Online First
Articles online first have been peer-reviewed and accepted, which are not yet assigned to volumes/issues, but are citable by Digital Object Identifier (DOI).
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240058
Abstract:
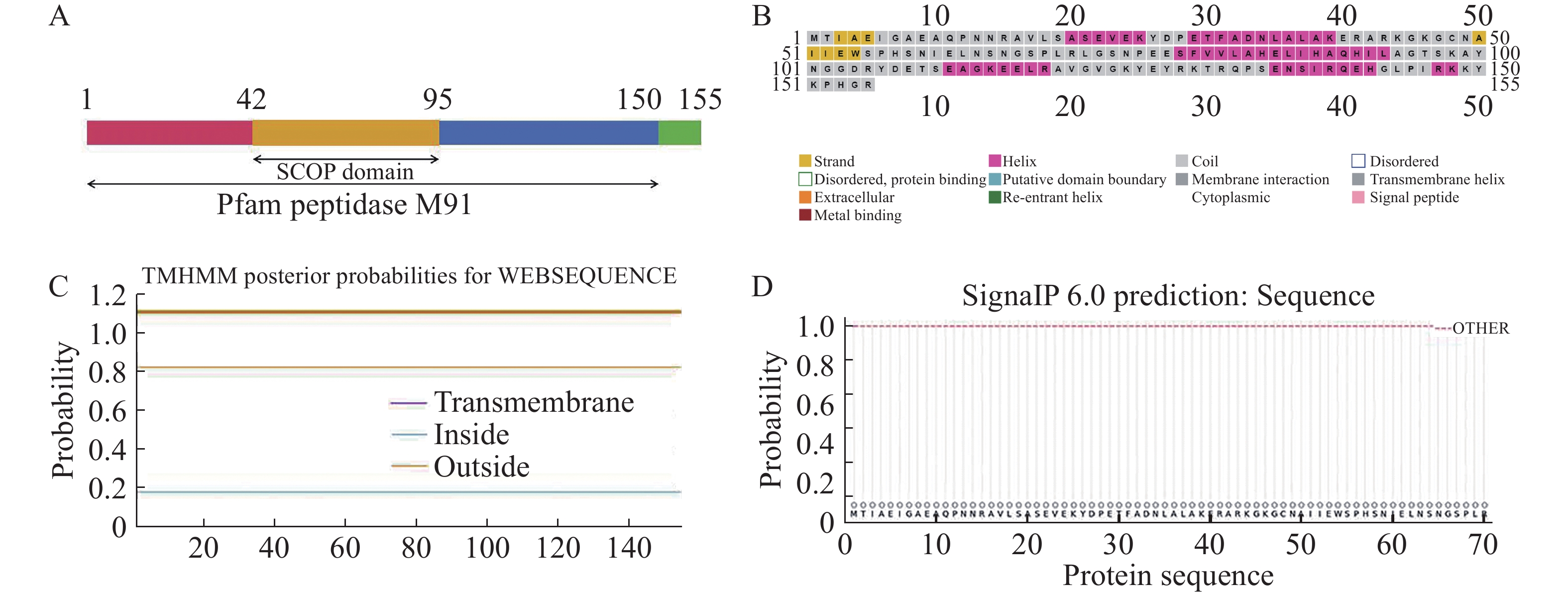
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae is the pathogen that causes bacterial leaf blight in rice. Type Ⅲ secretion effectors (T3SEs) play an important role in the virulence of Xoo. To study the function of XopG in Xoo virulence and the localization in plant cells, we carried out the informatics analysis, gene knockout, expression analysis, subcellular localization of XopG, and analyzed the effect of xopG mutation on Xoo virulence. The results showed that the xopG promoter sequence contains an atypical plant-induced motif (PIP-box), indicating that xopG expression is regulated by HrpX. The promoter activity of xopG in hrpX deletion mutant was significantly lower than that in the wild type strain T7174, suggesting that HrpX positively regulates the expression of xopG. Compared to the wild type T7174, the virulence of xopG mutant was significantly reduced, indicating that XopG is a key effector for Xoo to infect rice. Subcellular localization showed that XopG locates in the nucleus, cell membrane and cytoplasm in plant cells. This study laid a foundation for exploring the molecular mechanism of XopG-Xoo interaction.
Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae is the pathogen that causes bacterial leaf blight in rice. Type Ⅲ secretion effectors (T3SEs) play an important role in the virulence of Xoo. To study the function of XopG in Xoo virulence and the localization in plant cells, we carried out the informatics analysis, gene knockout, expression analysis, subcellular localization of XopG, and analyzed the effect of xopG mutation on Xoo virulence. The results showed that the xopG promoter sequence contains an atypical plant-induced motif (PIP-box), indicating that xopG expression is regulated by HrpX. The promoter activity of xopG in hrpX deletion mutant was significantly lower than that in the wild type strain T7174, suggesting that HrpX positively regulates the expression of xopG. Compared to the wild type T7174, the virulence of xopG mutant was significantly reduced, indicating that XopG is a key effector for Xoo to infect rice. Subcellular localization showed that XopG locates in the nucleus, cell membrane and cytoplasm in plant cells. This study laid a foundation for exploring the molecular mechanism of XopG-Xoo interaction.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240071
Abstract:
Euprojoannisia Brèthes is one of the 35 subgenera of genus Forcipomyia Meigen, known as the third largest subgenus in terms of the number of species just behind subgenus Forcipomyia s.str. and subgenus Lasiohelea Kieffer. The specimens of subgenus Euprojoannisia were collected from the mangrove forests in Hainan Province and identified by morphological characters and DNA barcodes. A new species, F. (E.) quadrata sp. nov., and a new record species of Hainan Province, F. (E.) psilonota Kieffer, 1911, were found and described. Besides, the characteristics of the females of F. (E.) appendicular Liu, Yan and Liu, 1996, were first reported.
Euprojoannisia Brèthes is one of the 35 subgenera of genus Forcipomyia Meigen, known as the third largest subgenus in terms of the number of species just behind subgenus Forcipomyia s.str. and subgenus Lasiohelea Kieffer. The specimens of subgenus Euprojoannisia were collected from the mangrove forests in Hainan Province and identified by morphological characters and DNA barcodes. A new species, F. (E.) quadrata sp. nov., and a new record species of Hainan Province, F. (E.) psilonota Kieffer, 1911, were found and described. Besides, the characteristics of the females of F. (E.) appendicular Liu, Yan and Liu, 1996, were first reported.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240033
Abstract:
Liriomyza trifolii (Burgess) is one of the important invasive pests infesting melons and vegetables in China. An attempt was made to further explore the adaptive mechanism of L. trifolii to temperature stress. The sequence characteristics, structure and phylogenetic analysis of catalase (CAT) in L. trifolii were analyzed by using bioinformatics, and the expression of LtCAT gene at different developmental stages and under temperature stress was detected by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. The CAT gene sequence of L. trifolii was cloned, and its open reading frame length was1542 bp, encoding 513 amino acids. The construction of phylogenetic tree showed that the CAT gene of L. trifolii was closely related to those of Bactrocera dorsalis, Zeugodacus cucurbitae and Ceratitis capitata, and hence clustered into one branch with a confidence level of 90%. The LtCAT gene was differentially expressed in larvae, pupae and adults, and the expression level was the highest in pupae. After temperature stress treatment, the expression of LtCAT gene responded positively to temperature changes. This study provides a basis for further study on the function of CAT gene in L. trifolii.
Liriomyza trifolii (Burgess) is one of the important invasive pests infesting melons and vegetables in China. An attempt was made to further explore the adaptive mechanism of L. trifolii to temperature stress. The sequence characteristics, structure and phylogenetic analysis of catalase (CAT) in L. trifolii were analyzed by using bioinformatics, and the expression of LtCAT gene at different developmental stages and under temperature stress was detected by real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR. The CAT gene sequence of L. trifolii was cloned, and its open reading frame length was
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250041
Abstract:
The insect olfactory system plays a pivotal role in host recognition, mating, and oviposition, with odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) serving critical functions in olfactory signal transduction. An attempt was made to analyze the sequence characteristics and ligand-binding properties of two OBPs (TrufOBP1 and TrufOBP5) in Tirathaba rufivena, a major pest infesting inflorescences and fruit of arecanut (Areca catechu), and to validate their behavioral regulatory roles through wind tunnel experiments. Sequence analysis revealed that TrufOBP1 contains four conserved cysteines and is classified as a Minus-C OBP, whereas TrufOBP5 possesses ten conserved cysteines and is categorized as a Plus-C OBP. Fluorescence competitive binding assays demonstrated that TrufOBP1 exhibited broad ligand specificity and was bound to 11 compounds, including nine volatiles from areca nut (Areca catechu) inflorescences and two sex pheromones. In contrast, TrufOBP5 displayed high binding specificity, and interacted exclusively with octyl p-methoxycinnamate and vanillin, suggesting its potential role in host plant recognition. Wind tunnel experiments identified β-myrcene, octyl p-methoxycinnamate, and 3-hexenyl acetate as attractants for female adults from host volatiles. Among sex pheromone components, 2,2,6-trimethyl-6-vinyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-OL exhibited the highest attraction activity, while vanillin also demonstrated significant attractant effects. This study elucidates the functional roles of TrufOBP1 and TrufOBP5 in host recognition and sex pheromone perception in T. rufivena, providing a theoretical foundation for pest behavior regulation and supporting the development of olfaction-based green control strategies.
The insect olfactory system plays a pivotal role in host recognition, mating, and oviposition, with odorant-binding proteins (OBPs) serving critical functions in olfactory signal transduction. An attempt was made to analyze the sequence characteristics and ligand-binding properties of two OBPs (TrufOBP1 and TrufOBP5) in Tirathaba rufivena, a major pest infesting inflorescences and fruit of arecanut (Areca catechu), and to validate their behavioral regulatory roles through wind tunnel experiments. Sequence analysis revealed that TrufOBP1 contains four conserved cysteines and is classified as a Minus-C OBP, whereas TrufOBP5 possesses ten conserved cysteines and is categorized as a Plus-C OBP. Fluorescence competitive binding assays demonstrated that TrufOBP1 exhibited broad ligand specificity and was bound to 11 compounds, including nine volatiles from areca nut (Areca catechu) inflorescences and two sex pheromones. In contrast, TrufOBP5 displayed high binding specificity, and interacted exclusively with octyl p-methoxycinnamate and vanillin, suggesting its potential role in host plant recognition. Wind tunnel experiments identified β-myrcene, octyl p-methoxycinnamate, and 3-hexenyl acetate as attractants for female adults from host volatiles. Among sex pheromone components, 2,2,6-trimethyl-6-vinyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-3-OL exhibited the highest attraction activity, while vanillin also demonstrated significant attractant effects. This study elucidates the functional roles of TrufOBP1 and TrufOBP5 in host recognition and sex pheromone perception in T. rufivena, providing a theoretical foundation for pest behavior regulation and supporting the development of olfaction-based green control strategies.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240204
Abstract:
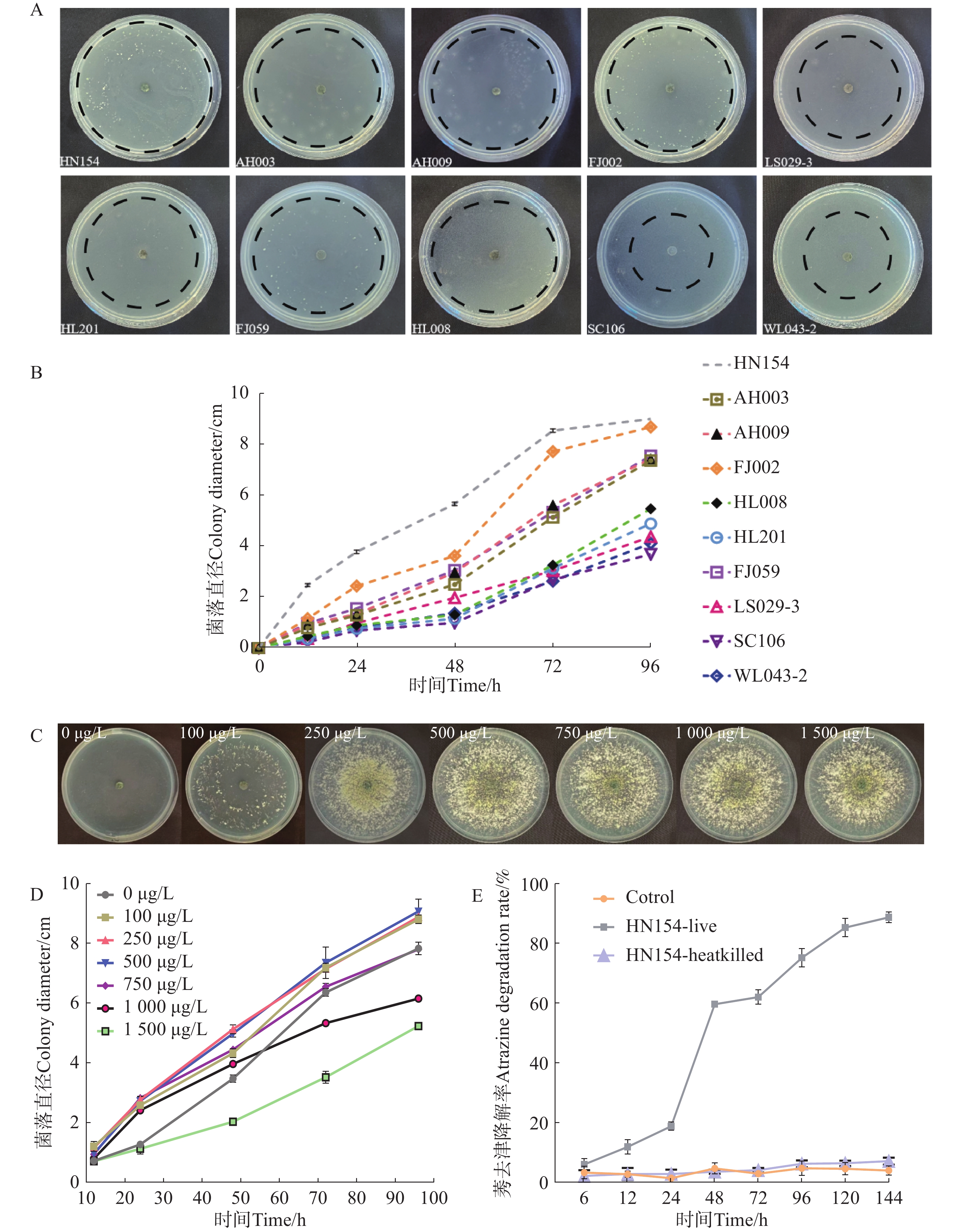
The inorganic salt medium with atrazine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source was used to screen a Trichoderma strain with the best growth performance among 10 Trichoderma strains, and the Trichoderma strain HN154 was selected. The degradation test of atrazine demonstrated that this strain had a high ability to degrade atrazine. Strain HN154 was identified as Trichoderma lentiforme based on morphological characteristics and ITS/RPB2 gene sequence analysis. Optimization of atrazine degradation conditions showed that the atrazine degradation rate was as high as 87.79% when cultured in inorganic salt medium with 10 g/L glucose, pH 7, 25 ℃, and 1% inoculum. Response surface optimization further improved degradation to 89.02% under the conditions of 5.24 g/L glucose, pH 7.78, 0.77% inoculum, and 25.5 ℃. This study provides microbial resources and technical support for efficient atrazine degradation, offering insights into degradation of microbial pesticide residues.
The inorganic salt medium with atrazine as the sole carbon and nitrogen source was used to screen a Trichoderma strain with the best growth performance among 10 Trichoderma strains, and the Trichoderma strain HN154 was selected. The degradation test of atrazine demonstrated that this strain had a high ability to degrade atrazine. Strain HN154 was identified as Trichoderma lentiforme based on morphological characteristics and ITS/RPB2 gene sequence analysis. Optimization of atrazine degradation conditions showed that the atrazine degradation rate was as high as 87.79% when cultured in inorganic salt medium with 10 g/L glucose, pH 7, 25 ℃, and 1% inoculum. Response surface optimization further improved degradation to 89.02% under the conditions of 5.24 g/L glucose, pH 7.78, 0.77% inoculum, and 25.5 ℃. This study provides microbial resources and technical support for efficient atrazine degradation, offering insights into degradation of microbial pesticide residues.
Spatiotemporal dynamics of butterfly diversity in Wuyuan River National Wetland Park, Haikou, Hainan
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240164
Abstract:
Butterfly is an important indicator organism for environmental monitoring, its community composition and diversity are closely related to habitat type, and its diversity and distribution can well reflect local ecological and environmental quality to a certain extent. In order to explore the relationship between habitats and butterfly diversity, a systematic survey of butterflies in four habitats of Wuyuan River National Wetland Park, Haikou, Hainan Province was conducted from February 2023 to January 2024 by using line transects method, and the distribution of butterflies in different habitats of Wuyuan River National Wetland Park was analyzed. In the survey a total of2107 individuals of butterfly belonging to 6 families 90 genera 128 species were recorded, most species were from Oriental Region, and Nymphalidae contain the most species and abundance. There were significant spatiotemporal differences in community diversity, and the monthly dynamics of adult insects indicate that the changes of species and individual numbers were bimodal with peaks in May and September, respectively. There were obvious differences in species composition and diversity index in different habitats. The diversity index, richness index and evenness index of butterfly community in laurifruticeta were the highest, and the diversity index and evenness index of butterfly community in emersiherbosa were the lowest. This survey improved the basic data of butterfly resources in Wuyuan River National Wetland Park, and provided references for the conservation and utilization of butterfly diversity and the ecological environment assessment.
Butterfly is an important indicator organism for environmental monitoring, its community composition and diversity are closely related to habitat type, and its diversity and distribution can well reflect local ecological and environmental quality to a certain extent. In order to explore the relationship between habitats and butterfly diversity, a systematic survey of butterflies in four habitats of Wuyuan River National Wetland Park, Haikou, Hainan Province was conducted from February 2023 to January 2024 by using line transects method, and the distribution of butterflies in different habitats of Wuyuan River National Wetland Park was analyzed. In the survey a total of
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250004
Abstract:
For early and rapid detection of Xanthomonas. oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc), the cause of bacterial leaf streak in rice, specific recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) primers, and Exo fluorescent and nfo probes were designed and screened, respectively, according to the publicly available gene sequence XOCgx_RS03090 of Xoc genome sequence in GenBank. The recombinant plasmid containing Xoc gene was constructed as a positive control. One fluorescent Exo-RPA assay and the other lateral flow strip detection (LFD-RPA) assay were established for rapid detection of Xoc. The sensitivity and specificity of the RPA methods were assessed, and the amplification effects of the RPA methods were explored by optimizing the reaction temperature and reaction time. The results showed that the sensitivity of both the Exo-RPA and LFD-RPA assays for the detection of Xoc were both 4.96 copies·μL−1, and that the optimal temperatures for the reaction were both 39 ℃. Xoc was detected within 12 min by the optimized Exo-RPA method, and within 5 min by the optimized LFD-RPA. The Exo-RPA and LFD-RPA assays developed were highly specific and could specifically and uniquely identify Xoc among plant pathogens in test. Both the RPA methods are highly sensitive, specific and fast, which pose a high potential to the monitoring of the target pathogen and early diagnosis of the disease.
For early and rapid detection of Xanthomonas. oryzae pv. oryzicola (Xoc), the cause of bacterial leaf streak in rice, specific recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) primers, and Exo fluorescent and nfo probes were designed and screened, respectively, according to the publicly available gene sequence XOCgx_RS03090 of Xoc genome sequence in GenBank. The recombinant plasmid containing Xoc gene was constructed as a positive control. One fluorescent Exo-RPA assay and the other lateral flow strip detection (LFD-RPA) assay were established for rapid detection of Xoc. The sensitivity and specificity of the RPA methods were assessed, and the amplification effects of the RPA methods were explored by optimizing the reaction temperature and reaction time. The results showed that the sensitivity of both the Exo-RPA and LFD-RPA assays for the detection of Xoc were both 4.96 copies·μL−1, and that the optimal temperatures for the reaction were both 39 ℃. Xoc was detected within 12 min by the optimized Exo-RPA method, and within 5 min by the optimized LFD-RPA. The Exo-RPA and LFD-RPA assays developed were highly specific and could specifically and uniquely identify Xoc among plant pathogens in test. Both the RPA methods are highly sensitive, specific and fast, which pose a high potential to the monitoring of the target pathogen and early diagnosis of the disease.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240148
Abstract:
An attempt was made to analyze the function and mechanism of auxin response factor (ARF) in cassava. A MeARF gene was cloned from different tissues of cassava and analyzed by using bioinformatics, and an evolutionary tree was constructed to illustrate its homologous relationship. The analysis of the protein structure of MeARF found that the protein contained the conserved B3 domain (B3 DNA binding domain, B3) and PB1 domain (Phox and Bem1p, PB1). The analysis of the expression levels of MeARF in different tissues showed that the expression level of MeARF was relatively high in the lateral buds of cassava. Furthermore, the gene expression vector of pGADT7-MeARF was constructed, and the cDNA library of cassava was screened by yeast two-hybrid experiments. The candidate proteins related to plant growth, development and immunity were screened. The results indicate that MeARF might be involved in growth, development and immunity of cassava.
An attempt was made to analyze the function and mechanism of auxin response factor (ARF) in cassava. A MeARF gene was cloned from different tissues of cassava and analyzed by using bioinformatics, and an evolutionary tree was constructed to illustrate its homologous relationship. The analysis of the protein structure of MeARF found that the protein contained the conserved B3 domain (B3 DNA binding domain, B3) and PB1 domain (Phox and Bem1p, PB1). The analysis of the expression levels of MeARF in different tissues showed that the expression level of MeARF was relatively high in the lateral buds of cassava. Furthermore, the gene expression vector of pGADT7-MeARF was constructed, and the cDNA library of cassava was screened by yeast two-hybrid experiments. The candidate proteins related to plant growth, development and immunity were screened. The results indicate that MeARF might be involved in growth, development and immunity of cassava.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240187
Abstract:
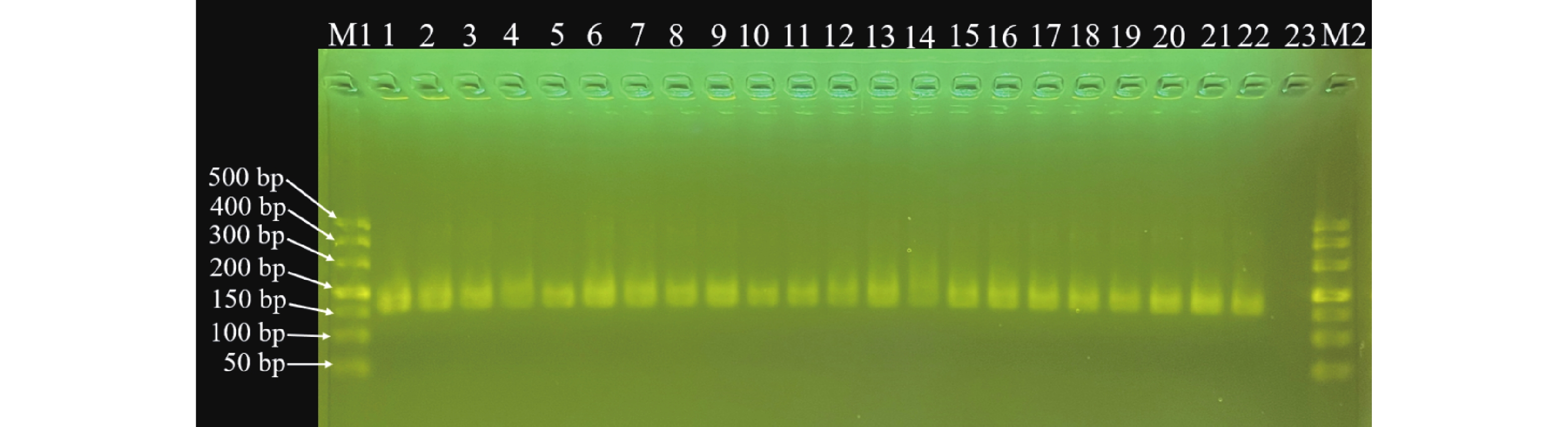
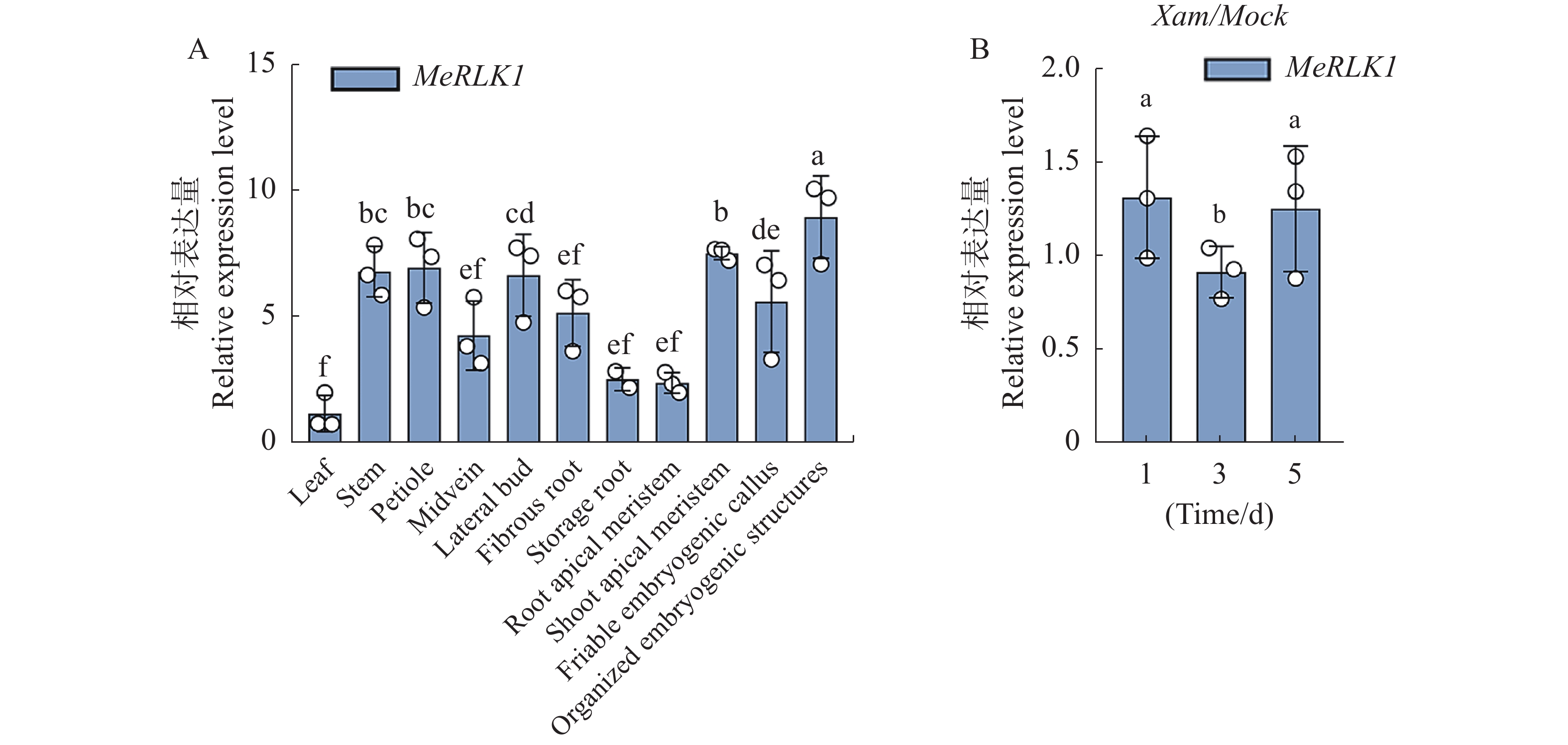
In order to screen proteins in cassava (Manihot esculenta) that jointly regulate cassava disease resistance with MeRLK1, 24 candidate interacting proteins of the MeRLK1 protein including heat shock protein (Hsp), ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1), aquaporin transported protein (AQP), etc were selected through screening from the yeast two-hybrid library. Further analysis of the spatiotemporal expression correlation between MeRLK1 and 24 candidate interacting genes revealed that genes including Pentatricopeptide repeat 2 (PPR2) and BR-signaling kinase (BSK) exhibited high correlations (R>0.7) with MeRLK1 expression across diverse tissues and under stress conditions. Based on the screening, the full-length sequence vector of MeBSK, a protein related to the brassinosteroid (BR) signaling pathway was constructed. Through the yeast two-hybrid experiment, it was found that there might be an interaction between MeRLK1 and MeBSK. Subsequently, bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) will be needed to further verify this interaction in vivo.
In order to screen proteins in cassava (Manihot esculenta) that jointly regulate cassava disease resistance with MeRLK1, 24 candidate interacting proteins of the MeRLK1 protein including heat shock protein (Hsp), ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1), aquaporin transported protein (AQP), etc were selected through screening from the yeast two-hybrid library. Further analysis of the spatiotemporal expression correlation between MeRLK1 and 24 candidate interacting genes revealed that genes including Pentatricopeptide repeat 2 (PPR2) and BR-signaling kinase (BSK) exhibited high correlations (R>0.7) with MeRLK1 expression across diverse tissues and under stress conditions. Based on the screening, the full-length sequence vector of MeBSK, a protein related to the brassinosteroid (BR) signaling pathway was constructed. Through the yeast two-hybrid experiment, it was found that there might be an interaction between MeRLK1 and MeBSK. Subsequently, bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) will be needed to further verify this interaction in vivo.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250029
Abstract:
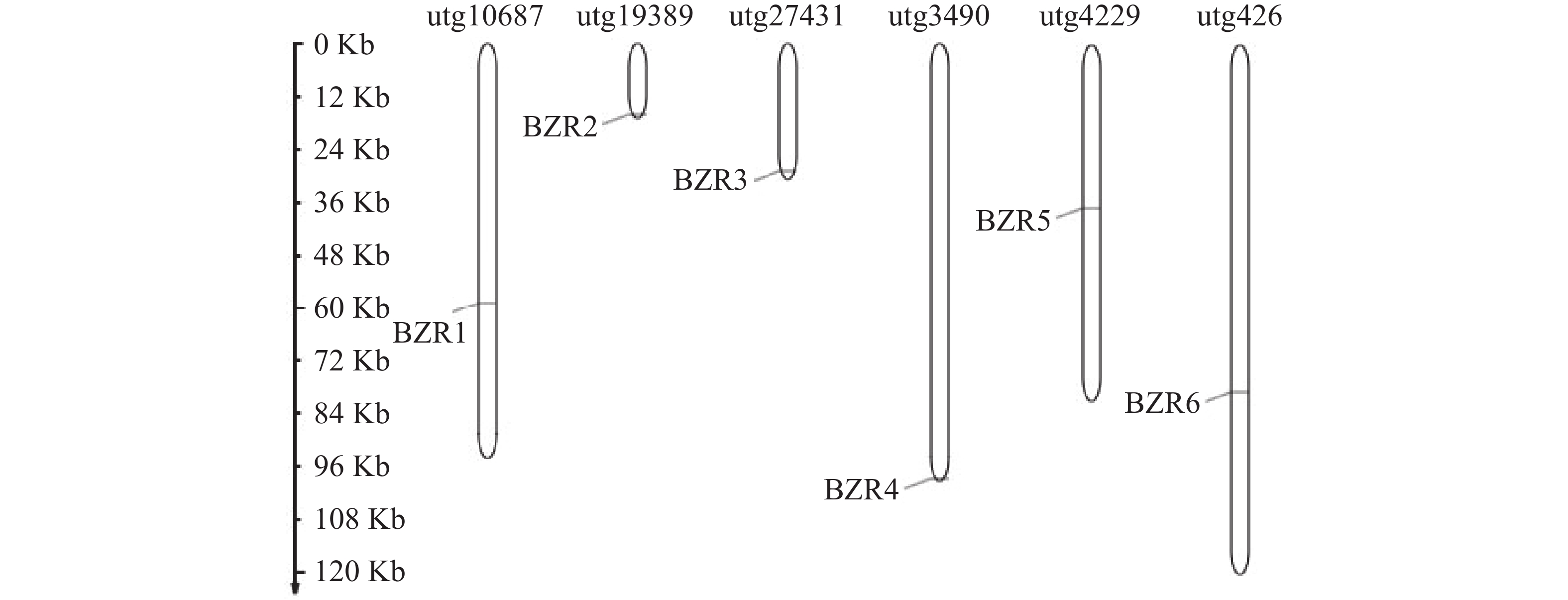
To further understand the role of the TkBZR family genes in the growth, development, and stress resistance of rubber dandelion (Taraxacum kok-saghyz), the TkBZR/BES family genes were identified and analyzed by examining the whole genome sequencing data of T. kok-saghyz. A total of 6 members of the TkBZR family were identified, named from TkBZR1 to TkBZR6, and their distribution on chromosomes, domain characteristics, tissue expression profiles and the spatial-temporal gene expression were analyzed. The results revealed that TkBZR/BES gene family members were distributed on 6 independent scaffolds. Phylogenetic trees indicate that TkBZR/BES gene family members are evolutionarily conserved, with rubber dandelion and lettuce genes clustering in the same subgroup, suggesting a possible close evolutionary relationship between the two. Gene structure and conserved domain analysis show that except for TkBZR5, all the other TkBZR genes contain two exons and one intron, and that all the family members exhibit a highly conserved BES1_N domain. Expression pattern analysis reveals that 5 members are expressed in all five tissues, while one member is almost unexpressed. Additionally, the TkBZR2 gene with the highest expression abundance was successfully cloned, encoding 307 amino acids. Homologous recombination of TkBZR2 was made into prokaryotic expression vector, and the recombinant plasmid was transferred into E. coli BL21(DE3) .The recombinant protein TkBZR2 was expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3).
To further understand the role of the TkBZR family genes in the growth, development, and stress resistance of rubber dandelion (Taraxacum kok-saghyz), the TkBZR/BES family genes were identified and analyzed by examining the whole genome sequencing data of T. kok-saghyz. A total of 6 members of the TkBZR family were identified, named from TkBZR1 to TkBZR6, and their distribution on chromosomes, domain characteristics, tissue expression profiles and the spatial-temporal gene expression were analyzed. The results revealed that TkBZR/BES gene family members were distributed on 6 independent scaffolds. Phylogenetic trees indicate that TkBZR/BES gene family members are evolutionarily conserved, with rubber dandelion and lettuce genes clustering in the same subgroup, suggesting a possible close evolutionary relationship between the two. Gene structure and conserved domain analysis show that except for TkBZR5, all the other TkBZR genes contain two exons and one intron, and that all the family members exhibit a highly conserved BES1_N domain. Expression pattern analysis reveals that 5 members are expressed in all five tissues, while one member is almost unexpressed. Additionally, the TkBZR2 gene with the highest expression abundance was successfully cloned, encoding 307 amino acids. Homologous recombination of TkBZR2 was made into prokaryotic expression vector, and the recombinant plasmid was transferred into E. coli BL21(DE3) .The recombinant protein TkBZR2 was expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3).
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240085
Abstract:
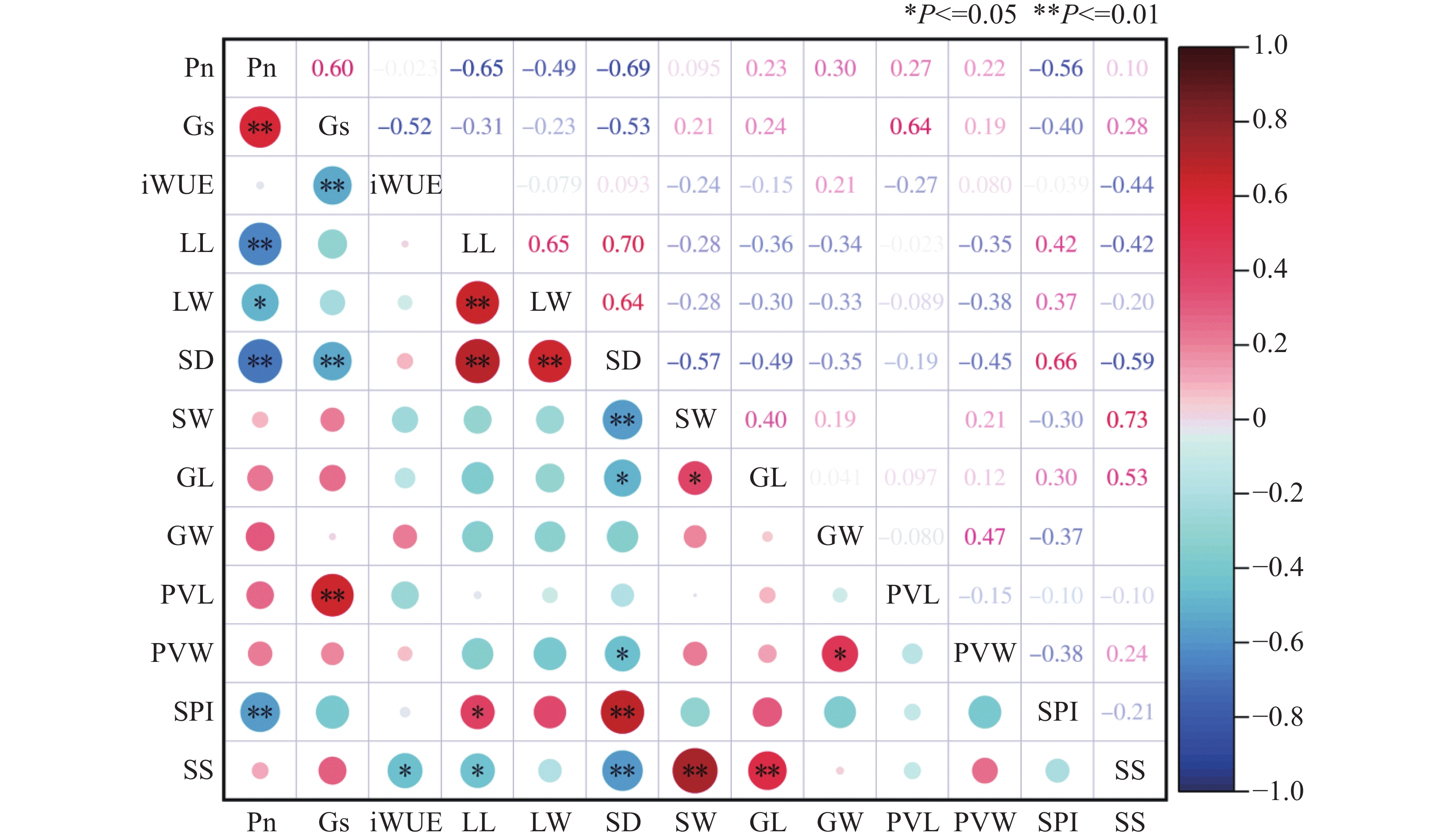
An attempt was made to analyze the relationship between stomatal and photosynthetic characteristics of different accessions of seashore paspalum (Paspalum vaginatum Sw.), and 25 seashore Paspalum germplasm were analyzed in terms of photosynthetic parameters, leaf length, leaf width and stomatal characteristics. The results showed that all traits of the paspalum germplasm were significantly different (P < 0.05), and were significantly (P < 0.05) positively or negatively correlated with each other. The net photosynthetic rate was significantly negatively correlated with the leaf length, stomatal density and stomatal area index (P < 0.01), and significantly negatively correlated with leaf width (P < 0.05). Stomatal conductance was significantly negatively correlated with stomatal density (P < 0.05), and positively with stomatal pore length (P < 0.01), while water utilization was negatively correlated with stomatal size (P < 0.05), but not with other stomatal characteristics (P > 0.05). The principal component analysis showed that the cumulative contribution rate of the four main components (net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, stomatal size and guard cell length) was 75.80%. Twenty-five accessions of the paspalum germplasm were classified into three groups (A, B and C) by using four indexes. Group C includes 14 accessions that have the highest net photosynthetic rate with the largest stomatal size, the widest stomatal pore and low stomatal density. Group C are accessions of seashore Paspalum germplasm with better photosynthetic characteristics, with their photosynthetic capacity regulated through the function of stomatal accessory cells, and the stomatal traits are also key indicators for regulating net photosynthetic rate.
An attempt was made to analyze the relationship between stomatal and photosynthetic characteristics of different accessions of seashore paspalum (Paspalum vaginatum Sw.), and 25 seashore Paspalum germplasm were analyzed in terms of photosynthetic parameters, leaf length, leaf width and stomatal characteristics. The results showed that all traits of the paspalum germplasm were significantly different (P < 0.05), and were significantly (P < 0.05) positively or negatively correlated with each other. The net photosynthetic rate was significantly negatively correlated with the leaf length, stomatal density and stomatal area index (P < 0.01), and significantly negatively correlated with leaf width (P < 0.05). Stomatal conductance was significantly negatively correlated with stomatal density (P < 0.05), and positively with stomatal pore length (P < 0.01), while water utilization was negatively correlated with stomatal size (P < 0.05), but not with other stomatal characteristics (P > 0.05). The principal component analysis showed that the cumulative contribution rate of the four main components (net photosynthetic rate, stomatal conductance, stomatal size and guard cell length) was 75.80%. Twenty-five accessions of the paspalum germplasm were classified into three groups (A, B and C) by using four indexes. Group C includes 14 accessions that have the highest net photosynthetic rate with the largest stomatal size, the widest stomatal pore and low stomatal density. Group C are accessions of seashore Paspalum germplasm with better photosynthetic characteristics, with their photosynthetic capacity regulated through the function of stomatal accessory cells, and the stomatal traits are also key indicators for regulating net photosynthetic rate.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240135
Abstract:
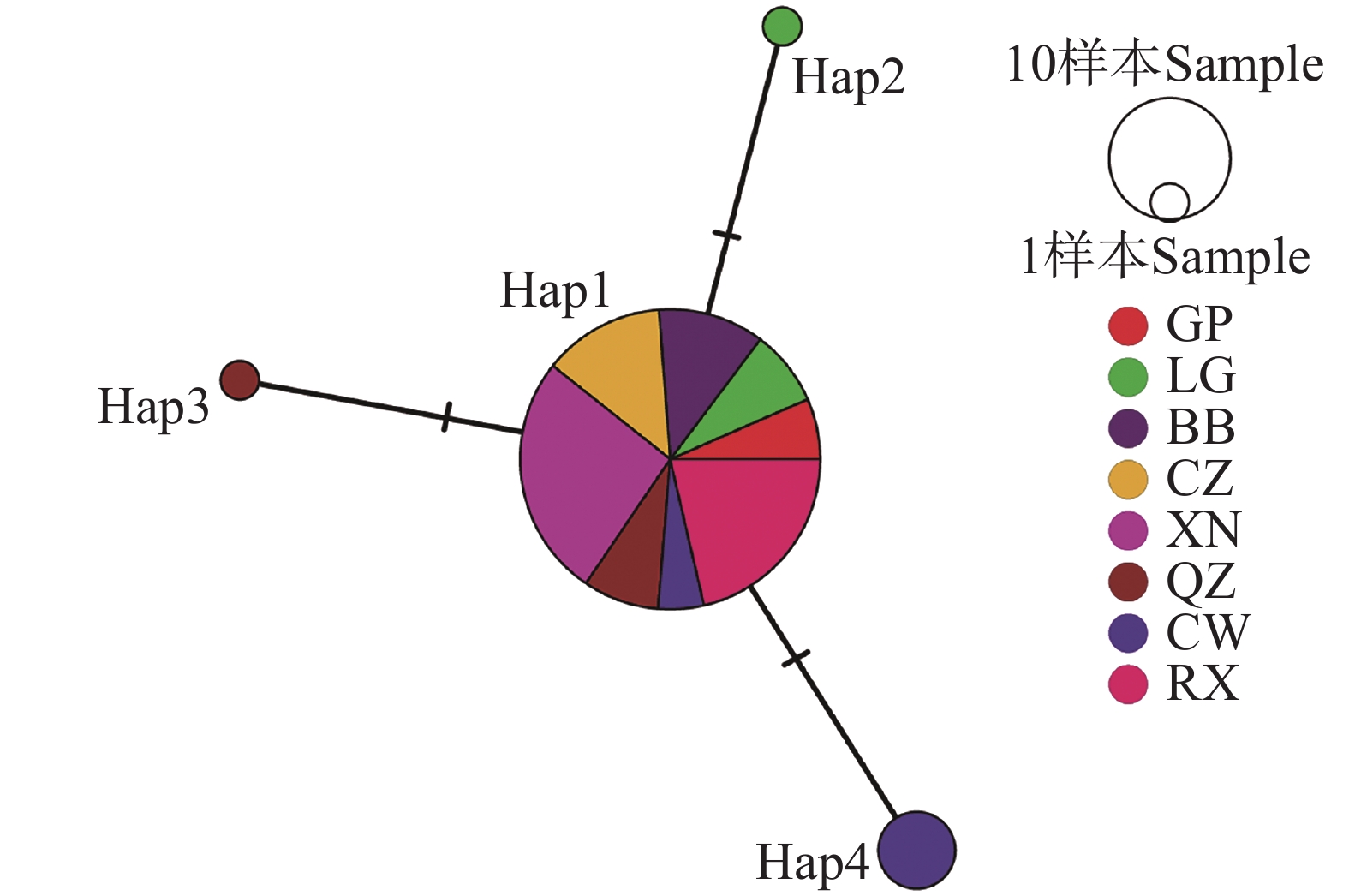
An attempt was made to investigate the genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, the causative agent of pine wilt disease, which is posing a severe threat to the forest ecosystem and economic development in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Sixty seven strains of B. xylophilus collected from eight different districts/counties within Guangxi were analyzed by using the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit Ⅰ (mt COI) gene fragment. The results indicated that there were three polymorphic sites and one parsimony-informative site within a 647 bp region, with genetic diversity indices at extremely low levels. Four haplotypes of B. xylophilus were identified in Guangxi, with an overall haplotype diversity of 0.170, where Hap1 was the predominant haplotype. The B. xylophilus strains in Guangxi were clearly distinct from those found in other regions both domestically and internationally, forming an independent branch. In recent years, the spread of B. xylophilus in Guangxi occurred primarily through natural dispersion. All these findings might provide a theoretical basis for developing targeted prevention and control strategies for B. xylophilus in Guangxi.
An attempt was made to investigate the genetic diversity and genetic differentiation of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus, the causative agent of pine wilt disease, which is posing a severe threat to the forest ecosystem and economic development in Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region. Sixty seven strains of B. xylophilus collected from eight different districts/counties within Guangxi were analyzed by using the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit Ⅰ (mt COI) gene fragment. The results indicated that there were three polymorphic sites and one parsimony-informative site within a 647 bp region, with genetic diversity indices at extremely low levels. Four haplotypes of B. xylophilus were identified in Guangxi, with an overall haplotype diversity of 0.170, where Hap1 was the predominant haplotype. The B. xylophilus strains in Guangxi were clearly distinct from those found in other regions both domestically and internationally, forming an independent branch. In recent years, the spread of B. xylophilus in Guangxi occurred primarily through natural dispersion. All these findings might provide a theoretical basis for developing targeted prevention and control strategies for B. xylophilus in Guangxi.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240084
Abstract:
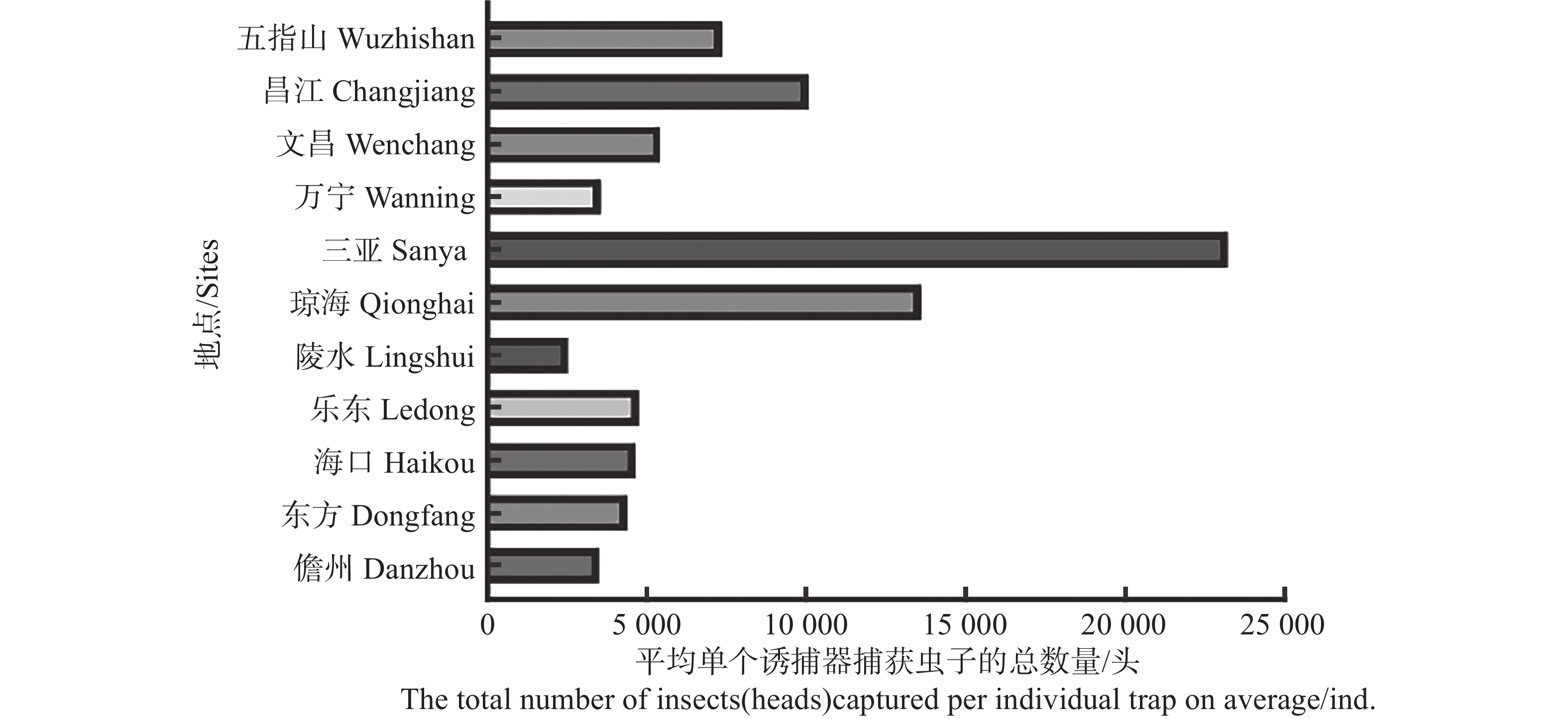
To clarify the population dynamics of Bactrocera dorsalis in Hainan region, surveys were conducted on the population of B. dorsalis in the main agricultural production areas of Hainan, and the correlation between the population and meteorological factors was explored. The results showed that B. dorsalis can occur throughout the year in Hainan, with the peak occurrence period from May to August, and the low occurrence period in winter from November to December. The monitoring data of B. dorsalis populations in some areas were positively correlated rwith average temperature, maximum temperature, and minimum temperature, but not significantly with precipitation, relative humidity, and rainy days was. This provides a good referece for formulating control strategies for B. dorsalis in Hainan.
To clarify the population dynamics of Bactrocera dorsalis in Hainan region, surveys were conducted on the population of B. dorsalis in the main agricultural production areas of Hainan, and the correlation between the population and meteorological factors was explored. The results showed that B. dorsalis can occur throughout the year in Hainan, with the peak occurrence period from May to August, and the low occurrence period in winter from November to December. The monitoring data of B. dorsalis populations in some areas were positively correlated rwith average temperature, maximum temperature, and minimum temperature, but not significantly with precipitation, relative humidity, and rainy days was. This provides a good referece for formulating control strategies for B. dorsalis in Hainan.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240069
Abstract:
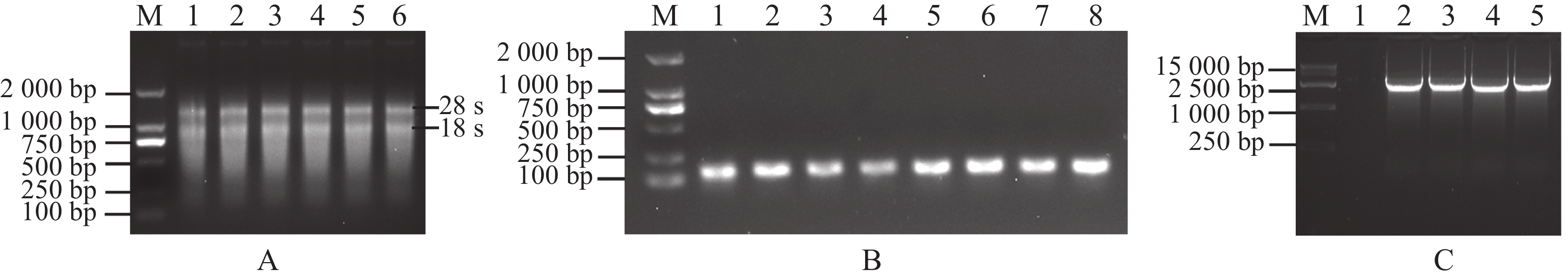
Pathogenic bacterial infections release large amounts of lipopolysaccharides that disrupt the structure of intestinal tight junction proteins, leading to increased intestinal permeability, causing dysfunction of the intestinal epithelial barrier, and inducing severe intestinal inflammation. Sodium butyrate, as a type of short-chain fatty acid, has an important role in relieving intestinal inflammation. However, its properties such as volatility and low utilization rate seriously affect its application. Therefore, the design and development of sodium butyrate drug delivery system is important to improve the utilization and effect of sodium butyrate. In this context the nature of cross-linking of chitosan (CS) and hyaluronic acid in the presence of sodium tripolyphosphate was made full use of to form CS-SB nanoparticles by encapsulating sodium butyrate (SB) in the particles. CS-SB was characterized by transmission electron microscopy and laser particle size analysis, and was found to be irregularly spherical with a particle size of approximately 97.30 ± 4.20 nm. SB was able to release in PBS buffer, reaching a cumulative release of 116.27 ± 7.75 ng over 24 h. A lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal cellular inflammation model was constructed, and it was found that CS-SB could effectively inhibit the expression of cellular pro-inflammatory factors and play a role in alleviating inflammation. The drug delivery system developed using natural products such as chitosan can effectively overcome the shortcomings of sodium butyrate, which is volatile, and provides a new idea for designing new bioactive oral drug delivery systems.
Pathogenic bacterial infections release large amounts of lipopolysaccharides that disrupt the structure of intestinal tight junction proteins, leading to increased intestinal permeability, causing dysfunction of the intestinal epithelial barrier, and inducing severe intestinal inflammation. Sodium butyrate, as a type of short-chain fatty acid, has an important role in relieving intestinal inflammation. However, its properties such as volatility and low utilization rate seriously affect its application. Therefore, the design and development of sodium butyrate drug delivery system is important to improve the utilization and effect of sodium butyrate. In this context the nature of cross-linking of chitosan (CS) and hyaluronic acid in the presence of sodium tripolyphosphate was made full use of to form CS-SB nanoparticles by encapsulating sodium butyrate (SB) in the particles. CS-SB was characterized by transmission electron microscopy and laser particle size analysis, and was found to be irregularly spherical with a particle size of approximately 97.30 ± 4.20 nm. SB was able to release in PBS buffer, reaching a cumulative release of 116.27 ± 7.75 ng over 24 h. A lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal cellular inflammation model was constructed, and it was found that CS-SB could effectively inhibit the expression of cellular pro-inflammatory factors and play a role in alleviating inflammation. The drug delivery system developed using natural products such as chitosan can effectively overcome the shortcomings of sodium butyrate, which is volatile, and provides a new idea for designing new bioactive oral drug delivery systems.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250012
Abstract:
In order to improve the propagation efficiency of Curcuma wenyujin plants, tissue cultured plants of C. wenyujin was cultured on in vitro rooting medium (1/2MS + NAA 0.5 mg·L−1) supplemented with broad spectrum plant growth regulators, choline chloride (CC) and compound sodium nitrophenolate (CSN), at different concentrations and ratios to induce the differentiation of their microrhizomes, and the growth status of the tissue-cultured plants after transplantation was observed. The results showed that the tissue cultured plants cultured on the medium supplemented with a combination of CC at 1.0 mg·L−1 and CSN at 2.0 mg·L−1 were induced to form microrhizomes obviously, with an inducing rate of 62%. In the medium supplemented with a combination of CC at 3.0 mg·L−1 and CSN at 1.0 mg·L−1, the induction rate was 46%, but the swelling and thickening of microrhizomes were the most obvious, with a transverse diameter of about 6.8 mm. There was no significant difference in the length of microrhizomes between the two groups. All the tissue-cultured rooted plants with microrhizomes survived after transplantation, and their survival rate, growth rate, tiller number, number of new leaves, and the weights of tuberous roots and rhizomes increased by 36.4%, 112.5%, 83.0%, 103.9%, and 83.2%, respectively compared with the control tissue-cultured rooted plants.
In order to improve the propagation efficiency of Curcuma wenyujin plants, tissue cultured plants of C. wenyujin was cultured on in vitro rooting medium (1/2MS + NAA 0.5 mg·L−1) supplemented with broad spectrum plant growth regulators, choline chloride (CC) and compound sodium nitrophenolate (CSN), at different concentrations and ratios to induce the differentiation of their microrhizomes, and the growth status of the tissue-cultured plants after transplantation was observed. The results showed that the tissue cultured plants cultured on the medium supplemented with a combination of CC at 1.0 mg·L−1 and CSN at 2.0 mg·L−1 were induced to form microrhizomes obviously, with an inducing rate of 62%. In the medium supplemented with a combination of CC at 3.0 mg·L−1 and CSN at 1.0 mg·L−1, the induction rate was 46%, but the swelling and thickening of microrhizomes were the most obvious, with a transverse diameter of about 6.8 mm. There was no significant difference in the length of microrhizomes between the two groups. All the tissue-cultured rooted plants with microrhizomes survived after transplantation, and their survival rate, growth rate, tiller number, number of new leaves, and the weights of tuberous roots and rhizomes increased by 36.4%, 112.5%, 83.0%, 103.9%, and 83.2%, respectively compared with the control tissue-cultured rooted plants.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240048
Abstract:
An attempt was made to establish an in vitro identification system for resistance of rice to bacterial blight. Detached rice leaves of varying lengths were treated with 6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BA), Kinetin (KT), and Thidiazuron (TDZ) at different concentrations to select an optimized system for maintaining leaf greenness in vitro, based on which in vitro identification systems for resistance of rice to bacterial blight were established. The results indicated that regardless of the type of hormone used as a greening agent, the efficacy of greening was closely correlated with the length of the detached leaves, with shorter leaves exhibiting better greening effects. Further analysis of the relative chlorophyll content data revealed that the optimal concentration for each hormone that yielded the best greening effects were 0.28 mg·L−1 for TDZ, 4 mg·L−1 for 6-BA, and 4 mg·L−1 for KT, with 0.28 mg·L−1 for TDZ being the most effective concentration for detached rice leaves, and 4 mg·L−1 for 6-BA and 4 mg·L−1 for KT being similarly effective. Using 0.28 mg·L−1 TDZ as the greening agent, the detached leaves from rice plants with five different levels of field disease resistance were inoculated with Xanthomonas oryzae via the "clipping method." The results demonstrated a positive correlation between the lesion lengths of the detached leaves and those from field inoculations after 7 days of inoculation, with the regression equation of y = −0.62 + 1.32x (R2 = 0.98). The findings of this study contribute to the molecular breeding efforts for rice resistance to bacterial blight.
An attempt was made to establish an in vitro identification system for resistance of rice to bacterial blight. Detached rice leaves of varying lengths were treated with 6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BA), Kinetin (KT), and Thidiazuron (TDZ) at different concentrations to select an optimized system for maintaining leaf greenness in vitro, based on which in vitro identification systems for resistance of rice to bacterial blight were established. The results indicated that regardless of the type of hormone used as a greening agent, the efficacy of greening was closely correlated with the length of the detached leaves, with shorter leaves exhibiting better greening effects. Further analysis of the relative chlorophyll content data revealed that the optimal concentration for each hormone that yielded the best greening effects were 0.28 mg·L−1 for TDZ, 4 mg·L−1 for 6-BA, and 4 mg·L−1 for KT, with 0.28 mg·L−1 for TDZ being the most effective concentration for detached rice leaves, and 4 mg·L−1 for 6-BA and 4 mg·L−1 for KT being similarly effective. Using 0.28 mg·L−1 TDZ as the greening agent, the detached leaves from rice plants with five different levels of field disease resistance were inoculated with Xanthomonas oryzae via the "clipping method." The results demonstrated a positive correlation between the lesion lengths of the detached leaves and those from field inoculations after 7 days of inoculation, with the regression equation of y = −0.62 + 1.32x (R2 = 0.98). The findings of this study contribute to the molecular breeding efforts for rice resistance to bacterial blight.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240172
Abstract:
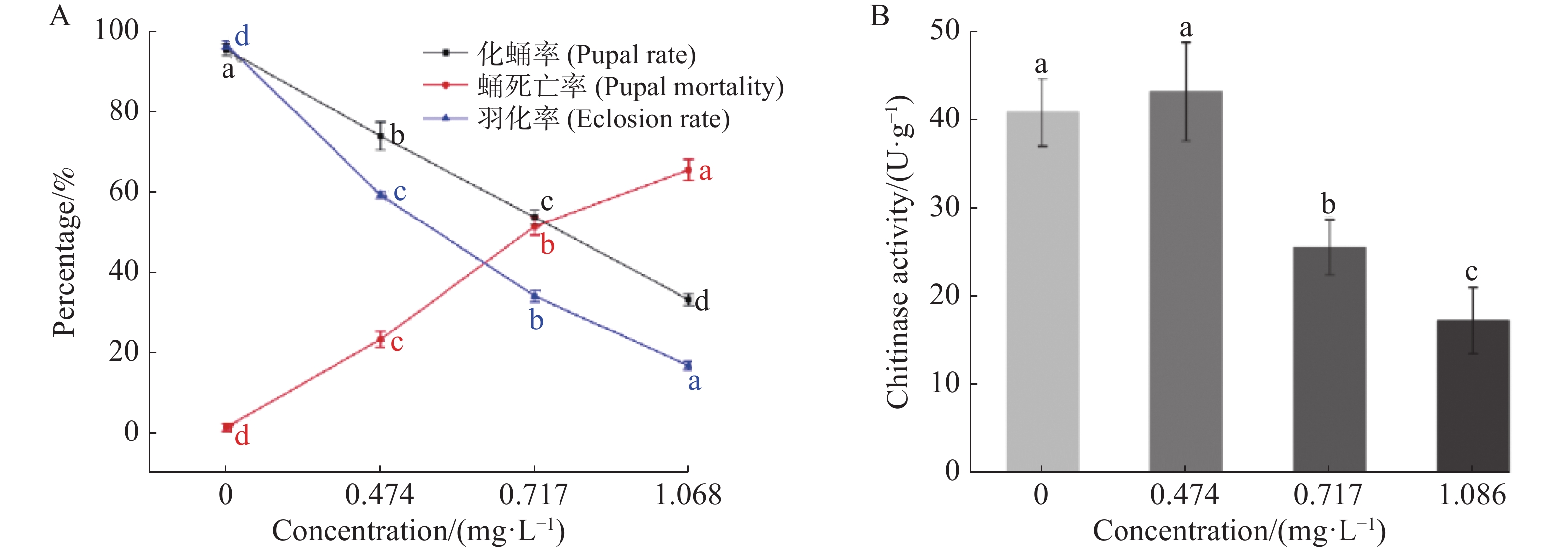
In order to develop insecticides with photoactivation activity, Aedes aegypti was used as the target organism to determine the insecticidal activity of 6 acridine derivatives and explore the activity mechanism of the highly active compound. The results showed that all the tested compounds were photosensitive and had no insecticidal activity under dark conditions. The insecticidal activity of all compounds increased significantly after UV irradiation, among which 9-phenylacridine had the highest activity (LC50 = 0.717 mg/L ). At the concentrations of LC50 and LC75, the 9-phenylacridine could significantly reduce the pupation rate and emergence rate and increase the mortality rate of pupae while inhibit chitinase activity; the ROS level was increased in the tested insects; the activities of SOD and CAT showed a trend of increasing first and then decreasing; the activity of POD increased. What’s more the AchE activity was inhibited by 9-phenylacridine with LC75 concentration. It is speculated that 9-phenylacridine can induce the organism to produce ROS and cause oxidative damage to the organism, thus exerting insecticidal activity. It is concluded that 9-phenylacridine has the potential to be developed into photoactivated insecticide.
In order to develop insecticides with photoactivation activity, Aedes aegypti was used as the target organism to determine the insecticidal activity of 6 acridine derivatives and explore the activity mechanism of the highly active compound. The results showed that all the tested compounds were photosensitive and had no insecticidal activity under dark conditions. The insecticidal activity of all compounds increased significantly after UV irradiation, among which 9-phenylacridine had the highest activity (LC50 = 0.717 mg/L ). At the concentrations of LC50 and LC75, the 9-phenylacridine could significantly reduce the pupation rate and emergence rate and increase the mortality rate of pupae while inhibit chitinase activity; the ROS level was increased in the tested insects; the activities of SOD and CAT showed a trend of increasing first and then decreasing; the activity of POD increased. What’s more the AchE activity was inhibited by 9-phenylacridine with LC75 concentration. It is speculated that 9-phenylacridine can induce the organism to produce ROS and cause oxidative damage to the organism, thus exerting insecticidal activity. It is concluded that 9-phenylacridine has the potential to be developed into photoactivated insecticide.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240158
Abstract:
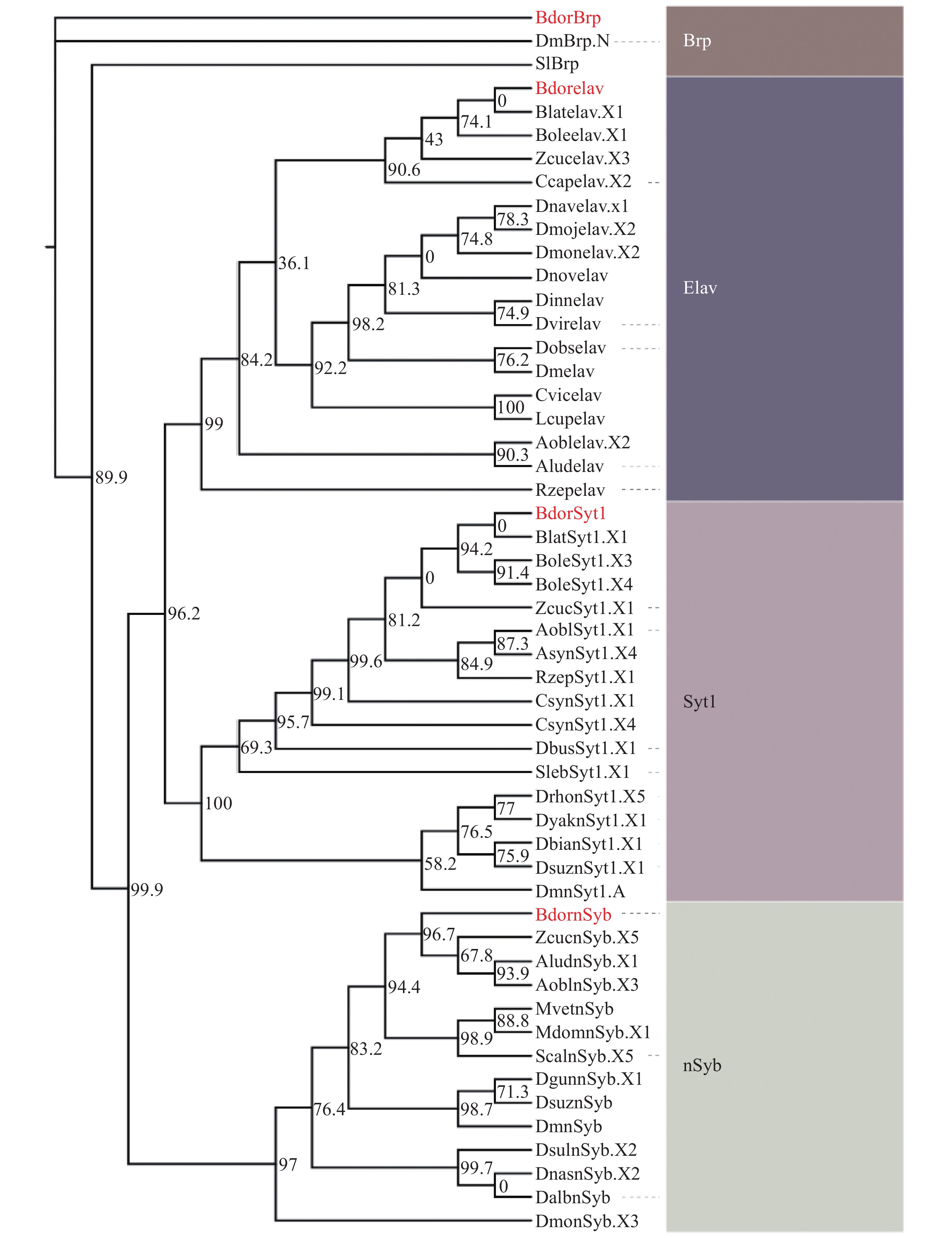
Research on the central nervous system function of pests forms the foundation for developing precise behavior control technologies. Despite the significant role of neuron-labeling techniques based on genetic manipulation in this field, such techniques remain relatively scarce for non-model insects, such as the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis. In this context an attempt was made to identify four pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis with a view to laying the groundwork for constructing a neuron-labeling system for this species. The genomic structures of the pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis were identified and analyzed by employing bioinformatics and molecular biology to verify their full-length sequences and peripheral expression patterns. The results indicate that, by referring to four pan-neuronal expression genes from Drosophila, four homologous genes were identified in the B. dorsalis, namely BdornSyb, BdorSyt1, Bdorelav, and BdorBrp. The full genomic lengths of these four genes are 19,337 bp (5 exons, 4 introns), 26,884 bp (8 exons, 7 introns), 1,341 bp (1 exon), and 49,692 bp (14 exons, 13 introns), respectively. The domains of BdornSyb, BdorSyt1, and Bdorelav are highly conserved among closely related species. PCR cloning results indicated that the CDS sequence lengths of these four genes are all over 500 bp, consistent with the bioinformatics analysis results. Evolutionary and genomic structure analyses demonstrated that the four genes are highly conserved among Diptera insects. Expression pattern analysis revealed that all the four genes are expressed in the peripheral sensory organs of B. dorsalis, with three genes, BdornSyb, BdorSyt1 and BdorBrp, showing higher expression levels in the primary olfactory organs, the antennae, and the maxillary palp. The four genes identified are candidate pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis, providing a foundation for constructing a pan-neuronal labeling system for this species in the future.
Research on the central nervous system function of pests forms the foundation for developing precise behavior control technologies. Despite the significant role of neuron-labeling techniques based on genetic manipulation in this field, such techniques remain relatively scarce for non-model insects, such as the oriental fruit fly, Bactrocera dorsalis. In this context an attempt was made to identify four pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis with a view to laying the groundwork for constructing a neuron-labeling system for this species. The genomic structures of the pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis were identified and analyzed by employing bioinformatics and molecular biology to verify their full-length sequences and peripheral expression patterns. The results indicate that, by referring to four pan-neuronal expression genes from Drosophila, four homologous genes were identified in the B. dorsalis, namely BdornSyb, BdorSyt1, Bdorelav, and BdorBrp. The full genomic lengths of these four genes are 19,337 bp (5 exons, 4 introns), 26,884 bp (8 exons, 7 introns), 1,341 bp (1 exon), and 49,692 bp (14 exons, 13 introns), respectively. The domains of BdornSyb, BdorSyt1, and Bdorelav are highly conserved among closely related species. PCR cloning results indicated that the CDS sequence lengths of these four genes are all over 500 bp, consistent with the bioinformatics analysis results. Evolutionary and genomic structure analyses demonstrated that the four genes are highly conserved among Diptera insects. Expression pattern analysis revealed that all the four genes are expressed in the peripheral sensory organs of B. dorsalis, with three genes, BdornSyb, BdorSyt1 and BdorBrp, showing higher expression levels in the primary olfactory organs, the antennae, and the maxillary palp. The four genes identified are candidate pan-neuronal expression genes in B. dorsalis, providing a foundation for constructing a pan-neuronal labeling system for this species in the future.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240134
Abstract:
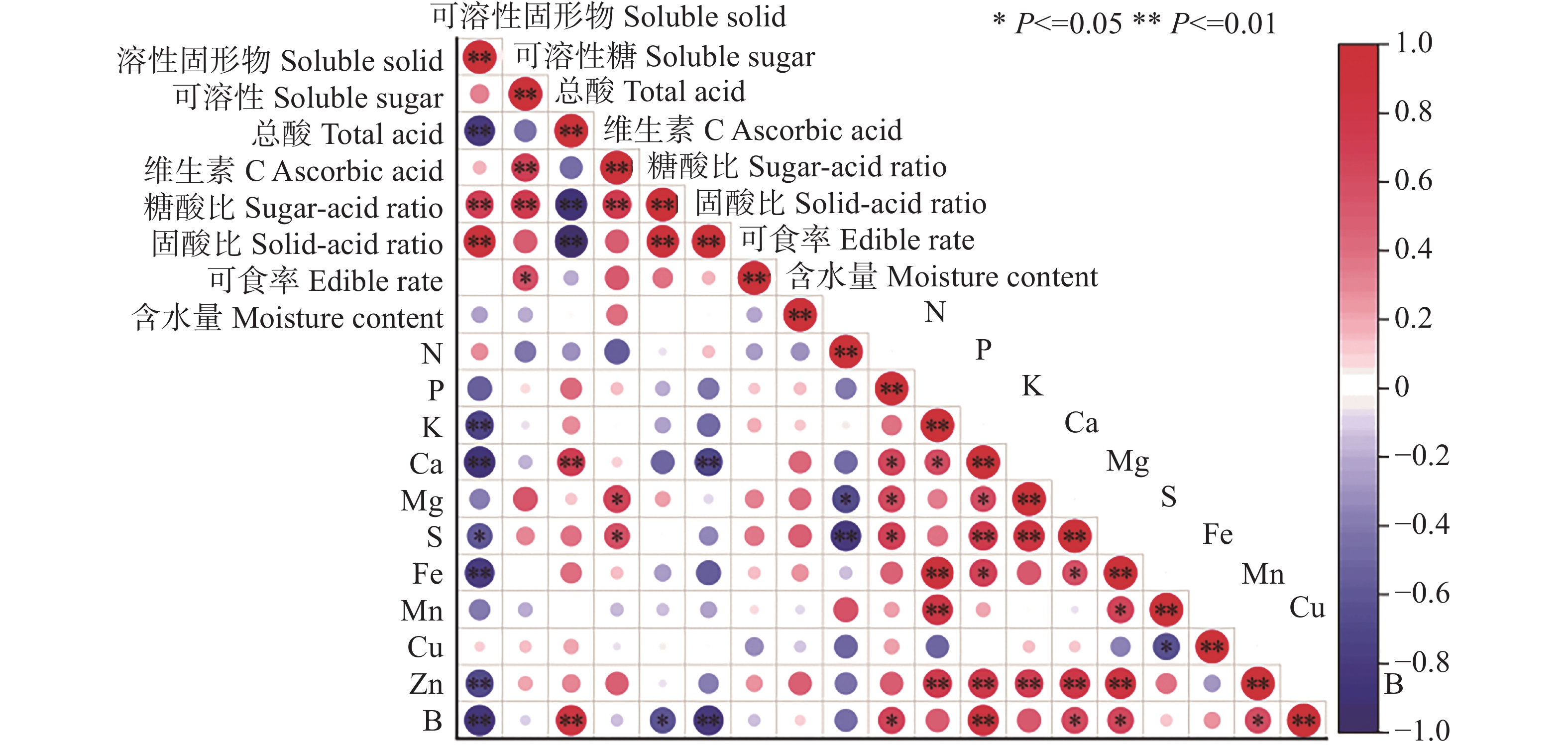
In order to explore the effect of mineral nutrient elements on fruit quality and screen the main mineral element factors affecting fruit quality, fruit of durian (Durio zibethinus Murr) Jinzhen planted in Hainan Province were selected for correlation and path coefficient analysis of the external morphology and internal quality indexes of the fruit as well as 11 mineral elements. The correlation analysis showed that there was a significantly negative correlation between soluble solids content and sulfur (S) content. The total acid content was significantly positively correlated with calcium (C) and boron (B) contents. There was a significantly positive correlation between vitamin C content and magnesium (Mg) and S contents. There was a significantly negative correlation between sugar-acid ratio and B content. The solid-acid ratio was significantly negatively correlated with Ca and B contents. The path analysis showed that there were some differences in the effects of mineral elements on fruit quality indexes. The main elements influencing soluble solids content were nitrogen (N), Mg, zinc (Zn) and manganese (Mn). The main factors influencing soluble sugar content were B, Mn, Zn and N, and the main elements affecting the total acid content of the fruit were potassium (K), N, Mg and Zn. The main elements affecting the content of vitamin C were S, iron (Fe), Mg and Zn. The main elements affecting the ratio of sugar to acid are K, Zn, Mn and B, and the main elements influencing solid acid ratio were Mg, Zn, Fe and Mn. In summary, K, N, Ca, Mg, Zn and B are the main elements affecting the quality of the durian fruit, and are the comprehensive results of the synergistic regulation of various mineral elements. Considering the local soil and fruit nutrient content in Hainan, the fruit yield and quality can be improved through application of K, Mg, Zn and B fertilizers at a slightly higher rate and a coordinated ratio.
In order to explore the effect of mineral nutrient elements on fruit quality and screen the main mineral element factors affecting fruit quality, fruit of durian (Durio zibethinus Murr) Jinzhen planted in Hainan Province were selected for correlation and path coefficient analysis of the external morphology and internal quality indexes of the fruit as well as 11 mineral elements. The correlation analysis showed that there was a significantly negative correlation between soluble solids content and sulfur (S) content. The total acid content was significantly positively correlated with calcium (C) and boron (B) contents. There was a significantly positive correlation between vitamin C content and magnesium (Mg) and S contents. There was a significantly negative correlation between sugar-acid ratio and B content. The solid-acid ratio was significantly negatively correlated with Ca and B contents. The path analysis showed that there were some differences in the effects of mineral elements on fruit quality indexes. The main elements influencing soluble solids content were nitrogen (N), Mg, zinc (Zn) and manganese (Mn). The main factors influencing soluble sugar content were B, Mn, Zn and N, and the main elements affecting the total acid content of the fruit were potassium (K), N, Mg and Zn. The main elements affecting the content of vitamin C were S, iron (Fe), Mg and Zn. The main elements affecting the ratio of sugar to acid are K, Zn, Mn and B, and the main elements influencing solid acid ratio were Mg, Zn, Fe and Mn. In summary, K, N, Ca, Mg, Zn and B are the main elements affecting the quality of the durian fruit, and are the comprehensive results of the synergistic regulation of various mineral elements. Considering the local soil and fruit nutrient content in Hainan, the fruit yield and quality can be improved through application of K, Mg, Zn and B fertilizers at a slightly higher rate and a coordinated ratio.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240140
Abstract:
Solanum lycopersicum is a model plant for research in genetics and molecular biology. Recently selection of tomato internal reference genes has been reported but with less types of exogenous hormones used for treatment. An attempt was hence made to select internal reference genes with stable expression in different tissues of tomato and under treatment with plant hormones. DANJ, EF-1α, ACT, UBI, APT, CAC, TIP41 and RPL8 were used as candidate internal reference genes, and selected under the 8 experimental conditions: exogenous hormone treatment with auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, cytokinin, salicylic acid, brassinolide and ethylene and various plant parts. The stability of the candidate reference genes was comprehensively evaluated using algorithms such as geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper, Delta CT and RefFinder. The stability of the reference genes was validated using the auxin-responsive gene SlGH3.4. The results showed that APT is the most stable reference gene expressed in auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, brassinosteroid treatment and various plant parts, that UBI is the most stable reference gene expressed in all samples under cytokinin and salicylic acid treatment, and that TIP41 is the most stable reference gene expressed under ethylene treatment. Finally, when APT, which has a relatively stable comprehensive ranking, was used as an internal reference gene, it was found that the expression level of SlGH3.4 gene showed a similar trend under IAA treatment conditions, while the less stable RPL8 gene failed to accurately correct the expression level of the target gene. All these results may provide theoretical support for the analysis of gene expression networks and molecular regulatory mechanisms in the response of tomato to exogenous hormone treatment.
Solanum lycopersicum is a model plant for research in genetics and molecular biology. Recently selection of tomato internal reference genes has been reported but with less types of exogenous hormones used for treatment. An attempt was hence made to select internal reference genes with stable expression in different tissues of tomato and under treatment with plant hormones. DANJ, EF-1α, ACT, UBI, APT, CAC, TIP41 and RPL8 were used as candidate internal reference genes, and selected under the 8 experimental conditions: exogenous hormone treatment with auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, cytokinin, salicylic acid, brassinolide and ethylene and various plant parts. The stability of the candidate reference genes was comprehensively evaluated using algorithms such as geNorm, NormFinder, BestKeeper, Delta CT and RefFinder. The stability of the reference genes was validated using the auxin-responsive gene SlGH3.4. The results showed that APT is the most stable reference gene expressed in auxin, gibberellin, abscisic acid, brassinosteroid treatment and various plant parts, that UBI is the most stable reference gene expressed in all samples under cytokinin and salicylic acid treatment, and that TIP41 is the most stable reference gene expressed under ethylene treatment. Finally, when APT, which has a relatively stable comprehensive ranking, was used as an internal reference gene, it was found that the expression level of SlGH3.4 gene showed a similar trend under IAA treatment conditions, while the less stable RPL8 gene failed to accurately correct the expression level of the target gene. All these results may provide theoretical support for the analysis of gene expression networks and molecular regulatory mechanisms in the response of tomato to exogenous hormone treatment.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240170
Abstract:
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves as a crucial site for protein processing in eukaryotic cells. Sec62, an essential component of the ER translocation complex, plays a significant role in growth, development, and stress regulation. An attempt was made to examine the transcription levels of the PcSec62 gene at various growth stages and during pathogenic processes. The PcSec62 gene was knocked out by using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to produce knockout mutants (ΔPcsec62) and a complementary strain (ΔPcsec62-C). The results showed that the transcriptional expression of PcSec62 significantly increased during the sporangia and infection stages. The ΔPcsec62 mutants exhibited notably reduced growth and sporulation abilities, alongside stunted hyphal growth. Additionally, the ΔPcsec62 strain showed significantly low tolerance to abiotic stress and reduced pathogenicity. These findings indicate that PcSec62 is involved in regulating the growth, development, abiotic stress responses, and pathogenicity of Phytophthora capsici.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) serves as a crucial site for protein processing in eukaryotic cells. Sec62, an essential component of the ER translocation complex, plays a significant role in growth, development, and stress regulation. An attempt was made to examine the transcription levels of the PcSec62 gene at various growth stages and during pathogenic processes. The PcSec62 gene was knocked out by using CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing to produce knockout mutants (ΔPcsec62) and a complementary strain (ΔPcsec62-C). The results showed that the transcriptional expression of PcSec62 significantly increased during the sporangia and infection stages. The ΔPcsec62 mutants exhibited notably reduced growth and sporulation abilities, alongside stunted hyphal growth. Additionally, the ΔPcsec62 strain showed significantly low tolerance to abiotic stress and reduced pathogenicity. These findings indicate that PcSec62 is involved in regulating the growth, development, abiotic stress responses, and pathogenicity of Phytophthora capsici.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240147
Abstract:
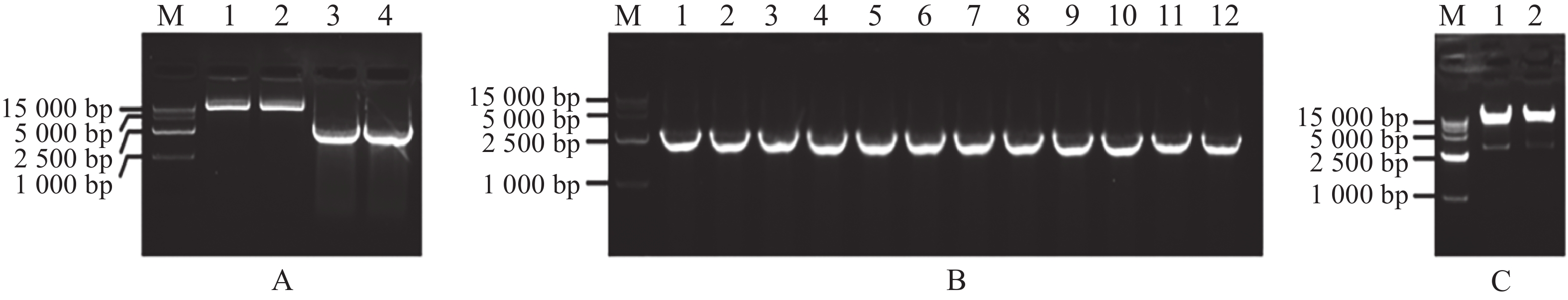
Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) has important economic value. Exploring the key genes of cassava is of great significance for improving cassava quality. To mine disease-resistant genes of cassava, a specific immune receptor-related gene resistant to Xam (MeRXam2) was cloned, and its protein structure was analyzed. The analysis was found that the coding sequence (CDS) region of this gene is3561 bp, with the protein size of about 132.847 kD, Real-time fluorescent quantitative (Real-time quantitative reverse transcription PCR, qRT-PCR) analysis showed that the expression level of MeRXam2 increased with time under pathogen infection and reached the maximum at 24 h, indicating that MeRXam2 was involved in the resistance response to cassava disease. In addition, a MeRXam2-pET32a protein expression vector was constructed by homologous recombination, and the protein was induced and determined. After exogenous spraying of MeRXam2 protein on cassava leaf tissues, the number of bacteria was found significantly lower than that of the control strain, indicating that this protein could slow down bacterial infection. This founding might provide a theoretical basis and candidate protein for cassava molecular breeding.
Cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) has important economic value. Exploring the key genes of cassava is of great significance for improving cassava quality. To mine disease-resistant genes of cassava, a specific immune receptor-related gene resistant to Xam (MeRXam2) was cloned, and its protein structure was analyzed. The analysis was found that the coding sequence (CDS) region of this gene is
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240116
Abstract:
To explore the volatile components and aroma composition of the flowers of longan (Dimocarpus longan), and to investigate the antioxidant activity of their extracts, the flowers of longan were collected from Fujian and extracted with different solvents, and their volatile components and the aroma of the components were analyzed by using the GC-MS technology. Meanwhile, DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging assays were used to detect the antioxidant activity of the longan flower extracts. The results showed that 59 components were identified from the essential oil extracted from the longan flowers, accounting for approximately 82.2% of the total volatile components. In the essential oil 4 key aroma compounds, 3 potential aroma compounds and 1 modified aroma compound were found. The DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging assay showed that different solvent extracts of longan flowers had a certain degree of antioxidant activity. Water extract, methanol extract and ethanol extract had significant antioxidant activity, while n-butyl alcohol extract and ethyl acetate extract had low antioxidant activity. All the results show that longan flowers have a great development potential in the fields of medicine, cosmetics, health products, functional foods and so on, which provides a scientific basis for the development and utilization of longan flowers.
To explore the volatile components and aroma composition of the flowers of longan (Dimocarpus longan), and to investigate the antioxidant activity of their extracts, the flowers of longan were collected from Fujian and extracted with different solvents, and their volatile components and the aroma of the components were analyzed by using the GC-MS technology. Meanwhile, DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging assays were used to detect the antioxidant activity of the longan flower extracts. The results showed that 59 components were identified from the essential oil extracted from the longan flowers, accounting for approximately 82.2% of the total volatile components. In the essential oil 4 key aroma compounds, 3 potential aroma compounds and 1 modified aroma compound were found. The DPPH and ABTS free radical scavenging assay showed that different solvent extracts of longan flowers had a certain degree of antioxidant activity. Water extract, methanol extract and ethanol extract had significant antioxidant activity, while n-butyl alcohol extract and ethyl acetate extract had low antioxidant activity. All the results show that longan flowers have a great development potential in the fields of medicine, cosmetics, health products, functional foods and so on, which provides a scientific basis for the development and utilization of longan flowers.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240169
Abstract:
Cassava is an important food crop in tropical regions, but the yield of cassava is affected by salt stress, which endangers food security. JAZ (jasmonate ZIM-domain, JAZ) proteins, as essential components in the jasmonate signaling pathway, are involved in regulating the tolerance to salt stress in a variety of crops. In order to investigate response of JAZ proteins in cassava to salt stress, as well as the underlying regulatory mechanisms two homologous genes MeJAZ2.1 and MeJAZ2.2 were identified from cassava variety SC124 through bioinformatics. The evolutionary tree and conserved domain analysis indicated that they both contain two conserved domains, ZIM and Jas, which belong to the JAZ gene family. Further research discovered that the expression level of MeJAZ2.2 changed more significantly in response to salt stress in cassava. MeJAZ2.2-silenced cassava plants were more susceptibility to salt stress compared to the wild type, indicating that MeJAZ2.2 may positively regulate cassava resistance to salt stress. The pGADT7-MeJAZ2.2 bait vector was constructed and no self-activating activity was found by yeast two-hybrid experiment. Moreover, three candidate interacting proteins of MeJAZ2.2 were screened, including glutamine synthetase (GS), ubiquitin 3 (Ub3), and FRIGIDA-LIKE PROTEIN (FRI-L), which provides a preliminary framework for analyzing the function and molecular mechanism of JAZ proteins to salt stress in cassava.
Cassava is an important food crop in tropical regions, but the yield of cassava is affected by salt stress, which endangers food security. JAZ (jasmonate ZIM-domain, JAZ) proteins, as essential components in the jasmonate signaling pathway, are involved in regulating the tolerance to salt stress in a variety of crops. In order to investigate response of JAZ proteins in cassava to salt stress, as well as the underlying regulatory mechanisms two homologous genes MeJAZ2.1 and MeJAZ2.2 were identified from cassava variety SC124 through bioinformatics. The evolutionary tree and conserved domain analysis indicated that they both contain two conserved domains, ZIM and Jas, which belong to the JAZ gene family. Further research discovered that the expression level of MeJAZ2.2 changed more significantly in response to salt stress in cassava. MeJAZ2.2-silenced cassava plants were more susceptibility to salt stress compared to the wild type, indicating that MeJAZ2.2 may positively regulate cassava resistance to salt stress. The pGADT7-MeJAZ2.2 bait vector was constructed and no self-activating activity was found by yeast two-hybrid experiment. Moreover, three candidate interacting proteins of MeJAZ2.2 were screened, including glutamine synthetase (GS), ubiquitin 3 (Ub3), and FRIGIDA-LIKE PROTEIN (FRI-L), which provides a preliminary framework for analyzing the function and molecular mechanism of JAZ proteins to salt stress in cassava.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240149
Abstract:
The bactericidal effects of different antibiotics on Escherichia coli were analyzed by using fluorescence photoelectric microbial detection devices. The results prove that the antimicrobial analysis using fluorescence photoelectric microbial detection devices is equivalent to the K-B disk diffusion method. Compared to the traditional methods, the fluorescence photoelectric microbial detection method can be used to quickly identify microbial resistance in clinical specimens, especially of fastidious bacteria and other slow-growing strains, providing timely reference for the clinical application of antibiotics and drug resistance analysis of pathogens. The detection of the drug resistance of E. coli to 9 antibiotics showed that E. coli had the highest resistance to nalidixic acid, with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 100 μg.mL-1. E. coli had the lowest resistance to cefotaxime, with a minimal inhibitory concentration of 0.2 μg.mL-1. Combination of nalidixic acid with ciprofloxacin, cefotaxime, or chloramphenicol indicated that the combination of 0.5 MIC concentration of nalidixic acid with 0.5 MIC concentration of ciprofloxacin had the best bactericidal effect.
The bactericidal effects of different antibiotics on Escherichia coli were analyzed by using fluorescence photoelectric microbial detection devices. The results prove that the antimicrobial analysis using fluorescence photoelectric microbial detection devices is equivalent to the K-B disk diffusion method. Compared to the traditional methods, the fluorescence photoelectric microbial detection method can be used to quickly identify microbial resistance in clinical specimens, especially of fastidious bacteria and other slow-growing strains, providing timely reference for the clinical application of antibiotics and drug resistance analysis of pathogens. The detection of the drug resistance of E. coli to 9 antibiotics showed that E. coli had the highest resistance to nalidixic acid, with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 100 μg.mL-1. E. coli had the lowest resistance to cefotaxime, with a minimal inhibitory concentration of 0.2 μg.mL-1. Combination of nalidixic acid with ciprofloxacin, cefotaxime, or chloramphenicol indicated that the combination of 0.5 MIC concentration of nalidixic acid with 0.5 MIC concentration of ciprofloxacin had the best bactericidal effect.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240175
Abstract:
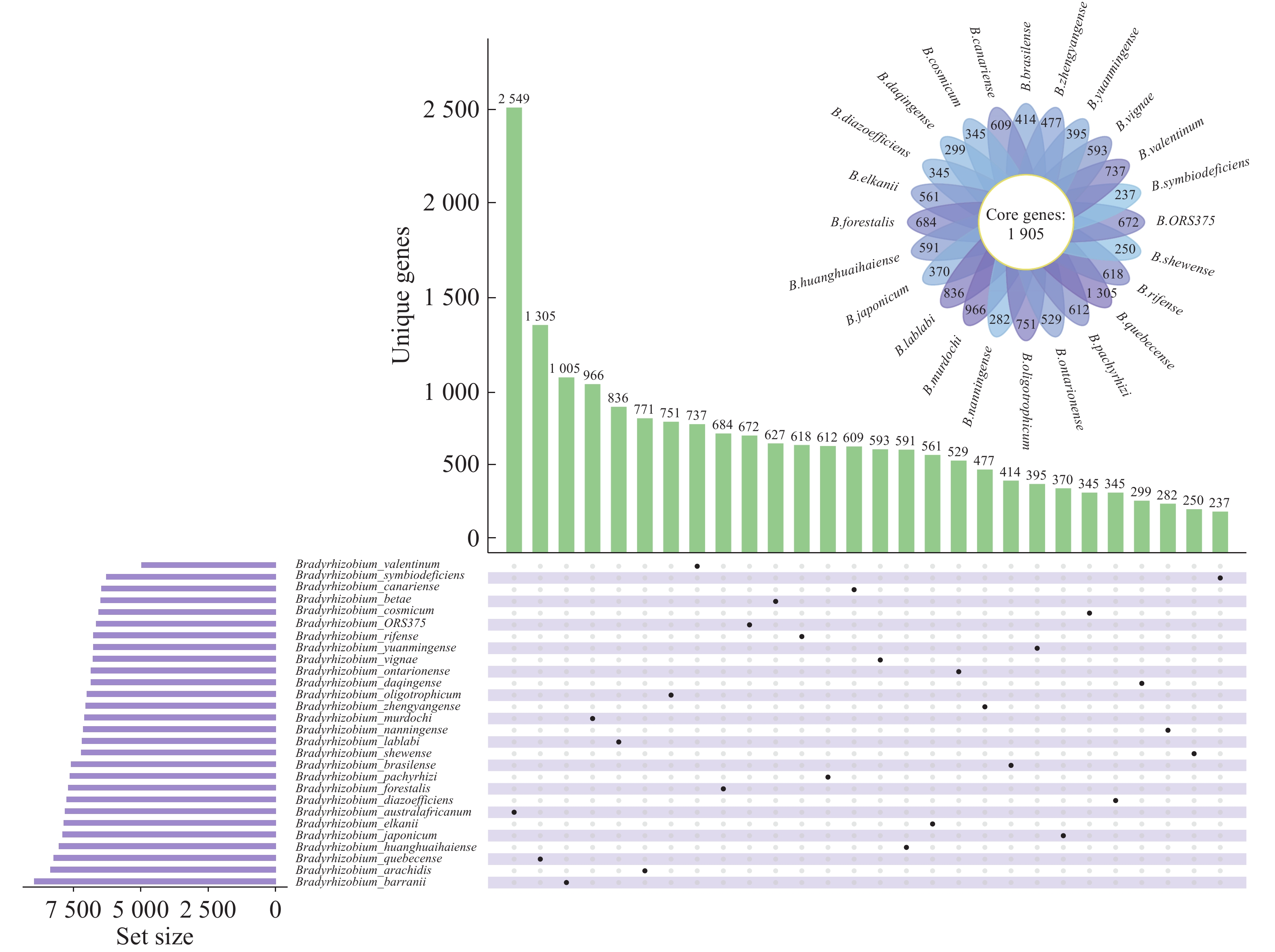
To explore the evolutionary history of the Bradyrhizobium and its plastic degradation-related gene the hydroxylase gene CYP450, and to understand the mechanisms by which the genus acquires its plastic degradation potential. In this study, 28 fully assembled strains of Bradyrhizobium were collected to investigate the evolution and dissemination of Bradyrhizobium and their hydroxylase genes CYP450 through comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses. The results revealed that, compared to the core genes, the unique and accessory genes of Bradyrhizobium exhibited an increase in functions related to plastic degradation, such as membrane transport, xenobiotic biodegradation and metabolism, lipid metabolism, and signal transduction. Bradyrhizobium has an open pan-genome, enabling it to acquire genes from other species, adapt to new environments, and evolve new functions. Analysis of the flow of the hydroxylase gene CYP450 in bacteria and archaea revealed that Bradyrhizobium likely acquired hydroxylase gene CYP450 from the Actinobacteria phylum through horizontal gene transfer, thus gaining the potential for plastic degradation.
To explore the evolutionary history of the Bradyrhizobium and its plastic degradation-related gene the hydroxylase gene CYP450, and to understand the mechanisms by which the genus acquires its plastic degradation potential. In this study, 28 fully assembled strains of Bradyrhizobium were collected to investigate the evolution and dissemination of Bradyrhizobium and their hydroxylase genes CYP450 through comparative genomic and phylogenetic analyses. The results revealed that, compared to the core genes, the unique and accessory genes of Bradyrhizobium exhibited an increase in functions related to plastic degradation, such as membrane transport, xenobiotic biodegradation and metabolism, lipid metabolism, and signal transduction. Bradyrhizobium has an open pan-genome, enabling it to acquire genes from other species, adapt to new environments, and evolve new functions. Analysis of the flow of the hydroxylase gene CYP450 in bacteria and archaea revealed that Bradyrhizobium likely acquired hydroxylase gene CYP450 from the Actinobacteria phylum through horizontal gene transfer, thus gaining the potential for plastic degradation.
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20250014
Abstract:
Cost accounting for rural waste treatment is vital for advancing the sustainability of agricultural and rural development. However, there is a severe lack of publicly accessible first-hand data on full-chain technological pathways and economic cost analyses in China’s tropical rural regions, which constrains the evaluation of integrated waste management strategies. This study, conducted in Sandao Town, Baoting Li-Miao Autonomous County, Hainan Province, applies life cycle assessment to quantify waste treatment costs across multiple technological scenarios. Findings reveal centralized municipal solid waste treatment costs of9.4132 million yuan·a−1, household kitchen waste treatment costs of 4.7274 million yuan·a−1, crop residue treatment costs of 3.3028 million yuan·a−1, and orchard pruning waste treatment costs of 0.5147 million yuan·a−1. For domestic sewage, 39% is processed via centralized systems at 3.185 million yuan·a−1, 60% undergoes decentralized village-level treatment before discharge at 8.2713 million yuan·a−1, and only 1% is reused as fertilizer at 37,700 yuan·a−1. A holistic cost-benefit analysis recommends enhancing municipal waste management efficiency through staff optimization, workflow refinement, and new energy logistics, alongside prioritizing crop residue recycling and wastewater-to-fertilizer technologies as the most viable integrated solutions. This research not only offers a scientific foundation for global economic assessments of waste treatment technologies but also delivers quantitative insights to refine ecological compensation mechanisms, promoting rural sustainability through synergies between environmental preservation and economic growth.
Cost accounting for rural waste treatment is vital for advancing the sustainability of agricultural and rural development. However, there is a severe lack of publicly accessible first-hand data on full-chain technological pathways and economic cost analyses in China’s tropical rural regions, which constrains the evaluation of integrated waste management strategies. This study, conducted in Sandao Town, Baoting Li-Miao Autonomous County, Hainan Province, applies life cycle assessment to quantify waste treatment costs across multiple technological scenarios. Findings reveal centralized municipal solid waste treatment costs of
, Available online , doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240194
Abstract:
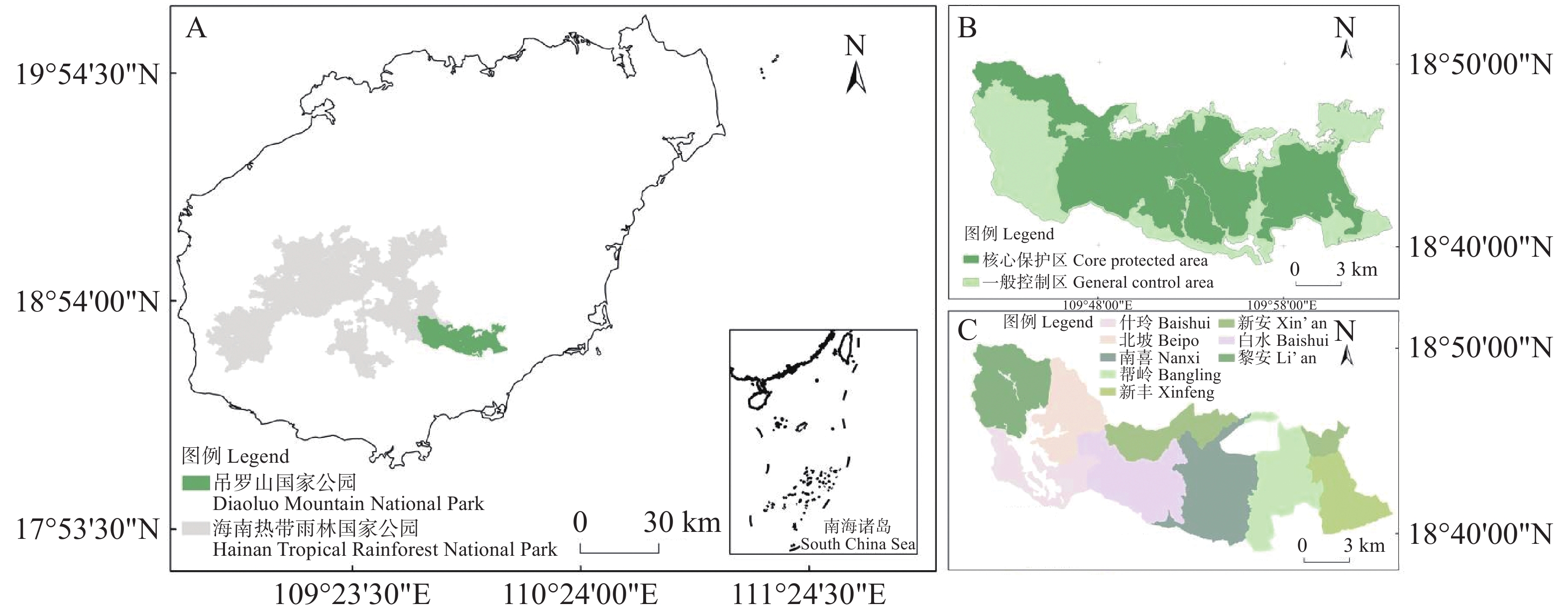
To identify Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) within national parks and allocate limited conservation resources effectively, this study takes the Diaoluo Mountain core protection area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park as a case study. A grid-based methodology was employed to conduct plant taxa surveys, and priority plant species within the study area were determined according to the Checklist of Priority Protected Species in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. KBAs were identified based on the number of priority protected species present within the sample plots. The results revealed that a total of 67 priority protected plant species were recorded in the 195 surveyed sample plots, which accounted for 65.05% of all priority protected plant species listed in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. When the number of priority protected species was no less than 4, the proportion of plots identified as KBAs was 57.44%. When the number of priority protected species was no less than 5, the proportion of KBA-identified plots was 40.00%. When the number of priority protected species was no less than 6, the proportion of KBA-identified plots was 25.64%. The Baishui、 Xin'an and Nanxi management jurisdictions have higher conservation value, contributing over 70% to the overall KBAs identification results. This study provides critical insights into plant conservation within Diaoluo Mountain National Park and offers specific guidance for biodiversity conservation actions in national parks. It also delivers vital technical support for systematic KBA identification in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, serving as a model for similar efforts in China's national park system.
To identify Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs) within national parks and allocate limited conservation resources effectively, this study takes the Diaoluo Mountain core protection area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park as a case study. A grid-based methodology was employed to conduct plant taxa surveys, and priority plant species within the study area were determined according to the Checklist of Priority Protected Species in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. KBAs were identified based on the number of priority protected species present within the sample plots. The results revealed that a total of 67 priority protected plant species were recorded in the 195 surveyed sample plots, which accounted for 65.05% of all priority protected plant species listed in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. When the number of priority protected species was no less than 4, the proportion of plots identified as KBAs was 57.44%. When the number of priority protected species was no less than 5, the proportion of KBA-identified plots was 40.00%. When the number of priority protected species was no less than 6, the proportion of KBA-identified plots was 25.64%. The Baishui、 Xin'an and Nanxi management jurisdictions have higher conservation value, contributing over 70% to the overall KBAs identification results. This study provides critical insights into plant conservation within Diaoluo Mountain National Park and offers specific guidance for biodiversity conservation actions in national parks. It also delivers vital technical support for systematic KBA identification in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, serving as a model for similar efforts in China's national park system.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML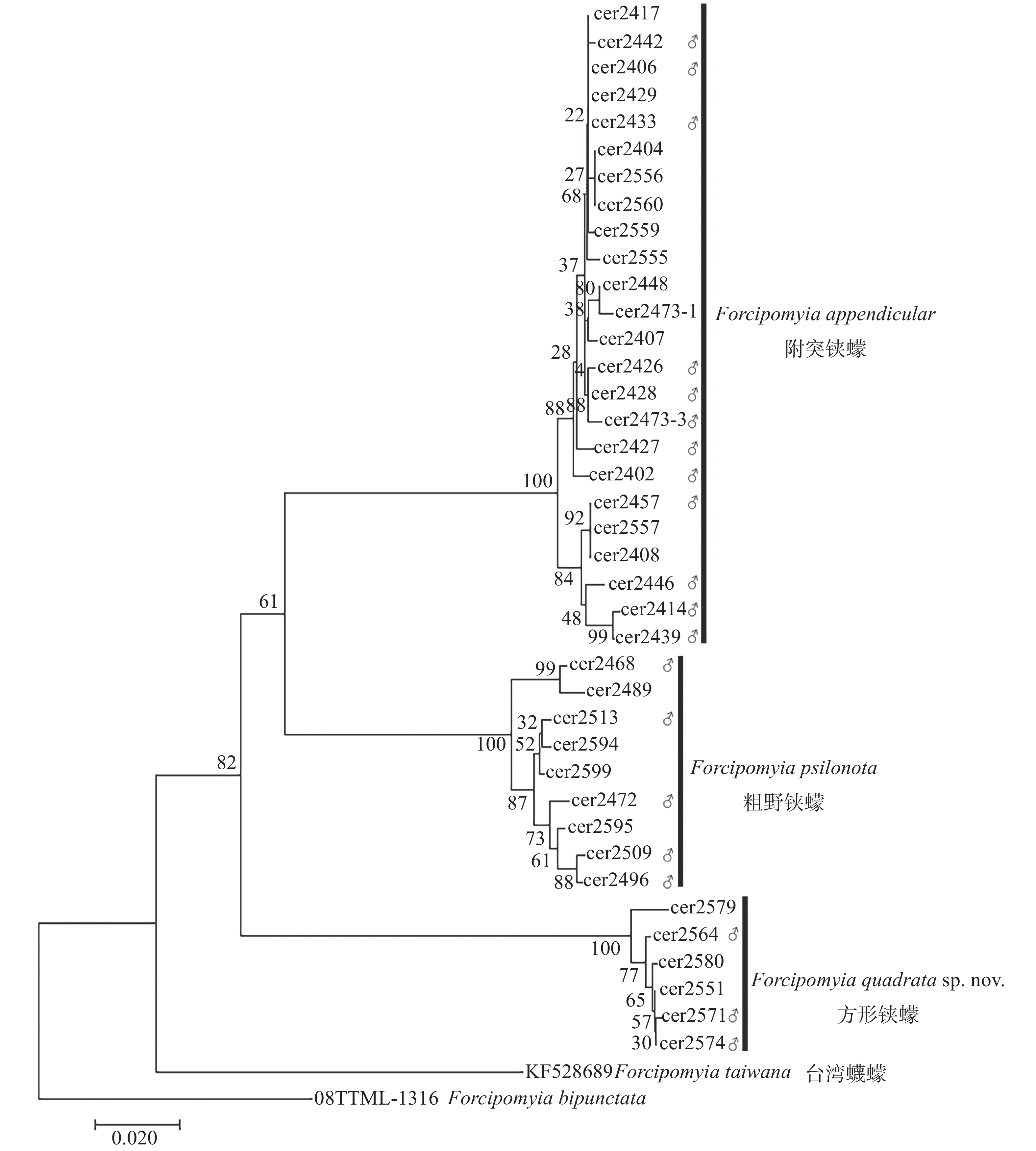









 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS