the incidence and grade of TPD. In summary, aluminum solution with a high concentration of 50 mmol·L−1 can increase latex yield in the short term and maintain the stability of dry latex production in a certain period of time, but it leads to the decline of the latex flow and regeneration capacity, inducing the occurrence of TPD. High concentration of Al is not conducive to maintaining the long-term latex production stability.
To clarify the effects of aluminum stress on latex yield, physiological parameters and tapping panel dryness (TPD) of mature rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), rubber trees of clone Reyan7-33-97 tapped for eight-years were treated with AlCl3 solution at different concentrations. Two control solutions with different pH values (T0 was treated with ultrapure water of pH7.0 and T1 was treated with ultrapure water solution of pH adjusted to 4.2 by hydrochloric acid) and four concentrations (i.e. 50, 100, 200 and 400 mmol·L−1) of AlCl3 solutions with pH4.2 were applied just above the tapping cut. The rubber trees were tapped regularly and the latex volume, dry rubber yield, latex physiological parameters, TPD incidence and grade were observed in the early, middle and late stage of the treatment. The results showed that the harvested latex volume and dry rubber yield increased in the early stage of aluminum treatment, decreased to the same level as the control in the middle stage, and was lower than the control in the late stage, while the total latex volume and dry rubber yield of the 10 tappings after Al treatment were not significantly different from those of the control. Aluminum treatment increased dry rubber content, lutoid bursting index of the early latex and thiols content of late latex, indicating that aluminum treatment led to the decrease of latex flow capacity. Meanwhile aluminum treatment decreased latex sucrose content, and Mg2+ content of latex at the middle and late stages, and increased the inorganic phosphor content of latex at the late stage, which indicates that aluminum treatment also led to the decrease of rubber regeneration ability. High concentration aluminum treatment increased the incidence and grade of TPD. In summary, aluminum solution with a high concentration of 50 mmol·L−1 can increase latex yield in the short term and maintain the stability of dry latex production in a certain period of time, but it leads to the decline of the latex flow and regeneration capacity, inducing the occurrence of TPD. High concentration of Al is not conducive to maintaining the long-term latex production stability.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250126
Abstract:
Agarwood is a traditional precious medicinal material and a natural aromatic material, which is highly valuable due to its rich secondary metabolites. ABC transporters are a type of transmembrane proteins widely distributed in organisms and play a crucial role in the transport and accumulation of secondary metabolites in plants. To deeply explore the function of ABC transporters in the transport process of secondary metabolites in agarwood, a gene encoding an ABC transporter AsABCG1; was identified by analyzing the transcriptome data of Aquilaria sinensis. The coding sequence (CDS) length of this gene is 1986 bp, encoding a protein consisting of 661 amino acids. AsABCG1 has typical structural characteristics of plant ABC transporters, including two conserved domains, Motif A and Motif B. The promoter region of AsABCG1 contains various hormone response elements such as jasmonic acid, auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, as well as stress response elements such as anaerobic induction and mechanical injury. The real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis showed that methyl jasmonic acid and mechanical injury treatments could significantly induce the expression of AsABCG1 in the stems of A. sinensis. All these findings laid the foundation for further elucidating the function of the AsABCG1 gene in the defense response to stress and the accumulation of secondary metabolites in A. sinensis.
Agarwood is a traditional precious medicinal material and a natural aromatic material, which is highly valuable due to its rich secondary metabolites. ABC transporters are a type of transmembrane proteins widely distributed in organisms and play a crucial role in the transport and accumulation of secondary metabolites in plants. To deeply explore the function of ABC transporters in the transport process of secondary metabolites in agarwood, a gene encoding an ABC transporter AsABCG1; was identified by analyzing the transcriptome data of Aquilaria sinensis. The coding sequence (CDS) length of this gene is 1986 bp, encoding a protein consisting of 661 amino acids. AsABCG1 has typical structural characteristics of plant ABC transporters, including two conserved domains, Motif A and Motif B. The promoter region of AsABCG1 contains various hormone response elements such as jasmonic acid, auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, as well as stress response elements such as anaerobic induction and mechanical injury. The real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis showed that methyl jasmonic acid and mechanical injury treatments could significantly induce the expression of AsABCG1 in the stems of A. sinensis. All these findings laid the foundation for further elucidating the function of the AsABCG1 gene in the defense response to stress and the accumulation of secondary metabolites in A. sinensis.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250184
Abstract:
To investigate the shade tolerance of Axonopus compressus, shade tolerance evaluation was performed on six accessions of superior Axonopus compressus germplasm (A03, A12, A58, A59, A69, A135) with Axonopus compressus ‘Huanan’ as the control variety, so as to provide a theoretical basis for breeding shade-tolerant varieties of A. compressus. A. compressus was treated with 75% shading or natural light under hydroponic culture and 18 indicators including chlorophyll content, leaf length, leaf width, biomass, and turf quality were measured after 28 days of treatment for comprehensive evaluation. The results show that compared to the control group, the 75% shading stress treatment, significantly increased the leaf length, but significantly decreased, leaf width, chlorophyll content, turf height, biomass, and turf quality of A. compressus. Comprehensive analysis showed that the germplasm accessions were classified into three categories: shade-tolerant, moderately shade-tolerant, and shade-sensitive. Among them, Accession A69 exhibited the highest shade tolerance and was listed in, the shade-tolerant category along with Accession A03 and the control variety; Accessions A58 and A59 were listed in the moderately shade-tolerant category; Accessions A12 and A135 were listed in the shade-sensitive category, demonstrating the poorest shade tolerance.
To investigate the shade tolerance of Axonopus compressus, shade tolerance evaluation was performed on six accessions of superior Axonopus compressus germplasm (A03, A12, A58, A59, A69, A135) with Axonopus compressus ‘Huanan’ as the control variety, so as to provide a theoretical basis for breeding shade-tolerant varieties of A. compressus. A. compressus was treated with 75% shading or natural light under hydroponic culture and 18 indicators including chlorophyll content, leaf length, leaf width, biomass, and turf quality were measured after 28 days of treatment for comprehensive evaluation. The results show that compared to the control group, the 75% shading stress treatment, significantly increased the leaf length, but significantly decreased, leaf width, chlorophyll content, turf height, biomass, and turf quality of A. compressus. Comprehensive analysis showed that the germplasm accessions were classified into three categories: shade-tolerant, moderately shade-tolerant, and shade-sensitive. Among them, Accession A69 exhibited the highest shade tolerance and was listed in, the shade-tolerant category along with Accession A03 and the control variety; Accessions A58 and A59 were listed in the moderately shade-tolerant category; Accessions A12 and A135 were listed in the shade-sensitive category, demonstrating the poorest shade tolerance.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20260017
Abstract:
Yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus) is an emerging oil crop characterized by its efficient oil accumulation in tubers. However, the regulatory mechanisms underlying oil biosynthesis remain unclear. Previous studies have demonstrated that CeWRI2 not only complements the Arabidopsis wri1-1 mutant but also significantly increases oil content when overexpressed in tobacco leaves. To dissect the molecular network by which CeWRI2 regulates oil accumulation in tubers, 17 candidate interacting proteins were identified through yeast two-hybrid screening, including CeHB1 belonging to the HD-ZIP transcription factor family. Furthermore, yeast two-hybrid assays confirmed the interaction between CeWRI2 and CeHB1. Gene expression analysis showed that CeHB1 was expressed in various tissues including leaves, leaf sheaths, flowers, flower stems, stolons, roots and tubers, with the highest expression level observed in tubers. This expression pattern was similar to that of CeWRI2 , suggesting that CeHB1 may regulate tuber development and oil biosynthesis and accumulation by modulating CeWRI2 .
Yellow nutsedge (Cyperus esculentus) is an emerging oil crop characterized by its efficient oil accumulation in tubers. However, the regulatory mechanisms underlying oil biosynthesis remain unclear. Previous studies have demonstrated that CeWRI2 not only complements the Arabidopsis wri1-1 mutant but also significantly increases oil content when overexpressed in tobacco leaves. To dissect the molecular network by which CeWRI2 regulates oil accumulation in tubers, 17 candidate interacting proteins were identified through yeast two-hybrid screening, including CeHB1 belonging to the HD-ZIP transcription factor family. Furthermore, yeast two-hybrid assays confirmed the interaction between CeWRI2 and CeHB1. Gene expression analysis showed that CeHB1 was expressed in various tissues including leaves, leaf sheaths, flowers, flower stems, stolons, roots and tubers, with the highest expression level observed in tubers. This expression pattern was similar to that of CeWRI2 , suggesting that CeHB1 may regulate tuber development and oil biosynthesis and accumulation by modulating CeWRI2 .
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250191
Abstract:
The belowground interactions of rice varieties during the seedling stage play a critical role in population structure establishment and resource acquisition, whereas their underlying chemical ecological mechanisms remain poorly understood. Under controlled conditions, paired mixed-cultivation experiments were conducted to compare the root interaction effects between ‘Kasalath’ and three companion rice varieties (‘FL47’, ‘IRGC126961 ’, ‘IRGC 117406 ’). Root morphological traits and root exudate metabolic profiles were systematically analyzed. The results showed that under mixed cultivation, root growth of ‘Kasalath’ remained stable, whereas all the three companion varieties exhibited significant inhibition in root surface area and maximum root length, the decrease of which ranged from 30% to 46%, indicating a clear asymmetric inhibitory effect. Metabolomics analysis identified a total of 1,307 metabolites. The inhibited varieties underwent significant metabolic reprogramming after mixed cultivation, primarily involving lipid, amino acid derivative, flavonoid, and polyamine metabolism pathways. Despite its stable phenotype, ‘Kasalath’ also displayed specific metabolic profile changes across different mixed combinations, including pathways such as nucleotide metabolism, phenylpropanoid metabolism, and glutathione metabolism. Integrating phenotypic and metabolomics data, it is demonstrated that ‘Kasalath’ suppresses root growth of companion varieties through stronger rhizosphere competitive ability and metabolic homeostasis maintenance mechanisms, while the limited metabolic compensation capacity of the companion varieties leads to growth inhibition. These findings reveal the chemical basis of root interactions between rice varieties at the metabolic level, providing a theoretical foundation for mixed-cultivation design and the development of efficient plant communities.
The belowground interactions of rice varieties during the seedling stage play a critical role in population structure establishment and resource acquisition, whereas their underlying chemical ecological mechanisms remain poorly understood. Under controlled conditions, paired mixed-cultivation experiments were conducted to compare the root interaction effects between ‘Kasalath’ and three companion rice varieties (‘FL47’, ‘IRGC
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250106
Abstract:
Seashore paspalum (Paspalum vaginatum Sw.) were treated with different concentrations of salt to observe the effect of salt treatment on the growth of seashore paspalum, and the PvMYB1 gene was cloned from seashore paspalum under different treatments and analyzed by using bioinformatics and gene expression analysis methods in a view to investigating whether MYB transcription factor genes are involved in the regulation of growth and development of seashore paspalum under salt stress. The results showed that salt stress inhibited the growth of both shoots and roots in seashore paspalum, manifested by reduction in total root length, root surface area, and root volume. The full length of the seashore paspalum PvMYB1 gene was1098 bp, encoding 365 amino acid residues, with a protein molecular weight of 39.26 kDa, and.this gene belongs to the R2R3-MYB family. Subcellular localization prediction indicated that the PvMYB1 protein was located in the nucleus. RT-qPCR analysis demonstrated that the expression of PvMYB1 was higher in leaves than in roots. The results of salt treatment at different time periods showed that 30 g·L-1 salt treatment significantly increased the transcription level of the PvMYB1 gene. Moreover, under different salt concentration treatments, the expression levels of the PvMYB1 gene in the roots and leaves were significantly upregulated when the salt concentration was 15 g·L-1. All these results revealed that PvMYB1 is implicated in the response of seashore paspalum to salt stress.
Seashore paspalum (Paspalum vaginatum Sw.) were treated with different concentrations of salt to observe the effect of salt treatment on the growth of seashore paspalum, and the PvMYB1 gene was cloned from seashore paspalum under different treatments and analyzed by using bioinformatics and gene expression analysis methods in a view to investigating whether MYB transcription factor genes are involved in the regulation of growth and development of seashore paspalum under salt stress. The results showed that salt stress inhibited the growth of both shoots and roots in seashore paspalum, manifested by reduction in total root length, root surface area, and root volume. The full length of the seashore paspalum PvMYB1 gene was
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250200
Abstract:
The phenotypic traits of 32 accessions of Qinan agarwood germplasm of Aquilaria sinensis conserved in Danzhou City, Hainan Province were selected for evaluation and analysis to reveal their genetic diversity and variation patterns, thereby providing a theoretical basis and technical support for the identification, evaluation, development, and utilization of superior A. sinensis germplasm. A total of 23 quantitative traits and 19 qualitative traits from leaves, flowers, and fruits of the 32 accessions of Qinan agarwood germplasm were selected for observation, and evaluated by using genetic diversity indices, correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis. The results showed a rich phenotypic genetic diversity among the germplasm accessions. The coefficients of variation for quantitative traits ranged from 9.04% to 34.77%, with Shannon’s diversity index ranging from 1.73 to 2.09. Higher diversity indices were observed for leaf length/width ratio, calyx tube length, sepal length/width ratio, and fruit width. For qualitative traits, H′ ranged from 0.234 to 1.285, with leaf shape exhibiting the highest diversity. Correlation analysis indicated that most of the leaf, petiole, and floral traits showed highly significant positive correlations, while leaf thickness was significantly negatively correlated with floral traits and fruit stalk length. Comprehensive analysis suggested that leaf shape and young branch color could serve as ideal phenotypic indicators for identification. Eight principal components were extracted from PCA, cumulatively explaining 72.68% of the total variance. The first four principal components primarily reflected variation in petals, sepals, fruits, and leaves, contributing substantially to the phenotypic variation. Cluster analysis divided the 32 germplasm accessions into three groups: Group I (16 accessions) was characterized by rich trait variation, gray-brown young branches, relatively large and slightly curled leaves; Group II (12 accessions) showed significant individual differences in leaf and floral traits, with asymmetric capsules and fewer pericarp wrinkles; Group III (4 accessions) displayed high trait consistency, featuring relatively small, broad-elliptical leaves, capsules with a pointed apex, and an inconspicuous midline. The 32 accessions of A. sinensis germplasm possess high phenotypic diversity. Traits such as leaf shape, young branch color, and fruit shape showed good distinguishing potential and can be used for phenotypic identification. All the findings provide a basis for the classification, core germplasm screening, and breeding of A. sinensis.
The phenotypic traits of 32 accessions of Qinan agarwood germplasm of Aquilaria sinensis conserved in Danzhou City, Hainan Province were selected for evaluation and analysis to reveal their genetic diversity and variation patterns, thereby providing a theoretical basis and technical support for the identification, evaluation, development, and utilization of superior A. sinensis germplasm. A total of 23 quantitative traits and 19 qualitative traits from leaves, flowers, and fruits of the 32 accessions of Qinan agarwood germplasm were selected for observation, and evaluated by using genetic diversity indices, correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis. The results showed a rich phenotypic genetic diversity among the germplasm accessions. The coefficients of variation for quantitative traits ranged from 9.04% to 34.77%, with Shannon’s diversity index ranging from 1.73 to 2.09. Higher diversity indices were observed for leaf length/width ratio, calyx tube length, sepal length/width ratio, and fruit width. For qualitative traits, H′ ranged from 0.234 to 1.285, with leaf shape exhibiting the highest diversity. Correlation analysis indicated that most of the leaf, petiole, and floral traits showed highly significant positive correlations, while leaf thickness was significantly negatively correlated with floral traits and fruit stalk length. Comprehensive analysis suggested that leaf shape and young branch color could serve as ideal phenotypic indicators for identification. Eight principal components were extracted from PCA, cumulatively explaining 72.68% of the total variance. The first four principal components primarily reflected variation in petals, sepals, fruits, and leaves, contributing substantially to the phenotypic variation. Cluster analysis divided the 32 germplasm accessions into three groups: Group I (16 accessions) was characterized by rich trait variation, gray-brown young branches, relatively large and slightly curled leaves; Group II (12 accessions) showed significant individual differences in leaf and floral traits, with asymmetric capsules and fewer pericarp wrinkles; Group III (4 accessions) displayed high trait consistency, featuring relatively small, broad-elliptical leaves, capsules with a pointed apex, and an inconspicuous midline. The 32 accessions of A. sinensis germplasm possess high phenotypic diversity. Traits such as leaf shape, young branch color, and fruit shape showed good distinguishing potential and can be used for phenotypic identification. All the findings provide a basis for the classification, core germplasm screening, and breeding of A. sinensis.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250167
Abstract:
To elucidate the characteristics, potential functions, and role of the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) gene family in durian (Durio zibethinus) (DzLEAs) in response to low-temperature stress, a genome-wide identification of the LEA gene family in durian was conducted using bioinformatics approaches. Comprehensive analyses were performed, including assessments of physicochemical properties, phylogenetic relationships, chromosomal localization, subcellular localization, synteny, promoter cis-acting elements, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment, as well as expression profiles under cold stress. A total of 46 DzLEAs members were identified and classified into eight subgroups: LEA1, LEA2, LEA3, LEA4, LEA5, LEA6, DHN, and SMP. These genes were distributed across 18 chromosomes. The encoded proteins ranged from 65 to 467 amino acids in length, with isoelectric points (pI) varying between 4.33 and 9.79. Most DzLEA proteins were predicted to be small hydrophilic molecules localized to multiple cellular compartments, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, chloroplast, plasma membrane, and extracellular space. Gene structure analysis revealed that 91% of DzLEAs possessed a relatively low number of introns (<3). Promoter analysis identified low-temperature-responsive cis-acting elements (LTRs) in 16 DzLEAs genes. Synteny analysis detected 28 and 46 pairs of homologous genes within the durian genome and between durian and Arabidopsis thaliana, respectively. GO enrichment analysis indicated that six DzLEAs were significantly enriched in the biological processes, "response to cold" and "response to water stress." Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) validation showed that the expression patterns of six selected DzLEAs and four non-DzLEA genes were largely consistent with the transcriptomic data, with all genes being up-regulated to varying degrees under cold stress. These findings provide a valuable foundation for further exploration of the molecular mechanisms underlying the response of DzLEAs genes to low-temperature stress in durian.
To elucidate the characteristics, potential functions, and role of the late embryogenesis abundant (LEA) gene family in durian (Durio zibethinus) (DzLEAs) in response to low-temperature stress, a genome-wide identification of the LEA gene family in durian was conducted using bioinformatics approaches. Comprehensive analyses were performed, including assessments of physicochemical properties, phylogenetic relationships, chromosomal localization, subcellular localization, synteny, promoter cis-acting elements, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment, as well as expression profiles under cold stress. A total of 46 DzLEAs members were identified and classified into eight subgroups: LEA1, LEA2, LEA3, LEA4, LEA5, LEA6, DHN, and SMP. These genes were distributed across 18 chromosomes. The encoded proteins ranged from 65 to 467 amino acids in length, with isoelectric points (pI) varying between 4.33 and 9.79. Most DzLEA proteins were predicted to be small hydrophilic molecules localized to multiple cellular compartments, including the nucleus, cytoplasm, mitochondria, chloroplast, plasma membrane, and extracellular space. Gene structure analysis revealed that 91% of DzLEAs possessed a relatively low number of introns (<3). Promoter analysis identified low-temperature-responsive cis-acting elements (LTRs) in 16 DzLEAs genes. Synteny analysis detected 28 and 46 pairs of homologous genes within the durian genome and between durian and Arabidopsis thaliana, respectively. GO enrichment analysis indicated that six DzLEAs were significantly enriched in the biological processes, "response to cold" and "response to water stress." Quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) validation showed that the expression patterns of six selected DzLEAs and four non-DzLEA genes were largely consistent with the transcriptomic data, with all genes being up-regulated to varying degrees under cold stress. These findings provide a valuable foundation for further exploration of the molecular mechanisms underlying the response of DzLEAs genes to low-temperature stress in durian.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250128
Abstract:
To explore the potential relationship between the leaf papillae of different accessions of Paspalum vaginatum and salt tolerance, 40 accessions of Paspalum vaginatum were selected and treated with 200mmol/L NaCl salt in the experiment, and their leaf papillae traits such as the length and width of individual leaf papilla, and cluster width were measured and analyzed by using correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis. The results showed that there were significant differences (P<0.05) in leaf papillae traits among different accessions of P. vaginatum, and that the traits were significantly (P<0.05) positively or negatively correlated. Before and after salt stress, the length, width and area of individual leaf papilla were highly significantly positively correlated (P<0.001). After stress, the cluster width of leaf papillae and the individual width showed a significant negative correlation with the second day after rehydration (P<0.05). Principal component analysis indicates that principal components 1 and 2 collectively account for 79.75% of the variance. Variation in leaf papilla morphology primarily stems from the individual length, individual width, and area of the leaf papillae. Cluster analysis grouped the accessions of the germplasm into four. Group A exhibited significantly reduced leaf papillae following stress, with papillae area decreasing by 38.09%, and demonstrated poor salt tolerance. Group D showed enlarged leaf papillae after stress, with total papilla cluster width increasing by 14.77%, and exhibited good salt tolerance. Group B and C displayed that most of the parameters in leaf papillae were reduced except for few parameters.
To explore the potential relationship between the leaf papillae of different accessions of Paspalum vaginatum and salt tolerance, 40 accessions of Paspalum vaginatum were selected and treated with 200mmol/L NaCl salt in the experiment, and their leaf papillae traits such as the length and width of individual leaf papilla, and cluster width were measured and analyzed by using correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and cluster analysis. The results showed that there were significant differences (P<0.05) in leaf papillae traits among different accessions of P. vaginatum, and that the traits were significantly (P<0.05) positively or negatively correlated. Before and after salt stress, the length, width and area of individual leaf papilla were highly significantly positively correlated (P<0.001). After stress, the cluster width of leaf papillae and the individual width showed a significant negative correlation with the second day after rehydration (P<0.05). Principal component analysis indicates that principal components 1 and 2 collectively account for 79.75% of the variance. Variation in leaf papilla morphology primarily stems from the individual length, individual width, and area of the leaf papillae. Cluster analysis grouped the accessions of the germplasm into four. Group A exhibited significantly reduced leaf papillae following stress, with papillae area decreasing by 38.09%, and demonstrated poor salt tolerance. Group D showed enlarged leaf papillae after stress, with total papilla cluster width increasing by 14.77%, and exhibited good salt tolerance. Group B and C displayed that most of the parameters in leaf papillae were reduced except for few parameters.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250142
Abstract:
A field survey of Rhynchostylis gigantea was made in fragmented fengshui forest landscapes in Changjiang, Hainan and samples of R. gigantea was collected to analyzed its genetic diversity and population structure by using SNP molecular markers. The results showed that all three local populations (B, M, and J) of R. gigantea maintained moderate levels of genetic diversity (Pi = 0.137–0.147, He = 0.132–0.145), whereas the observed heterozygosity was relatively low (Ho = 0.105–0.122), indicating mild to moderate inbreeding (Fis = 0.049–0.107). The genetic differentiation among the populations was moderate to low (Fst = 0.026–0.058), with the greatest divergence observed between the populations M and J. STRUCTURE, PCA, and UPGMA analyses consistently revealed moderate genetic differentiation among the three populations occurring in human-influenced environments, suggesting the presence of some gene flow. The field survey indicated that remnant traditional trees serve as important ecological corridors facilitating the dispersal of R. gigantea between primary and secondary habitats. However, the expansion of areca and rubber plantations surrounding these remnant trees, along with increased agrochemical use, may further weaken gene flow and population regeneration. This study highlights the genetic status of R. gigantea in fragmented landscapes and provides essential scientific insights for the conservation of its genetic resources and populations within human-influenced environments.
A field survey of Rhynchostylis gigantea was made in fragmented fengshui forest landscapes in Changjiang, Hainan and samples of R. gigantea was collected to analyzed its genetic diversity and population structure by using SNP molecular markers. The results showed that all three local populations (B, M, and J) of R. gigantea maintained moderate levels of genetic diversity (Pi = 0.137–0.147, He = 0.132–0.145), whereas the observed heterozygosity was relatively low (Ho = 0.105–0.122), indicating mild to moderate inbreeding (Fis = 0.049–0.107). The genetic differentiation among the populations was moderate to low (Fst = 0.026–0.058), with the greatest divergence observed between the populations M and J. STRUCTURE, PCA, and UPGMA analyses consistently revealed moderate genetic differentiation among the three populations occurring in human-influenced environments, suggesting the presence of some gene flow. The field survey indicated that remnant traditional trees serve as important ecological corridors facilitating the dispersal of R. gigantea between primary and secondary habitats. However, the expansion of areca and rubber plantations surrounding these remnant trees, along with increased agrochemical use, may further weaken gene flow and population regeneration. This study highlights the genetic status of R. gigantea in fragmented landscapes and provides essential scientific insights for the conservation of its genetic resources and populations within human-influenced environments.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250155
Abstract:
To clarify the species of ticks on the body surface of animals, characteristics of tick microbial composition, as well as the species and distribution of tick-borne Ehrlichia pathogens in different habitats of Hainan Province, ticks were collected from the body surface of swine and dogs in three administrative regions of Hainan, namely Ding'an County (central Hainan), Baisha Li and Miao Autonomous County (western Hainan), and Wanning City (southern Hainan). Tick species were identified through morphological observation and PCR assay: Haemaphysalis longicornis was collected from dogs in Wanning, while Rhipicephalus sanguineus was isolated from dogs in Ding'an and swine in Baisha. Metagenomic approaches were further employed to analyze the microbial composition, functional pathways and species of tick-borne Ehrlichia in the collected ticks. The results showed that, Proteobacteria was the absolutely dominant bacterial phylum in ticks across the three regions. For fungi, Ascomycota was the dominant phylum in Ding'an ticks, whereas Mucoromycota predominated in ticks from Baisha and Wanning. In terms of viruses, Chrysoviridae was the dominant viral phylum in Ding'an ticks, while Negarnaviricota was the major one in Baisha and Wanning ticks. At the species level, a variety of important zoonotic pathogens were detected, including Coxiella burnetii, Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia spp., with Ehrlichia minasensis being identified in ticks from Hainan for the first time. The functional pathways of the tick microbial communities exhibited obvious intergroup divergence: ticks from Baisha showed high abundances of pathways related to metabolism and drug resistance, while those from Ding'an were characterized by a prominent enrichment of pathways associated with human diseases. Comprehensive analysis revealed that sampling location, tick species and host species exerted significant effects on the tick microbial community structure. Further verification via PCR assays confirmed that the dominant species of Ehrlichia carried by ticks in Hainan were E.canis and E. minasensis. The findings provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and control of tick-borne diseases in Hainan Province, and also offer fundamental data support for the subsequent development of diagnostic methods for tick-borne ehrlichiosis.
To clarify the species of ticks on the body surface of animals, characteristics of tick microbial composition, as well as the species and distribution of tick-borne Ehrlichia pathogens in different habitats of Hainan Province, ticks were collected from the body surface of swine and dogs in three administrative regions of Hainan, namely Ding'an County (central Hainan), Baisha Li and Miao Autonomous County (western Hainan), and Wanning City (southern Hainan). Tick species were identified through morphological observation and PCR assay: Haemaphysalis longicornis was collected from dogs in Wanning, while Rhipicephalus sanguineus was isolated from dogs in Ding'an and swine in Baisha. Metagenomic approaches were further employed to analyze the microbial composition, functional pathways and species of tick-borne Ehrlichia in the collected ticks. The results showed that, Proteobacteria was the absolutely dominant bacterial phylum in ticks across the three regions. For fungi, Ascomycota was the dominant phylum in Ding'an ticks, whereas Mucoromycota predominated in ticks from Baisha and Wanning. In terms of viruses, Chrysoviridae was the dominant viral phylum in Ding'an ticks, while Negarnaviricota was the major one in Baisha and Wanning ticks. At the species level, a variety of important zoonotic pathogens were detected, including Coxiella burnetii, Anaplasma phagocytophilum and Ehrlichia spp., with Ehrlichia minasensis being identified in ticks from Hainan for the first time. The functional pathways of the tick microbial communities exhibited obvious intergroup divergence: ticks from Baisha showed high abundances of pathways related to metabolism and drug resistance, while those from Ding'an were characterized by a prominent enrichment of pathways associated with human diseases. Comprehensive analysis revealed that sampling location, tick species and host species exerted significant effects on the tick microbial community structure. Further verification via PCR assays confirmed that the dominant species of Ehrlichia carried by ticks in Hainan were E.canis and E. minasensis. The findings provide a theoretical basis for the prevention and control of tick-borne diseases in Hainan Province, and also offer fundamental data support for the subsequent development of diagnostic methods for tick-borne ehrlichiosis.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250183
Abstract:
An attempt was made to analyze the therapeutic effect of combined DNA and protein vaccines on a mouse model of dust mite allergy induced by a fusion allergen. In this attempt eukaryotic and prokaryotic expression plasmids of the major dust mite allergen fusion epitope were constructed to prepare a combined DNA and protein vaccine. A mouse model of dust mite allergy was induced by the fusion allergen Der p 1-Der f 1-Blo t 5. The mice were randomly divided into an allergy group (Allergy) and a vaccine group, with 6 mice in each group. A normal group (Naïve) was set as a control. The vaccine group was injected with the corresponding vaccine, the allergy group was injected with an equal volume of PBS (phosphate buffered saline), and the normal group received no treatment. The therapeutic effect of the vaccine was comprehensively evaluated by detecting the total IgE (immunoglobulin E) level in the mouse serum, changes in airway hyperresponsiveness, the area of dye leakage in the ear, and pathological features of lung sections. The results showed that compared with the allergy group, the combined DNA and protein vaccine group had significantly lower total IgE levels of serum, significantly reduced airway hyper-responsiveness, had significantly smaller area of dye leakage in the mouse ear, alleviated lung tissue inflammatory cell infiltration, reduced average goblet cell numbers in the bronchus, and decreased collagen fiber deposition. It is concluded that the combined DNA and protein vaccine has a good immunotherapeutic effect on the dust mite allergy mouse model, which can provide an important reference for the development of preventive and therapeutic vaccines for dust mite allergy.
An attempt was made to analyze the therapeutic effect of combined DNA and protein vaccines on a mouse model of dust mite allergy induced by a fusion allergen. In this attempt eukaryotic and prokaryotic expression plasmids of the major dust mite allergen fusion epitope were constructed to prepare a combined DNA and protein vaccine. A mouse model of dust mite allergy was induced by the fusion allergen Der p 1-Der f 1-Blo t 5. The mice were randomly divided into an allergy group (Allergy) and a vaccine group, with 6 mice in each group. A normal group (Naïve) was set as a control. The vaccine group was injected with the corresponding vaccine, the allergy group was injected with an equal volume of PBS (phosphate buffered saline), and the normal group received no treatment. The therapeutic effect of the vaccine was comprehensively evaluated by detecting the total IgE (immunoglobulin E) level in the mouse serum, changes in airway hyperresponsiveness, the area of dye leakage in the ear, and pathological features of lung sections. The results showed that compared with the allergy group, the combined DNA and protein vaccine group had significantly lower total IgE levels of serum, significantly reduced airway hyper-responsiveness, had significantly smaller area of dye leakage in the mouse ear, alleviated lung tissue inflammatory cell infiltration, reduced average goblet cell numbers in the bronchus, and decreased collagen fiber deposition. It is concluded that the combined DNA and protein vaccine has a good immunotherapeutic effect on the dust mite allergy mouse model, which can provide an important reference for the development of preventive and therapeutic vaccines for dust mite allergy.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250160
Abstract:
To investigate the infection status, molecular characteristics, and genetic relationship of Ehrlichia canis in Hainan black goats, a total of 1 061 anti-coagulated blood samples were collected from eight cities/counties (Haikou, Chengmai, Dingan, Baisha, Dongfang, Wenchang, Wuzhishan, Danzhou) of Hainan Province. Detection and phylogenetic analysis were performed by PCR amplification targeting the 16S rRNA and groEL genes of E. canis. The results showed there were 34 positive samples, with an overall positive rate of 3.2%. The samples in Dingan County had the highest detection rate (11.40%), suggesting regional prevalence of the pathogen in this area. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that E. canis strains from Hainan black goats were clustered into the same branch, possibly originating from a common infection source. The 16S rRNA sequences of E. canis from Hainan black goats were most closely related to those of a Brazilian strain (KF972447.1), while the groEL gene showed the highest affinity with a Beijing strain from China (MW428317.1), forming a paralogous group with sequences from Beijing and Yunnan in China, reflecting geographic genetic differentiation. These findings provide the first molecular evidence of E. canis in Hainan black goats, suggesting that E. canis may achieve cross-host transmission via ticks, which offers a reference for further research on the molecular epidemiology and control of E. canis.
To investigate the infection status, molecular characteristics, and genetic relationship of Ehrlichia canis in Hainan black goats, a total of 1 061 anti-coagulated blood samples were collected from eight cities/counties (Haikou, Chengmai, Dingan, Baisha, Dongfang, Wenchang, Wuzhishan, Danzhou) of Hainan Province. Detection and phylogenetic analysis were performed by PCR amplification targeting the 16S rRNA and groEL genes of E. canis. The results showed there were 34 positive samples, with an overall positive rate of 3.2%. The samples in Dingan County had the highest detection rate (11.40%), suggesting regional prevalence of the pathogen in this area. Phylogenetic analysis indicated that E. canis strains from Hainan black goats were clustered into the same branch, possibly originating from a common infection source. The 16S rRNA sequences of E. canis from Hainan black goats were most closely related to those of a Brazilian strain (KF972447.1), while the groEL gene showed the highest affinity with a Beijing strain from China (MW428317.1), forming a paralogous group with sequences from Beijing and Yunnan in China, reflecting geographic genetic differentiation. These findings provide the first molecular evidence of E. canis in Hainan black goats, suggesting that E. canis may achieve cross-host transmission via ticks, which offers a reference for further research on the molecular epidemiology and control of E. canis.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250148
Abstract:
An analysis was made of the molecular characteristics of type III polyketide synthases (PKSIII) in Alpinia oxyphylla and their potential role in the biosynthesis of diphenylheptanoid compounds. The PKSIII gene family was identified from the A. oxyphylla genome, and the candidate gene AoPKS5 was selected for structural and expression analysis. Based on genomic and transcriptomic data, PKSIII genes were systematically screened and analyzed for expression levels, and phylogenetic analysis was conducted to explore their evolutionary relationships. Bioinformatics tools were used to predict the physicochemical properties and catalytic sites of AoPKS5. Tissue-specific expression was analyzed by using RT-qPCR, and the recombinant vector pNC-ET28-AoPKS5 was constructed for heterologous expression in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). The results showed that AoPKS5 contained a1170 bp ORF encoding 389 amino acids, with a theoretical molecular weight of 42 kDa and an isoelectric point of 5.96, lacking both signal peptide and transmembrane domains, but possessing the conserved Cys–His–Asn catalytic triad and GFGPG motif. Phylogenetic analysis indicated high homology with DCS proteins from Curcuma longa and Zingiber officinale. RT-qPCR revealed that AoPKS5 was most highly expressed in leaves. The AoPKS5 gene was successfully cloned and characterized and its prokaryotic expression system established, providing a theoretical and technical foundation for elucidating the molecular mechanisms of PKSIII involvement in diphenylheptanoid biosynthesis in A. oxyphylla.
An analysis was made of the molecular characteristics of type III polyketide synthases (PKSIII) in Alpinia oxyphylla and their potential role in the biosynthesis of diphenylheptanoid compounds. The PKSIII gene family was identified from the A. oxyphylla genome, and the candidate gene AoPKS5 was selected for structural and expression analysis. Based on genomic and transcriptomic data, PKSIII genes were systematically screened and analyzed for expression levels, and phylogenetic analysis was conducted to explore their evolutionary relationships. Bioinformatics tools were used to predict the physicochemical properties and catalytic sites of AoPKS5. Tissue-specific expression was analyzed by using RT-qPCR, and the recombinant vector pNC-ET28-AoPKS5 was constructed for heterologous expression in Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). The results showed that AoPKS5 contained a
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250156
Abstract:
Vibrio alginolyticus, a conditionally pathogenic bacterium widely present in marine environments, can utilize various inorganic nitrogen sources such as ammonium, nitrate, and nitrite for growth, causing significant economic losses in the marine aquaculture industry. The nirB gene encodes nitrite reductase, which plays an important role in bacterial nitrogen metabolism and environmental adaptation. An attempt was made to analyze the function of the nirB gene in V. alginolyticus during the utilization of inorganic nitrogen sources. Two nirB gene-related knockout strains of V. alginolyticus were constructed: a nirB1 deletion strain (ΔnirB1) and a nirB2 deletion strain (ΔnirB2), and a double deletion strain lacking both nirB1 and nirB2 (ΔnirB12) was also constructed. These strains were cultured in different types of inorganic nitrogen media to observe their growth. The results showed that the nirB gene promotes the utilization of ammonium and nitrate in V. alginolyticus, with the nirB1 gene playing a key role in the conversion of nitrate to nitrite. In nitrite media, deletion of the nirB gene significantly inhibited the growth of V. alginolyticus, indicating that the gene also plays an important role in nitrite utilization, and the nirB2 gene has a more critical function in this process. Moreover, the presence of ammonium was also found to affect the utilization of nitrite by V. alginolyticus, suggesting a possible competitive relationship. All the results provide a foundation for further understanding of the function of the nirB gene in V. alginolyticus and its role in nitrogen metabolism.
Vibrio alginolyticus, a conditionally pathogenic bacterium widely present in marine environments, can utilize various inorganic nitrogen sources such as ammonium, nitrate, and nitrite for growth, causing significant economic losses in the marine aquaculture industry. The nirB gene encodes nitrite reductase, which plays an important role in bacterial nitrogen metabolism and environmental adaptation. An attempt was made to analyze the function of the nirB gene in V. alginolyticus during the utilization of inorganic nitrogen sources. Two nirB gene-related knockout strains of V. alginolyticus were constructed: a nirB1 deletion strain (ΔnirB1) and a nirB2 deletion strain (ΔnirB2), and a double deletion strain lacking both nirB1 and nirB2 (ΔnirB12) was also constructed. These strains were cultured in different types of inorganic nitrogen media to observe their growth. The results showed that the nirB gene promotes the utilization of ammonium and nitrate in V. alginolyticus, with the nirB1 gene playing a key role in the conversion of nitrate to nitrite. In nitrite media, deletion of the nirB gene significantly inhibited the growth of V. alginolyticus, indicating that the gene also plays an important role in nitrite utilization, and the nirB2 gene has a more critical function in this process. Moreover, the presence of ammonium was also found to affect the utilization of nitrite by V. alginolyticus, suggesting a possible competitive relationship. All the results provide a foundation for further understanding of the function of the nirB gene in V. alginolyticus and its role in nitrogen metabolism.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250176
Abstract:
Based on forest resource data of Hainan Province from the third to the ninth national forest resource inventories and relevant ecological station data from the same period, the dynamic characteristics of forest resources over more than 30 years (1984–2018) were systematically analyzed in terms of "quantity-quality-structure", and the evolutionary patterns of key ecosystem service functions were quantified in accordance with national standards, aiming to reveal their intrinsic coupling relationships. The results showed that forest resources in Hainan Province had achieved remarkable growth, with forest area, stock volume, and forest coverage increasing by 124.48%, 163.84%, and 31.96 percentage points, respectively. The forest age structure had been continuously optimized, and forest quality had steadily improved, with policy and institutional factors identified as key drivers of these changes. All assessed ecosystem service functions had significantly enhanced, particularly water regulation and negative ion provision, which had increased by over 240%. Correlation analysis further revealed that the area of mature and overmature forests had the greatest dominant effect on water conservation and soil fixation services, while stock volume per unit area was the key determining factor for carbon sequestration service. This highlighted the central role of forest quality and maturity in enhancing ecosystem services, underscoring the central importance of indicators of forest quantity (area, stock volume) and indicators of maturity. All these findings elucidate the coupling relationship between the growth of forest resources and the dynamic changes in ecosystem service functions, providing a scientific basis for the sustainable management of regional forests.
Based on forest resource data of Hainan Province from the third to the ninth national forest resource inventories and relevant ecological station data from the same period, the dynamic characteristics of forest resources over more than 30 years (1984–2018) were systematically analyzed in terms of "quantity-quality-structure", and the evolutionary patterns of key ecosystem service functions were quantified in accordance with national standards, aiming to reveal their intrinsic coupling relationships. The results showed that forest resources in Hainan Province had achieved remarkable growth, with forest area, stock volume, and forest coverage increasing by 124.48%, 163.84%, and 31.96 percentage points, respectively. The forest age structure had been continuously optimized, and forest quality had steadily improved, with policy and institutional factors identified as key drivers of these changes. All assessed ecosystem service functions had significantly enhanced, particularly water regulation and negative ion provision, which had increased by over 240%. Correlation analysis further revealed that the area of mature and overmature forests had the greatest dominant effect on water conservation and soil fixation services, while stock volume per unit area was the key determining factor for carbon sequestration service. This highlighted the central role of forest quality and maturity in enhancing ecosystem services, underscoring the central importance of indicators of forest quantity (area, stock volume) and indicators of maturity. All these findings elucidate the coupling relationship between the growth of forest resources and the dynamic changes in ecosystem service functions, providing a scientific basis for the sustainable management of regional forests.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250182
Abstract:
Vatica mangachapoi Blanco, a member of the genus Vatica (Dipterocarpaceae), is a dominant species in the tropical lowland rainforests of Hainan Island. Understanding its genetic dynamics and fine-scale gene dispersal patterns is essential for elucidating the ecological adaptation of dominant tree species in tropical ecosystems. In this context 372 individuals across different elevational gradients were sampled from Bawangling and Diaoluoshan within Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park to evaluate genetic diversity, population structure, and fine-scale spatial genetic structure (FSGS) using seven microsatellite loci. The results revealed a relatively high overall genetic diversity in V. mangachapoi (Na = 7.107, He = 0.726), markedly higher than that of other two dipterocarps on Hainan Island, Hopea hainanensis (Na = 2.458, He = 0.432) and H. reticulata (Na = 3.636, He = 0.599). STRUCTURE analysis found that the high altitude population at Bawangling (BW-H) differentiated to some extent with the other three populations, while PCoA and NJ tree analyses could not detect clear genetic differentiation among the four populations. FSGS analyses indicated stronger spatial clustering of genotypes in high-elevation populations (Sp =0.0360 -0.0440 ) than that in low-elevation populations (Sp = 0.0096 -0.0168 ). Overall, all the findings indicate that the genetic dynamics of V. mangachapoi populations are influenced by elevational environmental gradients and provide scientific insights for the conservation and management of tropical dipterocarps.
Vatica mangachapoi Blanco, a member of the genus Vatica (Dipterocarpaceae), is a dominant species in the tropical lowland rainforests of Hainan Island. Understanding its genetic dynamics and fine-scale gene dispersal patterns is essential for elucidating the ecological adaptation of dominant tree species in tropical ecosystems. In this context 372 individuals across different elevational gradients were sampled from Bawangling and Diaoluoshan within Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park to evaluate genetic diversity, population structure, and fine-scale spatial genetic structure (FSGS) using seven microsatellite loci. The results revealed a relatively high overall genetic diversity in V. mangachapoi (Na = 7.107, He = 0.726), markedly higher than that of other two dipterocarps on Hainan Island, Hopea hainanensis (Na = 2.458, He = 0.432) and H. reticulata (Na = 3.636, He = 0.599). STRUCTURE analysis found that the high altitude population at Bawangling (BW-H) differentiated to some extent with the other three populations, while PCoA and NJ tree analyses could not detect clear genetic differentiation among the four populations. FSGS analyses indicated stronger spatial clustering of genotypes in high-elevation populations (Sp =
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250179
Abstract:
To address the issues of high cost and low yield in the cultivation of Dictyophora rubrovolvata in Hainan, this study conducted a gradient experiment to optimize the mushroom-stick substrate and casing soil composition. Key parameters, including mycelial growth rate, bag-filling time, primordia formation time, fruiting time, fruiting body morphological characteristics, and yield, were measured to evaluate the effects of different carbon sources, nitrogen sources, and organic matter on the growth of D. rubrovolvata. The results indicated that the A5 substrates formula, containing rubberwood as the carbon source and soybean as the nitrogen source, exhibited the best performance. It achieved a mycelial growth rate of 12.62 mm·d-1, a bag-filling time of 16.33 d, and produced dense, robust, and pure white mycelia. The addition of sphagnum peat to the casing soil at varying ratios enhanced mycelial growth, shortened the time to primordia formation and fruiting, and increased yield. Specifically, the highest yield per stick (93.76 g) were achieved with the application of 20% peat to the base soil from Guangcun Town. The application of 30% peat to the base soil from Dacheng Town resulted in the highest yield per stick (103.58 g) and. Similarly, the addition of 30% peat to the Xinzhou Town base soil yielded at 92.66 g per stick This study provides a theoretical basis and technical support for the efficient and low-cost cultivation of D. rubrovolvata in tropical regions.
To address the issues of high cost and low yield in the cultivation of Dictyophora rubrovolvata in Hainan, this study conducted a gradient experiment to optimize the mushroom-stick substrate and casing soil composition. Key parameters, including mycelial growth rate, bag-filling time, primordia formation time, fruiting time, fruiting body morphological characteristics, and yield, were measured to evaluate the effects of different carbon sources, nitrogen sources, and organic matter on the growth of D. rubrovolvata. The results indicated that the A5 substrates formula, containing rubberwood as the carbon source and soybean as the nitrogen source, exhibited the best performance. It achieved a mycelial growth rate of 12.62 mm·d-1, a bag-filling time of 16.33 d, and produced dense, robust, and pure white mycelia. The addition of sphagnum peat to the casing soil at varying ratios enhanced mycelial growth, shortened the time to primordia formation and fruiting, and increased yield. Specifically, the highest yield per stick (93.76 g) were achieved with the application of 20% peat to the base soil from Guangcun Town. The application of 30% peat to the base soil from Dacheng Town resulted in the highest yield per stick (103.58 g) and. Similarly, the addition of 30% peat to the Xinzhou Town base soil yielded at 92.66 g per stick This study provides a theoretical basis and technical support for the efficient and low-cost cultivation of D. rubrovolvata in tropical regions.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250147
Abstract:
During the field survey in Jianfengling district of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, four plant species newly recorded in Hainan Province were reported, including: Viola nanlingensis J. S. Zhou & F. W. Xing, Capparis tenera Dalz and Primulina flavimaculata (W. T. Wang) Mich. Möller & A. Weber, Amorphophallus tonkinensis Engl. & Gehrm. For each species, field photographs were provided along with descriptions of their morphological characteristics. Additionally, the gaps in the original literature and the Flora of China regarding the fruit and seed descriptions of Capparis tenera were supplemented. Voucher specimens are deposited in the Shanghai Chenshan National Botanical Garden Herbarium (CSH) and the South China Botanical Garden Herbarium (IBSC). Furthermore, a correction was made regarding the 1981 publication by Chen Bangyu in the Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, which proposed two new species of Engelhardia from Hainan and stated that "Engelhardia spicata does not occur in Hainan, and that the plants previously misidentified as Engelhardia spicata should be recognized as a new species, Engelhardia hainanensis." It has now been confirmed that Engelhardia spicata does indeed exist in Hainan, with voucher specimens deposited in the South China Botanical Garden Herbarium (IBSC).
During the field survey in Jianfengling district of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, four plant species newly recorded in Hainan Province were reported, including: Viola nanlingensis J. S. Zhou & F. W. Xing, Capparis tenera Dalz and Primulina flavimaculata (W. T. Wang) Mich. Möller & A. Weber, Amorphophallus tonkinensis Engl. & Gehrm. For each species, field photographs were provided along with descriptions of their morphological characteristics. Additionally, the gaps in the original literature and the Flora of China regarding the fruit and seed descriptions of Capparis tenera were supplemented. Voucher specimens are deposited in the Shanghai Chenshan National Botanical Garden Herbarium (CSH) and the South China Botanical Garden Herbarium (IBSC). Furthermore, a correction was made regarding the 1981 publication by Chen Bangyu in the Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, which proposed two new species of Engelhardia from Hainan and stated that "Engelhardia spicata does not occur in Hainan, and that the plants previously misidentified as Engelhardia spicata should be recognized as a new species, Engelhardia hainanensis." It has now been confirmed that Engelhardia spicata does indeed exist in Hainan, with voucher specimens deposited in the South China Botanical Garden Herbarium (IBSC).
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250145
Abstract:
Grassland ecosystems are an important component of terrestrial ecosystems and play a critical role in maintaining ecological security and supporting livestock production. Due to climate warming and overgrazing, grassland productivity has declined, increasing the risk of ecological degradation. Existing studies on grazing intensity and grazing thresholds largely rely on empirical or static data, making it difficult to capture the dynamic changes of grasslands under grazing pressure. This study takes the grasslands on the northern Tianshan Mountains as an example, using LAI time series unaffected by grazing to simulate ungrazed growth trajectories and applying a light-use efficiency model to calculate ungrazed net primary productivity (NPP). Based on this, a grazing threshold model was established using ungrazed NPP to describe degradation time and threshold distribution under different grazing pressures. The results show that the spatial distribution of ungrazed NPP exhibits a “higher in the west and in mountainous areas, lower in the east and on plains” pattern. Under current stocking rates and scenarios with 10% and 30% reduced grazing, grassland degradation generally occurs within 1–18 years, with some areas reaching a critical stocking rate of zero, indicating that current grazing pressure has reached or exceeded the ecological carrying limit. As stocking rates decrease, the time for some pixels to reach the degradation threshold is significantly delayed, suggesting that moderate grazing reduction can locally postpone grassland degradation. Under the RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios, the critical stocking rate ranges from 3.59 to 9.60 SU/ha, with limited overall differences in grazing thresholds and degradation time, but notable regional variability. The proposed ungrazed NPP–based grazing threshold simulation approach provides a scientific basis for quantitatively identifying grassland ecological carrying capacity and supporting differentiated grazing management strategies.
Grassland ecosystems are an important component of terrestrial ecosystems and play a critical role in maintaining ecological security and supporting livestock production. Due to climate warming and overgrazing, grassland productivity has declined, increasing the risk of ecological degradation. Existing studies on grazing intensity and grazing thresholds largely rely on empirical or static data, making it difficult to capture the dynamic changes of grasslands under grazing pressure. This study takes the grasslands on the northern Tianshan Mountains as an example, using LAI time series unaffected by grazing to simulate ungrazed growth trajectories and applying a light-use efficiency model to calculate ungrazed net primary productivity (NPP). Based on this, a grazing threshold model was established using ungrazed NPP to describe degradation time and threshold distribution under different grazing pressures. The results show that the spatial distribution of ungrazed NPP exhibits a “higher in the west and in mountainous areas, lower in the east and on plains” pattern. Under current stocking rates and scenarios with 10% and 30% reduced grazing, grassland degradation generally occurs within 1–18 years, with some areas reaching a critical stocking rate of zero, indicating that current grazing pressure has reached or exceeded the ecological carrying limit. As stocking rates decrease, the time for some pixels to reach the degradation threshold is significantly delayed, suggesting that moderate grazing reduction can locally postpone grassland degradation. Under the RCP4.5 and RCP8.5 scenarios, the critical stocking rate ranges from 3.59 to 9.60 SU/ha, with limited overall differences in grazing thresholds and degradation time, but notable regional variability. The proposed ungrazed NPP–based grazing threshold simulation approach provides a scientific basis for quantitatively identifying grassland ecological carrying capacity and supporting differentiated grazing management strategies.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250111
Abstract:
The umbrella species theory emphasizes that protecting a focal species and its habitat can indirectly benefit co-occurring species within the same ecosystem. The Hainan gibbon (Nomascus hainanus), one of the most endangered primates worldwide, is restricted to the Bawangling area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park and is recognized as both a flagship species and a potential umbrella species. Based on camera-trapping data, the biodiversity patterns were compared between the gibbon-inhabited Bawangling area and the adjacent Yajialing area without gibbons, aiming to evaluate the umbrella effect of the Hainan gibbon. Results showed that although the two regions share similar geographic location, elevation, and vegetation types, their species composition and community structure differ significantly. A total of 47 bird and mammal species were recorded in Bawangling, compared with 40 species in Yajiadaling. Species accumulation curves indicated that species richness in both areas tended to stabilize over time, yet Bawangling consistently exhibited higher richness and evenness. Furthermore, the higher occurrence frequencies of resource competitors and potential predators in Bawangling suggest more complex interspecific interactions and greater ecosystem robustness. Overall, our findings confirm the umbrella effect of the Hainan gibbon: its distribution area harbors not only higher biodiversity but also a more complete community structure and ecological functionality, providing empirical support for applying the umbrella species concept in tropical island ecosystems.
The umbrella species theory emphasizes that protecting a focal species and its habitat can indirectly benefit co-occurring species within the same ecosystem. The Hainan gibbon (Nomascus hainanus), one of the most endangered primates worldwide, is restricted to the Bawangling area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park and is recognized as both a flagship species and a potential umbrella species. Based on camera-trapping data, the biodiversity patterns were compared between the gibbon-inhabited Bawangling area and the adjacent Yajialing area without gibbons, aiming to evaluate the umbrella effect of the Hainan gibbon. Results showed that although the two regions share similar geographic location, elevation, and vegetation types, their species composition and community structure differ significantly. A total of 47 bird and mammal species were recorded in Bawangling, compared with 40 species in Yajiadaling. Species accumulation curves indicated that species richness in both areas tended to stabilize over time, yet Bawangling consistently exhibited higher richness and evenness. Furthermore, the higher occurrence frequencies of resource competitors and potential predators in Bawangling suggest more complex interspecific interactions and greater ecosystem robustness. Overall, our findings confirm the umbrella effect of the Hainan gibbon: its distribution area harbors not only higher biodiversity but also a more complete community structure and ecological functionality, providing empirical support for applying the umbrella species concept in tropical island ecosystems.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250065
Abstract:
Coral reef ecosystem is one of the most biodiverse and productive ecosystems in the ocean.However, coral reefs have been degraded to different degrees in recent years due to the impact of global environmental changes.As microorganisms that live in symbiosis with corals, the isolation and purification of Symbiodiniaceae clades can provide a deeper understanding of their biological properties and provide an experimental basis for revealing their important physiology, such as coral-associated physiology mechanisms.In this context Cladocopium C1 sp.was isolated from Acropora formosa, and then rinsed or sheared to make the coral released symbiotic Symbiodiniaceae.Observations were made using an inverted microscope microscope to determine whether Symbiodiniaceae were isolated or not, and the Symbiodiniaceae were centrifuged, diluted, transferred, and cultured every two weeks.Sanger sequencing and high-throughput sequencing were performed on the cultured Symbiodiniaceae.Observations under inverted microscope and electron microscope showed that the cells of the Symbiodiniaceae Cladocopium C1 sp.had a complete structure with multiple well-developed chlorophylls, mitochondria, pyrenoids, etc in the cytoplasm.The Sanger sequencing results were compared on the NCBI platform, and the isolated Symbiodiniaceae were the dominant Symbiodiniaceae Cladocopium C1 sp.of A.formosa.The high-throughput sequencing results showed that the relative abundance of Symbiodiniaceae Cladocopium C1 sp.cells was 98%.The successful isolation of Cladocopium C1 sp.from A.formosa provides a scientific basis for a deeper understanding of the roles of Symbiodiniaceae in the symbiosis with corals and the mechanism of their interactions with corals.
Coral reef ecosystem is one of the most biodiverse and productive ecosystems in the ocean.However, coral reefs have been degraded to different degrees in recent years due to the impact of global environmental changes.As microorganisms that live in symbiosis with corals, the isolation and purification of Symbiodiniaceae clades can provide a deeper understanding of their biological properties and provide an experimental basis for revealing their important physiology, such as coral-associated physiology mechanisms.In this context Cladocopium C1 sp.was isolated from Acropora formosa, and then rinsed or sheared to make the coral released symbiotic Symbiodiniaceae.Observations were made using an inverted microscope microscope to determine whether Symbiodiniaceae were isolated or not, and the Symbiodiniaceae were centrifuged, diluted, transferred, and cultured every two weeks.Sanger sequencing and high-throughput sequencing were performed on the cultured Symbiodiniaceae.Observations under inverted microscope and electron microscope showed that the cells of the Symbiodiniaceae Cladocopium C1 sp.had a complete structure with multiple well-developed chlorophylls, mitochondria, pyrenoids, etc in the cytoplasm.The Sanger sequencing results were compared on the NCBI platform, and the isolated Symbiodiniaceae were the dominant Symbiodiniaceae Cladocopium C1 sp.of A.formosa.The high-throughput sequencing results showed that the relative abundance of Symbiodiniaceae Cladocopium C1 sp.cells was 98%.The successful isolation of Cladocopium C1 sp.from A.formosa provides a scientific basis for a deeper understanding of the roles of Symbiodiniaceae in the symbiosis with corals and the mechanism of their interactions with corals.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250197
Abstract:
Anther connation is an important floral trait that influences pollination accuracy and efficiency by altering anther arrangement and anther-stigma separation (herkogamy). The flowering biology, the mechanical properties of connate anthers, and the pollination process of Aeschynanthus moningeriae (Gesneriaceae)at Mt. Wuzhi in Hainan Island, China were examined to investigate the developmental pattern of anther connation and pollination adaptation in the bird-pollinated A. moningeriae. The results showed that A. moningeriae is hermaphroditic, with didynamous stamens containing anthers in pairs from the bud stage and that anthers were coherent throughout the whole flowering period. The long anther pair ultimately formed an angle of approximately 180° (parallel) while the short anther pair grow at 115° (inverted V-shape). The short anther pair was connated with more fused part than the long anther pair. The mechanical strength of the short anther pair was F=0.159 ± 0.031 N and F=0.211 ± 0.034 N in the upward and downward directions respectively, which is significantly higher than that of the long anther pair (upward: F=0.127 ± 0.020 N; downward: F=0.117 ± 0.018 N). The fork-tailed sunbird (Aethopyga latouchii) was the only effective pollinator. The red corolla, along with the black stripes on the lobes, function as a nectar guide. The long anther pair was mainly touched by the bird forehead, while the short anther pair was contacted mainly by the narrow base of the bird beak. Such separated pollen deposition increased the contact probobality of the stigma with pollen. Because the bird beak exerted stronger force on anthers, the higher mechanical strength with higher fusion proportion of the short anther pair can thus maintain at a fusion mode and spatial position of the connate anthers under stronger force, increasing pollen removal ratio.
Anther connation is an important floral trait that influences pollination accuracy and efficiency by altering anther arrangement and anther-stigma separation (herkogamy). The flowering biology, the mechanical properties of connate anthers, and the pollination process of Aeschynanthus moningeriae (Gesneriaceae)at Mt. Wuzhi in Hainan Island, China were examined to investigate the developmental pattern of anther connation and pollination adaptation in the bird-pollinated A. moningeriae. The results showed that A. moningeriae is hermaphroditic, with didynamous stamens containing anthers in pairs from the bud stage and that anthers were coherent throughout the whole flowering period. The long anther pair ultimately formed an angle of approximately 180° (parallel) while the short anther pair grow at 115° (inverted V-shape). The short anther pair was connated with more fused part than the long anther pair. The mechanical strength of the short anther pair was F=0.159 ± 0.031 N and F=0.211 ± 0.034 N in the upward and downward directions respectively, which is significantly higher than that of the long anther pair (upward: F=0.127 ± 0.020 N; downward: F=0.117 ± 0.018 N). The fork-tailed sunbird (Aethopyga latouchii) was the only effective pollinator. The red corolla, along with the black stripes on the lobes, function as a nectar guide. The long anther pair was mainly touched by the bird forehead, while the short anther pair was contacted mainly by the narrow base of the bird beak. Such separated pollen deposition increased the contact probobality of the stigma with pollen. Because the bird beak exerted stronger force on anthers, the higher mechanical strength with higher fusion proportion of the short anther pair can thus maintain at a fusion mode and spatial position of the connate anthers under stronger force, increasing pollen removal ratio.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250159
Abstract:
To understand the resource status of aquatic plants in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, the species composition and floristic characteristics of aquatic plants in the park were analyzed based on field surveys and literature review. The results show that a total of 468 species of aquatic plants belonging to 255 genera and 95 families were recorded, among which angiosperms were absolutely dominant with 432 species. Both family- and genus-level species richness showed a "core–periphery" distribution pattern, i.e., species were highly concentrated in a few dominant families and genera. In terms of growth form, herbaceous plants predominated; regarding life form, perennials were the majority; and concerning ecological type, helophytes–emergent plants were dominant. There were 11 key protected wild plants, 26 Chinese endemic species, and 13 threatened plants. A total of 57 alien invasive plant species were recorded, among which harmful invasive species accounted for up to 80.70%, mostly originating from the Americas. The floristic composition at both family and genus levels exhibited strong tropical affinities, with the R/T ratio at the genus level reaching 8.95. All these findings indicate that the aquatic plants in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park are distinctly tropical and of high conservation value, yet they face threats from multiple alien invasive species. It is recommended to strengthen the conservation of rare species and the prevention and control of invasive plants.
To understand the resource status of aquatic plants in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, the species composition and floristic characteristics of aquatic plants in the park were analyzed based on field surveys and literature review. The results show that a total of 468 species of aquatic plants belonging to 255 genera and 95 families were recorded, among which angiosperms were absolutely dominant with 432 species. Both family- and genus-level species richness showed a "core–periphery" distribution pattern, i.e., species were highly concentrated in a few dominant families and genera. In terms of growth form, herbaceous plants predominated; regarding life form, perennials were the majority; and concerning ecological type, helophytes–emergent plants were dominant. There were 11 key protected wild plants, 26 Chinese endemic species, and 13 threatened plants. A total of 57 alien invasive plant species were recorded, among which harmful invasive species accounted for up to 80.70%, mostly originating from the Americas. The floristic composition at both family and genus levels exhibited strong tropical affinities, with the R/T ratio at the genus level reaching 8.95. All these findings indicate that the aquatic plants in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park are distinctly tropical and of high conservation value, yet they face threats from multiple alien invasive species. It is recommended to strengthen the conservation of rare species and the prevention and control of invasive plants.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250136
Abstract:
Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park is the only national park in China with an expressway traversing the Park. To reveal possible potential impacts of the expressway section crossing the National Park, three sites (Zayun, Maoyang, Fanyang) along the expressway section were selected to determine the soil heavy metal (Cr, Ni, Pb, Cu and Zn) contents and analyze the distribution pattern of the heavy metals on both sides of the expressway section. The main sources and affecting factors of each heavy metal were also examined. The results showed that Cr and Ni were the main heavy metals with the highest accumulative rate in the soil, particularly at Zayun and Maoyang, where the soil Cr content exceeded that of the control by 100% and 83.33%, respectively. Soil heavy metal content showed a decreasing trend with increased distance from the expressway or an increasing and then decreasing trend, with the peak appearing within 0-10 m from the expressway. The Geo-accumulation Index showed that the soil Cr, Ni and Zn were at the level of non-pollution or low pollution and thus the overall ecological risk was low. The main source of the soil Cr was traffic emission, while the soil Pb, Cu and Zn were mainly affected by the parent material, with the soil Ni showing mixed sources. All these results suggested that the current ecological risk of soil heavy metal along the expressway section was low, but the soil Cr and Ni were gradually accumulated in the soil near the expressway. It is recommended to strengthen the vegetation restoration and management of the expressway section, to improve the measures for collection and treatment of the expressway runoffs, and to focus on monitoring the dynamics at ecological sensitive sites such as Changhua River, which are crucial for preventing the potential accumulation and migration of soil heavy metals and to ensure the ecological security and high-quality construction of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park.
Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park is the only national park in China with an expressway traversing the Park. To reveal possible potential impacts of the expressway section crossing the National Park, three sites (Zayun, Maoyang, Fanyang) along the expressway section were selected to determine the soil heavy metal (Cr, Ni, Pb, Cu and Zn) contents and analyze the distribution pattern of the heavy metals on both sides of the expressway section. The main sources and affecting factors of each heavy metal were also examined. The results showed that Cr and Ni were the main heavy metals with the highest accumulative rate in the soil, particularly at Zayun and Maoyang, where the soil Cr content exceeded that of the control by 100% and 83.33%, respectively. Soil heavy metal content showed a decreasing trend with increased distance from the expressway or an increasing and then decreasing trend, with the peak appearing within 0-10 m from the expressway. The Geo-accumulation Index showed that the soil Cr, Ni and Zn were at the level of non-pollution or low pollution and thus the overall ecological risk was low. The main source of the soil Cr was traffic emission, while the soil Pb, Cu and Zn were mainly affected by the parent material, with the soil Ni showing mixed sources. All these results suggested that the current ecological risk of soil heavy metal along the expressway section was low, but the soil Cr and Ni were gradually accumulated in the soil near the expressway. It is recommended to strengthen the vegetation restoration and management of the expressway section, to improve the measures for collection and treatment of the expressway runoffs, and to focus on monitoring the dynamics at ecological sensitive sites such as Changhua River, which are crucial for preventing the potential accumulation and migration of soil heavy metals and to ensure the ecological security and high-quality construction of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250137
Abstract:
Hainan Island, as one of the global biodiversity hotspots, has its biodiversity concentrated in National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest. Primulina heterotricha, an endemic plant of Hainan Island, has a widespread distribution and consists of two floral color morphs: yellow-flowered and purple-flowered individuals. First, to clarify the differentiation pattern of floral traits among different geographical populations, we measured key floral traits including flower size, floral mouth width, and corolla tube length across various geographical populations, and analyzed the potential driving effect of geographical isolation on the differentiation of these floral traits. Second, focusing on the differentiation of two floral color morphs and the differences in pollination mechanisms, we comparatively analyzed the flowering dynamics of yellow-flowered and purple-flowered individuals, as well as flower-visiting insects and their visiting behaviors, to reveal the possible differences in pollination mechanisms between populations with different flower colors. A multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) revealed significant differences in floral traits among different geographical populations (P < 0.05), but geographical distance and altitude had no significant effect on floral traits. Populations with different floral colors also did not show significant difference in floral traits (P > 0.05). Moreover, at different flowering stages, there were no significant differences in stamen length, pistil length and herkogamy degree between the two floral color populations (P > 0.05), but the stigma gradually elongated and exceeded the position of the anthers as the flowering period progressed. Observations on flower-visiting insects indicated that the main flower-visiting insects of yellow-flowered populations were Amegilla leptocoma and A. yunnanensis, while the main flower-visiting insect of the purple-flowered populations was A. leptocoma. Thus, yellow-flowered individuals have a more generalized assemblage of flower visitors, whereas purple-flowered individuals exhibit a more specialized pollination system. This study investigated the differentiation pattern of floral traits among different geographical populations, floral color diversity and pollination adaptation process of P. heterotricha, and provides a scientific basis for biodiversity conservation and pollination service function assessment in National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest..
Hainan Island, as one of the global biodiversity hotspots, has its biodiversity concentrated in National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest. Primulina heterotricha, an endemic plant of Hainan Island, has a widespread distribution and consists of two floral color morphs: yellow-flowered and purple-flowered individuals. First, to clarify the differentiation pattern of floral traits among different geographical populations, we measured key floral traits including flower size, floral mouth width, and corolla tube length across various geographical populations, and analyzed the potential driving effect of geographical isolation on the differentiation of these floral traits. Second, focusing on the differentiation of two floral color morphs and the differences in pollination mechanisms, we comparatively analyzed the flowering dynamics of yellow-flowered and purple-flowered individuals, as well as flower-visiting insects and their visiting behaviors, to reveal the possible differences in pollination mechanisms between populations with different flower colors. A multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) revealed significant differences in floral traits among different geographical populations (P < 0.05), but geographical distance and altitude had no significant effect on floral traits. Populations with different floral colors also did not show significant difference in floral traits (P > 0.05). Moreover, at different flowering stages, there were no significant differences in stamen length, pistil length and herkogamy degree between the two floral color populations (P > 0.05), but the stigma gradually elongated and exceeded the position of the anthers as the flowering period progressed. Observations on flower-visiting insects indicated that the main flower-visiting insects of yellow-flowered populations were Amegilla leptocoma and A. yunnanensis, while the main flower-visiting insect of the purple-flowered populations was A. leptocoma. Thus, yellow-flowered individuals have a more generalized assemblage of flower visitors, whereas purple-flowered individuals exhibit a more specialized pollination system. This study investigated the differentiation pattern of floral traits among different geographical populations, floral color diversity and pollination adaptation process of P. heterotricha, and provides a scientific basis for biodiversity conservation and pollination service function assessment in National Park of Hainan Tropical Rainforest..
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250067
Abstract:
Sequencing batch reactor (SBR) was used to treat domestic wastewater, and the start-up conditions of slightly bulking activated sludge process was investigated under the combined effects of low dissolved oxygen (DO) and low sludge loading (Ns). Moreover, different influent COD/NH4+-N(C/N) ratios (C/N) were designed to examine their impact on nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency. The results indicated that under conditions of DO ranging from 0.5 to 0.8 mg·L−1 and Ns between 215.4~258.48 mg COD/L·d, the slightly bulking activated sludge process could be successfully initiated after a brief period of severe bulking, with the sludge volume index (SVI) stabilizing at about 262 mL·g−1. As the influent C/N ratio increased, the number and size of mycelial clumps within the system gradually increased, leading to significant changes in the microbial community, with the abundance of Thiothrix increasing from 30.21% to 54.41%. The influent C/N ratio had a minor impact on COD and NH4+-N removal efficiencies, with COD removal rates reaching 97.21% and NH4+-N removal rates exceeding 98%. But it significantly affected TN and TP removal efficiencies. When the influent C/N ratios were 4, 6, and 11, the average TN removal efficiencies of the system were 37.15%, 52.65%, and 77.94%, respectively, and the average TP removal efficiencies were 36.82%, 45.71%, and 64.30%.
Sequencing batch reactor (SBR) was used to treat domestic wastewater, and the start-up conditions of slightly bulking activated sludge process was investigated under the combined effects of low dissolved oxygen (DO) and low sludge loading (Ns). Moreover, different influent COD/NH4+-N(C/N) ratios (C/N) were designed to examine their impact on nitrogen and phosphorus removal efficiency. The results indicated that under conditions of DO ranging from 0.5 to 0.8 mg·L−1 and Ns between 215.4~258.48 mg COD/L·d, the slightly bulking activated sludge process could be successfully initiated after a brief period of severe bulking, with the sludge volume index (SVI) stabilizing at about 262 mL·g−1. As the influent C/N ratio increased, the number and size of mycelial clumps within the system gradually increased, leading to significant changes in the microbial community, with the abundance of Thiothrix increasing from 30.21% to 54.41%. The influent C/N ratio had a minor impact on COD and NH4+-N removal efficiencies, with COD removal rates reaching 97.21% and NH4+-N removal rates exceeding 98%. But it significantly affected TN and TP removal efficiencies. When the influent C/N ratios were 4, 6, and 11, the average TN removal efficiencies of the system were 37.15%, 52.65%, and 77.94%, respectively, and the average TP removal efficiencies were 36.82%, 45.71%, and 64.30%.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240159
Abstract:
Vibrio alginolyticus is a common marine Gram-negative bacterium widely found in aquaculture environments. It exhibits strong infectivity and pathogenicity toward cultured fish, shellfish, and shrimp, causing significant economic losses in the aquaculture industry due to vibriosis. The tatD gene encodes a protein with nuclease activity, which is related to the formation of bacterial biofilms and the regulation of virulence. An attempt was made to investigate the role of tatD gene in the growth and biofilm formation of V. alginolyticus strain HN08155 by utilizing gene knockout technology. The results indicate that the strain HN08155 contains three tatD genes. Under normal nutrient conditions, the tatD gene does not affect bacterial growth, whereas it plays a regulatory role in bacterial growth under low-nutrient conditions. The extracellular tatD protein demonstrates nuclease activity, with the wild-type strain showing a greater capacity for DNA degradation in the culture supernatant compared to the tatD knockout strain. Induction with 0.1% Triton X-100 significantly increased the autolysis rate of the tatD knockout strain compared to the wild-type strain. Additionally, the absence of the tatD gene resulted in a significant increase in both the quantity and thickness of the biofilm formed by V. alginolyticus.
Vibrio alginolyticus is a common marine Gram-negative bacterium widely found in aquaculture environments. It exhibits strong infectivity and pathogenicity toward cultured fish, shellfish, and shrimp, causing significant economic losses in the aquaculture industry due to vibriosis. The tatD gene encodes a protein with nuclease activity, which is related to the formation of bacterial biofilms and the regulation of virulence. An attempt was made to investigate the role of tatD gene in the growth and biofilm formation of V. alginolyticus strain HN08155 by utilizing gene knockout technology. The results indicate that the strain HN08155 contains three tatD genes. Under normal nutrient conditions, the tatD gene does not affect bacterial growth, whereas it plays a regulatory role in bacterial growth under low-nutrient conditions. The extracellular tatD protein demonstrates nuclease activity, with the wild-type strain showing a greater capacity for DNA degradation in the culture supernatant compared to the tatD knockout strain. Induction with 0.1% Triton X-100 significantly increased the autolysis rate of the tatD knockout strain compared to the wild-type strain. Additionally, the absence of the tatD gene resulted in a significant increase in both the quantity and thickness of the biofilm formed by V. alginolyticus.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.202500077
Abstract:
This study investigated the diversity and phenology of Saturniidae moths in Limushan, Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. Through light trapping and transect surveys from 2020 to 2024, we recorded 15 Saturniidae species comprising 2 subfamilies and 9 genera, including 3 Hainan-endemic species. Analysis of flight periods revealed peak activity between November and the following August, with 56.34% of moths showing peak phototactic response at 03:00–06:00. Laboratory rearing indicated 6 univoltine species, 2 bivoltine species, and 7 multivoltine species. The faunal composition of Saturniidae in Limushan aligned with tropical zoogeographic regions, reflecting the area's distinctive ecological environment and biodiversity. These findings offer critical data for future species conservation and resource utilization .
This study investigated the diversity and phenology of Saturniidae moths in Limushan, Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. Through light trapping and transect surveys from 2020 to 2024, we recorded 15 Saturniidae species comprising 2 subfamilies and 9 genera, including 3 Hainan-endemic species. Analysis of flight periods revealed peak activity between November and the following August, with 56.34% of moths showing peak phototactic response at 03:00–06:00. Laboratory rearing indicated 6 univoltine species, 2 bivoltine species, and 7 multivoltine species. The faunal composition of Saturniidae in Limushan aligned with tropical zoogeographic regions, reflecting the area's distinctive ecological environment and biodiversity. These findings offer critical data for future species conservation and resource utilization .
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240183
Abstract:
To assess the current status of vascular plants in Mangzhou Wetland Park of the Guangdong-Macao in-Depth Cooperation Zone in Hengqin, the composition, floristic characteristics, and distribution of alien invasive species of vascular plants were systematically investigated through field surveys and historical data analysis. The results revealed that a total of 245 vascular plant species were recorded, belonging to 86 families and 202 genera. Of the vascular plant species angiosperms dominated (95.51%, 234 species), followed by ferns (3.7%) and gymnosperms (0.8%), and herbaceous plants constituted the predominant life form (47.3%), with terrestrial species accounting for 89.4% of the total. The flora exhibited significant tropical affinity, with the families and genera of the plants distributed in the tropics representing 56.98% and 83.17%, respectively, consistent with the floristic patterns of other Pearl River Delta wetland parks. Forty-three alien invasive species were identified, including high-risk Category I invaders (e.g., Lantana camara, Mikania micrantha), which comprised 30.23% of invasive taxa, indicating substantial ecological threats. Three species of second-level national protected plants (e.g., Ormosia pinnata, Dracaena cambodiana) and one Guangdong Province key protected species (Diospyros vaccinioides) were documented. This study clarifies the post-2017 plant resource status of Mangzhou Wetland Park and identifies invasive alien plants as potential ecological risks. We recommend to adopt Nature-based Solutions (NbS) to enhance native plant utilization, optimize invasive species monitoring systems, and integrate ecological restoration with community co-management to improve wetland ecosystem stability and management efficacy. This study provides critical data support for the ecological management of coastal wetlands in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area.
To assess the current status of vascular plants in Mangzhou Wetland Park of the Guangdong-Macao in-Depth Cooperation Zone in Hengqin, the composition, floristic characteristics, and distribution of alien invasive species of vascular plants were systematically investigated through field surveys and historical data analysis. The results revealed that a total of 245 vascular plant species were recorded, belonging to 86 families and 202 genera. Of the vascular plant species angiosperms dominated (95.51%, 234 species), followed by ferns (3.7%) and gymnosperms (0.8%), and herbaceous plants constituted the predominant life form (47.3%), with terrestrial species accounting for 89.4% of the total. The flora exhibited significant tropical affinity, with the families and genera of the plants distributed in the tropics representing 56.98% and 83.17%, respectively, consistent with the floristic patterns of other Pearl River Delta wetland parks. Forty-three alien invasive species were identified, including high-risk Category I invaders (e.g., Lantana camara, Mikania micrantha), which comprised 30.23% of invasive taxa, indicating substantial ecological threats. Three species of second-level national protected plants (e.g., Ormosia pinnata, Dracaena cambodiana) and one Guangdong Province key protected species (Diospyros vaccinioides) were documented. This study clarifies the post-2017 plant resource status of Mangzhou Wetland Park and identifies invasive alien plants as potential ecological risks. We recommend to adopt Nature-based Solutions (NbS) to enhance native plant utilization, optimize invasive species monitoring systems, and integrate ecological restoration with community co-management to improve wetland ecosystem stability and management efficacy. This study provides critical data support for the ecological management of coastal wetlands in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250098
Abstract:
.The effects of different nitrogen treatments on root growth and fungal community structures in both the roots and rhizosphere of budded seedling of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) were investigated to determine optimal nitrogen application rate for robust growth of the budded seedlings. Mini-seedling buddings of Clone Reyan 7-33-97 of rubber tree at the age of 3 months old were selected as budded seedlings for experiment and applied with nitrogen fertilizer at different rates. An outdoor pot experiment was conducted with four treatments, control (CK, no nitrogen), low nitrogen (LN, 0.32 g/kg), medium nitrogen (MN, 0.64 g/kg), and high nitrogen (HN, 1.28 g/kg), and root morphological parameters and compositional and diversity shifts in fungal communities in the roots and rhizosphere were determined and analyzed. Results revealed significant effect of different nitrogen treatments on species composition in the roots and rhyzosphere of the mini-seedling buddings. For root fungi, the LN treatment maintained dominance of Basidiomycota and Thelephorales, whereas the HN treatment substantially increased Ascomycota and Sordariales; in the rhizosphere, the LN and MN treatments elevated unclassified fungi and Hypocreales, while HN significantly suppressed Basidiomycota and Annulatascales. The LN treatment (0.32 g/kg) maximized alpha diversity, with root fungal Shannon (3.22) and Simpson (0.904) indices increasing by 15.84% and 12.26% respectively as against the CK, while rhizosphere Shannon (3.13) and Simpson (0.914) indices rose by 18.11% and 16.46%, respectively. Root Chao1 (385.97) and ACE (391.43) indices peaked in the LN treatment, 1.16-fold and 1.27-fold higher than that of CK; rhizosphere Chao1 and ACE indices in the LN treatment still elevated significantly, 72.01% and 68.61% higher than those of CK. Beta diversity exhibited highly significant differences (*p* < 0.001) in the roots and rhyzosphere among nitrogen treatments and application location, with higher difference in the rhizosphere than in the roots among the nitrogen treatments. Principal Co-ordinates Analysis demonstrated convergent clustering among nitrogen treatments (LN-HN), which was distinctly separated from CK, and higher nitrogen sensitivity in rhizosphere fungi than in the root fungi (R2 difference: 6.07%). The LN treatment (0.32 g/kg) was hence recommended as it helps enhance the diversity and richness of the fungal community in both the root system and the rhizosphere, thereby optimizing the fungal community structure in the rhizosphere of mini-seedling buddings.
.The effects of different nitrogen treatments on root growth and fungal community structures in both the roots and rhizosphere of budded seedling of rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) were investigated to determine optimal nitrogen application rate for robust growth of the budded seedlings. Mini-seedling buddings of Clone Reyan 7-33-97 of rubber tree at the age of 3 months old were selected as budded seedlings for experiment and applied with nitrogen fertilizer at different rates. An outdoor pot experiment was conducted with four treatments, control (CK, no nitrogen), low nitrogen (LN, 0.32 g/kg), medium nitrogen (MN, 0.64 g/kg), and high nitrogen (HN, 1.28 g/kg), and root morphological parameters and compositional and diversity shifts in fungal communities in the roots and rhizosphere were determined and analyzed. Results revealed significant effect of different nitrogen treatments on species composition in the roots and rhyzosphere of the mini-seedling buddings. For root fungi, the LN treatment maintained dominance of Basidiomycota and Thelephorales, whereas the HN treatment substantially increased Ascomycota and Sordariales; in the rhizosphere, the LN and MN treatments elevated unclassified fungi and Hypocreales, while HN significantly suppressed Basidiomycota and Annulatascales. The LN treatment (0.32 g/kg) maximized alpha diversity, with root fungal Shannon (3.22) and Simpson (0.904) indices increasing by 15.84% and 12.26% respectively as against the CK, while rhizosphere Shannon (3.13) and Simpson (0.914) indices rose by 18.11% and 16.46%, respectively. Root Chao1 (385.97) and ACE (391.43) indices peaked in the LN treatment, 1.16-fold and 1.27-fold higher than that of CK; rhizosphere Chao1 and ACE indices in the LN treatment still elevated significantly, 72.01% and 68.61% higher than those of CK. Beta diversity exhibited highly significant differences (*p* < 0.001) in the roots and rhyzosphere among nitrogen treatments and application location, with higher difference in the rhizosphere than in the roots among the nitrogen treatments. Principal Co-ordinates Analysis demonstrated convergent clustering among nitrogen treatments (LN-HN), which was distinctly separated from CK, and higher nitrogen sensitivity in rhizosphere fungi than in the root fungi (R2 difference: 6.07%). The LN treatment (0.32 g/kg) was hence recommended as it helps enhance the diversity and richness of the fungal community in both the root system and the rhizosphere, thereby optimizing the fungal community structure in the rhizosphere of mini-seedling buddings.
Antioxidant activity and LC-MS component analysis of water extracts from the flowers of Bombax ceiba
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250100
Abstract:
To explore the potential of the aqueous extract of Bombax ceiba flower (BWE) in the field of antioxidation, the effects of different solid-liquid ratios and decoction times on the total flavonoid content and in vitro antioxidant indices such as DPPH radical scavenging rate, ABTS cation radical scavenging rate, and Fe3+ reducing ability of the extract were investigated. The optimal process parameters of solid-liquid ratio and decoction time were screened out. Subsequently, the chemical components of BWE were identified and analyzed by using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to provide key scientific basis for the development and application of BWE in the field of antioxidation. The results showed that within a certain range, the scavenging ability of BWE on DPPH and ABTS radicals and the reducing ability of Fe3+ increased with the concentration. The optimal parameters were a solid-liquid ratio of 1∶12.5 and a decoction time of 1.5 h, with IC50 values being 87.44 mg·L−1 and 46.77 mg·L−1, respectively. However, the Fe3+ reducing ability of BWE was higher than that of vitamin C. These results indicated that BWE had high antioxidant activity. A total of 73 flavonoids were identified in BWE, among which four chemical components in BWE, i.e. quercetin 3-O-glucuronide (49.99%), Delphinidin-3-O-(6''-O-alpha-rhamnopyranosyl-beta-glucopyranoside) (8.24%), rutin (7.45%), and gallocatechin (5.65%), were the highest in relative content and are important pharmacologically active substances. This provides a theoretical basis for further in-depth exploration and utilization of the medicinal potential of flavonoids in BWE.
To explore the potential of the aqueous extract of Bombax ceiba flower (BWE) in the field of antioxidation, the effects of different solid-liquid ratios and decoction times on the total flavonoid content and in vitro antioxidant indices such as DPPH radical scavenging rate, ABTS cation radical scavenging rate, and Fe3+ reducing ability of the extract were investigated. The optimal process parameters of solid-liquid ratio and decoction time were screened out. Subsequently, the chemical components of BWE were identified and analyzed by using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) to provide key scientific basis for the development and application of BWE in the field of antioxidation. The results showed that within a certain range, the scavenging ability of BWE on DPPH and ABTS radicals and the reducing ability of Fe3+ increased with the concentration. The optimal parameters were a solid-liquid ratio of 1∶12.5 and a decoction time of 1.5 h, with IC50 values being 87.44 mg·L−1 and 46.77 mg·L−1, respectively. However, the Fe3+ reducing ability of BWE was higher than that of vitamin C. These results indicated that BWE had high antioxidant activity. A total of 73 flavonoids were identified in BWE, among which four chemical components in BWE, i.e. quercetin 3-O-glucuronide (49.99%), Delphinidin-3-O-(6''-O-alpha-rhamnopyranosyl-beta-glucopyranoside) (8.24%), rutin (7.45%), and gallocatechin (5.65%), were the highest in relative content and are important pharmacologically active substances. This provides a theoretical basis for further in-depth exploration and utilization of the medicinal potential of flavonoids in BWE.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250089
Abstract:
This study systematically investigated the effects of two distinct cultivation models, land-based industrial farming and seafloor sowing, on the growth characteristics and nutritional quality of Betaphycus gelatinus, aiming to provide a theoretical foundation for optimizing large-scale cultivation practices. Through a 60-day cultivation experiment, it was observed that seafloor-sown B. gelatinus exhibited significantly higher branch number, branch length, relative growth rate, and mass increase rate compared to land-based industrial farming (P<0.05). Specifically, the mass increase rate for land-based industrially cultivated B. gelatinus was 117.18±6.02%, with a relative growth rate of 1.29±0.06 %·d−1, whereas seafloor-sown B. gelatinus demonstrated a mass increase rate of 196.87±5.72% and a relative growth rate of 1.81±0.04 %·d−1. In terms of pigment content, land-based industrially cultivated B. gelatinus showed significantly higher levels of chlorophyll a, carotenoids, phycoerythrin, and phycocyanin compared to seafloor-sown specimens (P<0.05). No significant differences were observed in carrageenan content and gel strength between the two cultivation models (P>0.05). Industrially cultivated B. gelatinus contained higher levels of flavor-enhancing amino acids, while seafloor-sown B. gelatinus exhibited superior amino acid chemical scores. Additionally, industrially cultivated B. gelatinus had higher potassium and zinc content but lower levels of calcium, sodium, magnesium, manganese, and aluminum compared to seafloor-sown B. gelatinus. The findings indicate that seafloor sowing is more conducive to algal growth and yield formation, whereas industrial farming promotes the synthesis of photosynthetic pigments and flavor-enhancing amino acids.
This study systematically investigated the effects of two distinct cultivation models, land-based industrial farming and seafloor sowing, on the growth characteristics and nutritional quality of Betaphycus gelatinus, aiming to provide a theoretical foundation for optimizing large-scale cultivation practices. Through a 60-day cultivation experiment, it was observed that seafloor-sown B. gelatinus exhibited significantly higher branch number, branch length, relative growth rate, and mass increase rate compared to land-based industrial farming (P<0.05). Specifically, the mass increase rate for land-based industrially cultivated B. gelatinus was 117.18±6.02%, with a relative growth rate of 1.29±0.06 %·d−1, whereas seafloor-sown B. gelatinus demonstrated a mass increase rate of 196.87±5.72% and a relative growth rate of 1.81±0.04 %·d−1. In terms of pigment content, land-based industrially cultivated B. gelatinus showed significantly higher levels of chlorophyll a, carotenoids, phycoerythrin, and phycocyanin compared to seafloor-sown specimens (P<0.05). No significant differences were observed in carrageenan content and gel strength between the two cultivation models (P>0.05). Industrially cultivated B. gelatinus contained higher levels of flavor-enhancing amino acids, while seafloor-sown B. gelatinus exhibited superior amino acid chemical scores. Additionally, industrially cultivated B. gelatinus had higher potassium and zinc content but lower levels of calcium, sodium, magnesium, manganese, and aluminum compared to seafloor-sown B. gelatinus. The findings indicate that seafloor sowing is more conducive to algal growth and yield formation, whereas industrial farming promotes the synthesis of photosynthetic pigments and flavor-enhancing amino acids.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230113
Abstract:
Pitaya (Hylocereus spp.), a high-value tropical fruit crop, has seen continuous expansion in pitaya producing areas across Hainan, Guangdong, and Guangxi in China. However, yield limitations caused by differential self-compatibility among cultivars remain a critical challenge. Optimal pollination strategies for three major pitaya cultivars ('Dahong', 'Spineless Huanglong', and 'Yanwuo') were systematically evaluated through controlled pollination experiments. Significant phenological variations were observed in these experiments. Pitaya 'Dahong' and 'Spineless Huanglong' required 18 days for floral development and 30 days for fruit maturation, while pitaya 'Yanwuo' needed 50 days and 90 days, respectively. Reproductive analysis revealed complete self-incompatibility in 'Spineless Huanglong' (0% fruit set) and partial self-compatibility in other cultivars. Cross-pollination exhibited genotype-specific effects. 'Spineless Huanglong' pollen increased 'Dahong' fruit set by 37% (p<0.05) and single fruit weight by 21.5%, while 'Dahong' pollen enabled 'Spineless Huanglong' to achieve an average fruit weight of 322.1 g. 'Spineless Huanglong' pollen also optimized 'Yanwuo' performance (90% fruit set; 231.6 g/fruit). Fruit trait correlations showed significant positive relationships between fruit weight and diameter (r=0.82-0.91, p<0.01), but negative correlations with soluble solids content. It is the first time that a reciprocal high-efficiency pollination system between pitaya 'Dahong' and 'Spineless Huanglong' was established, and 'Spineless Huanglong' was identified as the optimal pollinizer for 'Yanwuo''. These findings provide both theoretical and practical foundations for enhancing yield and quality in commercial pitaya production.
Pitaya (Hylocereus spp.), a high-value tropical fruit crop, has seen continuous expansion in pitaya producing areas across Hainan, Guangdong, and Guangxi in China. However, yield limitations caused by differential self-compatibility among cultivars remain a critical challenge. Optimal pollination strategies for three major pitaya cultivars ('Dahong', 'Spineless Huanglong', and 'Yanwuo') were systematically evaluated through controlled pollination experiments. Significant phenological variations were observed in these experiments. Pitaya 'Dahong' and 'Spineless Huanglong' required 18 days for floral development and 30 days for fruit maturation, while pitaya 'Yanwuo' needed 50 days and 90 days, respectively. Reproductive analysis revealed complete self-incompatibility in 'Spineless Huanglong' (0% fruit set) and partial self-compatibility in other cultivars. Cross-pollination exhibited genotype-specific effects. 'Spineless Huanglong' pollen increased 'Dahong' fruit set by 37% (p<0.05) and single fruit weight by 21.5%, while 'Dahong' pollen enabled 'Spineless Huanglong' to achieve an average fruit weight of 322.1 g. 'Spineless Huanglong' pollen also optimized 'Yanwuo' performance (90% fruit set; 231.6 g/fruit). Fruit trait correlations showed significant positive relationships between fruit weight and diameter (r=0.82-0.91, p<0.01), but negative correlations with soluble solids content. It is the first time that a reciprocal high-efficiency pollination system between pitaya 'Dahong' and 'Spineless Huanglong' was established, and 'Spineless Huanglong' was identified as the optimal pollinizer for 'Yanwuo''. These findings provide both theoretical and practical foundations for enhancing yield and quality in commercial pitaya production.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250061
Abstract:
Nine tea samples, including Hainan assamica black tea (Camellia sinensis var. assamica), Yunnan assamica black tea and their blended black tea at different ratios, were selected to investigate the quality evolution pattern of Hainan assamica black tea in the blended processing process. The effects of tea variety, harvesting season, and blending ratio on volatile compounds, sensory attributes, and nutrient components were analyzed. Results demonstrated that early-spring Hainan assamica black tea exhibited optimal performance in appearance, infusion color, and taste (83.02 score). Key nutritional determinants of tea flavor included ash content, soluble sugars, total phenols, total flavonoids, and catechin levels. Volatile profiling identified linalool, methyl salicylate, phenylacetaldehyde, and α-ionone as characteristic aroma compounds. Multivariate analysis revealed that blending ratio, harvesting season, and tea variety constituted principal factors influencing compositional differences. The tea sample LH6 (20% Hainan assamica black tea + 80% Yunnan assamica black tea) had the highest sensory score (80.46 score), which was closest to that of the tea sample LH1 and significantly higher than those of the other blended samples. Its infusion color was bright indigo red, and its aroma was honey-like, fat, and minty refreshing. It is concluded that early-spring Hainan assamica black tea combines superior sensory attributes with functional component enrichment. The research results can clarify the contribution threshold of Hainan assamica variety in blending, and reveal the regulatory mechanism of season and variety on its characteristic flavor.
Nine tea samples, including Hainan assamica black tea (Camellia sinensis var. assamica), Yunnan assamica black tea and their blended black tea at different ratios, were selected to investigate the quality evolution pattern of Hainan assamica black tea in the blended processing process. The effects of tea variety, harvesting season, and blending ratio on volatile compounds, sensory attributes, and nutrient components were analyzed. Results demonstrated that early-spring Hainan assamica black tea exhibited optimal performance in appearance, infusion color, and taste (83.02 score). Key nutritional determinants of tea flavor included ash content, soluble sugars, total phenols, total flavonoids, and catechin levels. Volatile profiling identified linalool, methyl salicylate, phenylacetaldehyde, and α-ionone as characteristic aroma compounds. Multivariate analysis revealed that blending ratio, harvesting season, and tea variety constituted principal factors influencing compositional differences. The tea sample LH6 (20% Hainan assamica black tea + 80% Yunnan assamica black tea) had the highest sensory score (80.46 score), which was closest to that of the tea sample LH1 and significantly higher than those of the other blended samples. Its infusion color was bright indigo red, and its aroma was honey-like, fat, and minty refreshing. It is concluded that early-spring Hainan assamica black tea combines superior sensory attributes with functional component enrichment. The research results can clarify the contribution threshold of Hainan assamica variety in blending, and reveal the regulatory mechanism of season and variety on its characteristic flavor.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250096
Abstract:
To investigate the potential for large-scale cultivation of Ocimum gratissimum L. in Quanzhou, O. gratissimum L. was introduced for trial planting to comprehensively evaluate its ecological adaptability. The agronomic traits, yield, and essential oil yield and composition were systematically compared. The results indicated that O. gratissimum L. at the Luojiang experiment site had the best performance in plant height, plant spread, individual plant weight, and yield, showing strong environmental adaptability and growth stability. The essential oil yield was closely related to the phenological period, with the highest yield (6.53~6.87 mL·kg−1) and eugenol content (69.49%) being observed during the harvest period (early flowering stage), meeting the standards of the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. GC-MS analysis identified 27 compounds, with eugenol, germacrene D, and β-caryophyllene as the main components. Phenolic compounds exhibited the highest relative abundance, while terpenes and alcohols were the most diverse categories. Overall, Luojiang in Quanzhou is identified as a suitable cultivation area. This trial planting with reasonable planting density (39 000~45 000 plants per hm2) in Luojiang, Quanchou, combined with timely harvesting, provides a practical basis for achieving high yield and high-quality essential oil production.
To investigate the potential for large-scale cultivation of Ocimum gratissimum L. in Quanzhou, O. gratissimum L. was introduced for trial planting to comprehensively evaluate its ecological adaptability. The agronomic traits, yield, and essential oil yield and composition were systematically compared. The results indicated that O. gratissimum L. at the Luojiang experiment site had the best performance in plant height, plant spread, individual plant weight, and yield, showing strong environmental adaptability and growth stability. The essential oil yield was closely related to the phenological period, with the highest yield (6.53~6.87 mL·kg−1) and eugenol content (69.49%) being observed during the harvest period (early flowering stage), meeting the standards of the Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China. GC-MS analysis identified 27 compounds, with eugenol, germacrene D, and β-caryophyllene as the main components. Phenolic compounds exhibited the highest relative abundance, while terpenes and alcohols were the most diverse categories. Overall, Luojiang in Quanzhou is identified as a suitable cultivation area. This trial planting with reasonable planting density (39 000~45 000 plants per hm2) in Luojiang, Quanchou, combined with timely harvesting, provides a practical basis for achieving high yield and high-quality essential oil production.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250113
Abstract:
Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) is an important staple and economic crop in China, but its yield and quality are severely constrained by root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.) infections. To identify effective and safe control agents, a field trial was conducted in Changjiang County, Hainan Province, to evaluate the efficacy of 30% fosthiazate emulsion and 450 g·L−1 cyclobutrifluram suspension concentrate against root-knot nematodes in sweet potato. The results showed that both nematicides significantly (P < 0.05) reduced the disease severity index and tuber infection rate. Among them, cyclobutrifluram showed significantly higher and more persistent efficacy, with relative efficacies of 93.82% and 88.08% at 58 and 77 days after planting, respectively—significantly greater than those of fosthiazate (80.58% and 71.30%). Microscopic observation further revealed that cyclobutrifluram reduced nematode population density in the treated roots by more than 96%, markedly outperforming fosthiazate (47.1%). These findings indicate that cyclobutrifluram possesses strong potential for field application and represents a promising alternative nematicide, particularly under the current scenario of increasing nematode resistance.
Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) is an important staple and economic crop in China, but its yield and quality are severely constrained by root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne spp.) infections. To identify effective and safe control agents, a field trial was conducted in Changjiang County, Hainan Province, to evaluate the efficacy of 30% fosthiazate emulsion and 450 g·L−1 cyclobutrifluram suspension concentrate against root-knot nematodes in sweet potato. The results showed that both nematicides significantly (P < 0.05) reduced the disease severity index and tuber infection rate. Among them, cyclobutrifluram showed significantly higher and more persistent efficacy, with relative efficacies of 93.82% and 88.08% at 58 and 77 days after planting, respectively—significantly greater than those of fosthiazate (80.58% and 71.30%). Microscopic observation further revealed that cyclobutrifluram reduced nematode population density in the treated roots by more than 96%, markedly outperforming fosthiazate (47.1%). These findings indicate that cyclobutrifluram possesses strong potential for field application and represents a promising alternative nematicide, particularly under the current scenario of increasing nematode resistance.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250083
Abstract:
Oil-tea Camellia is a perennial woody oil tree species, and reasonable fertilizer application is of great significance for increasing the oil-tea yield. Compound fertilizer at a reasonable ratio of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) can provide balanced nutrition, which is crucial for improving the growth and yield of oil-tea Camellia. In order to develop a specialized compound fertilizer suitable for the soil conditions of oil-tea Camellia plantations in tropical areas, compound fertilizers at four authoritative ratios of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium were applied to a plantation of oil-tea Camellia. vietnamensis ‘Houchen 3’, and the leaf nutrient contents, the soil physical and chemical properties, and the enzyme activities in the oil-tea plantation were determined. The results showed that the application of compound fertilizers at different NPK ratios can significantly improve the nutritional elements of oil-tea Camellia leaves, as well as the soil physical and chemical properties and soil enzyme activity in the oil-tea plantation. In terms of improving leaf nutrients, soil nutrients and biological activity, the C (N∶P∶K = 1∶2∶2) and D (N∶P∶K = 10∶6∶8) treatments largely have the best effect on oil-tea Camellia in the tropical regions, and had the greatest promoting effect especially on the content of available potassium in soil, with an increase of 92.68% and 116.17% in the 0-20 cm and 20-40 cm soil layers, respectively, compared to the control without fertilization (CK2), which is of great significance for targeted improvement of soil fertility and available potassium content in Hainan oil-tea Camellia plantations. These results provide data for screening specialized compound fertilizers suitable for oil-tea Camellia in the tropical regions, laying a scientific foundation for further research of specialized compound fertilizers for oil-tea Camellia in the tropical regions.
Oil-tea Camellia is a perennial woody oil tree species, and reasonable fertilizer application is of great significance for increasing the oil-tea yield. Compound fertilizer at a reasonable ratio of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) can provide balanced nutrition, which is crucial for improving the growth and yield of oil-tea Camellia. In order to develop a specialized compound fertilizer suitable for the soil conditions of oil-tea Camellia plantations in tropical areas, compound fertilizers at four authoritative ratios of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium were applied to a plantation of oil-tea Camellia. vietnamensis ‘Houchen 3’, and the leaf nutrient contents, the soil physical and chemical properties, and the enzyme activities in the oil-tea plantation were determined. The results showed that the application of compound fertilizers at different NPK ratios can significantly improve the nutritional elements of oil-tea Camellia leaves, as well as the soil physical and chemical properties and soil enzyme activity in the oil-tea plantation. In terms of improving leaf nutrients, soil nutrients and biological activity, the C (N∶P∶K = 1∶2∶2) and D (N∶P∶K = 10∶6∶8) treatments largely have the best effect on oil-tea Camellia in the tropical regions, and had the greatest promoting effect especially on the content of available potassium in soil, with an increase of 92.68% and 116.17% in the 0-20 cm and 20-40 cm soil layers, respectively, compared to the control without fertilization (CK2), which is of great significance for targeted improvement of soil fertility and available potassium content in Hainan oil-tea Camellia plantations. These results provide data for screening specialized compound fertilizers suitable for oil-tea Camellia in the tropical regions, laying a scientific foundation for further research of specialized compound fertilizers for oil-tea Camellia in the tropical regions.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250072
Abstract:
Biston suppressaria is a pest threatening eucalyptus plantations. Bacteria from its intestine were isolated and identified by using traditional culture and molecular biology methods to find pathogenic strains for biocontrol of this pest. Fifteen bacteria with distinct morphological traits were isolated from naturally infected, lethal B. suppressarias and identified into ten genera, including Enterobacter, Serratia, and Bacillus via 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The Bacillaceae strain B6 showed the highest pathogenicity. After treated with B6 by using the feeding method, B. suppressarias had a cumulative corrected mortality of 60.0% at day 7, with specific pathogenic characteristics observed in the dead insects. Re-isolation yielded colonies morphologically consistent with B6, with a sequence similarity of 99.80%. Moreover, B6 exhibited certain pathogenicity to the other two types of Geometridae larvae, including the common cutworm and small emerald moth, and showed significant insecticidal effects on B. suppressarias at the early infection stage. This study provides a theoretical basis for the use of the Bacillaceae strain B6 to control B. suppressarias and develop eco-friendly control strategies.
Biston suppressaria is a pest threatening eucalyptus plantations. Bacteria from its intestine were isolated and identified by using traditional culture and molecular biology methods to find pathogenic strains for biocontrol of this pest. Fifteen bacteria with distinct morphological traits were isolated from naturally infected, lethal B. suppressarias and identified into ten genera, including Enterobacter, Serratia, and Bacillus via 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The Bacillaceae strain B6 showed the highest pathogenicity. After treated with B6 by using the feeding method, B. suppressarias had a cumulative corrected mortality of 60.0% at day 7, with specific pathogenic characteristics observed in the dead insects. Re-isolation yielded colonies morphologically consistent with B6, with a sequence similarity of 99.80%. Moreover, B6 exhibited certain pathogenicity to the other two types of Geometridae larvae, including the common cutworm and small emerald moth, and showed significant insecticidal effects on B. suppressarias at the early infection stage. This study provides a theoretical basis for the use of the Bacillaceae strain B6 to control B. suppressarias and develop eco-friendly control strategies.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250097
Abstract:
Hainan is an important growing area of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) in China, and its tropical climatic conditions lead to severe problems such as serious overlapping generations of pests and prominent pesticide resistance, making pest control quite challenging. Screening for insect-resistant varieties is an effective means of controlling crop pests. Given the relative scarcity of research on cowpea varieties resistant to Megalurothrips usitatus, the main pest species and their occurrence patterns on cowpea were identified through a systematic survey of pest occurrences on 57 cowpea varieties throughout the entire growth period in Danzhou City, Hainan Province. Additionally, cowpea varieties resistant to thrips were selected. The results showed that the main pests of cowpea grown in Danzhou, Hainan include Megalurothrips usitatus, Aphis craccivora, Trialeurodes vaporariorum, and Etiella zinckenella, among which M. usitatus, A. craccivora, and T. vaporariorum are the dominant pests. The peak numbers of the main pests were as follows: M. usitatus reached a peak of 154 individuals per plant on April 10th; A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum reached the peaks of 179 individuals per plant and 117 individuals per plant, respectively on April 23; E. zinckenella caused relatively slight damage, with a peak of 43 individuals per plant on April 24th. The population dynamics of the dominant pests were characterized by low density in the early growth stage of cowpea and reaching a peak in mid-April. From a spatial perspective, the concentrated damage sites were the tender parts at the top of the plants. From a time series analysis, M. usitatus was dominant at the early growth stage of cowpea; multiple pests broke out in combination at the middle growth stage; and A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum were the dominant populations at the late growth stage. The above research results suggest that in terms of timing, field control of cowpea should focus on the early stage, with an emphasis on the prevention and control of M. usitatus. Meanwhile, monitoring and management of A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum at the late stage should be strengthened. This study evaluated 7 cowpea varieties (‘Liangfei No. 8’, ‘Rejiang No. 1’, ‘Nongwang Nongbao 118’, ‘Yafeng 708’, ‘Cuilu 18’, ‘RADC755’, ‘Yibazhua No. 3’) that showed relatively high resistance to M. usitatus in the field. These varieties have the potential for popularization and planting in the field; however, further research is needed regarding their resistance mechanisms.
Hainan is an important growing area of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) in China, and its tropical climatic conditions lead to severe problems such as serious overlapping generations of pests and prominent pesticide resistance, making pest control quite challenging. Screening for insect-resistant varieties is an effective means of controlling crop pests. Given the relative scarcity of research on cowpea varieties resistant to Megalurothrips usitatus, the main pest species and their occurrence patterns on cowpea were identified through a systematic survey of pest occurrences on 57 cowpea varieties throughout the entire growth period in Danzhou City, Hainan Province. Additionally, cowpea varieties resistant to thrips were selected. The results showed that the main pests of cowpea grown in Danzhou, Hainan include Megalurothrips usitatus, Aphis craccivora, Trialeurodes vaporariorum, and Etiella zinckenella, among which M. usitatus, A. craccivora, and T. vaporariorum are the dominant pests. The peak numbers of the main pests were as follows: M. usitatus reached a peak of 154 individuals per plant on April 10th; A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum reached the peaks of 179 individuals per plant and 117 individuals per plant, respectively on April 23; E. zinckenella caused relatively slight damage, with a peak of 43 individuals per plant on April 24th. The population dynamics of the dominant pests were characterized by low density in the early growth stage of cowpea and reaching a peak in mid-April. From a spatial perspective, the concentrated damage sites were the tender parts at the top of the plants. From a time series analysis, M. usitatus was dominant at the early growth stage of cowpea; multiple pests broke out in combination at the middle growth stage; and A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum were the dominant populations at the late growth stage. The above research results suggest that in terms of timing, field control of cowpea should focus on the early stage, with an emphasis on the prevention and control of M. usitatus. Meanwhile, monitoring and management of A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum at the late stage should be strengthened. This study evaluated 7 cowpea varieties (‘Liangfei No. 8’, ‘Rejiang No. 1’, ‘Nongwang Nongbao 118’, ‘Yafeng 708’, ‘Cuilu 18’, ‘RADC755’, ‘Yibazhua No. 3’) that showed relatively high resistance to M. usitatus in the field. These varieties have the potential for popularization and planting in the field; however, further research is needed regarding their resistance mechanisms.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250095
Abstract:
In order to screen out marine actinomycetes and natural products that can effectively control Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4 (Foc TR4), a marine actinomycete strain HNM0301 isolated from a mangrove and exhibiting anti - Foc TR4 activity was identified taxonomically at a species level through whole - genome sequence analysis. The antiSMASH 6.0 online software was used to predict the biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites encoded by this strain. Moreover, modern separation and identification techniques for natural products were applied to isolate and elucidate the structures of the active ingredients against Foc TR4. The results demonstrated that the strain HNM0301 was identified as Streptomyces sanyensis. Its genome has a total length of 6,635,340 base pairs (bp) and contains 5,859 protein-coding genes (CDS). Among the protein-coding genes, 2,137, 1,243, and 4,297 CDS were functionally annotated in the Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) databases, respectively. A total of 27 biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites were predicted within the genome, with Cluster 16 containing 14 genes involved in the biosynthesis of staurosporine. A staurosporine monomer compound was successfully isolated from the fermentation broth of the strain HNM0301. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of this compound against Foc TR4 was determined to be 1.56 μg/mL. This compound exhibited an 85.4% inhibition rate of Foc TR4 conidial germination and also induced swelling and malformation of Foc TR4 mycelia. Evidently, the strain HNM0301 holds certain potentials for development and application in the control of Foc TR4.
In order to screen out marine actinomycetes and natural products that can effectively control Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4 (Foc TR4), a marine actinomycete strain HNM0301 isolated from a mangrove and exhibiting anti - Foc TR4 activity was identified taxonomically at a species level through whole - genome sequence analysis. The antiSMASH 6.0 online software was used to predict the biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites encoded by this strain. Moreover, modern separation and identification techniques for natural products were applied to isolate and elucidate the structures of the active ingredients against Foc TR4. The results demonstrated that the strain HNM0301 was identified as Streptomyces sanyensis. Its genome has a total length of 6,635,340 base pairs (bp) and contains 5,859 protein-coding genes (CDS). Among the protein-coding genes, 2,137, 1,243, and 4,297 CDS were functionally annotated in the Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) databases, respectively. A total of 27 biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites were predicted within the genome, with Cluster 16 containing 14 genes involved in the biosynthesis of staurosporine. A staurosporine monomer compound was successfully isolated from the fermentation broth of the strain HNM0301. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of this compound against Foc TR4 was determined to be 1.56 μg/mL. This compound exhibited an 85.4% inhibition rate of Foc TR4 conidial germination and also induced swelling and malformation of Foc TR4 mycelia. Evidently, the strain HNM0301 holds certain potentials for development and application in the control of Foc TR4.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240157
Abstract:
In order to understand the effects of cadmium and phenanthrene on the oxidative stress and detoxification in the mantle of Meretrix meretrix, the SOD, CAT, GST activities and MDA content were detected under single and combined exposure to cadmium and phenanthrene. The metallothionein (MT) and heat shock protein) hsp70 gene expressions were also measured. The results showed that the SOD activity and GST activity in all the treatments were significantly increased compared with those in the control group (P<0.05), that the CAT activity and MDA content were significantly increased compared with that in the control group (P<0.05) except for the group exposed to Cd. MT gene expression was significantly induced in all treatments, and that the hsp70 gene expression was significantly induced except for the group exposed to Phe. At the 3 d of exposure, interactive effects were observed in all the indexes except for hsp70; at the 7 d of exposure, interactive effects were observed in all the indexes except for CAT activity and MDA content. It is indicated that Cd and Phe have significant effects on the oxidative stress responses in M. meretrix. The MT gene and hsp70 gene are induced to detoxify and regulate the body, improving its ability to resist stimuli and survive.
In order to understand the effects of cadmium and phenanthrene on the oxidative stress and detoxification in the mantle of Meretrix meretrix, the SOD, CAT, GST activities and MDA content were detected under single and combined exposure to cadmium and phenanthrene. The metallothionein (MT) and heat shock protein) hsp70 gene expressions were also measured. The results showed that the SOD activity and GST activity in all the treatments were significantly increased compared with those in the control group (P<0.05), that the CAT activity and MDA content were significantly increased compared with that in the control group (P<0.05) except for the group exposed to Cd. MT gene expression was significantly induced in all treatments, and that the hsp70 gene expression was significantly induced except for the group exposed to Phe. At the 3 d of exposure, interactive effects were observed in all the indexes except for hsp70; at the 7 d of exposure, interactive effects were observed in all the indexes except for CAT activity and MDA content. It is indicated that Cd and Phe have significant effects on the oxidative stress responses in M. meretrix. The MT gene and hsp70 gene are induced to detoxify and regulate the body, improving its ability to resist stimuli and survive.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250071
Abstract:
In order to understand the current research hotspots and trends of stem end rot disease, a bibliometric analysis was conducted using CiteSpace software on 367 stem end rot disease-related articles indexed in the Web of Science core database between 2009 and 2024. The distribution of research efforts, knowledge base, research hotspots, and frontier trends in the field of stem end rot disease were analyzed. The results indicate that the number of publications on stem end rot disease has been increasing, with China, the United States, and Brazil having the highest publication volumes. There is also significant international collaboration among countries. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is a leading research institution in this field, while Hainan University is the leading institution in China. Research institutions collaborate closely, although Chinese institutions still have room to improve in terms of international cooperation and academic influence. Prominent authors in the field of stem end rot disease research include Alkan Noam and Bai Jinhe. Keyword co-occurrence and burst detection analysis reveal that current research hotspots in the field include pathogen identification, resistance, and genomics. Future research should focus on strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration, further exploring the pathological mechanisms of stem end rot disease, and developing control strategies to ensure the healthy growth of crops.
In order to understand the current research hotspots and trends of stem end rot disease, a bibliometric analysis was conducted using CiteSpace software on 367 stem end rot disease-related articles indexed in the Web of Science core database between 2009 and 2024. The distribution of research efforts, knowledge base, research hotspots, and frontier trends in the field of stem end rot disease were analyzed. The results indicate that the number of publications on stem end rot disease has been increasing, with China, the United States, and Brazil having the highest publication volumes. There is also significant international collaboration among countries. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is a leading research institution in this field, while Hainan University is the leading institution in China. Research institutions collaborate closely, although Chinese institutions still have room to improve in terms of international cooperation and academic influence. Prominent authors in the field of stem end rot disease research include Alkan Noam and Bai Jinhe. Keyword co-occurrence and burst detection analysis reveal that current research hotspots in the field include pathogen identification, resistance, and genomics. Future research should focus on strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration, further exploring the pathological mechanisms of stem end rot disease, and developing control strategies to ensure the healthy growth of crops.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250082
Abstract:
To explore the substrate formula for cultivating S. rugosoannulata with high yield and high quality under rubber plantations, rice straw and rubber wood chips were used as raw materials to investigate the impact of their ratios on the yield and quality of S. rugosoannulata. Five treatments with rice and rubber wood chips at the dry mass ratios (1∶0, 3∶1, 1∶1, 1∶3, 0∶1) were arranged in this experiment for observation of mycelial growth and field fruiting. The results showed that the treatment with the ratio of 1∶3 had the highest comprehensive score. The mycelium of S. rugosoannulata cultivated with this substrate was robust and dense, with an average fruiting period of 52.75 days after inoculation and a harvesting period of 29 days. The yield of fruiting bodies in this treatment reached 5.22 kg·m−2, and the biological conversion rate was 26.11%.
To explore the substrate formula for cultivating S. rugosoannulata with high yield and high quality under rubber plantations, rice straw and rubber wood chips were used as raw materials to investigate the impact of their ratios on the yield and quality of S. rugosoannulata. Five treatments with rice and rubber wood chips at the dry mass ratios (1∶0, 3∶1, 1∶1, 1∶3, 0∶1) were arranged in this experiment for observation of mycelial growth and field fruiting. The results showed that the treatment with the ratio of 1∶3 had the highest comprehensive score. The mycelium of S. rugosoannulata cultivated with this substrate was robust and dense, with an average fruiting period of 52.75 days after inoculation and a harvesting period of 29 days. The yield of fruiting bodies in this treatment reached 5.22 kg·m−2, and the biological conversion rate was 26.11%.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250005
Abstract:
An attempt was made to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of layered double hydroxides (LDH) nanofusion protein vaccines in cat and dog fusion allergens-induced mouse model, which provides a potential novel vaccine strategy for the treatment of canine and feline allergic diseases. A cat and dog fusion allergen was prepared and loaded onto layered double hydroxide nanomate vials to construct a vaccine. BALB/c mice were selected and sensitized to the cat and dog fusion allergen by intraperitoneal injection and lung perfusion to establish a mouse allergy model. Subsequently, the allergy model mice were randomly divided into four groups: normal (naïve) group, allergy model group (allergic model), LDH group and vaccine group, with six mice in each group. Among them, the normal group was not treated, and the mice in the allergic model group, LDH group and vaccine group were given phosphate buffered saline (PBS), LDH nanosuspension, and LDH nanofusion protein vaccine injections, respectively, and the results of serum IgE, pulmonary respiratory resistance, temperature change, ear prick, and pathological section were detected to comprehensively evaluate the vaccine treatment effect. The results showed that compared with the Allergic model group, the vaccine group treated with LDH nanofusion protein vaccine significantly decreased the serum-specific IgE levels of mice, alleviated lung respiratory resistance, highly significantly reduced allergen-induced body temperature and the area of ear dye leakage, significantly reduced inflammatory infiltration in the lungs, reduced the number of cuprocytes although not significantly, and reduced the degree of collagen deposition and fibrosis. Taken together, these results indicate that the laminar double hydroxide nanocat-dog fusion protein vaccine has a good therapeutic effect on the cat-dog fusion allergen-induced mouse allergy model, and is able to effectively improve the allergy symptoms and reduce the inflammatory reaction of allergy-associated tissues in mice.
An attempt was made to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of layered double hydroxides (LDH) nanofusion protein vaccines in cat and dog fusion allergens-induced mouse model, which provides a potential novel vaccine strategy for the treatment of canine and feline allergic diseases. A cat and dog fusion allergen was prepared and loaded onto layered double hydroxide nanomate vials to construct a vaccine. BALB/c mice were selected and sensitized to the cat and dog fusion allergen by intraperitoneal injection and lung perfusion to establish a mouse allergy model. Subsequently, the allergy model mice were randomly divided into four groups: normal (naïve) group, allergy model group (allergic model), LDH group and vaccine group, with six mice in each group. Among them, the normal group was not treated, and the mice in the allergic model group, LDH group and vaccine group were given phosphate buffered saline (PBS), LDH nanosuspension, and LDH nanofusion protein vaccine injections, respectively, and the results of serum IgE, pulmonary respiratory resistance, temperature change, ear prick, and pathological section were detected to comprehensively evaluate the vaccine treatment effect. The results showed that compared with the Allergic model group, the vaccine group treated with LDH nanofusion protein vaccine significantly decreased the serum-specific IgE levels of mice, alleviated lung respiratory resistance, highly significantly reduced allergen-induced body temperature and the area of ear dye leakage, significantly reduced inflammatory infiltration in the lungs, reduced the number of cuprocytes although not significantly, and reduced the degree of collagen deposition and fibrosis. Taken together, these results indicate that the laminar double hydroxide nanocat-dog fusion protein vaccine has a good therapeutic effect on the cat-dog fusion allergen-induced mouse allergy model, and is able to effectively improve the allergy symptoms and reduce the inflammatory reaction of allergy-associated tissues in mice.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250027
Abstract:
Stem rot causes extensive rotting at the base of the stems of bloodleaf orchid plants, affecting nutrient uptake. Studies have shown that Trichoderma can effectively inhibit a wide range of pathogenic bacteria and is an important biocontrol fungus. A strain of pathogen X.9 with the strongest pathogenic effect was isolated from the diseased tissues at the stem base of Ludisia discolor(Ker-Gawl.)A.Rich, which was identified as Fusarium oxysporum by morphology and molecular biology. The plate confrontation assay between Trichoderma strains and the F. oxysporum X.9 showed that 17 Trichoderma strains could completely cover F. oxysporum X.9 an inhibition rate of more than 75%. Further observation of the inhibition effect of 17 strains of Trichoderma non-volatile metabolites on X.9 showed that JX013 and SC009 had better inhibition effect, with their inhibition rates being 41.27% and 41.26%, respectively. Through morphological and molecular biological identification, both JX013 and SC009 were confirmed to be Trichoderma asperellum. Both JX013 and SC009 showed a significant increase in chitinase and glucanase after interacted with X.9, indicating that Trichoderma secretes more cell wall degrading enzymes to degrade the pathogenic mycelium when interacted with pathogenic bacteria, thus inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
Stem rot causes extensive rotting at the base of the stems of bloodleaf orchid plants, affecting nutrient uptake. Studies have shown that Trichoderma can effectively inhibit a wide range of pathogenic bacteria and is an important biocontrol fungus. A strain of pathogen X.9 with the strongest pathogenic effect was isolated from the diseased tissues at the stem base of Ludisia discolor(Ker-Gawl.)A.Rich, which was identified as Fusarium oxysporum by morphology and molecular biology. The plate confrontation assay between Trichoderma strains and the F. oxysporum X.9 showed that 17 Trichoderma strains could completely cover F. oxysporum X.9 an inhibition rate of more than 75%. Further observation of the inhibition effect of 17 strains of Trichoderma non-volatile metabolites on X.9 showed that JX013 and SC009 had better inhibition effect, with their inhibition rates being 41.27% and 41.26%, respectively. Through morphological and molecular biological identification, both JX013 and SC009 were confirmed to be Trichoderma asperellum. Both JX013 and SC009 showed a significant increase in chitinase and glucanase after interacted with X.9, indicating that Trichoderma secretes more cell wall degrading enzymes to degrade the pathogenic mycelium when interacted with pathogenic bacteria, thus inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250001
Abstract:
Clerodendranthus spicatus (Kidney tea, KT), a traditional Chinese medicine, has a variety of biological activities. In recent years there are many studies on the antioxidant activity of kidney tea in vitro, but the research on the antioxidant activity and health effects of its ethanol extract in vivo is not sufficiently documented. In this case, the antioxidant activity of KTe (kidney tea ethanol extract) in vitro was evaluated by measuring the DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging ability. Caenorhabditis elegans was used to evaluate the antioxidant activity of KTe in vivo. The physiological indexes, such as lifespan, oviposition and hatching, lipofuscin content and movement ability of C.elegans, were determined to evaluate the antioxidant tivity of KTe in vivo. The results showed that KTe had good antioxidant activity in vitro, which could promote the physiological indexes of young nematodes and inhibit the physiological indexes of old nematodes. At the same time, it can significantly increase the number of eggs laid by C.elegans, and has no significant effect on the hatching rate. All these results can provide reference for the subsequent development and utilization of KT.
Clerodendranthus spicatus (Kidney tea, KT), a traditional Chinese medicine, has a variety of biological activities. In recent years there are many studies on the antioxidant activity of kidney tea in vitro, but the research on the antioxidant activity and health effects of its ethanol extract in vivo is not sufficiently documented. In this case, the antioxidant activity of KTe (kidney tea ethanol extract) in vitro was evaluated by measuring the DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging ability. Caenorhabditis elegans was used to evaluate the antioxidant activity of KTe in vivo. The physiological indexes, such as lifespan, oviposition and hatching, lipofuscin content and movement ability of C.elegans, were determined to evaluate the antioxidant tivity of KTe in vivo. The results showed that KTe had good antioxidant activity in vitro, which could promote the physiological indexes of young nematodes and inhibit the physiological indexes of old nematodes. At the same time, it can significantly increase the number of eggs laid by C.elegans, and has no significant effect on the hatching rate. All these results can provide reference for the subsequent development and utilization of KT.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250041
Abstract:
The insect olfactory system plays a pivotal role in host recognition, mating, and oviposition, with odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) serving critical functions in olfactory signal transduction. An attempt was made to analyze the sequence characteristics and ligand-binding properties of two OBPs (TrufOBP1 and TrufOBP5) in Tirathaba rufivena, a major pest infesting inflorescences and fruit of arecanut (Areca catechu), and to validate their behavioral regulatory roles through wind tunnel experiments. Sequence analysis revealed that TrufOBP1 contains four conserved cysteines and is classified as a Minus-C OBP, whereas TrufOBP5 possesses ten conserved cysteines and is categorized as a Plus-C OBP. Fluorescence competitive binding assays demonstrated that TrufOBP1 exhibited broad ligand specificity and was bound to 11 compounds, including nine volatiles from areca nut (Areca catechu) inflorescences and two sex pheromones. In contrast, TrufOBP5 displayed high binding specificity, and interacted exclusively with octyl p-methoxycinnamate and vanillin, suggesting its potential role in host plant recognition. Wind tunnel experiments identified β-myrcene, octyl p-methoxycinnamate, and 3-hexenyl acetate as attractants for female adults from host volatiles. Among sex pheromone components, 2,2,6-trimethyl-6-vinyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-OL exhibited the highest attraction activity, while vanillin also demonstrated significant attractant effects. This study elucidates the functional roles of TrufOBP1 and TrufOBP5 in host recognition and sex pheromone perception in T. rufivena, providing a theoretical foundation for pest behavior regulation and supporting the development of olfaction-based green control strategies.
The insect olfactory system plays a pivotal role in host recognition, mating, and oviposition, with odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) serving critical functions in olfactory signal transduction. An attempt was made to analyze the sequence characteristics and ligand-binding properties of two OBPs (TrufOBP1 and TrufOBP5) in Tirathaba rufivena, a major pest infesting inflorescences and fruit of arecanut (Areca catechu), and to validate their behavioral regulatory roles through wind tunnel experiments. Sequence analysis revealed that TrufOBP1 contains four conserved cysteines and is classified as a Minus-C OBP, whereas TrufOBP5 possesses ten conserved cysteines and is categorized as a Plus-C OBP. Fluorescence competitive binding assays demonstrated that TrufOBP1 exhibited broad ligand specificity and was bound to 11 compounds, including nine volatiles from areca nut (Areca catechu) inflorescences and two sex pheromones. In contrast, TrufOBP5 displayed high binding specificity, and interacted exclusively with octyl p-methoxycinnamate and vanillin, suggesting its potential role in host plant recognition. Wind tunnel experiments identified β-myrcene, octyl p-methoxycinnamate, and 3-hexenyl acetate as attractants for female adults from host volatiles. Among sex pheromone components, 2,2,6-trimethyl-6-vinyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-OL exhibited the highest attraction activity, while vanillin also demonstrated significant attractant effects. This study elucidates the functional roles of TrufOBP1 and TrufOBP5 in host recognition and sex pheromone perception in T. rufivena, providing a theoretical foundation for pest behavior regulation and supporting the development of olfaction-based green control strategies.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240204
Abstract:
The inorganic salt medium with atrazine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source was used to screen a Trichoderma strain with the best growth performance among 10 Trichoderma strains, and the Trichoderma strain HN154 was selected. The degradation test of atrazine demonstrated that this strain had a high ability to degrade atrazine. Strain HN154 was identified as Trichoderma lentiforme based on morphological characteristics and ITS/RPB2 gene sequence analysis. Optimization of atrazine degradation conditions showed that the atrazine degradation rate was as high as 87.79% when cultured in inorganic salt medium with 10 g/L glucose, pH 7, 25 ℃, and 1% inoculum. Response surface optimization further improved degradation to 89.02% under the conditions of 5.24 g/L glucose, pH 7.78, 0.77% inoculum, and 25.5 ℃. This study provides microbial resources and technical support for efficient atrazine degradation, offering insights into degradation of microbial pesticide residues.
The inorganic salt medium with atrazine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source was used to screen a Trichoderma strain with the best growth performance among 10 Trichoderma strains, and the Trichoderma strain HN154 was selected. The degradation test of atrazine demonstrated that this strain had a high ability to degrade atrazine. Strain HN154 was identified as Trichoderma lentiforme based on morphological characteristics and ITS/RPB2 gene sequence analysis. Optimization of atrazine degradation conditions showed that the atrazine degradation rate was as high as 87.79% when cultured in inorganic salt medium with 10 g/L glucose, pH 7, 25 ℃, and 1% inoculum. Response surface optimization further improved degradation to 89.02% under the conditions of 5.24 g/L glucose, pH 7.78, 0.77% inoculum, and 25.5 ℃. This study provides microbial resources and technical support for efficient atrazine degradation, offering insights into degradation of microbial pesticide residues.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250004
Abstract:
For early and rapid detection of Xanthomonas. oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc), the cause of bacterial leaf streak in rice, specific recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) primers, and Exo fluorescent and nfo probes were designed and screened, respectively, according to the publicly available gene sequence XOCgx_RS03090 of Xoc genome sequence in GenBank. The recombinant plasmid containing Xoc gene was constructed as a positive control. One fluorescent Exo-RPA assay and the other lateral flow strip detection (LFD-RPA) assay were established for rapid detection of Xoc. The sensitivity and specificity of the RPA methods were assessed, and the amplification effects of the RPA methods were explored by optimizing the reaction temperature and reaction time. The results showed that the sensitivity of both the Exo-RPA and LFD-RPA assays for the detection of Xoc were both 4.96 copies·μL−1, and that the optimal temperatures for the reaction were both 39 ℃. Xoc was detected within 12 min by the optimized Exo-RPA method, and within 5 min by the optimized LFD-RPA. The Exo-RPA and LFD-RPA assays developed were highly specific and could specifically and uniquely identify Xoc among plant pathogens in test. Both the RPA methods are highly sensitive, specific and fast, which pose a high potential to the monitoring of the target pathogen and early diagnosis of the disease.
For early and rapid detection of Xanthomonas. oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc), the cause of bacterial leaf streak in rice, specific recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) primers, and Exo fluorescent and nfo probes were designed and screened, respectively, according to the publicly available gene sequence XOCgx_RS03090 of Xoc genome sequence in GenBank. The recombinant plasmid containing Xoc gene was constructed as a positive control. One fluorescent Exo-RPA assay and the other lateral flow strip detection (LFD-RPA) assay were established for rapid detection of Xoc. The sensitivity and specificity of the RPA methods were assessed, and the amplification effects of the RPA methods were explored by optimizing the reaction temperature and reaction time. The results showed that the sensitivity of both the Exo-RPA and LFD-RPA assays for the detection of Xoc were both 4.96 copies·μL−1, and that the optimal temperatures for the reaction were both 39 ℃. Xoc was detected within 12 min by the optimized Exo-RPA method, and within 5 min by the optimized LFD-RPA. The Exo-RPA and LFD-RPA assays developed were highly specific and could specifically and uniquely identify Xoc among plant pathogens in test. Both the RPA methods are highly sensitive, specific and fast, which pose a high potential to the monitoring of the target pathogen and early diagnosis of the disease.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250025
Abstract:
The sugar transporter SWEET (Sugars Will Eventually be Exported Transporter) plays a crucial role in plant responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses. To elucidate the function of the SWEET gene family in Dendrobium catenatum, 27 DcSWEET genes were identified and characterized from D. catenatum by using whole-genome data, and their expression patterns under drought stress were analyzed. The molecular weight of the DcSWEET proteins were found to range from 22.44 to 39.10 kDa, with heir isoelectric points being between 8.47 and 9.63. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the DcSWEET proteins could be classified into four subgroups, each characterized by conserved motif compositions and gene structures. Cis-acting element analysis indicated that the promoters of DcSWEET genes contain various elements associated with hormone signaling, plant growth and development, light responsiveness, and stress response. RNA-seq analysis demonstrated that 17 DcSWEET genes were up-regulated under drought stress. Coexpression network analysis suggested that DcSWEET4, DcSWEET11, DcSWEET13, DcSWEET18, and DcSWEET27 may play pivotal roles in response to drought stress in D. catenatum. RT-qPCR confirmed that DcSWEET11, DcSWEET13, and DcSWEET18 were significantly up-regulated in stems and leaves under drought conditions, making them potential candidate genes for enhancing drought tolerance in D. catenatum. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of key SWEET genes involved in drought stress responses in D. catenatum, offering a molecular foundation for future efforts to improve its drought resistance.
The sugar transporter SWEET (Sugars Will Eventually be Exported Transporter) plays a crucial role in plant responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses. To elucidate the function of the SWEET gene family in Dendrobium catenatum, 27 DcSWEET genes were identified and characterized from D. catenatum by using whole-genome data, and their expression patterns under drought stress were analyzed. The molecular weight of the DcSWEET proteins were found to range from 22.44 to 39.10 kDa, with heir isoelectric points being between 8.47 and 9.63. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the DcSWEET proteins could be classified into four subgroups, each characterized by conserved motif compositions and gene structures. Cis-acting element analysis indicated that the promoters of DcSWEET genes contain various elements associated with hormone signaling, plant growth and development, light responsiveness, and stress response. RNA-seq analysis demonstrated that 17 DcSWEET genes were up-regulated under drought stress. Coexpression network analysis suggested that DcSWEET4, DcSWEET11, DcSWEET13, DcSWEET18, and DcSWEET27 may play pivotal roles in response to drought stress in D. catenatum. RT-qPCR confirmed that DcSWEET11, DcSWEET13, and DcSWEET18 were significantly up-regulated in stems and leaves under drought conditions, making them potential candidate genes for enhancing drought tolerance in D. catenatum. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of key SWEET genes involved in drought stress responses in D. catenatum, offering a molecular foundation for future efforts to improve its drought resistance.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250036
Abstract:
With the intensification of aquaculture and the over-exploitation of offshore fishery resources, the fishery economy in coastal areas has shown a rapid growth trend. This development has directly led to the demand for large-scale construction of water intake and drainage pipeline systems. As the core carrier of material cycling in coastal wetlands, the speciation and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) in sediments are key indicators for assessing the sources and degradation status of organic matters. The construction of pipelines may further alter the C, N and P speciation and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments by changing hydrodynamic conditions, sedimentation processes, and microbial organic matter degradation processes. The pipeline-laid area (Area A) and the natural tidal flat area (Area B) in Wenchang City, Hainan Province were selected to analyze the impact of pipeline laying on the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments. The results showed that the total nitrogen (TN) and total organic carbon (TOC) contents, carbon-to-phosphorus ratio (C∶P), and nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio (N∶P) were significantly higher in Area A than in Area B (+53.3%, +38.0%, +52.4%, +50.0%), while the total carbon (TC) content and carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C∶N) were lower (−8.7%, −21.8%). In addition, the contents of C, N, and P in sediments and their ecological stoichiometric characteristics also changed the horizontal distribution pattern with increasing distance from the shore. Specifically, TC and TOC contents, C∶N, and C∶P in sediments decreased with increasing distance from the shore, while TN and TP contents showed the opposite trend. Under the interaction of pipeline laying and distance from the shore, the changes in TC and TOC contents, C∶N, and C∶P were greater in Area A than in Area B, and the differences were more significant near the shore than far from the shore. All these results indicate that pipeline laying and distance from the shore are important factors affecting the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments, and the interaction between distance from the shore and pipeline laying weakens the impact on the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments.
With the intensification of aquaculture and the over-exploitation of offshore fishery resources, the fishery economy in coastal areas has shown a rapid growth trend. This development has directly led to the demand for large-scale construction of water intake and drainage pipeline systems. As the core carrier of material cycling in coastal wetlands, the speciation and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) in sediments are key indicators for assessing the sources and degradation status of organic matters. The construction of pipelines may further alter the C, N and P speciation and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments by changing hydrodynamic conditions, sedimentation processes, and microbial organic matter degradation processes. The pipeline-laid area (Area A) and the natural tidal flat area (Area B) in Wenchang City, Hainan Province were selected to analyze the impact of pipeline laying on the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments. The results showed that the total nitrogen (TN) and total organic carbon (TOC) contents, carbon-to-phosphorus ratio (C∶P), and nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio (N∶P) were significantly higher in Area A than in Area B (+53.3%, +38.0%, +52.4%, +50.0%), while the total carbon (TC) content and carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C∶N) were lower (−8.7%, −21.8%). In addition, the contents of C, N, and P in sediments and their ecological stoichiometric characteristics also changed the horizontal distribution pattern with increasing distance from the shore. Specifically, TC and TOC contents, C∶N, and C∶P in sediments decreased with increasing distance from the shore, while TN and TP contents showed the opposite trend. Under the interaction of pipeline laying and distance from the shore, the changes in TC and TOC contents, C∶N, and C∶P were greater in Area A than in Area B, and the differences were more significant near the shore than far from the shore. All these results indicate that pipeline laying and distance from the shore are important factors affecting the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments, and the interaction between distance from the shore and pipeline laying weakens the impact on the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250016
Abstract:
Natural rubber is an important strategic resource in China. The infection of Colletotrichum gloeosporides in rubber tree would greatly affect the development of rubber industry. The functional study of the pathogenicity-related genes of C. gloeosporioides can provide a theoretical basis for disease prevention and control. A gene CgPEB encoding carboxypeptidase Y inhibitor protein was identified in C. gloeosporioides. The gene knockout mutant strain was constructed according to the principle of homologous recombination, and the phenotype and pathogenicity analysis were performed. The results showed that the growth rate and conidial production of ΔCgpeb, Cgpeb gene knockout mutant were reduced. Besides, both the appressorium and invasive hyphae formation rate of ΔCgpeb were significantly reduced. These findings suggested that CgPEB plays an important role in regulating the colony growth, conidial production and pathogenicity of C. gloeosporioides.
Natural rubber is an important strategic resource in China. The infection of Colletotrichum gloeosporides in rubber tree would greatly affect the development of rubber industry. The functional study of the pathogenicity-related genes of C. gloeosporioides can provide a theoretical basis for disease prevention and control. A gene CgPEB encoding carboxypeptidase Y inhibitor protein was identified in C. gloeosporioides. The gene knockout mutant strain was constructed according to the principle of homologous recombination, and the phenotype and pathogenicity analysis were performed. The results showed that the growth rate and conidial production of ΔCgpeb, Cgpeb gene knockout mutant were reduced. Besides, both the appressorium and invasive hyphae formation rate of ΔCgpeb were significantly reduced. These findings suggested that CgPEB plays an important role in regulating the colony growth, conidial production and pathogenicity of C. gloeosporioides.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240187
Abstract:
In order to screen proteins in cassava (Manihot esculenta) that jointly regulate cassava disease resistance with MeRLK1, 24 candidate interacting proteins of the MeRLK1 protein including heat shock protein (Hsp), ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1), aquaporin transported protein (AQP), etc were selected through screening from the yeast two-hybrid library. Further analysis of the spatiotemporal expression correlation between MeRLK1 and 24 candidate interacting genes revealed that genes including Pentatricopeptide repeat 2 (PPR2) and BR-signaling kinase (BSK) exhibited high correlations (R>0.7) with MeRLK1 expression across diverse tissues and under stress conditions. Based on the screening, the full-length sequence vector of MeBSK, a protein related to the brassinosteroid (BR) signaling pathway was constructed. Through the yeast two-hybrid experiment, it was found that there might be an interaction between MeRLK1 and MeBSK. Subsequently, bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) will be needed to further verify this interaction in vivo.
In order to screen proteins in cassava (Manihot esculenta) that jointly regulate cassava disease resistance with MeRLK1, 24 candidate interacting proteins of the MeRLK1 protein including heat shock protein (Hsp), ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1), aquaporin transported protein (AQP), etc were selected through screening from the yeast two-hybrid library. Further analysis of the spatiotemporal expression correlation between MeRLK1 and 24 candidate interacting genes revealed that genes including Pentatricopeptide repeat 2 (PPR2) and BR-signaling kinase (BSK) exhibited high correlations (R>0.7) with MeRLK1 expression across diverse tissues and under stress conditions. Based on the screening, the full-length sequence vector of MeBSK, a protein related to the brassinosteroid (BR) signaling pathway was constructed. Through the yeast two-hybrid experiment, it was found that there might be an interaction between MeRLK1 and MeBSK. Subsequently, bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) will be needed to further verify this interaction in vivo.
Identification and expression analysis of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene family in Persea americana
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250037
Abstract:
Avocado (Persea americana) is a fruit with high nutritional value, and fatty acids are among its key intrinsic nutrients. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a crucial enzyme in fatty acid synthesis, essential for oil accumulation and storage. The protein structure, evolutionary relationships, and cis-acting elements of the PaACC gene promoter in avocado were analyzed by employing bioinformatics tools, and the expression levels of the PaACC genes across different avocado organs and developmental stages of the fruit were analyzed by using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). A total of seven PaACC genes were identified in avocado, encoding three BC subunits, three BCCP subunits, and one α-CT subunit of ACC. The amino acid lengths of these genes range from 251 to 776, with an average molecular weight of 49.95 kDa. All the encoded proteins are hydrophilic and lack of transmembrane domains. Phylogenetic analysis of ACC proteins from various plant species reveals that ACC proteins are categorized into four subfamilies based on subunit composition. The gene structure shows that all the PaACC genes contain at least 5 exons, each member of which contains a certain number of introns. There are 25 different conserved motifs in the PaACC gene family. Specifically, PaACC1, PaACC2, and PaACC3 all have motif 14, while PaACC4, PaACC5, and PaACC6 all have motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. In the promoter region of the PaACC genes, several cis-acting elements associated with light response, hormone response, drought stress, and low-temperature stress were identified. These findings suggest that the PaACC genes play a significant role in regulating plant growth and development and may enhance the plant’s tolerance to abiotic stresses. Expression pattern analysis reveals that PaACC4, PaACC5, and PaACC7 exhibit significantly higher expression levels during the S5 stage of fruit development compared to other organs and stages. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further research on the role of the PaACC genes in avocado fatty acid biosynthesis.
Avocado (Persea americana) is a fruit with high nutritional value, and fatty acids are among its key intrinsic nutrients. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a crucial enzyme in fatty acid synthesis, essential for oil accumulation and storage. The protein structure, evolutionary relationships, and cis-acting elements of the PaACC gene promoter in avocado were analyzed by employing bioinformatics tools, and the expression levels of the PaACC genes across different avocado organs and developmental stages of the fruit were analyzed by using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). A total of seven PaACC genes were identified in avocado, encoding three BC subunits, three BCCP subunits, and one α-CT subunit of ACC. The amino acid lengths of these genes range from 251 to 776, with an average molecular weight of 49.95 kDa. All the encoded proteins are hydrophilic and lack of transmembrane domains. Phylogenetic analysis of ACC proteins from various plant species reveals that ACC proteins are categorized into four subfamilies based on subunit composition. The gene structure shows that all the PaACC genes contain at least 5 exons, each member of which contains a certain number of introns. There are 25 different conserved motifs in the PaACC gene family. Specifically, PaACC1, PaACC2, and PaACC3 all have motif 14, while PaACC4, PaACC5, and PaACC6 all have motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. In the promoter region of the PaACC genes, several cis-acting elements associated with light response, hormone response, drought stress, and low-temperature stress were identified. These findings suggest that the PaACC genes play a significant role in regulating plant growth and development and may enhance the plant’s tolerance to abiotic stresses. Expression pattern analysis reveals that PaACC4, PaACC5, and PaACC7 exhibit significantly higher expression levels during the S5 stage of fruit development compared to other organs and stages. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further research on the role of the PaACC genes in avocado fatty acid biosynthesis.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250032
Abstract:
Ascorbate peroxidases (APXs) play a significant role in plant resistance to abiotic stress. An attempt was made to investigate the role of APXs in cassava resistance to cassava common mosaic virus (CsCMV). APX activity and the expression level of MeAPXs during infection of cassava with CsCMV were analyzed. The results showed that APX activity and MeAPX2 transcript level were reduced. Therefore, MeAPX2 was identified as a candidate gene for further analysis. MeAPX2 positively regulated cassava resistance to CsCMV, as determined by the disease index in MeAPX2-silenced plants. Further analysis revealed that MeAPX2 directly interacts with the coat protein (CP) of CsCMV. Moreover, CP was found to inhibit the activity of MeAPX2 both in vivo and in vitro. The results demonstrated that CsCMV suppresses APX activity during infection in cassava. Furthermore, MeAPX2 positively regulates cassava resistance to CsCMV by targeting CP.
Ascorbate peroxidases (APXs) play a significant role in plant resistance to abiotic stress. An attempt was made to investigate the role of APXs in cassava resistance to cassava common mosaic virus (CsCMV). APX activity and the expression level of MeAPXs during infection of cassava with CsCMV were analyzed. The results showed that APX activity and MeAPX2 transcript level were reduced. Therefore, MeAPX2 was identified as a candidate gene for further analysis. MeAPX2 positively regulated cassava resistance to CsCMV, as determined by the disease index in MeAPX2-silenced plants. Further analysis revealed that MeAPX2 directly interacts with the coat protein (CP) of CsCMV. Moreover, CP was found to inhibit the activity of MeAPX2 both in vivo and in vitro. The results demonstrated that CsCMV suppresses APX activity during infection in cassava. Furthermore, MeAPX2 positively regulates cassava resistance to CsCMV by targeting CP.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250029
Abstract:
To further understand the role of the TkBZR family genes in the growth, development, and stress resistance of rubber dandelion (Taraxacum kok-saghyz), the TkBZR/BES family genes were identified and analyzed by examining the whole genome sequencing data of T. kok-saghyz. A total of 6 members of the TkBZR family were identified, named from TkBZR1 to TkBZR6, and their distribution on chromosomes, domain characteristics, tissue expression profiles and the spatial-temporal gene expression were analyzed. The results revealed that TkBZR/BES gene family members were distributed on 6 independent scaffolds. Phylogenetic trees indicate that TkBZR/BES gene family members are evolutionarily conserved, with rubber dandelion and lettuce genes clustering in the same subgroup, suggesting a possible close evolutionary relationship between the two. Gene structure and conserved domain analysis show that except for TkBZR5, all the other TkBZR genes contain two exons and one intron, and that all the family members exhibit a highly conserved BES1_N domain. Expression pattern analysis reveals that 5 members are expressed in all five tissues, while one member is almost unexpressed. Additionally, the TkBZR2 gene with the highest expression abundance was successfully cloned, encoding 307 amino acids. Homologous recombination of TkBZR2 was made into prokaryotic expression vector, and the recombinant plasmid was transferred into E. coli BL21(DE3) .The recombinant protein TkBZR2 was expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3).
To further understand the role of the TkBZR family genes in the growth, development, and stress resistance of rubber dandelion (Taraxacum kok-saghyz), the TkBZR/BES family genes were identified and analyzed by examining the whole genome sequencing data of T. kok-saghyz. A total of 6 members of the TkBZR family were identified, named from TkBZR1 to TkBZR6, and their distribution on chromosomes, domain characteristics, tissue expression profiles and the spatial-temporal gene expression were analyzed. The results revealed that TkBZR/BES gene family members were distributed on 6 independent scaffolds. Phylogenetic trees indicate that TkBZR/BES gene family members are evolutionarily conserved, with rubber dandelion and lettuce genes clustering in the same subgroup, suggesting a possible close evolutionary relationship between the two. Gene structure and conserved domain analysis show that except for TkBZR5, all the other TkBZR genes contain two exons and one intron, and that all the family members exhibit a highly conserved BES1_N domain. Expression pattern analysis reveals that 5 members are expressed in all five tissues, while one member is almost unexpressed. Additionally, the TkBZR2 gene with the highest expression abundance was successfully cloned, encoding 307 amino acids. Homologous recombination of TkBZR2 was made into prokaryotic expression vector, and the recombinant plasmid was transferred into E. coli BL21(DE3) .The recombinant protein TkBZR2 was expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3).
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250031
Abstract:
MYC2 is an important transcription factor that regulates the synthesis of terpenoid secondary metabolites in plants. However, little is known about the CdMYC2 transcription factor in C. drupifera. In this study, the related sequence information of CdMYC2 gene was obtained based on the transcriptome annotation data of C. drupifera. A CdMYC2 gene was successfully isolated and cloned from the leaves of C. drupifera for the first time. Its CDS sequence length was1515 bp, encoding 504 amino acids, with typical bHLH-MYC _ N super family and bHLH _ SF super family conserved domains. This gene was predicted to be located in the nucleus. Multiple sequence alignment further confirmed that the amplified CdMYC2 belongs to the MYC2 family transcription factor. The phylogenetic tree analysis showed that CdMYC2 was clustered into a clade with Camellia sinensis, a plant belonging to the same family and genus, while it was far away from the clades of Quercus lobata and Quercus robur. RT-qPCR results showed that the expression level of CdMYC2 gene was higher in the leaves than in other tissues. Among the different developmental stages of the fruit, the expression of CdMYC2 in the fruit reached the highest in September. This study provides an important reference for the subsequent exploration of the function of MYC2 transcription factor in the regulation of triterpenoid saponin biosynthesis pathway in C. drupifera.
MYC2 is an important transcription factor that regulates the synthesis of terpenoid secondary metabolites in plants. However, little is known about the CdMYC2 transcription factor in C. drupifera. In this study, the related sequence information of CdMYC2 gene was obtained based on the transcriptome annotation data of C. drupifera. A CdMYC2 gene was successfully isolated and cloned from the leaves of C. drupifera for the first time. Its CDS sequence length was
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250030
Abstract:
Myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) are critical regulators of skeletal muscle growth and development in animals. The full-length cDNA sequences of five MRFs from the giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus) were cloned using RT-PCR and RAC, including MyoD1 (1,962 bp), MyoD2 (1,466 bp), MyoG (926 bp), MRF4 (1,052 bp), and Myf5 (1,133 bp), encoding 297, 270, 251, 238, and 242 amino acids, respectively. Amino acid sequence alignment revealed that all five MRFs contain a conserved basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain consisting of 60 amino acids. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the MRF genes are clustered into two distinct branches: MyoD (MyoD1 and MyoD2) groups with Myf5 in one clade, while MRF4 and MyoG form the other. All genes showed closest evolutionary relationships with Perciformes homologs. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis revealed predominant expression of these MRFs in skeletal muscle, with significantly lower expression levels in the liver, heart, and intestine. These findings provide foundation for elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of MRFs in skeletal muscle development of the giant grouper.
Myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) are critical regulators of skeletal muscle growth and development in animals. The full-length cDNA sequences of five MRFs from the giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus) were cloned using RT-PCR and RAC, including MyoD1 (1,962 bp), MyoD2 (1,466 bp), MyoG (926 bp), MRF4 (1,052 bp), and Myf5 (1,133 bp), encoding 297, 270, 251, 238, and 242 amino acids, respectively. Amino acid sequence alignment revealed that all five MRFs contain a conserved basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain consisting of 60 amino acids. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the MRF genes are clustered into two distinct branches: MyoD (MyoD1 and MyoD2) groups with Myf5 in one clade, while MRF4 and MyoG form the other. All genes showed closest evolutionary relationships with Perciformes homologs. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis revealed predominant expression of these MRFs in skeletal muscle, with significantly lower expression levels in the liver, heart, and intestine. These findings provide foundation for elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of MRFs in skeletal muscle development of the giant grouper.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240197
Abstract:
To address the decreased cut flower yield caused by the bud jumping development phenomenon, where adventitious buds interrupt the normal growth cycle of flower bud differentiation in Oncidium cut flower production, flower buds and vegetative buds of Oncidium hybridum 'Boda NO1' were selected for high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. A total of 127,452,717 high-quality sequences (37.36 Gb) were obtained, and 7,671 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. COG functional classification revealed primary enrichment in signal transduction pathways and carbohydrate transport/metabolism pathways. KEGG analysis showed that DEGs were significantly enriched in starch and sucrose metabolism, phytohormone signaling, and other pathways. Among these, 78 DEGs were identified in the phytohormone signaling pathway, with the most pronounced differences involving auxin, cytokinins, salicylic acid, and gibberellins. Thirteen transcription factors and flowering-related genes, including MADS1, AP2, and FLK, were also screened. These results partially elucidate the effects of auxin, cytokinins, and flowering-related genes on the differentiation of flower buds and vegetative buds in Oncidium. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further research on the mechanism underlying the bud jumping development phenomenon during Oncidium production. Additionally, it supports subsequent improvement in production efficiency, quality enhancement, and optimization of cultivation and management. These findings hold significant practical value for advancing orchid breeding, seedling production, and industry development in China.
To address the decreased cut flower yield caused by the bud jumping development phenomenon, where adventitious buds interrupt the normal growth cycle of flower bud differentiation in Oncidium cut flower production, flower buds and vegetative buds of Oncidium hybridum 'Boda NO1' were selected for high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. A total of 127,452,717 high-quality sequences (37.36 Gb) were obtained, and 7,671 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. COG functional classification revealed primary enrichment in signal transduction pathways and carbohydrate transport/metabolism pathways. KEGG analysis showed that DEGs were significantly enriched in starch and sucrose metabolism, phytohormone signaling, and other pathways. Among these, 78 DEGs were identified in the phytohormone signaling pathway, with the most pronounced differences involving auxin, cytokinins, salicylic acid, and gibberellins. Thirteen transcription factors and flowering-related genes, including MADS1, AP2, and FLK, were also screened. These results partially elucidate the effects of auxin, cytokinins, and flowering-related genes on the differentiation of flower buds and vegetative buds in Oncidium. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further research on the mechanism underlying the bud jumping development phenomenon during Oncidium production. Additionally, it supports subsequent improvement in production efficiency, quality enhancement, and optimization of cultivation and management. These findings hold significant practical value for advancing orchid breeding, seedling production, and industry development in China.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240203
Abstract:
In order to understand the distribution of moss resources and species diversity in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, moss plant specimen collections were conducted several times on the main peak of Limu Mountain from 2022 to 2023, and the specimens collected were identified morphologically in combination of literature review. A new record genus of Pilotrichaceae plants for Hainan was confirmed: Actinodontium, along with the species Actinodontium rhaphidostegum (Müll. Hal.) Bosch & Sande Lac. The morphological characteristics of the newly recorded genus and species were described, and illustrated with characteristic plates. The habitat and geographical distribution of the genus and species was also introduced. This new record enriches the diversity of bryophytes in Hainan Island.
In order to understand the distribution of moss resources and species diversity in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, moss plant specimen collections were conducted several times on the main peak of Limu Mountain from 2022 to 2023, and the specimens collected were identified morphologically in combination of literature review. A new record genus of Pilotrichaceae plants for Hainan was confirmed: Actinodontium, along with the species Actinodontium rhaphidostegum (Müll. Hal.) Bosch & Sande Lac. The morphological characteristics of the newly recorded genus and species were described, and illustrated with characteristic plates. The habitat and geographical distribution of the genus and species was also introduced. This new record enriches the diversity of bryophytes in Hainan Island.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240170
Abstract:
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves as a crucial site for protein processing in eukaryotic cells. Sec62, an essential component of the ER translocation complex, plays a significant role in growth, development, and stress regulation. An attempt was made to examine the transcription levels of the PcSec62 gene at various growth stages and during pathogenic processes. The PcSec62 gene was knocked out by using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to produce knockout mutants (ΔPcsec62) and a complementary strain (ΔPcsec62-C). The results showed that the transcriptional expression of PcSec62 significantly increased during the sporangia and infection stages. The ΔPcsec62 mutants exhibited notably reduced growth and sporulation abilities, alongside stunted hyphal growth. Additionally, the ΔPcsec62 strain showed significantly low tolerance to abiotic stress and reduced pathogenicity. These findings indicate that PcSec62 is involved in regulating the growth, development, abiotic stress responses, and pathogenicity of Phytophthora capsici.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves as a crucial site for protein processing in eukaryotic cells. Sec62, an essential component of the ER translocation complex, plays a significant role in growth, development, and stress regulation. An attempt was made to examine the transcription levels of the PcSec62 gene at various growth stages and during pathogenic processes. The PcSec62 gene was knocked out by using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to produce knockout mutants (ΔPcsec62) and a complementary strain (ΔPcsec62-C). The results showed that the transcriptional expression of PcSec62 significantly increased during the sporangia and infection stages. The ΔPcsec62 mutants exhibited notably reduced growth and sporulation abilities, alongside stunted hyphal growth. Additionally, the ΔPcsec62 strain showed significantly low tolerance to abiotic stress and reduced pathogenicity. These findings indicate that PcSec62 is involved in regulating the growth, development, abiotic stress responses, and pathogenicity of Phytophthora capsici.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250035
Abstract:
In order to investigate the potential functions of the cassava (Manihot esculenta) Ⅶ subfamily of ERF gene family in response to biotic stress, we identified 161 ERF genes in the cassava genome, which were divided into 13 subfamilies. Analyses were performed on the conserved domains, cis-acting elements in promoter regions, interacting proteins, target genes, and expression patterns of the Ⅶ subfamily members. The results showed that all members of this subfamily contained a conserved AP2 domain, and their promoter regions included 13 types of cis-acting elements related to plant growth and development, and environmental stress responses. Expression pattern analysis revealed that the MeERF46, MeERF133, and MeERF92 genes responded actively to Xpm infection among them, the change of MeERF92 expression was the most significant. WGCNA and protein-protein interaction network analysis indicated that MeERF92 might be involved in the process of oxidative stress, while MeERF133 was widely involved in glycometabolism. These findings provide candidate genes for further research into the functions and mechanisms of ERFs in cassava's response to biotic stress.
In order to investigate the potential functions of the cassava (Manihot esculenta) Ⅶ subfamily of ERF gene family in response to biotic stress, we identified 161 ERF genes in the cassava genome, which were divided into 13 subfamilies. Analyses were performed on the conserved domains, cis-acting elements in promoter regions, interacting proteins, target genes, and expression patterns of the Ⅶ subfamily members. The results showed that all members of this subfamily contained a conserved AP2 domain, and their promoter regions included 13 types of cis-acting elements related to plant growth and development, and environmental stress responses. Expression pattern analysis revealed that the MeERF46, MeERF133, and MeERF92 genes responded actively to Xpm infection among them, the change of MeERF92 expression was the most significant. WGCNA and protein-protein interaction network analysis indicated that MeERF92 might be involved in the process of oxidative stress, while MeERF133 was widely involved in glycometabolism. These findings provide candidate genes for further research into the functions and mechanisms of ERFs in cassava's response to biotic stress.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240088
Abstract:
An attempt was made to determine the content of total saponins and antioxidant activity in the roots of Callerya speciosa (Champion ex Bentham) Schot at different ages, and provide reference for their rational development and utilization. The roots of C. speciosa were collected and extracted by using an ultrasonic-assisted extraction method, and the extraction process of total saponins from C. speciosa roots were optimized. Furthermore, the content of total saponins from the extracts of the C. speciosa roots at different ages (3-year-old, 6-year-old, 10-year-old and 15-year-old) was determined by using UV photometer.. The antioxidant activity of total saponins from the C. speciosa roots was determined by using the DPPH free radical method and hydroxyl free radical method. The results showed that the best extraction conditions for total saponins of the C. speciosa roots are 80% ethanol, 1∶ 40 solid-liquid ratio, 40 min ultrasound time, and 3 extraction times. Among the four materials, the 6-year-old C. speciosa roots had the highest total saponin content, while the 15-year-old C. speciosa had the lowest. The total saponin content of the C. speciosa roots tended to increase and then decrease with the ages of C. speciosa. The antioxidant activity test found that total saponins of the C. speciosa roots at different ages all possessed a certain level of antioxidant capacity in vitro, which can be developed and utilized as a potential natural antioxidant.
An attempt was made to determine the content of total saponins and antioxidant activity in the roots of Callerya speciosa (Champion ex Bentham) Schot at different ages, and provide reference for their rational development and utilization. The roots of C. speciosa were collected and extracted by using an ultrasonic-assisted extraction method, and the extraction process of total saponins from C. speciosa roots were optimized. Furthermore, the content of total saponins from the extracts of the C. speciosa roots at different ages (3-year-old, 6-year-old, 10-year-old and 15-year-old) was determined by using UV photometer.. The antioxidant activity of total saponins from the C. speciosa roots was determined by using the DPPH free radical method and hydroxyl free radical method. The results showed that the best extraction conditions for total saponins of the C. speciosa roots are 80% ethanol, 1∶ 40 solid-liquid ratio, 40 min ultrasound time, and 3 extraction times. Among the four materials, the 6-year-old C. speciosa roots had the highest total saponin content, while the 15-year-old C. speciosa had the lowest. The total saponin content of the C. speciosa roots tended to increase and then decrease with the ages of C. speciosa. The antioxidant activity test found that total saponins of the C. speciosa roots at different ages all possessed a certain level of antioxidant capacity in vitro, which can be developed and utilized as a potential natural antioxidant.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240191
Abstract:
To investigate the low-nitrogen tolerance characteristics of Paspalum vaginatum, this study selected 10 Paspalum vaginatum germplasm accessions as experimental materials. A hydroponic method was applied with two nitrogen concentration treatments: full nitrogen (5.0 mmol·L−1) and 1/100 nitrogen (0.05 mmol·L−1), for a duration of 30 days. Eighteen agronomic traits, including chlorophyll content, shoot fresh weight, and turfgrass height, were measured after treatment, and variance analysis was conducted to compare and explore the low-nitrogen tolerance characteristics of the 10 germplasm accessions. A comprehensive evaluation of low-nitrogen tolerance was performed. The results showed that, compared to normal nitrogen treatment, indicators such as shoot fresh weight, shoot dry weight, total tillers length and tillers number significantly decreased under low nitrogen treatment, while indicators such as fresh weight ratio of root shoot, dry weight ratio of root shoot, shoot dry matter content and root dry matter content significantly increased. Through correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and membership function analysis, two low-nitrogen-tolerant Paspalum vaginatum, 17USA-03 and 17HN-39, were selected.
To investigate the low-nitrogen tolerance characteristics of Paspalum vaginatum, this study selected 10 Paspalum vaginatum germplasm accessions as experimental materials. A hydroponic method was applied with two nitrogen concentration treatments: full nitrogen (5.0 mmol·L−1) and 1/100 nitrogen (0.05 mmol·L−1), for a duration of 30 days. Eighteen agronomic traits, including chlorophyll content, shoot fresh weight, and turfgrass height, were measured after treatment, and variance analysis was conducted to compare and explore the low-nitrogen tolerance characteristics of the 10 germplasm accessions. A comprehensive evaluation of low-nitrogen tolerance was performed. The results showed that, compared to normal nitrogen treatment, indicators such as shoot fresh weight, shoot dry weight, total tillers length and tillers number significantly decreased under low nitrogen treatment, while indicators such as fresh weight ratio of root shoot, dry weight ratio of root shoot, shoot dry matter content and root dry matter content significantly increased. Through correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and membership function analysis, two low-nitrogen-tolerant Paspalum vaginatum, 17USA-03 and 17HN-39, were selected.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250026
Abstract:
In order to understand the regulatory role of the BBR-BPC gene family in the growth and development of Dioscorea alata (greater yam), we analyzed the gene structure, phylogenetic evolution, conserved motifs, and physicochemical properties of the BBR-BPC gene family in greater yam. We also predicted the secondary and tertiary structures of BBR-BPC proteins and verified the interaction between the BBR-BPC gene and the DELLA gene. Through HMMsearch and BLAST analyses, we identified six members of the BBR-BPC family in the greater yam genome. These gene proteins exhibited significant differences and alternative splicing events, with a total of 10 splice variants detected. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that all members of the BBR-BPC family in greater yam are located in the nucleus.The yeast two-hybrid interaction results between Da4BBR-BPC2 and DaDELLA2 indicate that there is an interaction between Da4BBR-BPC2 and DaDELLA2, occurring at the N-terminus of the DaDELLA2 gene.
In order to understand the regulatory role of the BBR-BPC gene family in the growth and development of Dioscorea alata (greater yam), we analyzed the gene structure, phylogenetic evolution, conserved motifs, and physicochemical properties of the BBR-BPC gene family in greater yam. We also predicted the secondary and tertiary structures of BBR-BPC proteins and verified the interaction between the BBR-BPC gene and the DELLA gene. Through HMMsearch and BLAST analyses, we identified six members of the BBR-BPC family in the greater yam genome. These gene proteins exhibited significant differences and alternative splicing events, with a total of 10 splice variants detected. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that all members of the BBR-BPC family in greater yam are located in the nucleus.The yeast two-hybrid interaction results between Da4BBR-BPC2 and DaDELLA2 indicate that there is an interaction between Da4BBR-BPC2 and DaDELLA2, occurring at the N-terminus of the DaDELLA2 gene.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250015
Abstract:
In order to assess the role of the bZIP transcription factor in the biosynthesis of natural rubber in Hevea brasiliensis, HbbZIP74 gene was successfully cloned based on previous work in our laboratory. Bioinformatics analysis and expression pattern analysis were performed. The pET28-HbbZIP74 expression vector was constructed, and the recombinant protein was expressed in the strain E. coli BL21 (DE3) and then purified. The results showed that the open reading frame (ORF) of the gene HbbZIP74 is 486 bp, encoding 161 amino acids, with a bZIP domain, classifying it as a bZIP transcription factor S subgroup. The expression level of HbbZIP74 is higher in latex and leaves, and its expression can be induced by jasmonic acid, abscisic acid, ethylene, and salicylic acid in latex. The optimal condition for the heterologous expression of the HbbZIP74-His recombinant protein was induced at 1 mmol·L−1 IPTG and 37 ℃ for 3 h. The recombinant protein was mainly accumulated in inclusion bodies. The recombinant protein, approximately 22 kDa in size, was purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography, which was consistent with expectations. This study lays the foundation for further exploration of the role of HbbZIP74 in the biosynthesis of natural rubber.
In order to assess the role of the bZIP transcription factor in the biosynthesis of natural rubber in Hevea brasiliensis, HbbZIP74 gene was successfully cloned based on previous work in our laboratory. Bioinformatics analysis and expression pattern analysis were performed. The pET28-HbbZIP74 expression vector was constructed, and the recombinant protein was expressed in the strain E. coli BL21 (DE3) and then purified. The results showed that the open reading frame (ORF) of the gene HbbZIP74 is 486 bp, encoding 161 amino acids, with a bZIP domain, classifying it as a bZIP transcription factor S subgroup. The expression level of HbbZIP74 is higher in latex and leaves, and its expression can be induced by jasmonic acid, abscisic acid, ethylene, and salicylic acid in latex. The optimal condition for the heterologous expression of the HbbZIP74-His recombinant protein was induced at 1 mmol·L−1 IPTG and 37 ℃ for 3 h. The recombinant protein was mainly accumulated in inclusion bodies. The recombinant protein, approximately 22 kDa in size, was purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography, which was consistent with expectations. This study lays the foundation for further exploration of the role of HbbZIP74 in the biosynthesis of natural rubber.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240161
Abstract:
Torulaspora delbrueckii is one of non-Saccharomyces yeasts mostly used for research, and is widely used for brewing of various fruit wines. It is co-fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improving fruit wine flavors. In this experiment, a wild-type yeast strain was selected from the peel of cantaloupe in Fulo Town, Ledong County, Hainan Province. Through phenotypic observation of the strain and constructing a phylogenetic tree based on 18S rDNA sequencing, the strain was identified as T. delbrueckii. Under the fermentation condition of fruit wine, T. delbrueckii grew normally in the range of alcohol content 4−20%, pH value 2.8−3.6 and sulfur dioxide concentration 100−500 mg·L−1, and the growth rate was the highest under the condition of alcohol content 4%, pH value 3.6 and sulfur dioxide concentration 300 mg·L−1. The results show that T. delbrueckii did not produce hydrogen sulfide, had no killing effect on S. cerevisiae, and improved the flavor of cantaloupe fruit wine, which can be used in the production of cantaloupe fruit wine.
Torulaspora delbrueckii is one of non-Saccharomyces yeasts mostly used for research, and is widely used for brewing of various fruit wines. It is co-fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improving fruit wine flavors. In this experiment, a wild-type yeast strain was selected from the peel of cantaloupe in Fulo Town, Ledong County, Hainan Province. Through phenotypic observation of the strain and constructing a phylogenetic tree based on 18S rDNA sequencing, the strain was identified as T. delbrueckii. Under the fermentation condition of fruit wine, T. delbrueckii grew normally in the range of alcohol content 4−20%, pH value 2.8−3.6 and sulfur dioxide concentration 100−500 mg·L−1, and the growth rate was the highest under the condition of alcohol content 4%, pH value 3.6 and sulfur dioxide concentration 300 mg·L−1. The results show that T. delbrueckii did not produce hydrogen sulfide, had no killing effect on S. cerevisiae, and improved the flavor of cantaloupe fruit wine, which can be used in the production of cantaloupe fruit wine.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240177
Abstract:
In order to understand the anti-actinomycetes with biocontrol value isolated and screened from the soil in Hainan Island, actinomycetes were isolated from six soil samples from different regions of Hainan by using a gradient dilution method, and the actinomycete strains were screened by using the confrontation culture method and identified based on their morphology, physiological and biochemical characteristics and molecular biology methods. The potential application value of the active strains was determined by fruit soaking method and pot experiment. A total of 285 actinomycete strains were isolated from the soil samples, and the strain Q2-02 had the highest antibacterial activity. Its inhibition rates of Botryodiplodia theobromae, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Rhizoctonia solani were 92.8%, 90.0% and 88.2%, respectively, and the inhibition rates of the other six pathogens were also more than 60.0%. The identification of this strain showed that the strain Q2-02 was Streptomyces lunalinharesii. The pot experiments showed that the control effect of the 10-fold dilution of the fermented supernatant of the strain on mango stemend rot and rice sheath blight was significantly higher than that of the positive control 45% thiophandazim suspension diluted 800 times and 10% validacin aqueous solution diluted1000 times, indicating that the strain Q2-02 has the value of further development and application.
In order to understand the anti-actinomycetes with biocontrol value isolated and screened from the soil in Hainan Island, actinomycetes were isolated from six soil samples from different regions of Hainan by using a gradient dilution method, and the actinomycete strains were screened by using the confrontation culture method and identified based on their morphology, physiological and biochemical characteristics and molecular biology methods. The potential application value of the active strains was determined by fruit soaking method and pot experiment. A total of 285 actinomycete strains were isolated from the soil samples, and the strain Q2-02 had the highest antibacterial activity. Its inhibition rates of Botryodiplodia theobromae, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Rhizoctonia solani were 92.8%, 90.0% and 88.2%, respectively, and the inhibition rates of the other six pathogens were also more than 60.0%. The identification of this strain showed that the strain Q2-02 was Streptomyces lunalinharesii. The pot experiments showed that the control effect of the 10-fold dilution of the fermented supernatant of the strain on mango stemend rot and rice sheath blight was significantly higher than that of the positive control 45% thiophandazim suspension diluted 800 times and 10% validacin aqueous solution diluted
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250131
Abstract:
To clarify the species composition of major pests in pepper fields in Sanya, Hainan, and the relationship between thrips population dynamics and meteorological factors, a systematic survey of pest species and thrips population dynamics was conducted during the pepper growing season from November 2024 to May 2025, and their association with key meteorological factors was analyzed. The results showed that the dominant pests in Sanya pepper fields were thrips, with Thrips palmi and Frankliniella intonsa being the dominant species. Thrips pests occurred at all the growth stages of pepper, but their population dynamics exhibited distinct growth stage-specific differences: the seedling stage was a low-incidence period, and the flowering and fruit-setting stages were the peak population period, during which the number of F. intonsa significantly exceeded that of T. palmi. The damage decreased during the flowering and harvesting stages, and by the end of the survey, T. palmi once again became dominant. Correlation analysis indicated that meteorological factors during the flowering and fruit-setting stages had a significant influence on thrips population numbers, showing significant positive correlations with average temperature, minimum temperature, average surface temperature, daily maximum/minimum surface temperature, and maximum humidity. All these findings reveal the pest species composition, dominant pest populations, dynamics of dominant thrips pests, and the key influence of meteorological factors on thrips population dynamics in pepper fields, providing a scientific basis for the precise monitoring and formulation of control strategies against thrips pests in pepper fields in the Sanya region.
To clarify the species composition of major pests in pepper fields in Sanya, Hainan, and the relationship between thrips population dynamics and meteorological factors, a systematic survey of pest species and thrips population dynamics was conducted during the pepper growing season from November 2024 to May 2025, and their association with key meteorological factors was analyzed. The results showed that the dominant pests in Sanya pepper fields were thrips, with Thrips palmi and Frankliniella intonsa being the dominant species. Thrips pests occurred at all the growth stages of pepper, but their population dynamics exhibited distinct growth stage-specific differences: the seedling stage was a low-incidence period, and the flowering and fruit-setting stages were the peak population period, during which the number of F. intonsa significantly exceeded that of T. palmi. The damage decreased during the flowering and harvesting stages, and by the end of the survey, T. palmi once again became dominant. Correlation analysis indicated that meteorological factors during the flowering and fruit-setting stages had a significant influence on thrips population numbers, showing significant positive correlations with average temperature, minimum temperature, average surface temperature, daily maximum/minimum surface temperature, and maximum humidity. All these findings reveal the pest species composition, dominant pest populations, dynamics of dominant thrips pests, and the key influence of meteorological factors on thrips population dynamics in pepper fields, providing a scientific basis for the precise monitoring and formulation of control strategies against thrips pests in pepper fields in the Sanya region.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250081
Abstract:
The issue of pesticide residues in bee products and their impact on bee health is receiving increasing attention. Previous studies have shown that observations of the proboscis extension reflex (PER) are suitable for evaluating the behavioral effects of pesticides on honey bees. In this context an attempt was made to clarify the long-term effects of exposure to bifenthrin and its mixtures in beebread on the olfactory and learning ability of Apis cerana cerana worker. The results showed that after 10 days of oral administration of bifenthrin and its mixtures, either alone or in combination, the survival rate of worker honey bees was significantly reduced in the groups treated with various pesticide mixtures, but there was no significant effect on their body weight. Moreover, the olfactory sensitivity of honey bees in the treatment groups to 0.1%, 1%, 3% and 10% sucrose solutions was significantly reduced, and their learning ability was also significantly decreased. Therefore, long-term exposure of honey bees to multiple insecticides and fungicides with different mechanisms of action has a significant impact on their survival and learning abilities, which in turn threatens the healthy development of honey bee colonies.
The issue of pesticide residues in bee products and their impact on bee health is receiving increasing attention. Previous studies have shown that observations of the proboscis extension reflex (PER) are suitable for evaluating the behavioral effects of pesticides on honey bees. In this context an attempt was made to clarify the long-term effects of exposure to bifenthrin and its mixtures in beebread on the olfactory and learning ability of Apis cerana cerana worker. The results showed that after 10 days of oral administration of bifenthrin and its mixtures, either alone or in combination, the survival rate of worker honey bees was significantly reduced in the groups treated with various pesticide mixtures, but there was no significant effect on their body weight. Moreover, the olfactory sensitivity of honey bees in the treatment groups to 0.1%, 1%, 3% and 10% sucrose solutions was significantly reduced, and their learning ability was also significantly decreased. Therefore, long-term exposure of honey bees to multiple insecticides and fungicides with different mechanisms of action has a significant impact on their survival and learning abilities, which in turn threatens the healthy development of honey bee colonies.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20260019
Abstract:
Waltherione A is a plant-derived nematicidal compound with significant activity against root-knot nematodes (LC50 0.09–3.54 mg·L−1). Caenorhabditis elegans was used as a model organism to elucidate the action mechanism of Waltherinone A. Based on a pre-determined screening concentration of 10 mg·L−1, phenotypic differences between wild-type N2 and the Waltherione A-resistant mutant A1 were compared at treatment concentrations of 3 and 6 mg·L−1, enabling a basic phenotypic characterization of the mutant. Systematic screening via SNP mapping and whole-genome resequencing, combined with RNAi validation, identified three potential target genes: Y32H12A.4 (szy-2), F47D12.4 (hmg-1.2), and C28A5.4 (ceh-43). Molecular docking simulations indicated that Waltherione A can form stable, high-affinity complexes with the corresponding proteins (binding energies of −6.3, −7.1, and −6.9 kcal·mol−1, respectively). The results suggest that Waltherione A may exert its nematicidal effect by simultaneously targeting the transcription regulator HMG-1.2, the developmental programming factor CEH-43, and the phosphatase signaling protein SZY-2, thereby disrupting a coordinated response pathway governed by transcriptional and developmental regulation with phosphatase signaling as a key execution node. All these findings systematically reveal the multi-target network of Waltherione A, providing an important theoretical basis for its further development and mechanistic application as a novel green nematicide.
Waltherione A is a plant-derived nematicidal compound with significant activity against root-knot nematodes (LC50 0.09–3.54 mg·L−1). Caenorhabditis elegans was used as a model organism to elucidate the action mechanism of Waltherinone A. Based on a pre-determined screening concentration of 10 mg·L−1, phenotypic differences between wild-type N2 and the Waltherione A-resistant mutant A1 were compared at treatment concentrations of 3 and 6 mg·L−1, enabling a basic phenotypic characterization of the mutant. Systematic screening via SNP mapping and whole-genome resequencing, combined with RNAi validation, identified three potential target genes: Y32H12A.4 (szy-2), F47D12.4 (hmg-1.2), and C28A5.4 (ceh-43). Molecular docking simulations indicated that Waltherione A can form stable, high-affinity complexes with the corresponding proteins (binding energies of −6.3, −7.1, and −6.9 kcal·mol−1, respectively). The results suggest that Waltherione A may exert its nematicidal effect by simultaneously targeting the transcription regulator HMG-1.2, the developmental programming factor CEH-43, and the phosphatase signaling protein SZY-2, thereby disrupting a coordinated response pathway governed by transcriptional and developmental regulation with phosphatase signaling as a key execution node. All these findings systematically reveal the multi-target network of Waltherione A, providing an important theoretical basis for its further development and mechanistic application as a novel green nematicide.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250205
Abstract:
With arable land resources becoming increasingly scarce, extreme weather events occurring more frequently, and population growth accelerating, plant factories have gradually emerged as a vital form of agricultural production due to their advantages of minimal land requirements and controllable production environments. However, there remains a lack of wheat varieties specifically suited for cultivation and production in plant factories. Therefore, an attempt was made to develop new wheat germplasm suitable for plant factory production. Through marker-assisted selection, new accessions of dwarf, early-maturing wheat germplasm suitable for plant factory production were successfully developed. Furthermore, through exome sequencing, a novel genetic locus controlling wheat early maturity was identifiedon chromosome 1B. The development of these dwarf, early-maturing wheat germplasm and the identification of a novel genetic locus for early maturity provide a robust material and theoretical foundation for the industrialized production of wheat.
With arable land resources becoming increasingly scarce, extreme weather events occurring more frequently, and population growth accelerating, plant factories have gradually emerged as a vital form of agricultural production due to their advantages of minimal land requirements and controllable production environments. However, there remains a lack of wheat varieties specifically suited for cultivation and production in plant factories. Therefore, an attempt was made to develop new wheat germplasm suitable for plant factory production. Through marker-assisted selection, new accessions of dwarf, early-maturing wheat germplasm suitable for plant factory production were successfully developed. Furthermore, through exome sequencing, a novel genetic locus controlling wheat early maturity was identifiedon chromosome 1B. The development of these dwarf, early-maturing wheat germplasm and the identification of a novel genetic locus for early maturity provide a robust material and theoretical foundation for the industrialized production of wheat.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240158
Abstract:
Research on the central nervous system function of pests forms the foundation for developing precise behavior control technologies. Despite the significant role of neuron-labeling techniques based on genetic manipulation in this field, such techniques remain relatively scarce for non-model insects, such as the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis. In this context an attempt was made to identify four pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis with a view to laying the groundwork for constructing a neuron-labeling system for this species. The genomic structures of the pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis were identified and analyzed by employing bioinformatics and molecular biology to verify their full-length sequences and peripheral expression patterns. The results indicate that, by referring to four pan-neuronal expression genes from Drosophila, four homologous genes were identified in the B. dorsalis, namely BdornSyb, BdorSyt1, Bdorelav, and BdorBrp. The full genomic lengths of these four genes are 19,337 bp (5 exons, 4 introns), 26,884 bp (8 exons, 7 introns), 1,341 bp (1 exon), and 49,692 bp (14 exons, 13 introns), respectively. The domains of BdornSyb, BdorSyt1, and Bdorelav are highly conserved among closely related species. PCR cloning results indicated that the CDS sequence lengths of these four genes are all over 500 bp, consistent with the bioinformatics analysis results. Evolutionary and genomic structure analyses demonstrated that the four genes are highly conserved among Diptera insects. Expression pattern analysis revealed that all the four genes are expressed in the peripheral sensory organs of B. dorsalis, with three genes, BdornSyb, BdorSyt1 and BdorBrp, showing higher expression levels in the primary olfactory organs, the antennae, and the maxillary palp. The four genes identified are candidate pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis, providing a foundation for constructing a pan-neuronal labeling system for this species in the future.
Research on the central nervous system function of pests forms the foundation for developing precise behavior control technologies. Despite the significant role of neuron-labeling techniques based on genetic manipulation in this field, such techniques remain relatively scarce for non-model insects, such as the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis. In this context an attempt was made to identify four pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis with a view to laying the groundwork for constructing a neuron-labeling system for this species. The genomic structures of the pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis were identified and analyzed by employing bioinformatics and molecular biology to verify their full-length sequences and peripheral expression patterns. The results indicate that, by referring to four pan-neuronal expression genes from Drosophila, four homologous genes were identified in the B. dorsalis, namely BdornSyb, BdorSyt1, Bdorelav, and BdorBrp. The full genomic lengths of these four genes are 19,337 bp (5 exons, 4 introns), 26,884 bp (8 exons, 7 introns), 1,341 bp (1 exon), and 49,692 bp (14 exons, 13 introns), respectively. The domains of BdornSyb, BdorSyt1, and Bdorelav are highly conserved among closely related species. PCR cloning results indicated that the CDS sequence lengths of these four genes are all over 500 bp, consistent with the bioinformatics analysis results. Evolutionary and genomic structure analyses demonstrated that the four genes are highly conserved among Diptera insects. Expression pattern analysis revealed that all the four genes are expressed in the peripheral sensory organs of B. dorsalis, with three genes, BdornSyb, BdorSyt1 and BdorBrp, showing higher expression levels in the primary olfactory organs, the antennae, and the maxillary palp. The four genes identified are candidate pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis, providing a foundation for constructing a pan-neuronal labeling system for this species in the future.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240201
Abstract:
In order to screen for stable expression of cassava reference genes in cassava leaves infected with Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. manihotis(Xpm), we used Xpm resistant variety ‘G1301’ and susceptible variety ‘SC9’cassava leaves as research materials. Samples were collected from cassava leaves of ‘G1301’ and ‘SC9’ at 0 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 72 h, and 120 h after Xpm infection, and the stability of the commonly used reference genes Nascent, EF1a, ACT, GTPb, and TUB was determined. The results showed that there were differences in the expression levels of five reference genes after Xpm infection in the leaves of ‘G1301’ and ‘SC9’. Delta CT, GeNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper and RefFinder software were used to rank the stability of these candidate reference genes. We found that the most stable reference gene expressed in Xpm-infected leaves is EF1α. This study identified the stable internal reference genes expressed during Xpm infection in cassava leaves, laying the foundation for studying gene expression in response to Xpm infection and exploring disease resistance genes.
In order to screen for stable expression of cassava reference genes in cassava leaves infected with Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. manihotis(Xpm), we used Xpm resistant variety ‘G1301’ and susceptible variety ‘SC9’cassava leaves as research materials. Samples were collected from cassava leaves of ‘G1301’ and ‘SC9’ at 0 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 72 h, and 120 h after Xpm infection, and the stability of the commonly used reference genes Nascent, EF1a, ACT, GTPb, and TUB was determined. The results showed that there were differences in the expression levels of five reference genes after Xpm infection in the leaves of ‘G1301’ and ‘SC9’. Delta CT, GeNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper and RefFinder software were used to rank the stability of these candidate reference genes. We found that the most stable reference gene expressed in Xpm-infected leaves is EF1α. This study identified the stable internal reference genes expressed during Xpm infection in cassava leaves, laying the foundation for studying gene expression in response to Xpm infection and exploring disease resistance genes.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250178
Abstract:
The subgenus Dasyhelea are the most diverse group of the genus Dasyhelea (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae: Dasyhelea) including over 400 species worldwide, with 56 species from China and only four from Hainan Island. Based on the systematic collections in the tropical rainforests of Hainan Island and their morphological and DNA barcoding (COⅠ) analyses, two new species of Dasyhelea, Dasyhelea limushanensis sp. nov. and D. bifurca sp. nov., were described, and a newly recorded from Hainan Island, D. abronica Yu, 2001, were also reported. The morphological characteristics of the new species were described in detail, and their identification diagrams and the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) barcoding data were presented.
The subgenus Dasyhelea are the most diverse group of the genus Dasyhelea (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae: Dasyhelea) including over 400 species worldwide, with 56 species from China and only four from Hainan Island. Based on the systematic collections in the tropical rainforests of Hainan Island and their morphological and DNA barcoding (COⅠ) analyses, two new species of Dasyhelea, Dasyhelea limushanensis sp. nov. and D. bifurca sp. nov., were described, and a newly recorded from Hainan Island, D. abronica Yu, 2001, were also reported. The morphological characteristics of the new species were described in detail, and their identification diagrams and the cytochrome c oxidase subunit I (COI) barcoding data were presented.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250189
Abstract:
Cryptolaemus montrouzieri (Mulsant) is one of the most important predatory natural enemies for controlling Planococcus minor (Maskell). To screen chemical insecticides with high efficacy against P. minor while maintaining safety for C. montrouzieri, six insecticides were selected for evaluation of their toxicity against adult female P. minor and fourth-instar larvae and adults of C. montrouzieri using dipping and filter paper contact methods. The safety to the natural enemy was assessed by using beneficial-harmful toxicity ratios and safety coefficients. The results showed that after 24-h treatment, the toxicity of six insecticides against P. minor females ranked from the highest to the lowest: acetamiprid 10% EC (LC50 = 3.918 mg·L−1) > sulfoxaflor 22% SC (LC50 =13.343 mg·L−1) > thiamethoxam 25% WG (LC50 =23.290 mg·L−1) > abamectin 1.8% EC (LC50 = 58.173 mg·L−1) > dinotefuran 20% SC (LC50 = 111.008 mg·L−1) > bifenthrin 25 g·L−1 EC (LC50 =141.131 mg·L−1). Sulfoxaflor 22% SC exhibited the lowest toxicity to both fourth-instar larvae and adults of C. montrouzieri, while abamectin 1.8% EC showed the highest toxicity to fourth-instar larvae and bifenthrin 25 g·L−1 EC demonstrated the highest toxicity to adult lady beetles. Based on beneficial-harmful toxicity ratios and safety coefficients, both acetamiprid 10% EC and sulfoxaflor 22% SC exhibited high toxicity against P. minor and low toxicity to C. montrouzieri. It is recommended that these two insecticides be used in rotation for mealybug control in the field to achieve synergistic pest management with high efficacy and natural enemy conservation.
Cryptolaemus montrouzieri (Mulsant) is one of the most important predatory natural enemies for controlling Planococcus minor (Maskell). To screen chemical insecticides with high efficacy against P. minor while maintaining safety for C. montrouzieri, six insecticides were selected for evaluation of their toxicity against adult female P. minor and fourth-instar larvae and adults of C. montrouzieri using dipping and filter paper contact methods. The safety to the natural enemy was assessed by using beneficial-harmful toxicity ratios and safety coefficients. The results showed that after 24-h treatment, the toxicity of six insecticides against P. minor females ranked from the highest to the lowest: acetamiprid 10% EC (LC50 = 3.918 mg·L−1) > sulfoxaflor 22% SC (LC50 =13.343 mg·L−1) > thiamethoxam 25% WG (LC50 =23.290 mg·L−1) > abamectin 1.8% EC (LC50 = 58.173 mg·L−1) > dinotefuran 20% SC (LC50 = 111.008 mg·L−1) > bifenthrin 25 g·L−1 EC (LC50 =141.131 mg·L−1). Sulfoxaflor 22% SC exhibited the lowest toxicity to both fourth-instar larvae and adults of C. montrouzieri, while abamectin 1.8% EC showed the highest toxicity to fourth-instar larvae and bifenthrin 25 g·L−1 EC demonstrated the highest toxicity to adult lady beetles. Based on beneficial-harmful toxicity ratios and safety coefficients, both acetamiprid 10% EC and sulfoxaflor 22% SC exhibited high toxicity against P. minor and low toxicity to C. montrouzieri. It is recommended that these two insecticides be used in rotation for mealybug control in the field to achieve synergistic pest management with high efficacy and natural enemy conservation.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250144
Abstract:
An attempt was made to improve the utilization efficiency of the precious land resources for seed production in Hainan and to ensure the production of high-quality soybean seeds. The effects of planting density on the yield, photosynthetic physiology, agronomic traits, and quality characteristics of different soybean genotypes under Hainan's ecological conditions were analyzed to provide a theoretical basis for rational close planting. Ten dominant soybean varieties recommended by the General Office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China were selected, and planted at four planting densities, 400,000, 600,000, 800,000, and 1,000,000 plants per hectare (or D1 to D4, respectively). A systematic analysis was conducted on the effects of density on soybean agronomic traits, quality parameters, photosynthetic characteristics, and yield components. The results indicated that with an increase in planting density, the flowering and maturity stages of the soybeans showed no significant changes. The number of grains per plant, pods per plant, and effective nodes all decreased significantly. Plant height exhibited a trend of either gradual decline or an initial increase followed by a decrease. Density treatments significantly regulated quality traits and photosynthetic parameters: protein content generally showed a decreasing trend or an initial increase followed by a decrease, and fat content commonly declined while the net photosynthetic rate (Pn) demonstrated an increasing trend with density. The yield response to density varied significantly among varieties. Most varieties, such as Suinong 52 and Heinong 531, achieved their highest yield at low to medium densities (D1 or D2), whereas a few varieties, such as Zhonghuang 901 and Heinong 84, maintained high yield even at relatively high densities (D3). All these findings clarify the complex physiological mechanisms through which planting density regulates soybean yield and quality formation by influencing light use efficiency and plant architecture performance. The results highlight the necessity of determining suitable planting densities based on varietal characteristics, providing a scientific basis and theoretical reference for achieving high-quality and high-yield soybean cultivation in the Hainan region.
An attempt was made to improve the utilization efficiency of the precious land resources for seed production in Hainan and to ensure the production of high-quality soybean seeds. The effects of planting density on the yield, photosynthetic physiology, agronomic traits, and quality characteristics of different soybean genotypes under Hainan's ecological conditions were analyzed to provide a theoretical basis for rational close planting. Ten dominant soybean varieties recommended by the General Office of the Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of China were selected, and planted at four planting densities, 400,000, 600,000, 800,000, and 1,000,000 plants per hectare (or D1 to D4, respectively). A systematic analysis was conducted on the effects of density on soybean agronomic traits, quality parameters, photosynthetic characteristics, and yield components. The results indicated that with an increase in planting density, the flowering and maturity stages of the soybeans showed no significant changes. The number of grains per plant, pods per plant, and effective nodes all decreased significantly. Plant height exhibited a trend of either gradual decline or an initial increase followed by a decrease. Density treatments significantly regulated quality traits and photosynthetic parameters: protein content generally showed a decreasing trend or an initial increase followed by a decrease, and fat content commonly declined while the net photosynthetic rate (Pn) demonstrated an increasing trend with density. The yield response to density varied significantly among varieties. Most varieties, such as Suinong 52 and Heinong 531, achieved their highest yield at low to medium densities (D1 or D2), whereas a few varieties, such as Zhonghuang 901 and Heinong 84, maintained high yield even at relatively high densities (D3). All these findings clarify the complex physiological mechanisms through which planting density regulates soybean yield and quality formation by influencing light use efficiency and plant architecture performance. The results highlight the necessity of determining suitable planting densities based on varietal characteristics, providing a scientific basis and theoretical reference for achieving high-quality and high-yield soybean cultivation in the Hainan region.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250188
Abstract:
Natural rubber is a critical strategic resource in China, and anthracnose of rubber trees caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides directly threatens the healthy development of the rubber industry. During infection, C. gloeosporioides secretes numerous protein effectors, and their roles in overcoming plant immunity remain poorly understood. Investigating potential effector proteins in C. gloeosporioides can provide a theoretical basis for controlling anthracnose. In this context, two candidate effector proteins, Cg694 and Cg2346, were predicted in C. gloeosporioides. Quantitative real-time PCR revealed that the transcriptional expression of the genes Cg694 and Cg2346 was significantly upregulated during the development stages of spore, germination, and appressorium compared with the vegetative hyphal stage. Subcellular localization assays via transient expression (Green fluorescent protein) in Nicotiana benthamiana epidermal cells showed that both Cg694 and Cg2346 genes were localized to the nucleus and cell membrane, and their transient overexpression induced necrosis in tobacco leaves. Furthermore, gene knockout mutants ΔCg694 and ΔCg2346 were generated. Phenotypic analysis indicated that ΔCg694 and ΔCg2346 exhibit enhanced germ tube polar growth and reduced early invasive hyphal formation rates in onion epidermal cells. Notably, the ΔCg2346 mutant also show a decreased ability to form appressoria. However, neither ΔCg694 nor ΔCg2346 mutants display significant changes in pathogenicity on rubber tree leaves. These results demonstrate that Cg694 and Cg2346 are involved in modulating the polar growth and early invasion capabilities of C. gloeosporioides, though their precise functions require further investigation.
Natural rubber is a critical strategic resource in China, and anthracnose of rubber trees caused by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides directly threatens the healthy development of the rubber industry. During infection, C. gloeosporioides secretes numerous protein effectors, and their roles in overcoming plant immunity remain poorly understood. Investigating potential effector proteins in C. gloeosporioides can provide a theoretical basis for controlling anthracnose. In this context, two candidate effector proteins, Cg694 and Cg2346, were predicted in C. gloeosporioides. Quantitative real-time PCR revealed that the transcriptional expression of the genes Cg694 and Cg2346 was significantly upregulated during the development stages of spore, germination, and appressorium compared with the vegetative hyphal stage. Subcellular localization assays via transient expression (Green fluorescent protein) in Nicotiana benthamiana epidermal cells showed that both Cg694 and Cg2346 genes were localized to the nucleus and cell membrane, and their transient overexpression induced necrosis in tobacco leaves. Furthermore, gene knockout mutants ΔCg694 and ΔCg2346 were generated. Phenotypic analysis indicated that ΔCg694 and ΔCg2346 exhibit enhanced germ tube polar growth and reduced early invasive hyphal formation rates in onion epidermal cells. Notably, the ΔCg2346 mutant also show a decreased ability to form appressoria. However, neither ΔCg694 nor ΔCg2346 mutants display significant changes in pathogenicity on rubber tree leaves. These results demonstrate that Cg694 and Cg2346 are involved in modulating the polar growth and early invasion capabilities of C. gloeosporioides, though their precise functions require further investigation.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250163
Abstract:
As an important tropical fruit in China, mango holds a critical position in Hainan's agricultural economy. In recent years, the threat posed by bacterial diseases to local mango production has been increasingly severe. Field surveys were conducted from April to May 2025 in the major-producing areas of Hainan Province, including Changjiang, Dongfang, Ledong, and Sanya, and symptomatic samples were collected to perform pathogen isolation and identification. The surveys showed that, in addition to the known bacterial black spot disease, bacterial necrosis was also present. Morphological observation, physiological and biochemical characterization, multilocus phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA, fusA, leuS, pyrG, rplB, and rpoB gene sequences, and pathogenicity tests following Koch’s postulates showed five out of ten isolated strains from the symptomatic samples were identified as Pantoea dispersa, confirming their role as the causal agent of mango bacterial necrosis disease. This disease is reported for the first time to infect mango in Hainan, which provides an important basis for the prevention and control of the disease in the local mango industry.
As an important tropical fruit in China, mango holds a critical position in Hainan's agricultural economy. In recent years, the threat posed by bacterial diseases to local mango production has been increasingly severe. Field surveys were conducted from April to May 2025 in the major-producing areas of Hainan Province, including Changjiang, Dongfang, Ledong, and Sanya, and symptomatic samples were collected to perform pathogen isolation and identification. The surveys showed that, in addition to the known bacterial black spot disease, bacterial necrosis was also present. Morphological observation, physiological and biochemical characterization, multilocus phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA, fusA, leuS, pyrG, rplB, and rpoB gene sequences, and pathogenicity tests following Koch’s postulates showed five out of ten isolated strains from the symptomatic samples were identified as Pantoea dispersa, confirming their role as the causal agent of mango bacterial necrosis disease. This disease is reported for the first time to infect mango in Hainan, which provides an important basis for the prevention and control of the disease in the local mango industry.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250174
Abstract:
Cucumber fusarium wilt, caused by Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cucumerinum, is one of the most devastating soil-borne fungal diseases, and its effective control remains a significant challenge in agricultural production. A Trichoderma strain HL088 exhibiting pronounced antagonistic activity against the F. oxysporum was obtained through dual culture technique and screening of antifungal metabolites. Morphological and molecular identification showed the strain HL088 is Trichoderma paratroviride. Furthermore, a potential antifungal protein, chitosanase TriCho75 was identified from the solid-state fermentation extract of this strain by employing ammonium sulfate precipitation and mass spectrometry analysis. Prokaryotic expression and functional validation demonstrated that the recombinant protein TriCho75 (15 μmol·L−1) effectively inhibited both conidial germination (with an inhibition rate of 96.44%) and mycelial growth (with an inhibition rate of 60.59%) of F. oxysporum. Microscopic examination revealed that the recombinant protein TriCho75 caused shrinkage and malformation of the conidia, leading to hyphal distortion and irregular thickness in F. oxysporum. These results indicate that T. paratroviride HL088 displays its potential as a biocontrol agent for managing plant Fusarium wilt diseases.
Cucumber fusarium wilt, caused by Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cucumerinum, is one of the most devastating soil-borne fungal diseases, and its effective control remains a significant challenge in agricultural production. A Trichoderma strain HL088 exhibiting pronounced antagonistic activity against the F. oxysporum was obtained through dual culture technique and screening of antifungal metabolites. Morphological and molecular identification showed the strain HL088 is Trichoderma paratroviride. Furthermore, a potential antifungal protein, chitosanase TriCho75 was identified from the solid-state fermentation extract of this strain by employing ammonium sulfate precipitation and mass spectrometry analysis. Prokaryotic expression and functional validation demonstrated that the recombinant protein TriCho75 (15 μmol·L−1) effectively inhibited both conidial germination (with an inhibition rate of 96.44%) and mycelial growth (with an inhibition rate of 60.59%) of F. oxysporum. Microscopic examination revealed that the recombinant protein TriCho75 caused shrinkage and malformation of the conidia, leading to hyphal distortion and irregular thickness in F. oxysporum. These results indicate that T. paratroviride HL088 displays its potential as a biocontrol agent for managing plant Fusarium wilt diseases.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250055
Abstract:
Cassava residues, an organic solid waste generated from cassava processing, were digested in an anaerobic way under mesophilic (37±1)℃ and thermophilic (60±1)℃ conditions, and were batch fermentated at varying total solid (TS) concentrations (w/10%, w/20%, w/0%) and inoculum concentrations (w/30%, w/50%) to evaluate the biogas production potential, gas production patterns, and microbial community distribution characteristics during the anaerobic digestion process. The cumulative methane production was fitted using a modified Gompertz model. The results demonstrated that the thermophilic group exhibited significantly higher total gas production efficiency compared to the mesophilic group. Moreover, the thermophilic fermentation reached peak gas production within 3-6 days, which was 6-9 days shorter than the mesophilic fermentation. The optimal conditions, achieved at 10% TS and 50% inoculum dosage, yielded the highest biogas and methane production, with an average methane content of 54%, biogas yield of 666.48 mL·g−1 TS, methane yield of 346.96 mL·g−1 TS, and SCOD degradation rate of 71.25%. Analysis of microbial community distribution revealed that temperature and TS concentration significantly influenced the dominant bacterial and archaeal populations at both phylum and genus levels. Thermophilic conditions promoted the enrichment of hydrogenotrophic methanogens, such as Methanobacterium (49.84%) and Methanoculleus (24.92%), leading to improved methane recovery. The findings suggest that cassava residues alone could serve as a viable feedstock for biogas production, and that desirable biogas recovery could be achieved in a shorter time frame through controlling an appropriate TS concentration, increasing inoculum dosage, and optimizing fermentation temperature. All these findings provide valuable insights for optimizing the anaerobic fermentation process of cassava residues.
Cassava residues, an organic solid waste generated from cassava processing, were digested in an anaerobic way under mesophilic (37±1)℃ and thermophilic (60±1)℃ conditions, and were batch fermentated at varying total solid (TS) concentrations (w/10%, w/20%, w/0%) and inoculum concentrations (w/30%, w/50%) to evaluate the biogas production potential, gas production patterns, and microbial community distribution characteristics during the anaerobic digestion process. The cumulative methane production was fitted using a modified Gompertz model. The results demonstrated that the thermophilic group exhibited significantly higher total gas production efficiency compared to the mesophilic group. Moreover, the thermophilic fermentation reached peak gas production within 3-6 days, which was 6-9 days shorter than the mesophilic fermentation. The optimal conditions, achieved at 10% TS and 50% inoculum dosage, yielded the highest biogas and methane production, with an average methane content of 54%, biogas yield of 666.48 mL·g−1 TS, methane yield of 346.96 mL·g−1 TS, and SCOD degradation rate of 71.25%. Analysis of microbial community distribution revealed that temperature and TS concentration significantly influenced the dominant bacterial and archaeal populations at both phylum and genus levels. Thermophilic conditions promoted the enrichment of hydrogenotrophic methanogens, such as Methanobacterium (49.84%) and Methanoculleus (24.92%), leading to improved methane recovery. The findings suggest that cassava residues alone could serve as a viable feedstock for biogas production, and that desirable biogas recovery could be achieved in a shorter time frame through controlling an appropriate TS concentration, increasing inoculum dosage, and optimizing fermentation temperature. All these findings provide valuable insights for optimizing the anaerobic fermentation process of cassava residues.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240181
Abstract:
Hopea hainanensis Merrill & Chun, a large evergreen tree belonging to the family Dipterocarpaceae, is a representative species in tropical rainforests of Hainan Island. The population size of H. hainanensis has contracted seriously due to over exploitation and deforestation, and as a result this species has been listed as a national first-class protected plant in China. The reproductive system determines the transmission of genes between generations, which is an important research topic on endangered plant species. Mother trees of H. hainanensis and their seedlings were genotyped using both microsatellite markers and single nucleotide polymorphisms, on which the reproduction mode of this species was inferred. Results showed that the genotypes of the seedlings of 10 mother trees were identical to their corresponding parents at 12 microsatellite loci. Four randomly selected mother trees and their seedlings were further genotyped using single nucleotide polymorphisms generated by reduced-representation genome sequencing. Most of the SNP loci in the seedlings were found to be identical to their parents, which could be hardly explained by sexual reproduction. In summary, the reproduction of H. hainanensis was inferred to be apomictic based on both microsatellite and SNP markers. As an autotetraploid species, it is impossible for H. hainanensis to reproduce through meiosis, and apomixis is the only way to produce seeds thus maintaining its population. Somatic mutation is the main way to generate variation in apomictic species. In order to restore the genetic variation in H. hainanensis, the existing populations must be strictly conserved to avoid further loss of diversity. Moreover, high-throughput sequencing such as reduced-representation genome sequencing should be conducted to screen seedlings which are different from its parent. The seedlings with somatic mutations could be used to rebuild H. hainanensis populations in natural habitats, so that genetic diversity may be gradually restored and the long-term survival of this species could be achieved at last.
Hopea hainanensis Merrill & Chun, a large evergreen tree belonging to the family Dipterocarpaceae, is a representative species in tropical rainforests of Hainan Island. The population size of H. hainanensis has contracted seriously due to over exploitation and deforestation, and as a result this species has been listed as a national first-class protected plant in China. The reproductive system determines the transmission of genes between generations, which is an important research topic on endangered plant species. Mother trees of H. hainanensis and their seedlings were genotyped using both microsatellite markers and single nucleotide polymorphisms, on which the reproduction mode of this species was inferred. Results showed that the genotypes of the seedlings of 10 mother trees were identical to their corresponding parents at 12 microsatellite loci. Four randomly selected mother trees and their seedlings were further genotyped using single nucleotide polymorphisms generated by reduced-representation genome sequencing. Most of the SNP loci in the seedlings were found to be identical to their parents, which could be hardly explained by sexual reproduction. In summary, the reproduction of H. hainanensis was inferred to be apomictic based on both microsatellite and SNP markers. As an autotetraploid species, it is impossible for H. hainanensis to reproduce through meiosis, and apomixis is the only way to produce seeds thus maintaining its population. Somatic mutation is the main way to generate variation in apomictic species. In order to restore the genetic variation in H. hainanensis, the existing populations must be strictly conserved to avoid further loss of diversity. Moreover, high-throughput sequencing such as reduced-representation genome sequencing should be conducted to screen seedlings which are different from its parent. The seedlings with somatic mutations could be used to rebuild H. hainanensis populations in natural habitats, so that genetic diversity may be gradually restored and the long-term survival of this species could be achieved at last.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240198
Abstract:
In order to have a better picture of the plant resources of Danxia landform in Jiulian mountain, southern Jiangxi Province a survey was made of the plant resources min Danxia landform by using the line transect method. Justicia quadrifaria var. hirsuta G. L. Xu , which is a new variety of Justicia, was found in Xiao Wudang Mountain scenic spot, Longnan City. This variety differs from J. quadrifaria (Nees) T. Anderson in stem, both surfaces of blade, bracts, and outer parts of calyx and corolla tubes which are spread white hispid 1~3 mm long. J. championii are retrorsely pubescent or glabrescent on the stem, pubescent or glabrescent on both surfaces of blade, pubescent on the bracts, petiole, and outer parts of the calyx and corolla tube. Therefore, this variety is easy to distinguish from J. quadrifaria, and phylogenetic analysis also supports the division of this variety. The discovery of this variety further enriches the species diversity of this genus, and also provides a new reference for the development and utilization of this genus.
In order to have a better picture of the plant resources of Danxia landform in Jiulian mountain, southern Jiangxi Province a survey was made of the plant resources min Danxia landform by using the line transect method. Justicia quadrifaria var. hirsuta G. L. Xu , which is a new variety of Justicia, was found in Xiao Wudang Mountain scenic spot, Longnan City. This variety differs from J. quadrifaria (Nees) T. Anderson in stem, both surfaces of blade, bracts, and outer parts of calyx and corolla tubes which are spread white hispid 1~3 mm long. J. championii are retrorsely pubescent or glabrescent on the stem, pubescent or glabrescent on both surfaces of blade, pubescent on the bracts, petiole, and outer parts of the calyx and corolla tube. Therefore, this variety is easy to distinguish from J. quadrifaria, and phylogenetic analysis also supports the division of this variety. The discovery of this variety further enriches the species diversity of this genus, and also provides a new reference for the development and utilization of this genus.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250013
Abstract:
An attempt was made to understand the mosquito species and their carrying pathogenic microorganisms in pig farms from different regions of Hainan Province, and to provide reliable data support for the scientific prevention and control of mosquito-borne diseases in pig farms. Light catalyst mosquito traps were used to collect mosquitoes from four different pig farms in Baisha Li Autonomous County (BS), Ding 'an County (DA), Ledong Li Autonomous County (LD) and Wenchang City (WC) in Hainan Province. The mosquito species collected were identified by using morphological characteristics and the PCR method, and the composition of mosquito-borne microbial community and gene function were analyzed by using metagenomic sequencing. The results showed that the dominant mosquito species in the pig farms of different regions of Hainan were different. The dominant mosquito species in BS, DA, LD and WC were Anopheles dabryanus, Anopheles sinensis, Culex pipiens pallens and Culex tritaeniorhynchus, accounting for 58.43 %, 55.46 %, 88.65 % and 57.84 %, respectively. The analysis of metagenomic microbial sequencing showed the mosquito-borne microorganisms in BS, LD, WC and other regions were at the phylum level. Euryarchaeota was the dominant archaea, while the dominant archaea in DA pig farm was Thermoarchaeota. Proteobacteria was the dominant phylum of mosquito vectors in the pig farms from the four regions. Ascomycota was the dominant phylum of mosquitoes in the 4 regions; negarnaviricota was the dominant virus phylum in BS, DA and LD, while Cossaviricota was the dominant virus phylum in WC. At the species level bacteria such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brucella melitensis, Chlamydia abortus, Leptospira interrogans and Waddlia chondrophila, fungi such as Acremonium asperulatum, Aspergillus terreus and Microsporum canis, and viruses such as Aedes aegypti anphevirus and Anopheles annulipes orbivirus pose a pathogenic threat to humans and pigs. Moreover, the mosquito-borne microorganisms from the pig farms in different regions of Hainan maintain high stability at the phylum level and diversity at the species level, and there is a high risk of pathogenicity. This study provides a scientific basis for the prevention and control of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne diseases in Hainan pig farms, and provides basic data for assessing the threat of mosquito-borne diseases in public health in this area.
An attempt was made to understand the mosquito species and their carrying pathogenic microorganisms in pig farms from different regions of Hainan Province, and to provide reliable data support for the scientific prevention and control of mosquito-borne diseases in pig farms. Light catalyst mosquito traps were used to collect mosquitoes from four different pig farms in Baisha Li Autonomous County (BS), Ding 'an County (DA), Ledong Li Autonomous County (LD) and Wenchang City (WC) in Hainan Province. The mosquito species collected were identified by using morphological characteristics and the PCR method, and the composition of mosquito-borne microbial community and gene function were analyzed by using metagenomic sequencing. The results showed that the dominant mosquito species in the pig farms of different regions of Hainan were different. The dominant mosquito species in BS, DA, LD and WC were Anopheles dabryanus, Anopheles sinensis, Culex pipiens pallens and Culex tritaeniorhynchus, accounting for 58.43 %, 55.46 %, 88.65 % and 57.84 %, respectively. The analysis of metagenomic microbial sequencing showed the mosquito-borne microorganisms in BS, LD, WC and other regions were at the phylum level. Euryarchaeota was the dominant archaea, while the dominant archaea in DA pig farm was Thermoarchaeota. Proteobacteria was the dominant phylum of mosquito vectors in the pig farms from the four regions. Ascomycota was the dominant phylum of mosquitoes in the 4 regions; negarnaviricota was the dominant virus phylum in BS, DA and LD, while Cossaviricota was the dominant virus phylum in WC. At the species level bacteria such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brucella melitensis, Chlamydia abortus, Leptospira interrogans and Waddlia chondrophila, fungi such as Acremonium asperulatum, Aspergillus terreus and Microsporum canis, and viruses such as Aedes aegypti anphevirus and Anopheles annulipes orbivirus pose a pathogenic threat to humans and pigs. Moreover, the mosquito-borne microorganisms from the pig farms in different regions of Hainan maintain high stability at the phylum level and diversity at the species level, and there is a high risk of pathogenicity. This study provides a scientific basis for the prevention and control of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne diseases in Hainan pig farms, and provides basic data for assessing the threat of mosquito-borne diseases in public health in this area.


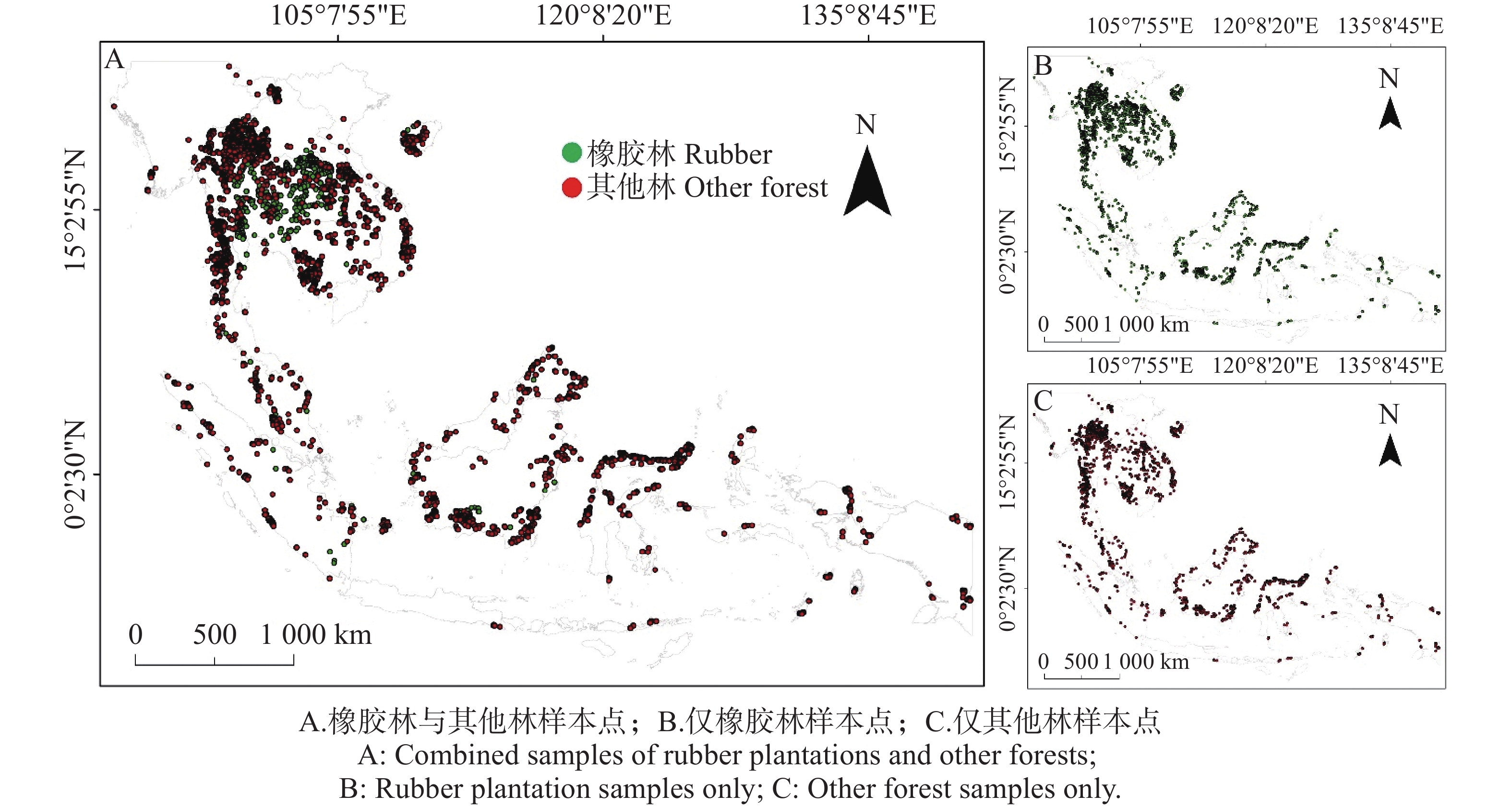
 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML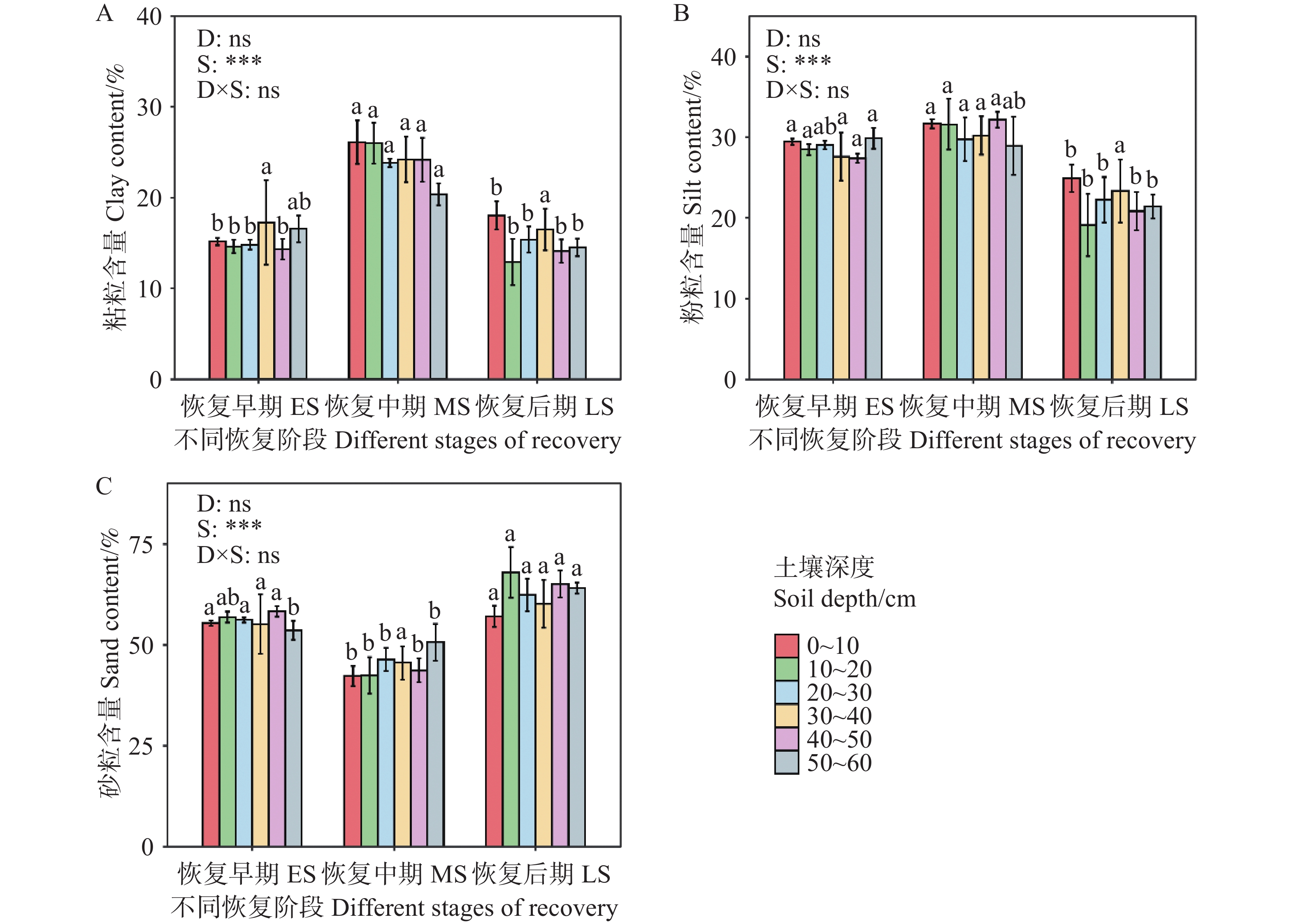
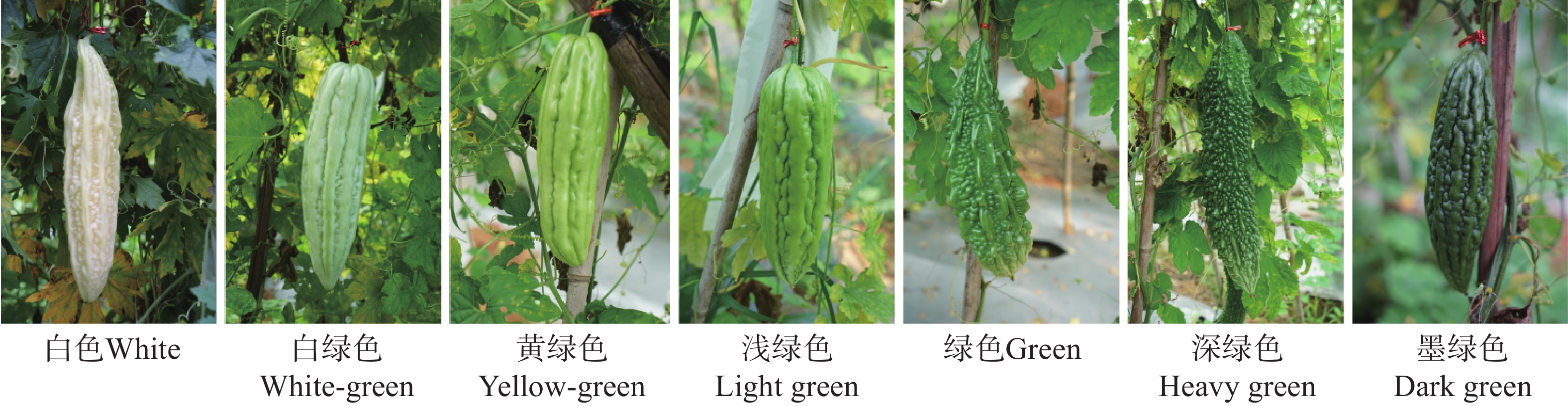
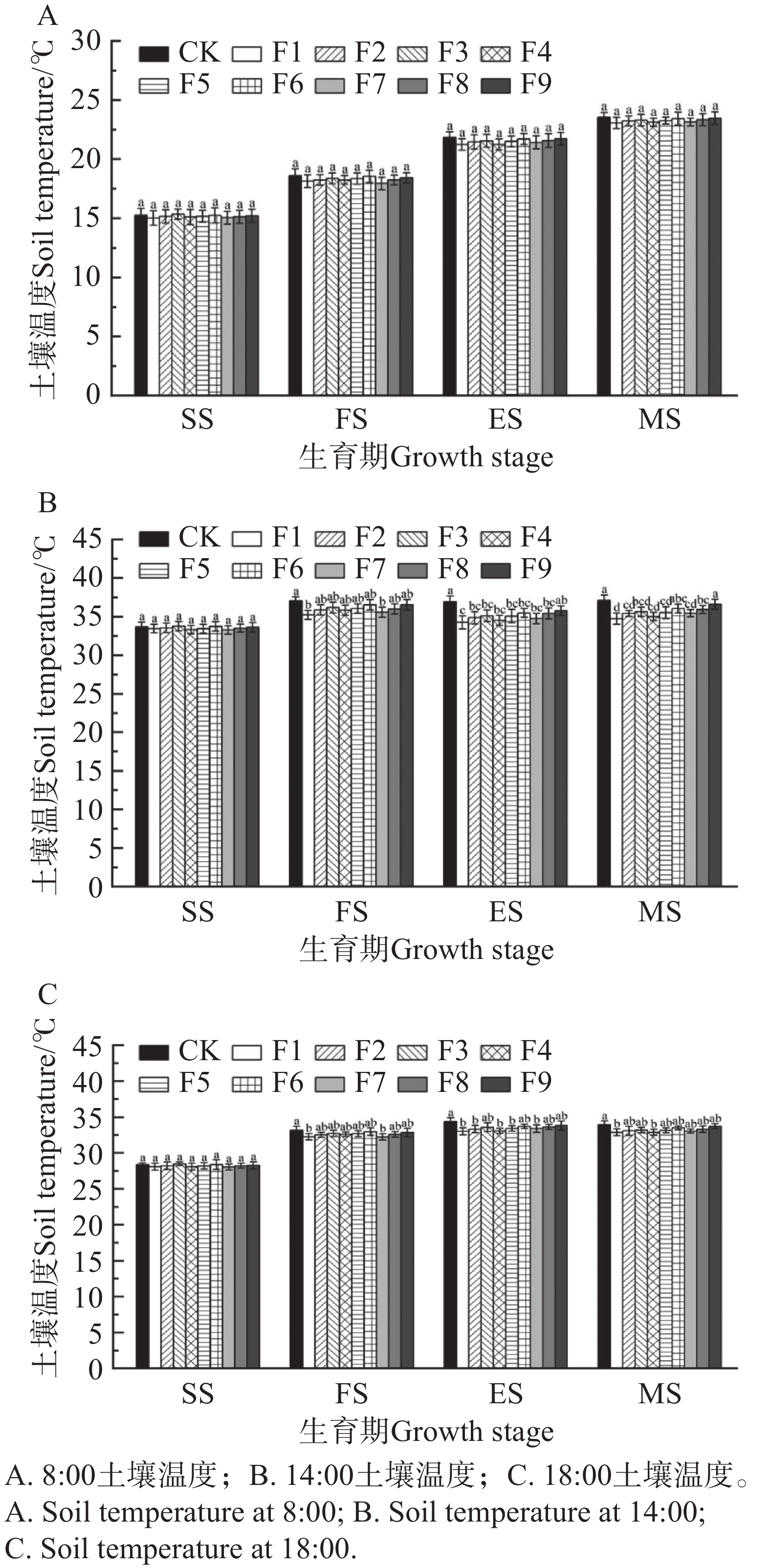
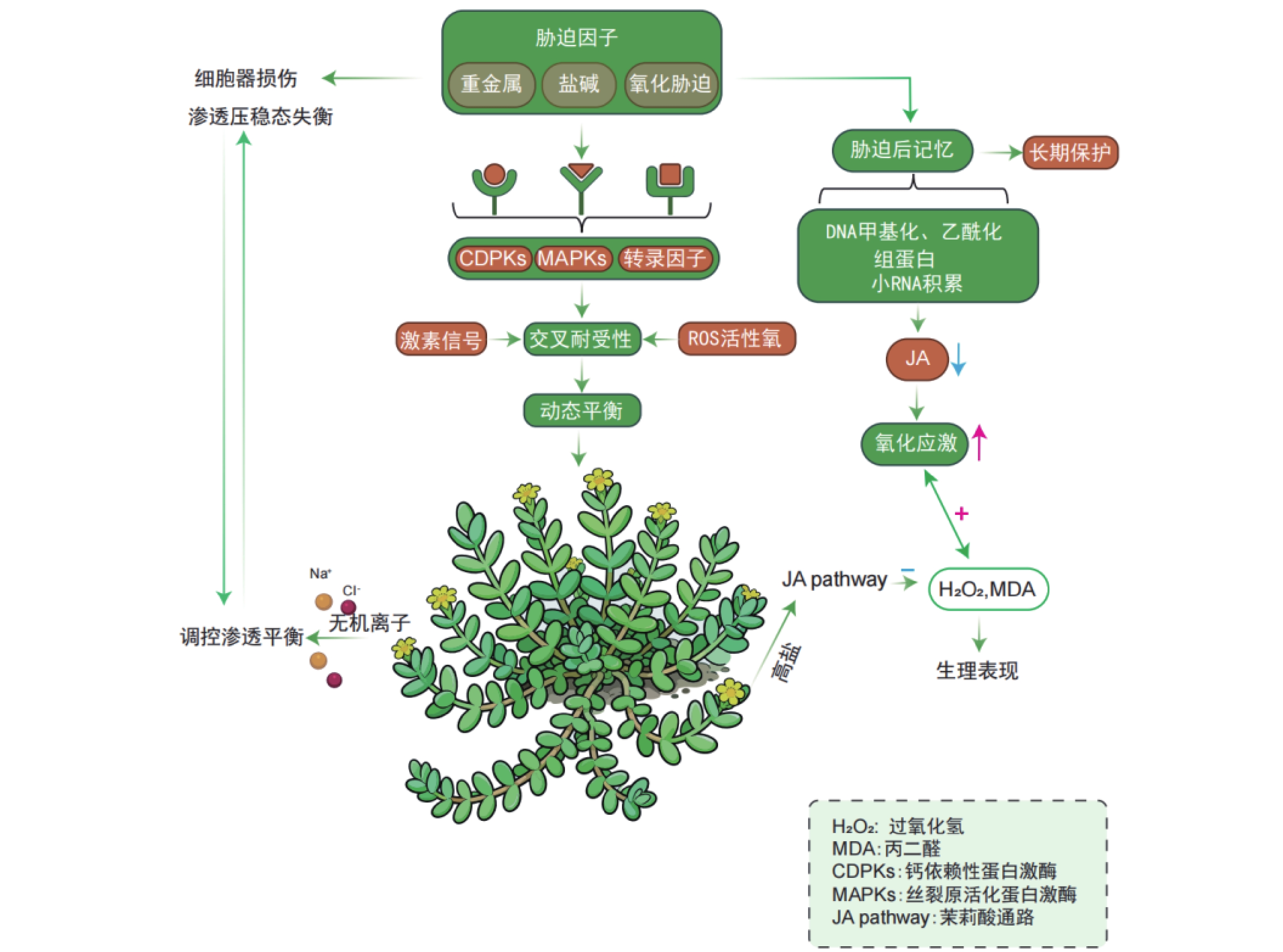

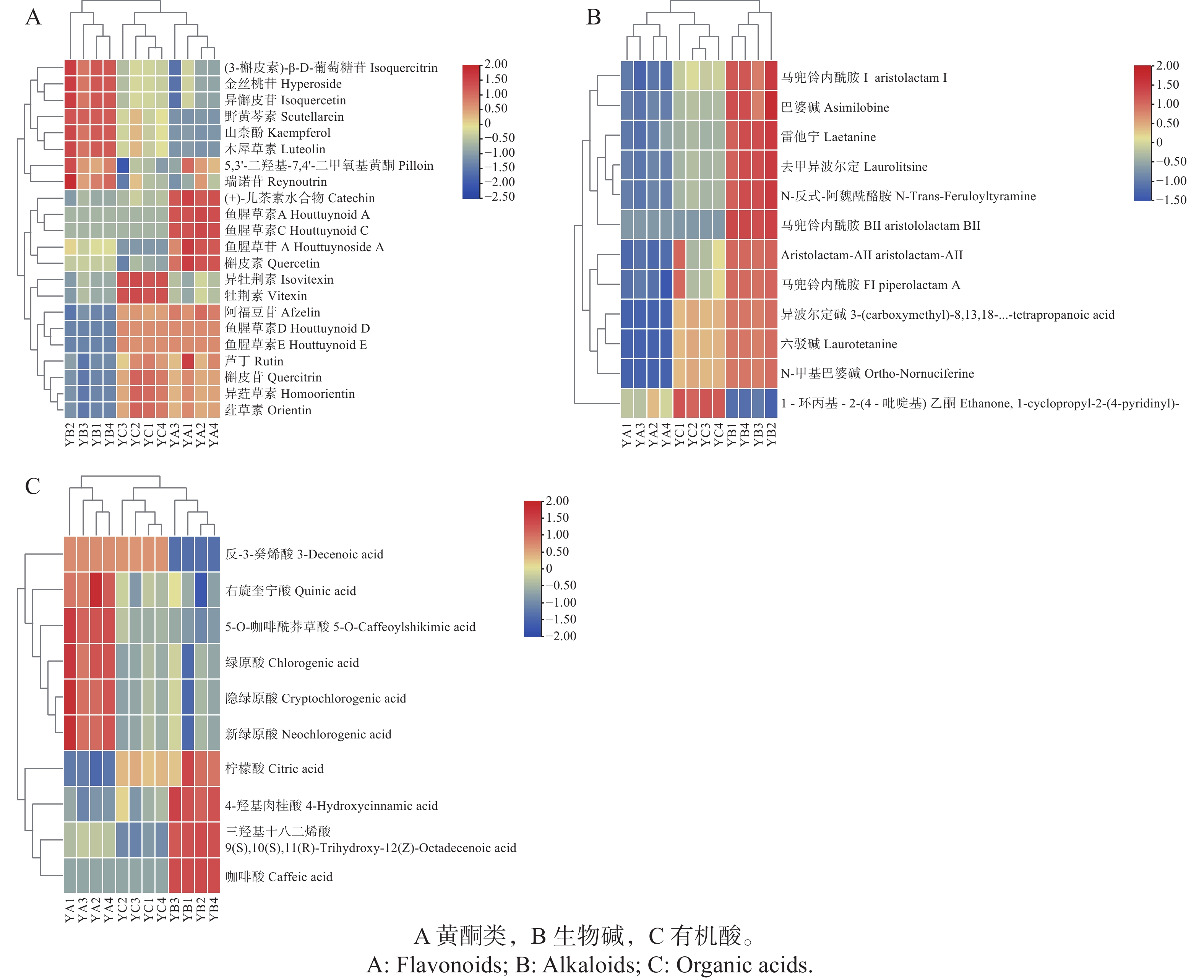
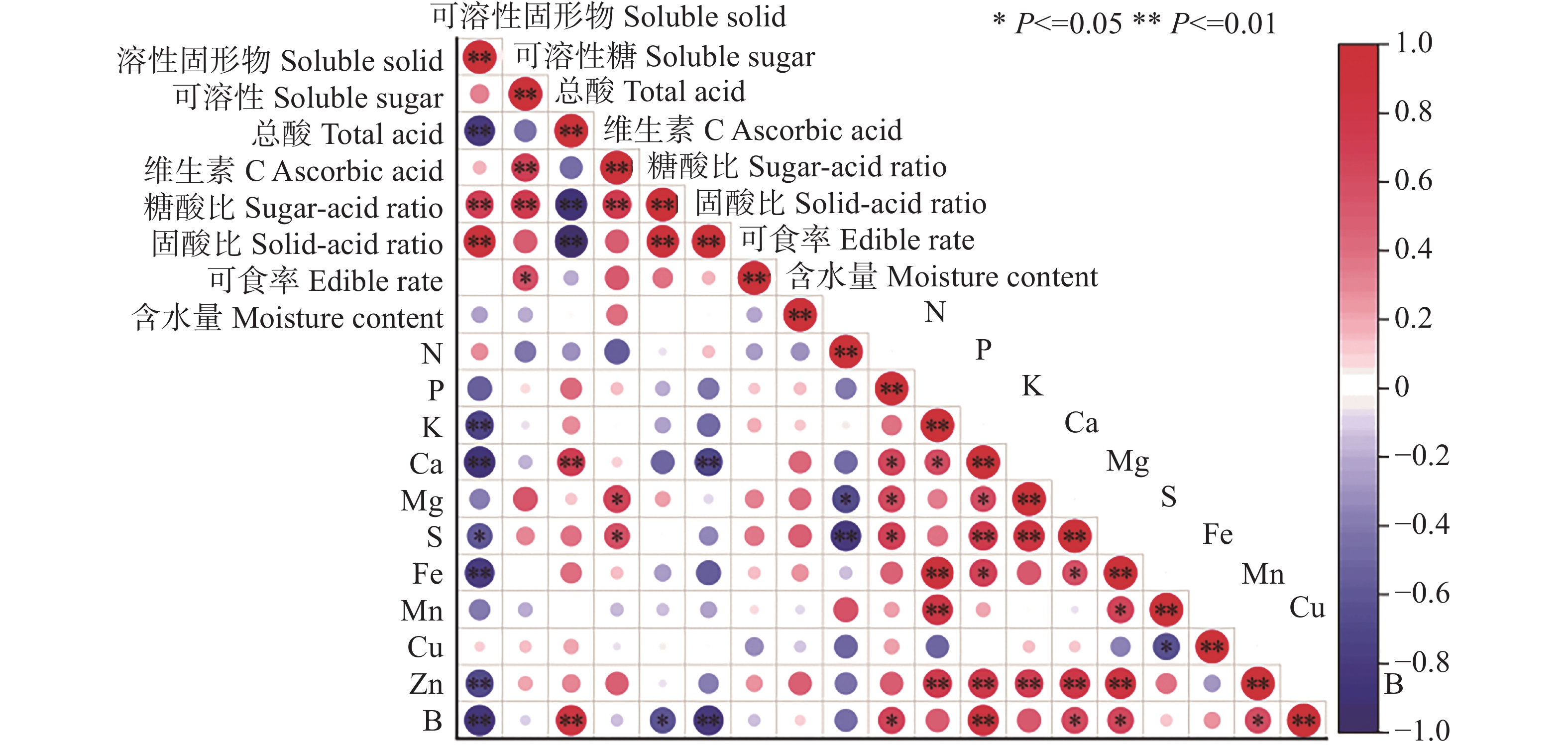
 PDF 794KB
PDF 794KB
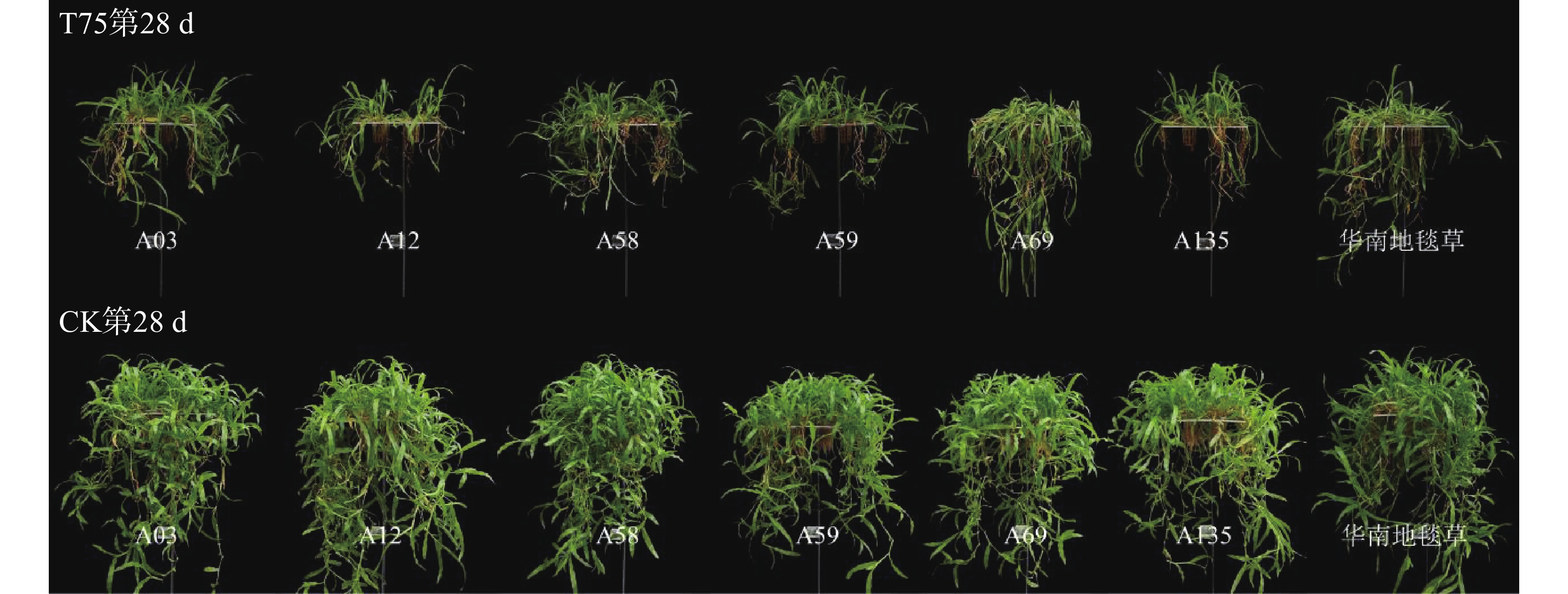
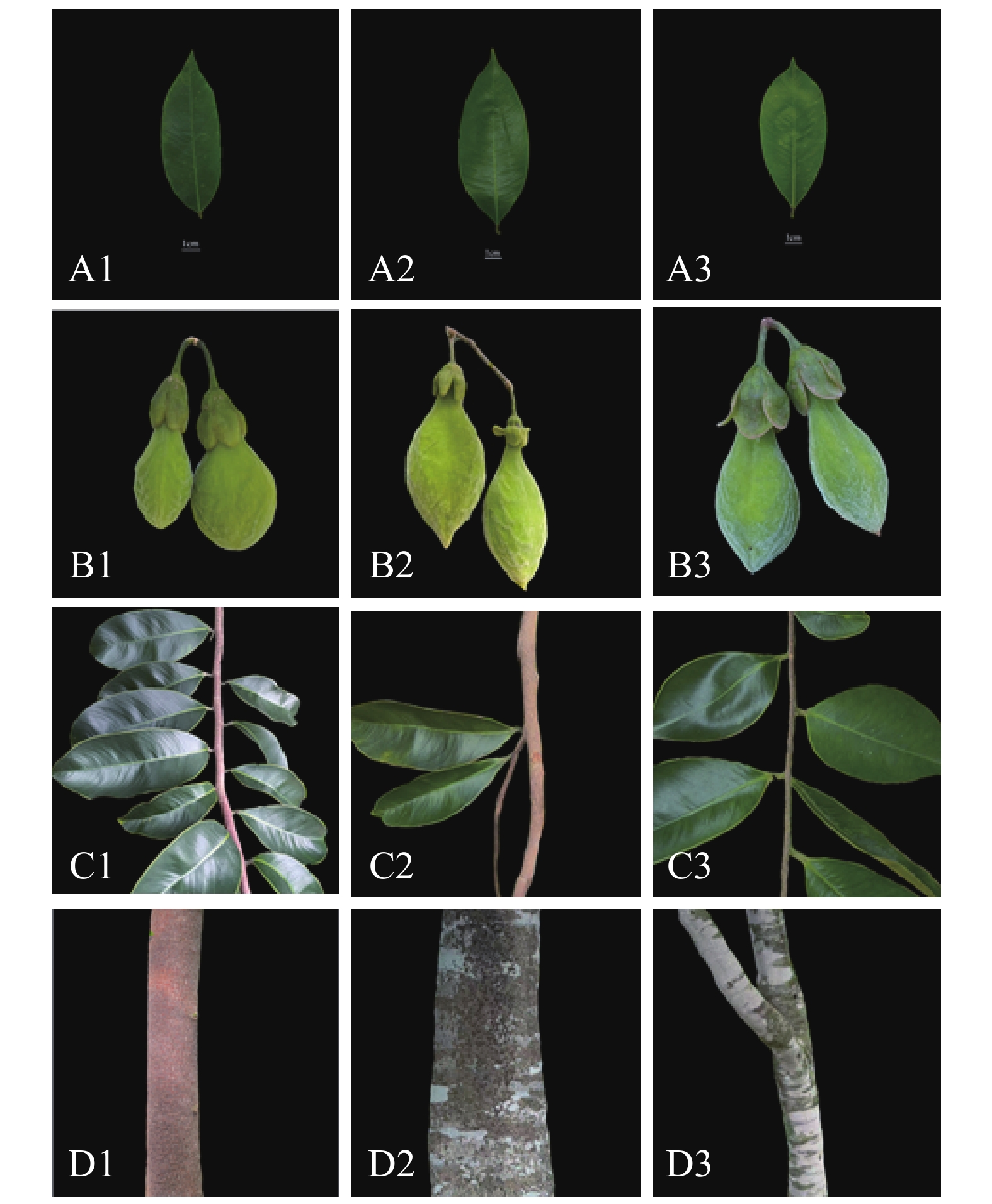
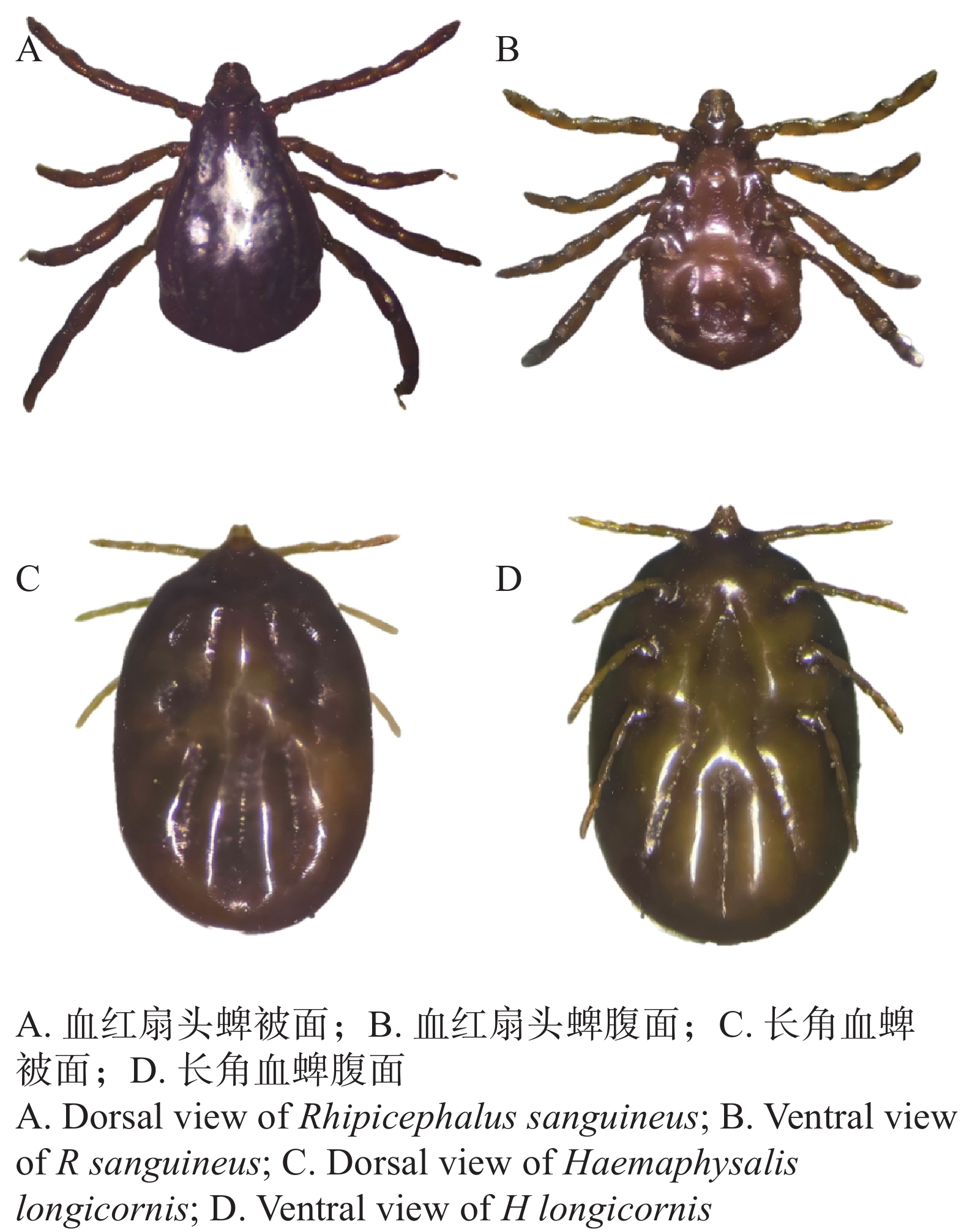
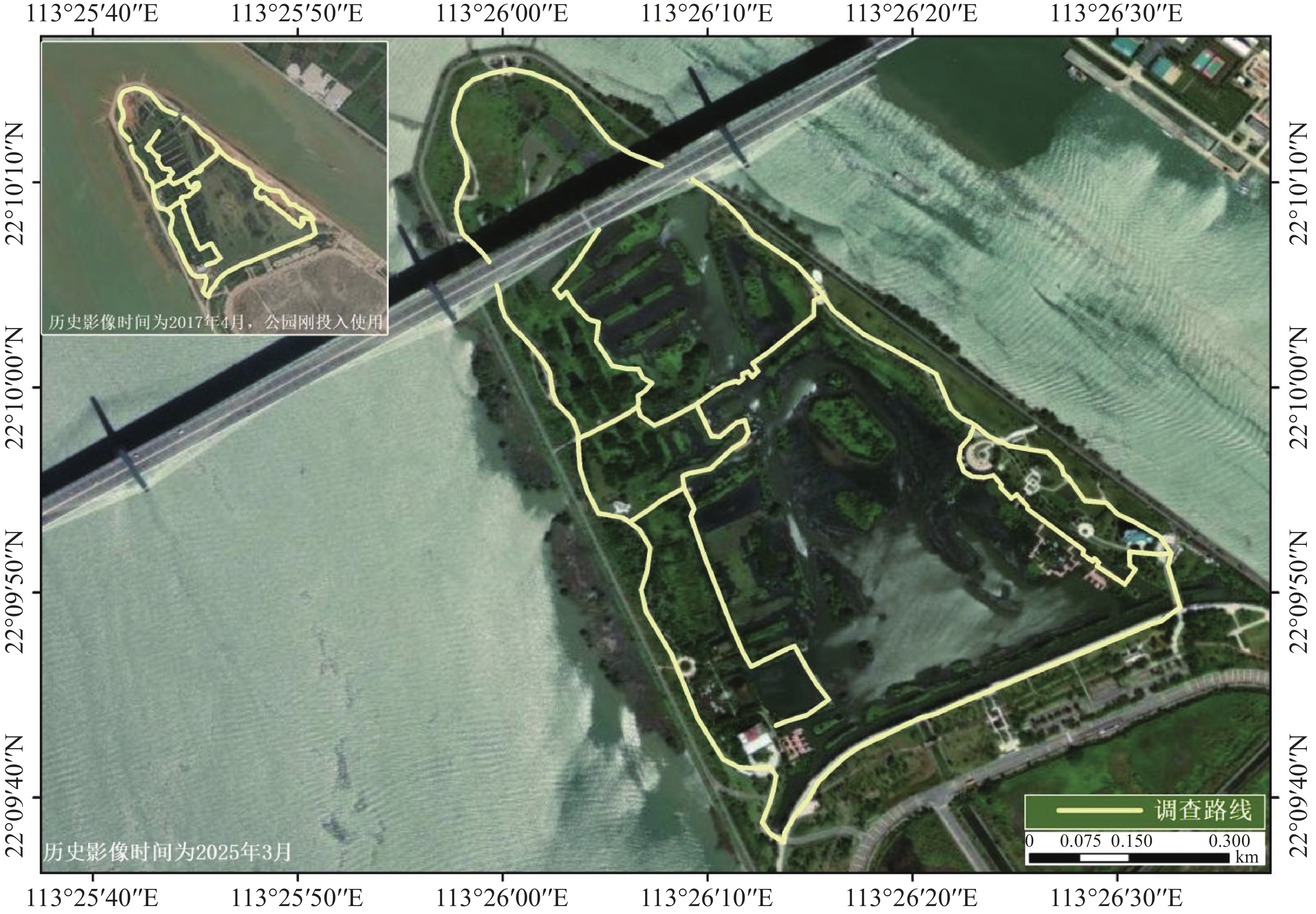
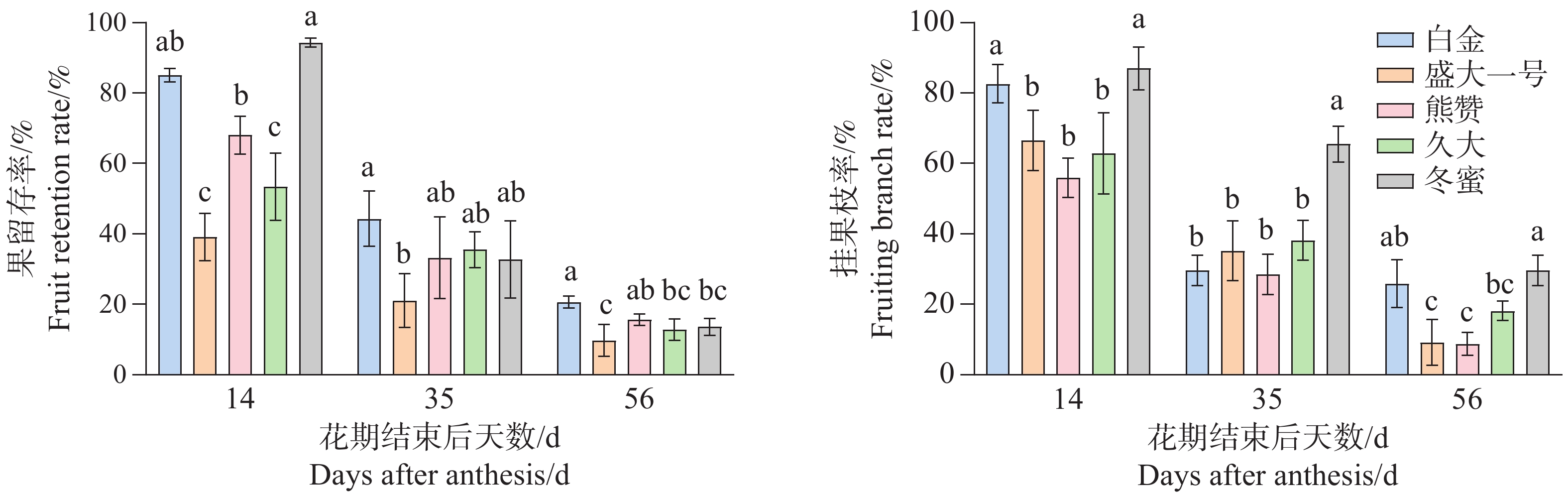
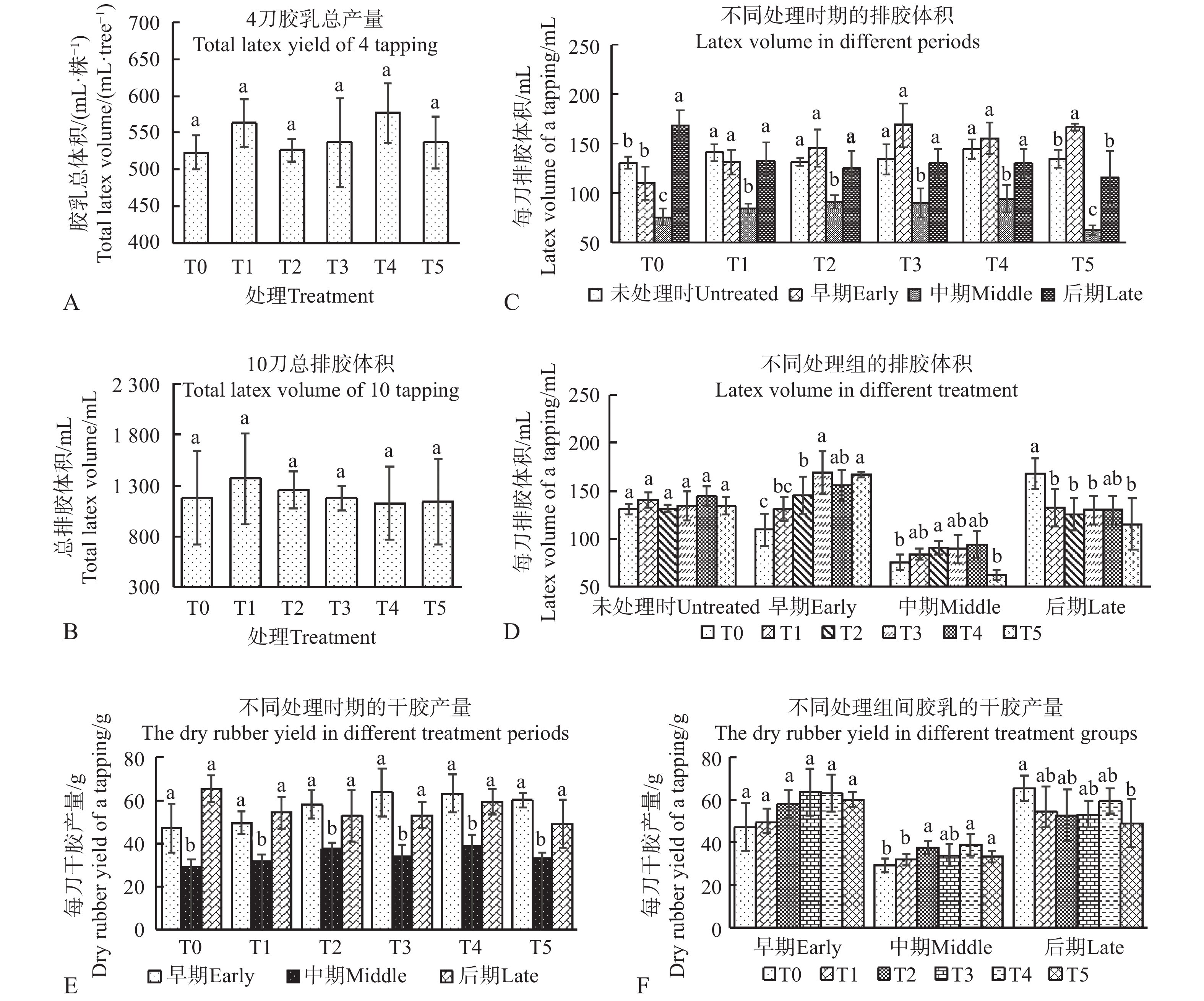


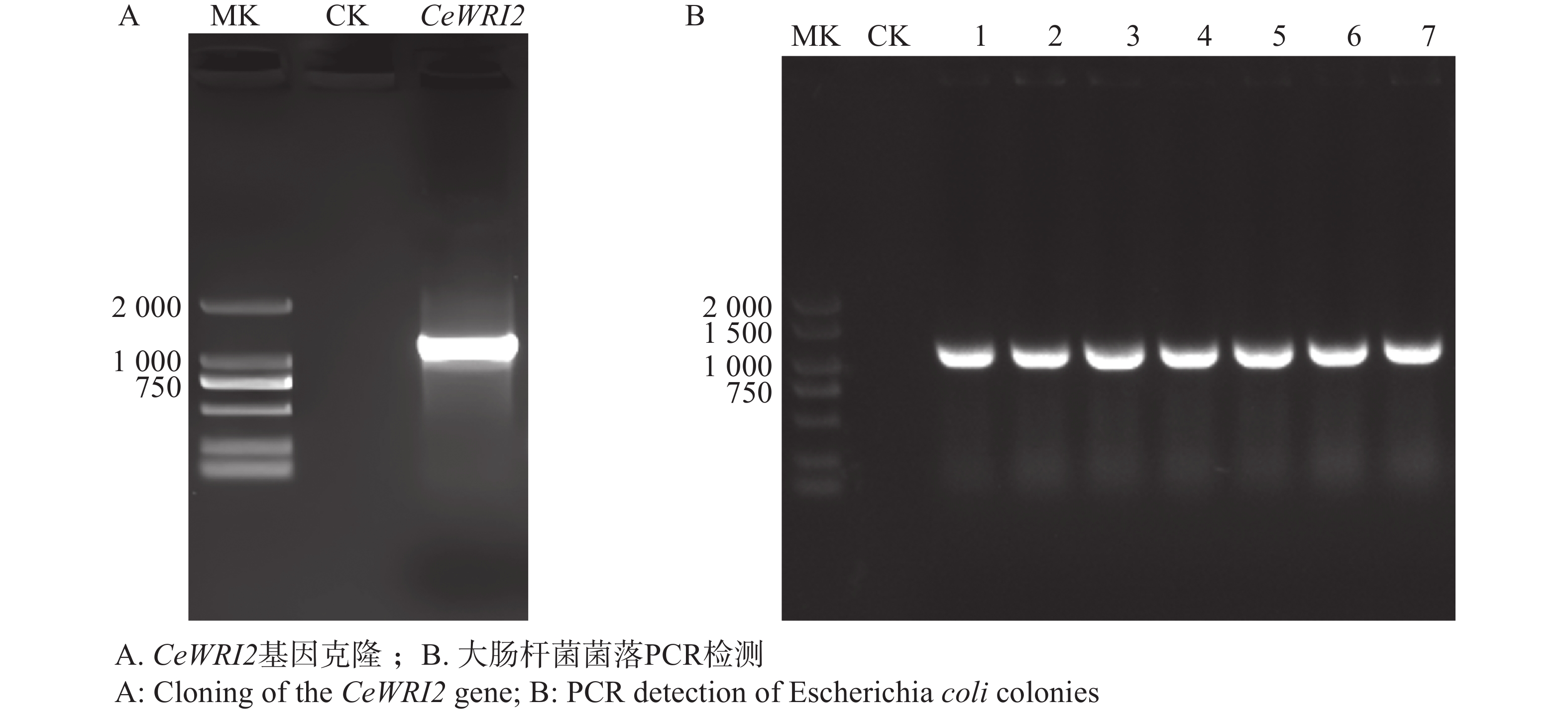
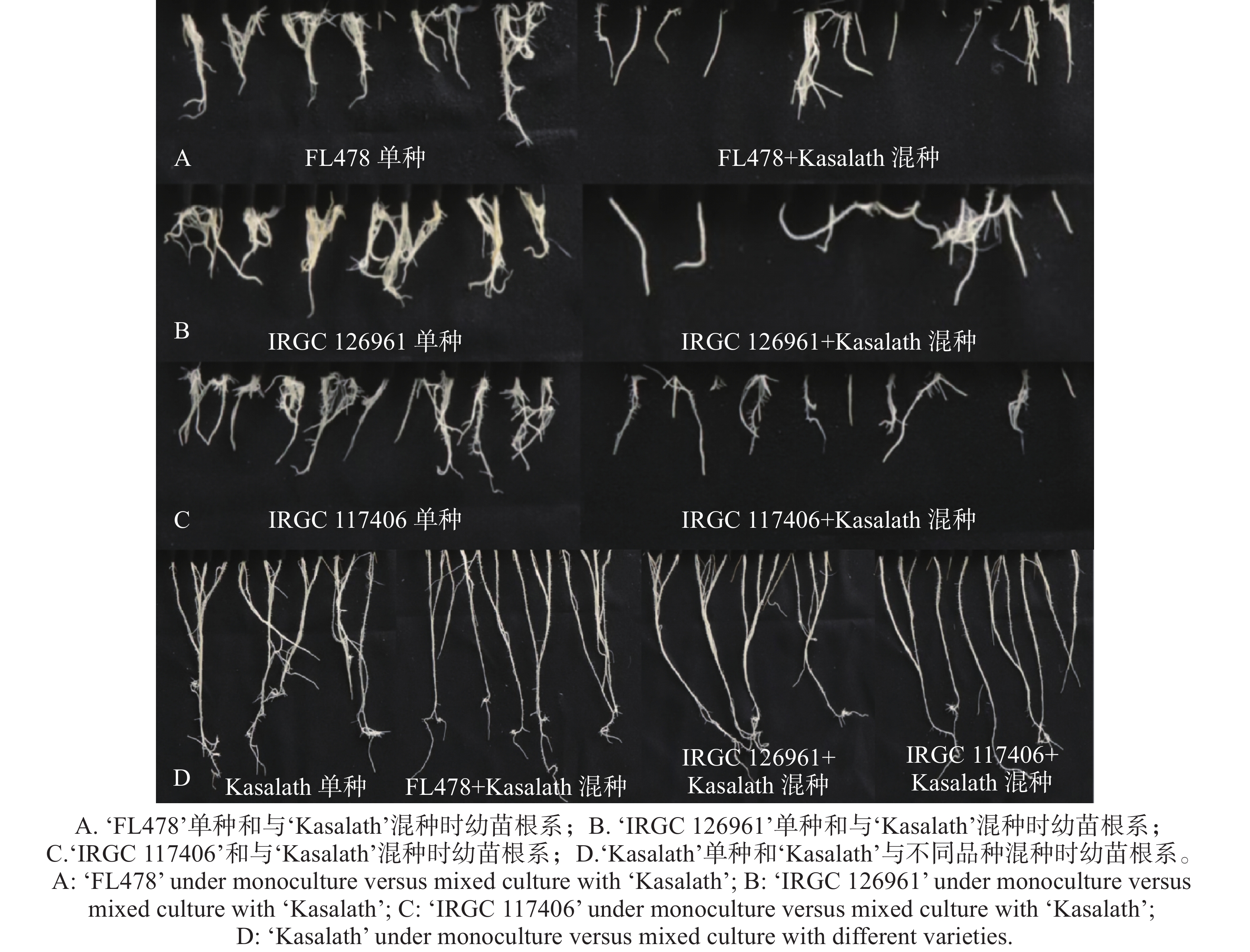
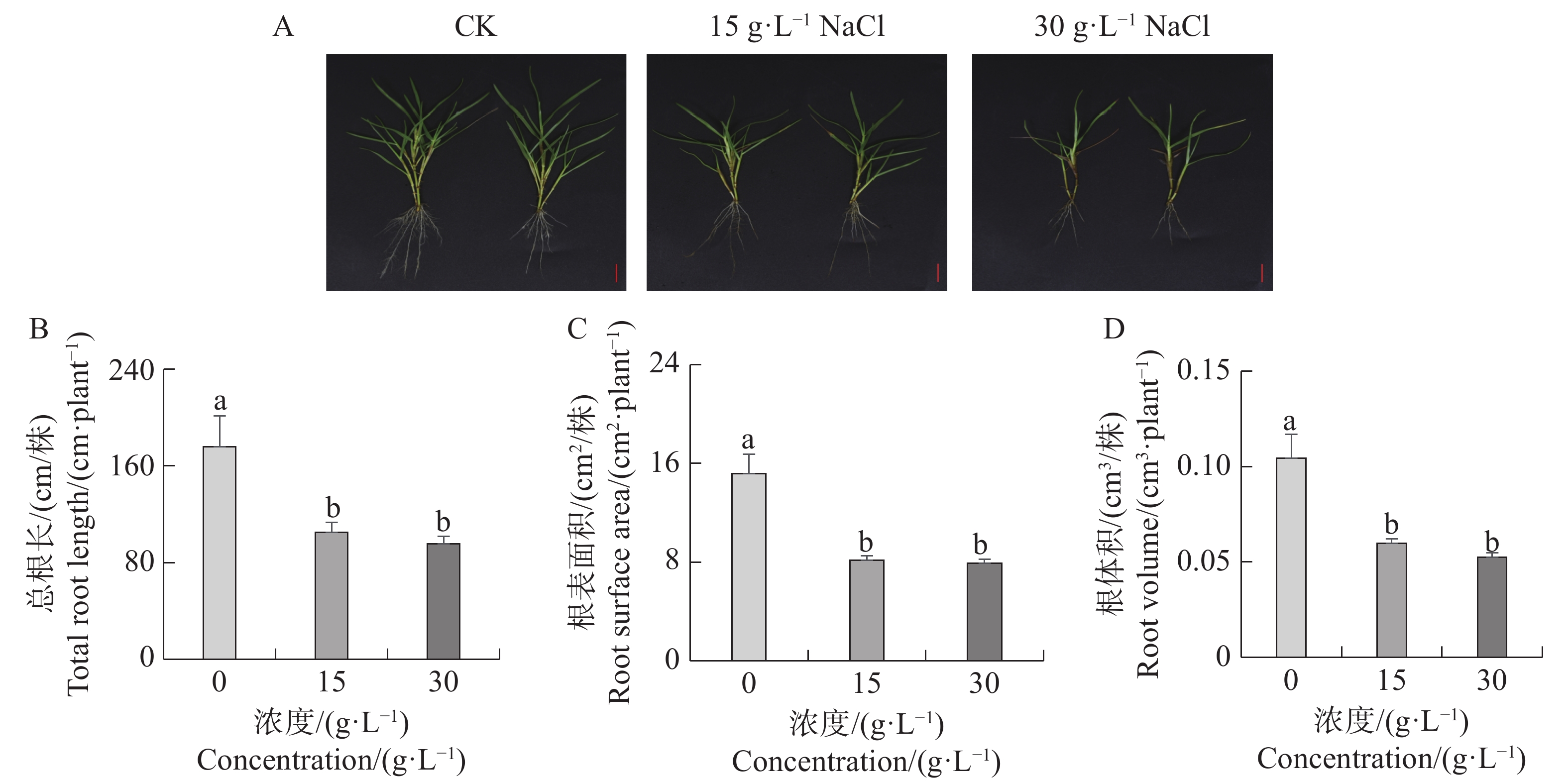

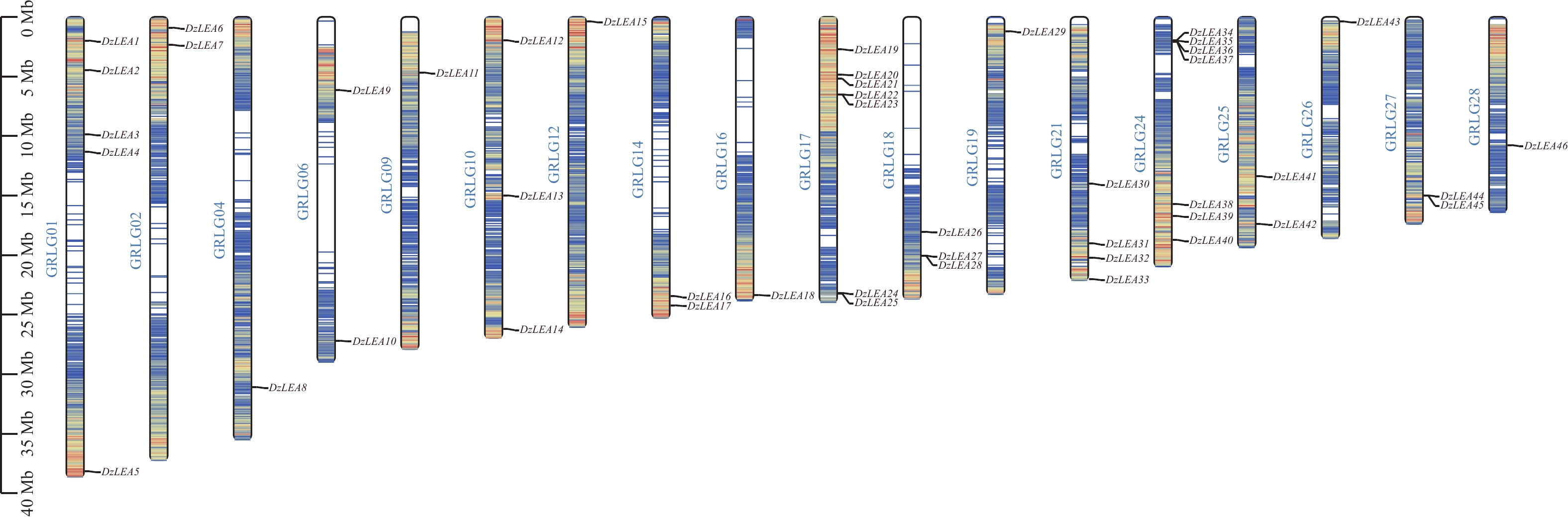
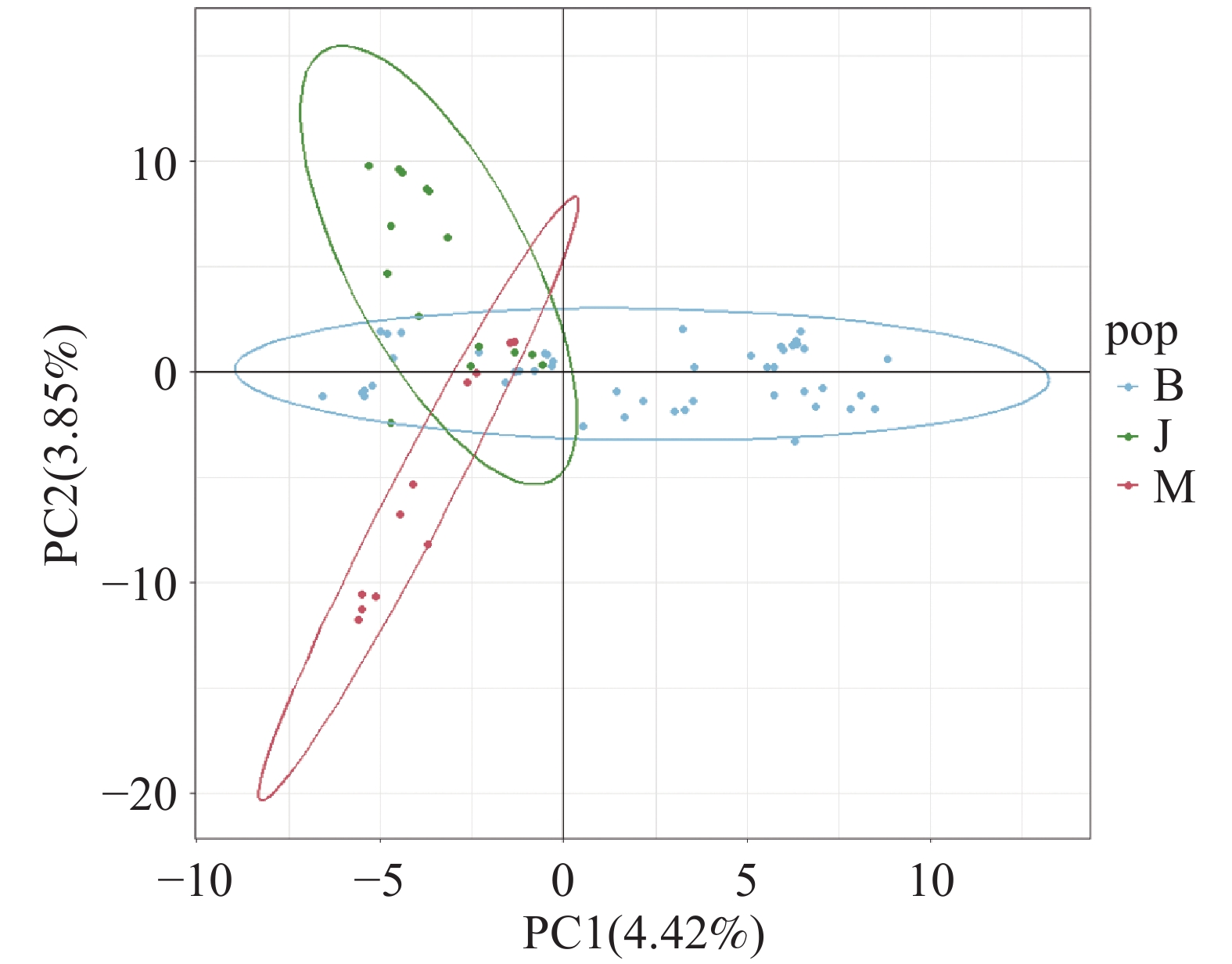

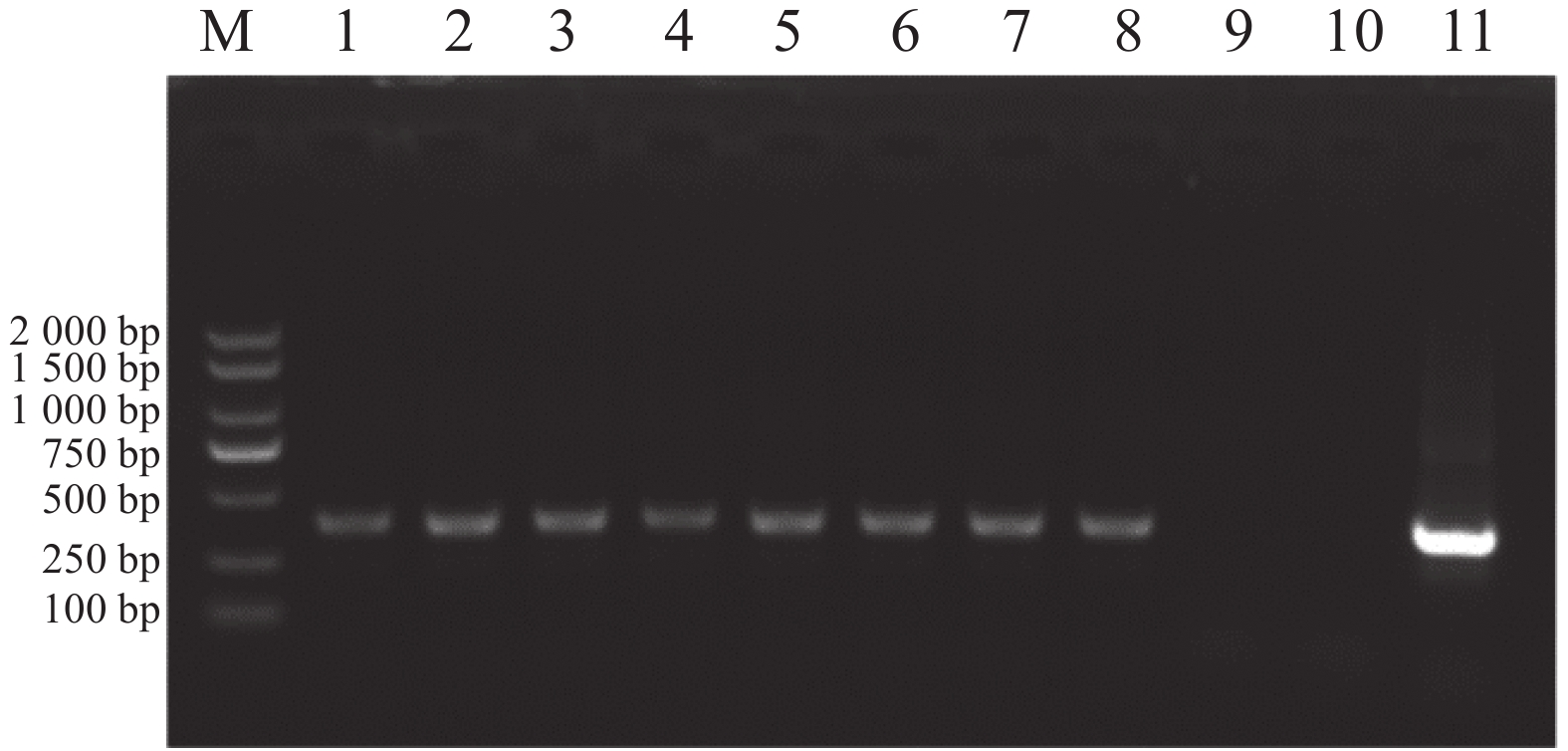
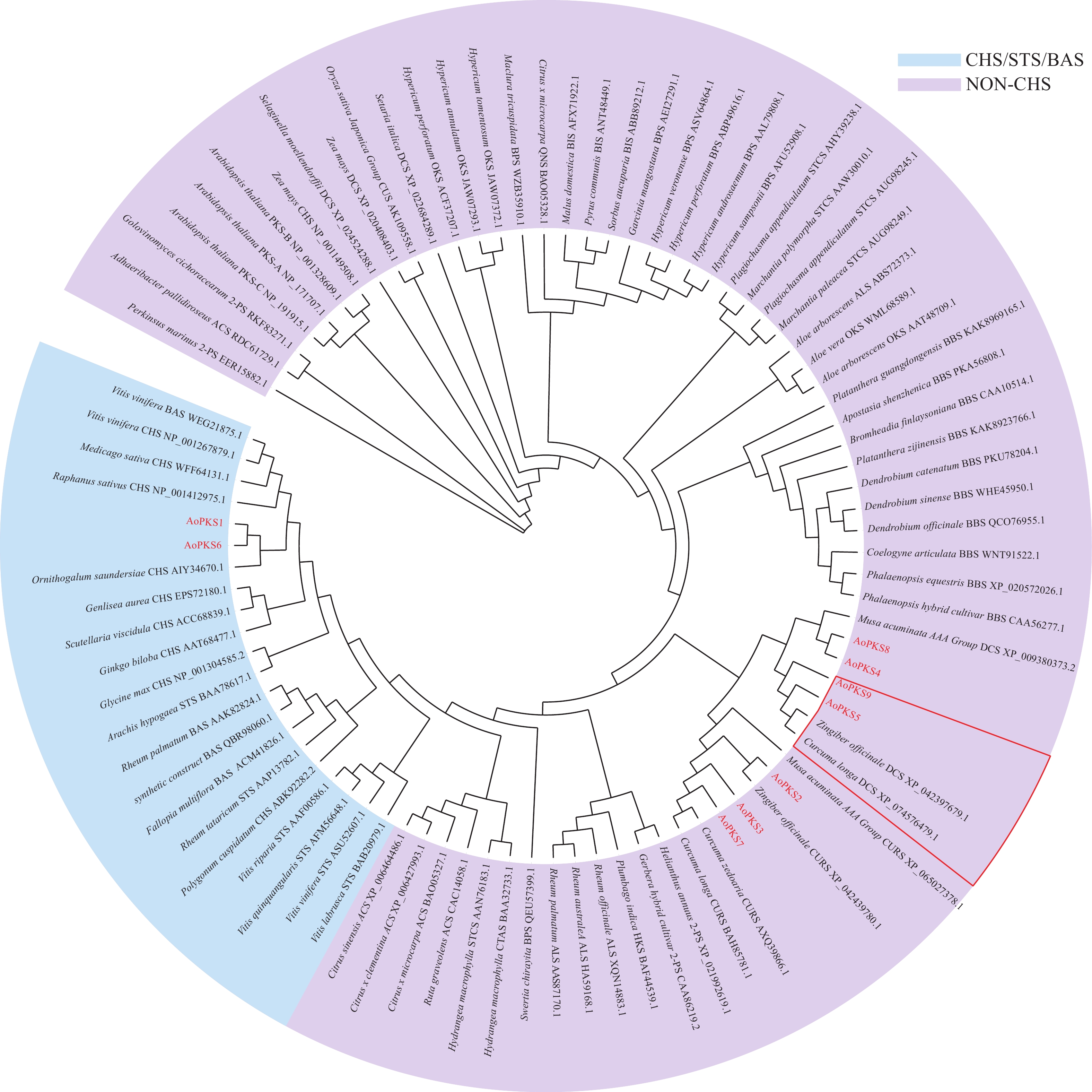
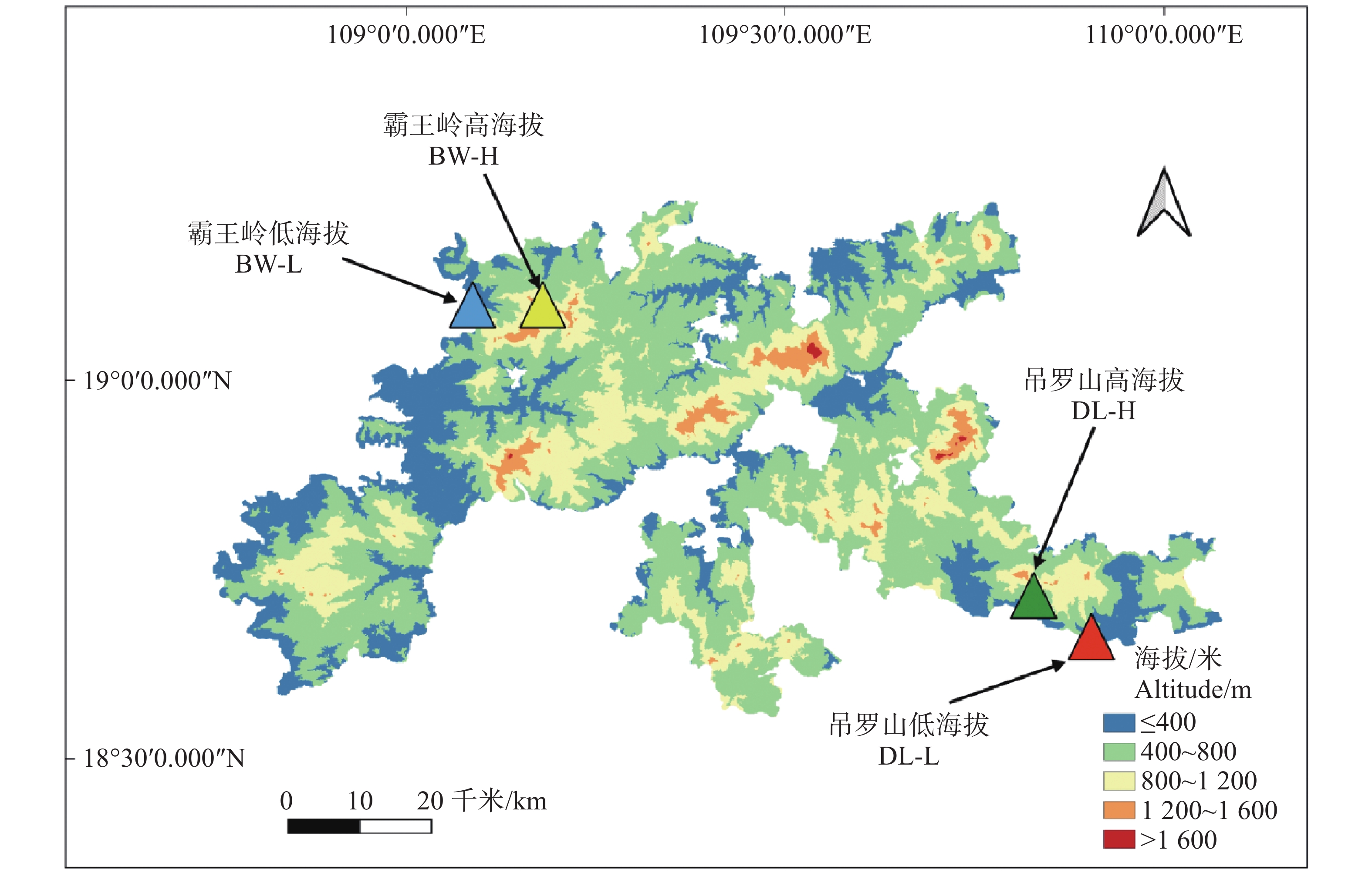


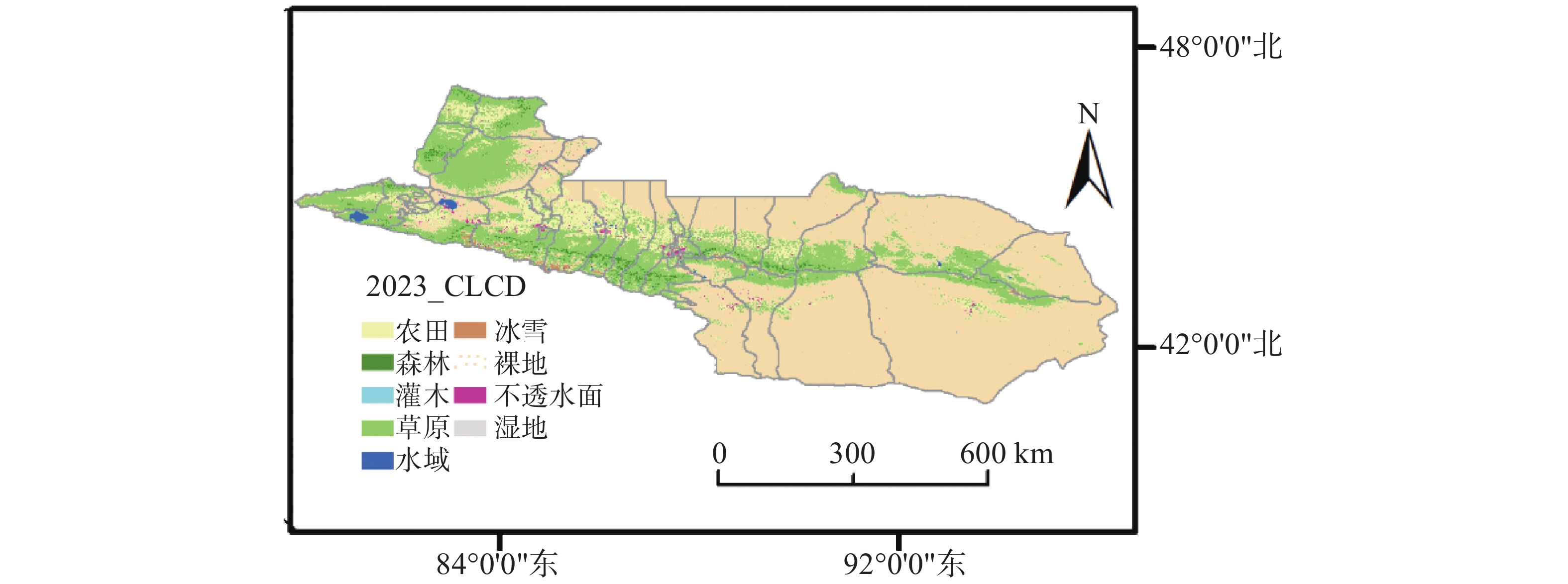
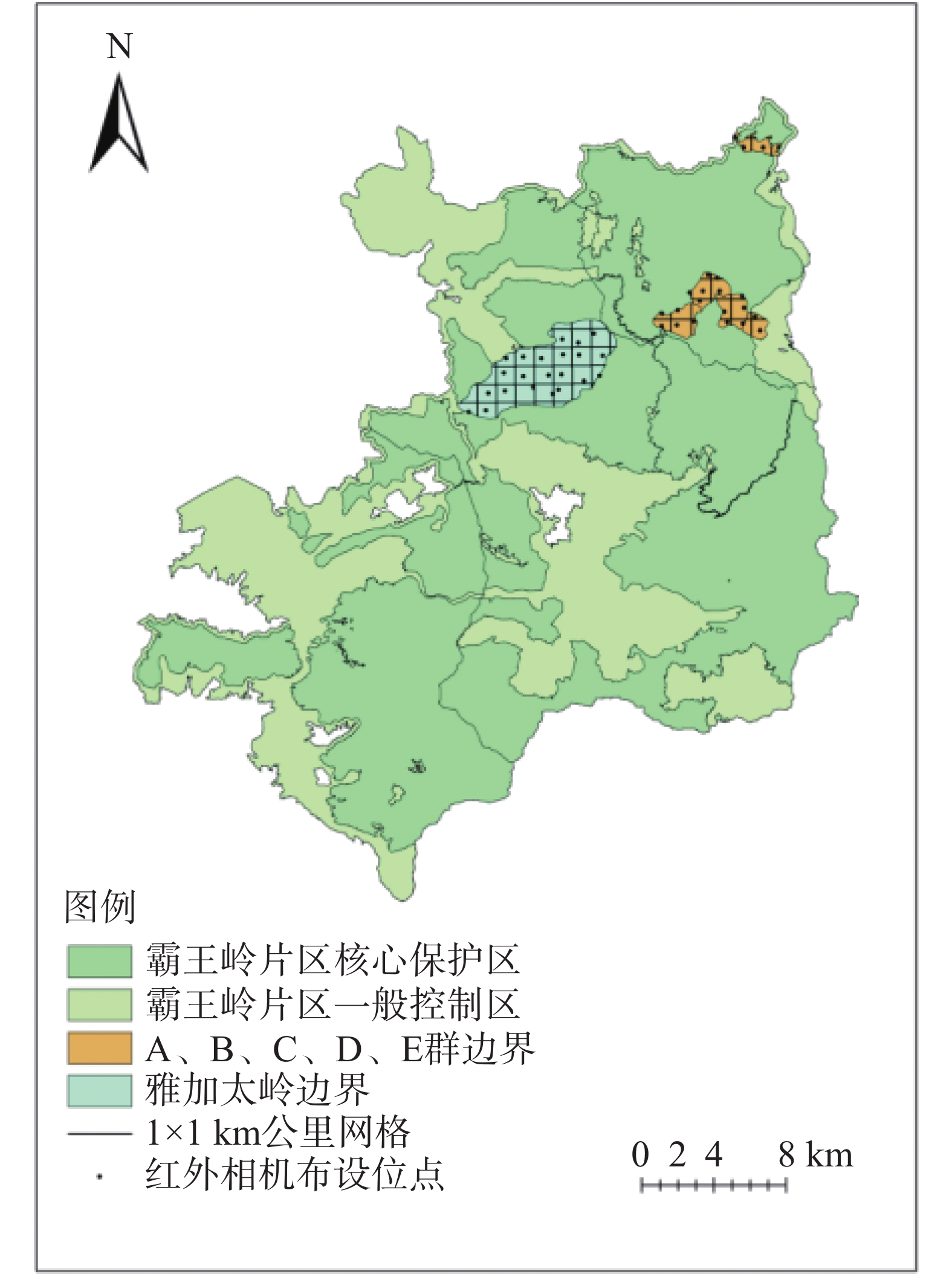
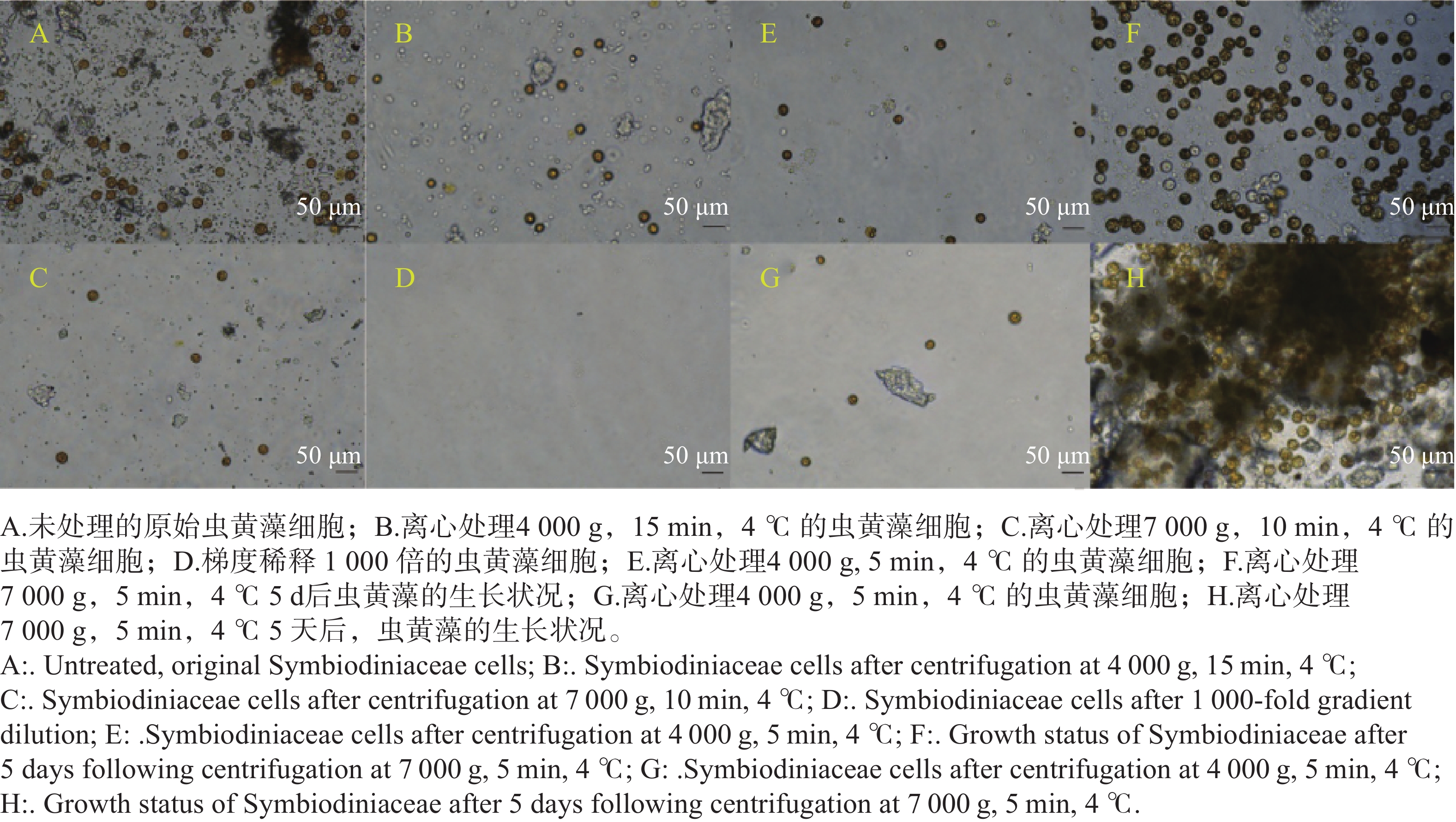

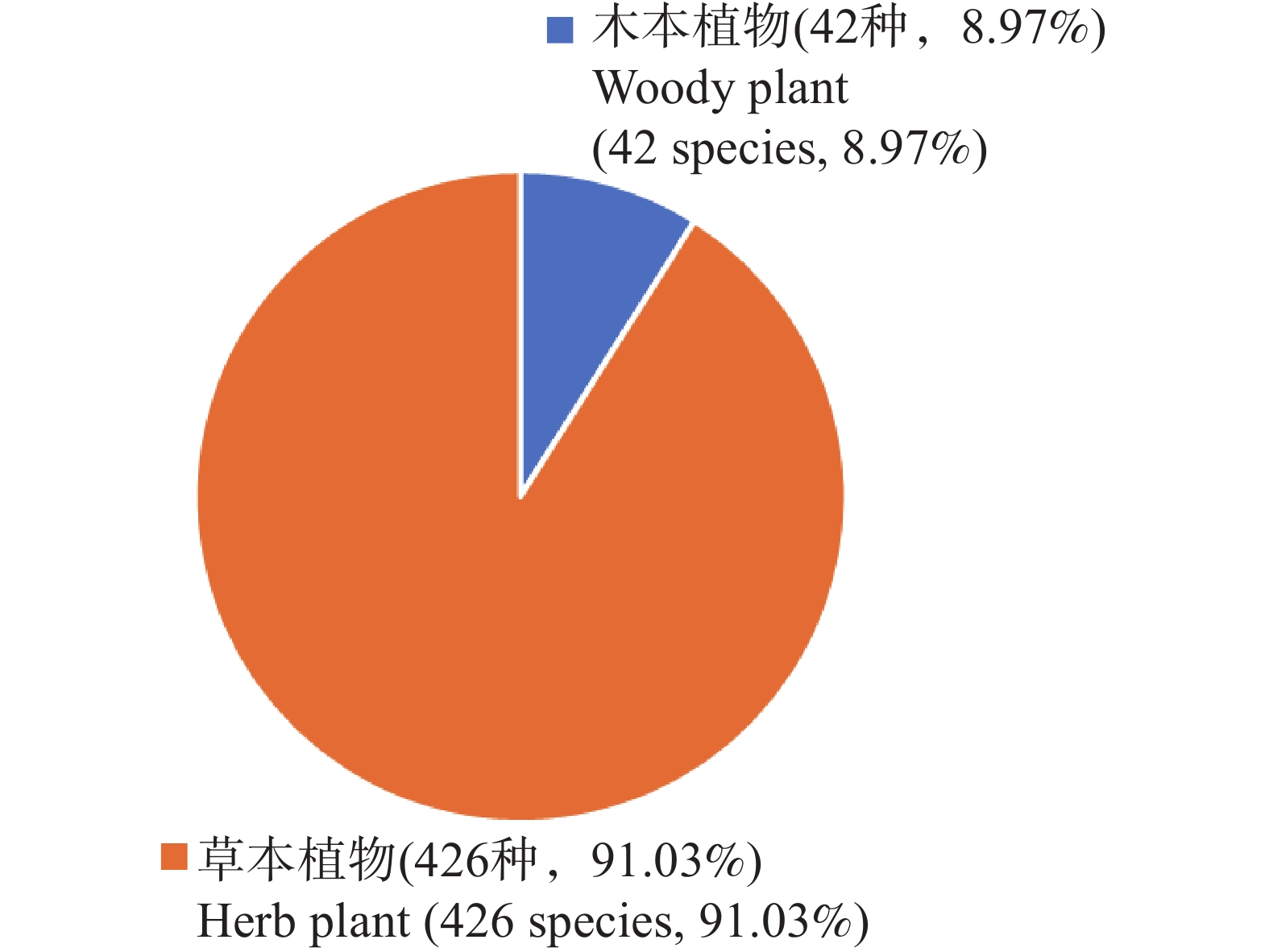
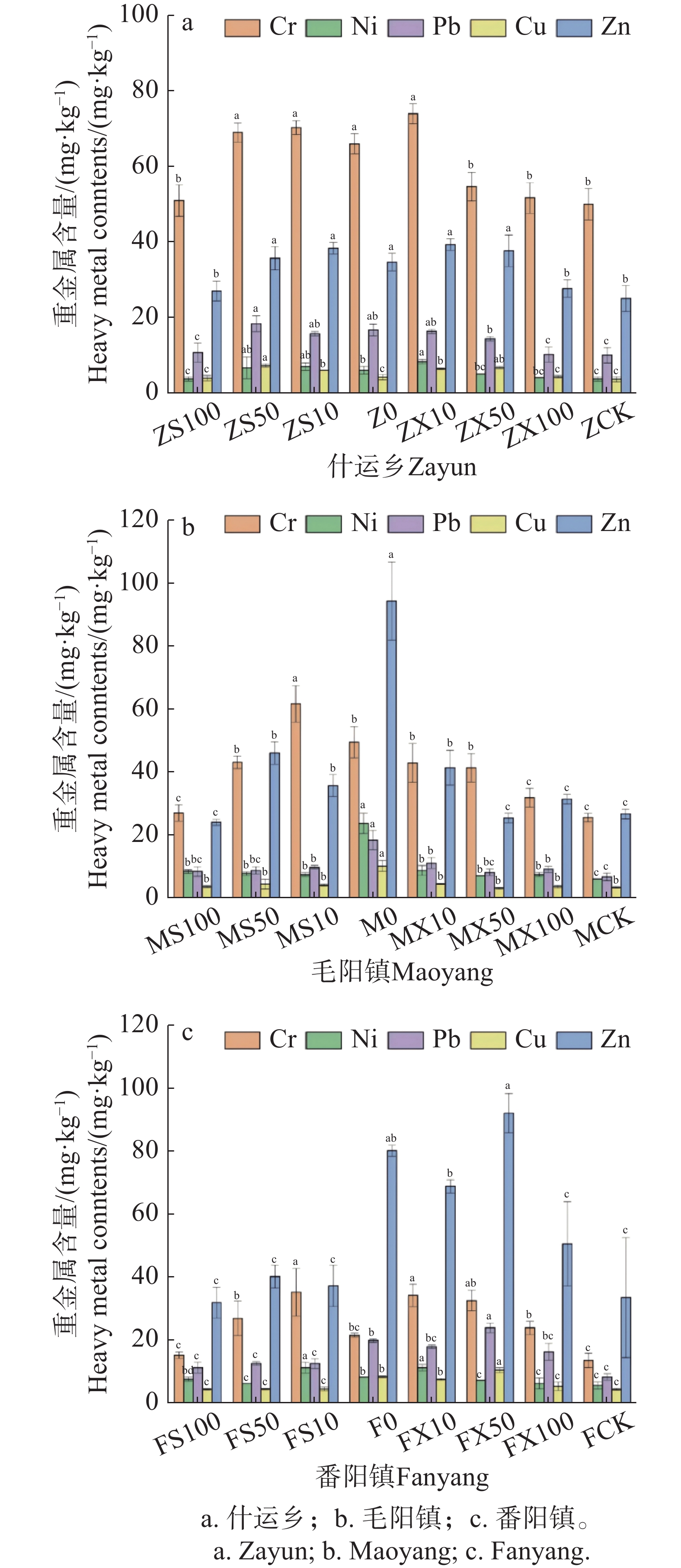

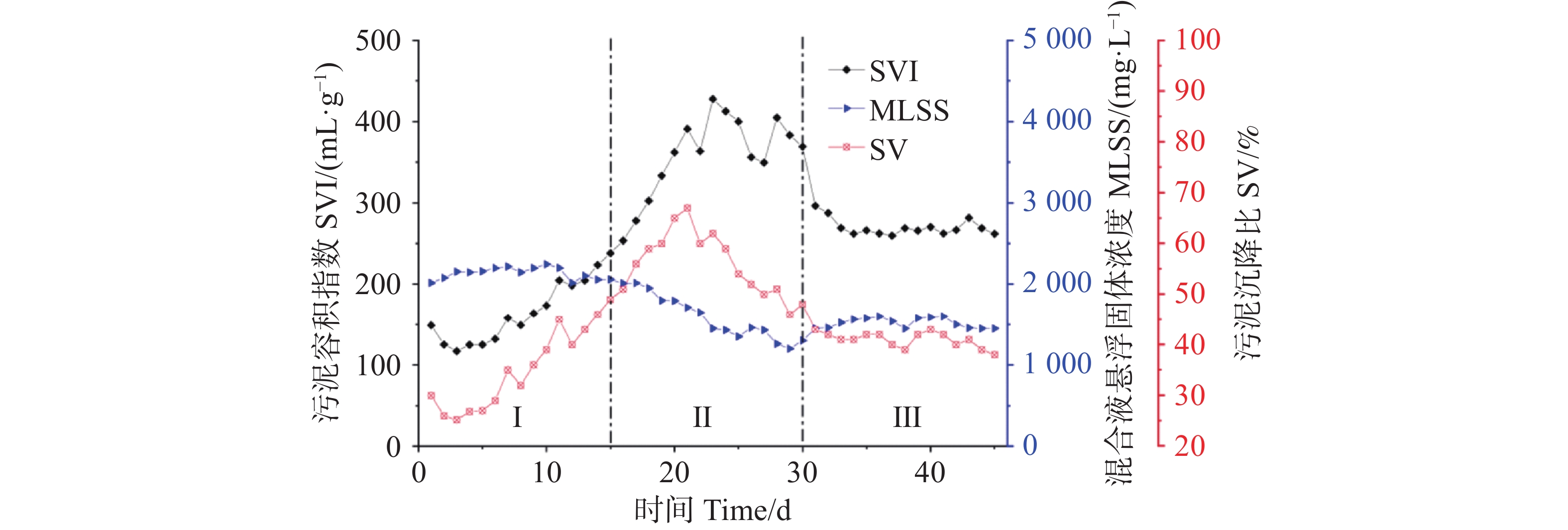
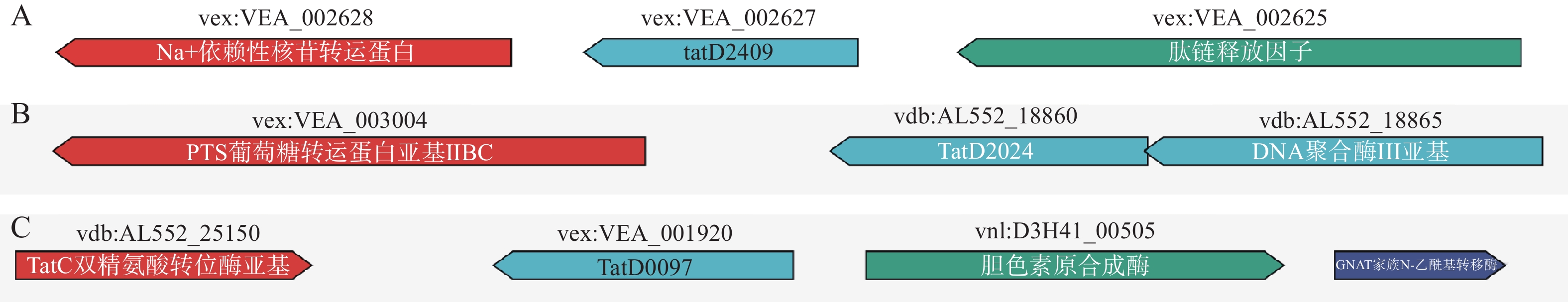
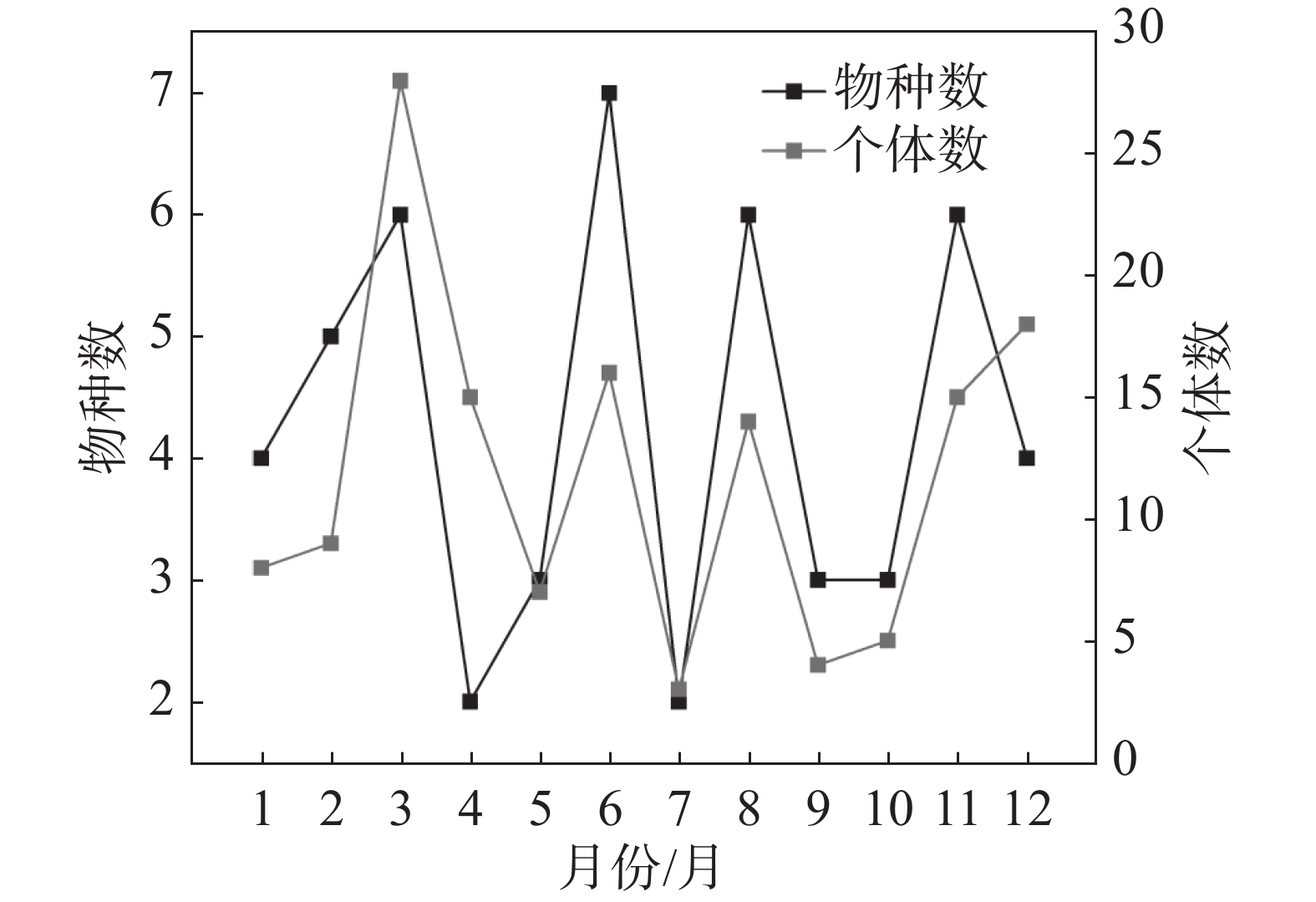

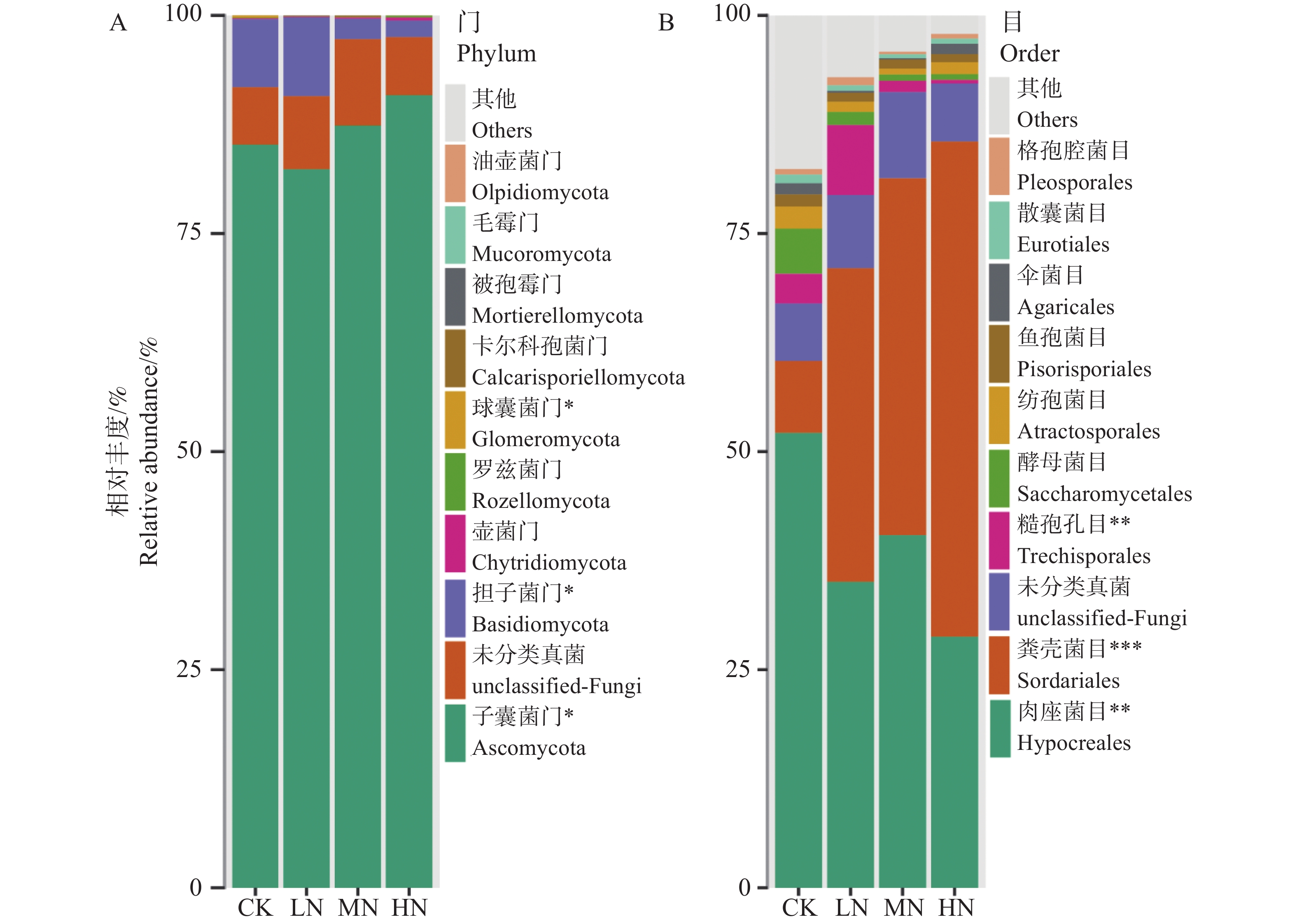
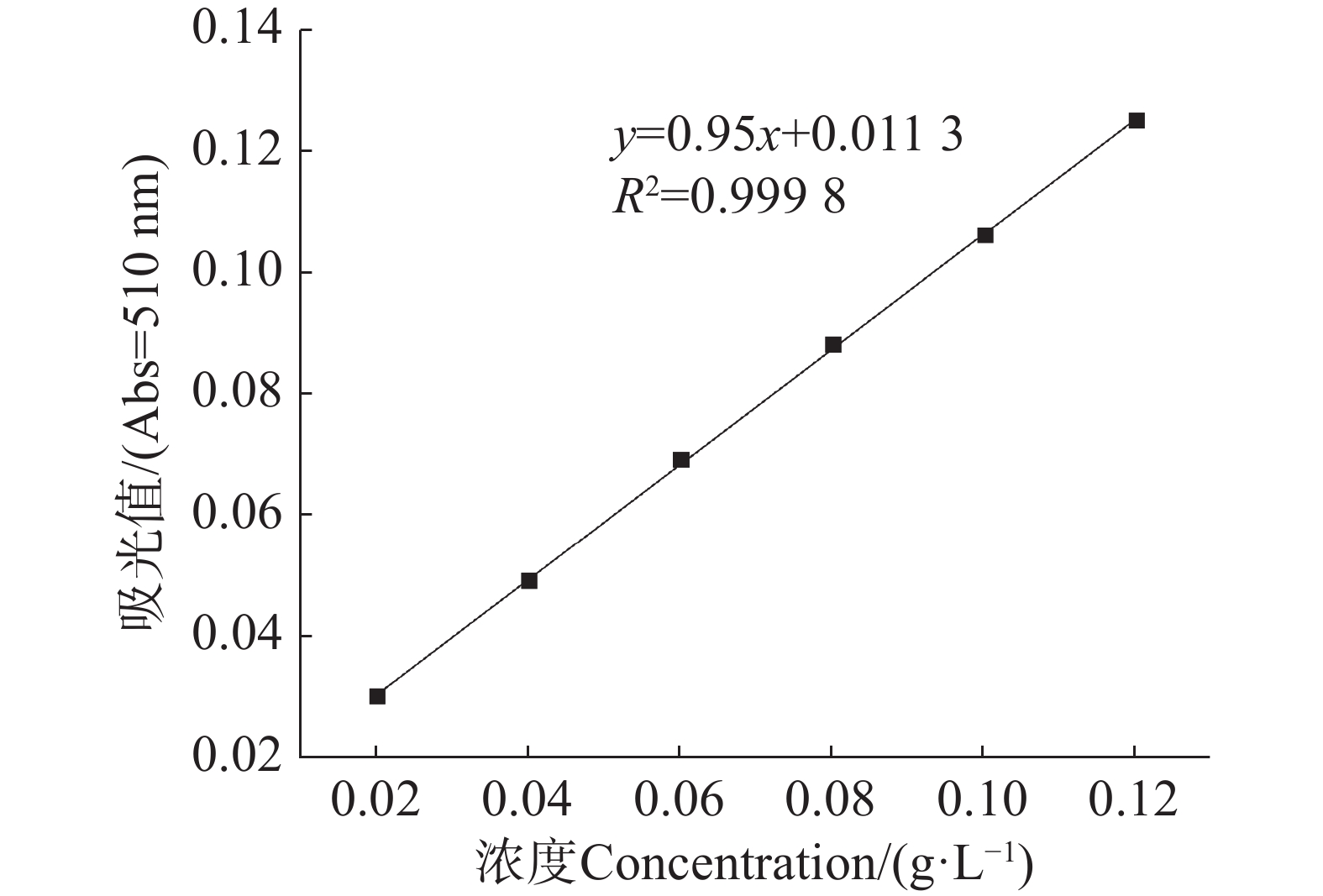
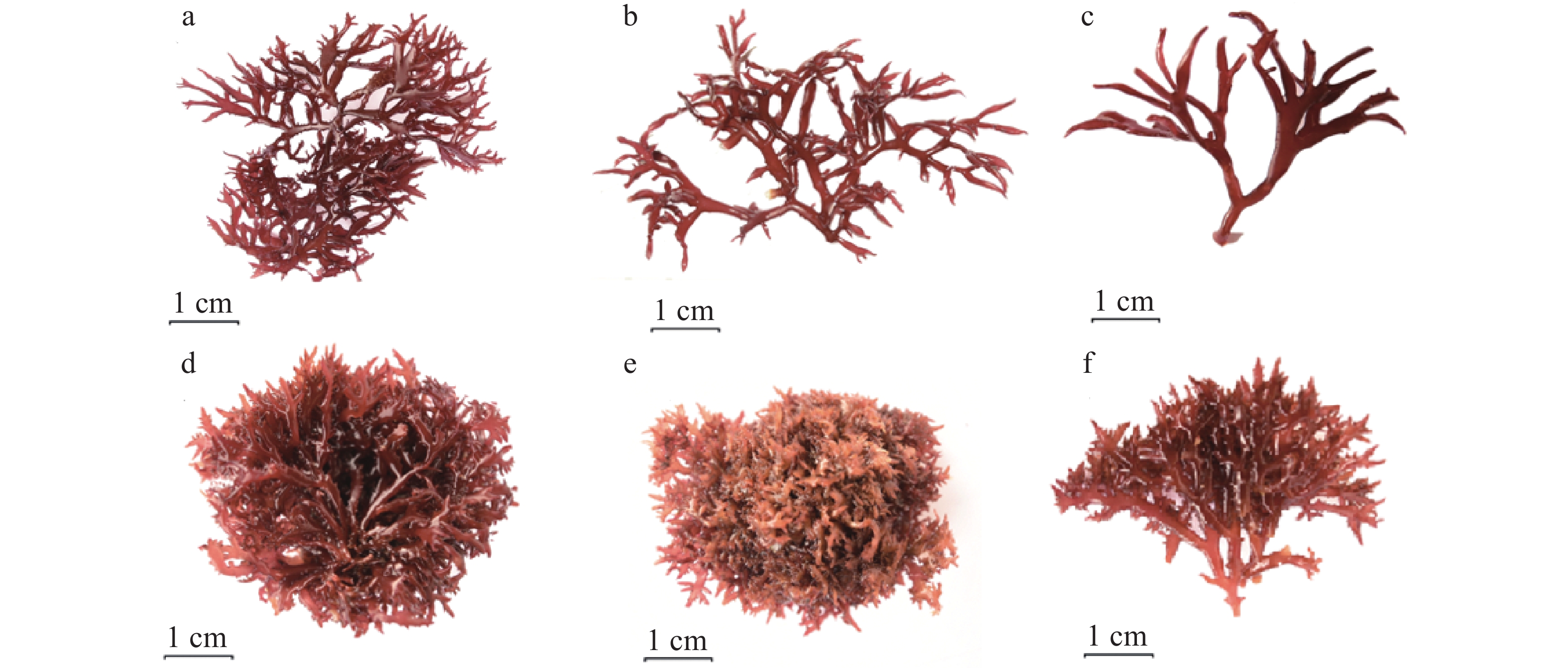
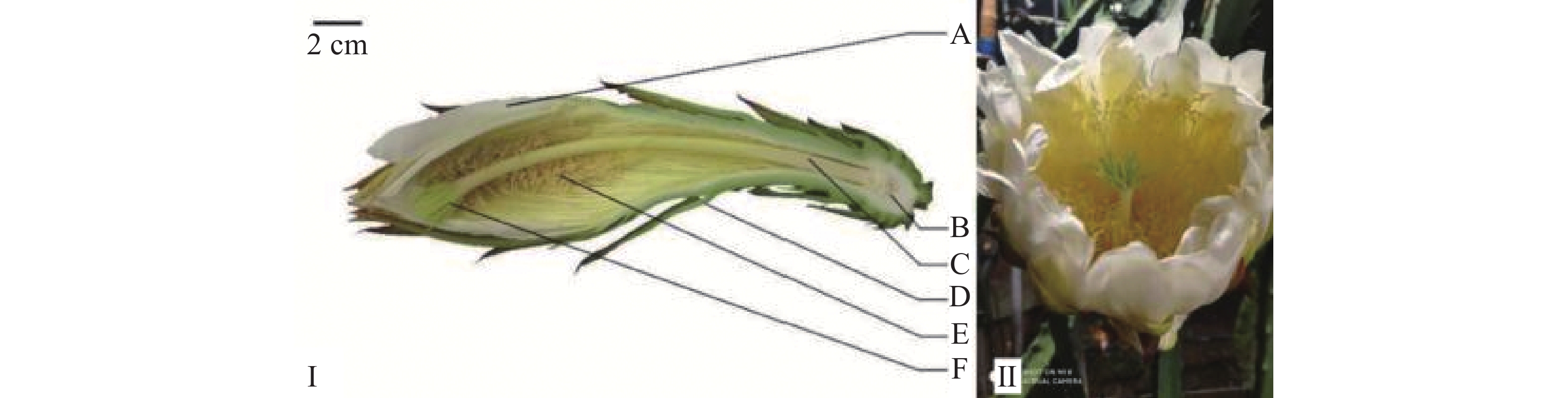

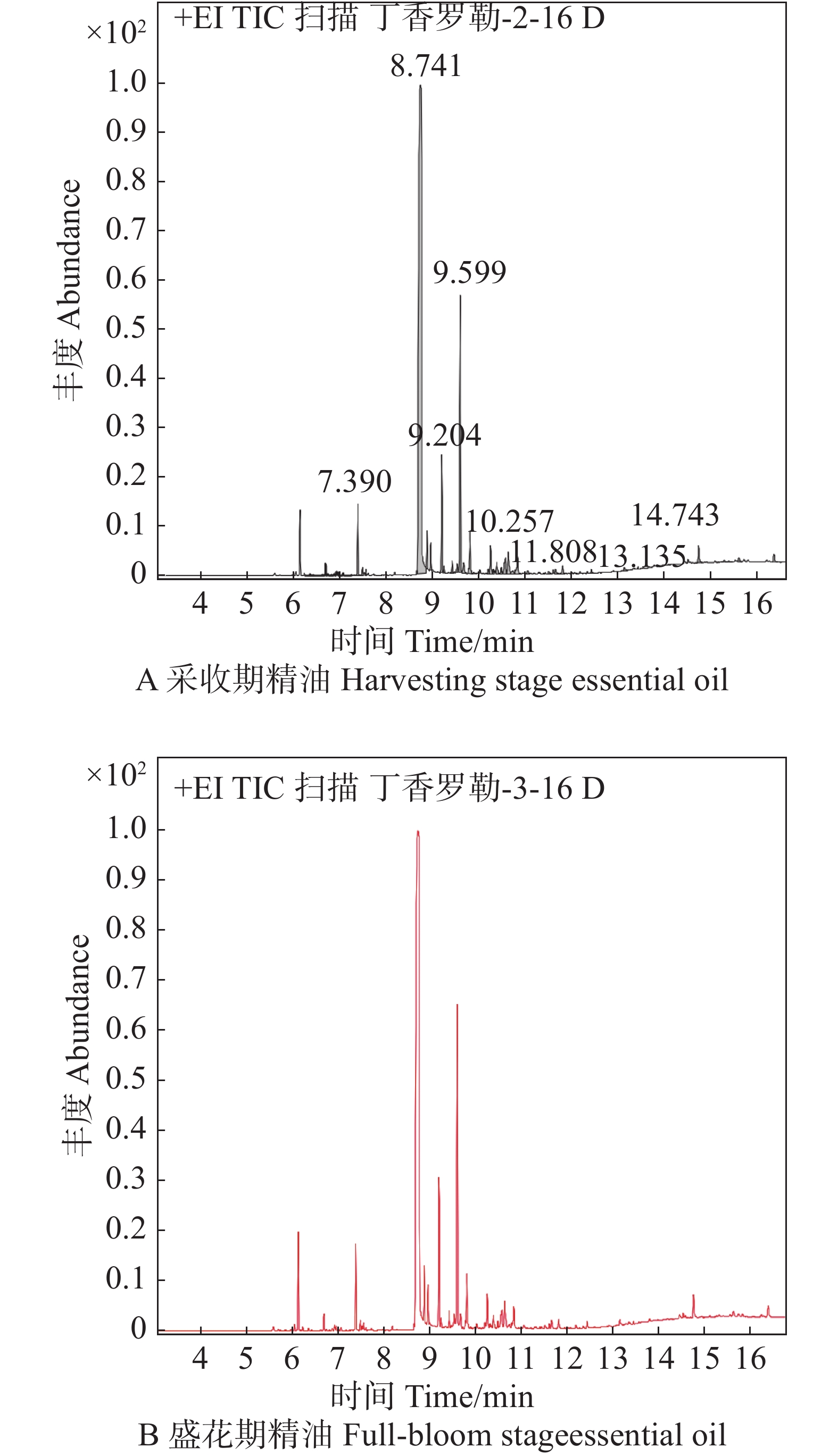
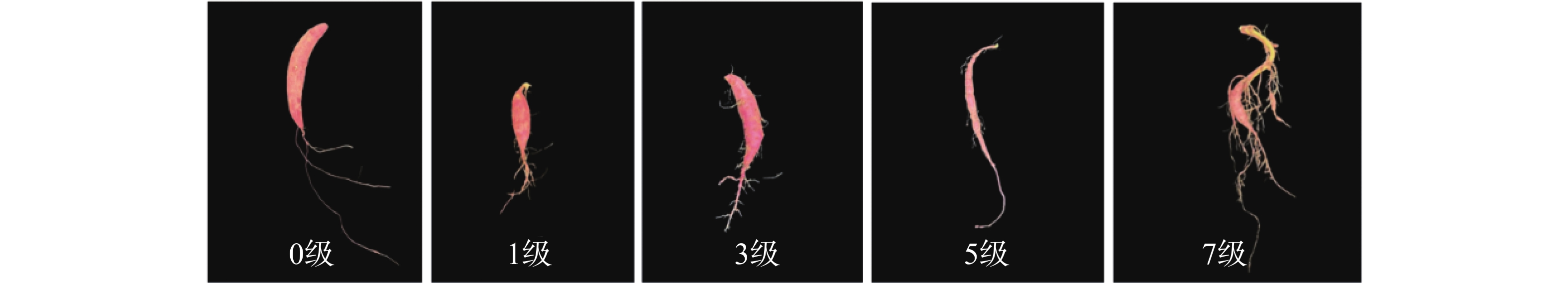
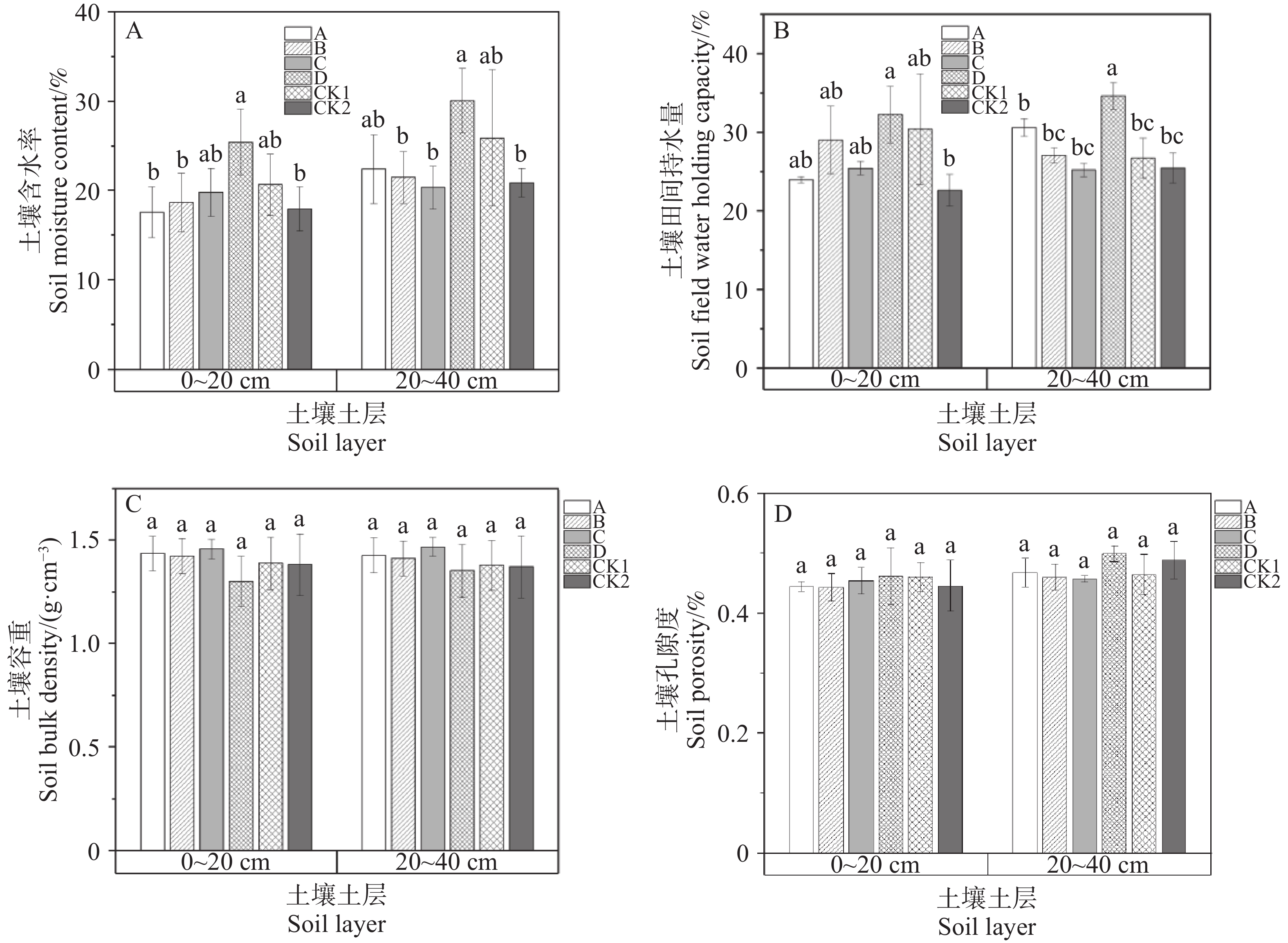
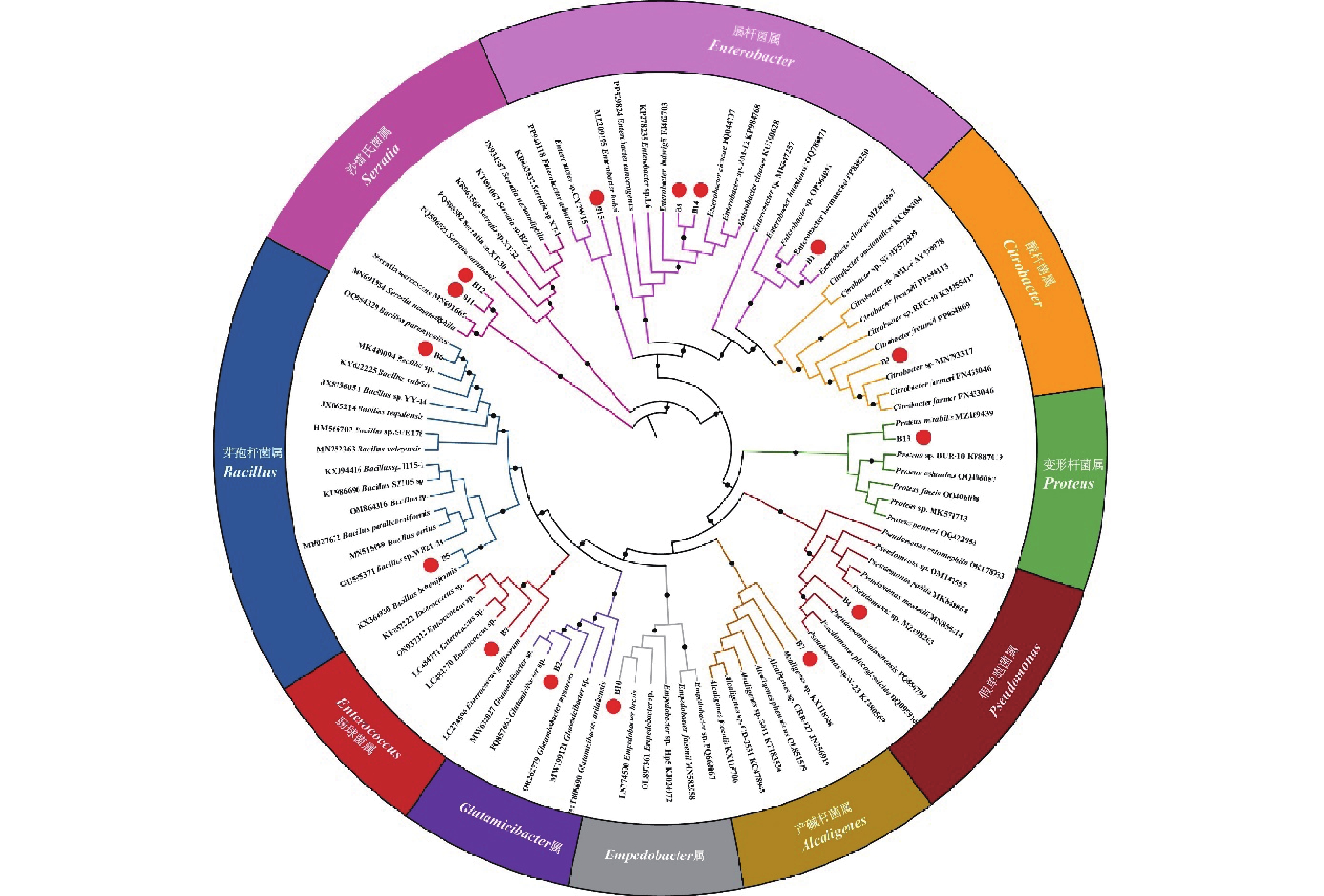
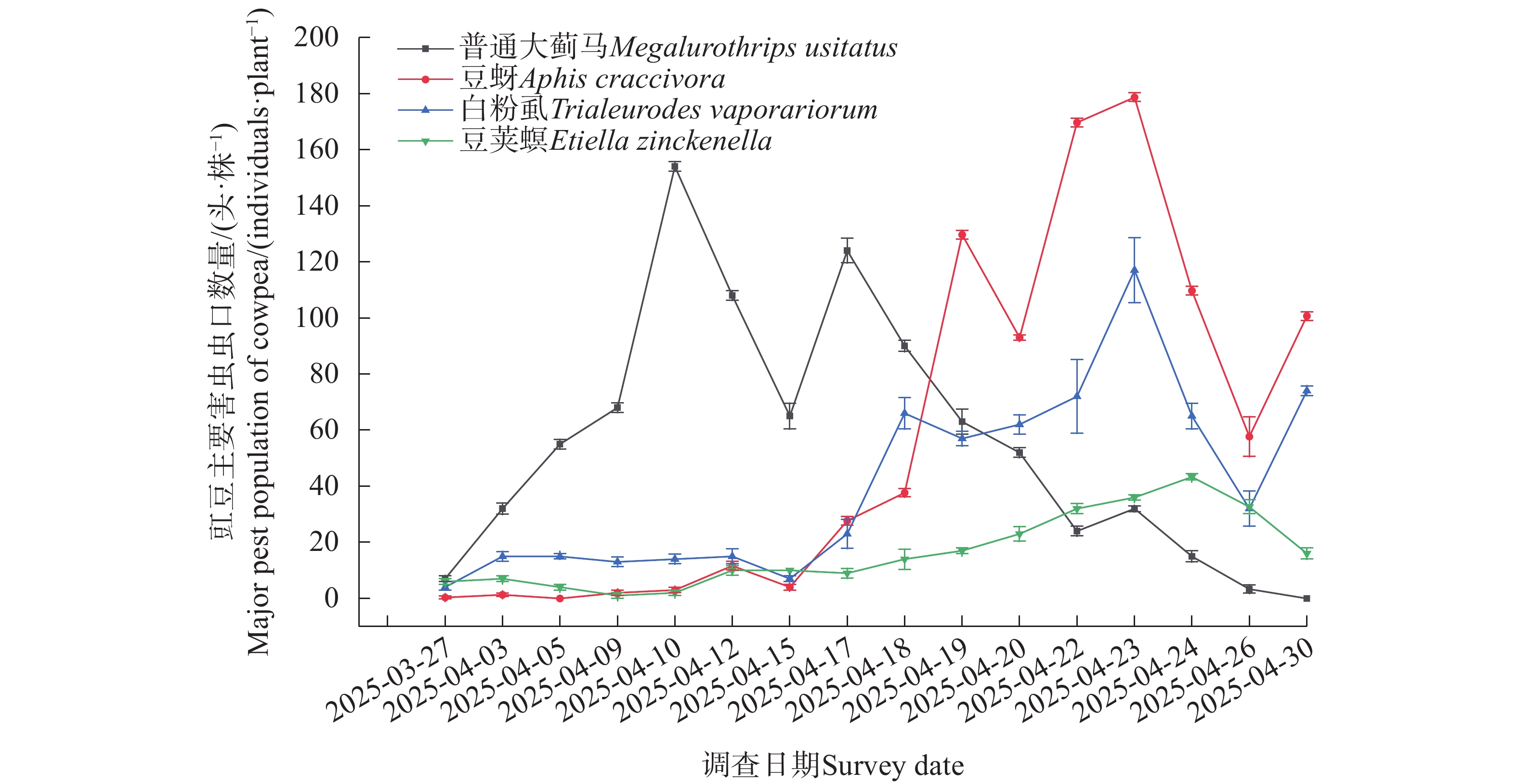
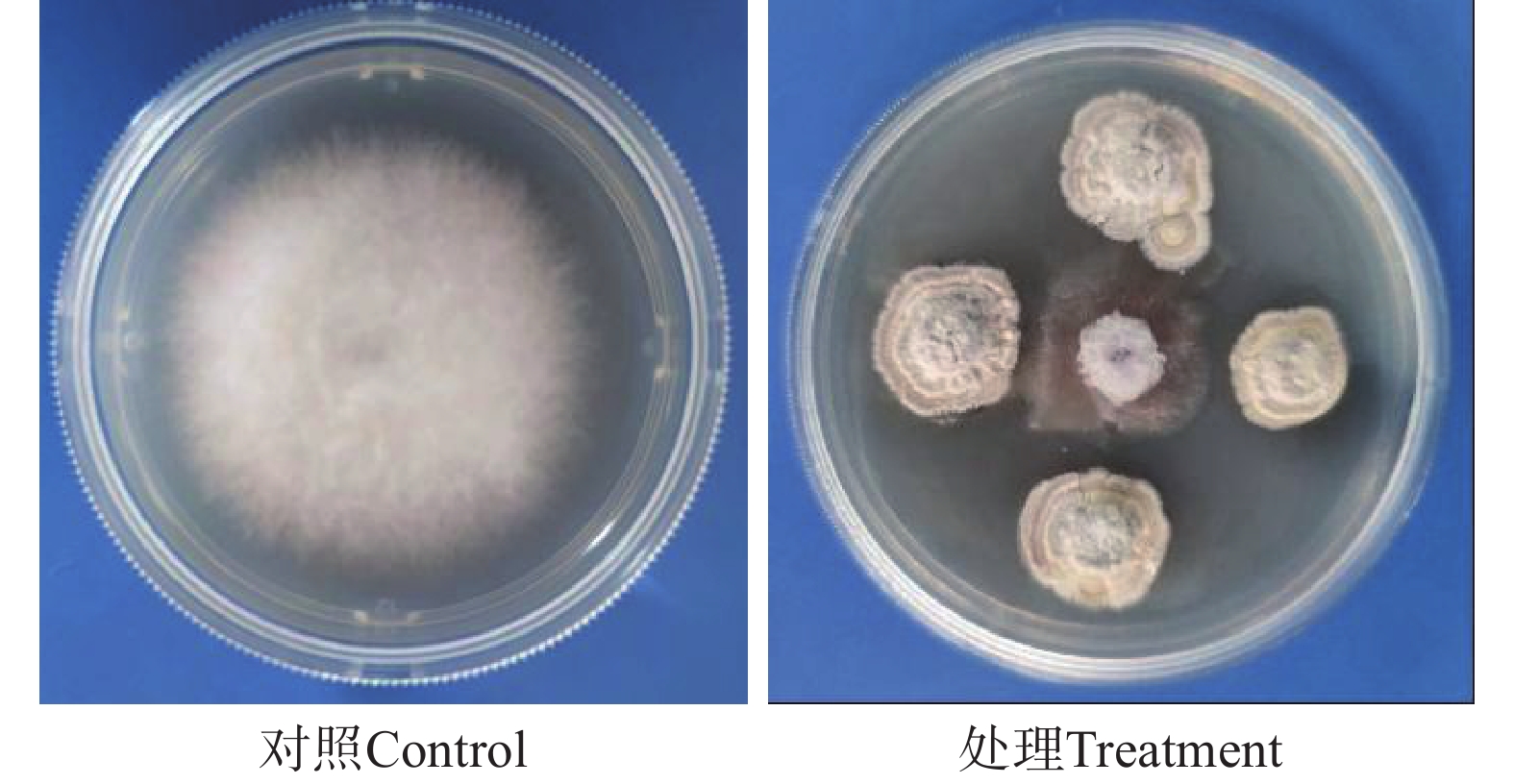
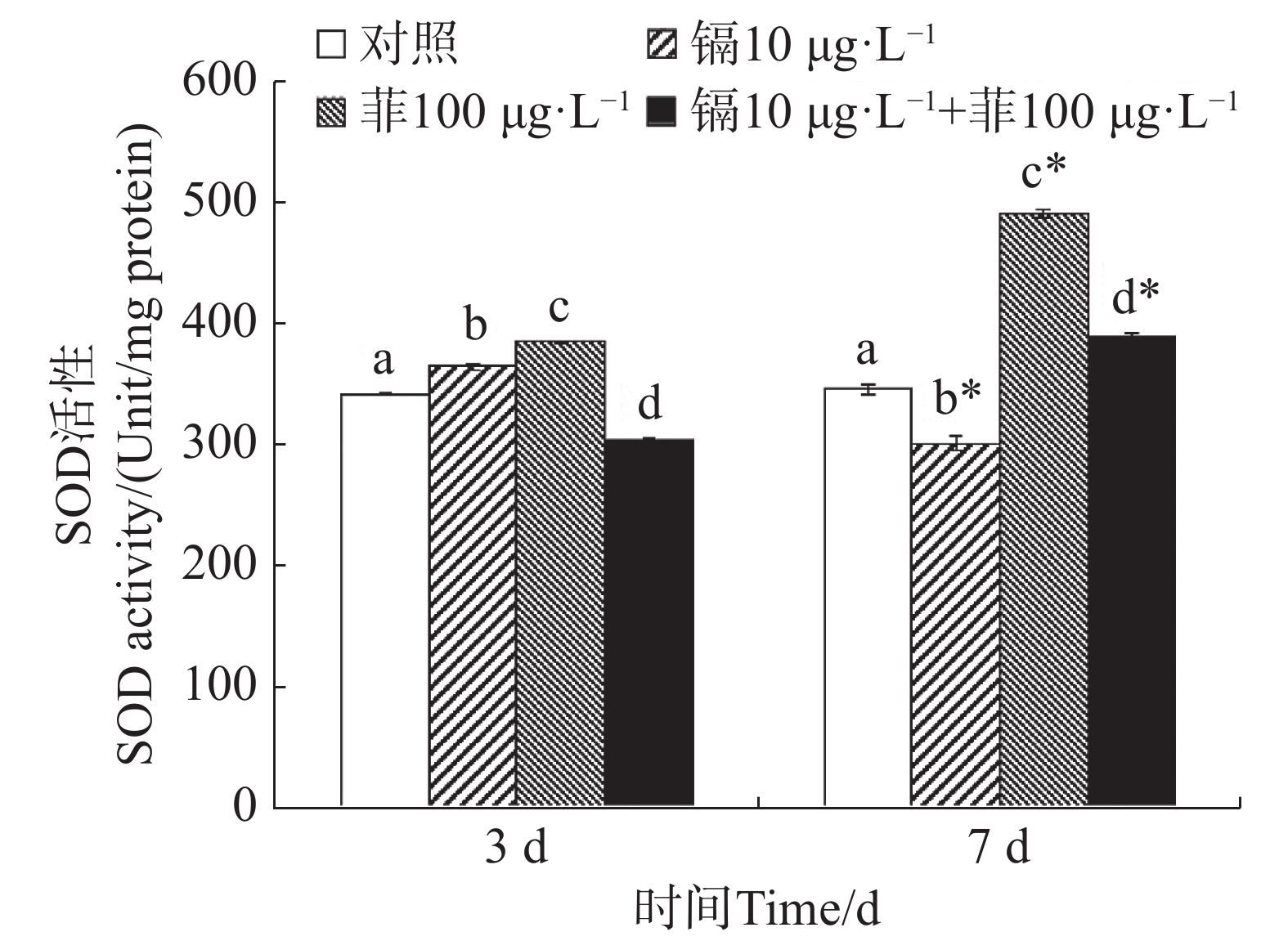
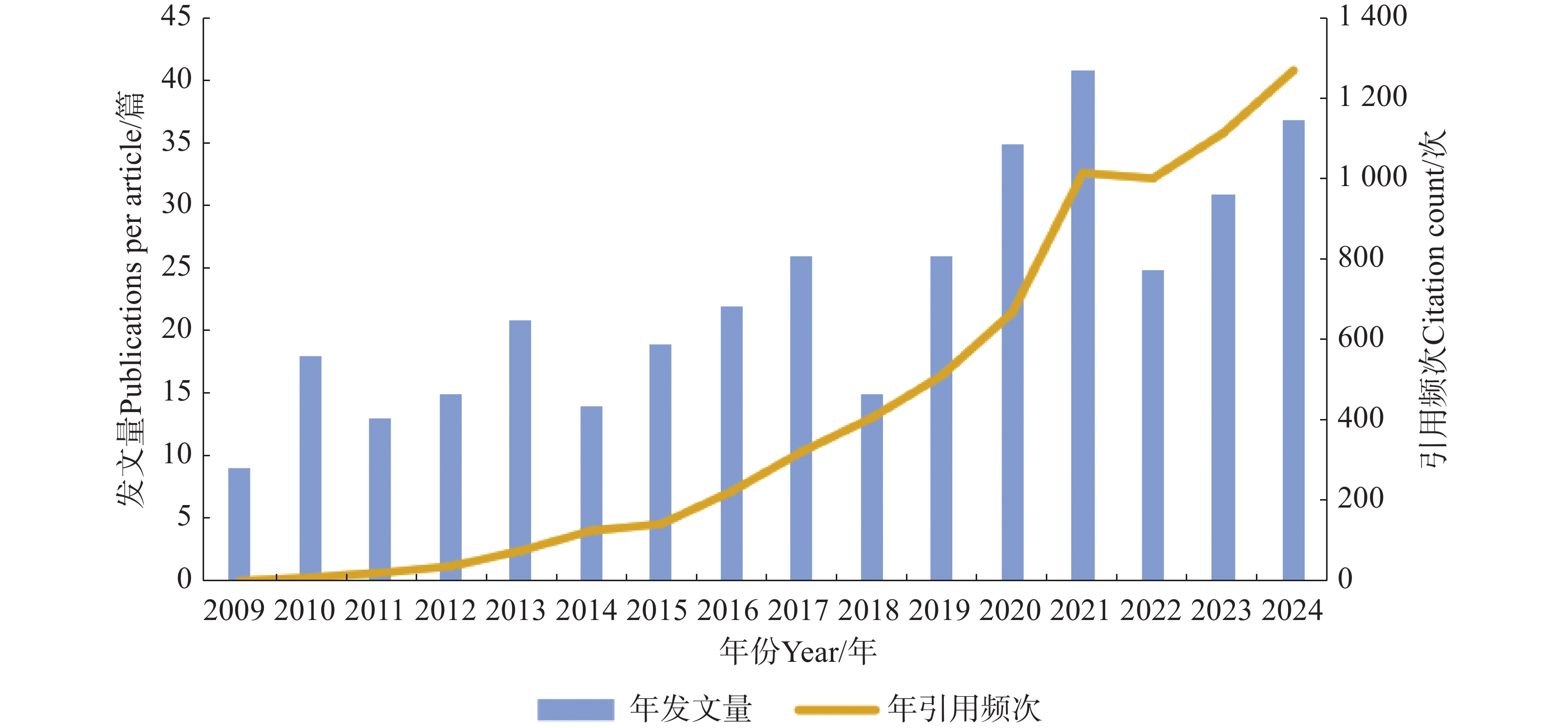
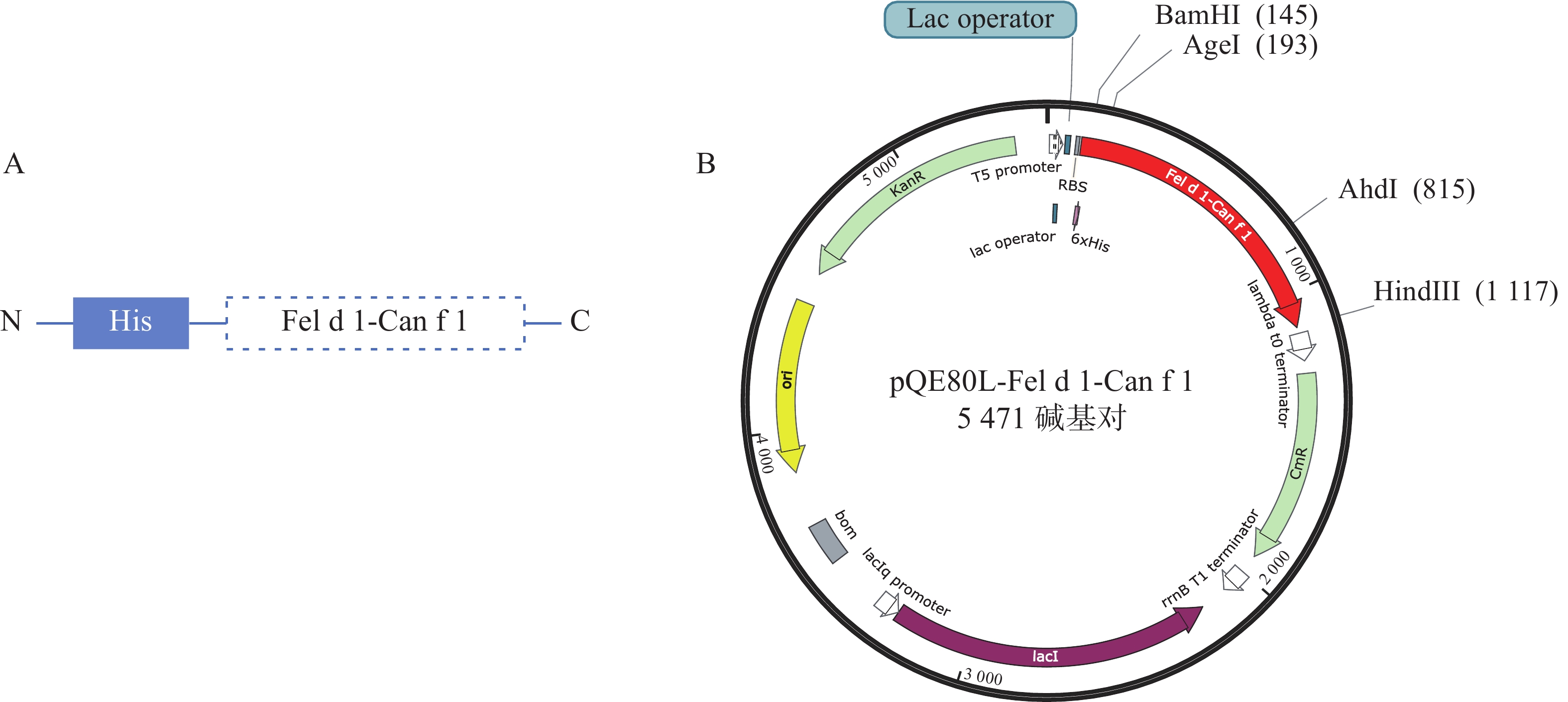
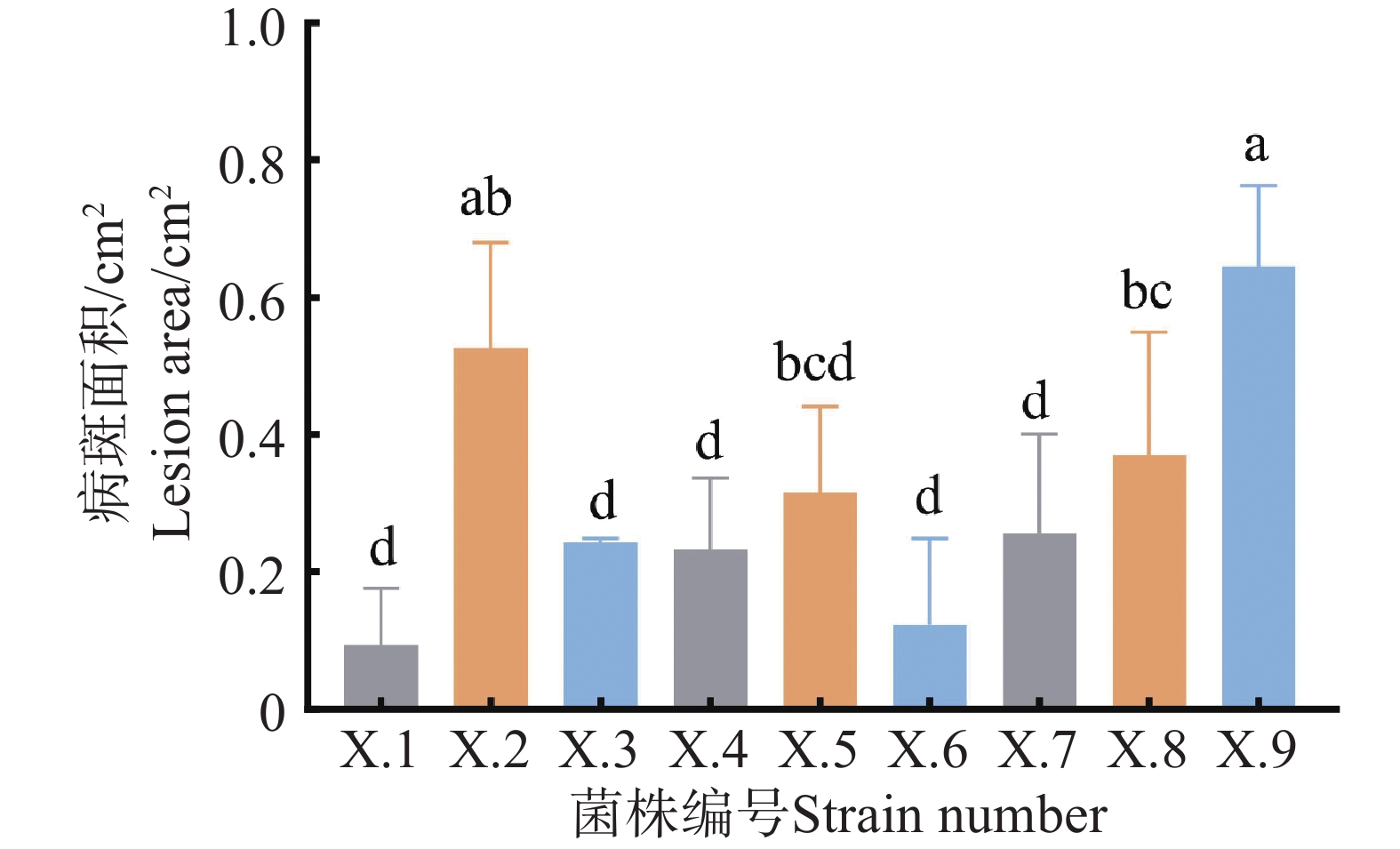
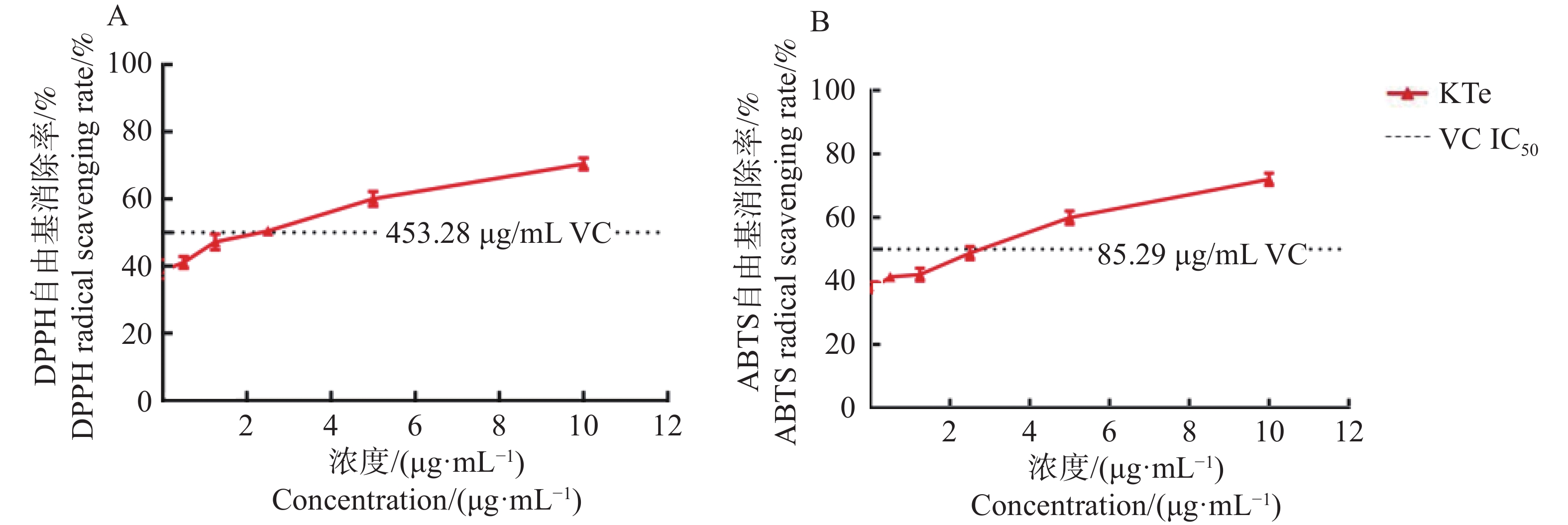
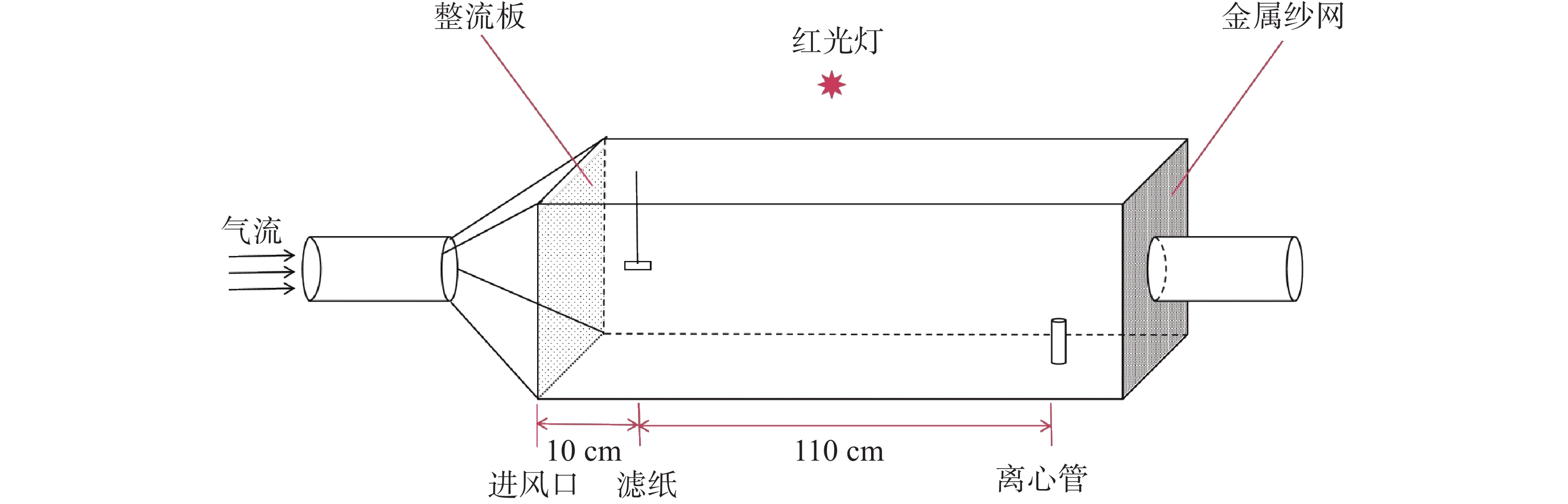
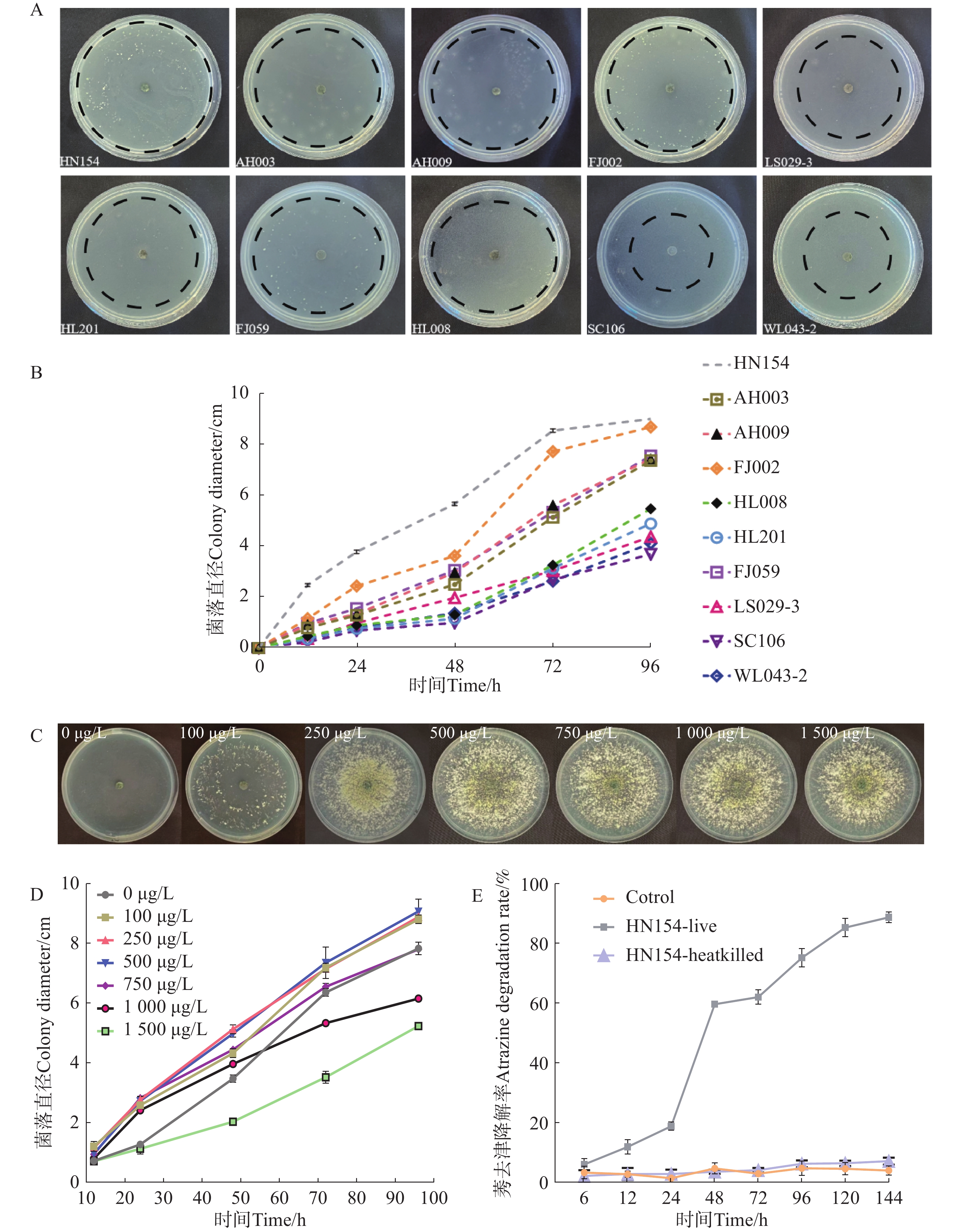
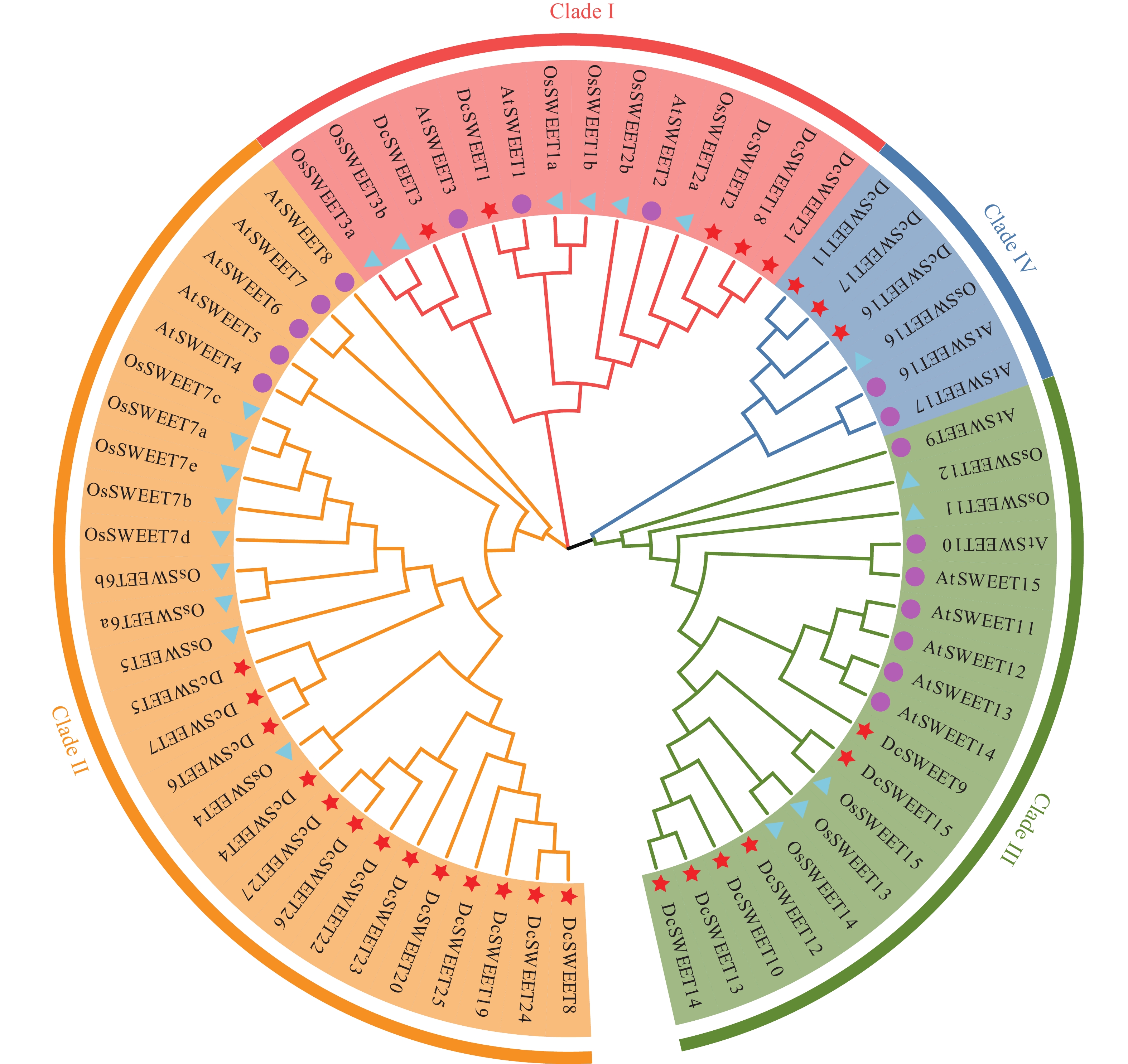

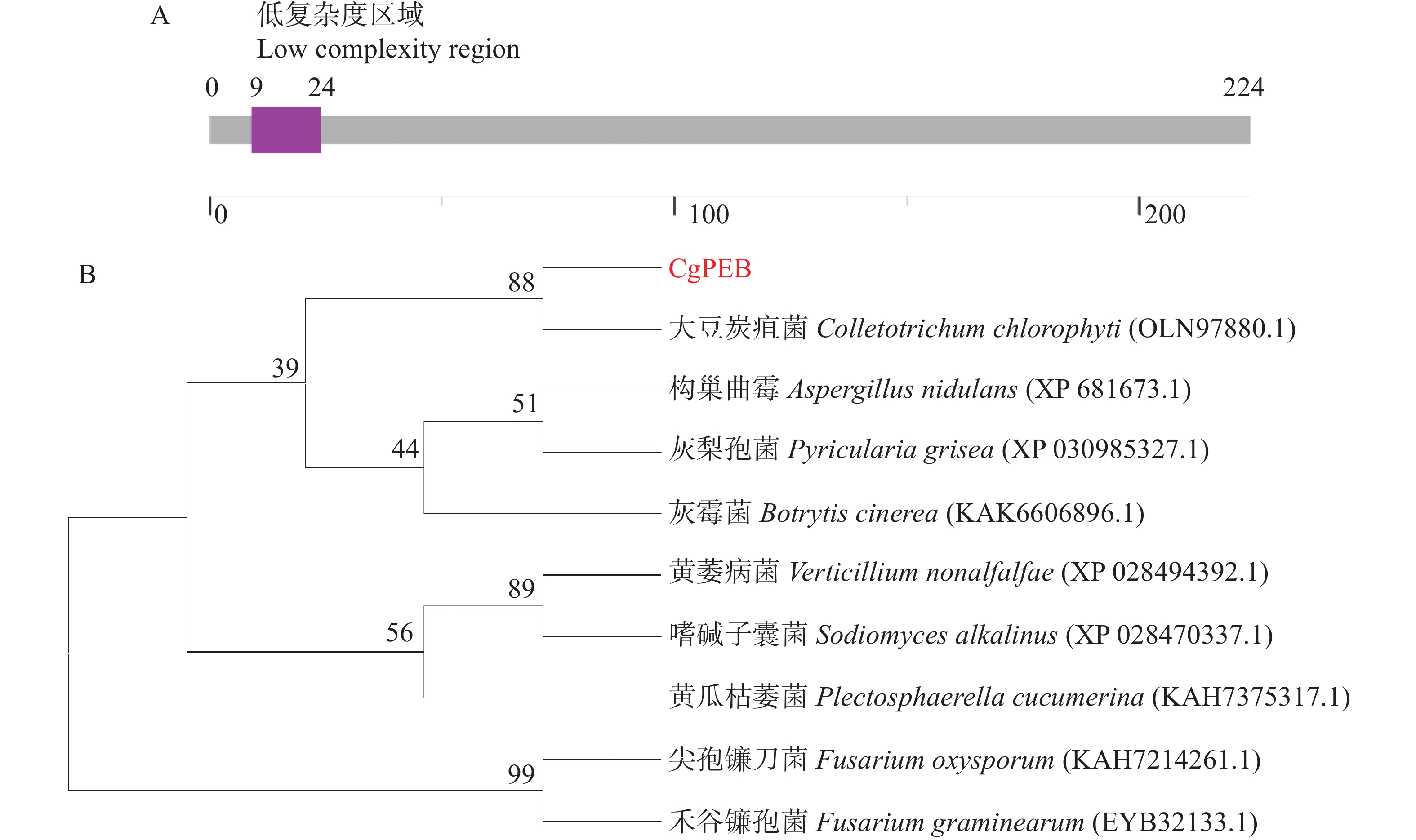
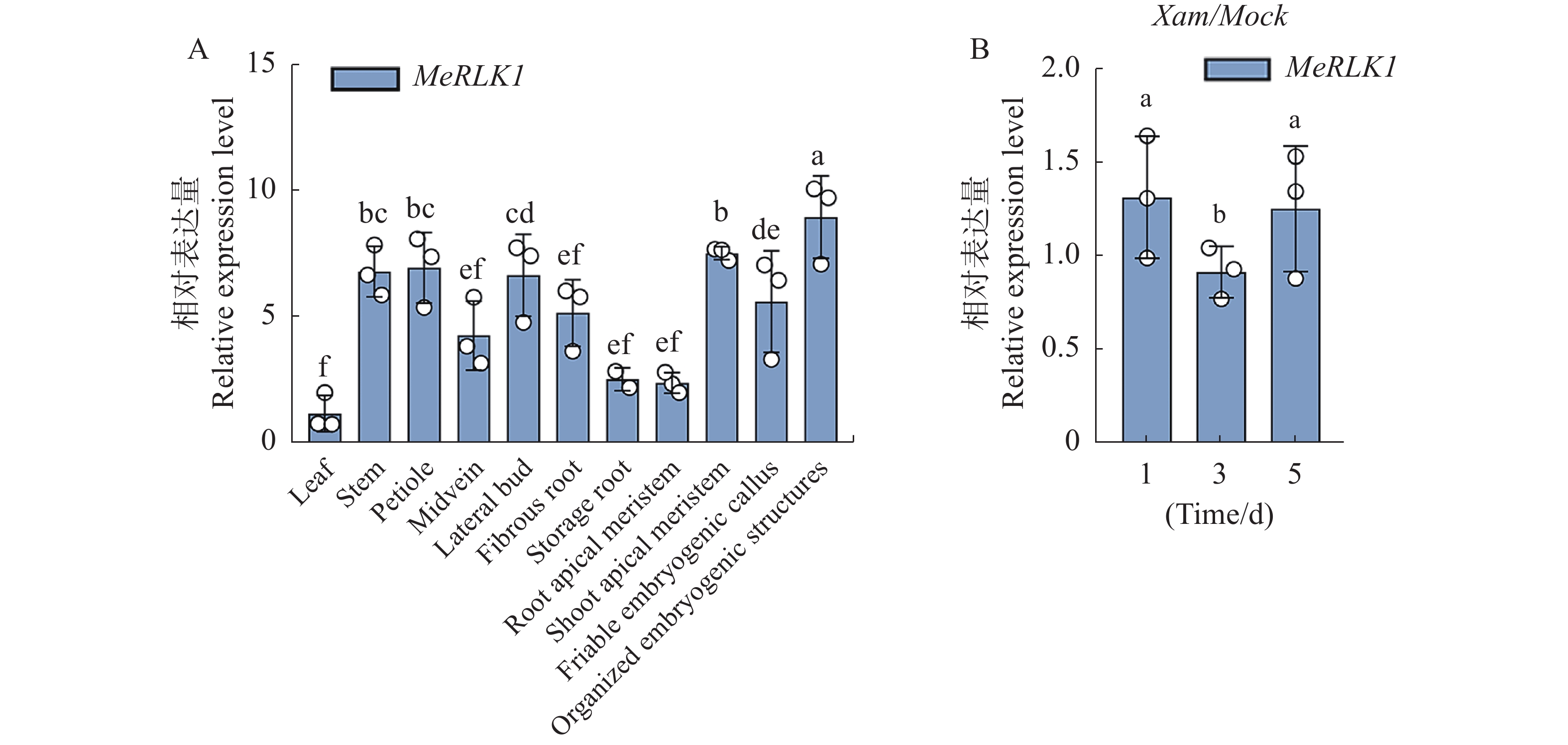
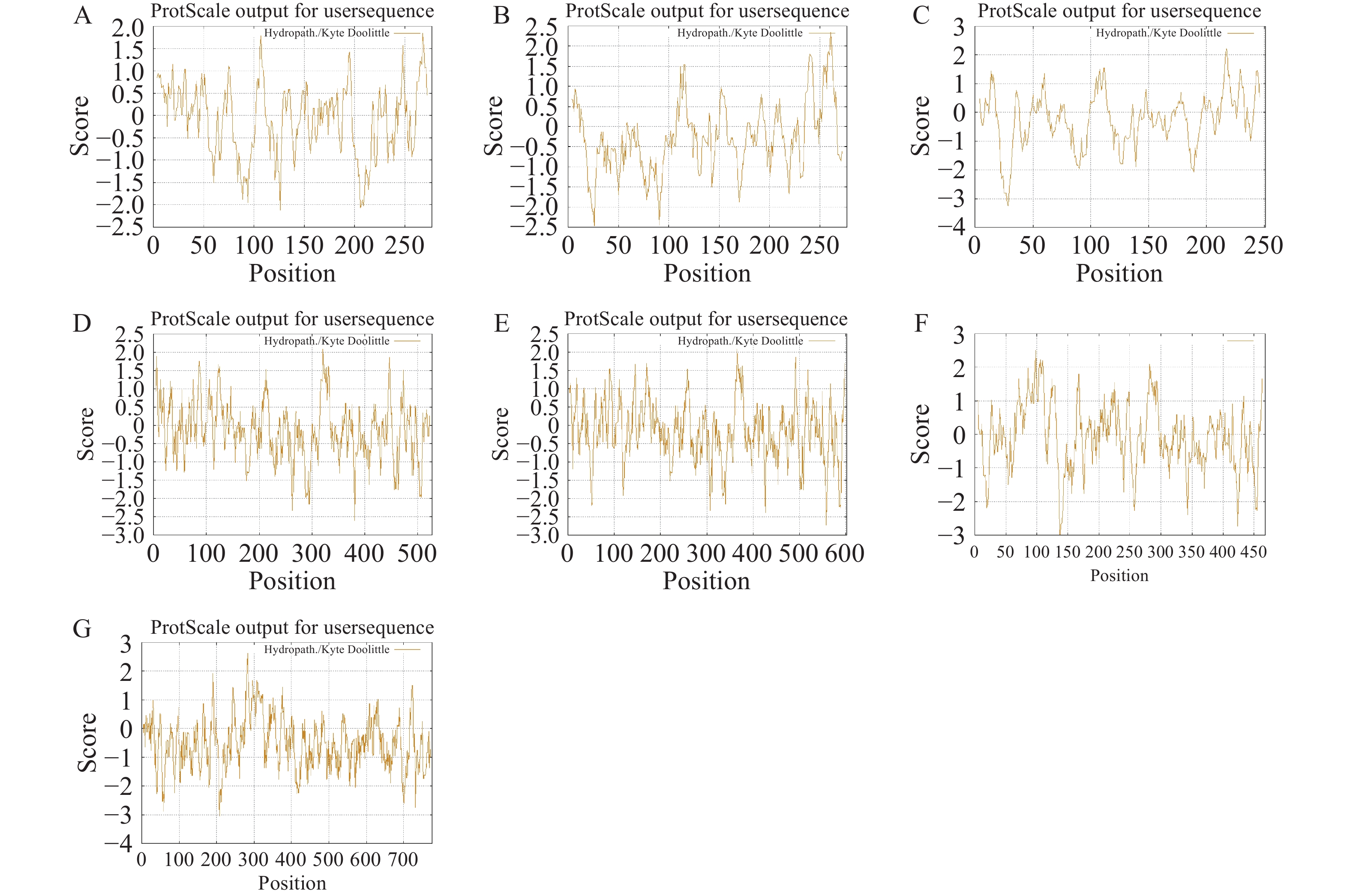
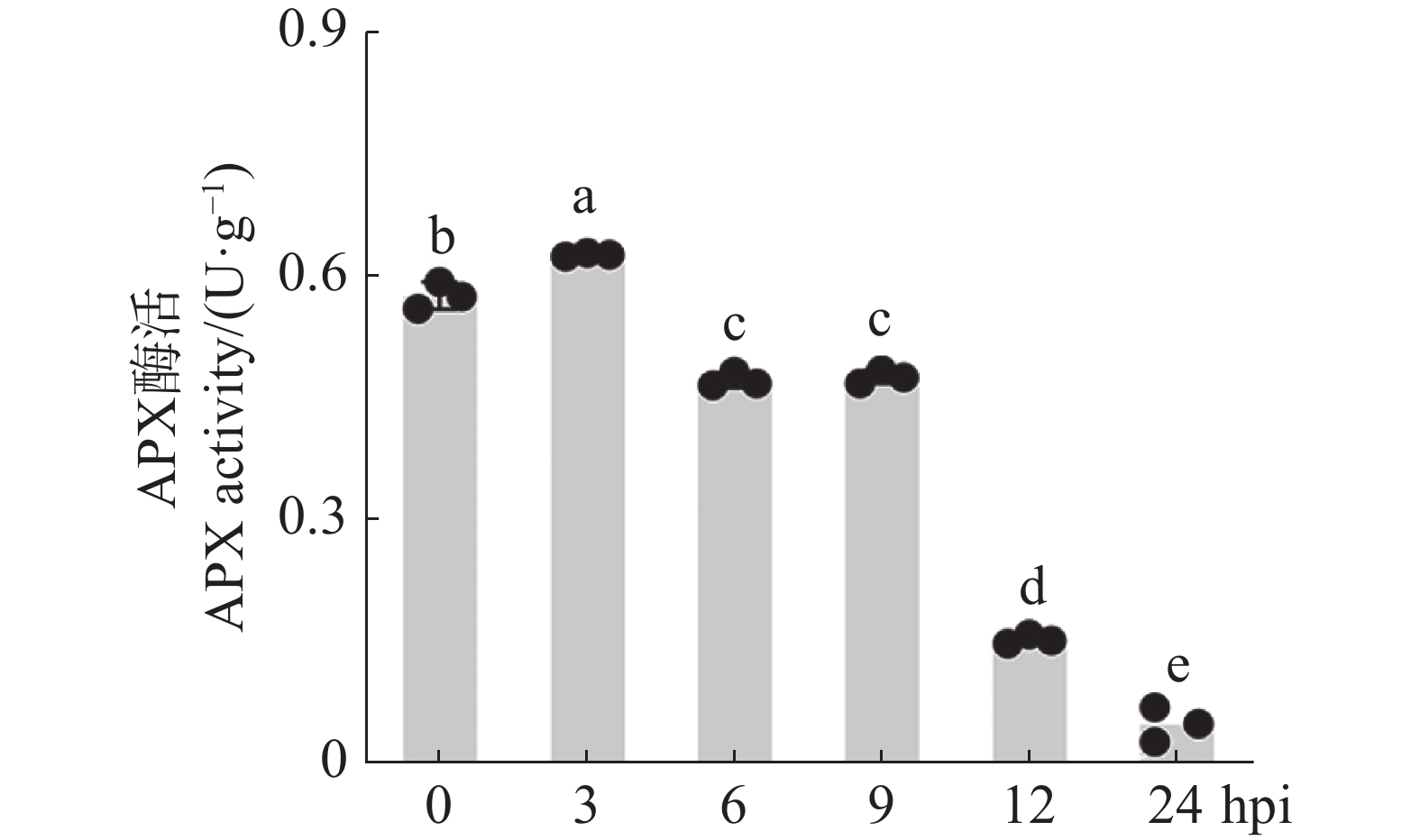
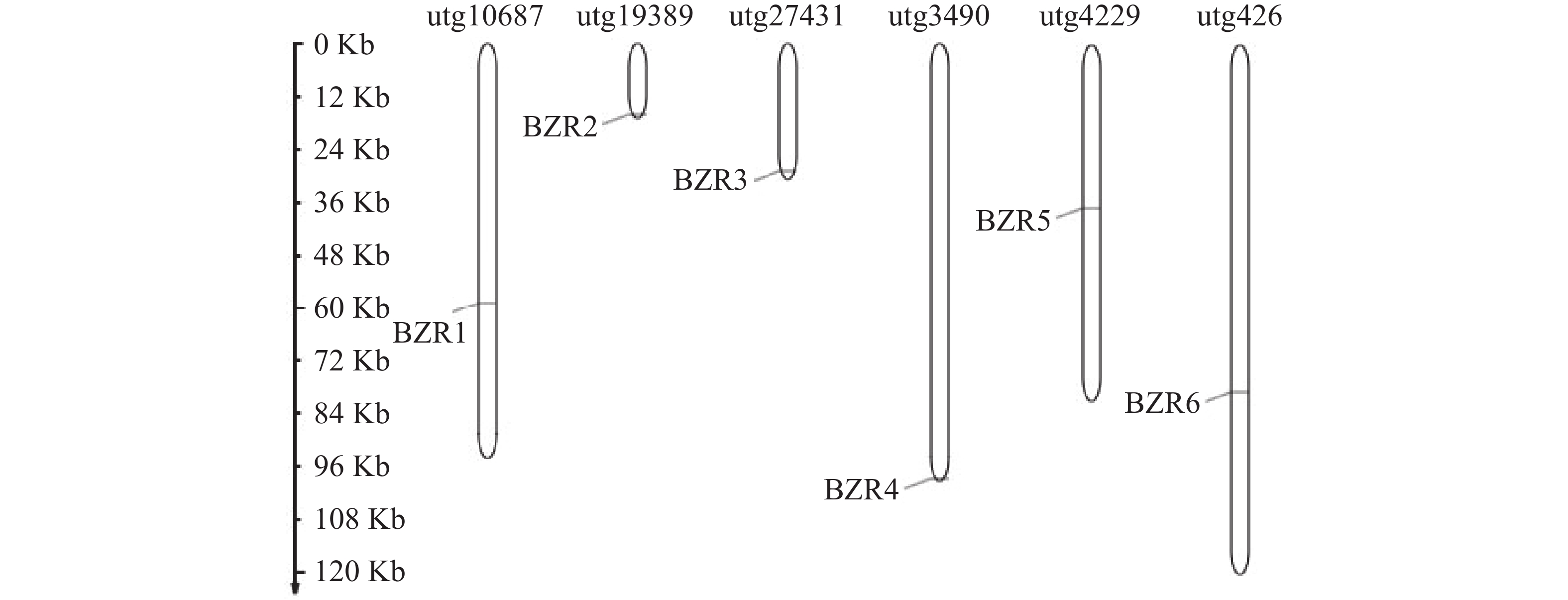
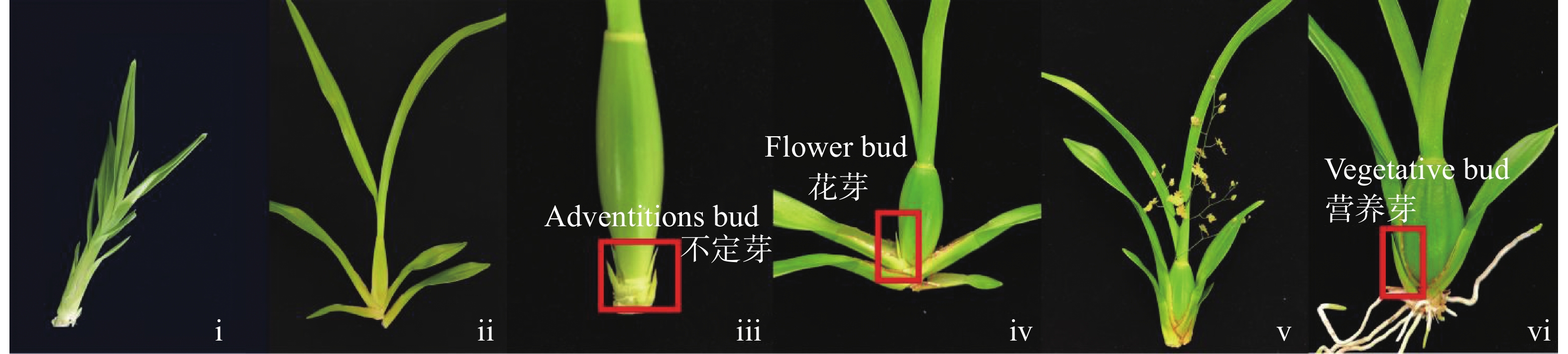


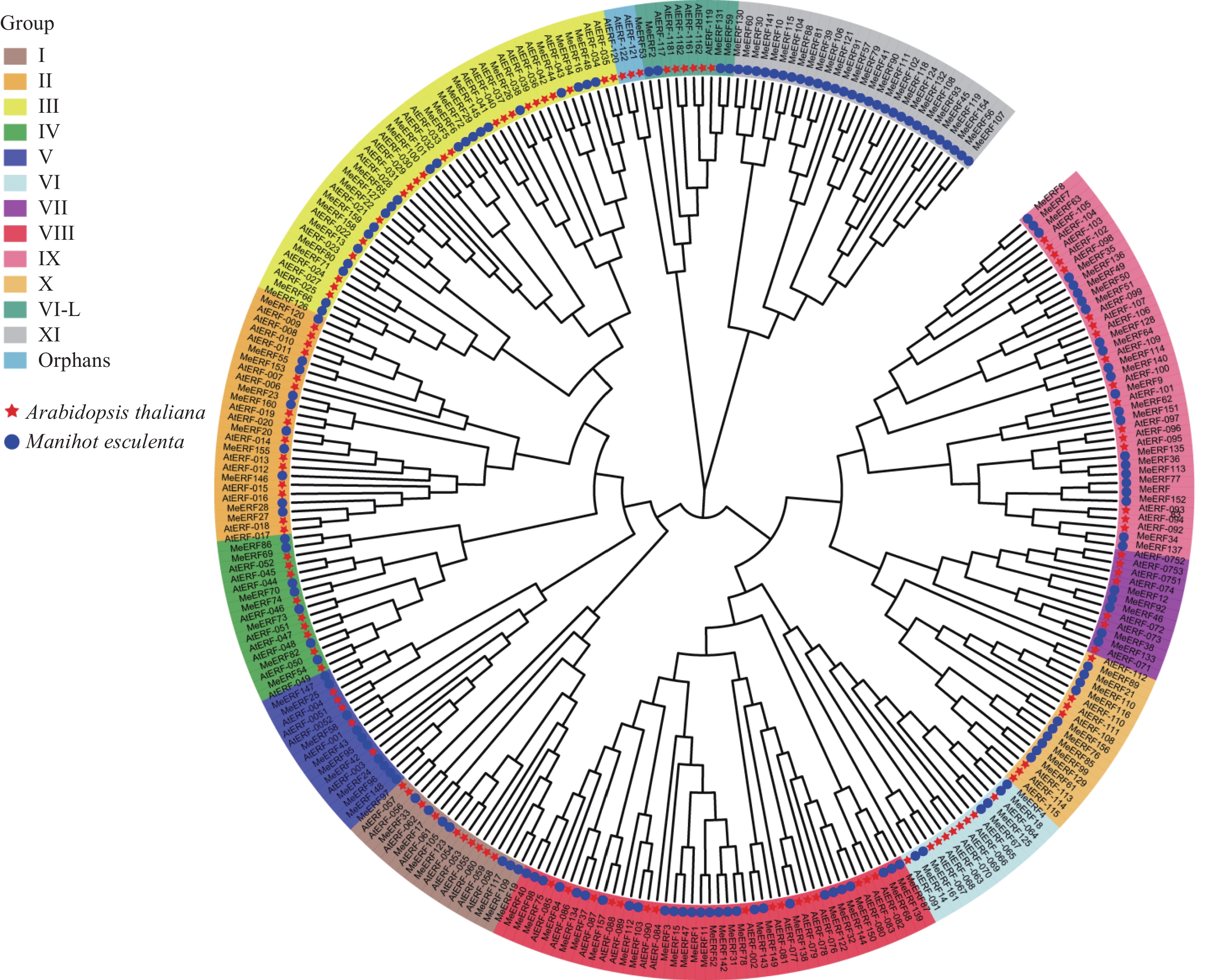
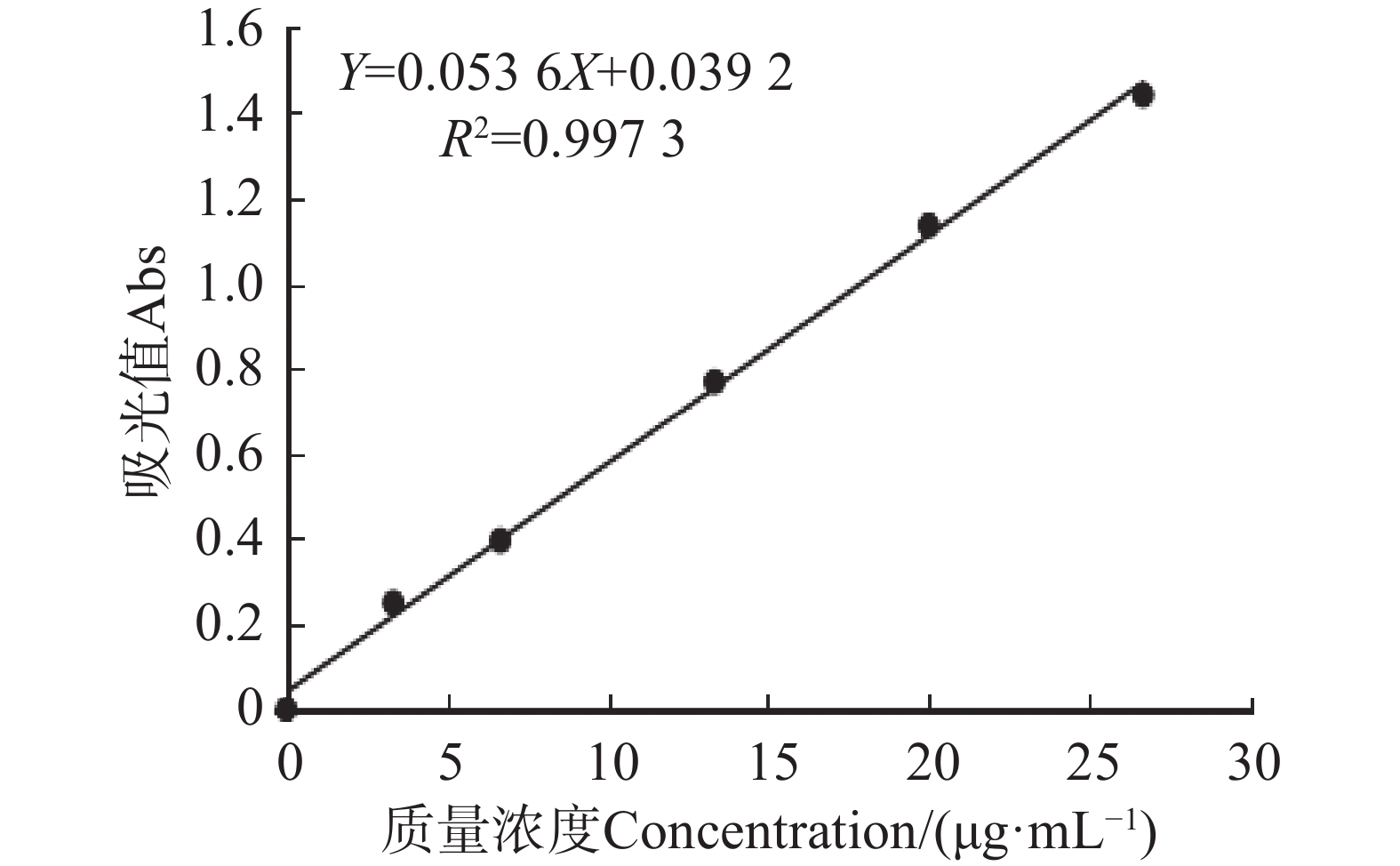
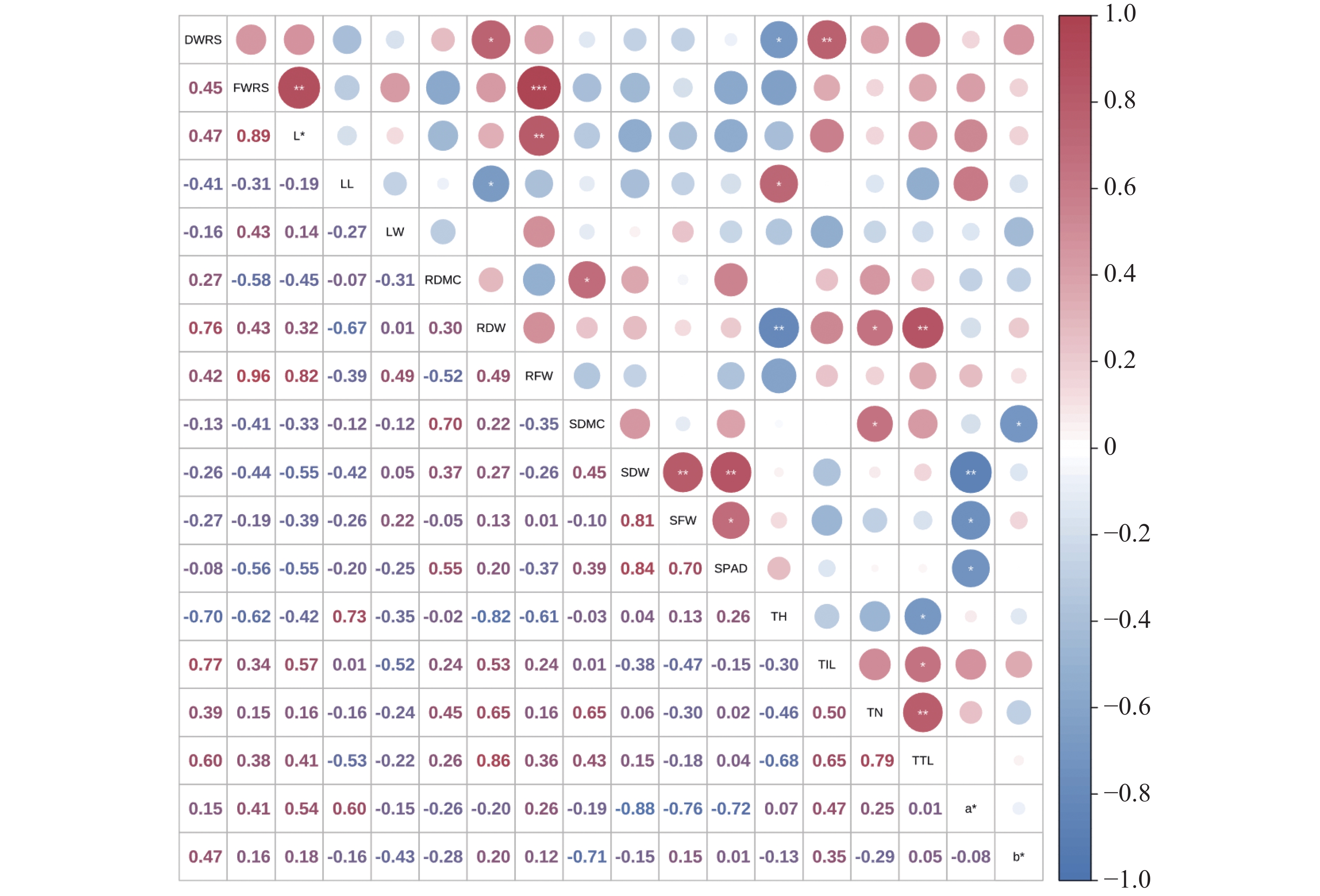
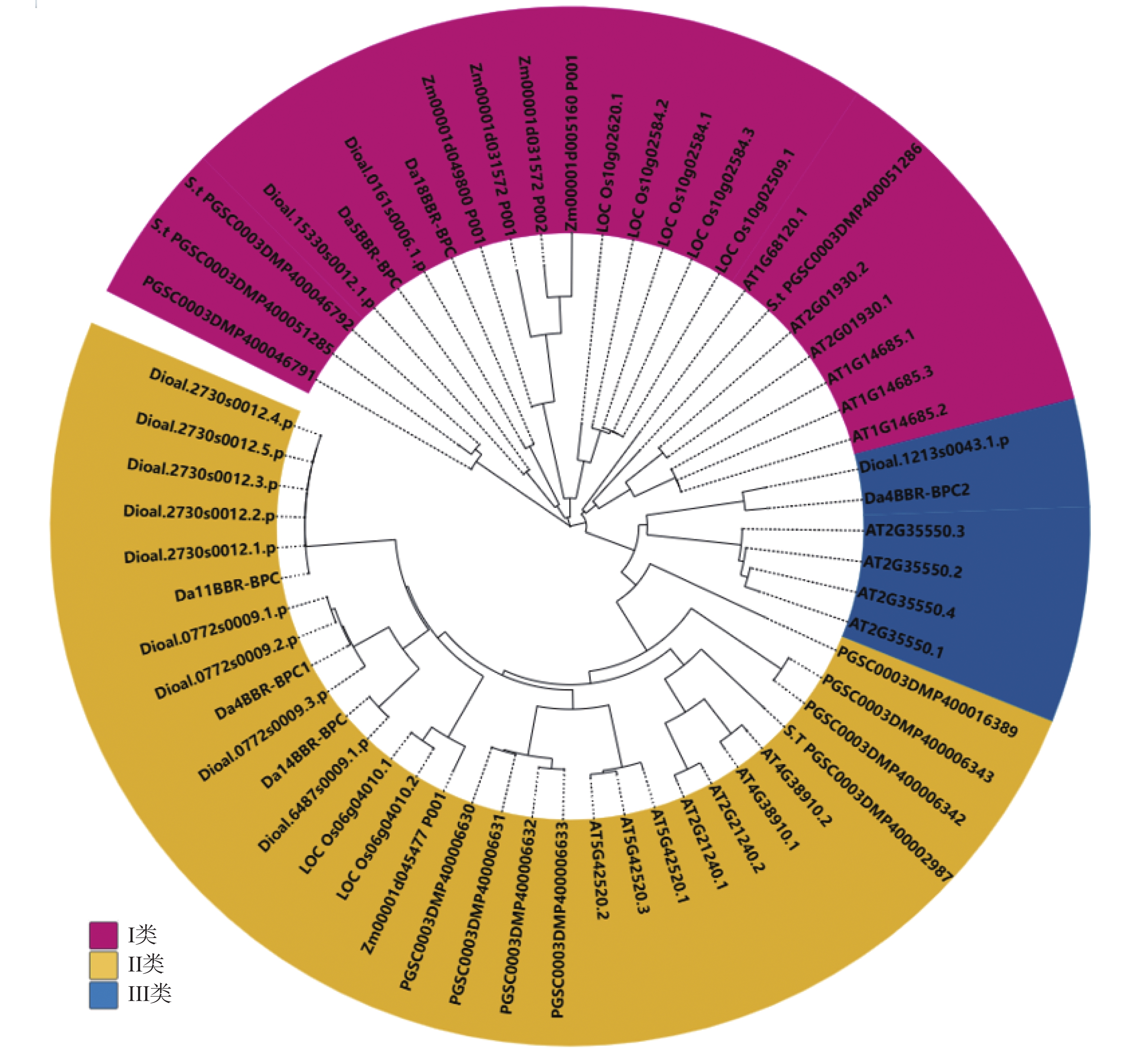
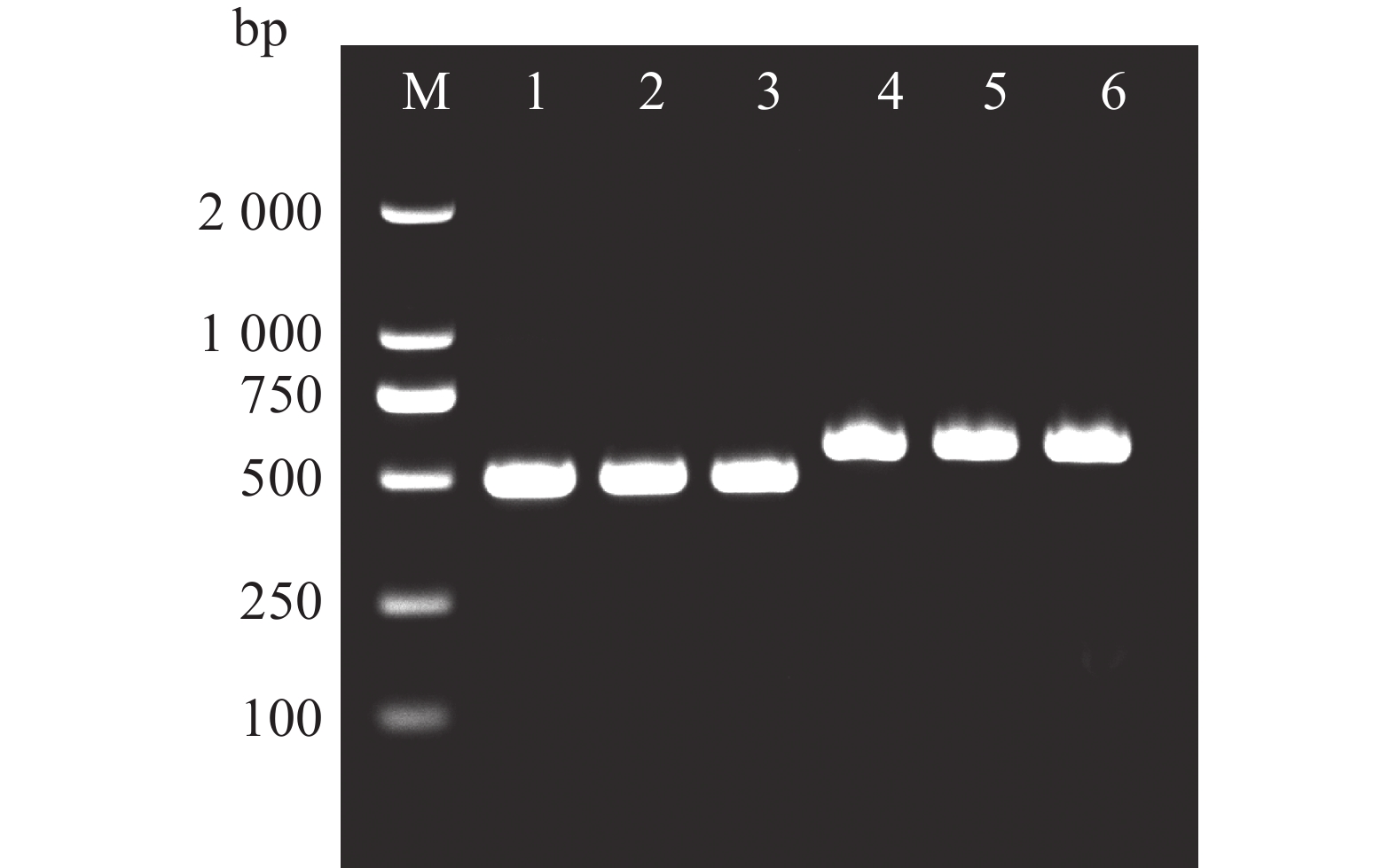

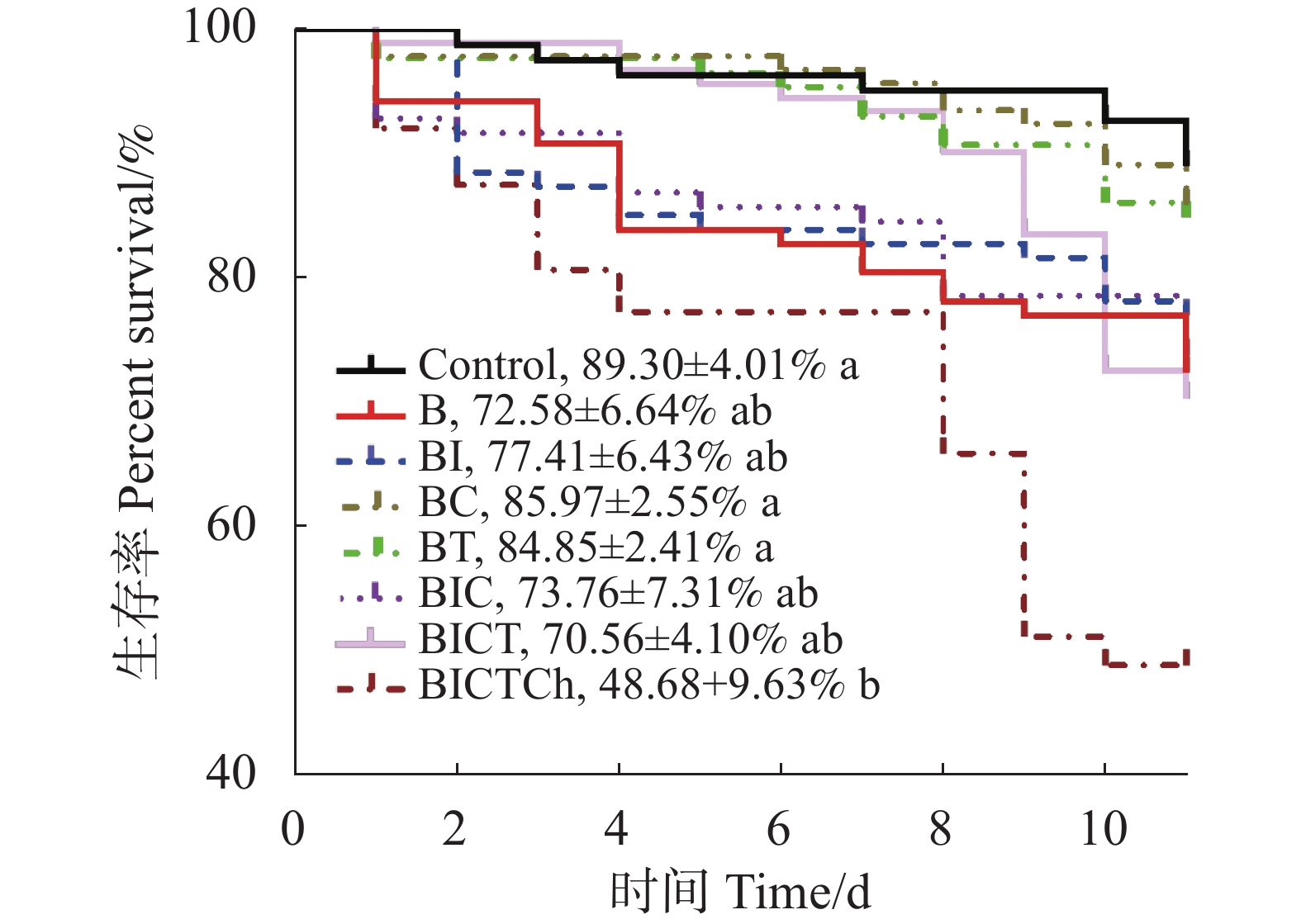
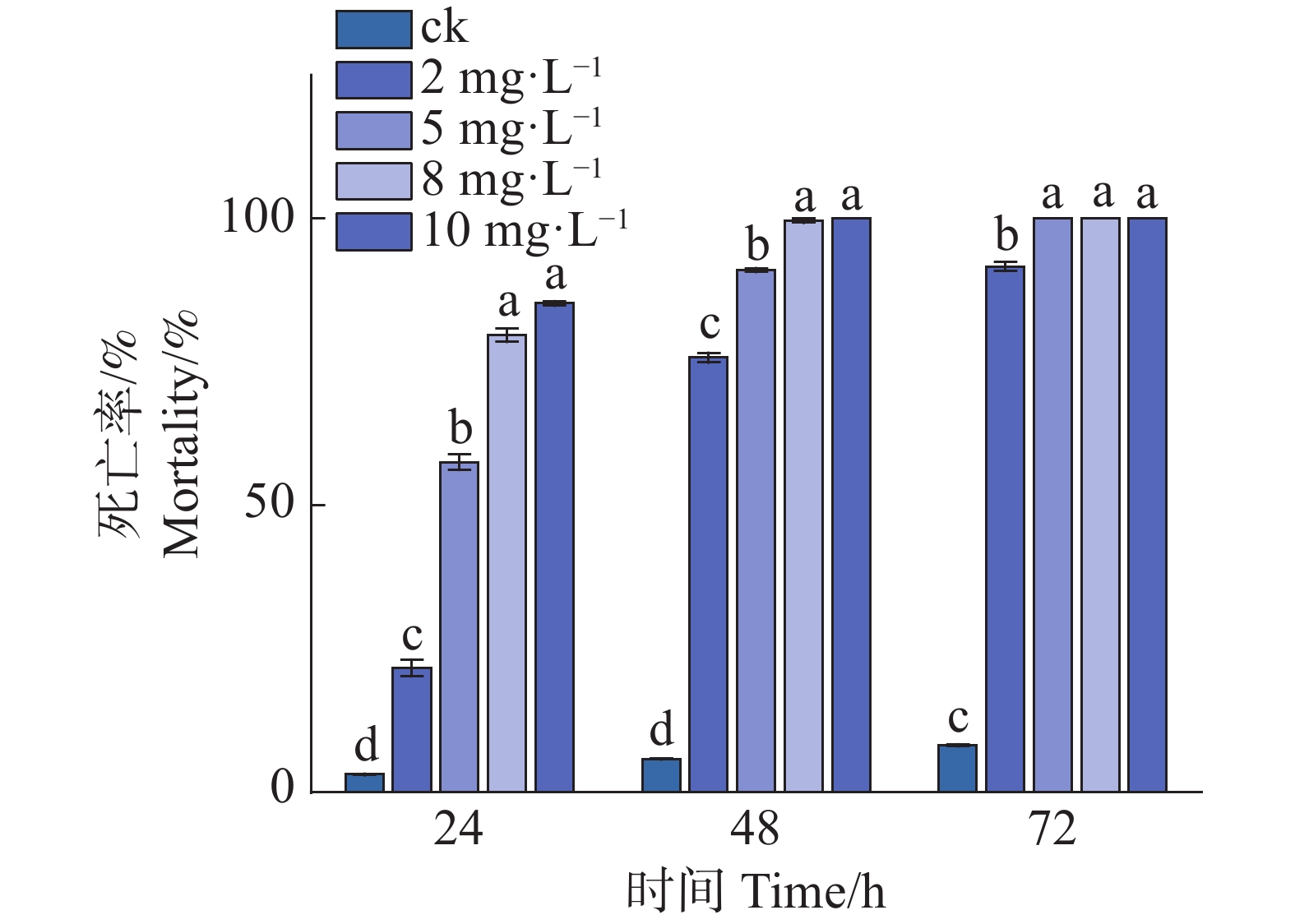
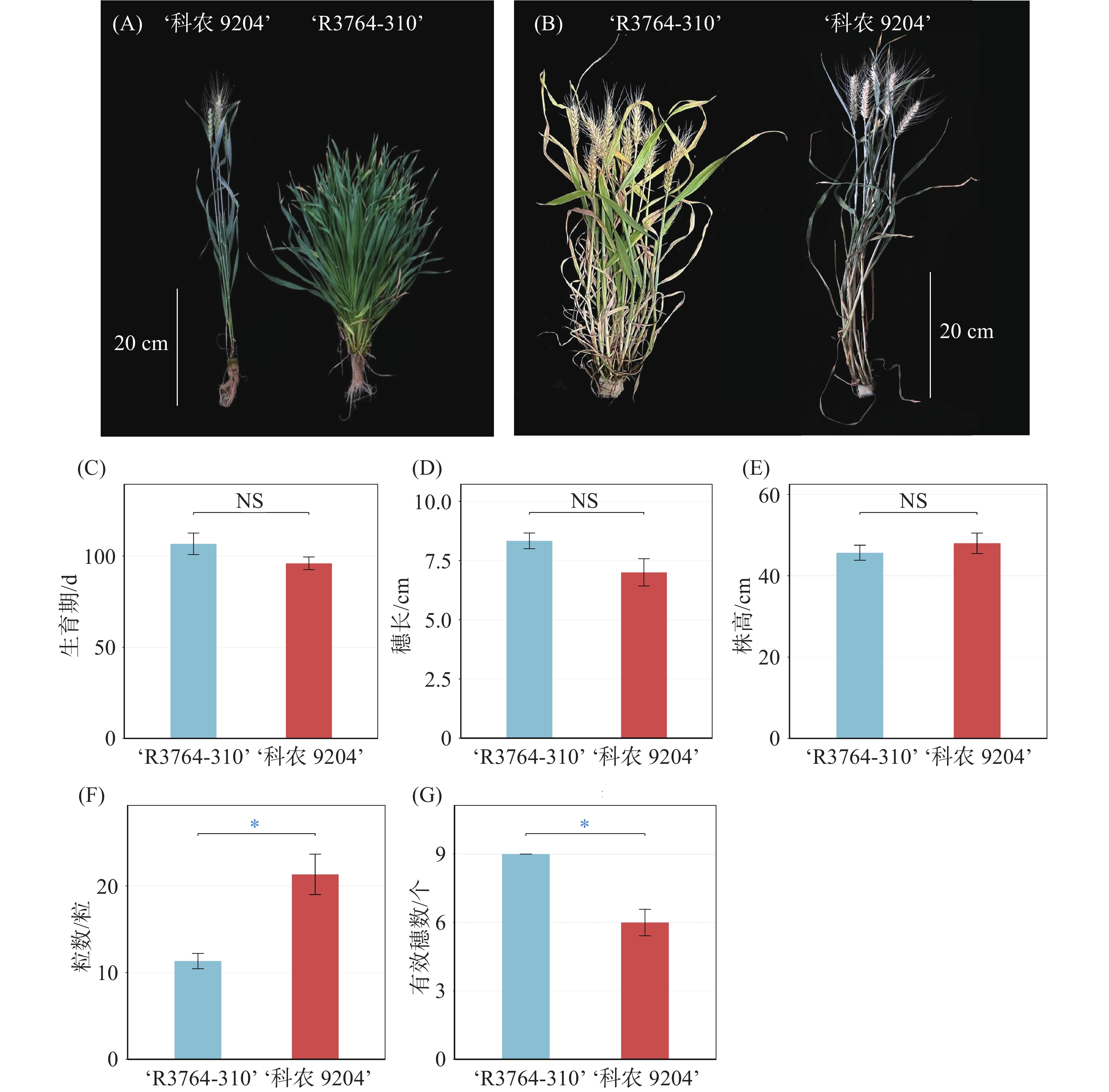
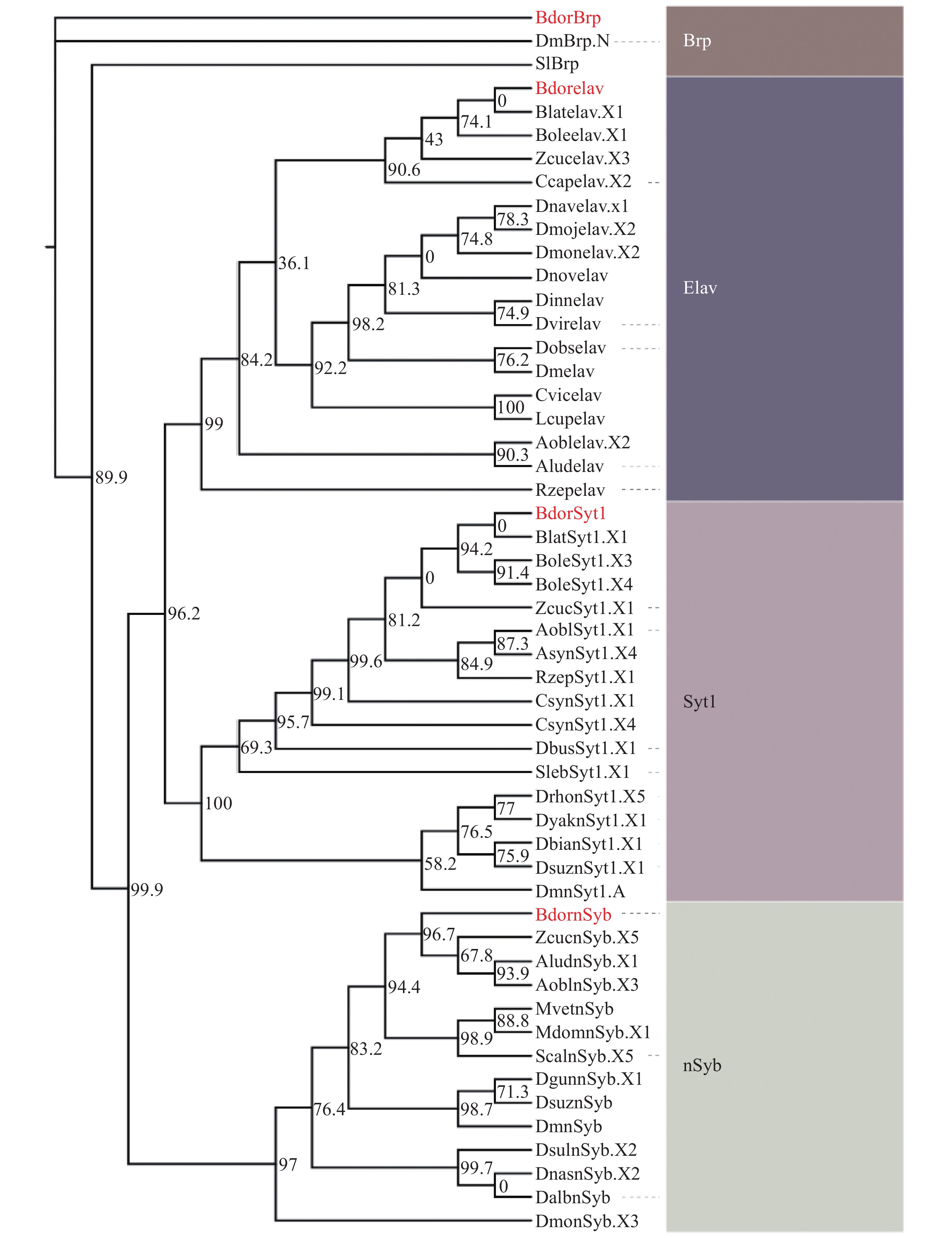
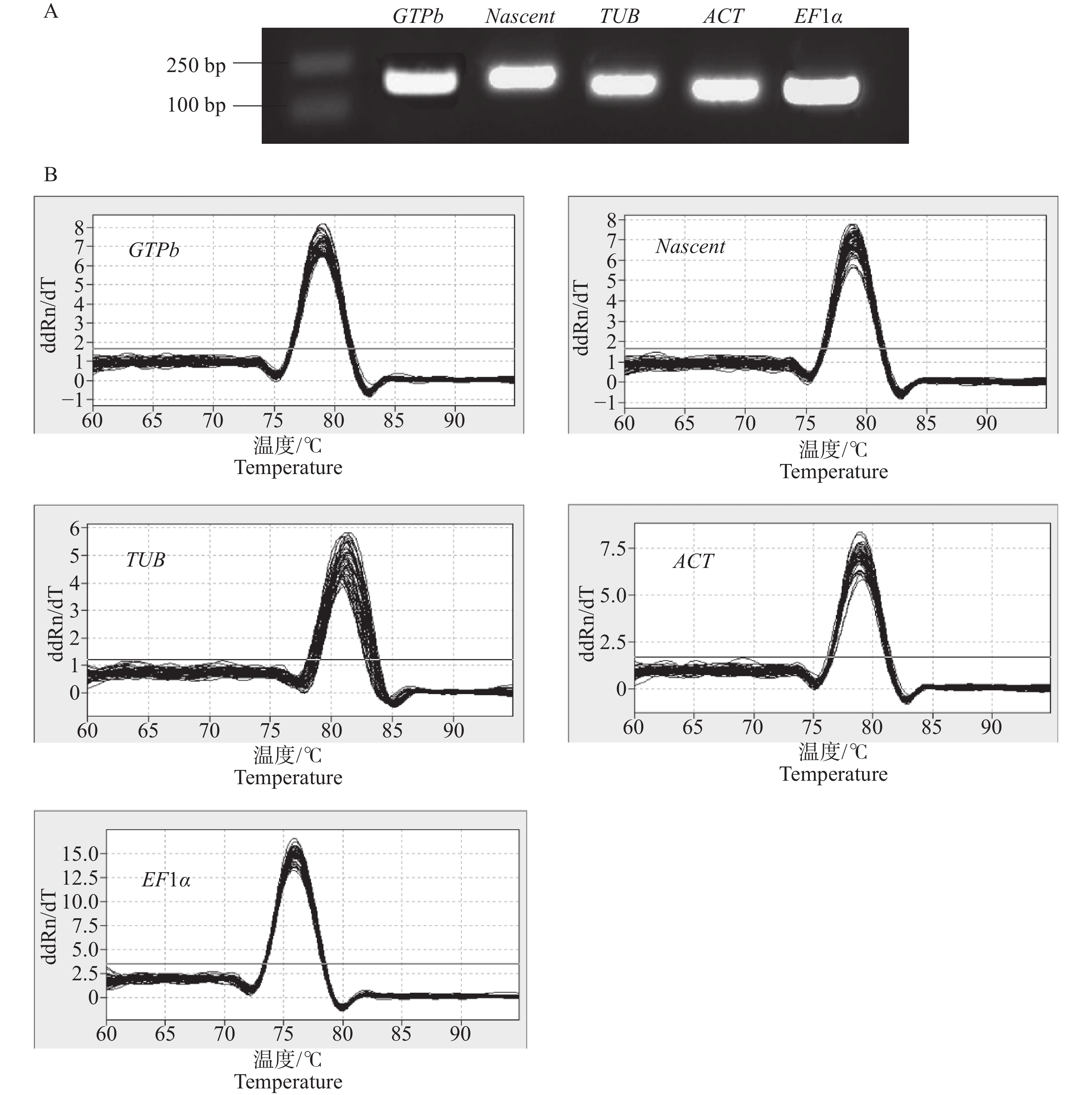
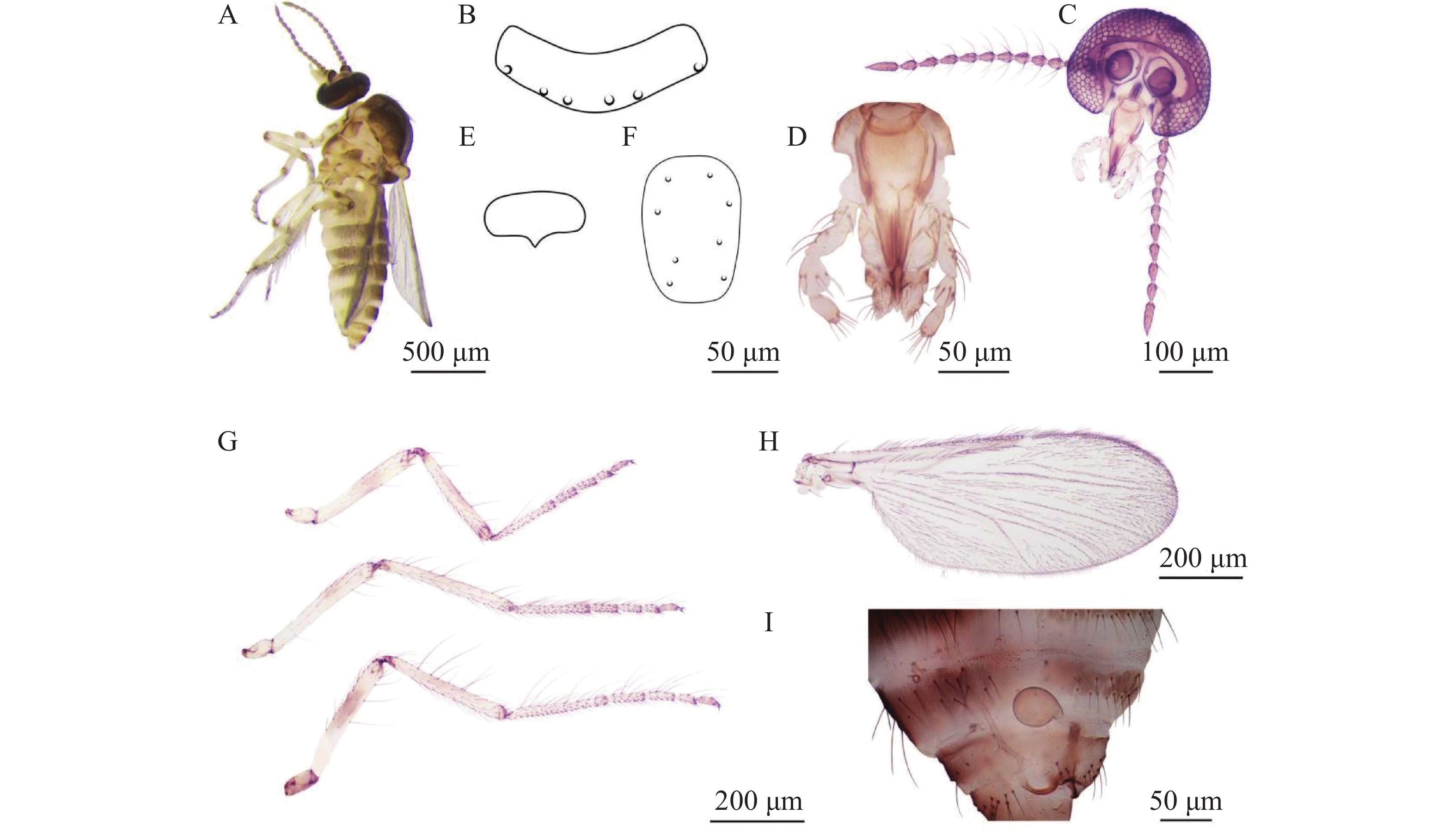

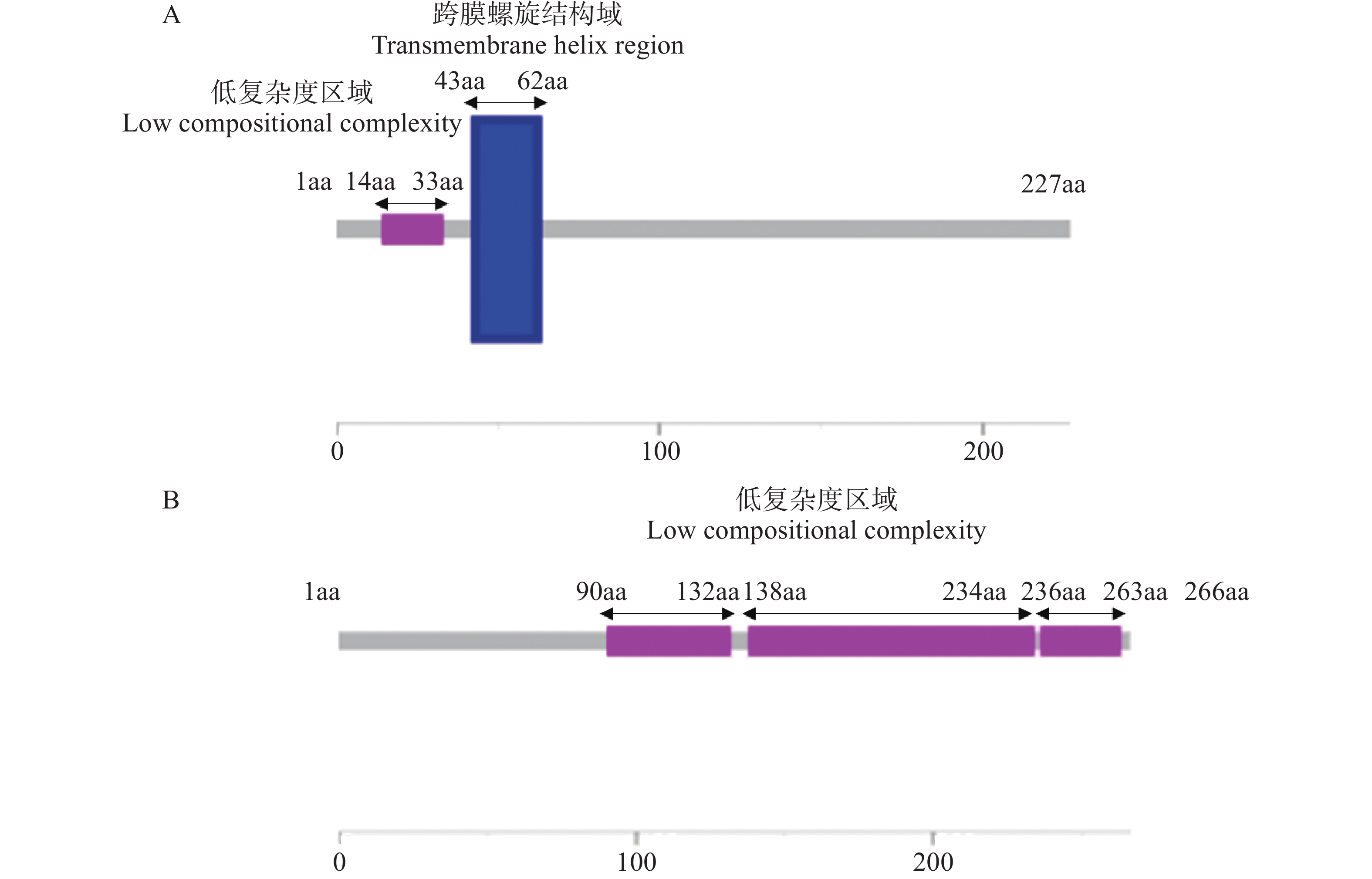
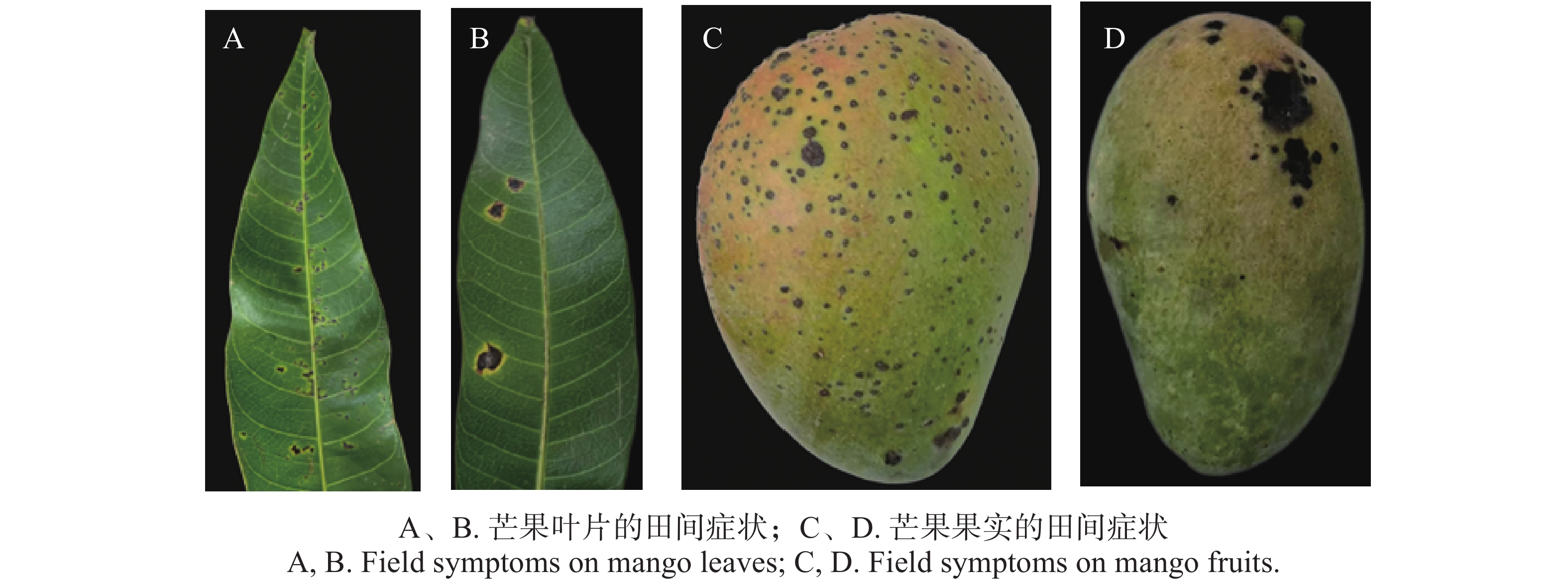
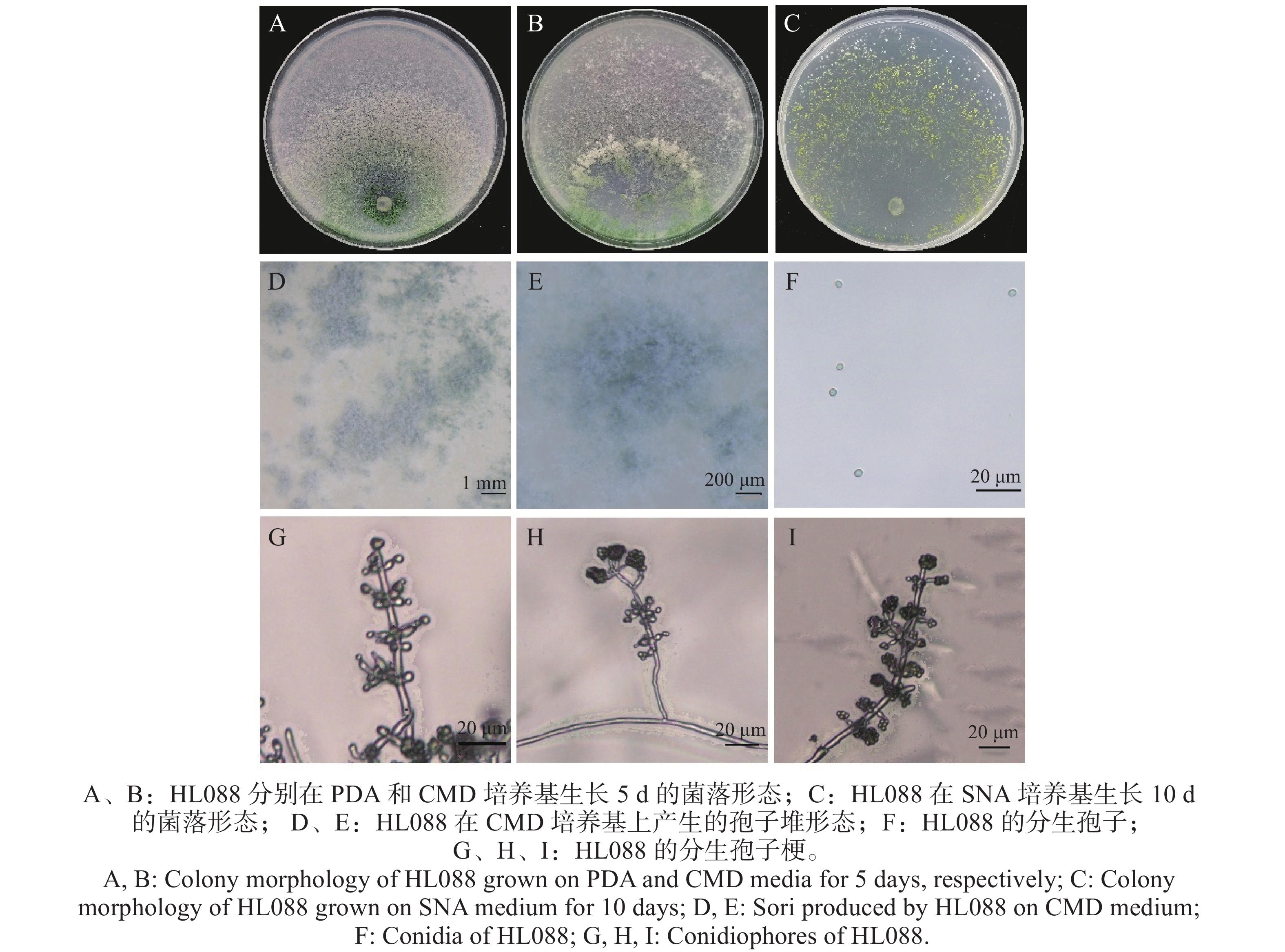
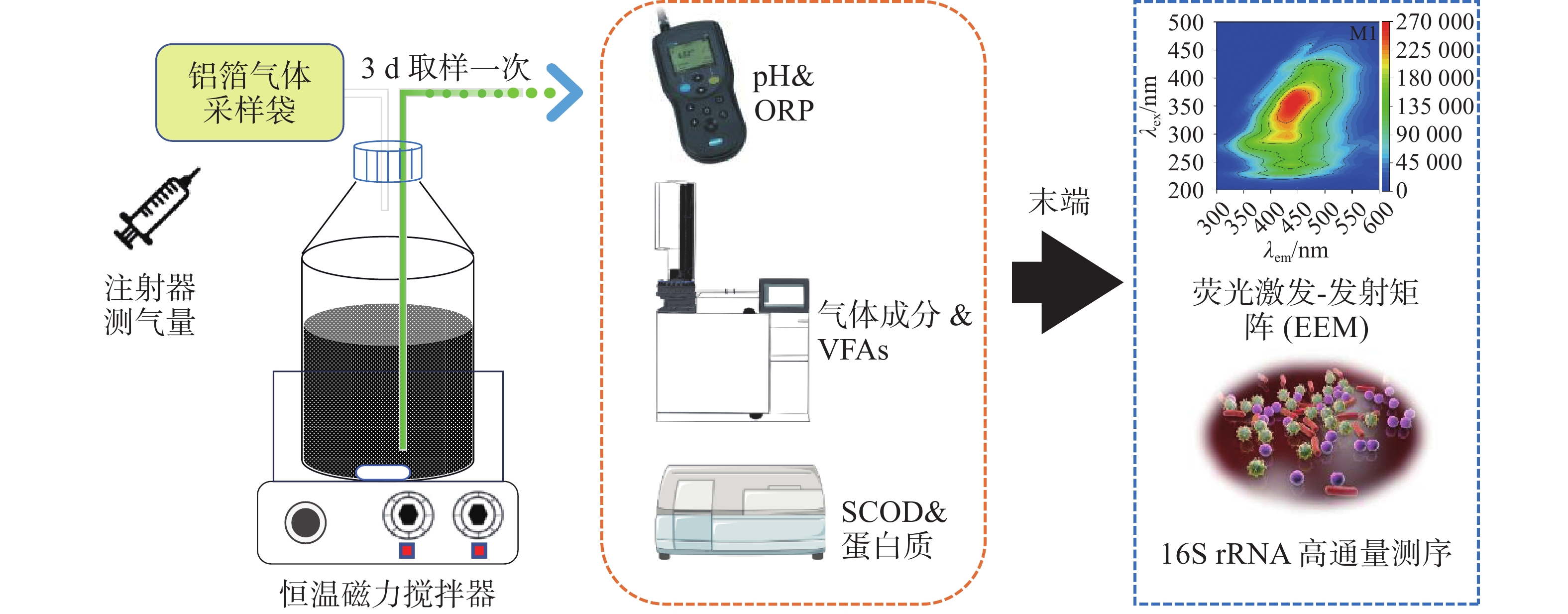
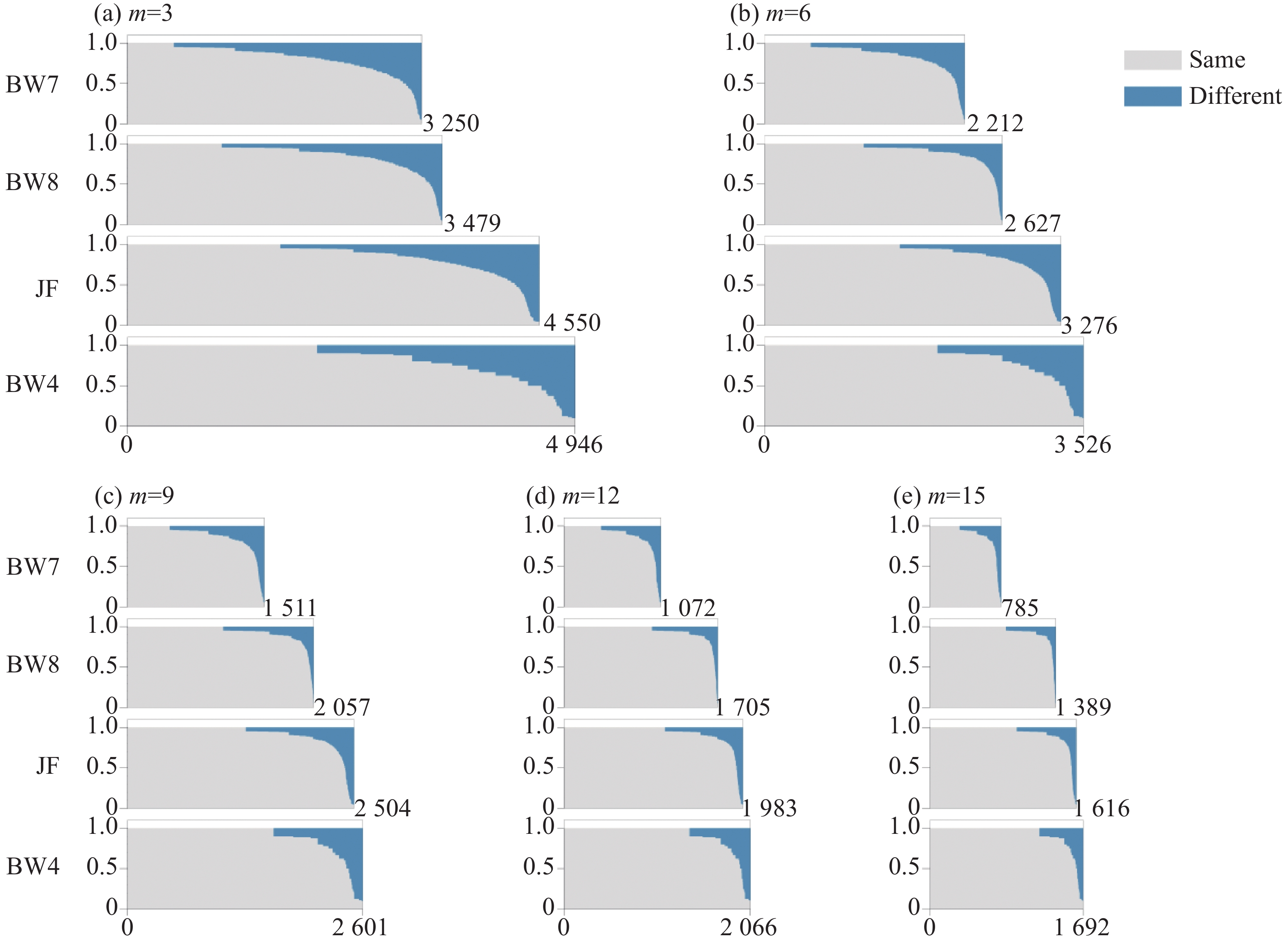





 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS