Current Issue
2026 Vol.17 NO.1
2026,
17(1):
1-12.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250075
Abstract:
The developmental duration and compound eye characteristics of Megalurothrips usitatus across its life stages were systematically investigated to elucidate the functional roles of opsin genes in M. usitatus. RNA interference (RNAi) was employed to suppress the expression of adult opsin genes Rhodopsin-1 (Rh-1) and Rhodopsin-2 (Rh-2), and the phototactic behavioral responses to 520 nm green light following gene knockdown were quantitatively assessed, along with potential mutual regulatory interactions between Rh-1 and Rh-2. Key findings revealed that compound eyes attained full development exclusively during the adult stage. No significant differences in survival curves (P > 0.05) were observed among adults fed on dsEGFP, dsRh-1, or dsRh-2 at a mass concentration of 100 μg·mL−1 over 24–96 hours. Notably, phototactic choice rates toward green light decreased to 26.67% and 32.00%, respectively at 72 hours after treatment with dsRh-1 and dsRh-2. Gene expression analyses demonstrated no compensatory regulation between Rh-1 and Rh-2, as evidenced by unaltered relative expression levels of Rh-2 following Rh-1 knockdown (P > 0.05), and vice versa. This investigation provides critical empirical data for advancing visual system-based pest management strategies.
The developmental duration and compound eye characteristics of Megalurothrips usitatus across its life stages were systematically investigated to elucidate the functional roles of opsin genes in M. usitatus. RNA interference (RNAi) was employed to suppress the expression of adult opsin genes Rhodopsin-1 (Rh-1) and Rhodopsin-2 (Rh-2), and the phototactic behavioral responses to 520 nm green light following gene knockdown were quantitatively assessed, along with potential mutual regulatory interactions between Rh-1 and Rh-2. Key findings revealed that compound eyes attained full development exclusively during the adult stage. No significant differences in survival curves (P > 0.05) were observed among adults fed on dsEGFP, dsRh-1, or dsRh-2 at a mass concentration of 100 μg·mL−1 over 24–96 hours. Notably, phototactic choice rates toward green light decreased to 26.67% and 32.00%, respectively at 72 hours after treatment with dsRh-1 and dsRh-2. Gene expression analyses demonstrated no compensatory regulation between Rh-1 and Rh-2, as evidenced by unaltered relative expression levels of Rh-2 following Rh-1 knockdown (P > 0.05), and vice versa. This investigation provides critical empirical data for advancing visual system-based pest management strategies.
2026,
17(1):
13-18.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240167
Abstract:
Cardiac fibrosis is an important cause of sudden death in animals with heart disease. Cardiac fibroblast is one of the main cell types involved in cardiac fibrosis. In this study, primary cardiac cells were successfully isolated from cats and successfully cultured in vitro for five generations. The cells were characterized by using cell morphology and molecular biology methods and were found to meet the characteristics of cardiac fibroblasts. After TGFβ1 stimulation, the activated fibroblast marker α-SMA protein increased its expression level after 48 hours of stimulation, indicating that TGFβ1 stimulation promoted the activation of primary cardiac fibroblasts in cats. The results can provide reference for exploring the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis and provide a cytological basis for the study of cardiac fibrosis.
Cardiac fibrosis is an important cause of sudden death in animals with heart disease. Cardiac fibroblast is one of the main cell types involved in cardiac fibrosis. In this study, primary cardiac cells were successfully isolated from cats and successfully cultured in vitro for five generations. The cells were characterized by using cell morphology and molecular biology methods and were found to meet the characteristics of cardiac fibroblasts. After TGFβ1 stimulation, the activated fibroblast marker α-SMA protein increased its expression level after 48 hours of stimulation, indicating that TGFβ1 stimulation promoted the activation of primary cardiac fibroblasts in cats. The results can provide reference for exploring the pathogenesis of cardiac fibrosis and provide a cytological basis for the study of cardiac fibrosis.
2026,
17(1):
19-28.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250107
Abstract:
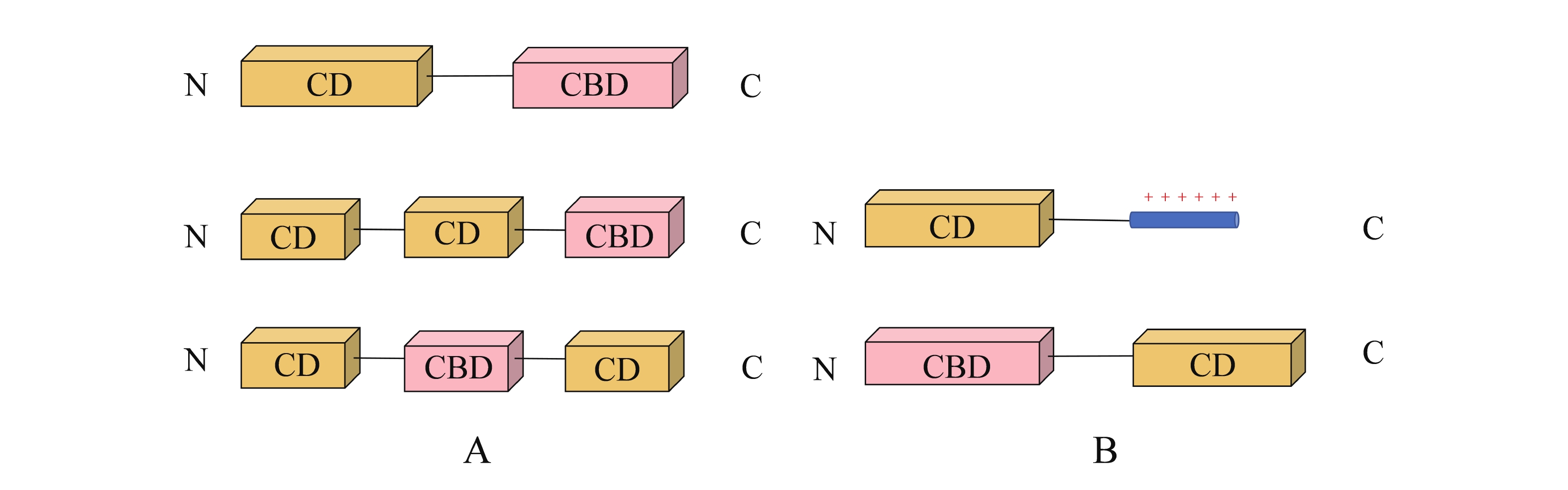
In recent years, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to the problem of bacterial drug resistance, and new safe alternative drugs are urgently needed. Bacteriophage lysin is a peptidoglycan hydrolase encoded by bacteriophages after infestation of host bacteria, which can hydrolyze bacterial peptidoglycan from the inside of bacteria, leading to bacterial rupture, death and release of progeny phage. Bacteriophage lysins have great potential in the treatment of bacterial infections due to their high specificity, efficient lysis, and the fact that they do not easily cause bacterial drug resistance. This article provides a systematic review of the research progress on bacteriophage lysins as novel antimicrobial drugs, focusing on the structural composition, mechanism of action, and engineering modification strategies of bacteriophage lysins, with the aim of providing theoretical basis and technical references for the design of efficient and high-quality novel antimicrobial drugs.
In recent years, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to the problem of bacterial drug resistance, and new safe alternative drugs are urgently needed. Bacteriophage lysin is a peptidoglycan hydrolase encoded by bacteriophages after infestation of host bacteria, which can hydrolyze bacterial peptidoglycan from the inside of bacteria, leading to bacterial rupture, death and release of progeny phage. Bacteriophage lysins have great potential in the treatment of bacterial infections due to their high specificity, efficient lysis, and the fact that they do not easily cause bacterial drug resistance. This article provides a systematic review of the research progress on bacteriophage lysins as novel antimicrobial drugs, focusing on the structural composition, mechanism of action, and engineering modification strategies of bacteriophage lysins, with the aim of providing theoretical basis and technical references for the design of efficient and high-quality novel antimicrobial drugs.
2026,
17(1):
29-38.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240199
Abstract:
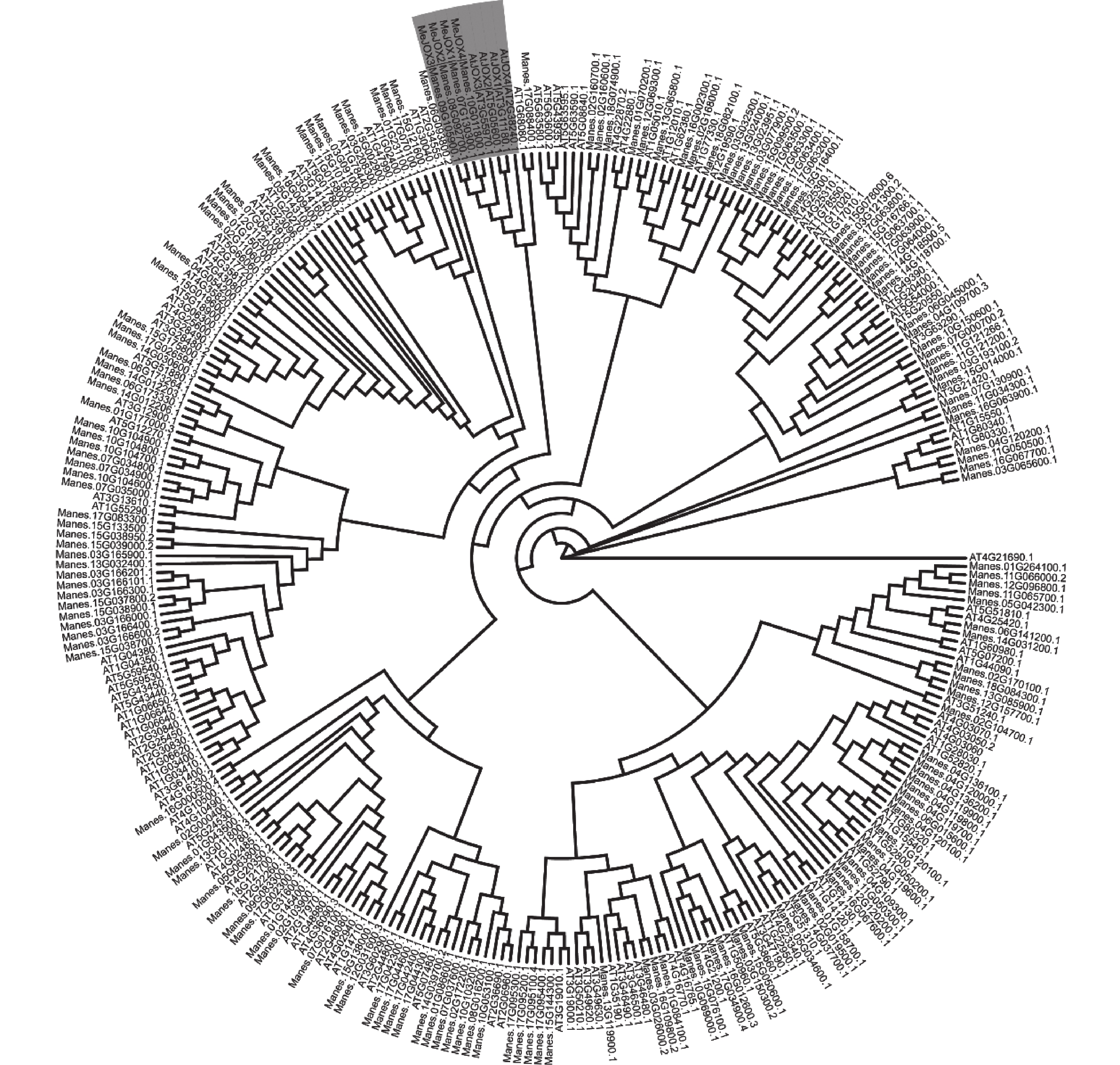
To explore the role of jasmonate-induced oxygenases JOX family genes in the growth, development, and stress resistance of cassava (Manihot esculenta), MeJOXs family members were identified in cassava genome by bioinformatics methods, and their gene structure, promoter cis-acting elements, evolutionary relationships and expression patterns were analyzed. The results showed that there were four MeJOXs family genes in cassava genome, and each member had similar gene structure, conserved motifs, and protein domains. Each gene member exhibited at least 68% protein homology, with the highest similarity observed between MeJOX1 and MeJOX4, as well as between MeJOX2 and MeJOX3. Promoter cis-acting elements analysis showed that MeJOXs contained numerous light-responsive elements. Furthermore, each gene member possessed a varying number of hormone-responsive elements. Phylogenetic analysis showed that MeJOXs were more closely related to JOX genes in dicotyledonous plants. Transcriptome analysis revealed that all the genes were differentially expressed in stems, leaves, midveins, and fibrous roots, with the exception of MeJOX2 that was scarcely expressed in various cassava tissues. MeJOXs were induced by MeJA in different cassava germplasm, with MeJOX3 demonstrating the most significant expression by inducing. Upon infection by pathogen Xpm, MeJOX1/3/4 responded promptly, but their response patterns were distinctly different. MeJOX1/3 were upregulated, whereas MeJOX4 exhibited a trend of downregulation, and MeJOX2 exhibited negligible response. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further elucidating the functions of the MeJOXs gene family in cassava.
To explore the role of jasmonate-induced oxygenases JOX family genes in the growth, development, and stress resistance of cassava (Manihot esculenta), MeJOXs family members were identified in cassava genome by bioinformatics methods, and their gene structure, promoter cis-acting elements, evolutionary relationships and expression patterns were analyzed. The results showed that there were four MeJOXs family genes in cassava genome, and each member had similar gene structure, conserved motifs, and protein domains. Each gene member exhibited at least 68% protein homology, with the highest similarity observed between MeJOX1 and MeJOX4, as well as between MeJOX2 and MeJOX3. Promoter cis-acting elements analysis showed that MeJOXs contained numerous light-responsive elements. Furthermore, each gene member possessed a varying number of hormone-responsive elements. Phylogenetic analysis showed that MeJOXs were more closely related to JOX genes in dicotyledonous plants. Transcriptome analysis revealed that all the genes were differentially expressed in stems, leaves, midveins, and fibrous roots, with the exception of MeJOX2 that was scarcely expressed in various cassava tissues. MeJOXs were induced by MeJA in different cassava germplasm, with MeJOX3 demonstrating the most significant expression by inducing. Upon infection by pathogen Xpm, MeJOX1/3/4 responded promptly, but their response patterns were distinctly different. MeJOX1/3 were upregulated, whereas MeJOX4 exhibited a trend of downregulation, and MeJOX2 exhibited negligible response. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further elucidating the functions of the MeJOXs gene family in cassava.
2026,
17(1):
39-48.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240169
Abstract:
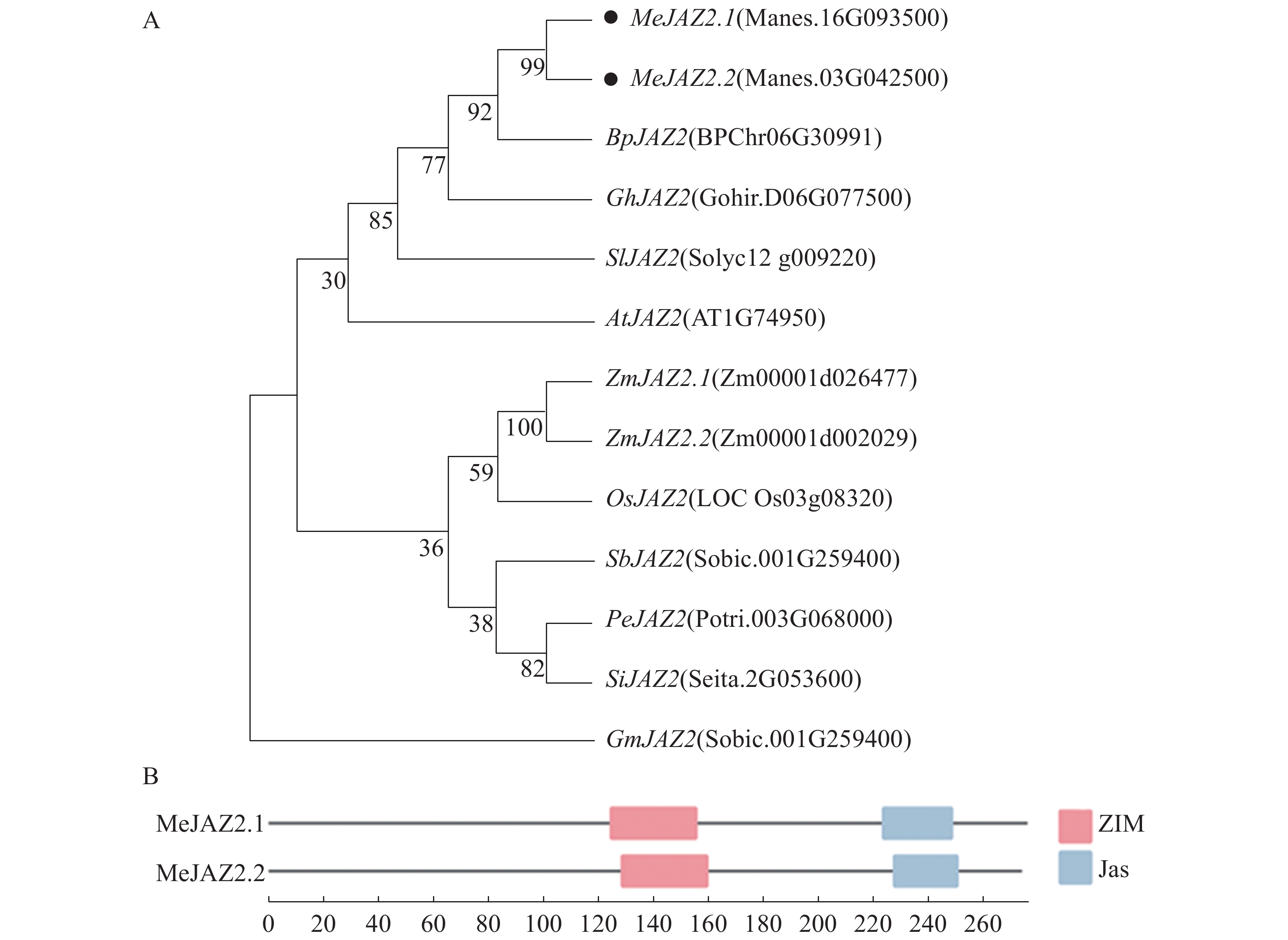
Cassava is an important food crop in tropical regions, but the yield of cassava is affected by salt stress, which endangers food security. JAZ (jasmonate ZIM-domain) proteins, as essential components in the jasmonate signaling pathway, are involved in regulating the tolerance to salt stress in a variety of crops. In order to investigate response of JAZ proteins in cassava to salt stress, as well as the underlying regulatory mechanisms two homologous genes MeJAZ2.1 and MeJAZ2.2 were identified from cassava variety SC124 through bioinformatics. The evolutionary tree and conserved domain analysis indicated that they both contain two conserved domains, ZIM and Jas, which belong to the JAZ gene family. Further research discovered that the expression level of MeJAZ2.2 changed more significantly in response to salt stress in cassava. MeJAZ2.2-silenced cassava plants were more susceptibility to salt stress compared to the wild type, indicating that MeJAZ2.2 may positively regulate cassava resistance to salt stress. The pGADT7-MeJAZ2.2 bait vector was constructed and no self-activating activity was found by yeast two-hybrid experiment. Moreover, three candidate interacting proteins of MeJAZ2.2 were screened, including glutamine synthetase (GS), ubiquitin 3 (Ub3), and FRIGIDA-LIKE PROTEIN (FRI-L), which provides a preliminary framework for analyzing the function and molecular mechanism of JAZ proteins to salt stress in cassava.
Cassava is an important food crop in tropical regions, but the yield of cassava is affected by salt stress, which endangers food security. JAZ (jasmonate ZIM-domain) proteins, as essential components in the jasmonate signaling pathway, are involved in regulating the tolerance to salt stress in a variety of crops. In order to investigate response of JAZ proteins in cassava to salt stress, as well as the underlying regulatory mechanisms two homologous genes MeJAZ2.1 and MeJAZ2.2 were identified from cassava variety SC124 through bioinformatics. The evolutionary tree and conserved domain analysis indicated that they both contain two conserved domains, ZIM and Jas, which belong to the JAZ gene family. Further research discovered that the expression level of MeJAZ2.2 changed more significantly in response to salt stress in cassava. MeJAZ2.2-silenced cassava plants were more susceptibility to salt stress compared to the wild type, indicating that MeJAZ2.2 may positively regulate cassava resistance to salt stress. The pGADT7-MeJAZ2.2 bait vector was constructed and no self-activating activity was found by yeast two-hybrid experiment. Moreover, three candidate interacting proteins of MeJAZ2.2 were screened, including glutamine synthetase (GS), ubiquitin 3 (Ub3), and FRIGIDA-LIKE PROTEIN (FRI-L), which provides a preliminary framework for analyzing the function and molecular mechanism of JAZ proteins to salt stress in cassava.
2026,
17(1):
49-56.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250008
Abstract:
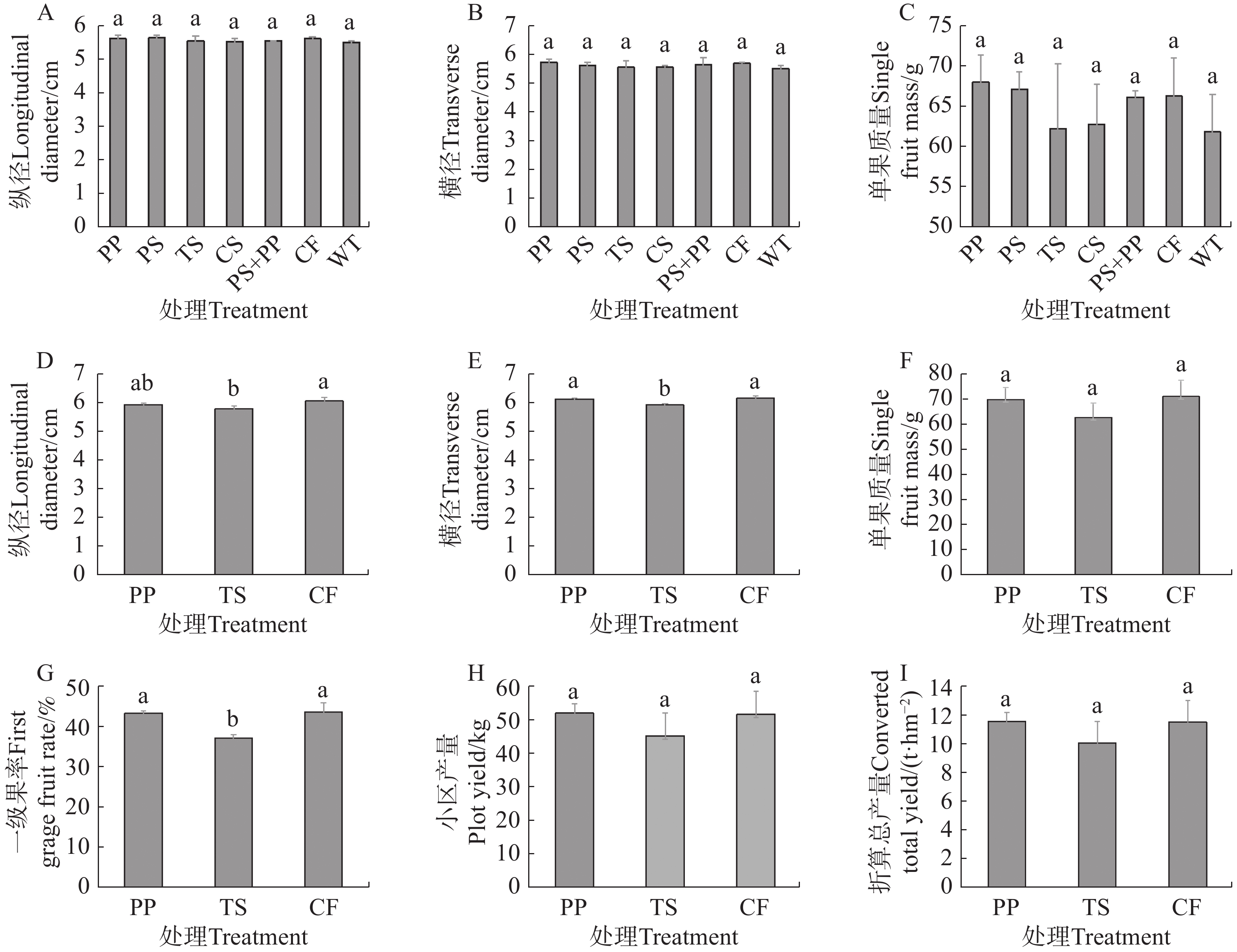
In order to select an agricultural Jiaosu that can effectively improve the quality and yield of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis), passion fruit seedlings were treated with agricultural Jiaosu formulations prepared from four different substrates, namely passion fruit peel, passion fruit straw, cherry tomato straw and corn straw, and chemical fertilizer as control to observe the effects of the treatments on the quality and yield of passion fruits in pot culture under anti-insect net and field experiments. The results showed that the fruit size, single fruit weight and first-class fruit rate of passion fruit under the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment were similar to those of the chemical fertilizer treatment, with the yield being 6.38% higher, and that this Jiaosu treatment was better than other Jiaosu treatments. In terms of quality, the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment significantly increased the content of Ca and total sugar in juice, decreased the content of organic acid, and had the highest TSS-TA ratio and sugar-acid ratio, and this treatment was better than the passion fruit straw Jiaosu and corn straw Jiaosu treatments. The cherry tomato straw Jiaosu treatment significantly increased the contents of Fe, Zn, total organic acids, total amino acids and vitamin C in the fruit. However, the fruits in this treatment were low in TSS-TA ratio and sugar-acid ratio due to the high acid content, and hence were poor in comprehensive quality. Based on the data of 2 years of experiments, the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment had the best effects on improving the comprehensive quality and yield of passion fruits, and the fruits under this treatment had a higher commercial value, which was suggested to be the best treatment.
In order to select an agricultural Jiaosu that can effectively improve the quality and yield of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis), passion fruit seedlings were treated with agricultural Jiaosu formulations prepared from four different substrates, namely passion fruit peel, passion fruit straw, cherry tomato straw and corn straw, and chemical fertilizer as control to observe the effects of the treatments on the quality and yield of passion fruits in pot culture under anti-insect net and field experiments. The results showed that the fruit size, single fruit weight and first-class fruit rate of passion fruit under the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment were similar to those of the chemical fertilizer treatment, with the yield being 6.38% higher, and that this Jiaosu treatment was better than other Jiaosu treatments. In terms of quality, the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment significantly increased the content of Ca and total sugar in juice, decreased the content of organic acid, and had the highest TSS-TA ratio and sugar-acid ratio, and this treatment was better than the passion fruit straw Jiaosu and corn straw Jiaosu treatments. The cherry tomato straw Jiaosu treatment significantly increased the contents of Fe, Zn, total organic acids, total amino acids and vitamin C in the fruit. However, the fruits in this treatment were low in TSS-TA ratio and sugar-acid ratio due to the high acid content, and hence were poor in comprehensive quality. Based on the data of 2 years of experiments, the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment had the best effects on improving the comprehensive quality and yield of passion fruits, and the fruits under this treatment had a higher commercial value, which was suggested to be the best treatment.
2026,
17(1):
57-65.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240074
Abstract:
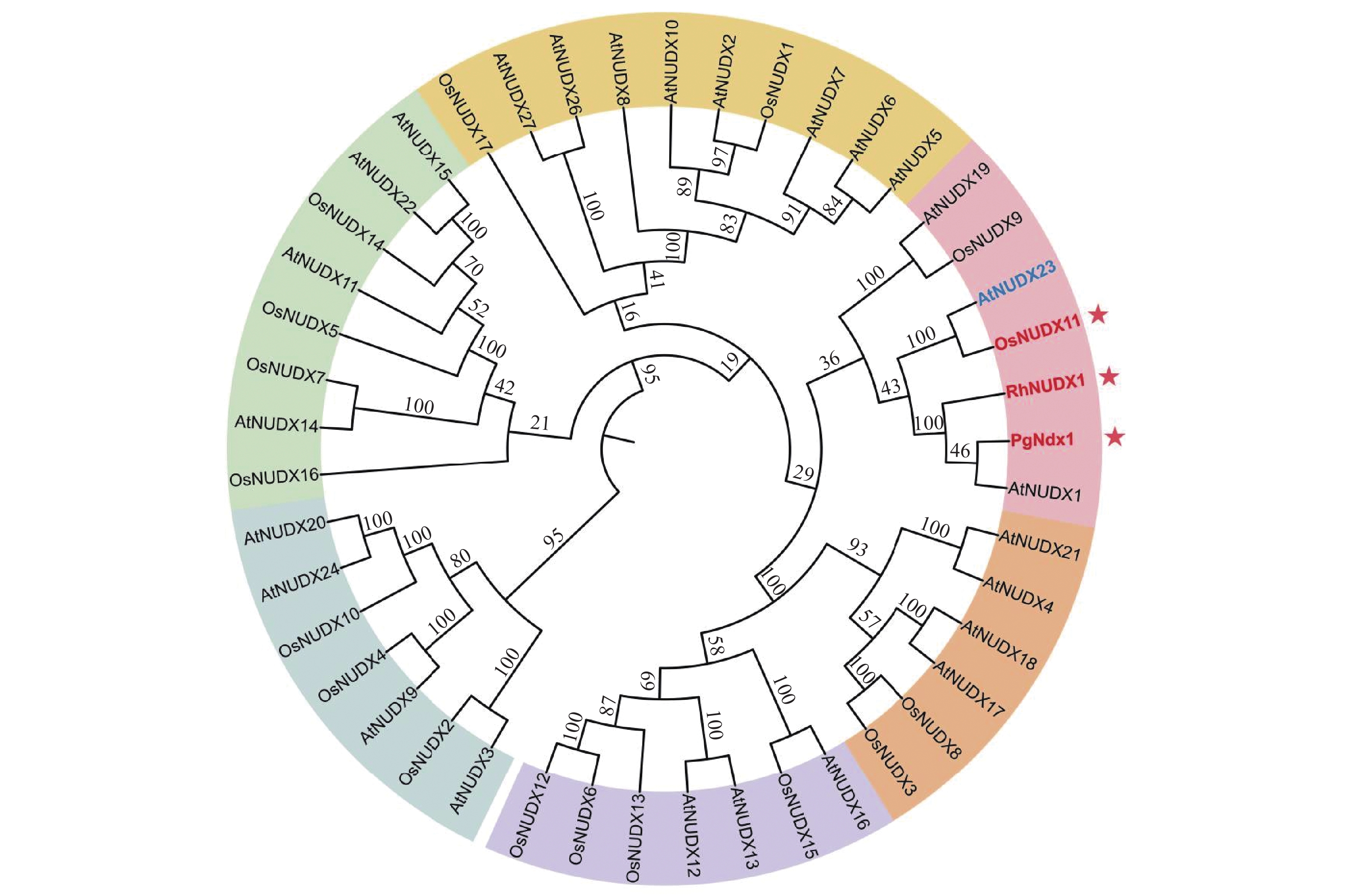
Fragrant rice has long been cherished for its superior quality, potent aroma, delicate flavor, and pleasant texture. Geraniol, a valuable monoterpene with a rose-like odor, exhibits a broad spectrum of medicinal and physiological activities. Despite its popularity, fragrant rice varieties typically contain low levels of geraniol, and the biochemical function of geraniol synthase in these plants remains undefined. In this context the previously reported geraniol synthase, terpene synthase (TPS), family and the nucleoside diphosphatase X (NUDIX) hydrolase family were employed to select candidate genes for geraniol synthase in rice by using homologous sequence alignment analysis and phylogenetic tree analysis of rice, combined with tissue-specific expression profiles, and OsNUDX11, a member of the NUDIX family that is highly expressed in rice roots and panicles was identified. This gene is closely related to geraniol synthases from Rosa rugosa (rose) and Pelargonium graveolens (geranium). Further analysis of protein physicochemical properties and tobacco transient expression assays confirmed that OsNUDX11 shares consistent subcellular localization with geraniol synthases from rose and geranium. It is, thus, inferred that OsNUDX11 be involved in geraniol biosynthesis, which provides a crucial basis for the large-scale synthesis of geraniol in rice.
Fragrant rice has long been cherished for its superior quality, potent aroma, delicate flavor, and pleasant texture. Geraniol, a valuable monoterpene with a rose-like odor, exhibits a broad spectrum of medicinal and physiological activities. Despite its popularity, fragrant rice varieties typically contain low levels of geraniol, and the biochemical function of geraniol synthase in these plants remains undefined. In this context the previously reported geraniol synthase, terpene synthase (TPS), family and the nucleoside diphosphatase X (NUDIX) hydrolase family were employed to select candidate genes for geraniol synthase in rice by using homologous sequence alignment analysis and phylogenetic tree analysis of rice, combined with tissue-specific expression profiles, and OsNUDX11, a member of the NUDIX family that is highly expressed in rice roots and panicles was identified. This gene is closely related to geraniol synthases from Rosa rugosa (rose) and Pelargonium graveolens (geranium). Further analysis of protein physicochemical properties and tobacco transient expression assays confirmed that OsNUDX11 shares consistent subcellular localization with geraniol synthases from rose and geranium. It is, thus, inferred that OsNUDX11 be involved in geraniol biosynthesis, which provides a crucial basis for the large-scale synthesis of geraniol in rice.
2026,
17(1):
66-74.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250012
Abstract:
In order to improve the propagation efficiency of Curcuma wenyujin plants, tissue cultured plants of C. wenyujin was cultured on in vitro rooting medium (1/2MS + NAA 0.5 mg·L−1) supplemented with broad spectrum plant growth regulators, choline chloride (CC) and compound sodium nitrophenolate (CSN), at different mass concentrations and ratios to induce the differentiation of their microrhizomes, and the growth status of the tissue-cultured plants after transplantation was observed. The results showed that the tissue cultured plants cultured on the medium supplemented with a combination of CC at 1.0 mg·L−1 and CSN at 2.0 mg·L−1 were induced to form microrhizomes obviously, with an inducing rate of 62%. In the medium supplemented with a combination of CC at 3.0 mg·L−1 and CSN at 1.0 mg·L−1, the induction rate was 46%, but the swelling and thickening of microrhizomes were the most obvious, with a transverse diameter of about 6.8 mm. There was no significant difference in the length of microrhizomes between the two groups. All the tissue-cultured rooted plants with microrhizomes survived after transplantation, and their survival rate, growth rate, tiller number, number of new leaves, and the weights of tuberous roots and rhizomes increased by 36.4%, 112.5%, 83.0%, 103.9%, and 83.2%, respectively compared with the control tissue-cultured rooted plants.
In order to improve the propagation efficiency of Curcuma wenyujin plants, tissue cultured plants of C. wenyujin was cultured on in vitro rooting medium (1/2MS + NAA 0.5 mg·L−1) supplemented with broad spectrum plant growth regulators, choline chloride (CC) and compound sodium nitrophenolate (CSN), at different mass concentrations and ratios to induce the differentiation of their microrhizomes, and the growth status of the tissue-cultured plants after transplantation was observed. The results showed that the tissue cultured plants cultured on the medium supplemented with a combination of CC at 1.0 mg·L−1 and CSN at 2.0 mg·L−1 were induced to form microrhizomes obviously, with an inducing rate of 62%. In the medium supplemented with a combination of CC at 3.0 mg·L−1 and CSN at 1.0 mg·L−1, the induction rate was 46%, but the swelling and thickening of microrhizomes were the most obvious, with a transverse diameter of about 6.8 mm. There was no significant difference in the length of microrhizomes between the two groups. All the tissue-cultured rooted plants with microrhizomes survived after transplantation, and their survival rate, growth rate, tiller number, number of new leaves, and the weights of tuberous roots and rhizomes increased by 36.4%, 112.5%, 83.0%, 103.9%, and 83.2%, respectively compared with the control tissue-cultured rooted plants.
2026,
17(1):
75-83.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250056
Abstract:
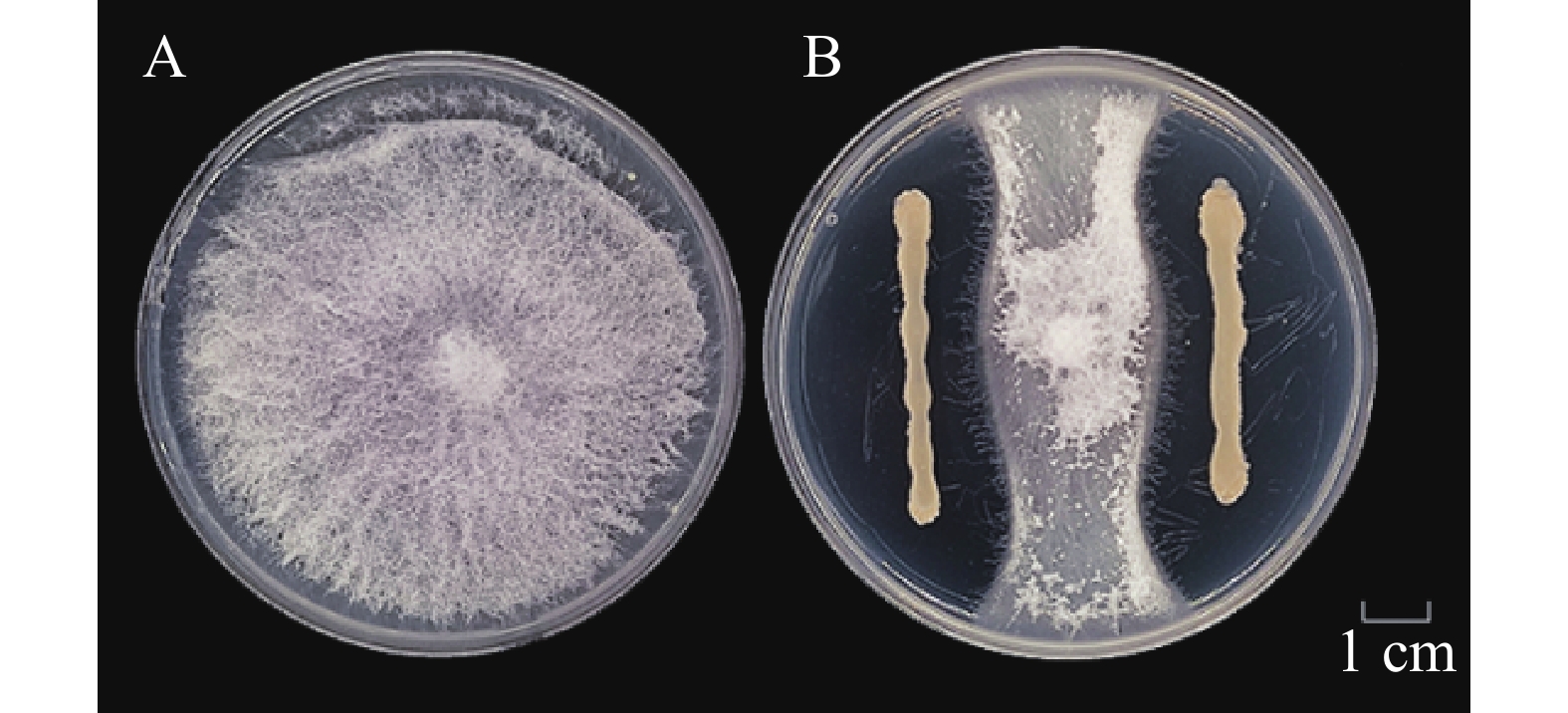
To obtain an efficient biocontrol bacterial strain for managing cucumber Fusarium wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum (Foc), a Bacillus strain (LTB49) with strong antagonistic activity (antagonism rate of 55.26%) was isolated and screened from the rhizosphere soil of cucumber plants affected by the wilt disease, using gradient dilution and plate confrontation methods. The strain was subsequently identified as Bacillus velezensis through morphological, physiological and biochemical tests, and molecular biological techniques. The 10-fold diluted fermentation filtrate of the strain LTB49 showed strong inhibition of mycelial growth of the wilt pathogen, with an inhibition rate of 42.16%, and a significant suppression of spore germination, with an inhibition rate of 90.82%. Pot experiment results demonstrated that the strain LTB49 exhibited good biocontrol efficacy against cucumber wilt disease (43.37%), with no significant difference compared to the commercial biocontrol agent Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 (50.60% efficacy). Further studies revealed that this strain enhanced resistance to the wilt disease by inducing increased activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD), and significantly suppressed the effect of the Fusarium species on cucumber plant growth, particularly dwarfing. These results suggest that B. velezensis LTB49 has a high potential for application in the biocontrol of cucumber wilt disease.
To obtain an efficient biocontrol bacterial strain for managing cucumber Fusarium wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum (Foc), a Bacillus strain (LTB49) with strong antagonistic activity (antagonism rate of 55.26%) was isolated and screened from the rhizosphere soil of cucumber plants affected by the wilt disease, using gradient dilution and plate confrontation methods. The strain was subsequently identified as Bacillus velezensis through morphological, physiological and biochemical tests, and molecular biological techniques. The 10-fold diluted fermentation filtrate of the strain LTB49 showed strong inhibition of mycelial growth of the wilt pathogen, with an inhibition rate of 42.16%, and a significant suppression of spore germination, with an inhibition rate of 90.82%. Pot experiment results demonstrated that the strain LTB49 exhibited good biocontrol efficacy against cucumber wilt disease (43.37%), with no significant difference compared to the commercial biocontrol agent Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 (50.60% efficacy). Further studies revealed that this strain enhanced resistance to the wilt disease by inducing increased activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD), and significantly suppressed the effect of the Fusarium species on cucumber plant growth, particularly dwarfing. These results suggest that B. velezensis LTB49 has a high potential for application in the biocontrol of cucumber wilt disease.
2026,
17(1):
84-90.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250068
Abstract:
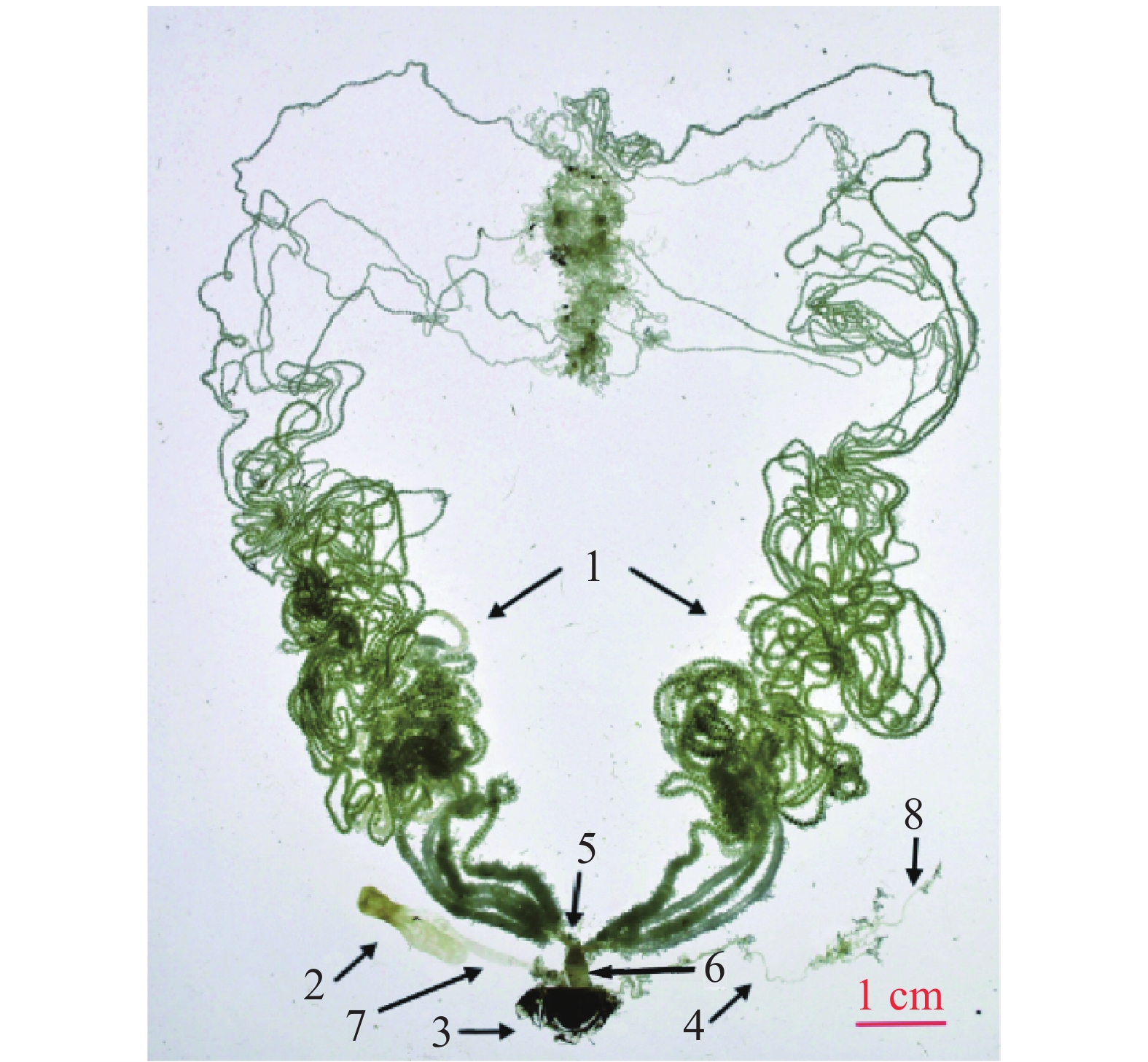
To clarify the structural characteristics and development of the female reproductive system of Endoclita vietnamensis, the main organs of E. vietnamensis and their developmental processes were analyzed through dissection, image acquisition, and structural observation of the reproductive system of female adults. The results indicated that the female reproductive system of E. vietnamensis comprises internal and external genitalia, with the external genitalia including the ovipositor and copulatory bursa, and the internal genitalia including the ovary and oviduct. With an increase in age, significant morphological changes occurred in the copulatory bursa, ovarian tubes, oviducts, and spermatheca of unmated female E. vietnamensis. Moreover, the reproductive system of mated 3-day-old female E. vietnamensis exhibited marked changes, such as thinned ovarian tubes, shrunken oviducts, and reduced fat bodies. These findings provide a scientific basis for understanding of the reproductive characteristics, biology, and occurrence patterns of E. vietnamensis, facilitating further research into its life habits and mating behaviors.
To clarify the structural characteristics and development of the female reproductive system of Endoclita vietnamensis, the main organs of E. vietnamensis and their developmental processes were analyzed through dissection, image acquisition, and structural observation of the reproductive system of female adults. The results indicated that the female reproductive system of E. vietnamensis comprises internal and external genitalia, with the external genitalia including the ovipositor and copulatory bursa, and the internal genitalia including the ovary and oviduct. With an increase in age, significant morphological changes occurred in the copulatory bursa, ovarian tubes, oviducts, and spermatheca of unmated female E. vietnamensis. Moreover, the reproductive system of mated 3-day-old female E. vietnamensis exhibited marked changes, such as thinned ovarian tubes, shrunken oviducts, and reduced fat bodies. These findings provide a scientific basis for understanding of the reproductive characteristics, biology, and occurrence patterns of E. vietnamensis, facilitating further research into its life habits and mating behaviors.
2026,
17(1):
91-100.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250066
Abstract:
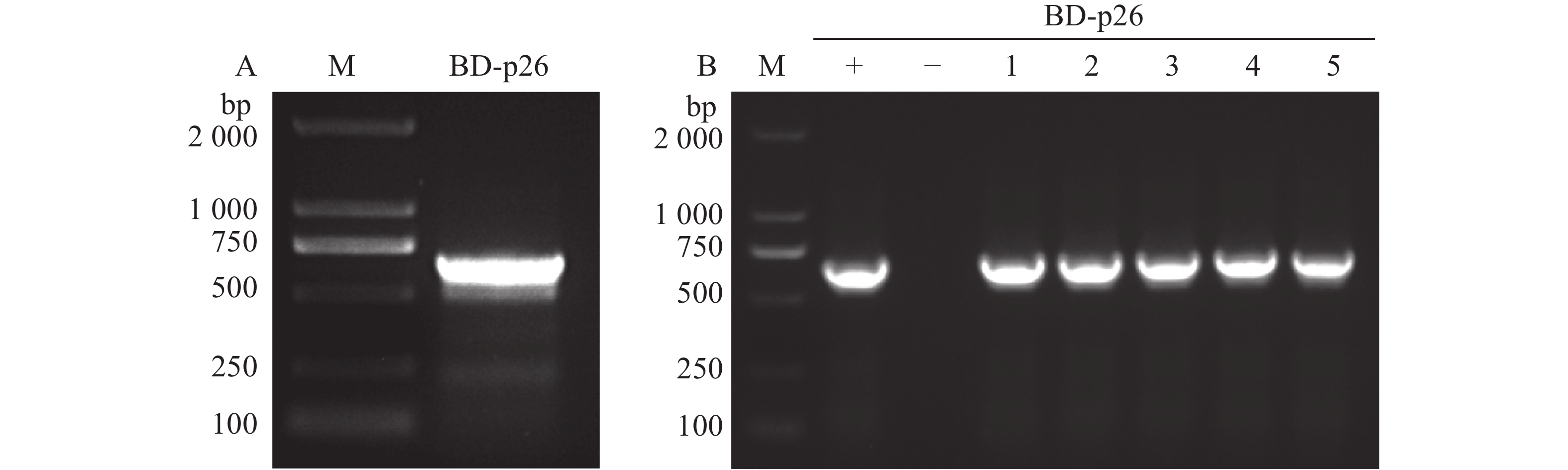
Areca Palm Yellow Leaf Disease, caused by areca palm velarivirus 1 (APV1), poses a severe threat to the areca palm (Areca catechu L.) industry in Hainan. The p26 protein encoded by APV1 plays a critical role in viral infection, yet its interacting host proteins remain unidentified. The yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) technique was employed to screen an Areca palm cDNA library using p26 as the bait to identify interaction partners. The pGBKT7-p26 bait vector was successfully constructed and passed toxicity and autoactivation assays, confirming its suitability for the interaction screening system. Six candidate interacting proteins were identified by library screening, including Ras-related protein RABE1c, chloroplast ferritin-4 (Ferritin-4), oil palm stress-responsive protein PHOS34, and three proteins of unknown function. Following secondary screening and sequencing alignment, the focus was converged on an uncharacterized protein harboring a coiled-coil domain—coiled-coil helix-coiled-coil helix domain-containing 2 (CHCHD2). Retransformation assays confirmed the specific interaction between p26 and CHCHD2 in yeast. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that CHCHD2 has a molecular formula of C628H1007N201O198S8 and a molecular weight of 14.8 kDa. It is predicted to be a hydrophilic, unstable protein, with its secondary structure dominated by random coils. Subcellular localization predictions target CHCHD2 to the chloroplast, and it lacks signal peptides or transmembrane domains. This study reveals an in vitro interaction between APV1 p26 and the host protein CHCHD2, laying the groundwork for elucidating the function of p26 in viral pathogenesis and the CHCHD2-mediated host defense mechanisms.
Areca Palm Yellow Leaf Disease, caused by areca palm velarivirus 1 (APV1), poses a severe threat to the areca palm (Areca catechu L.) industry in Hainan. The p26 protein encoded by APV1 plays a critical role in viral infection, yet its interacting host proteins remain unidentified. The yeast two-hybrid (Y2H) technique was employed to screen an Areca palm cDNA library using p26 as the bait to identify interaction partners. The pGBKT7-p26 bait vector was successfully constructed and passed toxicity and autoactivation assays, confirming its suitability for the interaction screening system. Six candidate interacting proteins were identified by library screening, including Ras-related protein RABE1c, chloroplast ferritin-4 (Ferritin-4), oil palm stress-responsive protein PHOS34, and three proteins of unknown function. Following secondary screening and sequencing alignment, the focus was converged on an uncharacterized protein harboring a coiled-coil domain—coiled-coil helix-coiled-coil helix domain-containing 2 (CHCHD2). Retransformation assays confirmed the specific interaction between p26 and CHCHD2 in yeast. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that CHCHD2 has a molecular formula of C628H1007N201O198S8 and a molecular weight of 14.8 kDa. It is predicted to be a hydrophilic, unstable protein, with its secondary structure dominated by random coils. Subcellular localization predictions target CHCHD2 to the chloroplast, and it lacks signal peptides or transmembrane domains. This study reveals an in vitro interaction between APV1 p26 and the host protein CHCHD2, laying the groundwork for elucidating the function of p26 in viral pathogenesis and the CHCHD2-mediated host defense mechanisms.
2026,
17(1):
101-107.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240135
Abstract:
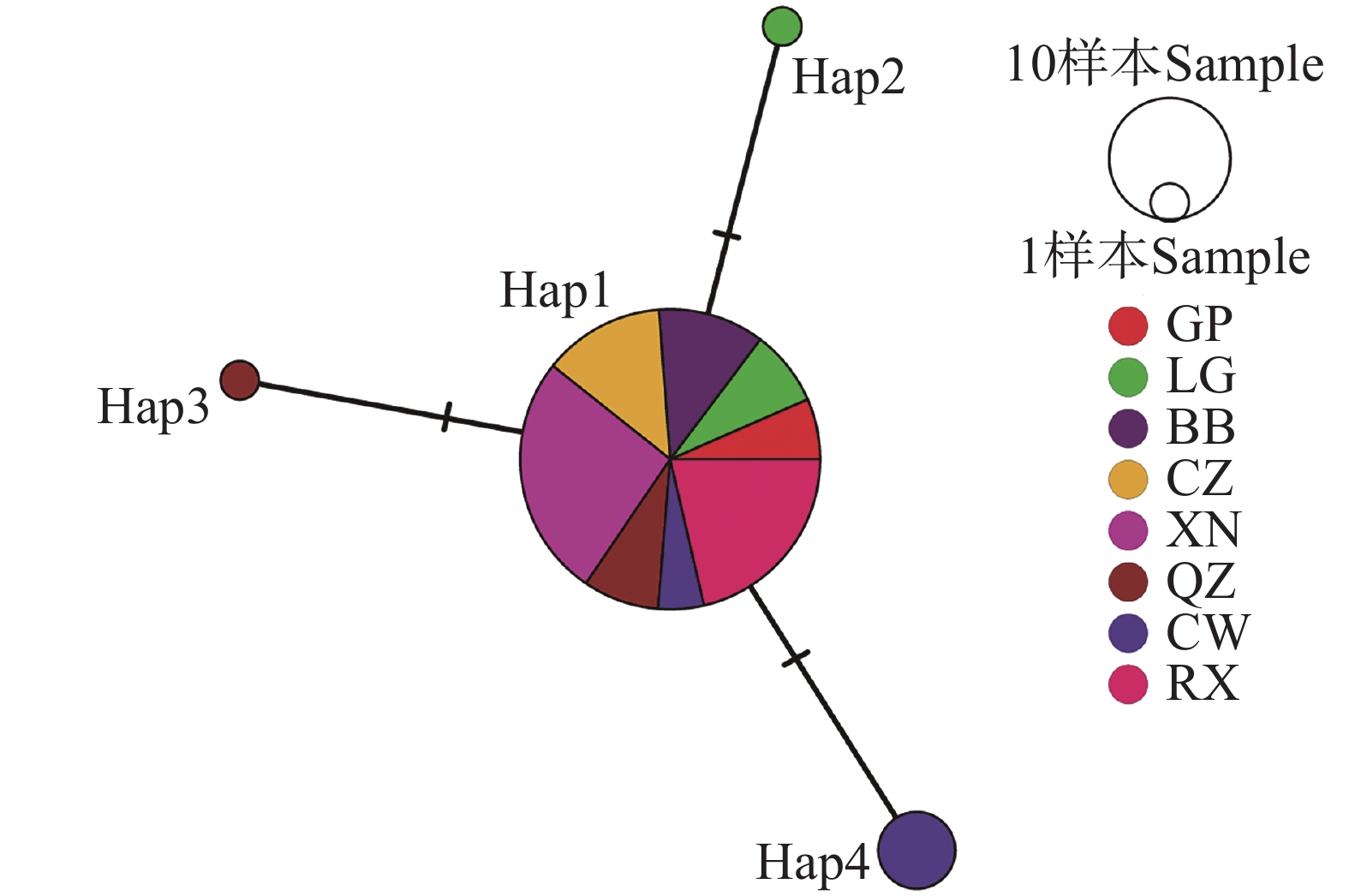
An attempt was made to investigate the genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, the causative agent of pine wilt disease, which is posing a severe threat to the forest ecosystem and economic development in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Sixty seven strains of B. xylophilus collected from eight different districts/counties within Guangxi were analyzed by using the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit Ⅰ (mt COⅠ) gene fragment. The results indicated that there were three polymorphic sites and one parsimony-informative site within a 647 bp region, with genetic diversity indices at extremely low levels. Four haplotypes of B. xylophilus were identified in Guangxi, with an overall haplotype diversity of 0.170, where Hap1 was the predominant haplotype. The B. xylophilus strains in Guangxi were clearly distinct from those found in other regions both domestically and internationally, forming an independent branch. In recent years, the spread of B. xylophilus in Guangxi occurred primarily through natural dispersion. All these findings might provide a theoretical basis for developing targeted prevention and control strategies for B. xylophilus in Guangxi.
An attempt was made to investigate the genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, the causative agent of pine wilt disease, which is posing a severe threat to the forest ecosystem and economic development in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Sixty seven strains of B. xylophilus collected from eight different districts/counties within Guangxi were analyzed by using the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit Ⅰ (mt COⅠ) gene fragment. The results indicated that there were three polymorphic sites and one parsimony-informative site within a 647 bp region, with genetic diversity indices at extremely low levels. Four haplotypes of B. xylophilus were identified in Guangxi, with an overall haplotype diversity of 0.170, where Hap1 was the predominant haplotype. The B. xylophilus strains in Guangxi were clearly distinct from those found in other regions both domestically and internationally, forming an independent branch. In recent years, the spread of B. xylophilus in Guangxi occurred primarily through natural dispersion. All these findings might provide a theoretical basis for developing targeted prevention and control strategies for B. xylophilus in Guangxi.
2026,
17(1):
108-116.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250060
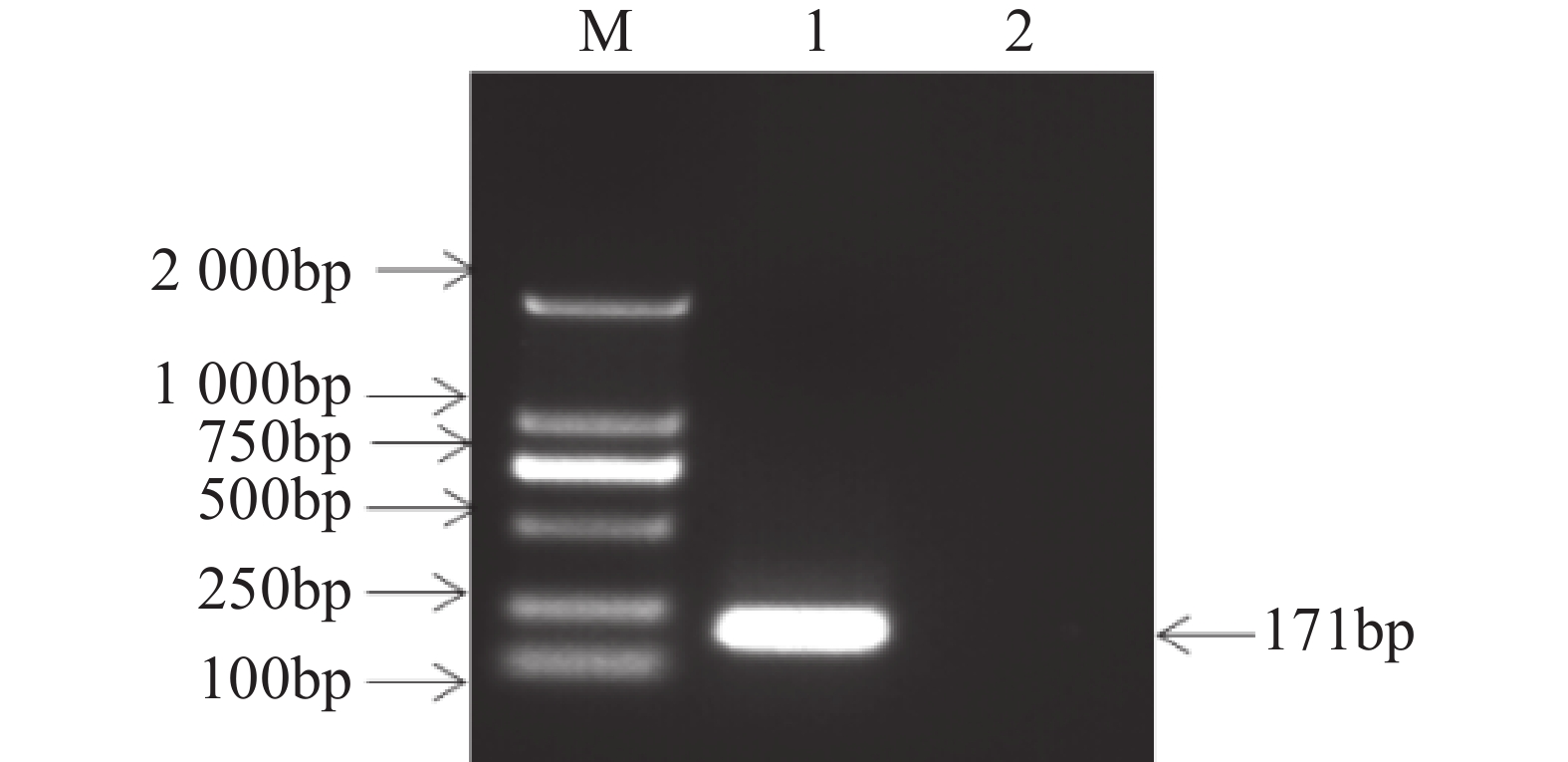
Abstract:
An attempt was made to establish an absolute quantitative real-time PCR method for the detection of sugarcane baculovirus (SCBV) to determine the load of SCBV in different tissue parts of sugarcane. Specific amplification primers were designed from the conserved region of the SCBV genome (SCBV-ORF1), and the recombinant plasmid pMD19T-SCBV-P1 was constructed as a positive plasmid standard and used as a template to establish an absolute quantitative real-time PCR detection method for SCBV. This established detection method was tested in sensitivity, specificity and stability and then used to determine the SCBV load in different tissues of sugarcane germplasm. The recombinant plasmid containing the SCBV genomic sequence was diluted 10 times into a standard, and it was used as a template for quantitative real-time PCR. The standard curve y =3.3397 × LOG(x) + 32.05 was obtained, and the correlation coefficient r2=0.999. The Cq value was linearly related to the logarithm of the copy number of the standard concentration. The absolute quantitative real-time PCR method established shows high sensitivity, and its lower limit of detection can reach 7 copies of recombinant plasmid·μL−1. Compared with conventional PCR detection methods, this method is about 100 times higher in sensitivity. The method is highly specific and can specifically detect SCBV, and the method has good repeatability with the coefficient of variation within and between batches being between 0.11% and 0.90%. There were significant differences in SCBV accumulation levels in different tissue parts of sugarcane, with the SCBV load in the fourth leaf significantly higher than that in other tissue parts (P<0.05). The study established an absolute quantitative real-time PCR method that can detect SCBV sensitively and specifically, providing an efficient quantitative detection method for the diagnosis of SCBV, and clarified that the best sampling site for SCBV detection in sugarcane is the fourth leaf.
An attempt was made to establish an absolute quantitative real-time PCR method for the detection of sugarcane baculovirus (SCBV) to determine the load of SCBV in different tissue parts of sugarcane. Specific amplification primers were designed from the conserved region of the SCBV genome (SCBV-ORF1), and the recombinant plasmid pMD19T-SCBV-P1 was constructed as a positive plasmid standard and used as a template to establish an absolute quantitative real-time PCR detection method for SCBV. This established detection method was tested in sensitivity, specificity and stability and then used to determine the SCBV load in different tissues of sugarcane germplasm. The recombinant plasmid containing the SCBV genomic sequence was diluted 10 times into a standard, and it was used as a template for quantitative real-time PCR. The standard curve y =
2026,
17(1):
117-127.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240139
Abstract:
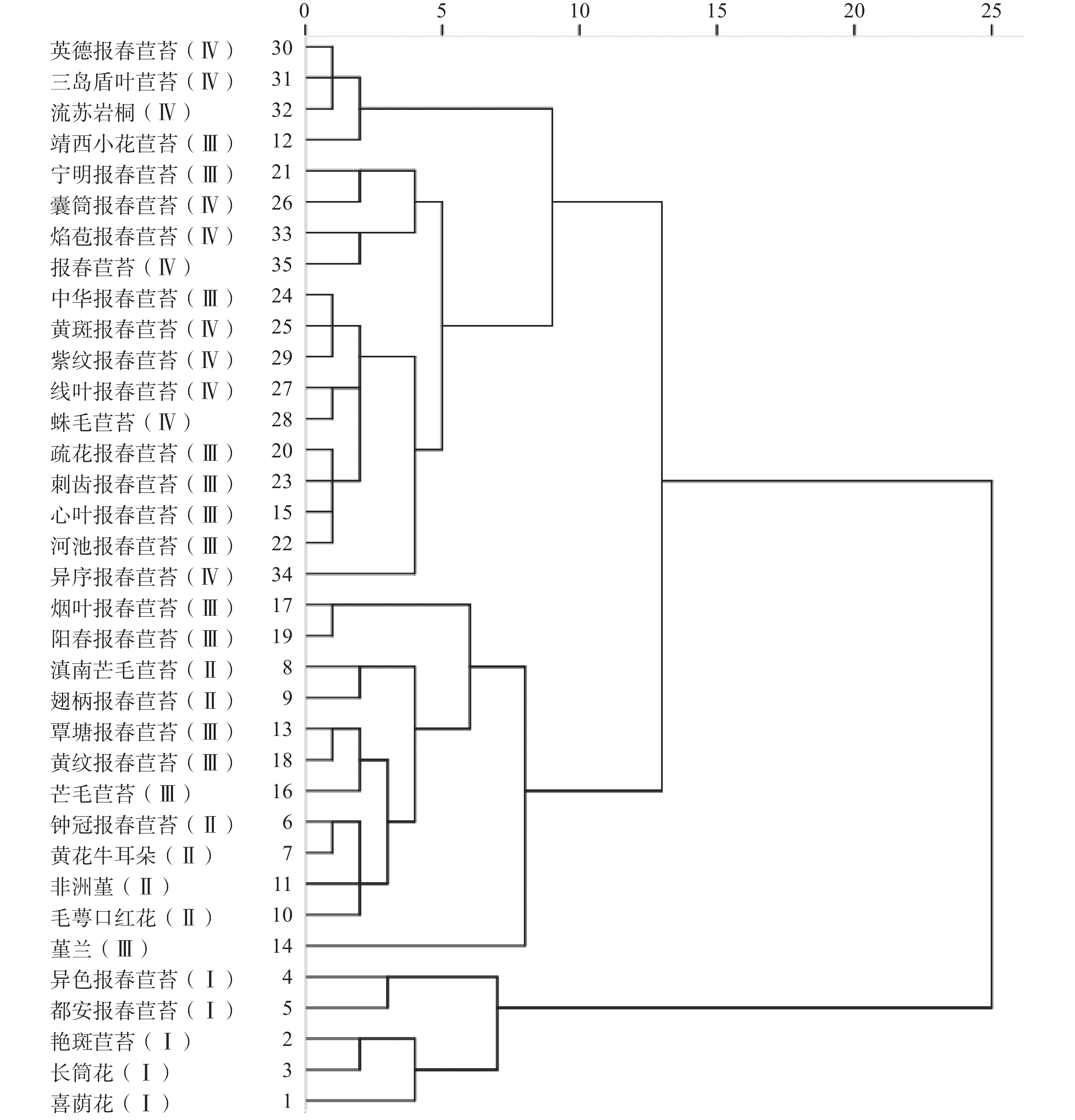
To scientifically evaluate the ornamental traits of Gesneriaceae plants, 35 species of Gesneriaceae plants were selected to establish a comprehensive evaluation system for the ornamental traits of the Gesneriaceae plants by employing the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). In this system 15 specific indicators were selected for assessment across four dimensions, i.e. floral characteristics, foliar features, plant architecture, and cultivation performance. The results showed that all the 35 species could be classified into four grades. The species in Grade I achieved the highest composite scores and ornamental value, comprising five species from four genera: Episcia cupreatasri, Kohleria bogotensis, Achimenes erecta, Primulina heterochroa, Primulina duanensis. Cluster analysis categorized the 35 species into five groups based on ornamental traits, with Group 1 containing the same five species identified as Grade I through AHP. This consistency confirms the exceptional ornamental potential of these species, indicating their significant prospects for breeding and horticultural production. These findings provide a foundation for developing proprietary ornamental cultivars with high aesthetic value in China, thereby advancing the horticultural industry of Gesneriaceae.
To scientifically evaluate the ornamental traits of Gesneriaceae plants, 35 species of Gesneriaceae plants were selected to establish a comprehensive evaluation system for the ornamental traits of the Gesneriaceae plants by employing the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). In this system 15 specific indicators were selected for assessment across four dimensions, i.e. floral characteristics, foliar features, plant architecture, and cultivation performance. The results showed that all the 35 species could be classified into four grades. The species in Grade I achieved the highest composite scores and ornamental value, comprising five species from four genera: Episcia cupreatasri, Kohleria bogotensis, Achimenes erecta, Primulina heterochroa, Primulina duanensis. Cluster analysis categorized the 35 species into five groups based on ornamental traits, with Group 1 containing the same five species identified as Grade I through AHP. This consistency confirms the exceptional ornamental potential of these species, indicating their significant prospects for breeding and horticultural production. These findings provide a foundation for developing proprietary ornamental cultivars with high aesthetic value in China, thereby advancing the horticultural industry of Gesneriaceae.
2026,
17(1):
128-135.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250053
Abstract:
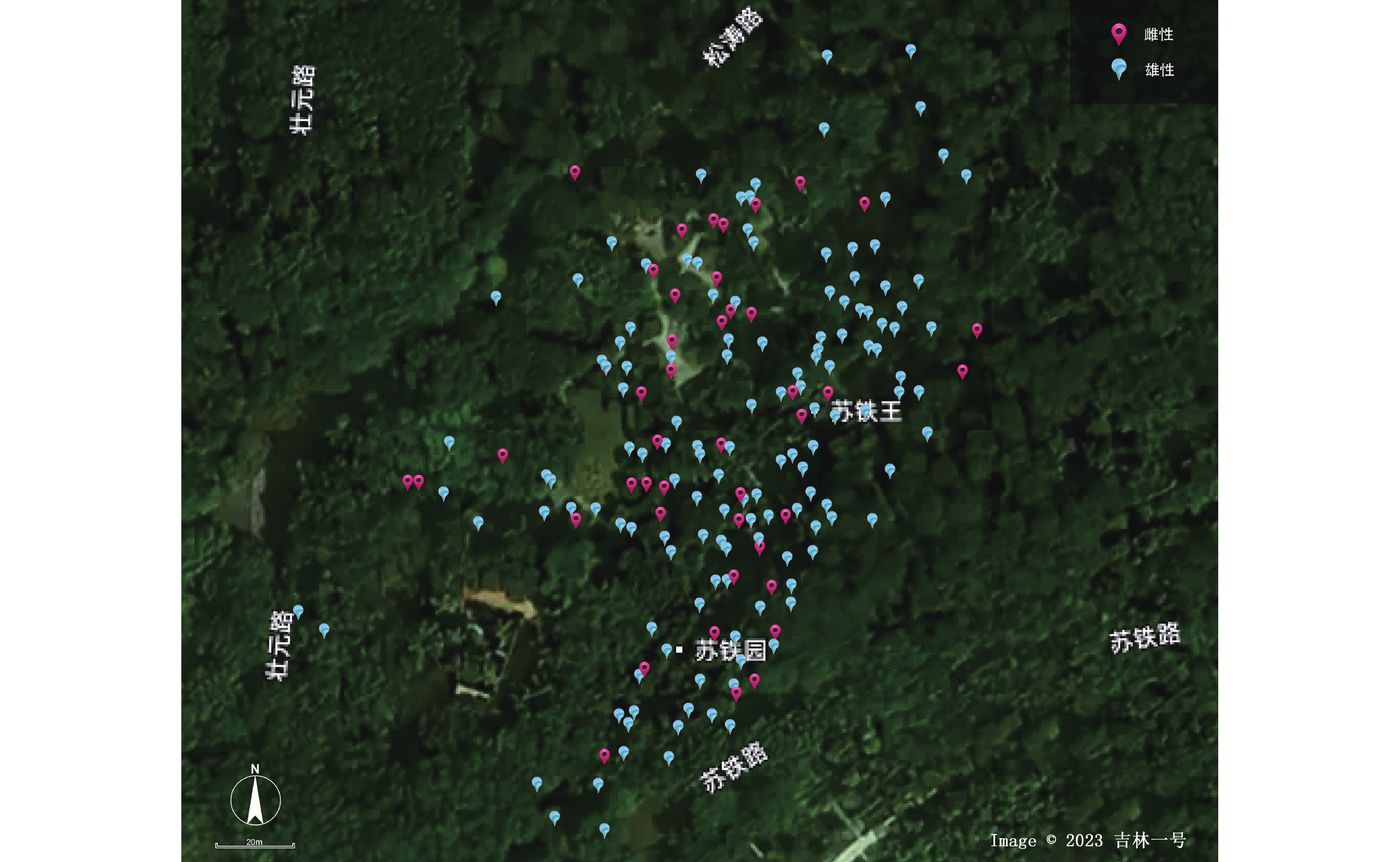
An survey was made of the ex-situ population of ancient plant Cycas pectinata at Nanning Botanical Garden for analysis of the sex ratio and morphological characteristics of this ancient plant, including stem height, diameter at breast height (DBH), crown width, branching, and growth points in an attempt to explore the phenotypic differences in stems between male and female plants, providing a theoretical basis for ex-situ conservation and scientific management. The results revealed a highly significant male-biased sex ratio (1:3.77) in this population. The average stem height of the male plants (452.92 cm) was significantly greater than that of the females (371.36 cm). The female plants had slightly higher DBH and crown width, but the differences were not statistically significant. Branching occurred in 93.18% of the female plants and 98.19% of the males, and 57.23% of the male plants branched more than twice. The male plants had a significantly higher average number of growing points per male plant (3.69) than the female plants (2.03). In conclusion, the male plants of the ancient plant C. pectinata exhibit superiority in stem height, number of growing points, and branching capacity compared to the female plants. In ex situ cultivation, stem traits can be used for preliminary sex determination, and protective measures should be strengthened to prioritize the growth of female plants in the plant management.
An survey was made of the ex-situ population of ancient plant Cycas pectinata at Nanning Botanical Garden for analysis of the sex ratio and morphological characteristics of this ancient plant, including stem height, diameter at breast height (DBH), crown width, branching, and growth points in an attempt to explore the phenotypic differences in stems between male and female plants, providing a theoretical basis for ex-situ conservation and scientific management. The results revealed a highly significant male-biased sex ratio (1:3.77) in this population. The average stem height of the male plants (452.92 cm) was significantly greater than that of the females (371.36 cm). The female plants had slightly higher DBH and crown width, but the differences were not statistically significant. Branching occurred in 93.18% of the female plants and 98.19% of the males, and 57.23% of the male plants branched more than twice. The male plants had a significantly higher average number of growing points per male plant (3.69) than the female plants (2.03). In conclusion, the male plants of the ancient plant C. pectinata exhibit superiority in stem height, number of growing points, and branching capacity compared to the female plants. In ex situ cultivation, stem traits can be used for preliminary sex determination, and protective measures should be strengthened to prioritize the growth of female plants in the plant management.
2026,
17(1):
136-143.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240176
Abstract:
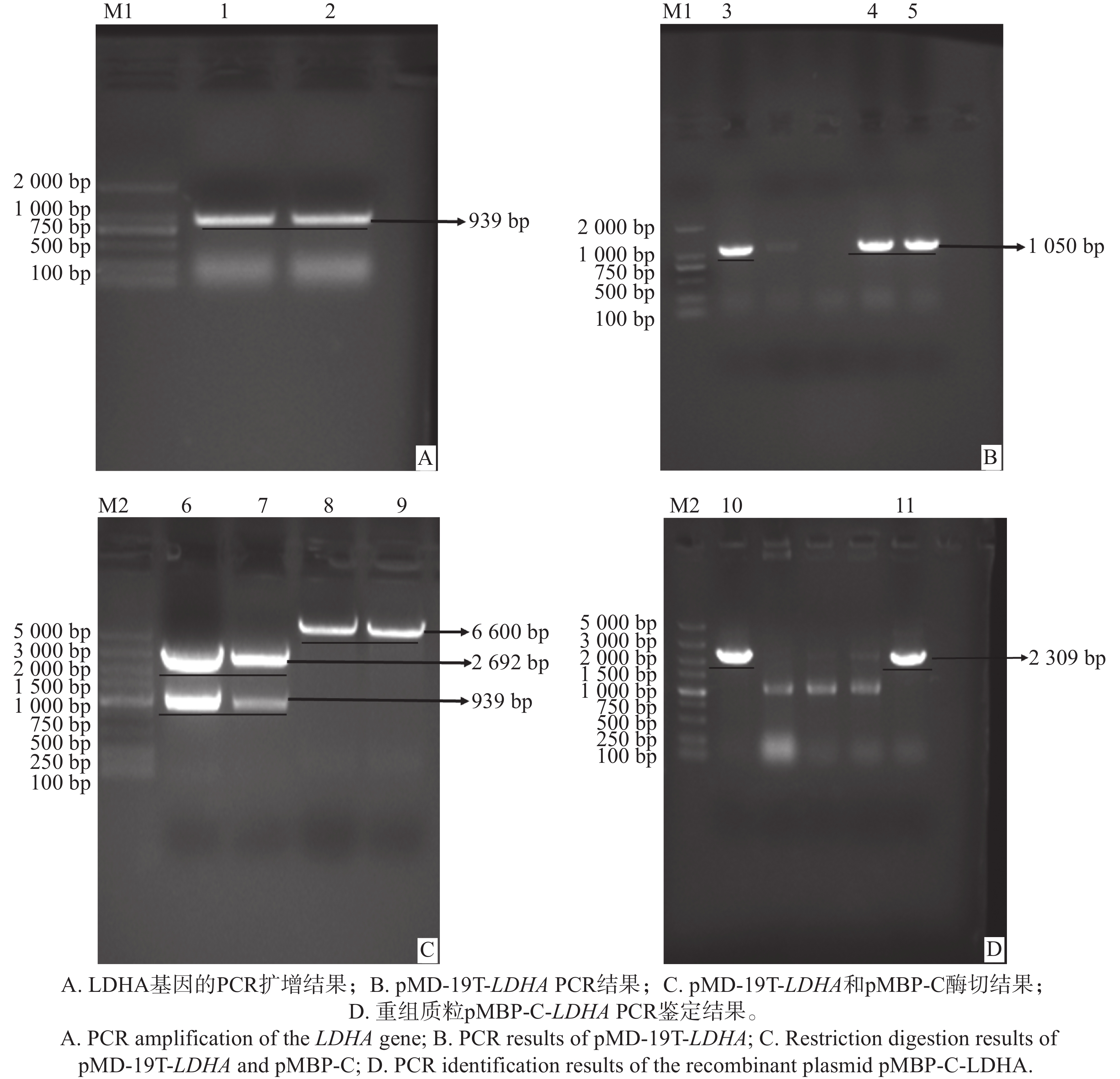
An attempt was made to investigate the expression of lactate dehydrogenase (ptLDHA), a key enzyme in lactate metabolism, and to explore the acetylation modification sites on ptLDHA and their potential role in the interplay between lactylation and acetylation modifications in Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin. The ptLDHA gene sequence was first cloned from P. tricornutum Bohlin cDNA, and then a prokaryotic expression vector, pMBP-C-LDHA, was constructed. The recombinant plasmid was then transferred into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) for induced expression. Under optimized conditions (16 ℃, 0.2 mmol·L−1 IPTG for 24 hours), ptLDHA protein was successfully expressed, predominantly in a soluble form. The fusion protein was purified using His-tag affinity chromatography and identified by Western blot with ptLDHA polyclonal antibodies. A single protein band at approximately 78 kDa was observed, confirming that the purified protein was ptLDHA. The expression and purification of ptLDHA in prokaryotic cells was successfully established, laying foundations for subsequent site-directed mutagenesis of acetylation modification sites and for investigation of the effects of modification and demodification on enzyme activity.
An attempt was made to investigate the expression of lactate dehydrogenase (ptLDHA), a key enzyme in lactate metabolism, and to explore the acetylation modification sites on ptLDHA and their potential role in the interplay between lactylation and acetylation modifications in Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin. The ptLDHA gene sequence was first cloned from P. tricornutum Bohlin cDNA, and then a prokaryotic expression vector, pMBP-C-LDHA, was constructed. The recombinant plasmid was then transferred into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) for induced expression. Under optimized conditions (16 ℃, 0.2 mmol·L−1 IPTG for 24 hours), ptLDHA protein was successfully expressed, predominantly in a soluble form. The fusion protein was purified using His-tag affinity chromatography and identified by Western blot with ptLDHA polyclonal antibodies. A single protein band at approximately 78 kDa was observed, confirming that the purified protein was ptLDHA. The expression and purification of ptLDHA in prokaryotic cells was successfully established, laying foundations for subsequent site-directed mutagenesis of acetylation modification sites and for investigation of the effects of modification and demodification on enzyme activity.
2026,
17(1):
144-154.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240142
Abstract:
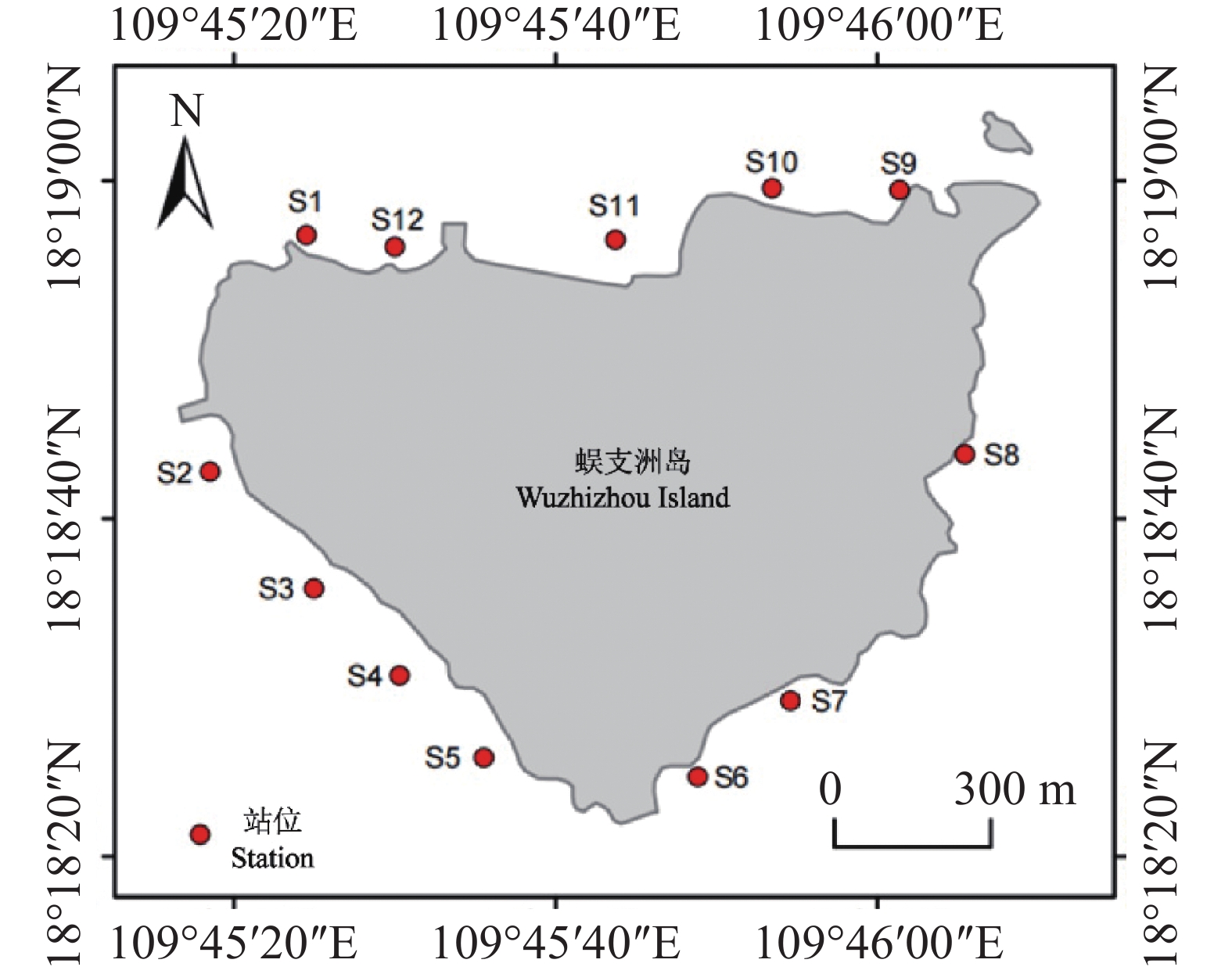
To explore the characteristics of macroalgae species and community structure in the Marine Ranch of Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya, sampling surveys were conducted from April 2023 to June 2023 at 12 different sites within the marine ranch area. A total of 29 species of macroalgae were collected, including 17 species from the Rhodophyta phylum, 9 species from the Chlorophyta phylum, and 3 species from the Phaeophyta phylum. The dominant species were Amphiroa fragilissima and Turbinaria ornata. The average biomass of macroalgae was (2.40 ± 1.89) g·m−2. The average carbon content and nitrogen content of different species of macroalgae were 18.80% and 0.98%, respectively, with an average C/N ratio of 24.04 ± 13.61. The mean values of species diversity index (H′), species richness index (D), and species evenness index (J) of the macroalgae community were 1.28 ± 0.59, 5.60 ± 4.61, and 0.87 ± 0.70, respectively. Cluster and ordination analysis revealed that the 12 sites were grouped into 3 clusters. SIMPER and ANOSIM analyses indicated significant differences in the community structure of macroalgae among these three clusters, with basic separation of community structures. These results suggest that the Marine Ranch of Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya harbors a rich diversity of macroalgae, but significant differences in community structure exist among different clusters due to specific dominant species and habitat variations.
To explore the characteristics of macroalgae species and community structure in the Marine Ranch of Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya, sampling surveys were conducted from April 2023 to June 2023 at 12 different sites within the marine ranch area. A total of 29 species of macroalgae were collected, including 17 species from the Rhodophyta phylum, 9 species from the Chlorophyta phylum, and 3 species from the Phaeophyta phylum. The dominant species were Amphiroa fragilissima and Turbinaria ornata. The average biomass of macroalgae was (2.40 ± 1.89) g·m−2. The average carbon content and nitrogen content of different species of macroalgae were 18.80% and 0.98%, respectively, with an average C/N ratio of 24.04 ± 13.61. The mean values of species diversity index (H′), species richness index (D), and species evenness index (J) of the macroalgae community were 1.28 ± 0.59, 5.60 ± 4.61, and 0.87 ± 0.70, respectively. Cluster and ordination analysis revealed that the 12 sites were grouped into 3 clusters. SIMPER and ANOSIM analyses indicated significant differences in the community structure of macroalgae among these three clusters, with basic separation of community structures. These results suggest that the Marine Ranch of Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya harbors a rich diversity of macroalgae, but significant differences in community structure exist among different clusters due to specific dominant species and habitat variations.
2026,
17(1):
155-164.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250101
Abstract:
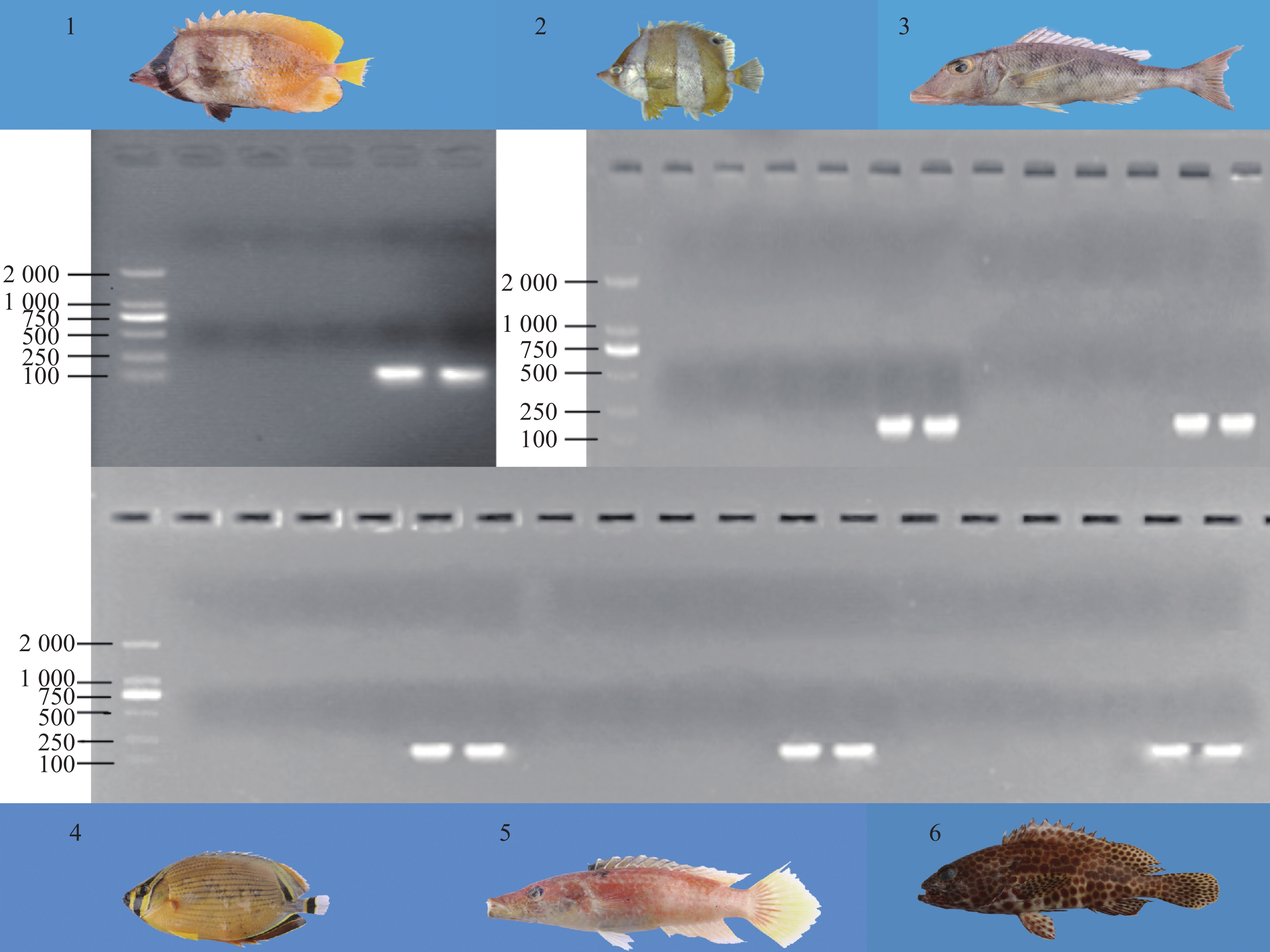
To understand the fish predators of crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster cf. solaris in the Xisha Islands, this study utilized 18S rRNA sequencing and morphological characteristics to identify the fish species collected in April 2023, and then detected the crown-of-thorns starfish mitochondrial cytochrome-C-oxidase subunit Ⅰ (CoTS-mtCOⅠ) gene fragments in fish intestinal content DNA. Analysis of 330 fish revealed 42 species across 37 genera, 24 families and 9 orders. The CoTS-mtCOⅠ fragment was detectable in the intestinal content DNA of six fish species, including Chaetodon kleinii, Chelmon rostratus, Chaetodon lunulatus, Lethrinus haematopterus, Oxycheilinus orientalis, and Epinephelus merra. The detection rate of CoTS-mtCOⅠ gene fragment was 100% in Chaetodon kleinii, while it was only detected in partial samples of the other five species. The six species were firstly reported fish predators of the crown-of-thorns starfish. Phylogenetic analysis based on 18S sequences grouped Chaetodon kleinii, Chelmon rostratus, and Chaetodon lunulatus within the family Chaetodontidae, and placed L. haematopterus, O. orientalis, and E. merra within the order Perciformes. This study contributes to understanding the fish predators of the crown-of-thorns starfish in the coral reef ecosystem of the Xisha Islands, providing a theoretical basis and scientific guidance for the prevention and control of the outbreak of the crown-of-thorns starfish in the South China Sea.
To understand the fish predators of crown-of-thorns starfish Acanthaster cf. solaris in the Xisha Islands, this study utilized 18S rRNA sequencing and morphological characteristics to identify the fish species collected in April 2023, and then detected the crown-of-thorns starfish mitochondrial cytochrome-C-oxidase subunit Ⅰ (CoTS-mtCOⅠ) gene fragments in fish intestinal content DNA. Analysis of 330 fish revealed 42 species across 37 genera, 24 families and 9 orders. The CoTS-mtCOⅠ fragment was detectable in the intestinal content DNA of six fish species, including Chaetodon kleinii, Chelmon rostratus, Chaetodon lunulatus, Lethrinus haematopterus, Oxycheilinus orientalis, and Epinephelus merra. The detection rate of CoTS-mtCOⅠ gene fragment was 100% in Chaetodon kleinii, while it was only detected in partial samples of the other five species. The six species were firstly reported fish predators of the crown-of-thorns starfish. Phylogenetic analysis based on 18S sequences grouped Chaetodon kleinii, Chelmon rostratus, and Chaetodon lunulatus within the family Chaetodontidae, and placed L. haematopterus, O. orientalis, and E. merra within the order Perciformes. This study contributes to understanding the fish predators of the crown-of-thorns starfish in the coral reef ecosystem of the Xisha Islands, providing a theoretical basis and scientific guidance for the prevention and control of the outbreak of the crown-of-thorns starfish in the South China Sea.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 2598KB
PDF 2598KB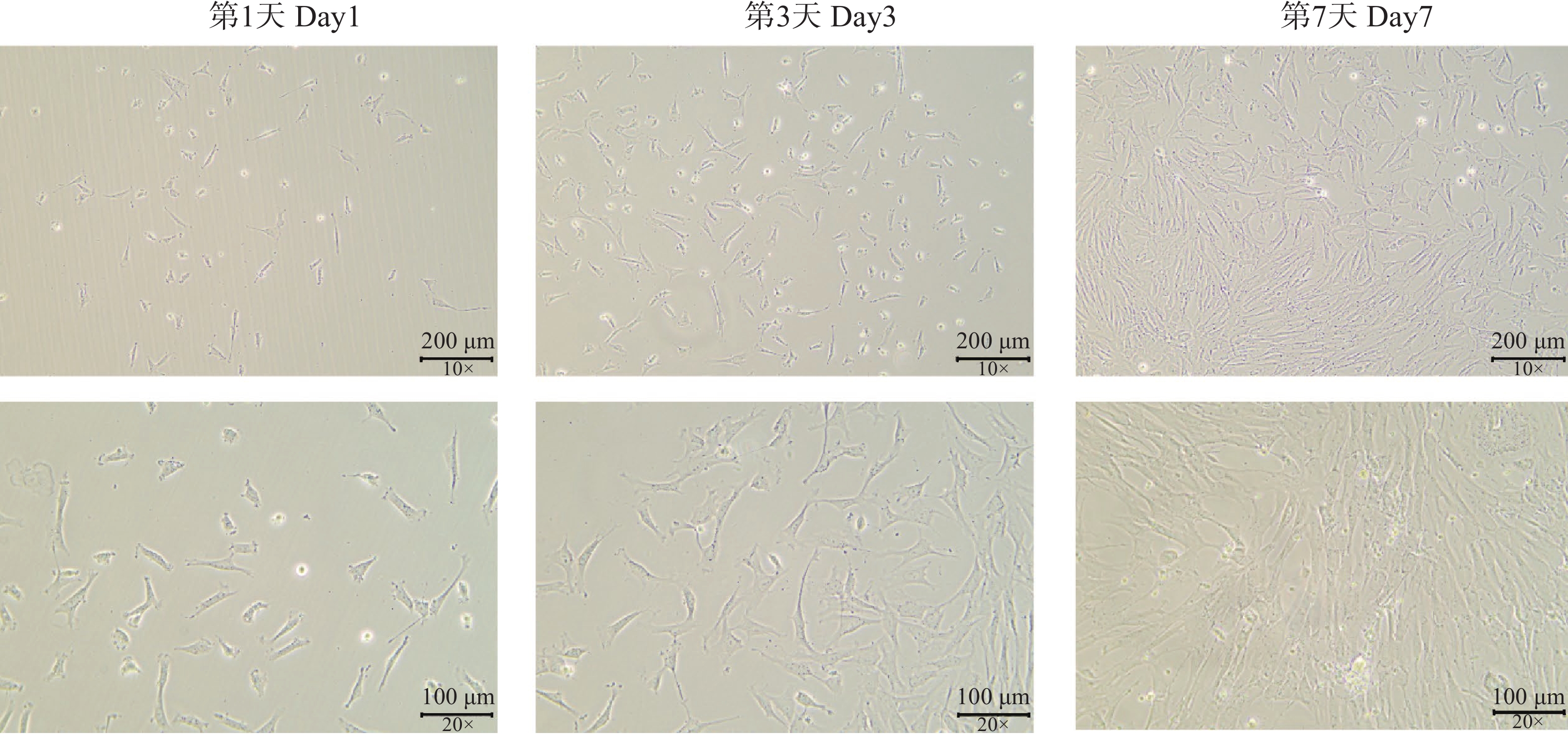





 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS