Just Accepted
Articles just accepted have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes /issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250056
Abstract:
To obtain an efficient biocontrol bacterial strain for managing cucumber Fusarium wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum (Foc), a Bacillus strain (LTB49) with strong antagonistic activity (antagonism rate of 55.26%) was isolated and screened from the rhizosphere soil of cucumber plants affected by the wilt disease, using gradient dilution and plate confrontation methods. The strain was subsequently identified as Bacillus velezensis through morphological, physiological and biochemical tests, and molecular biological techniques. The 10-fold diluted fermentation filtrate of the strain LTB49 showed strong inhibition of mycelial growth of the wilt pathogen, with an inhibition rate of 42.16%, and a significant suppression of spore germination, with an inhibition rate of 90.82%. Pot experiment results demonstrated that the strain LTB49 exhibited good biocontrol efficacy against cucumber wilt disease (43.37%), with no significant difference compared to the commercial biocontrol agent Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 (50.60% efficacy). Further studies revealed that this strain enhanced resistance to the wilt disease by inducing increased activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD), and significantly suppressed the effect of the Fusarium species on cucumber plant growth, particularly dwarfing. These results suggest that B. velezensis LTB49 has a high potential for application in the biocontrol of cucumber wilt disease.
To obtain an efficient biocontrol bacterial strain for managing cucumber Fusarium wilt caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum (Foc), a Bacillus strain (LTB49) with strong antagonistic activity (antagonism rate of 55.26%) was isolated and screened from the rhizosphere soil of cucumber plants affected by the wilt disease, using gradient dilution and plate confrontation methods. The strain was subsequently identified as Bacillus velezensis through morphological, physiological and biochemical tests, and molecular biological techniques. The 10-fold diluted fermentation filtrate of the strain LTB49 showed strong inhibition of mycelial growth of the wilt pathogen, with an inhibition rate of 42.16%, and a significant suppression of spore germination, with an inhibition rate of 90.82%. Pot experiment results demonstrated that the strain LTB49 exhibited good biocontrol efficacy against cucumber wilt disease (43.37%), with no significant difference compared to the commercial biocontrol agent Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 (50.60% efficacy). Further studies revealed that this strain enhanced resistance to the wilt disease by inducing increased activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD), and significantly suppressed the effect of the Fusarium species on cucumber plant growth, particularly dwarfing. These results suggest that B. velezensis LTB49 has a high potential for application in the biocontrol of cucumber wilt disease.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250078
Abstract:
As a new chemotypic germplasm of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Spreng., Chi-Nan germplasm has the excellent characteristics of the faster agarwood formation and higher quality of agarwood formation. In this study we successfully cloned the CNTPS18, an important sesquiterpene synthase (TPS) gene in the Chi-Nan germplasm, and analyzed its sequence bioinformatically and detected the expression pattern of the CNTPS18 gene in Chi-Nan germplasm within induction by injury. The results showed that the full-length sequence of the CDS of this gene is1632 bp, and that its encoded protein is mainly distributed in the cytoplasmic matrix, has no transmembrane structure, is unstable and hydrophilic, and belongs to non-secretory protein. The CNTPS18 gene possessed the conserved structural domains of eight sesquiterpene synthases such as terpene synthase-like, terpene cyclases, class 1, plant, and the tertiary structure is in high identity with vetispiradiene synthase; the CNTPS18 is evolutionarily closest to the TPS genes from the same genus of Aquilaria (A. malaccensis and A. agallochum), and is in the same branch with Durio zibethinus of Bomboideae and Herrania umbratica of Malvaceae, indicating a kinship under the same malvales order; CNTPS18 was expressed at the highest level in stems, followed by roots and fruits, and at the lowest level in leaves and seeds. Meanwhile, CNTPS18 was highly expressed in Chi-Nan germplasm after 15 d of injury induction, which assisted Chi-Nan germplasm in stabilizing the accumulation of secondary metabolites against injury stress. The present study provides some molecular biological basis for exploring the mechanism of agarwood formation in the Chi-Nan germplasm and further analyzing the function of CNTPSs.
As a new chemotypic germplasm of Aquilaria sinensis (Lour.) Spreng., Chi-Nan germplasm has the excellent characteristics of the faster agarwood formation and higher quality of agarwood formation. In this study we successfully cloned the CNTPS18, an important sesquiterpene synthase (TPS) gene in the Chi-Nan germplasm, and analyzed its sequence bioinformatically and detected the expression pattern of the CNTPS18 gene in Chi-Nan germplasm within induction by injury. The results showed that the full-length sequence of the CDS of this gene is
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250097
Abstract:
Hainan is an important growing area of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) in China, and its tropical climatic conditions lead to severe problems such as serious overlapping generations of pests and prominent pesticide resistance, making pest control quite challenging. Screening for insect-resistant varieties is an effective means of controlling crop pests. Given the relative scarcity of research on cowpea varieties resistant to Megalurothrips usitatus, the main pest species and their occurrence patterns on cowpea were identified through a systematic survey of pest occurrences on 57 cowpea varieties throughout the entire growth period in Danzhou City, Hainan Province. Additionally, cowpea varieties resistant to thrips were selected. The results showed that the main pests of cowpea grown in Danzhou, Hainan include Megalurothrips usitatus, Aphis craccivora, Trialeurodes vaporariorum, and Etiella zinckenella, among which M. usitatus, A. craccivora, and T. vaporariorum are the dominant pests. The peak numbers of the main pests were as follows: M. usitatus reached a peak of 154 individuals per plant on April 10th; A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum reached the peaks of 179 individuals per plant and 117 individuals per plant, respectively on April 23; E. zinckenella caused relatively slight damage, with a peak of 43 individuals per plant on April 24th. The population dynamics of the dominant pests were characterized by low density in the early growth stage of cowpea and reaching a peak in mid-April. From a spatial perspective, the concentrated damage sites were the tender parts at the top of the plants. From a time series analysis, M. usitatus was dominant at the early growth stage of cowpea; multiple pests broke out in combination at the middle growth stage; and A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum were the dominant populations at the late growth stage. The above research results suggest that in terms of timing, field control of cowpea should focus on the early stage, with an emphasis on the prevention and control of M. usitatus. Meanwhile, monitoring and management of A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum at the late stage should be strengthened. This study evaluated 7 cowpea varieties (‘Liangfei No. 8’, ‘Rejiang No. 1’, ‘Nongwang Nongbao 118’, ‘Yafeng 708’, ‘Cuilu 18’, ‘RADC755’, ‘Yibazhua No. 3’) that showed relatively high resistance to M. usitatus in the field. These varieties have the potential for popularization and planting in the field; however, further research is needed regarding their resistance mechanisms.
Hainan is an important growing area of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) in China, and its tropical climatic conditions lead to severe problems such as serious overlapping generations of pests and prominent pesticide resistance, making pest control quite challenging. Screening for insect-resistant varieties is an effective means of controlling crop pests. Given the relative scarcity of research on cowpea varieties resistant to Megalurothrips usitatus, the main pest species and their occurrence patterns on cowpea were identified through a systematic survey of pest occurrences on 57 cowpea varieties throughout the entire growth period in Danzhou City, Hainan Province. Additionally, cowpea varieties resistant to thrips were selected. The results showed that the main pests of cowpea grown in Danzhou, Hainan include Megalurothrips usitatus, Aphis craccivora, Trialeurodes vaporariorum, and Etiella zinckenella, among which M. usitatus, A. craccivora, and T. vaporariorum are the dominant pests. The peak numbers of the main pests were as follows: M. usitatus reached a peak of 154 individuals per plant on April 10th; A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum reached the peaks of 179 individuals per plant and 117 individuals per plant, respectively on April 23; E. zinckenella caused relatively slight damage, with a peak of 43 individuals per plant on April 24th. The population dynamics of the dominant pests were characterized by low density in the early growth stage of cowpea and reaching a peak in mid-April. From a spatial perspective, the concentrated damage sites were the tender parts at the top of the plants. From a time series analysis, M. usitatus was dominant at the early growth stage of cowpea; multiple pests broke out in combination at the middle growth stage; and A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum were the dominant populations at the late growth stage. The above research results suggest that in terms of timing, field control of cowpea should focus on the early stage, with an emphasis on the prevention and control of M. usitatus. Meanwhile, monitoring and management of A. craccivora and T. vaporariorum at the late stage should be strengthened. This study evaluated 7 cowpea varieties (‘Liangfei No. 8’, ‘Rejiang No. 1’, ‘Nongwang Nongbao 118’, ‘Yafeng 708’, ‘Cuilu 18’, ‘RADC755’, ‘Yibazhua No. 3’) that showed relatively high resistance to M. usitatus in the field. These varieties have the potential for popularization and planting in the field; however, further research is needed regarding their resistance mechanisms.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250095
Abstract:
In order to screen out marine actinomycetes and natural products that can effectively control Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4 (Foc TR4), a marine actinomycete strain HNM0301 isolated from a mangrove and exhibiting anti - Foc TR4 activity was identified taxonomically at a species level through whole - genome sequence analysis. The antiSMASH 6.0 online software was used to predict the biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites encoded by this strain. Moreover, modern separation and identification techniques for natural products were applied to isolate and elucidate the structures of the active ingredients against Foc TR4. The results demonstrated that the strain HNM0301 was identified as Streptomyces sanyensis. Its genome has a total length of 6,635,340 base pairs (bp) and contains 5,859 protein-coding genes (CDS). Among the protein-coding genes, 2,137, 1,243, and 4,297 CDS were functionally annotated in the Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) databases, respectively. A total of 27 biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites were predicted within the genome, with Cluster 16 containing 14 genes involved in the biosynthesis of staurosporine. A staurosporine monomer compound was successfully isolated from the fermentation broth of the strain HNM0301. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of this compound against Foc TR4 was determined to be 1.56 μg/mL. This compound exhibited an 85.4% inhibition rate of Foc TR4 conidial germination and also induced swelling and malformation of Foc TR4 mycelia. Evidently, the strain HNM0301 holds certain potentials for development and application in the control of Foc TR4.
In order to screen out marine actinomycetes and natural products that can effectively control Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense tropical race 4 (Foc TR4), a marine actinomycete strain HNM0301 isolated from a mangrove and exhibiting anti - Foc TR4 activity was identified taxonomically at a species level through whole - genome sequence analysis. The antiSMASH 6.0 online software was used to predict the biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites encoded by this strain. Moreover, modern separation and identification techniques for natural products were applied to isolate and elucidate the structures of the active ingredients against Foc TR4. The results demonstrated that the strain HNM0301 was identified as Streptomyces sanyensis. Its genome has a total length of 6,635,340 base pairs (bp) and contains 5,859 protein-coding genes (CDS). Among the protein-coding genes, 2,137, 1,243, and 4,297 CDS were functionally annotated in the Gene Ontology (GO), Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), and Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) databases, respectively. A total of 27 biosynthetic gene clusters of secondary metabolites were predicted within the genome, with Cluster 16 containing 14 genes involved in the biosynthesis of staurosporine. A staurosporine monomer compound was successfully isolated from the fermentation broth of the strain HNM0301. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of this compound against Foc TR4 was determined to be 1.56 μg/mL. This compound exhibited an 85.4% inhibition rate of Foc TR4 conidial germination and also induced swelling and malformation of Foc TR4 mycelia. Evidently, the strain HNM0301 holds certain potentials for development and application in the control of Foc TR4.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250072
Abstract:
Biston suppressaria is a pest threatening eucalyptus plantations. Bacteria from its intestine were isolated and identified by using traditional culture and molecular biology methods to find pathogenic strains for biocontrol of this pest. Fifteen bacteria with distinct morphological traits were isolated from naturally infected, lethal B. suppressarias and identified into ten genera, including Enterobacter, Serratia, and Bacillus via 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The Bacillaceae strain B6 showed the highest pathogenicity. After treated with B6 by using the feeding method, B. suppressarias had a cumulative corrected mortality of 60.0% at day 7, with specific pathogenic characteristics observed in the dead insects. Re-isolation yielded colonies morphologically consistent with B6, with a sequence similarity of 99.80%. Moreover, B6 exhibited certain pathogenicity to the other two types of Geometridae larvae, including the common cutworm and small emerald moth, and showed significant insecticidal effects on B. suppressarias at the early infection stage. This study provides a theoretical basis for the use of the Bacillaceae strain B6 to control B. suppressarias and develop eco-friendly control strategies.
Biston suppressaria is a pest threatening eucalyptus plantations. Bacteria from its intestine were isolated and identified by using traditional culture and molecular biology methods to find pathogenic strains for biocontrol of this pest. Fifteen bacteria with distinct morphological traits were isolated from naturally infected, lethal B. suppressarias and identified into ten genera, including Enterobacter, Serratia, and Bacillus via 16S rDNA sequence analysis. The Bacillaceae strain B6 showed the highest pathogenicity. After treated with B6 by using the feeding method, B. suppressarias had a cumulative corrected mortality of 60.0% at day 7, with specific pathogenic characteristics observed in the dead insects. Re-isolation yielded colonies morphologically consistent with B6, with a sequence similarity of 99.80%. Moreover, B6 exhibited certain pathogenicity to the other two types of Geometridae larvae, including the common cutworm and small emerald moth, and showed significant insecticidal effects on B. suppressarias at the early infection stage. This study provides a theoretical basis for the use of the Bacillaceae strain B6 to control B. suppressarias and develop eco-friendly control strategies.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250040
Abstract:
To investigate the molecular mechanisms by which pumpkin grafting enhances resistance to Fusarium wilt in wax gourd, pumpkin variety ‘Haizhen 1’ was used as the rootstock and wax gourd variety ‘Tiezhu 2’ as the scion in this experiment. Three types of seedling materials were produced through grafting: grafted wax gourd (GW) to pumpkin, self-grafted wax gourd (SW), and self-grafted pumpkin (SP). These graftings were cultivated in soil inoculated with Fusarium oxysporum at a concentration of 8.0 × 105 CFU·g−1, with a control group using soil at 0 CFU·g−1. After five days of cultivation, root and leaf samples were collected for transcriptome sequencing to analyze differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The results showed that 284 and 2 potential disease-resistant genes were identified in the leaves and roots, respectively. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis revealed that phenylpropane biosynthesis was a common metabolic pathway in both the leaves and roots of grafted wax gourd. Using DRAGO 3 for domain prediction of the potential disease-resistant genes, 16 disease resistance-related genes were predicted, mainly associated with the PTI (pattern-triggered immunity) pathway. Transcription factor (TF) analysis of all the transcriptome sequences in the leaves and roots showed that there were 2,828 and 5,426 differentially expressed TFs identified in the leaves and roots, respectively. A significant number of these TFs were concentrated in the MYB, bHLH, ERF, and NAC families. It is hence hypothesized that phenylpropane biosynthesis and transcription factors such as MYB, bHLH, ERF, and NAC play crucial roles in defending against Fusarium oxysporum infection.
To investigate the molecular mechanisms by which pumpkin grafting enhances resistance to Fusarium wilt in wax gourd, pumpkin variety ‘Haizhen 1’ was used as the rootstock and wax gourd variety ‘Tiezhu 2’ as the scion in this experiment. Three types of seedling materials were produced through grafting: grafted wax gourd (GW) to pumpkin, self-grafted wax gourd (SW), and self-grafted pumpkin (SP). These graftings were cultivated in soil inoculated with Fusarium oxysporum at a concentration of 8.0 × 105 CFU·g−1, with a control group using soil at 0 CFU·g−1. After five days of cultivation, root and leaf samples were collected for transcriptome sequencing to analyze differentially expressed genes (DEGs). The results showed that 284 and 2 potential disease-resistant genes were identified in the leaves and roots, respectively. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis revealed that phenylpropane biosynthesis was a common metabolic pathway in both the leaves and roots of grafted wax gourd. Using DRAGO 3 for domain prediction of the potential disease-resistant genes, 16 disease resistance-related genes were predicted, mainly associated with the PTI (pattern-triggered immunity) pathway. Transcription factor (TF) analysis of all the transcriptome sequences in the leaves and roots showed that there were 2,828 and 5,426 differentially expressed TFs identified in the leaves and roots, respectively. A significant number of these TFs were concentrated in the MYB, bHLH, ERF, and NAC families. It is hence hypothesized that phenylpropane biosynthesis and transcription factors such as MYB, bHLH, ERF, and NAC play crucial roles in defending against Fusarium oxysporum infection.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250071
Abstract:
In order to understand the current research hotspots and trends of stem end rot disease, a bibliometric analysis was conducted using CiteSpace software on 367 stem end rot disease-related articles indexed in the Web of Science core database between 2009 and 2024. The distribution of research efforts, knowledge base, research hotspots, and frontier trends in the field of stem end rot disease were analyzed. The results indicate that the number of publications on stem end rot disease has been increasing, with China, the United States, and Brazil having the highest publication volumes. There is also significant international collaboration among countries. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is a leading research institution in this field, while Hainan University is the leading institution in China. Research institutions collaborate closely, although Chinese institutions still have room to improve in terms of international cooperation and academic influence. Prominent authors in the field of stem end rot disease research include Alkan Noam and Bai Jinhe. Keyword co-occurrence and burst detection analysis reveal that current research hotspots in the field include pathogen identification, resistance, and genomics. Future research should focus on strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration, further exploring the pathological mechanisms of stem end rot disease, and developing control strategies to ensure the healthy growth of crops.
In order to understand the current research hotspots and trends of stem end rot disease, a bibliometric analysis was conducted using CiteSpace software on 367 stem end rot disease-related articles indexed in the Web of Science core database between 2009 and 2024. The distribution of research efforts, knowledge base, research hotspots, and frontier trends in the field of stem end rot disease were analyzed. The results indicate that the number of publications on stem end rot disease has been increasing, with China, the United States, and Brazil having the highest publication volumes. There is also significant international collaboration among countries. The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is a leading research institution in this field, while Hainan University is the leading institution in China. Research institutions collaborate closely, although Chinese institutions still have room to improve in terms of international cooperation and academic influence. Prominent authors in the field of stem end rot disease research include Alkan Noam and Bai Jinhe. Keyword co-occurrence and burst detection analysis reveal that current research hotspots in the field include pathogen identification, resistance, and genomics. Future research should focus on strengthening interdisciplinary collaboration, further exploring the pathological mechanisms of stem end rot disease, and developing control strategies to ensure the healthy growth of crops.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250074
Abstract:
In order to explore the possibility and potential molecular mechanism of Persicaria chinensis produced in Hainan against pullorum disease, the core active ingredients and their core targets were screened by network pharmacology and verified by molecular docking. Four factors and three levels of orthogonal test and Oxford cup bacteriostatic test were used to determine the optimum extraction conditions of Persicaria chinensis produced in Hainan, and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) were detected. The results showed that there were 61 intersection targets between the active components of Hainan-produced charcoal mother and pullorum disease. In GO functional analysis, 45 biological processes, 15 cell components and 12 molecular functions were enriched, and KEGG pathway was enriched to 18 signaling pathways. The results of macromolecular docking showed that the binding free energy of five active ingredients and five key targets were less than −5.0 kcal·moL−1. The results of orthogonal test showed that the optimum extraction conditions were as follows: the ratio of material to liquid was 1∶60, the extraction temperature was 70 ℃, the extraction time was 45 min, and the extraction was twice. The MIC and MBC were the same, both of which were 128 g·L−1. In summary, Persicaria chinensis produced in Hainan may regulate multiple targets such as MMP9 and PPARG through various active ingredients such as Quercetin and Kaempferol, thus affecting multiple pathways such as MAPK and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways to exert anti-pullorum effect. Among them, it has been proved that Persicaria chinensis produced in Hainan is mainly composed of flavonoids and multi-component synergistic effects to play an anti-pullorum effect.
In order to explore the possibility and potential molecular mechanism of Persicaria chinensis produced in Hainan against pullorum disease, the core active ingredients and their core targets were screened by network pharmacology and verified by molecular docking. Four factors and three levels of orthogonal test and Oxford cup bacteriostatic test were used to determine the optimum extraction conditions of Persicaria chinensis produced in Hainan, and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) were detected. The results showed that there were 61 intersection targets between the active components of Hainan-produced charcoal mother and pullorum disease. In GO functional analysis, 45 biological processes, 15 cell components and 12 molecular functions were enriched, and KEGG pathway was enriched to 18 signaling pathways. The results of macromolecular docking showed that the binding free energy of five active ingredients and five key targets were less than −5.0 kcal·moL−1. The results of orthogonal test showed that the optimum extraction conditions were as follows: the ratio of material to liquid was 1∶60, the extraction temperature was 70 ℃, the extraction time was 45 min, and the extraction was twice. The MIC and MBC were the same, both of which were 128 g·L−1. In summary, Persicaria chinensis produced in Hainan may regulate multiple targets such as MMP9 and PPARG through various active ingredients such as Quercetin and Kaempferol, thus affecting multiple pathways such as MAPK and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways to exert anti-pullorum effect. Among them, it has been proved that Persicaria chinensis produced in Hainan is mainly composed of flavonoids and multi-component synergistic effects to play an anti-pullorum effect.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250082
Abstract:
To explore the substrate formula for cultivating S. rugosoannulata with high yield and high quality under rubber plantations, rice straw and rubber wood chips were used as raw materials to investigate the impact of their ratios on the yield and quality of S. rugosoannulata. Five treatments with rice and rubber wood chips at the dry mass ratios (1∶0, 3∶1, 1∶1, 1∶3, 0∶1) were arranged in this experiment for observation of mycelial growth and field fruiting. The results showed that the treatment with the ratio of 1∶3 had the highest comprehensive score. The mycelium of S. rugosoannulata cultivated with this substrate was robust and dense, with an average fruiting period of 52.75 days after inoculation and a harvesting period of 29 days. The yield of fruiting bodies in this treatment reached 5.22 kg·m−2, and the biological conversion rate was 26.11%.
To explore the substrate formula for cultivating S. rugosoannulata with high yield and high quality under rubber plantations, rice straw and rubber wood chips were used as raw materials to investigate the impact of their ratios on the yield and quality of S. rugosoannulata. Five treatments with rice and rubber wood chips at the dry mass ratios (1∶0, 3∶1, 1∶1, 1∶3, 0∶1) were arranged in this experiment for observation of mycelial growth and field fruiting. The results showed that the treatment with the ratio of 1∶3 had the highest comprehensive score. The mycelium of S. rugosoannulata cultivated with this substrate was robust and dense, with an average fruiting period of 52.75 days after inoculation and a harvesting period of 29 days. The yield of fruiting bodies in this treatment reached 5.22 kg·m−2, and the biological conversion rate was 26.11%.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250005
Abstract:
An attempt was made to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of layered double hydroxides (LDH) nanofusion protein vaccines in cat and dog fusion allergens-induced mouse model, which provides a potential novel vaccine strategy for the treatment of canine and feline allergic diseases. A cat and dog fusion allergen was prepared and loaded onto layered double hydroxide nanomate vials to construct a vaccine. BALB/c mice were selected and sensitized to the cat and dog fusion allergen by intraperitoneal injection and lung perfusion to establish a mouse allergy model. Subsequently, the allergy model mice were randomly divided into four groups: normal (naïve) group, allergy model group (allergic model), LDH group and vaccine group, with six mice in each group. Among them, the normal group was not treated, and the mice in the allergic model group, LDH group and vaccine group were given phosphate buffered saline (PBS), LDH nanosuspension, and LDH nanofusion protein vaccine injections, respectively, and the results of serum IgE, pulmonary respiratory resistance, temperature change, ear prick, and pathological section were detected to comprehensively evaluate the vaccine treatment effect. The results showed that compared with the Allergic model group, the vaccine group treated with LDH nanofusion protein vaccine significantly decreased the serum-specific IgE levels of mice, alleviated lung respiratory resistance, highly significantly reduced allergen-induced body temperature and the area of ear dye leakage, significantly reduced inflammatory infiltration in the lungs, reduced the number of cuprocytes although not significantly, and reduced the degree of collagen deposition and fibrosis. Taken together, these results indicate that the laminar double hydroxide nanocat-dog fusion protein vaccine has a good therapeutic effect on the cat-dog fusion allergen-induced mouse allergy model, and is able to effectively improve the allergy symptoms and reduce the inflammatory reaction of allergy-associated tissues in mice.
An attempt was made to investigate the therapeutic efficacy of layered double hydroxides (LDH) nanofusion protein vaccines in cat and dog fusion allergens-induced mouse model, which provides a potential novel vaccine strategy for the treatment of canine and feline allergic diseases. A cat and dog fusion allergen was prepared and loaded onto layered double hydroxide nanomate vials to construct a vaccine. BALB/c mice were selected and sensitized to the cat and dog fusion allergen by intraperitoneal injection and lung perfusion to establish a mouse allergy model. Subsequently, the allergy model mice were randomly divided into four groups: normal (naïve) group, allergy model group (allergic model), LDH group and vaccine group, with six mice in each group. Among them, the normal group was not treated, and the mice in the allergic model group, LDH group and vaccine group were given phosphate buffered saline (PBS), LDH nanosuspension, and LDH nanofusion protein vaccine injections, respectively, and the results of serum IgE, pulmonary respiratory resistance, temperature change, ear prick, and pathological section were detected to comprehensively evaluate the vaccine treatment effect. The results showed that compared with the Allergic model group, the vaccine group treated with LDH nanofusion protein vaccine significantly decreased the serum-specific IgE levels of mice, alleviated lung respiratory resistance, highly significantly reduced allergen-induced body temperature and the area of ear dye leakage, significantly reduced inflammatory infiltration in the lungs, reduced the number of cuprocytes although not significantly, and reduced the degree of collagen deposition and fibrosis. Taken together, these results indicate that the laminar double hydroxide nanocat-dog fusion protein vaccine has a good therapeutic effect on the cat-dog fusion allergen-induced mouse allergy model, and is able to effectively improve the allergy symptoms and reduce the inflammatory reaction of allergy-associated tissues in mice.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250054
Abstract:
Magnolia liliflora cut flowers were treated with four preservatives, ascorbic acid, silver thiosulfate (STS), Aminoethoxyvinylgycine hydrochloride (AVG), and aminoethoxyacetic acid (AOA) to observe the effects of the preservatives on their vase life across developmental stages (blooming, early flowering, and ruddy). The 30 mg/L AOA treatment demonstrated optimal efficacy, extending the vase life to 86 h at the early flowering stage and 110 h at the ruddy stage while keeping the fresh weight ratio at a relatively high level. Both ascorbic acid (2 g/L) and silver thiosulfate (STS) (0.5, 2 mmol/L) promoted the opening of flowers at the ruddy stage, but they also accelerated the withering process. On the contrary the vase life of flowers treated with other preservatives was the shortest, ranging from 89.33 to 96 hours. Flowers at the blooming stage showed no statistically significant response to the treatments. This study revealed the stage-dependent vase life preservation effect of M. liliflora cut flowers, providing a theoretical basis for the application of M. liliflora cut flowers and the selection of preservative components.
Magnolia liliflora cut flowers were treated with four preservatives, ascorbic acid, silver thiosulfate (STS), Aminoethoxyvinylgycine hydrochloride (AVG), and aminoethoxyacetic acid (AOA) to observe the effects of the preservatives on their vase life across developmental stages (blooming, early flowering, and ruddy). The 30 mg/L AOA treatment demonstrated optimal efficacy, extending the vase life to 86 h at the early flowering stage and 110 h at the ruddy stage while keeping the fresh weight ratio at a relatively high level. Both ascorbic acid (2 g/L) and silver thiosulfate (STS) (0.5, 2 mmol/L) promoted the opening of flowers at the ruddy stage, but they also accelerated the withering process. On the contrary the vase life of flowers treated with other preservatives was the shortest, ranging from 89.33 to 96 hours. Flowers at the blooming stage showed no statistically significant response to the treatments. This study revealed the stage-dependent vase life preservation effect of M. liliflora cut flowers, providing a theoretical basis for the application of M. liliflora cut flowers and the selection of preservative components.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250027
Abstract:
Stem rot causes extensive rotting at the base of the stems of bloodleaf orchid plants, affecting nutrient uptake. Studies have shown that Trichoderma can effectively inhibit a wide range of pathogenic bacteria and is an important biocontrol fungus. A strain of pathogen X.9 with the strongest pathogenic effect was isolated from the diseased tissues at the stem base of Ludisia discolor(Ker-Gawl.)A.Rich, which was identified as Fusarium oxysporum by morphology and molecular biology. The plate confrontation assay between Trichoderma strains and the F. oxysporum X.9 showed that 17 Trichoderma strains could completely cover F. oxysporum X.9 an inhibition rate of more than 75%. Further observation of the inhibition effect of 17 strains of Trichoderma non-volatile metabolites on X.9 showed that JX013 and SC009 had better inhibition effect, with their inhibition rates being 41.27% and 41.26%, respectively. Through morphological and molecular biological identification, both JX013 and SC009 were confirmed to be Trichoderma asperellum. Both JX013 and SC009 showed a significant increase in chitinase and glucanase after interacted with X.9, indicating that Trichoderma secretes more cell wall degrading enzymes to degrade the pathogenic mycelium when interacted with pathogenic bacteria, thus inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
Stem rot causes extensive rotting at the base of the stems of bloodleaf orchid plants, affecting nutrient uptake. Studies have shown that Trichoderma can effectively inhibit a wide range of pathogenic bacteria and is an important biocontrol fungus. A strain of pathogen X.9 with the strongest pathogenic effect was isolated from the diseased tissues at the stem base of Ludisia discolor(Ker-Gawl.)A.Rich, which was identified as Fusarium oxysporum by morphology and molecular biology. The plate confrontation assay between Trichoderma strains and the F. oxysporum X.9 showed that 17 Trichoderma strains could completely cover F. oxysporum X.9 an inhibition rate of more than 75%. Further observation of the inhibition effect of 17 strains of Trichoderma non-volatile metabolites on X.9 showed that JX013 and SC009 had better inhibition effect, with their inhibition rates being 41.27% and 41.26%, respectively. Through morphological and molecular biological identification, both JX013 and SC009 were confirmed to be Trichoderma asperellum. Both JX013 and SC009 showed a significant increase in chitinase and glucanase after interacted with X.9, indicating that Trichoderma secretes more cell wall degrading enzymes to degrade the pathogenic mycelium when interacted with pathogenic bacteria, thus inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250001
Abstract:
Clerodendranthus spicatus (Kidney tea, KT), a traditional Chinese medicine, has a variety of biological activities. In recent years there are many studies on the antioxidant activity of kidney tea in vitro, but the research on the antioxidant activity and health effects of its ethanol extract in vivo is not sufficiently documented. In this case, the antioxidant activity of KTe (kidney tea ethanol extract) in vitro was evaluated by measuring the DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging ability. Caenorhabditis elegans was used to evaluate the antioxidant activity of KTe in vivo. The physiological indexes, such as lifespan, oviposition and hatching, lipofuscin content and movement ability of C.elegans, were determined to evaluate the antioxidant tivity of KTe in vivo. The results showed that KTe had good antioxidant activity in vitro, which could promote the physiological indexes of young nematodes and inhibit the physiological indexes of old nematodes. At the same time, it can significantly increase the number of eggs laid by C.elegans, and has no significant effect on the hatching rate. All these results can provide reference for the subsequent development and utilization of KT.
Clerodendranthus spicatus (Kidney tea, KT), a traditional Chinese medicine, has a variety of biological activities. In recent years there are many studies on the antioxidant activity of kidney tea in vitro, but the research on the antioxidant activity and health effects of its ethanol extract in vivo is not sufficiently documented. In this case, the antioxidant activity of KTe (kidney tea ethanol extract) in vitro was evaluated by measuring the DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging ability. Caenorhabditis elegans was used to evaluate the antioxidant activity of KTe in vivo. The physiological indexes, such as lifespan, oviposition and hatching, lipofuscin content and movement ability of C.elegans, were determined to evaluate the antioxidant tivity of KTe in vivo. The results showed that KTe had good antioxidant activity in vitro, which could promote the physiological indexes of young nematodes and inhibit the physiological indexes of old nematodes. At the same time, it can significantly increase the number of eggs laid by C.elegans, and has no significant effect on the hatching rate. All these results can provide reference for the subsequent development and utilization of KT.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240186
Abstract:
The characteristics of the changes in phosphorus flow from 1990 to 2020 were quantified in the food chain system of Hainan Island based on the NUFER model to explore the sustainable use of phosphorus. The results demonstrated that over the 30-year period, the phosphorus input to the crop production subsystem of the Hainan Island food chain system increased from 135.92 kt to 390.63 kt, with fertilizer input representing the primary source of phosphorus in this subsystem. The phosphorus input to the livestock and poultry subsystem exhibited an increase from 13.70 kt to 19.23 kt, while the phosphorus input to the aquaculture subsystem demonstrated an increase from 6.32 kt to 49.75 kt. All these findings demonstrate that the inputs and losses of phosphorus in the food chain system of Hainan Island in 2050 can be reduced through the implementation of comprehensive and optimal management measures. In order to ensure the long-term sustainability of the food chain system on Hainan Island, it is essential to implement measures that will control the excessive inputs of phosphorus nutrients, optimize farming methods and technologies, and strengthen management measures to improve the efficiency of phosphorus utilization. This will help to reduce the loss of phosphorus in the various subsystems. Concurrently, it is imperative to foster a harmonious interdependence between the disparate subsystems that comprise Hainan Island's food chain system. This will ensure the sustainable phosphorus utilization.
The characteristics of the changes in phosphorus flow from 1990 to 2020 were quantified in the food chain system of Hainan Island based on the NUFER model to explore the sustainable use of phosphorus. The results demonstrated that over the 30-year period, the phosphorus input to the crop production subsystem of the Hainan Island food chain system increased from 135.92 kt to 390.63 kt, with fertilizer input representing the primary source of phosphorus in this subsystem. The phosphorus input to the livestock and poultry subsystem exhibited an increase from 13.70 kt to 19.23 kt, while the phosphorus input to the aquaculture subsystem demonstrated an increase from 6.32 kt to 49.75 kt. All these findings demonstrate that the inputs and losses of phosphorus in the food chain system of Hainan Island in 2050 can be reduced through the implementation of comprehensive and optimal management measures. In order to ensure the long-term sustainability of the food chain system on Hainan Island, it is essential to implement measures that will control the excessive inputs of phosphorus nutrients, optimize farming methods and technologies, and strengthen management measures to improve the efficiency of phosphorus utilization. This will help to reduce the loss of phosphorus in the various subsystems. Concurrently, it is imperative to foster a harmonious interdependence between the disparate subsystems that comprise Hainan Island's food chain system. This will ensure the sustainable phosphorus utilization.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250050
Abstract:
An attempt was made to further optimize the indoor artificial propagation technology of Kappaphycus alvarezii. The effects of temperature and light on the growth, pigment and phycobiliprotein content of K. alvarezii were determined by conducting control experiments. The results showed that when the temperature was 27 ℃, the relative growth rate was significantly higher than that of other temperature test groups (P < 0.05), and that the contents of chlorophyll a and carotenoids in the algae were also higher, indicating that an appropriate increase of temperature would increase the accumulation level of pigment content in the algae, but the difference in culture temperature had little effect on the content of phycobiliprotein, and there was no significant difference in the content of phycobiliprotein in each group. At the same temperature, the relative growth rate of K. alvarezii increased first and then decreased with the change of light intensity. When the light intensity was4000 lx to 7000 lx, the algae grew faster, and the content of chlorophyll a in the algae was significantly higher than that in the other light groups when the light was 1000 lx, indicating that the appropriate low light intensity would promote the synthesis of more chlorophyll a in K. alvarezii. When the light intensity was 4000 lx, the phycobiliprotein content of the algae was significantly higher than that of the other light groups, and the change of light intensity could cause the fluctuation of the phycobiliprotein content of K. alvarezii.
An attempt was made to further optimize the indoor artificial propagation technology of Kappaphycus alvarezii. The effects of temperature and light on the growth, pigment and phycobiliprotein content of K. alvarezii were determined by conducting control experiments. The results showed that when the temperature was 27 ℃, the relative growth rate was significantly higher than that of other temperature test groups (P < 0.05), and that the contents of chlorophyll a and carotenoids in the algae were also higher, indicating that an appropriate increase of temperature would increase the accumulation level of pigment content in the algae, but the difference in culture temperature had little effect on the content of phycobiliprotein, and there was no significant difference in the content of phycobiliprotein in each group. At the same temperature, the relative growth rate of K. alvarezii increased first and then decreased with the change of light intensity. When the light intensity was
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250025
Abstract:
The sugar transporter SWEET (Sugars Will Eventually be Exported Transporter) plays a crucial role in plant responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses. To elucidate the function of the SWEET gene family in Dendrobium catenatum, 27 DcSWEET genes were identified and characterized from D. catenatum by using whole-genome data, and their expression patterns under drought stress were analyzed. The molecular weight of the DcSWEET proteins were found to range from 22.44 to 39.10 kDa, with heir isoelectric points being between 8.47 and 9.63. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the DcSWEET proteins could be classified into four subgroups, each characterized by conserved motif compositions and gene structures. Cis-acting element analysis indicated that the promoters of DcSWEET genes contain various elements associated with hormone signaling, plant growth and development, light responsiveness, and stress response. RNA-seq analysis demonstrated that 17 DcSWEET genes were up-regulated under drought stress. Coexpression network analysis suggested that DcSWEET4, DcSWEET11, DcSWEET13, DcSWEET18, and DcSWEET27 may play pivotal roles in response to drought stress in D. catenatum. RT-qPCR confirmed that DcSWEET11, DcSWEET13, and DcSWEET18 were significantly up-regulated in stems and leaves under drought conditions, making them potential candidate genes for enhancing drought tolerance in D. catenatum. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of key SWEET genes involved in drought stress responses in D. catenatum, offering a molecular foundation for future efforts to improve its drought resistance.
The sugar transporter SWEET (Sugars Will Eventually be Exported Transporter) plays a crucial role in plant responses to both biotic and abiotic stresses. To elucidate the function of the SWEET gene family in Dendrobium catenatum, 27 DcSWEET genes were identified and characterized from D. catenatum by using whole-genome data, and their expression patterns under drought stress were analyzed. The molecular weight of the DcSWEET proteins were found to range from 22.44 to 39.10 kDa, with heir isoelectric points being between 8.47 and 9.63. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that the DcSWEET proteins could be classified into four subgroups, each characterized by conserved motif compositions and gene structures. Cis-acting element analysis indicated that the promoters of DcSWEET genes contain various elements associated with hormone signaling, plant growth and development, light responsiveness, and stress response. RNA-seq analysis demonstrated that 17 DcSWEET genes were up-regulated under drought stress. Coexpression network analysis suggested that DcSWEET4, DcSWEET11, DcSWEET13, DcSWEET18, and DcSWEET27 may play pivotal roles in response to drought stress in D. catenatum. RT-qPCR confirmed that DcSWEET11, DcSWEET13, and DcSWEET18 were significantly up-regulated in stems and leaves under drought conditions, making them potential candidate genes for enhancing drought tolerance in D. catenatum. This study provides a comprehensive analysis of key SWEET genes involved in drought stress responses in D. catenatum, offering a molecular foundation for future efforts to improve its drought resistance.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250036
Abstract:
With the intensification of aquaculture and the over-exploitation of offshore fishery resources, the fishery economy in coastal areas has shown a rapid growth trend. This development has directly led to the demand for large-scale construction of water intake and drainage pipeline systems. As the core carrier of material cycling in coastal wetlands, the speciation and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) in sediments are key indicators for assessing the sources and degradation status of organic matters. The construction of pipelines may further alter the C, N and P speciation and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments by changing hydrodynamic conditions, sedimentation processes, and microbial organic matter degradation processes. The pipeline-laid area (Area A) and the natural tidal flat area (Area B) in Wenchang City, Hainan Province were selected to analyze the impact of pipeline laying on the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments. The results showed that the total nitrogen (TN) and total organic carbon (TOC) contents, carbon-to-phosphorus ratio (C∶P), and nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio (N∶P) were significantly higher in Area A than in Area B (+53.3%, +38.0%, +52.4%, +50.0%), while the total carbon (TC) content and carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C∶N) were lower (−8.7%, −21.8%). In addition, the contents of C, N, and P in sediments and their ecological stoichiometric characteristics also changed the horizontal distribution pattern with increasing distance from the shore. Specifically, TC and TOC contents, C∶N, and C∶P in sediments decreased with increasing distance from the shore, while TN and TP contents showed the opposite trend. Under the interaction of pipeline laying and distance from the shore, the changes in TC and TOC contents, C∶N, and C∶P were greater in Area A than in Area B, and the differences were more significant near the shore than far from the shore. All these results indicate that pipeline laying and distance from the shore are important factors affecting the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments, and the interaction between distance from the shore and pipeline laying weakens the impact on the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments.
With the intensification of aquaculture and the over-exploitation of offshore fishery resources, the fishery economy in coastal areas has shown a rapid growth trend. This development has directly led to the demand for large-scale construction of water intake and drainage pipeline systems. As the core carrier of material cycling in coastal wetlands, the speciation and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) in sediments are key indicators for assessing the sources and degradation status of organic matters. The construction of pipelines may further alter the C, N and P speciation and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments by changing hydrodynamic conditions, sedimentation processes, and microbial organic matter degradation processes. The pipeline-laid area (Area A) and the natural tidal flat area (Area B) in Wenchang City, Hainan Province were selected to analyze the impact of pipeline laying on the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments. The results showed that the total nitrogen (TN) and total organic carbon (TOC) contents, carbon-to-phosphorus ratio (C∶P), and nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratio (N∶P) were significantly higher in Area A than in Area B (+53.3%, +38.0%, +52.4%, +50.0%), while the total carbon (TC) content and carbon-to-nitrogen ratio (C∶N) were lower (−8.7%, −21.8%). In addition, the contents of C, N, and P in sediments and their ecological stoichiometric characteristics also changed the horizontal distribution pattern with increasing distance from the shore. Specifically, TC and TOC contents, C∶N, and C∶P in sediments decreased with increasing distance from the shore, while TN and TP contents showed the opposite trend. Under the interaction of pipeline laying and distance from the shore, the changes in TC and TOC contents, C∶N, and C∶P were greater in Area A than in Area B, and the differences were more significant near the shore than far from the shore. All these results indicate that pipeline laying and distance from the shore are important factors affecting the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments, and the interaction between distance from the shore and pipeline laying weakens the impact on the C, N and P contents and ecological stoichiometric characteristics of sediments.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240144
Abstract:
Agroforestry is an environment-friendly semi-natural system of agricultural production that introduces naturally occurring ecosystems into agricultural land management, using a mixed-planting approach of trees and agricultural crops to create a more stable agricultural ecosystem. Agroforestry systems help to enhance economic value, increase product diversity, improve resource recycling efficiency, enrich soil, and maintain local biodiversity, thus leading a trend toward modern, efficient, sustainable agriculture. This article summarizes common agroforestry systems found in tropical regions worldwide, and evaluates their ecological, economic, and social benefits. In Asia, important agroforestry systems include rubber-based, oil palm-based, and Kapok-rice agroforestry systems. Agroforestry systems in Africa are based on crops such as cocoa and acacia. Dominant species for agroforestry systems in Latin America are cashews and coffee. Nevertheless, there is still a lack of comprehensive macro-scale researches and understandings of ecological processes. The absence of a unified evaluation system, as well as insufficient public education, have prevented tropical agroforestry systems to reach their full potential. It is recommended that agroforestry systems in tropical regions should have nature-based solutions, including selection of appropriate local species combinations, promoting biodiversity and ecological processes, and integrating agriculture, culture, as well as tourism development strategies, eventually developing region-specific high-yield, high-quality agricultural technologies.
Agroforestry is an environment-friendly semi-natural system of agricultural production that introduces naturally occurring ecosystems into agricultural land management, using a mixed-planting approach of trees and agricultural crops to create a more stable agricultural ecosystem. Agroforestry systems help to enhance economic value, increase product diversity, improve resource recycling efficiency, enrich soil, and maintain local biodiversity, thus leading a trend toward modern, efficient, sustainable agriculture. This article summarizes common agroforestry systems found in tropical regions worldwide, and evaluates their ecological, economic, and social benefits. In Asia, important agroforestry systems include rubber-based, oil palm-based, and Kapok-rice agroforestry systems. Agroforestry systems in Africa are based on crops such as cocoa and acacia. Dominant species for agroforestry systems in Latin America are cashews and coffee. Nevertheless, there is still a lack of comprehensive macro-scale researches and understandings of ecological processes. The absence of a unified evaluation system, as well as insufficient public education, have prevented tropical agroforestry systems to reach their full potential. It is recommended that agroforestry systems in tropical regions should have nature-based solutions, including selection of appropriate local species combinations, promoting biodiversity and ecological processes, and integrating agriculture, culture, as well as tourism development strategies, eventually developing region-specific high-yield, high-quality agricultural technologies.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250016
Abstract:
Natural rubber is an important strategic resource in China. The infection of Colletotrichum gloeosporides in rubber tree would greatly affect the development of rubber industry. The functional study of the pathogenicity-related genes of C. gloeosporioides can provide a theoretical basis for disease prevention and control. A gene CgPEB encoding carboxypeptidase Y inhibitor protein was identified in C. gloeosporioides. The gene knockout mutant strain was constructed according to the principle of homologous recombination, and the phenotype and pathogenicity analysis were performed. The results showed that the growth rate and conidial production of ΔCgpeb, Cgpeb gene knockout mutant were reduced. Besides, both the appressorium and invasive hyphae formation rate of ΔCgpeb were significantly reduced. These findings suggested that CgPEB plays an important role in regulating the colony growth, conidial production and pathogenicity of C. gloeosporioides.
Natural rubber is an important strategic resource in China. The infection of Colletotrichum gloeosporides in rubber tree would greatly affect the development of rubber industry. The functional study of the pathogenicity-related genes of C. gloeosporioides can provide a theoretical basis for disease prevention and control. A gene CgPEB encoding carboxypeptidase Y inhibitor protein was identified in C. gloeosporioides. The gene knockout mutant strain was constructed according to the principle of homologous recombination, and the phenotype and pathogenicity analysis were performed. The results showed that the growth rate and conidial production of ΔCgpeb, Cgpeb gene knockout mutant were reduced. Besides, both the appressorium and invasive hyphae formation rate of ΔCgpeb were significantly reduced. These findings suggested that CgPEB plays an important role in regulating the colony growth, conidial production and pathogenicity of C. gloeosporioides.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250048
Abstract:
A new type of electron accelerator device in Sanya was utilized for the first time to mutagenize rice germinating seeds with seven radiation groups at doses of 80-200 Gy in a gradient of 20 Gy. Statistical analyses were performed on six agronomic traits, namely, germination potential, germination rate, survival rate, plant height, fruiting rate, and 1,000-grain weight of rice seeds of the M1 generation, and phenotypic mutations were screened and analyzed for the M2 generation. The results showed that all the agronomic indexes of the rice materials of the M1 generation irradiated at different doses tended to decrease significantly different with the increase of irradiation dose, except for the thousand grain weight, which did not change significantly, and the plant height, which was gradually restored to the level of the control group. The rice plants with mutation in disease resistance, early maturity, late maturity, plant height, tiller number, awn length, and hull color were selected from the M2 generation, with the mutation rates in the order of hull color (0.2349 %) > plant height (0.2148 %) > late maturity (0.1348 %) > plant height (0.1348 %) > late maturity (0.1348 %) > early maturity (0.1074 %) > awn length (0.0805 %) > number of tillers (0.0537 %) > disease resistance (0.0403 %). The optimal radiation doses for the rice sprouting seeds were determined to be 140-160 Gy.
A new type of electron accelerator device in Sanya was utilized for the first time to mutagenize rice germinating seeds with seven radiation groups at doses of 80-200 Gy in a gradient of 20 Gy. Statistical analyses were performed on six agronomic traits, namely, germination potential, germination rate, survival rate, plant height, fruiting rate, and 1,000-grain weight of rice seeds of the M1 generation, and phenotypic mutations were screened and analyzed for the M2 generation. The results showed that all the agronomic indexes of the rice materials of the M1 generation irradiated at different doses tended to decrease significantly different with the increase of irradiation dose, except for the thousand grain weight, which did not change significantly, and the plant height, which was gradually restored to the level of the control group. The rice plants with mutation in disease resistance, early maturity, late maturity, plant height, tiller number, awn length, and hull color were selected from the M2 generation, with the mutation rates in the order of hull color (
Identification and expression analysis of the acetyl-CoA carboxylase gene family in Persea americana
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250037
Abstract:
Avocado (Persea americana) is a fruit with high nutritional value, and fatty acids are among its key intrinsic nutrients. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a crucial enzyme in fatty acid synthesis, essential for oil accumulation and storage. The protein structure, evolutionary relationships, and cis-acting elements of the PaACC gene promoter in avocado were analyzed by employing bioinformatics tools, and the expression levels of the PaACC genes across different avocado organs and developmental stages of the fruit were analyzed by using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). A total of seven PaACC genes were identified in avocado, encoding three BC subunits, three BCCP subunits, and one α-CT subunit of ACC. The amino acid lengths of these genes range from 251 to 776, with an average molecular weight of 49.95 kDa. All the encoded proteins are hydrophilic and lack of transmembrane domains. Phylogenetic analysis of ACC proteins from various plant species reveals that ACC proteins are categorized into four subfamilies based on subunit composition. The gene structure shows that all the PaACC genes contain at least 5 exons, each member of which contains a certain number of introns. There are 25 different conserved motifs in the PaACC gene family. Specifically, PaACC1, PaACC2, and PaACC3 all have motif 14, while PaACC4, PaACC5, and PaACC6 all have motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. In the promoter region of the PaACC genes, several cis-acting elements associated with light response, hormone response, drought stress, and low-temperature stress were identified. These findings suggest that the PaACC genes play a significant role in regulating plant growth and development and may enhance the plant’s tolerance to abiotic stresses. Expression pattern analysis reveals that PaACC4, PaACC5, and PaACC7 exhibit significantly higher expression levels during the S5 stage of fruit development compared to other organs and stages. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further research on the role of the PaACC genes in avocado fatty acid biosynthesis.
Avocado (Persea americana) is a fruit with high nutritional value, and fatty acids are among its key intrinsic nutrients. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) is a crucial enzyme in fatty acid synthesis, essential for oil accumulation and storage. The protein structure, evolutionary relationships, and cis-acting elements of the PaACC gene promoter in avocado were analyzed by employing bioinformatics tools, and the expression levels of the PaACC genes across different avocado organs and developmental stages of the fruit were analyzed by using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). A total of seven PaACC genes were identified in avocado, encoding three BC subunits, three BCCP subunits, and one α-CT subunit of ACC. The amino acid lengths of these genes range from 251 to 776, with an average molecular weight of 49.95 kDa. All the encoded proteins are hydrophilic and lack of transmembrane domains. Phylogenetic analysis of ACC proteins from various plant species reveals that ACC proteins are categorized into four subfamilies based on subunit composition. The gene structure shows that all the PaACC genes contain at least 5 exons, each member of which contains a certain number of introns. There are 25 different conserved motifs in the PaACC gene family. Specifically, PaACC1, PaACC2, and PaACC3 all have motif 14, while PaACC4, PaACC5, and PaACC6 all have motifs 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5. In the promoter region of the PaACC genes, several cis-acting elements associated with light response, hormone response, drought stress, and low-temperature stress were identified. These findings suggest that the PaACC genes play a significant role in regulating plant growth and development and may enhance the plant’s tolerance to abiotic stresses. Expression pattern analysis reveals that PaACC4, PaACC5, and PaACC7 exhibit significantly higher expression levels during the S5 stage of fruit development compared to other organs and stages. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further research on the role of the PaACC genes in avocado fatty acid biosynthesis.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250032
Abstract:
Ascorbate peroxidases (APXs) play a significant role in plant resistance to abiotic stress. An attempt was made to investigate the role of APXs in cassava resistance to cassava common mosaic virus (CsCMV). APX activity and the expression level of MeAPXs during infection of cassava with CsCMV were analyzed. The results showed that APX activity and MeAPX2 transcript level were reduced. Therefore, MeAPX2 was identified as a candidate gene for further analysis. MeAPX2 positively regulated cassava resistance to CsCMV, as determined by the disease index in MeAPX2-silenced plants. Further analysis revealed that MeAPX2 directly interacts with the coat protein (CP) of CsCMV. Moreover, CP was found to inhibit the activity of MeAPX2 both in vivo and in vitro. The results demonstrated that CsCMV suppresses APX activity during infection in cassava. Furthermore, MeAPX2 positively regulates cassava resistance to CsCMV by targeting CP.
Ascorbate peroxidases (APXs) play a significant role in plant resistance to abiotic stress. An attempt was made to investigate the role of APXs in cassava resistance to cassava common mosaic virus (CsCMV). APX activity and the expression level of MeAPXs during infection of cassava with CsCMV were analyzed. The results showed that APX activity and MeAPX2 transcript level were reduced. Therefore, MeAPX2 was identified as a candidate gene for further analysis. MeAPX2 positively regulated cassava resistance to CsCMV, as determined by the disease index in MeAPX2-silenced plants. Further analysis revealed that MeAPX2 directly interacts with the coat protein (CP) of CsCMV. Moreover, CP was found to inhibit the activity of MeAPX2 both in vivo and in vitro. The results demonstrated that CsCMV suppresses APX activity during infection in cassava. Furthermore, MeAPX2 positively regulates cassava resistance to CsCMV by targeting CP.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250031
Abstract:
MYC2 is an important transcription factor that regulates the synthesis of terpenoid secondary metabolites in plants. However, little is known about the CdMYC2 transcription factor in C. drupifera. In this study, the related sequence information of CdMYC2 gene was obtained based on the transcriptome annotation data of C. drupifera. A CdMYC2 gene was successfully isolated and cloned from the leaves of C. drupifera for the first time. Its CDS sequence length was1515 bp, encoding 504 amino acids, with typical bHLH-MYC _ N super family and bHLH _ SF super family conserved domains. This gene was predicted to be located in the nucleus. Multiple sequence alignment further confirmed that the amplified CdMYC2 belongs to the MYC2 family transcription factor. The phylogenetic tree analysis showed that CdMYC2 was clustered into a clade with Camellia sinensis, a plant belonging to the same family and genus, while it was far away from the clades of Quercus lobata and Quercus robur. RT-qPCR results showed that the expression level of CdMYC2 gene was higher in the leaves than in other tissues. Among the different developmental stages of the fruit, the expression of CdMYC2 in the fruit reached the highest in September. This study provides an important reference for the subsequent exploration of the function of MYC2 transcription factor in the regulation of triterpenoid saponin biosynthesis pathway in C. drupifera.
MYC2 is an important transcription factor that regulates the synthesis of terpenoid secondary metabolites in plants. However, little is known about the CdMYC2 transcription factor in C. drupifera. In this study, the related sequence information of CdMYC2 gene was obtained based on the transcriptome annotation data of C. drupifera. A CdMYC2 gene was successfully isolated and cloned from the leaves of C. drupifera for the first time. Its CDS sequence length was
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250030
Abstract:
Myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) are critical regulators of skeletal muscle growth and development in animals. The full-length cDNA sequences of five MRFs from the giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus) were cloned using RT-PCR and RAC, including MyoD1 (1,962 bp), MyoD2 (1,466 bp), MyoG (926 bp), MRF4 (1,052 bp), and Myf5 (1,133 bp), encoding 297, 270, 251, 238, and 242 amino acids, respectively. Amino acid sequence alignment revealed that all five MRFs contain a conserved basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain consisting of 60 amino acids. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the MRF genes are clustered into two distinct branches: MyoD (MyoD1 and MyoD2) groups with Myf5 in one clade, while MRF4 and MyoG form the other. All genes showed closest evolutionary relationships with Perciformes homologs. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis revealed predominant expression of these MRFs in skeletal muscle, with significantly lower expression levels in the liver, heart, and intestine. These findings provide foundation for elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of MRFs in skeletal muscle development of the giant grouper.
Myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs) are critical regulators of skeletal muscle growth and development in animals. The full-length cDNA sequences of five MRFs from the giant grouper (Epinephelus lanceolatus) were cloned using RT-PCR and RAC, including MyoD1 (1,962 bp), MyoD2 (1,466 bp), MyoG (926 bp), MRF4 (1,052 bp), and Myf5 (1,133 bp), encoding 297, 270, 251, 238, and 242 amino acids, respectively. Amino acid sequence alignment revealed that all five MRFs contain a conserved basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) domain consisting of 60 amino acids. Phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the MRF genes are clustered into two distinct branches: MyoD (MyoD1 and MyoD2) groups with Myf5 in one clade, while MRF4 and MyoG form the other. All genes showed closest evolutionary relationships with Perciformes homologs. Real-time quantitative PCR analysis revealed predominant expression of these MRFs in skeletal muscle, with significantly lower expression levels in the liver, heart, and intestine. These findings provide foundation for elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of MRFs in skeletal muscle development of the giant grouper.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240197
Abstract:
To address the decreased cut flower yield caused by the bud jumping development phenomenon, where adventitious buds interrupt the normal growth cycle of flower bud differentiation in Oncidium cut flower production, flower buds and vegetative buds of Oncidium hybridum 'Boda NO1' were selected for high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. A total of 127,452,717 high-quality sequences (37.36 Gb) were obtained, and 7,671 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. COG functional classification revealed primary enrichment in signal transduction pathways and carbohydrate transport/metabolism pathways. KEGG analysis showed that DEGs were significantly enriched in starch and sucrose metabolism, phytohormone signaling, and other pathways. Among these, 78 DEGs were identified in the phytohormone signaling pathway, with the most pronounced differences involving auxin, cytokinins, salicylic acid, and gibberellins. Thirteen transcription factors and flowering-related genes, including MADS1, AP2, and FLK, were also screened. These results partially elucidate the effects of auxin, cytokinins, and flowering-related genes on the differentiation of flower buds and vegetative buds in Oncidium. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further research on the mechanism underlying the bud jumping development phenomenon during Oncidium production. Additionally, it supports subsequent improvement in production efficiency, quality enhancement, and optimization of cultivation and management. These findings hold significant practical value for advancing orchid breeding, seedling production, and industry development in China.
To address the decreased cut flower yield caused by the bud jumping development phenomenon, where adventitious buds interrupt the normal growth cycle of flower bud differentiation in Oncidium cut flower production, flower buds and vegetative buds of Oncidium hybridum 'Boda NO1' were selected for high-throughput transcriptome sequencing. A total of 127,452,717 high-quality sequences (37.36 Gb) were obtained, and 7,671 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. COG functional classification revealed primary enrichment in signal transduction pathways and carbohydrate transport/metabolism pathways. KEGG analysis showed that DEGs were significantly enriched in starch and sucrose metabolism, phytohormone signaling, and other pathways. Among these, 78 DEGs were identified in the phytohormone signaling pathway, with the most pronounced differences involving auxin, cytokinins, salicylic acid, and gibberellins. Thirteen transcription factors and flowering-related genes, including MADS1, AP2, and FLK, were also screened. These results partially elucidate the effects of auxin, cytokinins, and flowering-related genes on the differentiation of flower buds and vegetative buds in Oncidium. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further research on the mechanism underlying the bud jumping development phenomenon during Oncidium production. Additionally, it supports subsequent improvement in production efficiency, quality enhancement, and optimization of cultivation and management. These findings hold significant practical value for advancing orchid breeding, seedling production, and industry development in China.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240203
Abstract:
In order to understand the distribution of moss resources and species diversity in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, moss plant specimen collections were conducted several times on the main peak of Limu Mountain from 2022 to 2023, and the specimens collected were identified morphologically in combination of literature review. A new record genus of Pilotrichaceae plants for Hainan was confirmed: Actinodontium, along with the species Actinodontium rhaphidostegum (Müll. Hal.) Bosch & Sande Lac. The morphological characteristics of the newly recorded genus and species were described, and illustrated with characteristic plates. The habitat and geographical distribution of the genus and species was also introduced. This new record enriches the diversity of bryophytes in Hainan Island.
In order to understand the distribution of moss resources and species diversity in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, moss plant specimen collections were conducted several times on the main peak of Limu Mountain from 2022 to 2023, and the specimens collected were identified morphologically in combination of literature review. A new record genus of Pilotrichaceae plants for Hainan was confirmed: Actinodontium, along with the species Actinodontium rhaphidostegum (Müll. Hal.) Bosch & Sande Lac. The morphological characteristics of the newly recorded genus and species were described, and illustrated with characteristic plates. The habitat and geographical distribution of the genus and species was also introduced. This new record enriches the diversity of bryophytes in Hainan Island.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240160
Abstract:
Abstracts: Macroalgae, such as Acanthophora muscoides and Gracilaria coronopifolia, widely distributed in the water of Liusha Bay in the Leizhou Peninsula in Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province. The basic nutritional components of A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia were analyzed and their nutritional value was assessed in a view to exploring their potential value for development. The results showed that the fresh weight moisture contents of A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia were 93.10% and 88.60%, respectively. Additionally, A. muscoides had crude protein content of 9.4%, crude fat content of 2.89%, ash content of 55.07%, and crude fiber content of 5.7%, while G. coronopifolia contained 7.5% of crude protein, 1.78% of crude fat, 27.38% of ash, and 3.57% of crude fiber. In term of amino acid profile, A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia contained 13 types of amino acids, with a rational composition and high levels of essential and flavor amino acids. The DAA/TAA ratios of the two macroalgae were 56.74% and 48.14%, respectively, meeting the requirements of the FAO/WHO standard pattern. The first limiting amino acid for both species was leucine, while the second limiting amino acids were isoleucine and lysine for A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia, respectively. Moreover, these macroalgae had valuable minerals, such as calcium, iron, sodium, magnesium, zinc, and potassium, and had low content of heavy metals. All these results showed that A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia had diverse and patterned amino acids, and vital minerals, making them highly valuable for nutrition and offering broad prospects for development and application. This study provides some reference for further resource development and utilization of A. muscoides and G.coronopifolia.
Abstracts: Macroalgae, such as Acanthophora muscoides and Gracilaria coronopifolia, widely distributed in the water of Liusha Bay in the Leizhou Peninsula in Zhanjiang, Guangdong Province. The basic nutritional components of A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia were analyzed and their nutritional value was assessed in a view to exploring their potential value for development. The results showed that the fresh weight moisture contents of A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia were 93.10% and 88.60%, respectively. Additionally, A. muscoides had crude protein content of 9.4%, crude fat content of 2.89%, ash content of 55.07%, and crude fiber content of 5.7%, while G. coronopifolia contained 7.5% of crude protein, 1.78% of crude fat, 27.38% of ash, and 3.57% of crude fiber. In term of amino acid profile, A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia contained 13 types of amino acids, with a rational composition and high levels of essential and flavor amino acids. The DAA/TAA ratios of the two macroalgae were 56.74% and 48.14%, respectively, meeting the requirements of the FAO/WHO standard pattern. The first limiting amino acid for both species was leucine, while the second limiting amino acids were isoleucine and lysine for A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia, respectively. Moreover, these macroalgae had valuable minerals, such as calcium, iron, sodium, magnesium, zinc, and potassium, and had low content of heavy metals. All these results showed that A. muscoides and G. coronopifolia had diverse and patterned amino acids, and vital minerals, making them highly valuable for nutrition and offering broad prospects for development and application. This study provides some reference for further resource development and utilization of A. muscoides and G.coronopifolia.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240142
Abstract:
To explore the characteristics of macroalgae species and community structure in the Marine Ranch of Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya, sampling surveys were conducted from April 2023 to June 2023 at 12 different sites within the marine ranch area. A total of 29 species of macroalgae were collected, including 17 species from the Rhodophyta phylum, 9 species from the Chlorophyta phylum, and 3 species from the Phaeophyta phylum. The dominant species were Amphiroa fragilissima and Turbinaria ornata. The average biomass of macroalgae was 2.40±1.89 g·m−2. The average carbon content and nitrogen content of different species of macroalgae were 18.80% and 0.98%, respectively, with an average C/N ratio of 24.04±13.61. The mean values of species diversity index (H′), species richness index (D), and species evenness index (J) of the macroalgae community were 1.28±0.59, 5.60±4.61, and 0.87±0.70, respectively. Cluster and ordination analysis revealed that the 12 sites were grouped into 3 clusters. SIMPER and ANOSIM analyses indicated significant differences in the community structure of macroalgae among these three clusters, with basic separation of community structures. These results suggest that the Marine Ranch of Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya harbors a rich diversity of macroalgae, but significant differences in community structure exist among different clusters due to specific dominant species and habitat variations.
To explore the characteristics of macroalgae species and community structure in the Marine Ranch of Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya, sampling surveys were conducted from April 2023 to June 2023 at 12 different sites within the marine ranch area. A total of 29 species of macroalgae were collected, including 17 species from the Rhodophyta phylum, 9 species from the Chlorophyta phylum, and 3 species from the Phaeophyta phylum. The dominant species were Amphiroa fragilissima and Turbinaria ornata. The average biomass of macroalgae was 2.40±1.89 g·m−2. The average carbon content and nitrogen content of different species of macroalgae were 18.80% and 0.98%, respectively, with an average C/N ratio of 24.04±13.61. The mean values of species diversity index (H′), species richness index (D), and species evenness index (J) of the macroalgae community were 1.28±0.59, 5.60±4.61, and 0.87±0.70, respectively. Cluster and ordination analysis revealed that the 12 sites were grouped into 3 clusters. SIMPER and ANOSIM analyses indicated significant differences in the community structure of macroalgae among these three clusters, with basic separation of community structures. These results suggest that the Marine Ranch of Wuzhizhou Island, Sanya harbors a rich diversity of macroalgae, but significant differences in community structure exist among different clusters due to specific dominant species and habitat variations.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250024
Abstract:
The KNOX gene family encodes homeobox proteins that function as transcription factors and are integral to regulating plant growth and development. To investigate the bioinformatic characteristics of the KNOX gene family and its potential roles during viviparous seedling development in water lily (Nymphaea), this study identified 15 KNOX genes from the Nymphaea genome using bioinformatics approaches. These genes were distributed across chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, and 13. Detailed analyses were performed to assess their physicochemical properties, cis-regulatory elements, and interspecies collinearity. The physicochemical characterization revealed that the KNOX proteins ranged from 249 to2270 amino acids in length, were hydrophilic, and had molecular weights between 2.84 and 24.95 kDa. Subcellular localization predictions indicated that most KNOX proteins localized in the nucleus. Furthermore, the majority of these proteins contained four conserved domains — KNOX1, KNOX2, ELK, and Homeobox KN. Based on structural features and phylogenetic analysis, the KNOX gene family was classified into Class Ⅰ and Class Ⅱ, with Class Ⅱ-B potentially representing a specific clade unique to Nymphaea. Interspecies collinearity analysis revealed that 13 of the KNOX genes shared conserved synteny with KNOX genes from Arabidopsis thaliana, Solanum lycopersicum, Oryza sativa, and Zea mays, with the highest level of homology observed with tomato. Additionally, promoter analysis identified numerous cis-regulatory elements related to growth and development, hormone response, and stress response. Expression pattern analysis across different development stages of leaves suggested that Class Ⅰ genes likely played a pivotal role in the formation and development of leaf viviparous shoots in Nymphaea.
The KNOX gene family encodes homeobox proteins that function as transcription factors and are integral to regulating plant growth and development. To investigate the bioinformatic characteristics of the KNOX gene family and its potential roles during viviparous seedling development in water lily (Nymphaea), this study identified 15 KNOX genes from the Nymphaea genome using bioinformatics approaches. These genes were distributed across chromosomes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, and 13. Detailed analyses were performed to assess their physicochemical properties, cis-regulatory elements, and interspecies collinearity. The physicochemical characterization revealed that the KNOX proteins ranged from 249 to
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250033
Abstract:
Bidens pilosa, an invasive weed commonly found in South China, is considered as a companion weeds in various upland cropping systems and serves as an intermediate host for a range of phytopathogens. This study reports the occurrence of leaf spot lesions in a population of B. pilosa. To investigate the cause, pathogens were isolated from the infected leaves using a tissue isolation method, and pathogenicity was confirmed through detached-leaf inoculation assays. A combination of morphological characterization and phylogenetic analysis of concatenated rDNA-ITS and tef1 sequences enabled accurate identification of the pathogen. The pathogen was identified as Lasiodiplodia theobromae, which causes leaf wilt and rot in B. pilosa. Preliminary environmental studies indicated that the isolated strain exhibited optimal colony growth at 28 ℃, pH 6, on Potato Dextrose Agar(PDA) medium supplemented with sucrose and sodium nitrate, which served as the preferred carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively.
Bidens pilosa, an invasive weed commonly found in South China, is considered as a companion weeds in various upland cropping systems and serves as an intermediate host for a range of phytopathogens. This study reports the occurrence of leaf spot lesions in a population of B. pilosa. To investigate the cause, pathogens were isolated from the infected leaves using a tissue isolation method, and pathogenicity was confirmed through detached-leaf inoculation assays. A combination of morphological characterization and phylogenetic analysis of concatenated rDNA-ITS and tef1 sequences enabled accurate identification of the pathogen. The pathogen was identified as Lasiodiplodia theobromae, which causes leaf wilt and rot in B. pilosa. Preliminary environmental studies indicated that the isolated strain exhibited optimal colony growth at 28 ℃, pH 6, on Potato Dextrose Agar(PDA) medium supplemented with sucrose and sodium nitrate, which served as the preferred carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250008
Abstract:
In order to select an agricultural Jiaosu that can effectively improve the quality and yield of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis), passion fruit seedlings were treated with agricultural Jiaosu formulations prepared from four different substrates, namely passion fruit peel, passion fruit straw, cherry tomato straw and corn straw, and chemical fertilizer as control to observe the effects of the treatments on the quality and yield of passion fruits in pot culture under anti-insect net and field experiments. The results showed that the fruit size, single fruit weight and first-class fruit rate of passion fruit under the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment were similar to those of the chemical fertilizer treatment, with the yield being 6.38% higher, and that this Jiaosu treatment was better than other Jiaosu treatments. In terms of quality, the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment significantly increased the content of Ca and total sugar in juice, decreased the content of organic acid, and had the highest TSS-TA ratio and sugar-acid ratio, and this treatment was better than the passion fruit straw Jiaosu and corn straw Jiaosu treatments. The cherry tomato straw Jiaosu treatment significantly increased the contents of Fe, Zn, total organic acids, total amino acids and vitamin C in the fruit. However, the fruits in this treatment were low in TSS-TA ratio and sugar-acid ratio due to the high acid content, and hence were poor in comprehensive quality. Based on the data of 2 years of experiments, the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment had the best effects on improving the comprehensive quality and yield of passion fruits, and the fruits under this treatment had a higher commercial value, which was suggested to be the best treatment.
In order to select an agricultural Jiaosu that can effectively improve the quality and yield of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis), passion fruit seedlings were treated with agricultural Jiaosu formulations prepared from four different substrates, namely passion fruit peel, passion fruit straw, cherry tomato straw and corn straw, and chemical fertilizer as control to observe the effects of the treatments on the quality and yield of passion fruits in pot culture under anti-insect net and field experiments. The results showed that the fruit size, single fruit weight and first-class fruit rate of passion fruit under the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment were similar to those of the chemical fertilizer treatment, with the yield being 6.38% higher, and that this Jiaosu treatment was better than other Jiaosu treatments. In terms of quality, the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment significantly increased the content of Ca and total sugar in juice, decreased the content of organic acid, and had the highest TSS-TA ratio and sugar-acid ratio, and this treatment was better than the passion fruit straw Jiaosu and corn straw Jiaosu treatments. The cherry tomato straw Jiaosu treatment significantly increased the contents of Fe, Zn, total organic acids, total amino acids and vitamin C in the fruit. However, the fruits in this treatment were low in TSS-TA ratio and sugar-acid ratio due to the high acid content, and hence were poor in comprehensive quality. Based on the data of 2 years of experiments, the passion fruit peel Jiaosu treatment had the best effects on improving the comprehensive quality and yield of passion fruits, and the fruits under this treatment had a higher commercial value, which was suggested to be the best treatment.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250035
Abstract:
In order to investigate the potential functions of the cassava (Manihot esculenta) Ⅶ subfamily of ERF gene family in response to biotic stress, we identified 161 ERF genes in the cassava genome, which were divided into 13 subfamilies. Analyses were performed on the conserved domains, cis-acting elements in promoter regions, interacting proteins, target genes, and expression patterns of the Ⅶ subfamily members. The results showed that all members of this subfamily contained a conserved AP2 domain, and their promoter regions included 13 types of cis-acting elements related to plant growth and development, and environmental stress responses. Expression pattern analysis revealed that the MeERF46, MeERF133, and MeERF92 genes responded actively to Xpm infection among them, the change of MeERF92 expression was the most significant. WGCNA and protein-protein interaction network analysis indicated that MeERF92 might be involved in the process of oxidative stress, while MeERF133 was widely involved in glycometabolism. These findings provide candidate genes for further research into the functions and mechanisms of ERFs in cassava's response to biotic stress.
In order to investigate the potential functions of the cassava (Manihot esculenta) Ⅶ subfamily of ERF gene family in response to biotic stress, we identified 161 ERF genes in the cassava genome, which were divided into 13 subfamilies. Analyses were performed on the conserved domains, cis-acting elements in promoter regions, interacting proteins, target genes, and expression patterns of the Ⅶ subfamily members. The results showed that all members of this subfamily contained a conserved AP2 domain, and their promoter regions included 13 types of cis-acting elements related to plant growth and development, and environmental stress responses. Expression pattern analysis revealed that the MeERF46, MeERF133, and MeERF92 genes responded actively to Xpm infection among them, the change of MeERF92 expression was the most significant. WGCNA and protein-protein interaction network analysis indicated that MeERF92 might be involved in the process of oxidative stress, while MeERF133 was widely involved in glycometabolism. These findings provide candidate genes for further research into the functions and mechanisms of ERFs in cassava's response to biotic stress.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240088
Abstract:
An attempt was made to determine the content of total saponins and antioxidant activity in the roots of Callerya speciosa (Champion ex Bentham) Schot at different ages, and provide reference for their rational development and utilization. The roots of C. speciosa were collected and extracted by using an ultrasonic-assisted extraction method, and the extraction process of total saponins from C. speciosa roots were optimized. Furthermore, the content of total saponins from the extracts of the C. speciosa roots at different ages (3-year-old, 6-year-old, 10-year-old and 15-year-old) was determined by using UV photometer.. The antioxidant activity of total saponins from the C. speciosa roots was determined by using the DPPH free radical method and hydroxyl free radical method. The results showed that the best extraction conditions for total saponins of the C. speciosa roots are 80% ethanol, 1∶ 40 solid-liquid ratio, 40 min ultrasound time, and 3 extraction times. Among the four materials, the 6-year-old C. speciosa roots had the highest total saponin content, while the 15-year-old C. speciosa had the lowest. The total saponin content of the C. speciosa roots tended to increase and then decrease with the ages of C. speciosa. The antioxidant activity test found that total saponins of the C. speciosa roots at different ages all possessed a certain level of antioxidant capacity in vitro, which can be developed and utilized as a potential natural antioxidant.
An attempt was made to determine the content of total saponins and antioxidant activity in the roots of Callerya speciosa (Champion ex Bentham) Schot at different ages, and provide reference for their rational development and utilization. The roots of C. speciosa were collected and extracted by using an ultrasonic-assisted extraction method, and the extraction process of total saponins from C. speciosa roots were optimized. Furthermore, the content of total saponins from the extracts of the C. speciosa roots at different ages (3-year-old, 6-year-old, 10-year-old and 15-year-old) was determined by using UV photometer.. The antioxidant activity of total saponins from the C. speciosa roots was determined by using the DPPH free radical method and hydroxyl free radical method. The results showed that the best extraction conditions for total saponins of the C. speciosa roots are 80% ethanol, 1∶ 40 solid-liquid ratio, 40 min ultrasound time, and 3 extraction times. Among the four materials, the 6-year-old C. speciosa roots had the highest total saponin content, while the 15-year-old C. speciosa had the lowest. The total saponin content of the C. speciosa roots tended to increase and then decrease with the ages of C. speciosa. The antioxidant activity test found that total saponins of the C. speciosa roots at different ages all possessed a certain level of antioxidant capacity in vitro, which can be developed and utilized as a potential natural antioxidant.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250010
Abstract:
Banana 'Haigong' (Musa. AA) seedlings were treated with magnesium (Mg) and zinc (Zn) at gradient concentrations of 0%, 50%, and 100% of normal levels to observe the effects of magnesium and zinc deficiency on the growth and photosynthesis of the seedlings. The results show that after 120 days of treatment, the combined deficiency of Mg and Zn inhibited the growth and photosynthetic physiology of 'Haigong' seedlings. Under normal treatment, the plant height was 31.5 cm, stem diameter was 8.65 cm, and total root length was 1,051.47 cm; under deficiency treatment, plant height, stem diameter, and total root length were all reduced to varying degrees, with no significant difference in leaf morphology, and the relative growth rate of plant height varied among treatments. In terms of photosynthetic characteristics, there were significant differences in SPAD value, Pn value, Tr value, Ci value, and Gs value between normal and deficiency treatments, and under deficiency treatment the Y(Ⅱ) value and Fv/Fm value decreased, while the NPQ value fluctuated. This study monitored the growth and photosynthetic physiology of banana 'Haigong' seedlings under Mg and Zn deficiency, providing a reference for precise nutrient management.
Banana 'Haigong' (Musa. AA) seedlings were treated with magnesium (Mg) and zinc (Zn) at gradient concentrations of 0%, 50%, and 100% of normal levels to observe the effects of magnesium and zinc deficiency on the growth and photosynthesis of the seedlings. The results show that after 120 days of treatment, the combined deficiency of Mg and Zn inhibited the growth and photosynthetic physiology of 'Haigong' seedlings. Under normal treatment, the plant height was 31.5 cm, stem diameter was 8.65 cm, and total root length was 1,051.47 cm; under deficiency treatment, plant height, stem diameter, and total root length were all reduced to varying degrees, with no significant difference in leaf morphology, and the relative growth rate of plant height varied among treatments. In terms of photosynthetic characteristics, there were significant differences in SPAD value, Pn value, Tr value, Ci value, and Gs value between normal and deficiency treatments, and under deficiency treatment the Y(Ⅱ) value and Fv/Fm value decreased, while the NPQ value fluctuated. This study monitored the growth and photosynthetic physiology of banana 'Haigong' seedlings under Mg and Zn deficiency, providing a reference for precise nutrient management.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240191
Abstract:
To investigate the low-nitrogen tolerance characteristics of Paspalum vaginatum, this study selected 10 Paspalum vaginatum germplasm accessions as experimental materials. A hydroponic method was applied with two nitrogen concentration treatments: full nitrogen (5.0 mmol·L−1) and 1/100 nitrogen (0.05 mmol·L−1), for a duration of 30 days. Eighteen agronomic traits, including chlorophyll content, shoot fresh weight, and turfgrass height, were measured after treatment, and variance analysis was conducted to compare and explore the low-nitrogen tolerance characteristics of the 10 germplasm accessions. A comprehensive evaluation of low-nitrogen tolerance was performed. The results showed that, compared to normal nitrogen treatment, indicators such as shoot fresh weight, shoot dry weight, total tillers length and tillers number significantly decreased under low nitrogen treatment, while indicators such as fresh weight ratio of root shoot, dry weight ratio of root shoot, shoot dry matter content and root dry matter content significantly increased. Through correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and membership function analysis, two low-nitrogen-tolerant Paspalum vaginatum, 17USA-03 and 17HN-39, were selected.
To investigate the low-nitrogen tolerance characteristics of Paspalum vaginatum, this study selected 10 Paspalum vaginatum germplasm accessions as experimental materials. A hydroponic method was applied with two nitrogen concentration treatments: full nitrogen (5.0 mmol·L−1) and 1/100 nitrogen (0.05 mmol·L−1), for a duration of 30 days. Eighteen agronomic traits, including chlorophyll content, shoot fresh weight, and turfgrass height, were measured after treatment, and variance analysis was conducted to compare and explore the low-nitrogen tolerance characteristics of the 10 germplasm accessions. A comprehensive evaluation of low-nitrogen tolerance was performed. The results showed that, compared to normal nitrogen treatment, indicators such as shoot fresh weight, shoot dry weight, total tillers length and tillers number significantly decreased under low nitrogen treatment, while indicators such as fresh weight ratio of root shoot, dry weight ratio of root shoot, shoot dry matter content and root dry matter content significantly increased. Through correlation analysis, principal component analysis, and membership function analysis, two low-nitrogen-tolerant Paspalum vaginatum, 17USA-03 and 17HN-39, were selected.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250026
Abstract:
In order to understand the regulatory role of the BBR-BPC gene family in the growth and development of Dioscorea alata (greater yam), we analyzed the gene structure, phylogenetic evolution, conserved motifs, and physicochemical properties of the BBR-BPC gene family in greater yam. We also predicted the secondary and tertiary structures of BBR-BPC proteins and verified the interaction between the BBR-BPC gene and the DELLA gene. Through HMMsearch and BLAST analyses, we identified six members of the BBR-BPC family in the greater yam genome. These gene proteins exhibited significant differences and alternative splicing events, with a total of 10 splice variants detected. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that all members of the BBR-BPC family in greater yam are located in the nucleus.The yeast two-hybrid interaction results between Da4BBR-BPC2 and DaDELLA2 indicate that there is an interaction between Da4BBR-BPC2 and DaDELLA2, occurring at the N-terminus of the DaDELLA2 gene.
In order to understand the regulatory role of the BBR-BPC gene family in the growth and development of Dioscorea alata (greater yam), we analyzed the gene structure, phylogenetic evolution, conserved motifs, and physicochemical properties of the BBR-BPC gene family in greater yam. We also predicted the secondary and tertiary structures of BBR-BPC proteins and verified the interaction between the BBR-BPC gene and the DELLA gene. Through HMMsearch and BLAST analyses, we identified six members of the BBR-BPC family in the greater yam genome. These gene proteins exhibited significant differences and alternative splicing events, with a total of 10 splice variants detected. Subcellular localization analysis revealed that all members of the BBR-BPC family in greater yam are located in the nucleus.The yeast two-hybrid interaction results between Da4BBR-BPC2 and DaDELLA2 indicate that there is an interaction between Da4BBR-BPC2 and DaDELLA2, occurring at the N-terminus of the DaDELLA2 gene.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250015
Abstract:
In order to assess the role of the bZIP transcription factor in the biosynthesis of natural rubber in Hevea brasiliensis, HbbZIP74 gene was successfully cloned based on previous work in our laboratory. Bioinformatics analysis and expression pattern analysis were performed. The pET28-HbbZIP74 expression vector was constructed, and the recombinant protein was expressed in the strain E. coli BL21 (DE3) and then purified. The results showed that the open reading frame (ORF) of the gene HbbZIP74 is 486 bp, encoding 161 amino acids, with a bZIP domain, classifying it as a bZIP transcription factor S subgroup. The expression level of HbbZIP74 is higher in latex and leaves, and its expression can be induced by jasmonic acid, abscisic acid, ethylene, and salicylic acid in latex. The optimal condition for the heterologous expression of the HbbZIP74-His recombinant protein was induced at 1 mmol·L−1 IPTG and 37 ℃ for 3 h. The recombinant protein was mainly accumulated in inclusion bodies. The recombinant protein, approximately 22 kDa in size, was purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography, which was consistent with expectations. This study lays the foundation for further exploration of the role of HbbZIP74 in the biosynthesis of natural rubber.
In order to assess the role of the bZIP transcription factor in the biosynthesis of natural rubber in Hevea brasiliensis, HbbZIP74 gene was successfully cloned based on previous work in our laboratory. Bioinformatics analysis and expression pattern analysis were performed. The pET28-HbbZIP74 expression vector was constructed, and the recombinant protein was expressed in the strain E. coli BL21 (DE3) and then purified. The results showed that the open reading frame (ORF) of the gene HbbZIP74 is 486 bp, encoding 161 amino acids, with a bZIP domain, classifying it as a bZIP transcription factor S subgroup. The expression level of HbbZIP74 is higher in latex and leaves, and its expression can be induced by jasmonic acid, abscisic acid, ethylene, and salicylic acid in latex. The optimal condition for the heterologous expression of the HbbZIP74-His recombinant protein was induced at 1 mmol·L−1 IPTG and 37 ℃ for 3 h. The recombinant protein was mainly accumulated in inclusion bodies. The recombinant protein, approximately 22 kDa in size, was purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography, which was consistent with expectations. This study lays the foundation for further exploration of the role of HbbZIP74 in the biosynthesis of natural rubber.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240185
Abstract:
To clarify the effects of aluminum stress on latex yield, physiological parameters and tapping panel dryness (TPD) of mature rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), rubber trees of clone Reyan7-33-97 tapped for eight-years were treated with AlCl3 solution at different concentrations. Two control solutions with different pH values (T0 was treated with ultrapure water of pH7.0 and T1 was treated with ultrapure water solution of pH adjusted to 4.2 by hydrochloric acid) and four concentrations (i.e. 50, 100, 200 and 400 mmol·L−1) of AlCl3 solutions with pH4.2 were applied just above the tapping cut. The rubber trees were tapped regularly and the latex volume, dry rubber yield, latex physiological parameters, TPD incidence and grade were observed in the early, middle and late stage of the treatment. The results showed that the harvested latex volume and dry rubber yield increased in the early stage of aluminum treatment, decreased to the same level as the control in the middle stage, and was lower than the control in the late stage, while the total latex volume and dry rubber yield of the 10 tappings after Al treatment were not significantly different from those of the control. Aluminum treatment increased dry rubber content, lutoid bursting index of the early latex and thiols content of late latex, indicating that aluminum treatment led to the decrease of latex flow capacity. Meanwhile aluminum treatment decreased latex sucrose content, and Mg2+ content of latex at the middle and late stages, and increased the inorganic phosphor content of latex at the late stage, which indicates that aluminum treatment also led to the decrease of rubber regeneration ability. High concentration aluminum treatment increased the incidence and grade of TPD. In summary, aluminum solution with a high concentration of 50 mmol·L−1 can increase latex yield in the short term and maintain the stability of dry latex production in a certain period of time, but it leads to the decline of the latex flow and regeneration capacity, inducing the occurrence of TPD. High concentration of Al is not conducive to maintaining the long-term latex production stability.
To clarify the effects of aluminum stress on latex yield, physiological parameters and tapping panel dryness (TPD) of mature rubber trees (Hevea brasiliensis), rubber trees of clone Reyan7-33-97 tapped for eight-years were treated with AlCl3 solution at different concentrations. Two control solutions with different pH values (T0 was treated with ultrapure water of pH7.0 and T1 was treated with ultrapure water solution of pH adjusted to 4.2 by hydrochloric acid) and four concentrations (i.e. 50, 100, 200 and 400 mmol·L−1) of AlCl3 solutions with pH4.2 were applied just above the tapping cut. The rubber trees were tapped regularly and the latex volume, dry rubber yield, latex physiological parameters, TPD incidence and grade were observed in the early, middle and late stage of the treatment. The results showed that the harvested latex volume and dry rubber yield increased in the early stage of aluminum treatment, decreased to the same level as the control in the middle stage, and was lower than the control in the late stage, while the total latex volume and dry rubber yield of the 10 tappings after Al treatment were not significantly different from those of the control. Aluminum treatment increased dry rubber content, lutoid bursting index of the early latex and thiols content of late latex, indicating that aluminum treatment led to the decrease of latex flow capacity. Meanwhile aluminum treatment decreased latex sucrose content, and Mg2+ content of latex at the middle and late stages, and increased the inorganic phosphor content of latex at the late stage, which indicates that aluminum treatment also led to the decrease of rubber regeneration ability. High concentration aluminum treatment increased the incidence and grade of TPD. In summary, aluminum solution with a high concentration of 50 mmol·L−1 can increase latex yield in the short term and maintain the stability of dry latex production in a certain period of time, but it leads to the decline of the latex flow and regeneration capacity, inducing the occurrence of TPD. High concentration of Al is not conducive to maintaining the long-term latex production stability.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240201
Abstract:
In order to screen for stable expression of cassava reference genes in cassava leaves infected with Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. manihotis(Xpm), we used Xpm resistant variety ‘G1301’ and susceptible variety ‘SC9’cassava leaves as research materials. Samples were collected from cassava leaves of ‘G1301’ and ‘SC9’ at 0 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 72 h, and 120 h after Xpm infection, and the stability of the commonly used reference genes Nascent, EF1a, ACT, GTPb, and TUB was determined. The results showed that there were differences in the expression levels of five reference genes after Xpm infection in the leaves of ‘G1301’ and ‘SC9’. Delta CT, GeNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper and RefFinder software were used to rank the stability of these candidate reference genes. We found that the most stable reference gene expressed in Xpm-infected leaves is EF1α. This study identified the stable internal reference genes expressed during Xpm infection in cassava leaves, laying the foundation for studying gene expression in response to Xpm infection and exploring disease resistance genes.
In order to screen for stable expression of cassava reference genes in cassava leaves infected with Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. manihotis(Xpm), we used Xpm resistant variety ‘G1301’ and susceptible variety ‘SC9’cassava leaves as research materials. Samples were collected from cassava leaves of ‘G1301’ and ‘SC9’ at 0 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, 72 h, and 120 h after Xpm infection, and the stability of the commonly used reference genes Nascent, EF1a, ACT, GTPb, and TUB was determined. The results showed that there were differences in the expression levels of five reference genes after Xpm infection in the leaves of ‘G1301’ and ‘SC9’. Delta CT, GeNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper and RefFinder software were used to rank the stability of these candidate reference genes. We found that the most stable reference gene expressed in Xpm-infected leaves is EF1α. This study identified the stable internal reference genes expressed during Xpm infection in cassava leaves, laying the foundation for studying gene expression in response to Xpm infection and exploring disease resistance genes.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240161
Abstract:
Torulaspora delbrueckii is one of non-Saccharomyces yeasts mostly used for research, and is widely used for brewing of various fruit wines. It is co-fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improving fruit wine flavors. In this experiment, a wild-type yeast strain was selected from the peel of cantaloupe in Fulo Town, Ledong County, Hainan Province. Through phenotypic observation of the strain and constructing a phylogenetic tree based on 18S rDNA sequencing, the strain was identified as T. delbrueckii. Under the fermentation condition of fruit wine, T. delbrueckii grew normally in the range of alcohol content 4−20%, pH value 2.8−3.6 and sulfur dioxide concentration 100−500 mg·L−1, and the growth rate was the highest under the condition of alcohol content 4%, pH value 3.6 and sulfur dioxide concentration 300 mg·L−1. The results show that T. delbrueckii did not produce hydrogen sulfide, had no killing effect on S. cerevisiae, and improved the flavor of cantaloupe fruit wine, which can be used in the production of cantaloupe fruit wine.
Torulaspora delbrueckii is one of non-Saccharomyces yeasts mostly used for research, and is widely used for brewing of various fruit wines. It is co-fermented with Saccharomyces cerevisiae for improving fruit wine flavors. In this experiment, a wild-type yeast strain was selected from the peel of cantaloupe in Fulo Town, Ledong County, Hainan Province. Through phenotypic observation of the strain and constructing a phylogenetic tree based on 18S rDNA sequencing, the strain was identified as T. delbrueckii. Under the fermentation condition of fruit wine, T. delbrueckii grew normally in the range of alcohol content 4−20%, pH value 2.8−3.6 and sulfur dioxide concentration 100−500 mg·L−1, and the growth rate was the highest under the condition of alcohol content 4%, pH value 3.6 and sulfur dioxide concentration 300 mg·L−1. The results show that T. delbrueckii did not produce hydrogen sulfide, had no killing effect on S. cerevisiae, and improved the flavor of cantaloupe fruit wine, which can be used in the production of cantaloupe fruit wine.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240176
Abstract:
An attempt was made to investigate the expression of lactate dehydrogenase (ptLDHA), a key enzyme in lactate metabolism, and to explore the acetylation modification sites on ptLDHA and their potential role in the interplay between lactylation and acetylation modifications in Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin. The ptLDHA gene sequence was first cloned from P. tricornutum Bohlin cDNA, and then a prokaryotic expression vector, pMBP-C-LDHA, was constructed. The recombinant plasmid was then transferred into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) for induced expression. Under optimized conditions (16℃, 0.2 mmol·L−1 IPTG for 24 hours), ptLDHA protein was successfully expressed, predominantly in a soluble form. The fusion protein was purified using His-tag affinity chromatography and identified by Western blot with ptLDHA polyclonal antibodies. A single protein band at approximately 78 kDa was observed, confirming that the purified protein was ptLDHA. The expression and purification of ptLDHA in prokaryotic cells was successfully established, laying foundations for subsequent site-directed mutagenesis of acetylation modification sites and for investigation of the effects of modification and demodification on enzyme activity.
An attempt was made to investigate the expression of lactate dehydrogenase (ptLDHA), a key enzyme in lactate metabolism, and to explore the acetylation modification sites on ptLDHA and their potential role in the interplay between lactylation and acetylation modifications in Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin. The ptLDHA gene sequence was first cloned from P. tricornutum Bohlin cDNA, and then a prokaryotic expression vector, pMBP-C-LDHA, was constructed. The recombinant plasmid was then transferred into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) for induced expression. Under optimized conditions (16℃, 0.2 mmol·L−1 IPTG for 24 hours), ptLDHA protein was successfully expressed, predominantly in a soluble form. The fusion protein was purified using His-tag affinity chromatography and identified by Western blot with ptLDHA polyclonal antibodies. A single protein band at approximately 78 kDa was observed, confirming that the purified protein was ptLDHA. The expression and purification of ptLDHA in prokaryotic cells was successfully established, laying foundations for subsequent site-directed mutagenesis of acetylation modification sites and for investigation of the effects of modification and demodification on enzyme activity.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240199
Abstract:
To explore the role of jasmonate-induced oxygenases JOX family genes in the growth, development, and stress resistance of cassava (Manihot esculenta), MeJOXs family members were identified in cassava genome by bioinformatics methods, and their gene structure, promoter cis-acting elements, evolutionary relationships and expression patterns were analyzed. The results showed that there were four MeJOXs family genes in cassava genome, and each member had similar gene structure, conserved motifs, and protein domains. Each gene member exhibited at least 68% protein homology, with the highest similarity observed between MeJOX1 and MeJOX4, as well as between MeJOX2 and MeJOX3. Promoter cis-acting elements analysis showed that MeJOXs contained numerous light-responsive elements. Furthermore, each gene member possessed a varying number of hormone-responsive elements. Phylogenetic analysis showed that MeJOXs were more closely related to JOX genes in dicotyledonous plants. Transcriptome analysis revealed that all the genes were differentially expressed in stems, leaves, midveins, and fibrous roots, with the exception of MeJOX2 that was scarcely expressed in various cassava tissues. MeJOXs were induced by MeJA in different cassava germplasm, with MeJOX3 demonstrating the most significant expression by inducing. Upon infection by pathogen Xpm, MeJOX1/3/4 responded promptly, but their response patterns were distinctly different. MeJOX1/3 were upregulated, whereas MeJOX4 exhibited a trend of downregulation, and MeJOX2 exhibited negligible response. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further elucidating the functions of the MeJOXs gene family in cassava.
To explore the role of jasmonate-induced oxygenases JOX family genes in the growth, development, and stress resistance of cassava (Manihot esculenta), MeJOXs family members were identified in cassava genome by bioinformatics methods, and their gene structure, promoter cis-acting elements, evolutionary relationships and expression patterns were analyzed. The results showed that there were four MeJOXs family genes in cassava genome, and each member had similar gene structure, conserved motifs, and protein domains. Each gene member exhibited at least 68% protein homology, with the highest similarity observed between MeJOX1 and MeJOX4, as well as between MeJOX2 and MeJOX3. Promoter cis-acting elements analysis showed that MeJOXs contained numerous light-responsive elements. Furthermore, each gene member possessed a varying number of hormone-responsive elements. Phylogenetic analysis showed that MeJOXs were more closely related to JOX genes in dicotyledonous plants. Transcriptome analysis revealed that all the genes were differentially expressed in stems, leaves, midveins, and fibrous roots, with the exception of MeJOX2 that was scarcely expressed in various cassava tissues. MeJOXs were induced by MeJA in different cassava germplasm, with MeJOX3 demonstrating the most significant expression by inducing. Upon infection by pathogen Xpm, MeJOX1/3/4 responded promptly, but their response patterns were distinctly different. MeJOX1/3 were upregulated, whereas MeJOX4 exhibited a trend of downregulation, and MeJOX2 exhibited negligible response. This study provides a theoretical foundation for further elucidating the functions of the MeJOXs gene family in cassava.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240177
Abstract:
In order to understand the anti-actinomycetes with biocontrol value isolated and screened from the soil in Hainan Island, actinomycetes were isolated from six soil samples from different regions of Hainan by using a gradient dilution method, and the actinomycete strains were screened by using the confrontation culture method and identified based on their morphology, physiological and biochemical characteristics and molecular biology methods. The potential application value of the active strains was determined by fruit soaking method and pot experiment. A total of 285 actinomycete strains were isolated from the soil samples, and the strain Q2-02 had the highest antibacterial activity. Its inhibition rates of Botryodiplodia theobromae, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Rhizoctonia solani were 92.8%, 90.0% and 88.2%, respectively, and the inhibition rates of the other six pathogens were also more than 60.0%. The identification of this strain showed that the strain Q2-02 was Streptomyces lunalinharesii. The pot experiments showed that the control effect of the 10-fold dilution of the fermented supernatant of the strain on mango stemend rot and rice sheath blight was significantly higher than that of the positive control 45% thiophandazim suspension diluted 800 times and 10% validacin aqueous solution diluted1000 times, indicating that the strain Q2-02 has the value of further development and application.
In order to understand the anti-actinomycetes with biocontrol value isolated and screened from the soil in Hainan Island, actinomycetes were isolated from six soil samples from different regions of Hainan by using a gradient dilution method, and the actinomycete strains were screened by using the confrontation culture method and identified based on their morphology, physiological and biochemical characteristics and molecular biology methods. The potential application value of the active strains was determined by fruit soaking method and pot experiment. A total of 285 actinomycete strains were isolated from the soil samples, and the strain Q2-02 had the highest antibacterial activity. Its inhibition rates of Botryodiplodia theobromae, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Rhizoctonia solani were 92.8%, 90.0% and 88.2%, respectively, and the inhibition rates of the other six pathogens were also more than 60.0%. The identification of this strain showed that the strain Q2-02 was Streptomyces lunalinharesii. The pot experiments showed that the control effect of the 10-fold dilution of the fermented supernatant of the strain on mango stemend rot and rice sheath blight was significantly higher than that of the positive control 45% thiophandazim suspension diluted 800 times and 10% validacin aqueous solution diluted
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250013
Abstract:
An attempt was made to understand the mosquito species and their carrying pathogenic microorganisms in pig farms from different regions of Hainan Province, and to provide reliable data support for the scientific prevention and control of mosquito-borne diseases in pig farms. Light catalyst mosquito traps were used to collect mosquitoes from four different pig farms in Baisha Li Autonomous County (BS), Ding 'an County (DA), Ledong Li Autonomous County (LD) and Wenchang City (WC) in Hainan Province. The mosquito species collected were identified by using morphological characteristics and the PCR method, and the composition of mosquito-borne microbial community and gene function were analyzed by using metagenomic sequencing. The results showed that the dominant mosquito species in the pig farms of different regions of Hainan were different. The dominant mosquito species in BS, DA, LD and WC were Anopheles dabryanus, Anopheles sinensis, Culex pipiens pallens and Culex tritaeniorhynchus, accounting for 58.43 %, 55.46 %, 88.65 % and 57.84 %, respectively. The analysis of metagenomic microbial sequencing showed the mosquito-borne microorganisms in BS, LD, WC and other regions were at the phylum level. Euryarchaeota was the dominant archaea, while the dominant archaea in DA pig farm was Thermoarchaeota. Proteobacteria was the dominant phylum of mosquito vectors in the pig farms from the four regions. Ascomycota was the dominant phylum of mosquitoes in the 4 regions; negarnaviricota was the dominant virus phylum in BS, DA and LD, while Cossaviricota was the dominant virus phylum in WC. At the species level bacteria such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brucella melitensis, Chlamydia abortus, Leptospira interrogans and Waddlia chondrophila, fungi such as Acremonium asperulatum, Aspergillus terreus and Microsporum canis, and viruses such as Aedes aegypti anphevirus and Anopheles annulipes orbivirus pose a pathogenic threat to humans and pigs. Moreover, the mosquito-borne microorganisms from the pig farms in different regions of Hainan maintain high stability at the phylum level and diversity at the species level, and there is a high risk of pathogenicity. This study provides a scientific basis for the prevention and control of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne diseases in Hainan pig farms, and provides basic data for assessing the threat of mosquito-borne diseases in public health in this area.
An attempt was made to understand the mosquito species and their carrying pathogenic microorganisms in pig farms from different regions of Hainan Province, and to provide reliable data support for the scientific prevention and control of mosquito-borne diseases in pig farms. Light catalyst mosquito traps were used to collect mosquitoes from four different pig farms in Baisha Li Autonomous County (BS), Ding 'an County (DA), Ledong Li Autonomous County (LD) and Wenchang City (WC) in Hainan Province. The mosquito species collected were identified by using morphological characteristics and the PCR method, and the composition of mosquito-borne microbial community and gene function were analyzed by using metagenomic sequencing. The results showed that the dominant mosquito species in the pig farms of different regions of Hainan were different. The dominant mosquito species in BS, DA, LD and WC were Anopheles dabryanus, Anopheles sinensis, Culex pipiens pallens and Culex tritaeniorhynchus, accounting for 58.43 %, 55.46 %, 88.65 % and 57.84 %, respectively. The analysis of metagenomic microbial sequencing showed the mosquito-borne microorganisms in BS, LD, WC and other regions were at the phylum level. Euryarchaeota was the dominant archaea, while the dominant archaea in DA pig farm was Thermoarchaeota. Proteobacteria was the dominant phylum of mosquito vectors in the pig farms from the four regions. Ascomycota was the dominant phylum of mosquitoes in the 4 regions; negarnaviricota was the dominant virus phylum in BS, DA and LD, while Cossaviricota was the dominant virus phylum in WC. At the species level bacteria such as Brachyspira pilosicoli, Brucella melitensis, Chlamydia abortus, Leptospira interrogans and Waddlia chondrophila, fungi such as Acremonium asperulatum, Aspergillus terreus and Microsporum canis, and viruses such as Aedes aegypti anphevirus and Anopheles annulipes orbivirus pose a pathogenic threat to humans and pigs. Moreover, the mosquito-borne microorganisms from the pig farms in different regions of Hainan maintain high stability at the phylum level and diversity at the species level, and there is a high risk of pathogenicity. This study provides a scientific basis for the prevention and control of mosquitoes and mosquito-borne diseases in Hainan pig farms, and provides basic data for assessing the threat of mosquito-borne diseases in public health in this area.


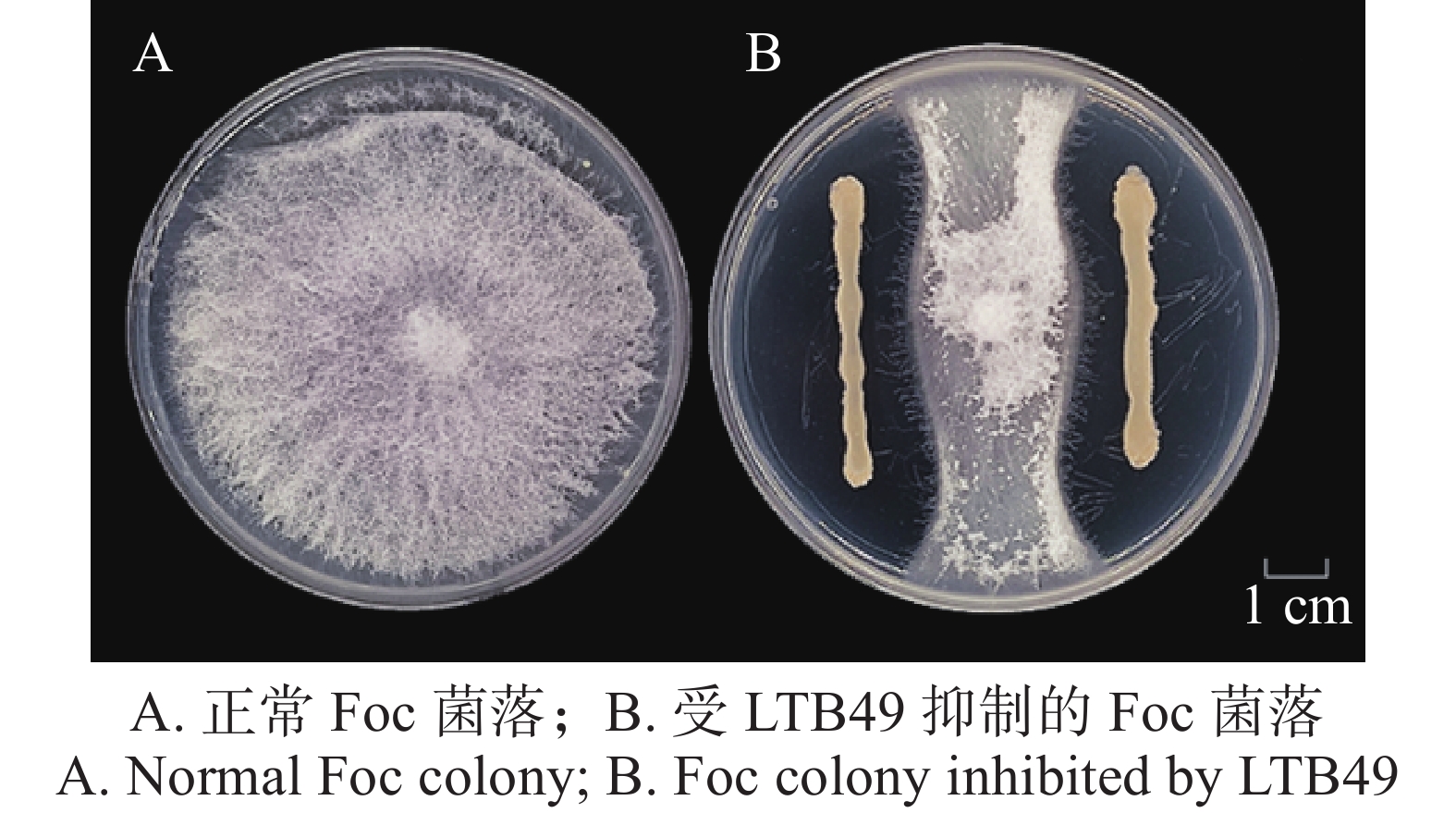
 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML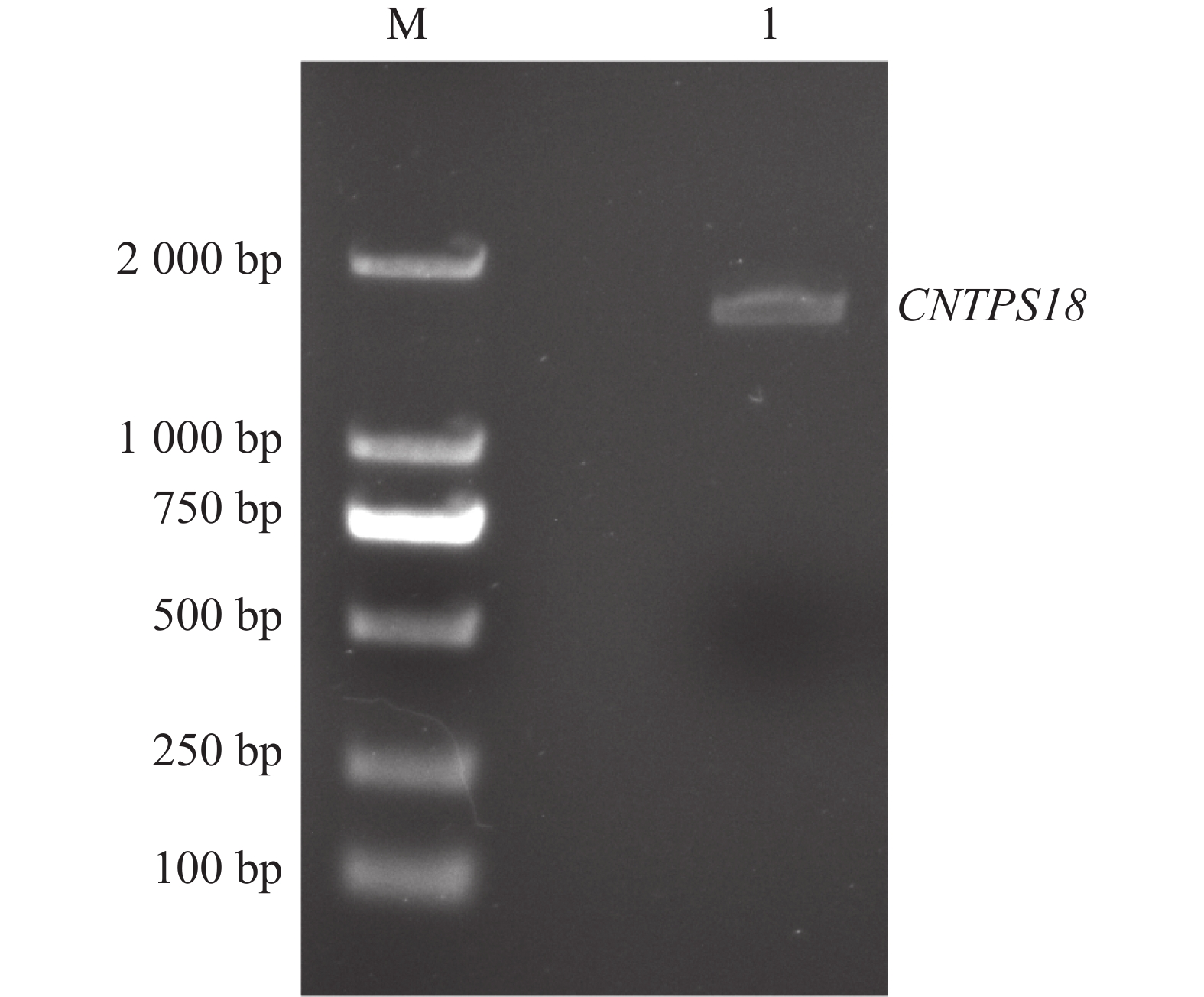
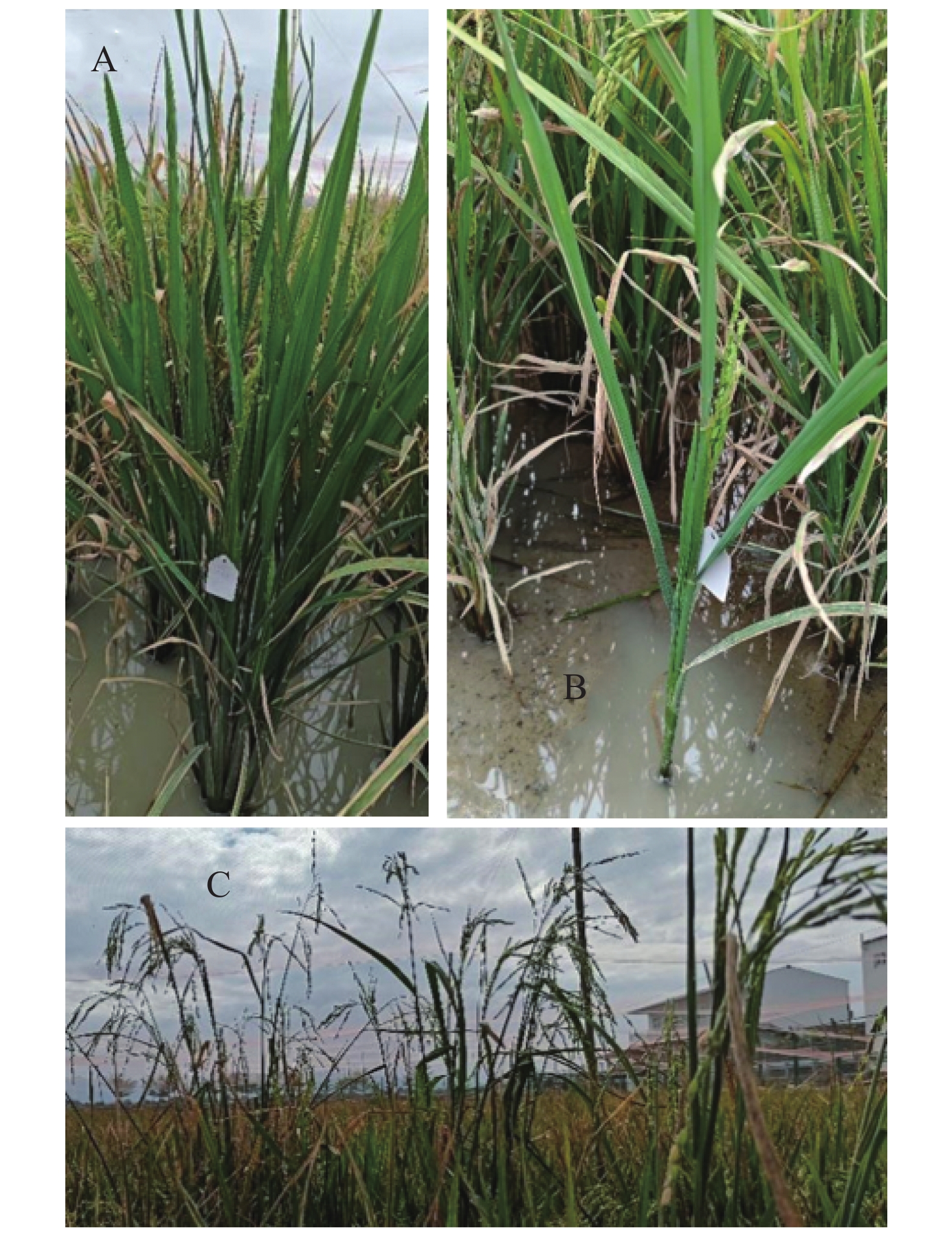
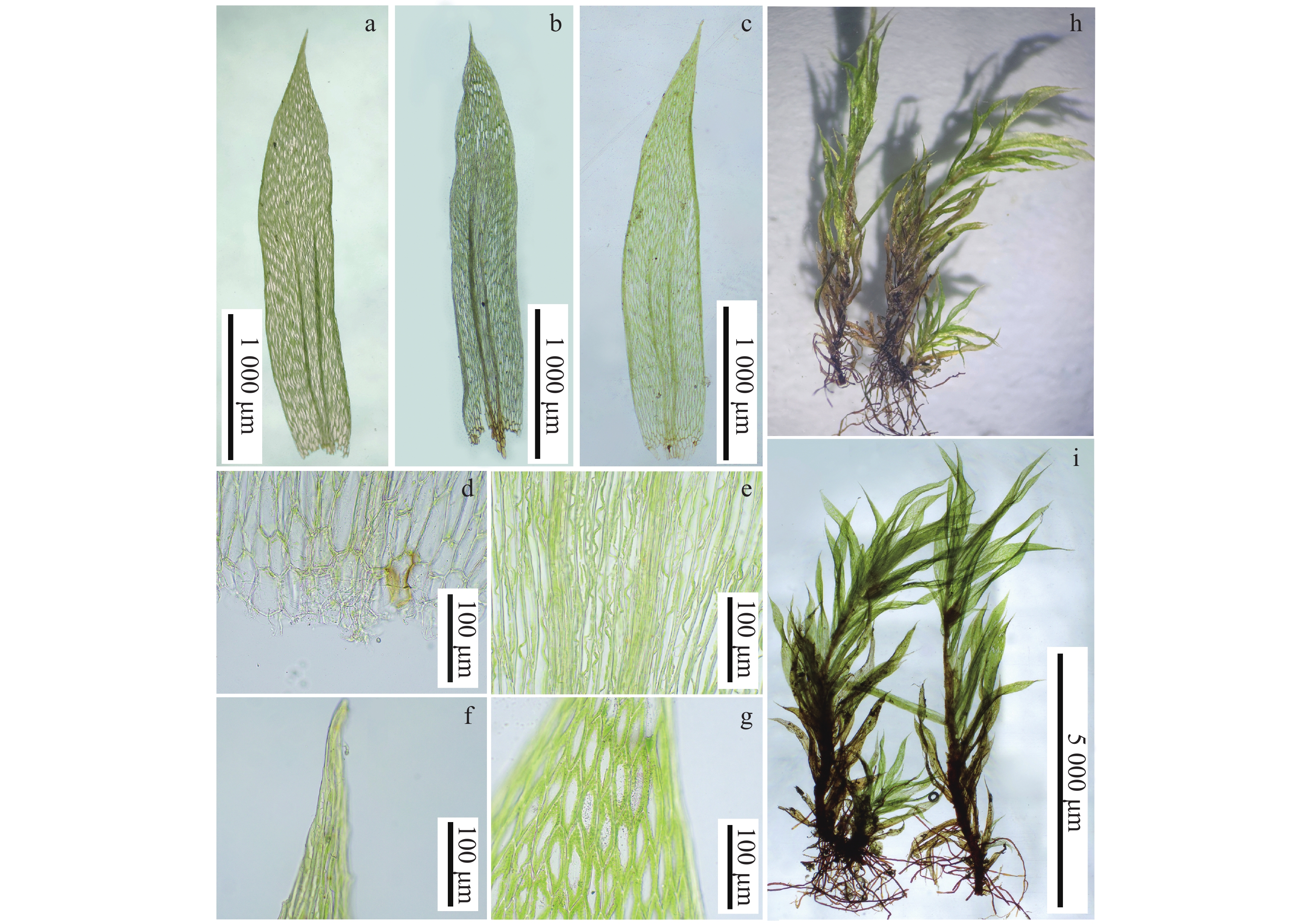
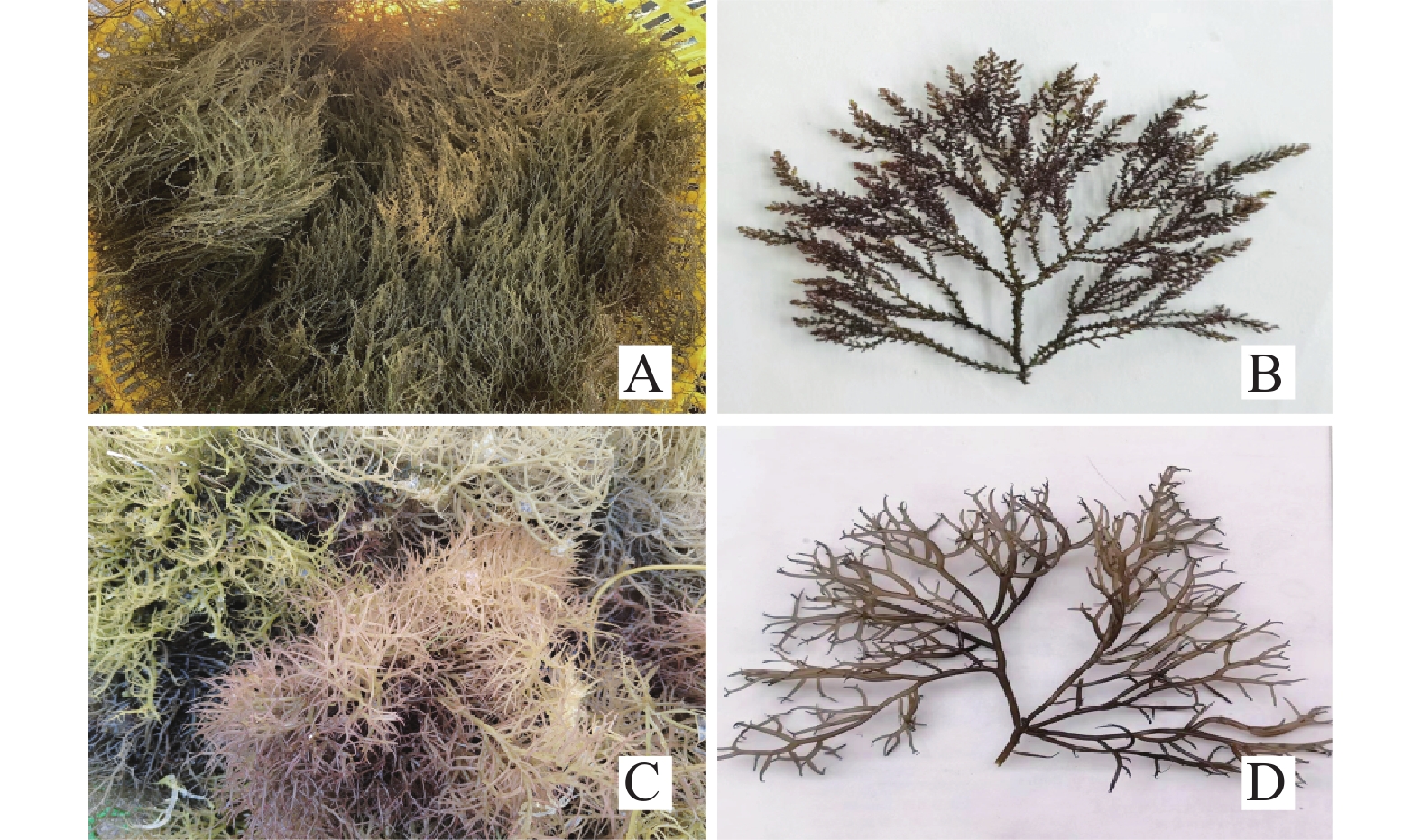
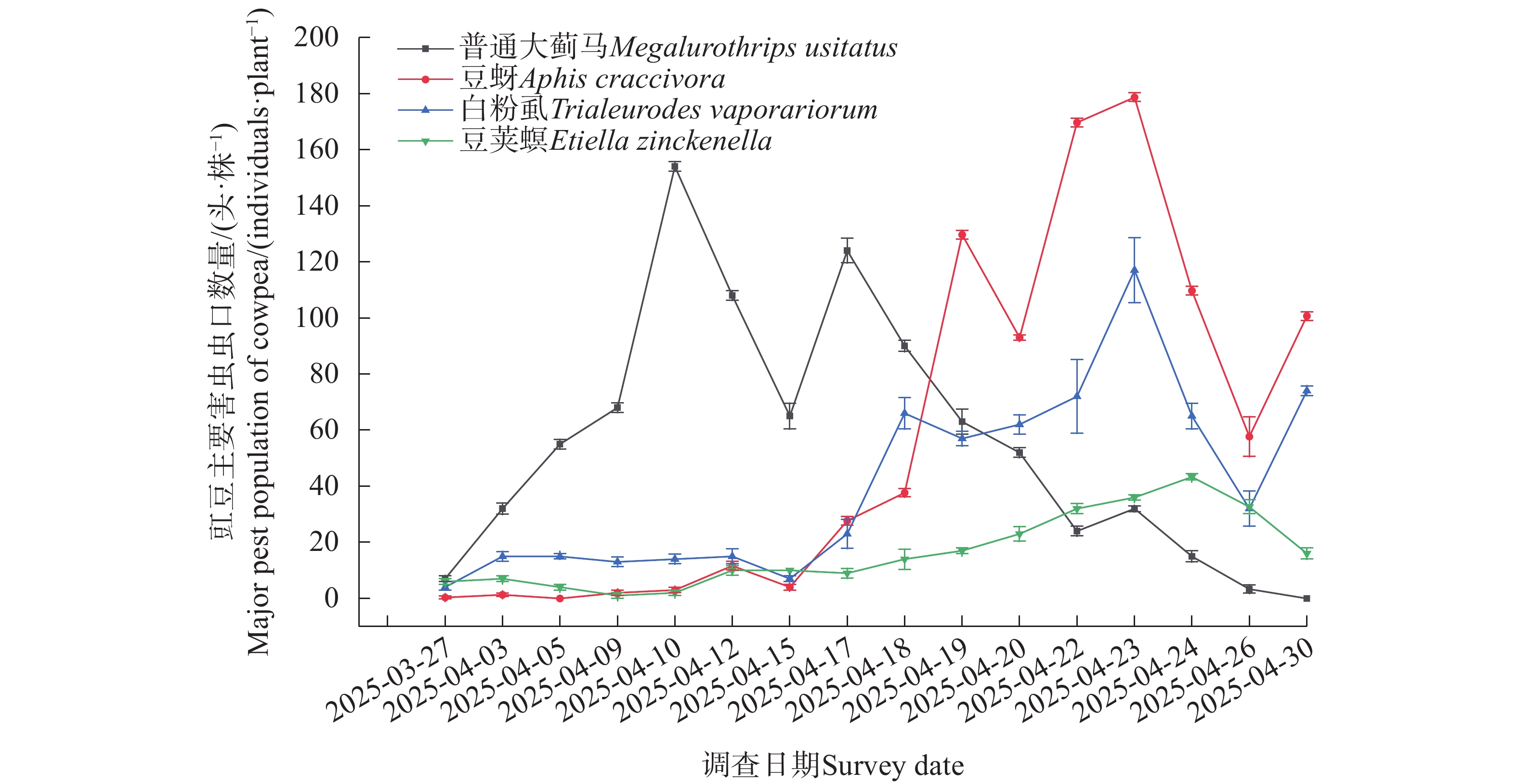
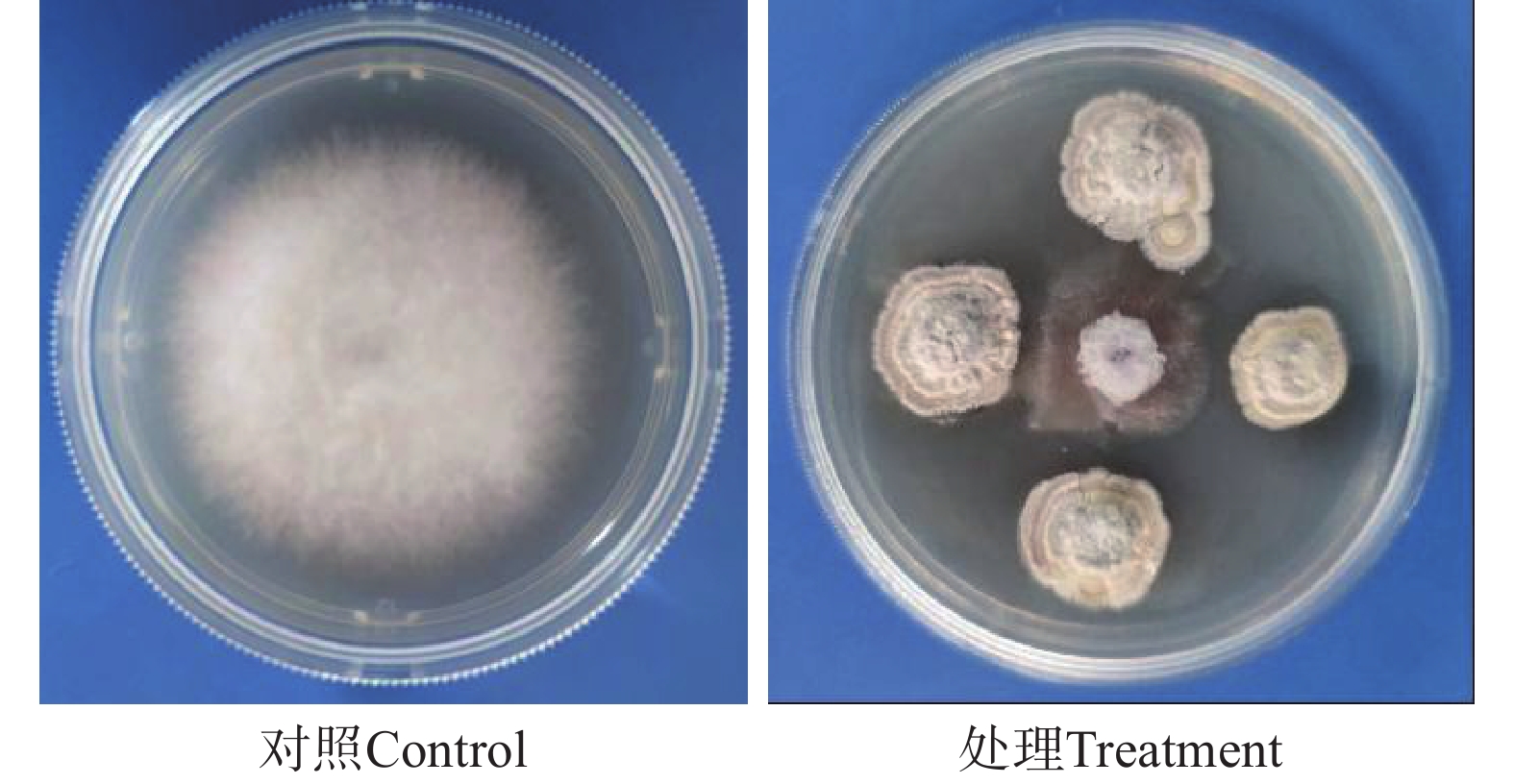
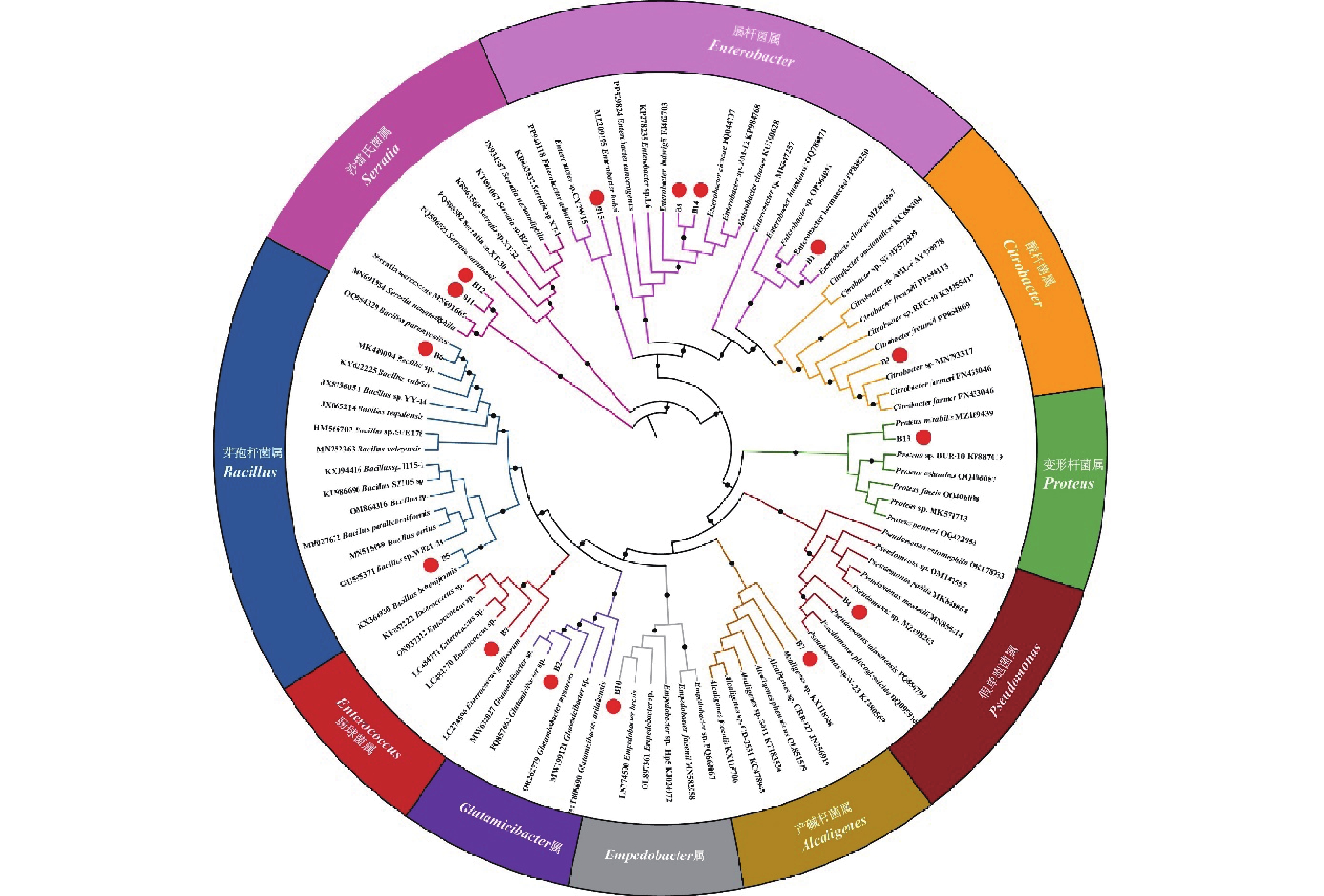
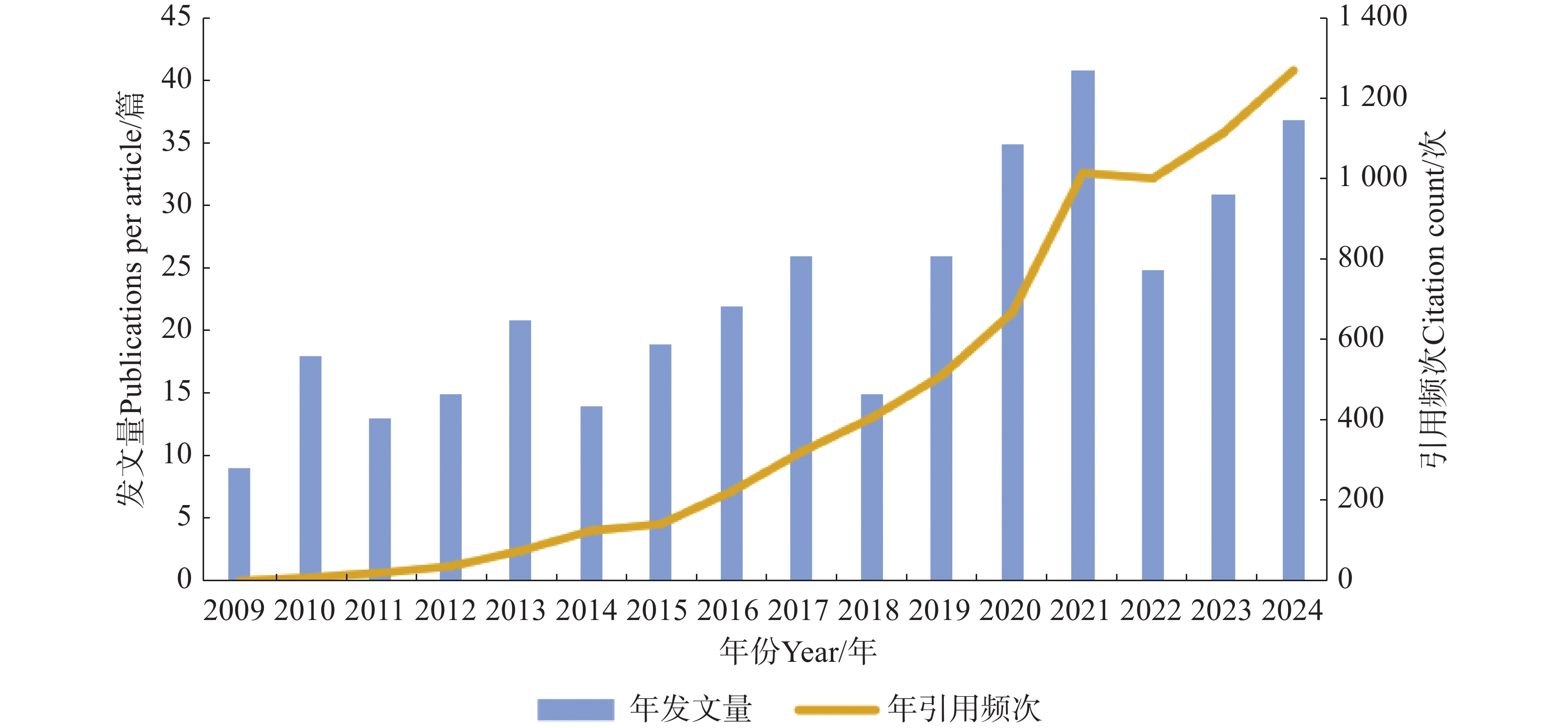
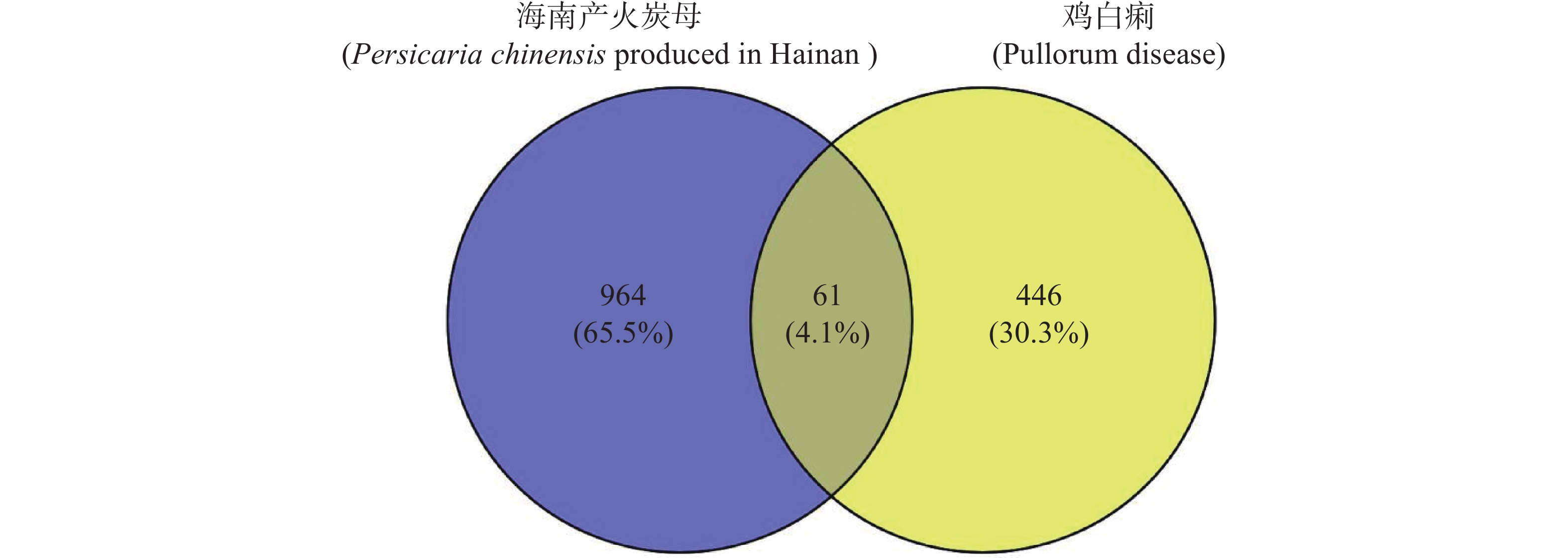
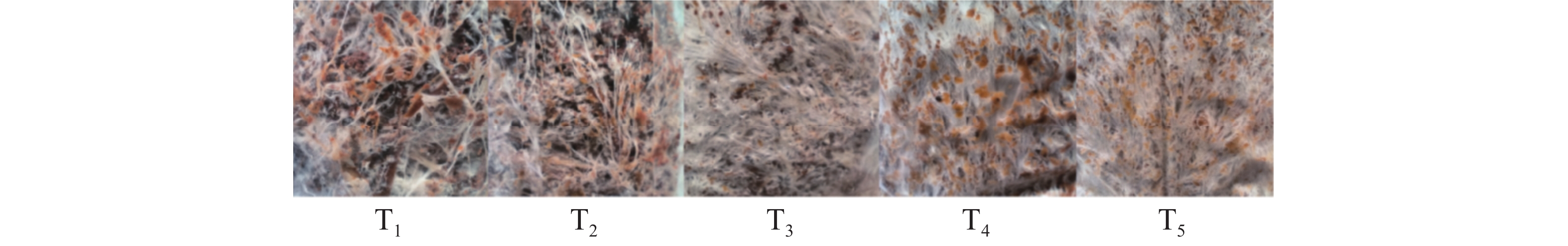
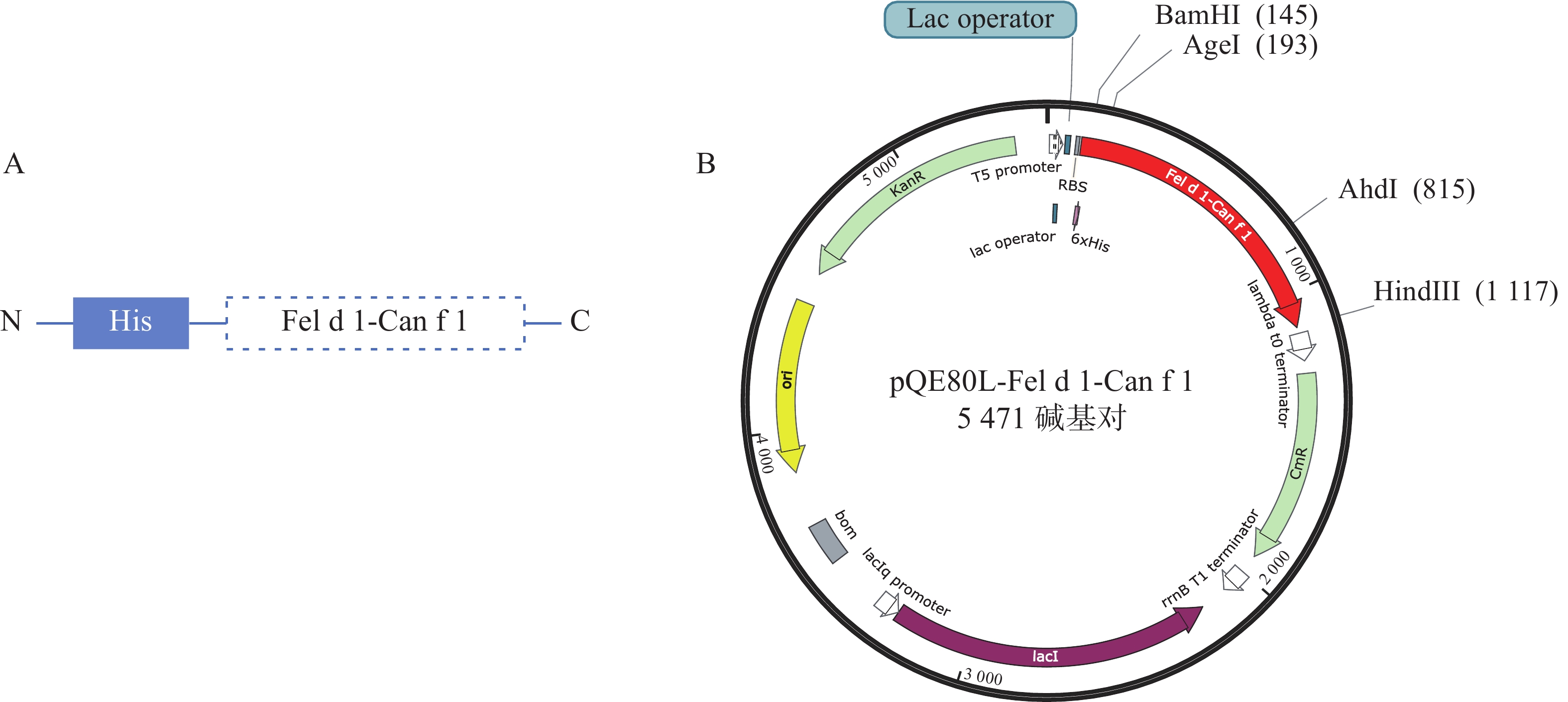
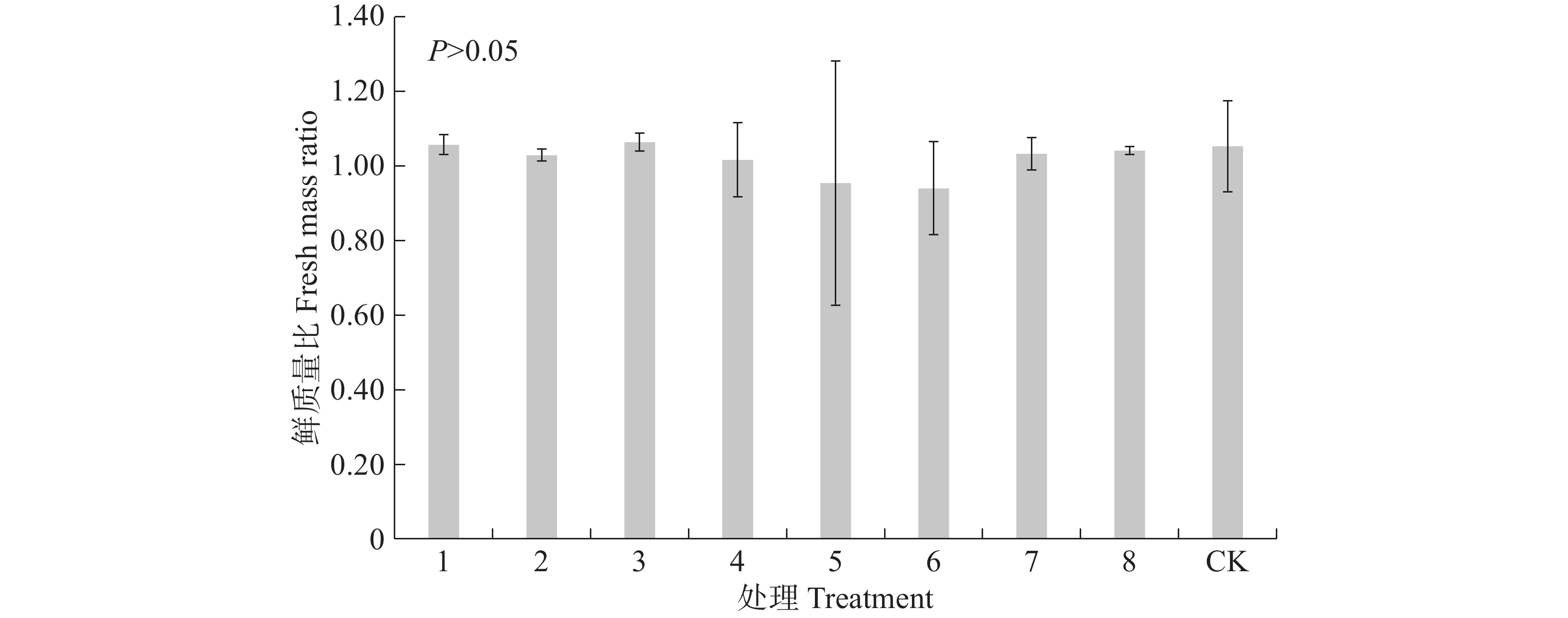
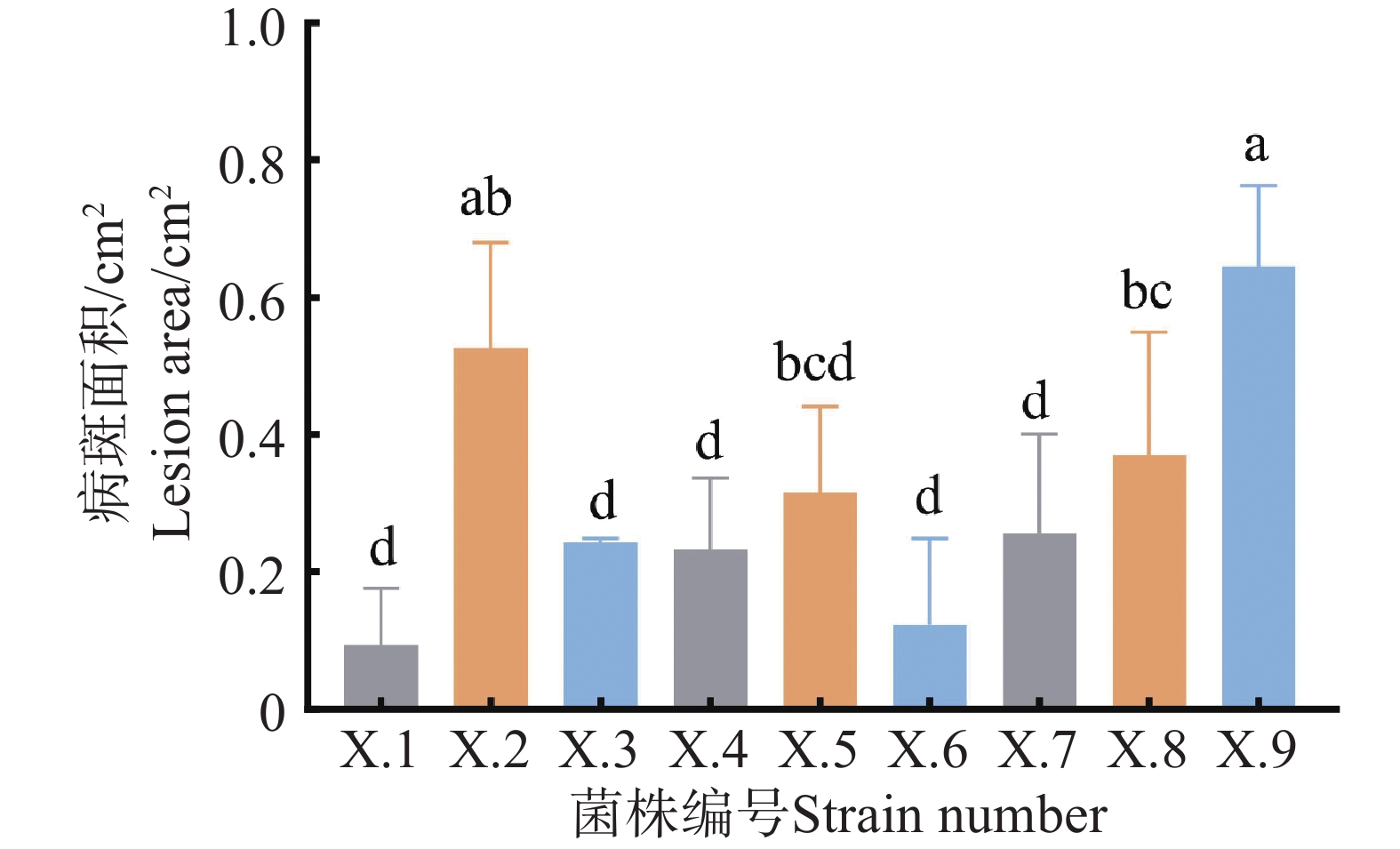
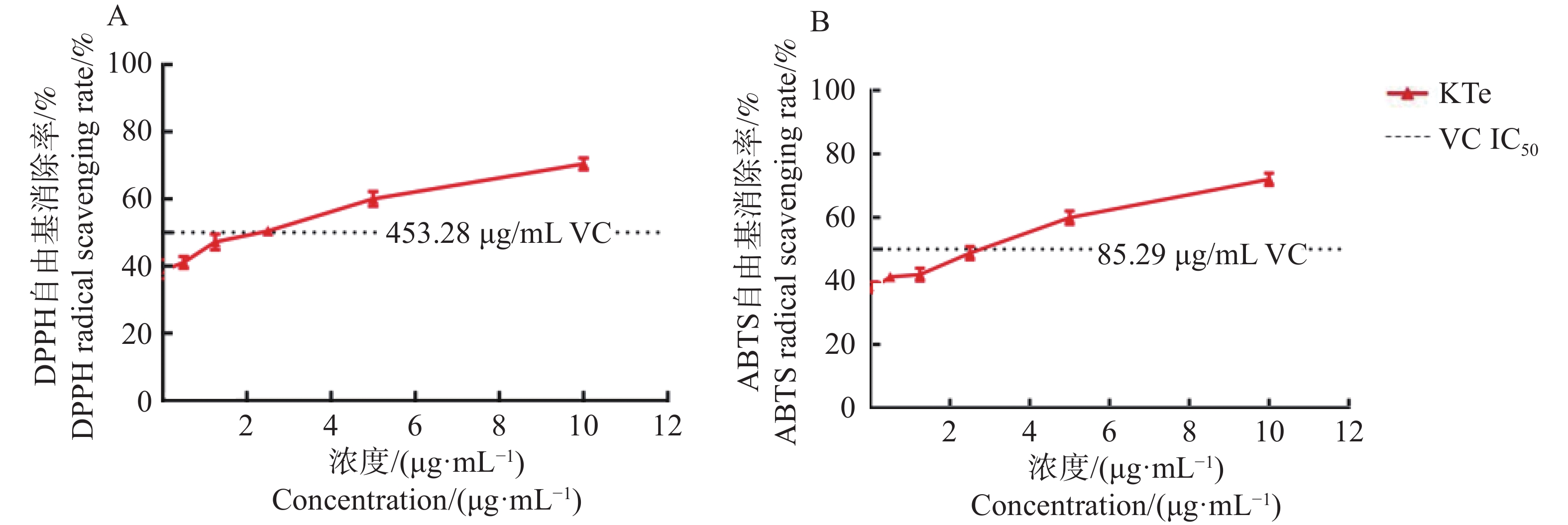
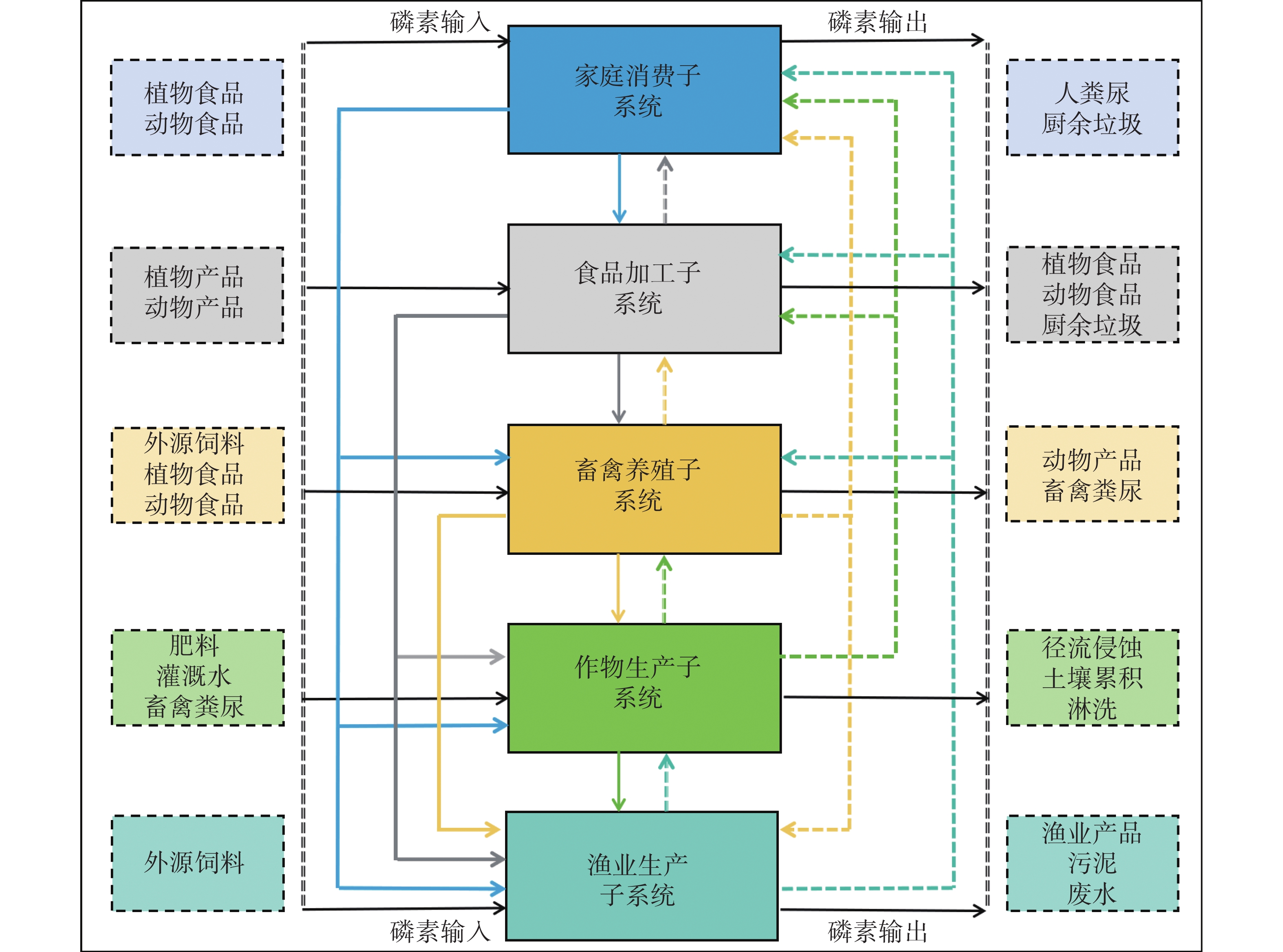

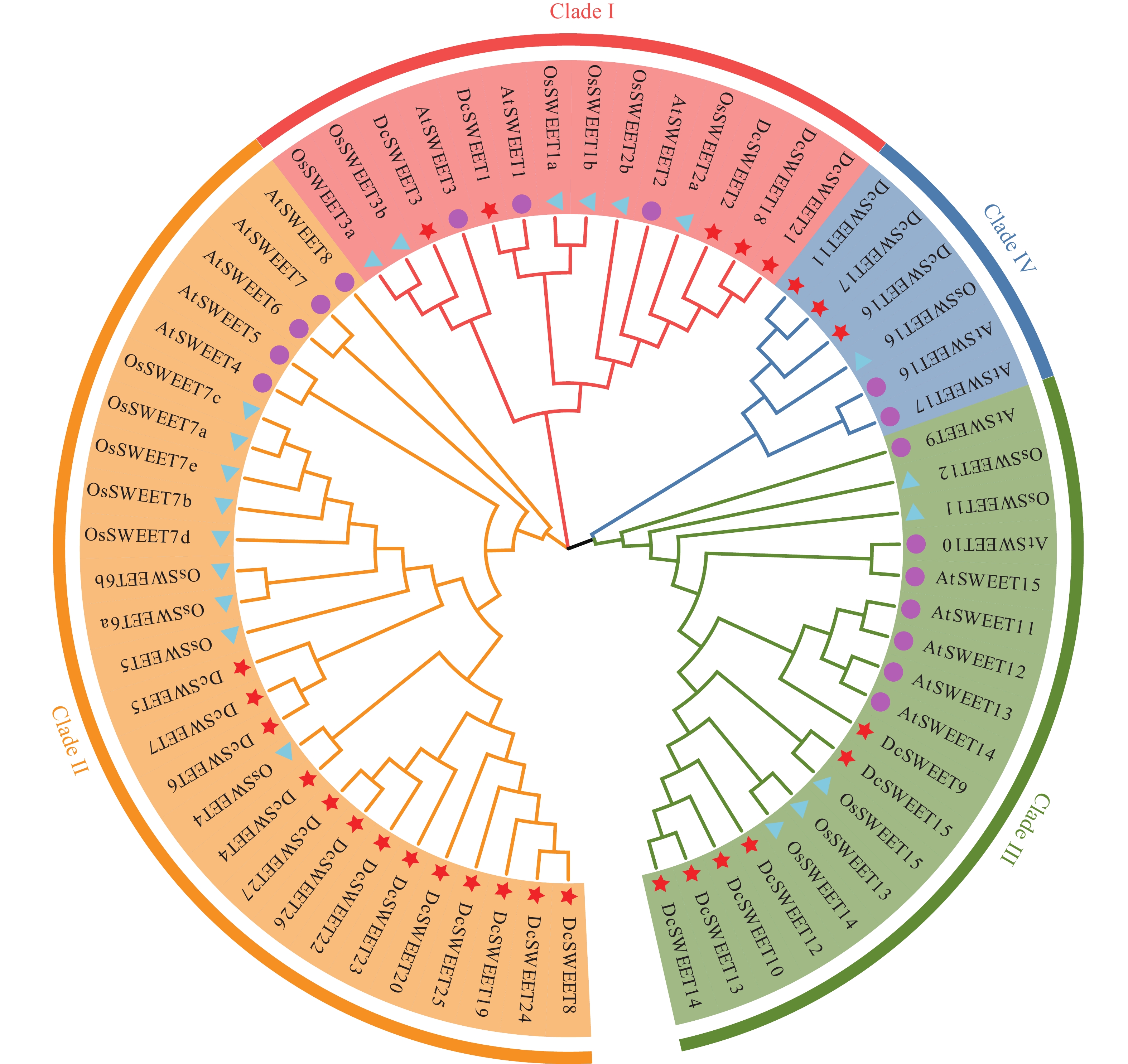

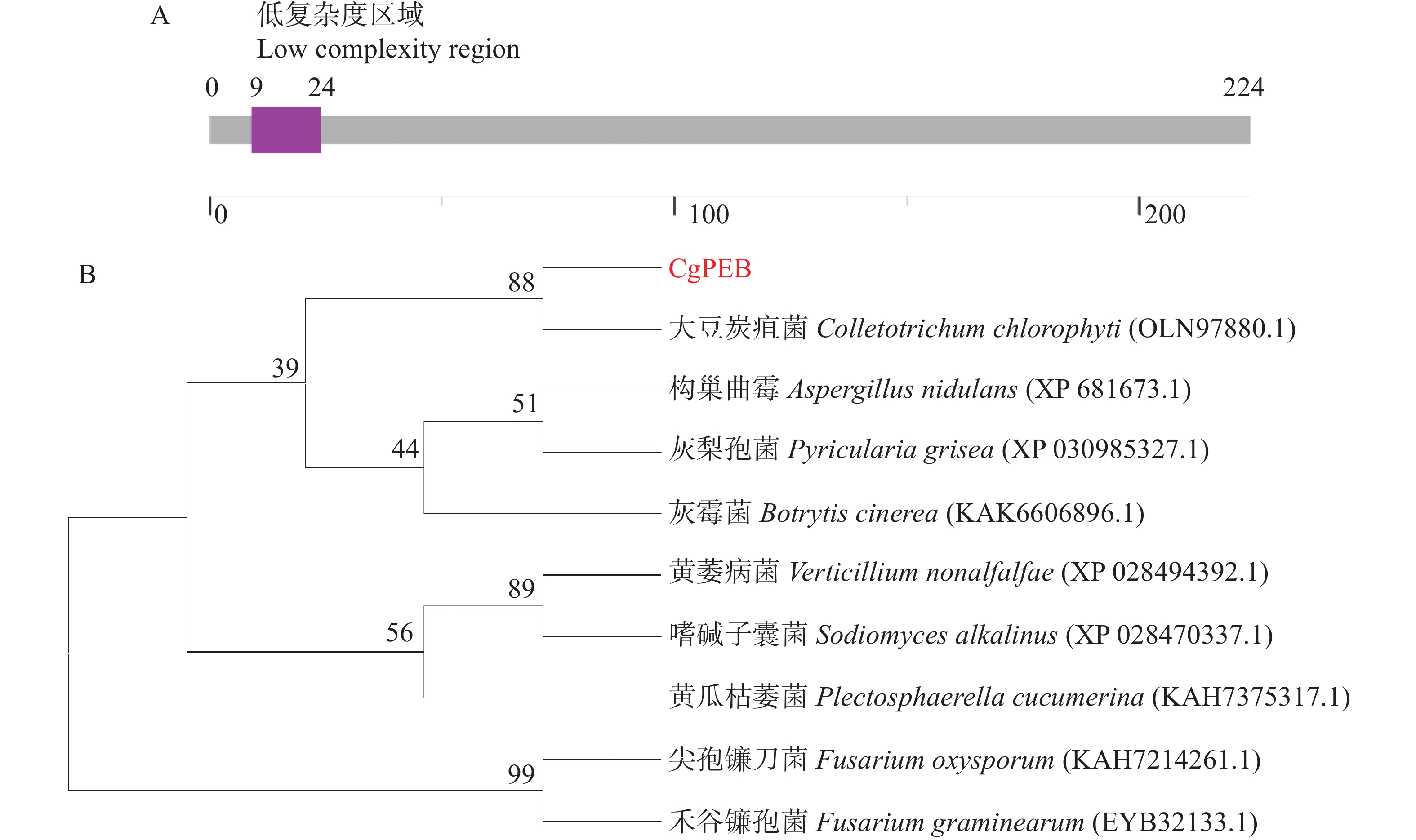

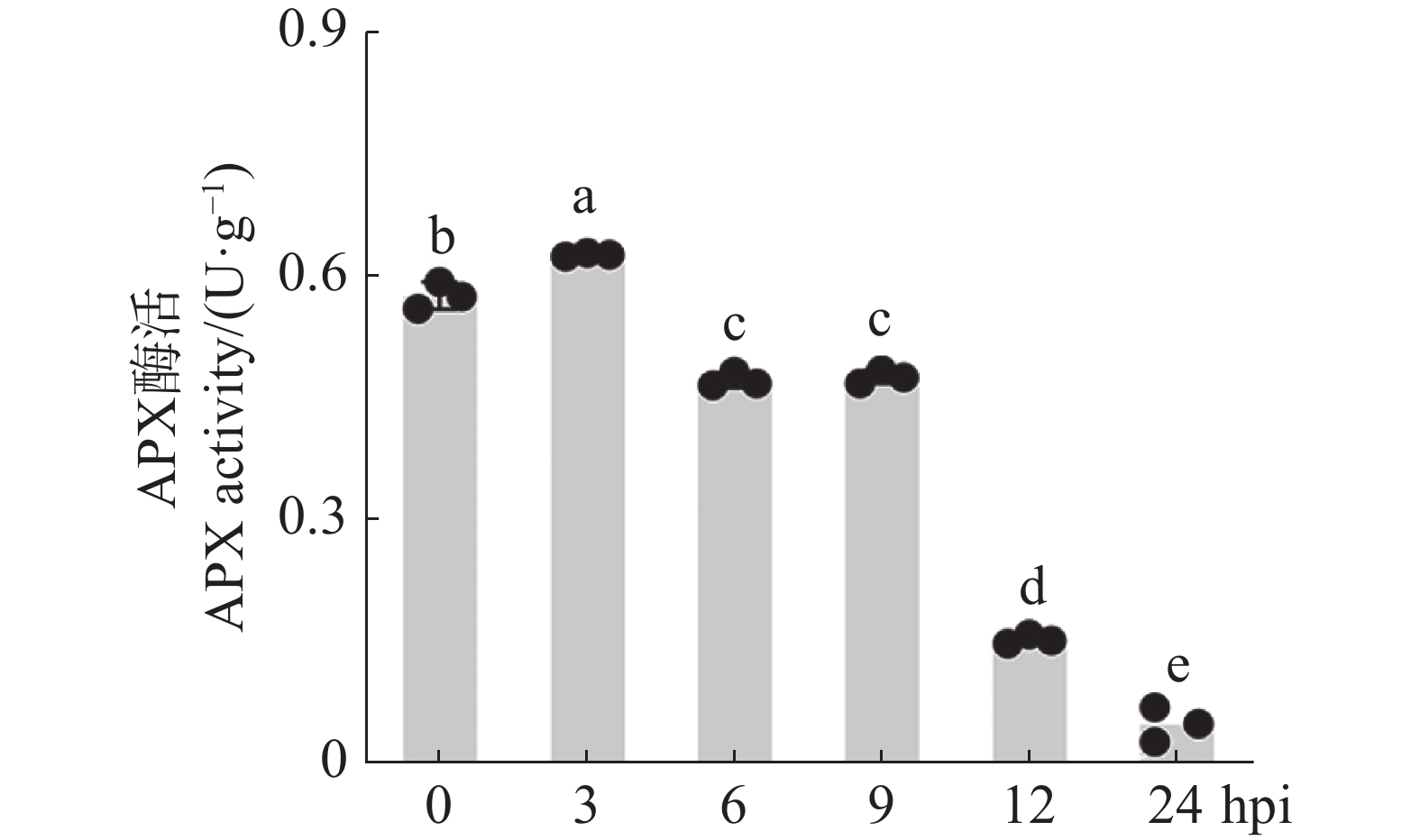
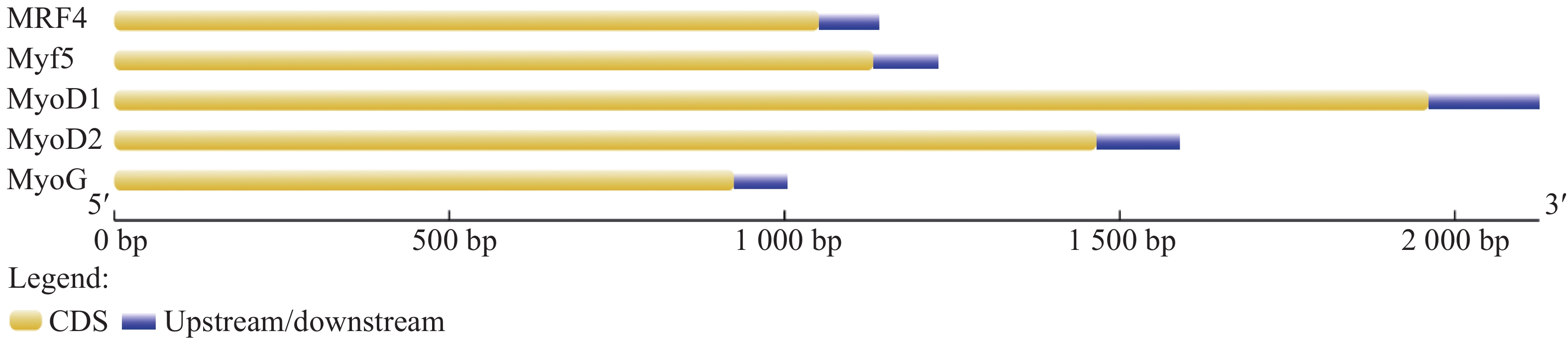
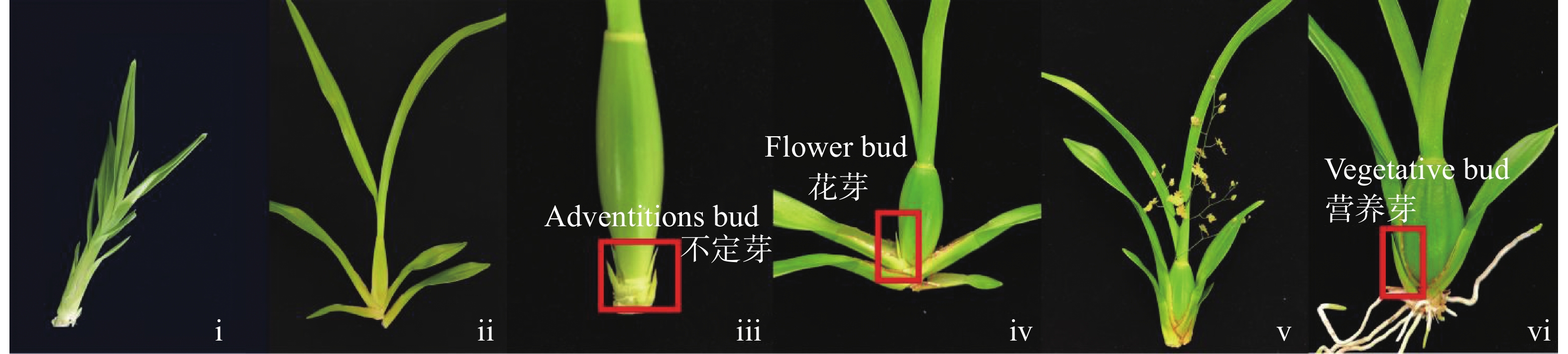



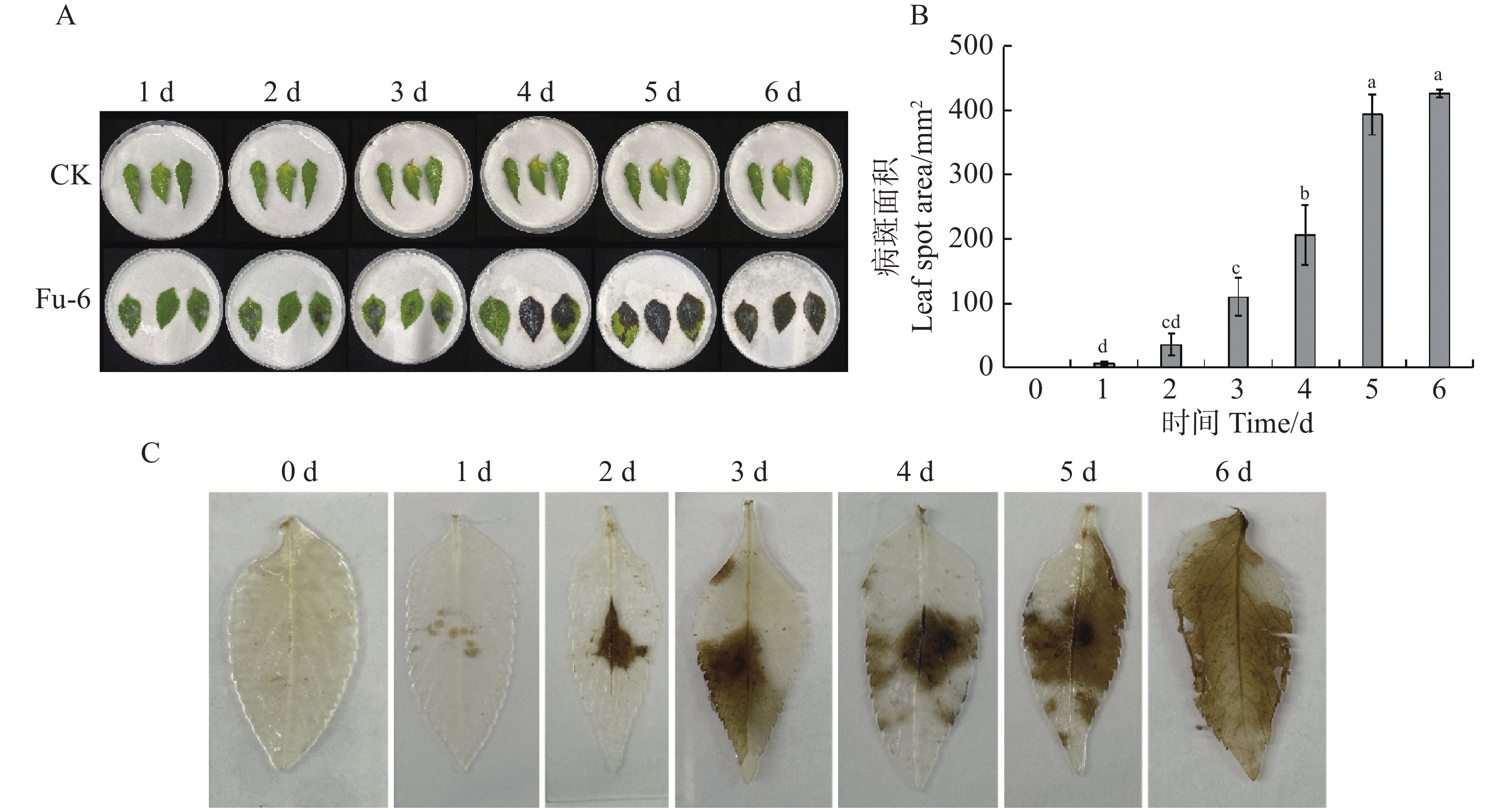
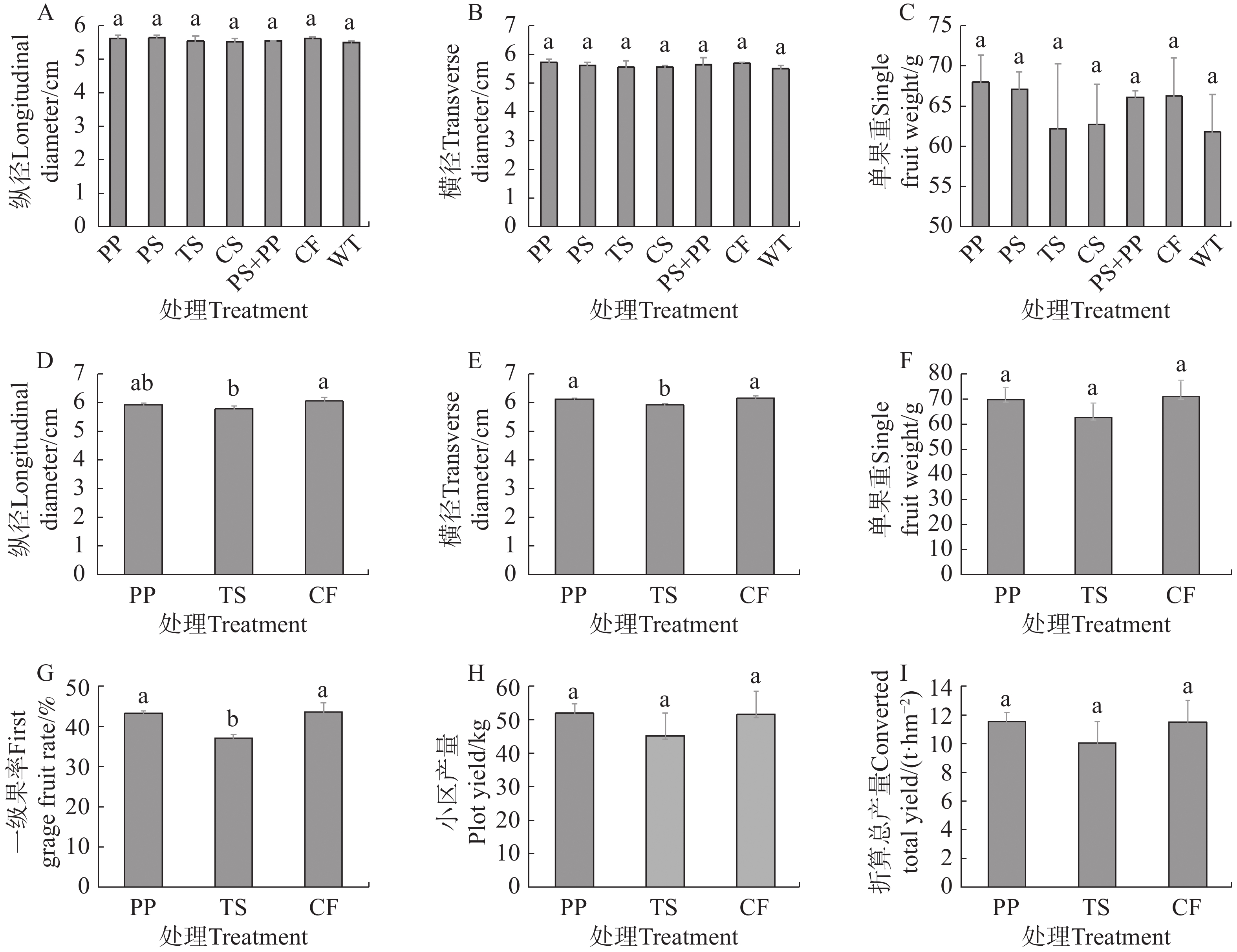
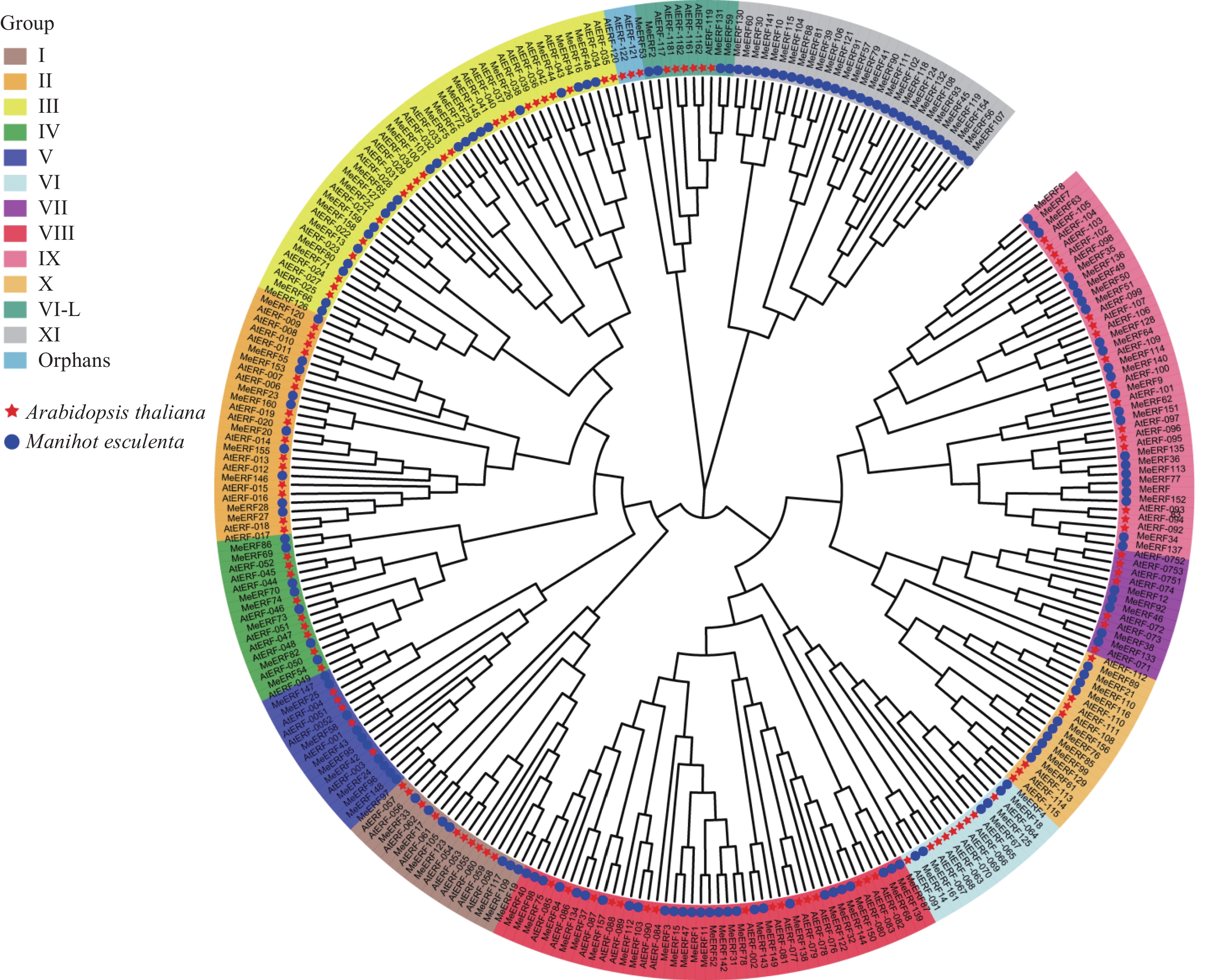
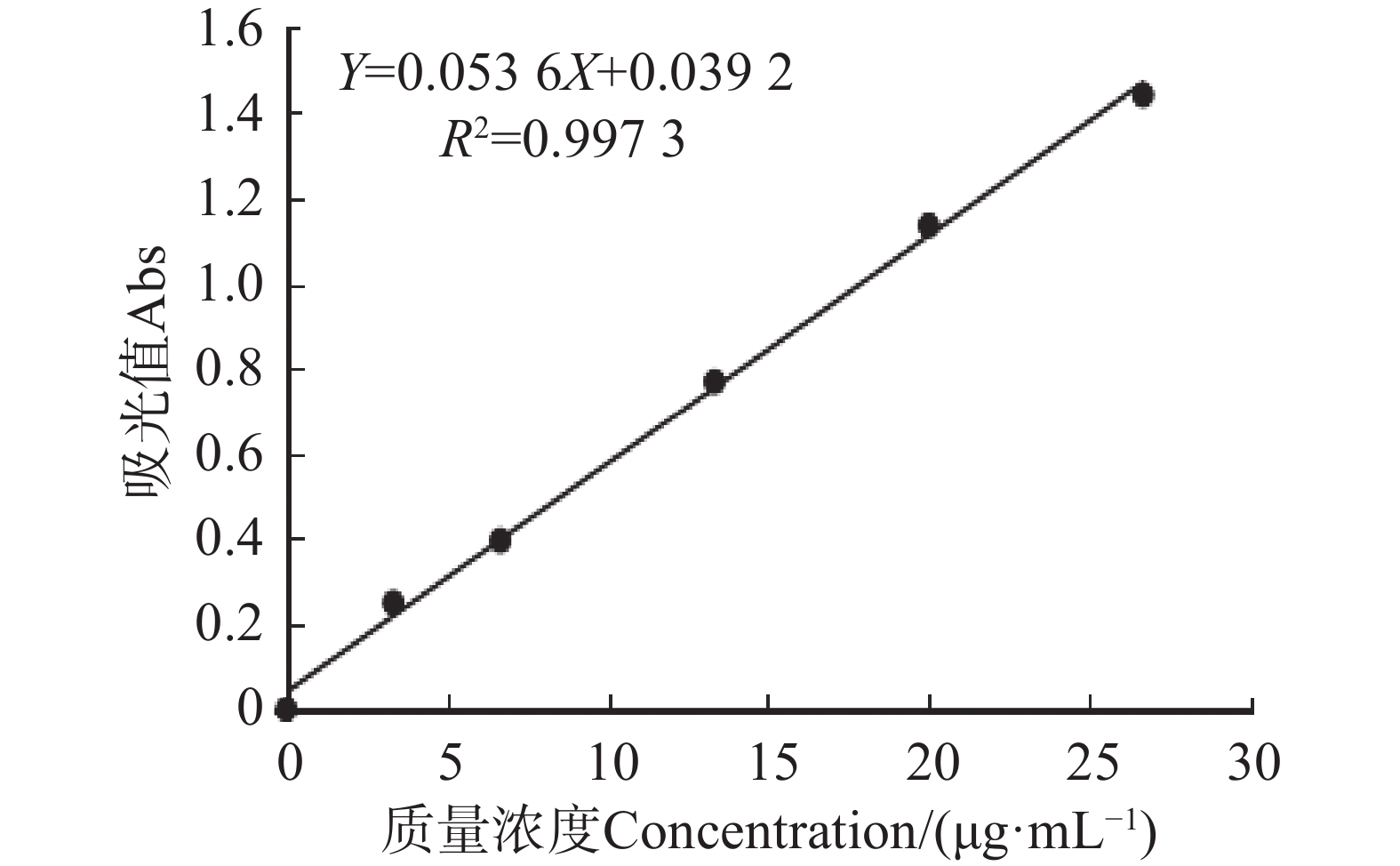
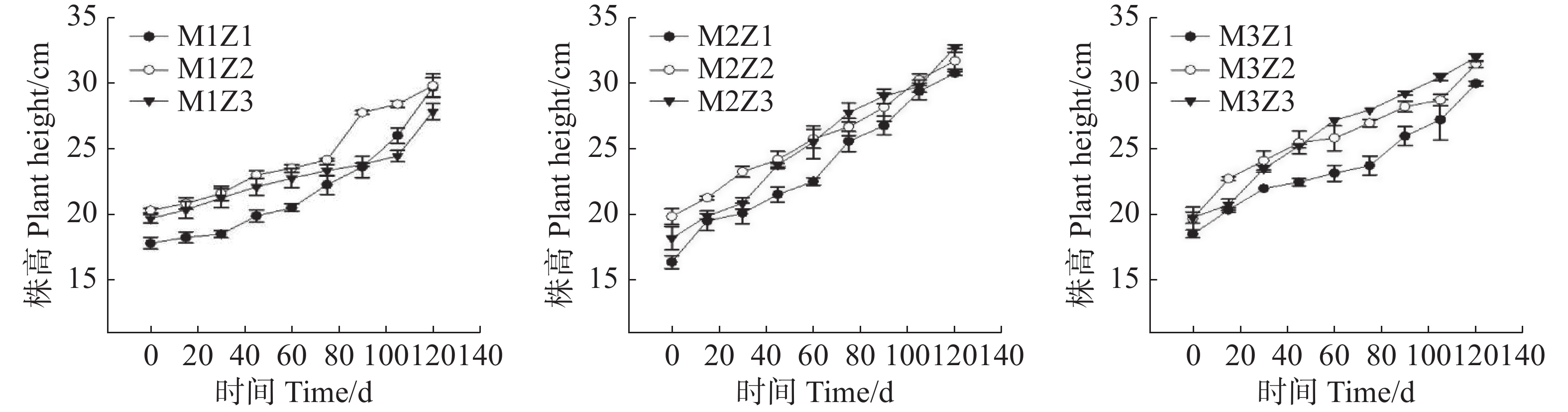
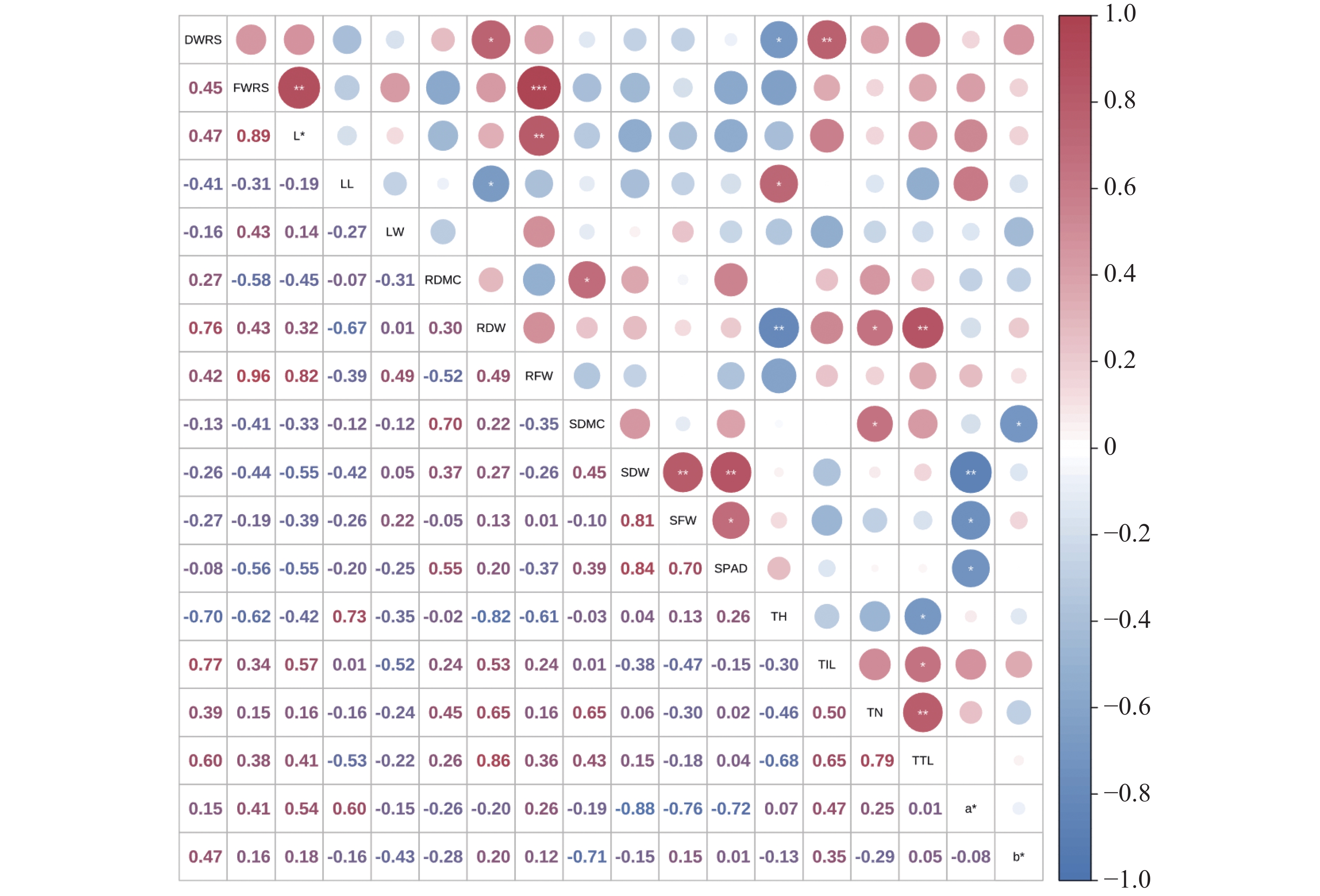
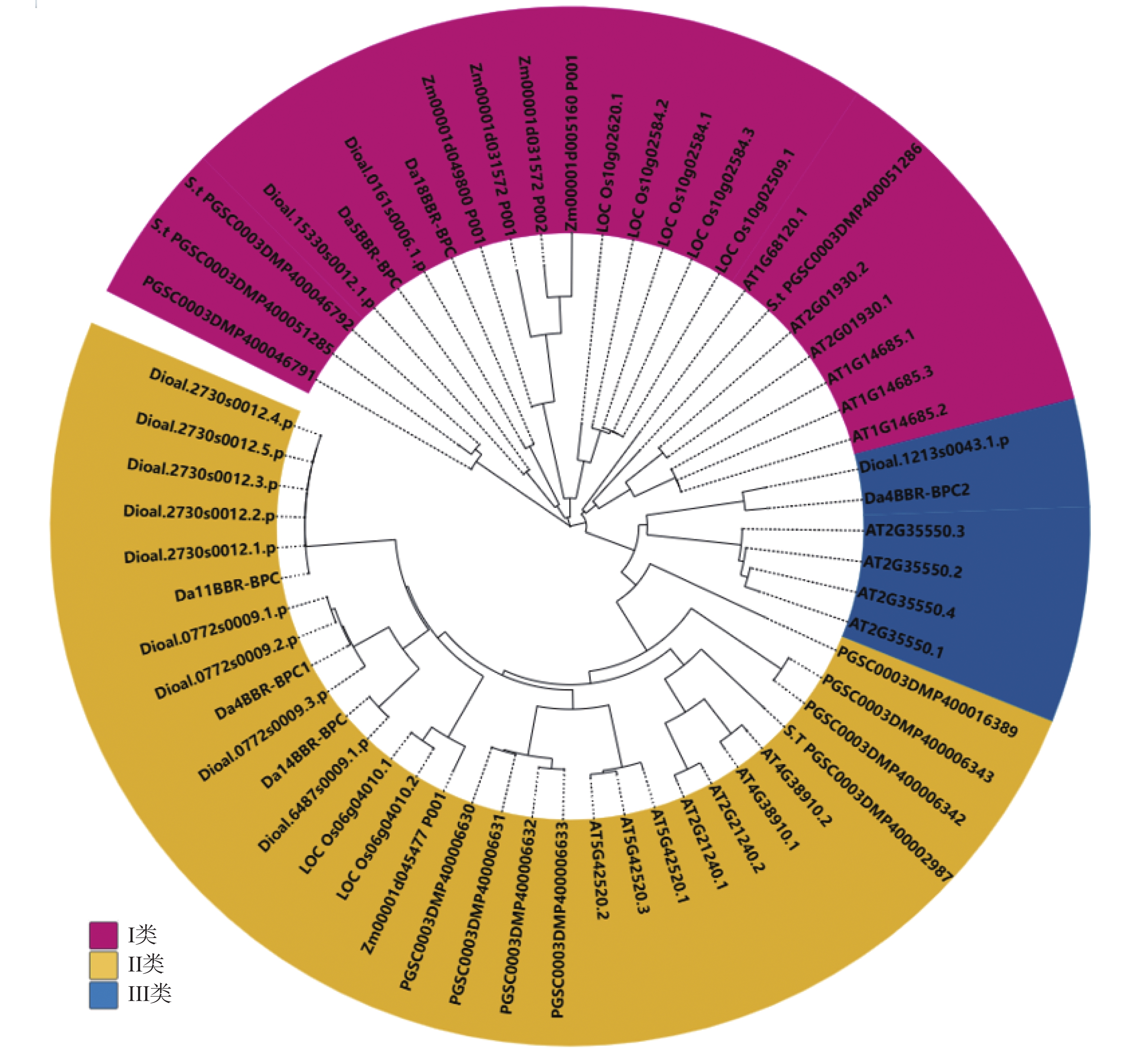
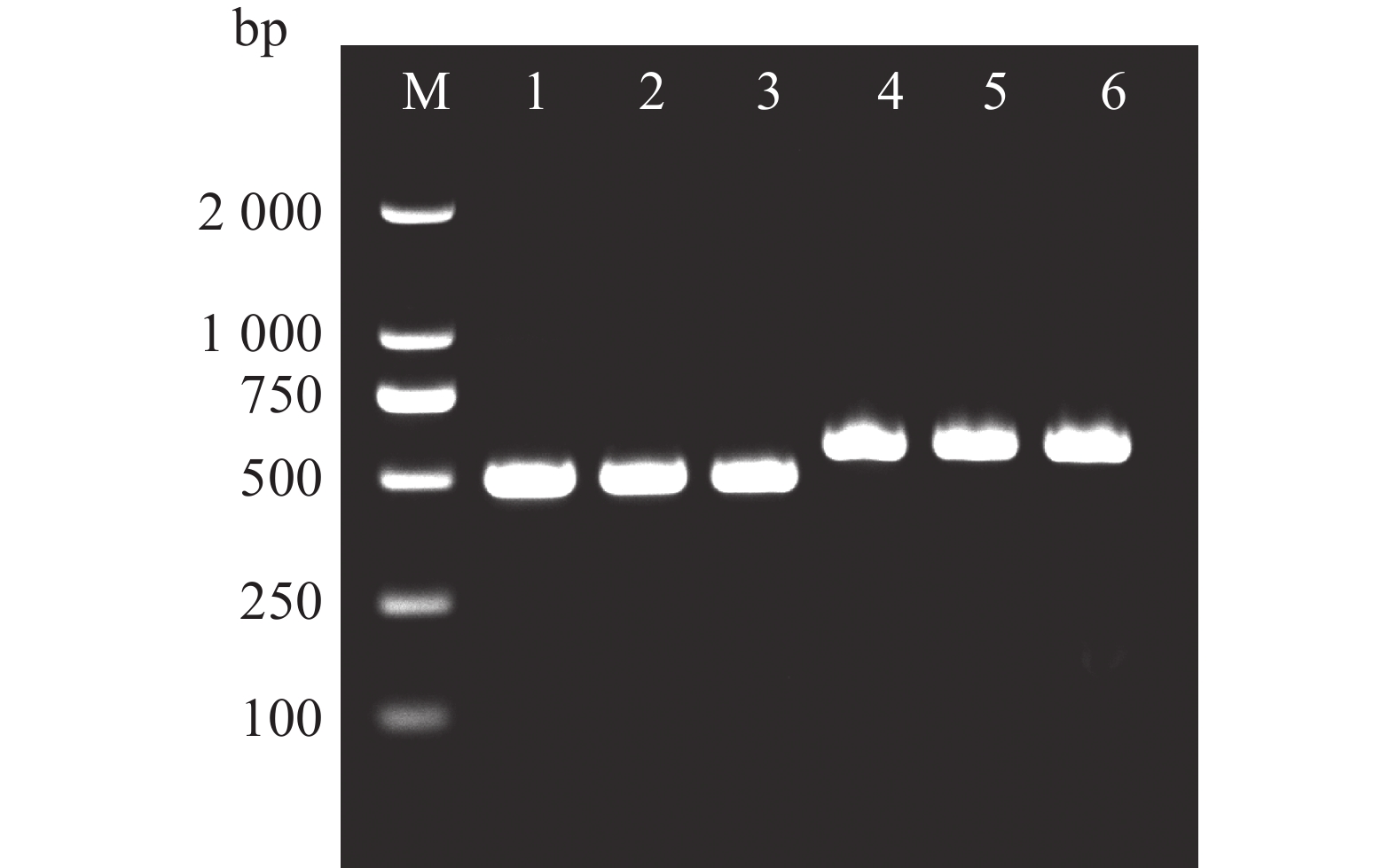
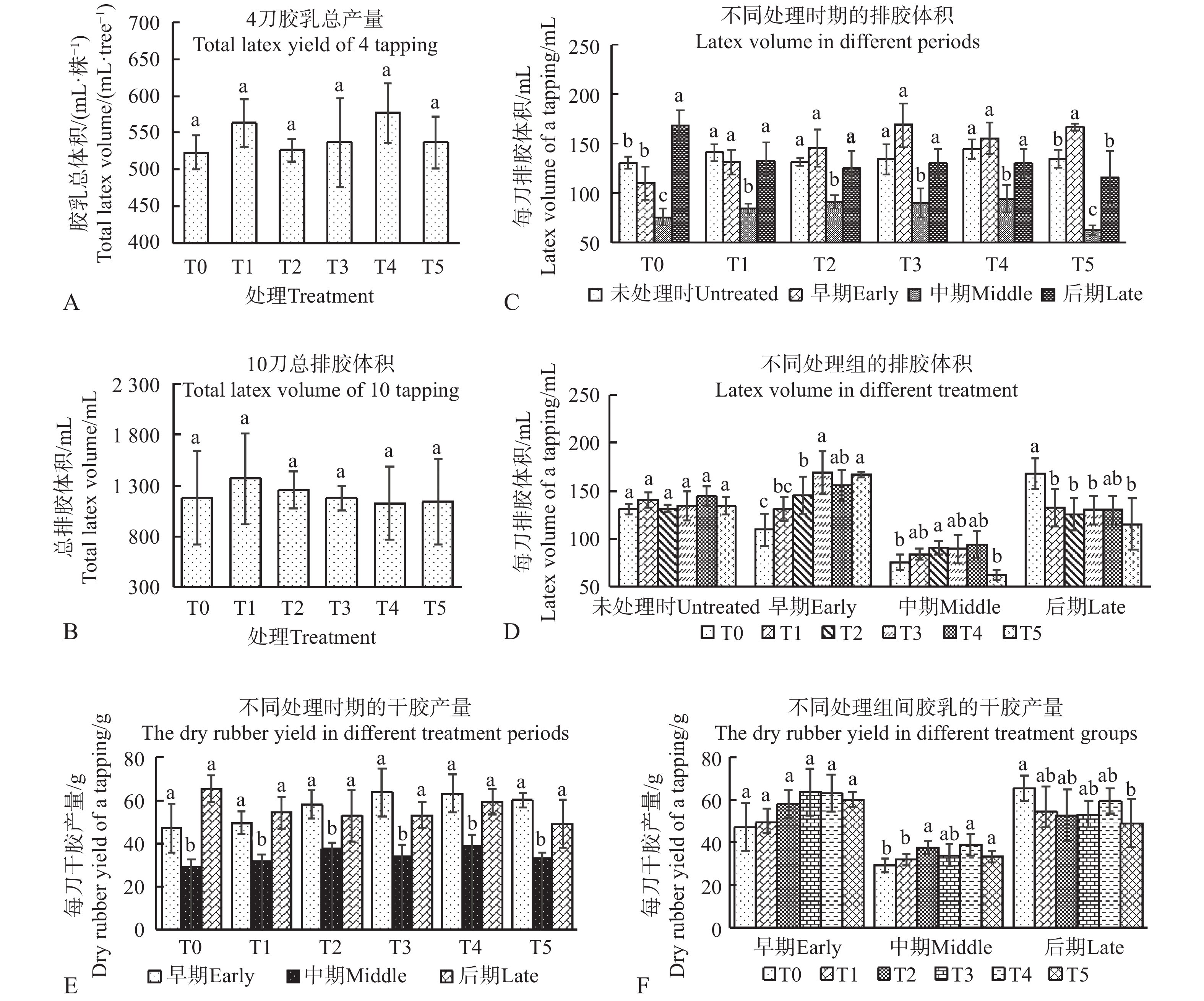
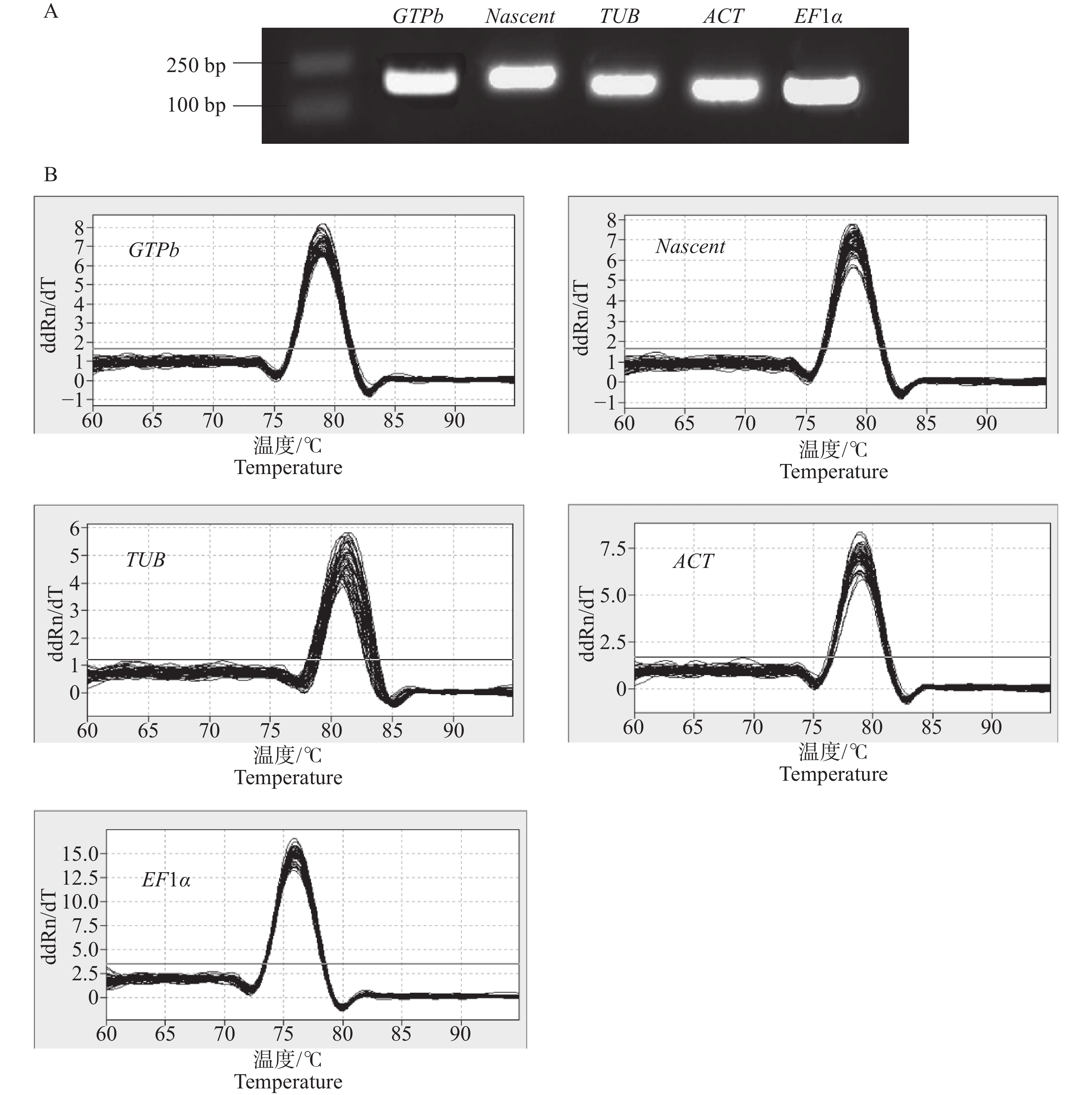

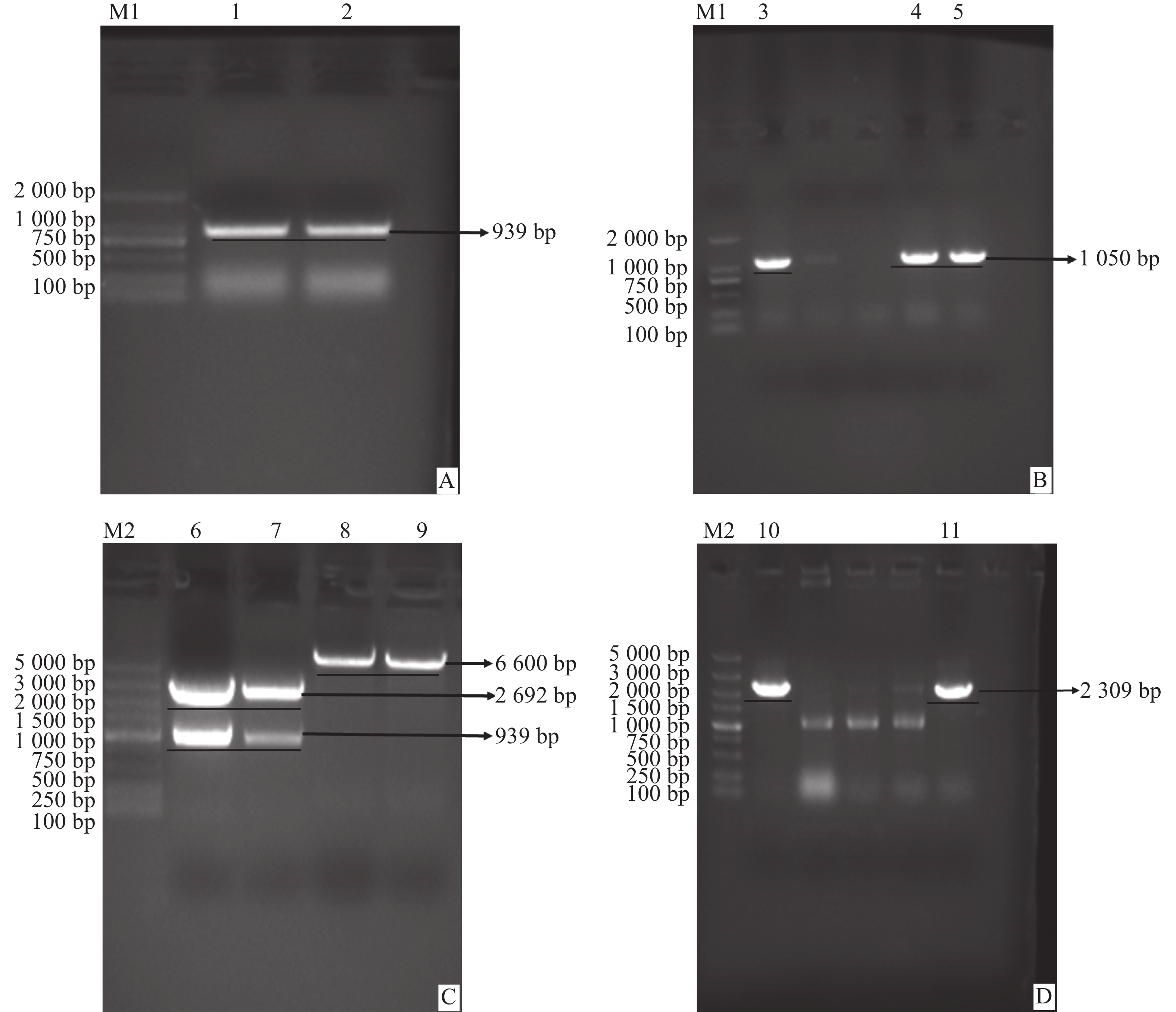
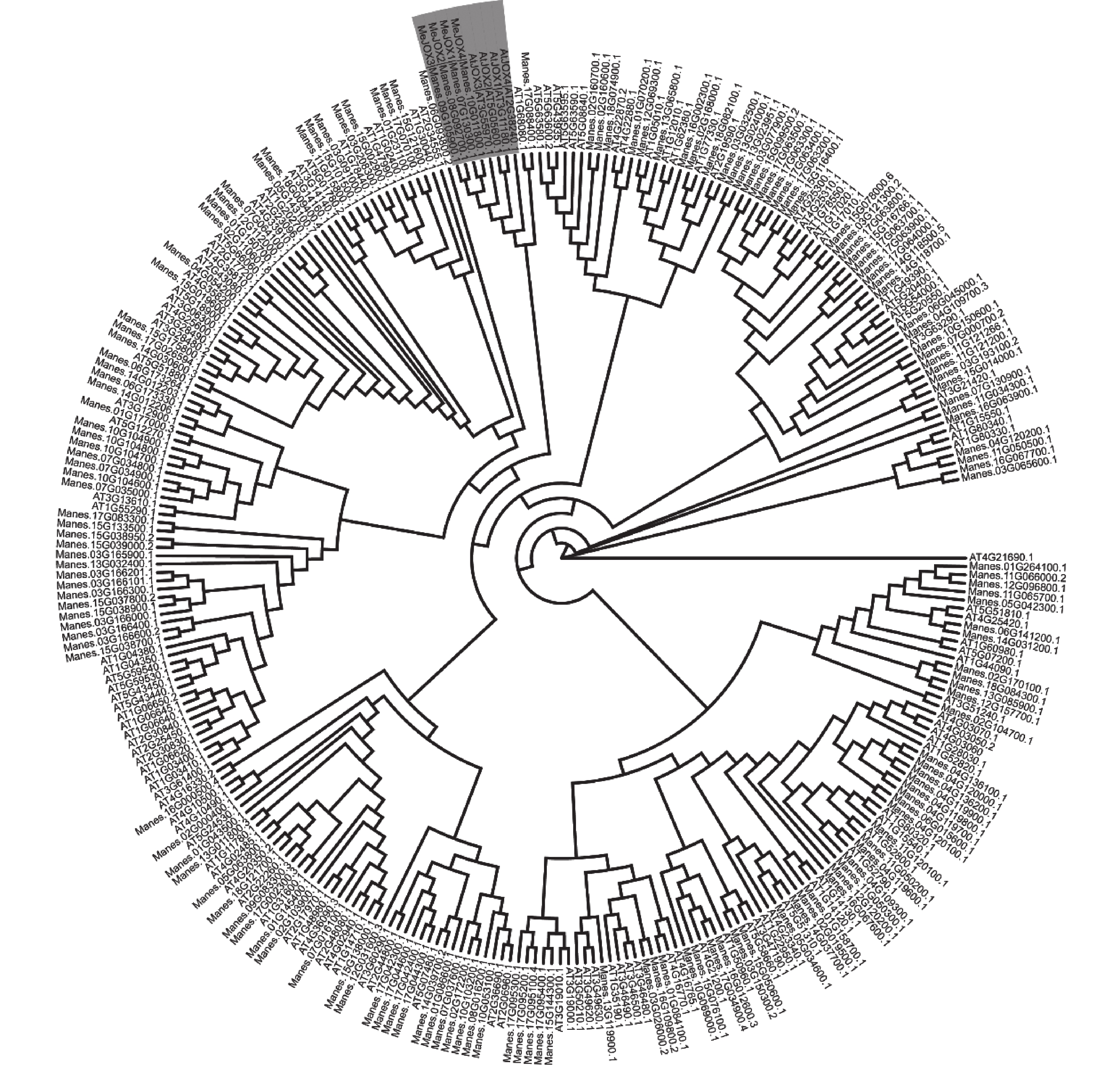
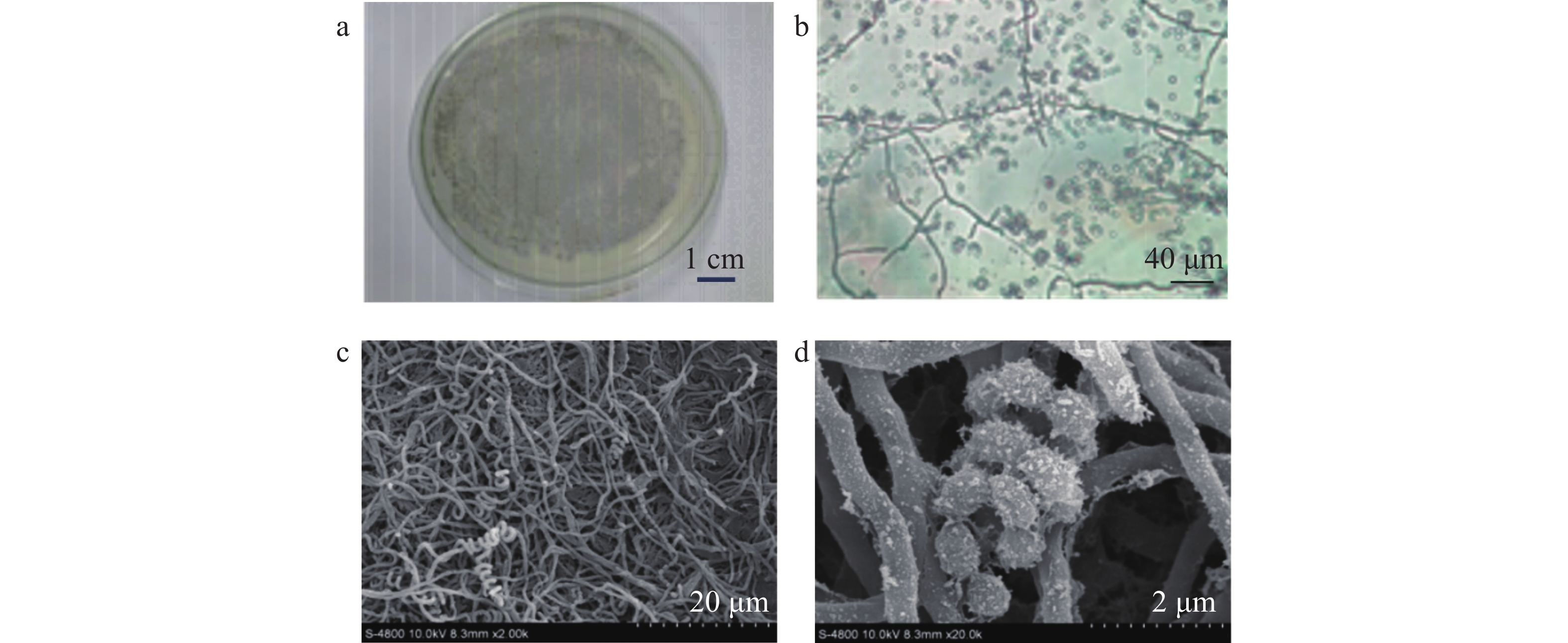
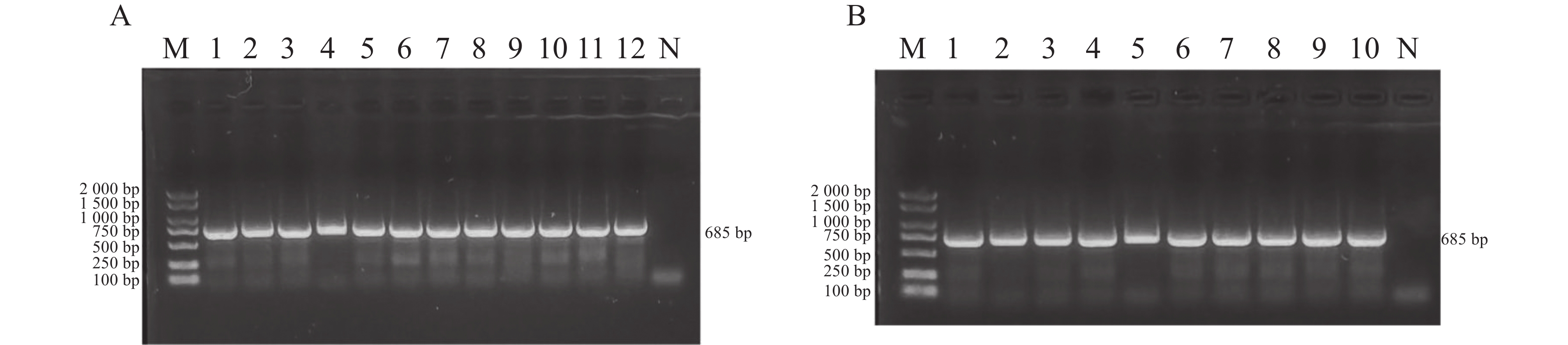


 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS