2023 Vol. 14, No. 5
2023, 14(5): 467-473.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220114
Abstract:
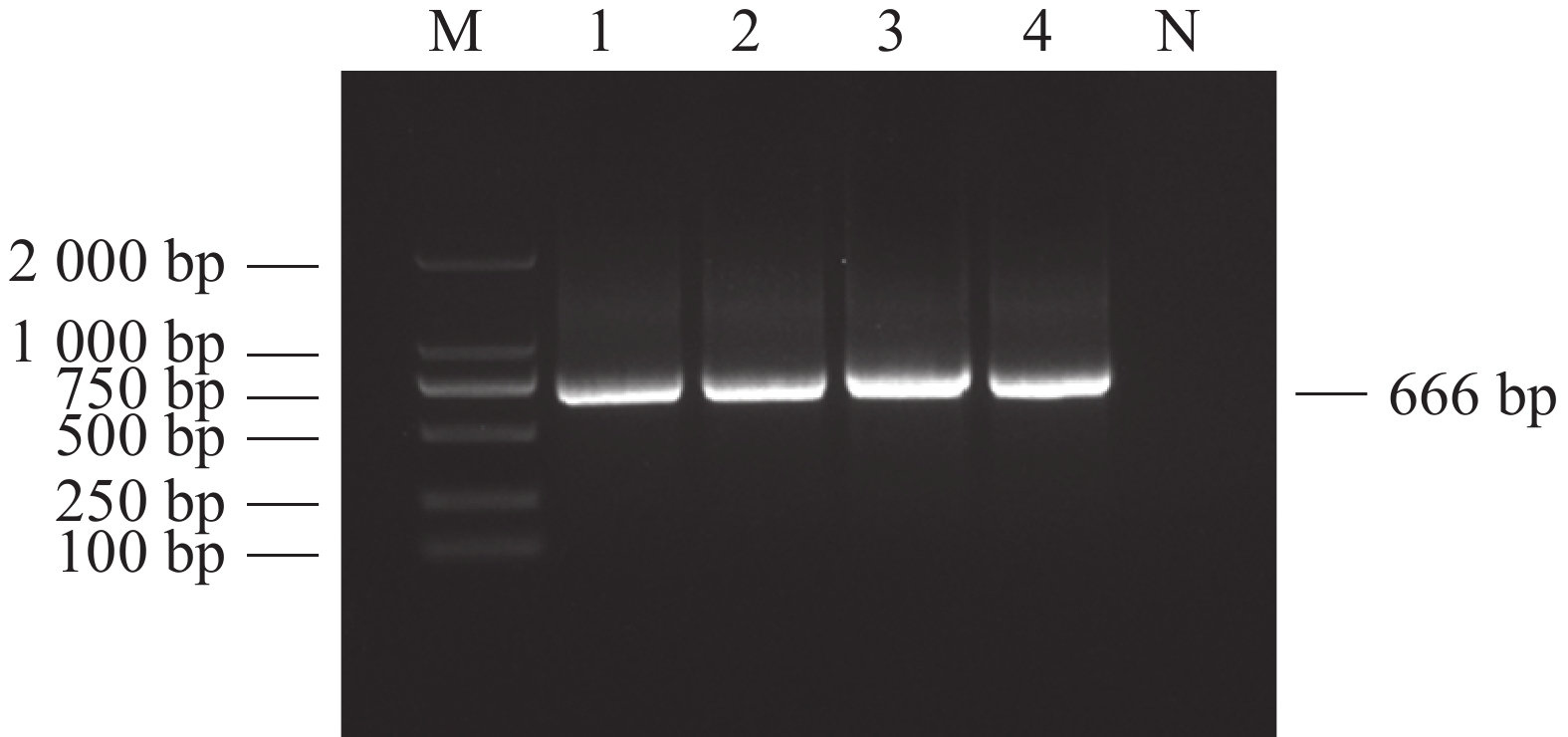
In order to understand the prevalence of Hepatozoon canis disease in Hainan in recent years, the prevention and control measures were evaluated for better control of Canine hepatozoonosis in Hainan. There were 1039 dog blood samples collected from 18 cities and counties in Hainan Province from October 2017 to May 2022, and they were detected for H. canis by PCR. Among the dog blood samples collected, 135 samples were found to be positive for H. canis, with an infection rate of 13.0%. Of the samples higher infection rates of H. canis were found in Haikou (20.7%), Sanya (20.6%), Tunchang (33.3%), and some infections of H. canis were also found in Wenchang (8.7%), Dingan (5.6%), Chengmai (6.3%), Danzhou (5.0%), Qiongzhong (15.8%), Ledong (18.8%) and Changjiang (6.7%). The positive samples from Sanya (OP699205), Ledong (OP699206), Dingan (OP699207) and Qiongzhong (OP699208) were selected to construct a phylogenetic tree based on the 18S rRNA of the H. canis. It was found that the homology of H. canis in Hainan was the closest to that of H. canis (AF176835) in India, which was 99.85%, and was also separated from that of the branches of H. felis and H. americanum. This shows that the dogs in Hainan Island has a high infection rate of H.canis. The prevention and treatment of H.canis requires regular elimination of the transmission vector Rhipicephalus sanguineus .
In order to understand the prevalence of Hepatozoon canis disease in Hainan in recent years, the prevention and control measures were evaluated for better control of Canine hepatozoonosis in Hainan. There were 1039 dog blood samples collected from 18 cities and counties in Hainan Province from October 2017 to May 2022, and they were detected for H. canis by PCR. Among the dog blood samples collected, 135 samples were found to be positive for H. canis, with an infection rate of 13.0%. Of the samples higher infection rates of H. canis were found in Haikou (20.7%), Sanya (20.6%), Tunchang (33.3%), and some infections of H. canis were also found in Wenchang (8.7%), Dingan (5.6%), Chengmai (6.3%), Danzhou (5.0%), Qiongzhong (15.8%), Ledong (18.8%) and Changjiang (6.7%). The positive samples from Sanya (OP699205), Ledong (OP699206), Dingan (OP699207) and Qiongzhong (OP699208) were selected to construct a phylogenetic tree based on the 18S rRNA of the H. canis. It was found that the homology of H. canis in Hainan was the closest to that of H. canis (AF176835) in India, which was 99.85%, and was also separated from that of the branches of H. felis and H. americanum. This shows that the dogs in Hainan Island has a high infection rate of H.canis. The prevention and treatment of H.canis requires regular elimination of the transmission vector Rhipicephalus sanguineus .
2023, 14(5): 474-480.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230010
Abstract:
In order to obtain exogenously expressed antimicrobial peptide, cathelicidin-1 expression recombinant vector was constructed using molecular cloning technique, and the secreted cathelicidin-1 was expressed in Pichia pastoris. The antimicrobial activity of the fermentation broth containing Cathelicidin-1 was evaluated. The full-length gene encoding cathelicidin-1 was synthesized by total DNA synthesis and amplified by PCR. The full-length gene was linked to the eukaryotic expression vector pGAPZαA, and the recombinant plasmid pGAPZαA-Cathelicidin-1 was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α for multiplication. The multiple plasmids were extracted, single digested, and transformed into the yeast Pichia pastoris GS115. The transformed yeast was cultured in the YPD culture medium, and the fermentation broth was collected after 72 hrs of culture and used to express the antimicrobial peptide Cathelicidin-1 in a secreted form by using Tricine-SDS-PAGE. The antimicrobial activities of the fermentation broth were evaluated by using inhibition zone of the antimicrobial peptide and the microbial growth curve. Measurements of inhibition zone and growth curve showed that the fermentation broth from the yeast expressing Cathelicidin-1 exhibited significant inhibitory activity against E. coli, but did not show any bacteriostatic effect on Staphylococcus aureus.
In order to obtain exogenously expressed antimicrobial peptide, cathelicidin-1 expression recombinant vector was constructed using molecular cloning technique, and the secreted cathelicidin-1 was expressed in Pichia pastoris. The antimicrobial activity of the fermentation broth containing Cathelicidin-1 was evaluated. The full-length gene encoding cathelicidin-1 was synthesized by total DNA synthesis and amplified by PCR. The full-length gene was linked to the eukaryotic expression vector pGAPZαA, and the recombinant plasmid pGAPZαA-Cathelicidin-1 was transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α for multiplication. The multiple plasmids were extracted, single digested, and transformed into the yeast Pichia pastoris GS115. The transformed yeast was cultured in the YPD culture medium, and the fermentation broth was collected after 72 hrs of culture and used to express the antimicrobial peptide Cathelicidin-1 in a secreted form by using Tricine-SDS-PAGE. The antimicrobial activities of the fermentation broth were evaluated by using inhibition zone of the antimicrobial peptide and the microbial growth curve. Measurements of inhibition zone and growth curve showed that the fermentation broth from the yeast expressing Cathelicidin-1 exhibited significant inhibitory activity against E. coli, but did not show any bacteriostatic effect on Staphylococcus aureus.
2023, 14(5): 481-489.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220088
Abstract:
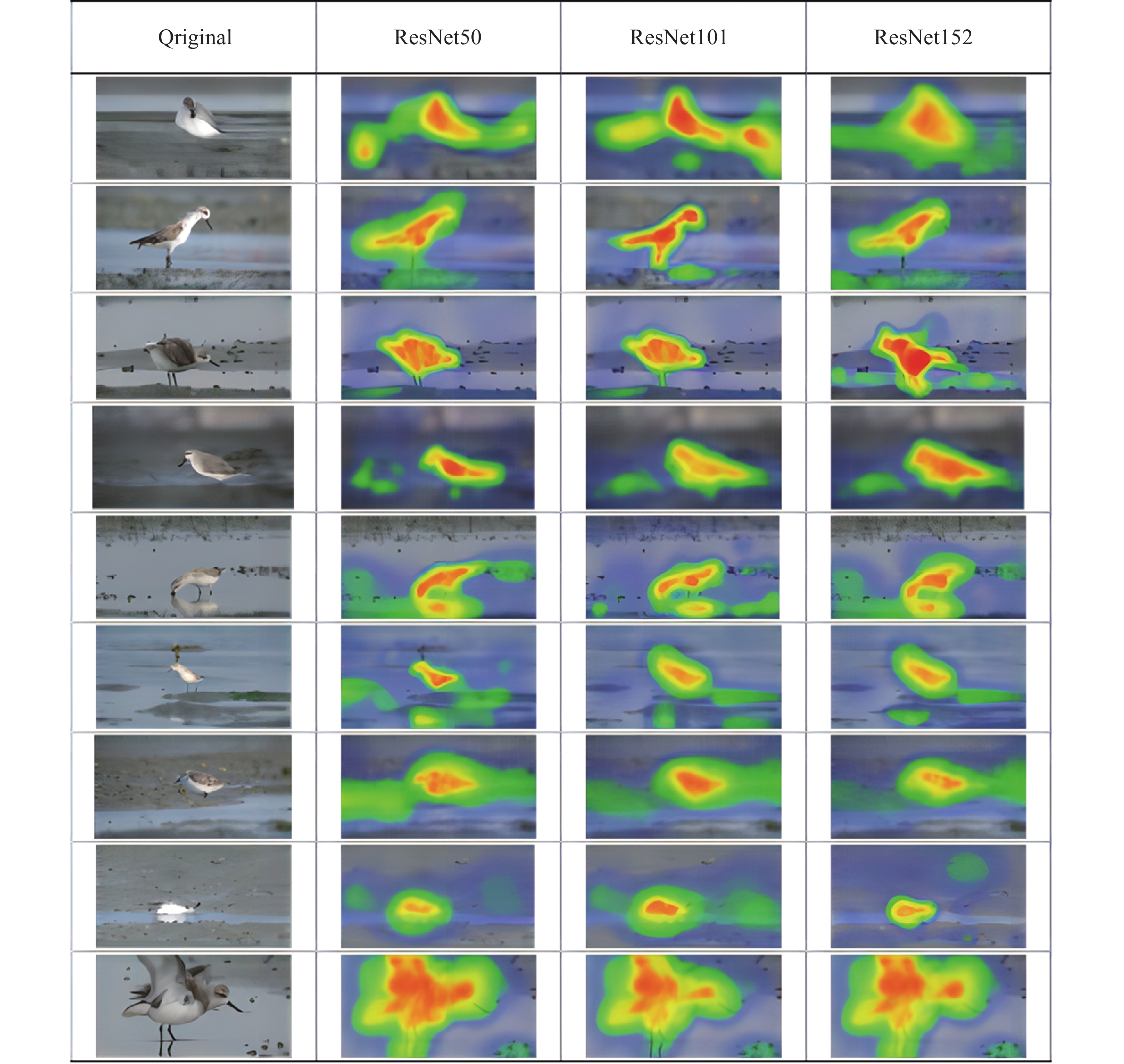
With the widespread application of image acquisition equipment and data sharing platform, the amount of bird image data has been increasing at an unprecedented speed. How to effectively deal with such a large amount of data has become a major challenge. In recent years, convolutional neural network has shown strong practicability and effectiveness in the application of automatic bird image processing. However, there has been no research on automatic recognition of movements in wild birds. In view of this, a special action image dataset of the sandpiper was established based on field images. The dataset was composed of nine action tags representing the main behavior patterns of spoon-billed sandpipers (Eurynorhynchus pygmeus). At the same time, three residual convolutional neural network models, ResNet50, ResNetT101 and ResNet152, were used to automatically recognize the movements of the spoon-billed sandpipers. The experimental results showed that the three models achieved excellent results in action recognition with their accuracy rates of the test set being 96.90% (ResNet50), 96.94%(ResNet101) and 96.90% (ResNet152), respectively. This indicates that these three models have a rapid recognition of the movements of the spoon-billed sandpiper.
With the widespread application of image acquisition equipment and data sharing platform, the amount of bird image data has been increasing at an unprecedented speed. How to effectively deal with such a large amount of data has become a major challenge. In recent years, convolutional neural network has shown strong practicability and effectiveness in the application of automatic bird image processing. However, there has been no research on automatic recognition of movements in wild birds. In view of this, a special action image dataset of the sandpiper was established based on field images. The dataset was composed of nine action tags representing the main behavior patterns of spoon-billed sandpipers (Eurynorhynchus pygmeus). At the same time, three residual convolutional neural network models, ResNet50, ResNetT101 and ResNet152, were used to automatically recognize the movements of the spoon-billed sandpipers. The experimental results showed that the three models achieved excellent results in action recognition with their accuracy rates of the test set being 96.90% (ResNet50), 96.94%(ResNet101) and 96.90% (ResNet152), respectively. This indicates that these three models have a rapid recognition of the movements of the spoon-billed sandpiper.
2023, 14(5): 490-498.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220116
Abstract:
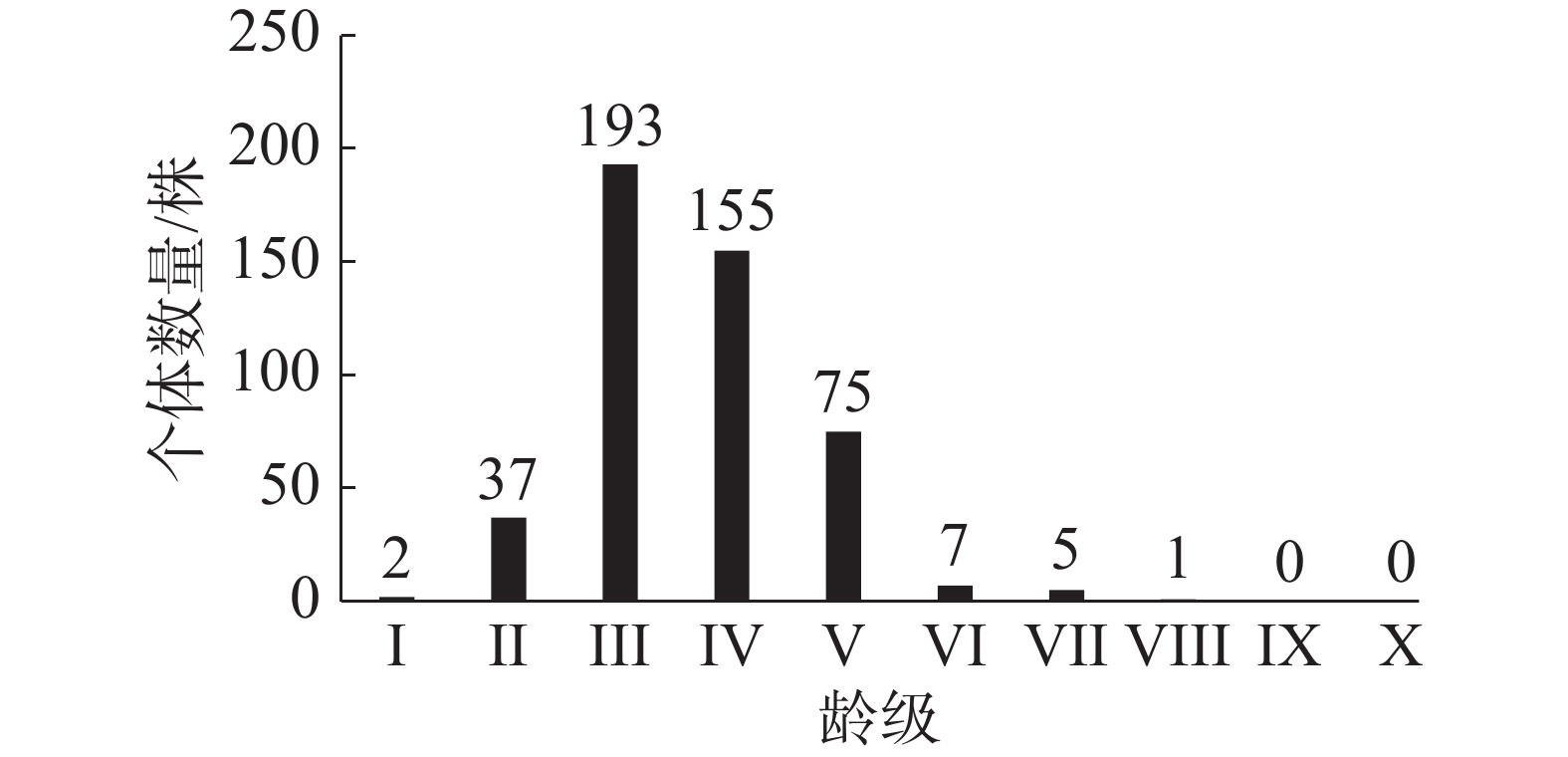
It is of great practical significance to carry out relevant research on mangrove plant population to understand the population structure and dynamics of mangroves at the present stage for improving mangrove conservation and ecological restoration. A survey of Rhizophora stylosa population in permanent sample plots covering 1 hm2 in Dongzhaigan National Mangrove Reserve, Haikou, Hainan Province was made to analyze the population structure and dynamics of R. stylosa. The analysis showed that the stem diameter structure of the R. stylosa population in these plots was of irregular pyramid type, with the total number of individuals in age class I to III accounting for 48.84% of the total number of individuals in the population, and the number of individuals in age class Ⅳ being significantly low. The population dynamic change index suggested that the R. stylosa population in this mangrove reserve is expanding, but not stable, and not significantly under external disturbance. The population had a Deevey type II survivorship curve. The static life table, mortality curve, disappearance rate curve and survivorship analysis of the R. stylosa population showed that the population dynamics in this mangrove reserve was relatively drastic at the younger stage, and relatively stable when the population developed into the older stage. The time series analysis of the R. stylosa population reveals that although there are more individuals at the lower age level in the current population, relatively few individuals will develop into the older age level after several age levels in the future, and that the future population will consist of individuals mainly at the middle and older age levels. The population of R. stylosa in Dongzhaigang National Mangrove Reserve is expanding, but is sensitive to external disturbance. The dynamic changes of the population are more intense in the lower age stage, and relatively stable in the middle and old stages. Therefore, the long-term monitoring and disaster prevention of the population should be strengthened, especially the protection and assisted restoration of the individuals at the younger stage.
It is of great practical significance to carry out relevant research on mangrove plant population to understand the population structure and dynamics of mangroves at the present stage for improving mangrove conservation and ecological restoration. A survey of Rhizophora stylosa population in permanent sample plots covering 1 hm2 in Dongzhaigan National Mangrove Reserve, Haikou, Hainan Province was made to analyze the population structure and dynamics of R. stylosa. The analysis showed that the stem diameter structure of the R. stylosa population in these plots was of irregular pyramid type, with the total number of individuals in age class I to III accounting for 48.84% of the total number of individuals in the population, and the number of individuals in age class Ⅳ being significantly low. The population dynamic change index suggested that the R. stylosa population in this mangrove reserve is expanding, but not stable, and not significantly under external disturbance. The population had a Deevey type II survivorship curve. The static life table, mortality curve, disappearance rate curve and survivorship analysis of the R. stylosa population showed that the population dynamics in this mangrove reserve was relatively drastic at the younger stage, and relatively stable when the population developed into the older stage. The time series analysis of the R. stylosa population reveals that although there are more individuals at the lower age level in the current population, relatively few individuals will develop into the older age level after several age levels in the future, and that the future population will consist of individuals mainly at the middle and older age levels. The population of R. stylosa in Dongzhaigang National Mangrove Reserve is expanding, but is sensitive to external disturbance. The dynamic changes of the population are more intense in the lower age stage, and relatively stable in the middle and old stages. Therefore, the long-term monitoring and disaster prevention of the population should be strengthened, especially the protection and assisted restoration of the individuals at the younger stage.
2023, 14(5): 499-505.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220009
Abstract:
Cassava bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis is one of the important diseases in the world, and it is also the most serious disease in the cassava plantations of China. Some strains in other countries with their whole genomes being sequenced were found to encode two candidate copper resistance gene clusters, copTAB and XmeRSA, and part of these strains were higher in resistance to copper ion. An attempt was made to clone copper resistance gene clusters of more strains from different other countries and analyze their copper resistance level. The results showed all the tested strains from China, Micronesia, Malaysia and other countries were also higher in resistance to copper ion. All the representative strains from these countries also encoded the copTAB and XmeRSA gene clusters. The two gene clusters from these countries were highly homologous, and they were not only involved in copper-resistance metabolism, but might also be related to other conservative functions such as pathogenicity.
Cassava bacterial blight caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis is one of the important diseases in the world, and it is also the most serious disease in the cassava plantations of China. Some strains in other countries with their whole genomes being sequenced were found to encode two candidate copper resistance gene clusters, copTAB and XmeRSA, and part of these strains were higher in resistance to copper ion. An attempt was made to clone copper resistance gene clusters of more strains from different other countries and analyze their copper resistance level. The results showed all the tested strains from China, Micronesia, Malaysia and other countries were also higher in resistance to copper ion. All the representative strains from these countries also encoded the copTAB and XmeRSA gene clusters. The two gene clusters from these countries were highly homologous, and they were not only involved in copper-resistance metabolism, but might also be related to other conservative functions such as pathogenicity.
2023, 14(5): 506-513.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220074
Abstract:
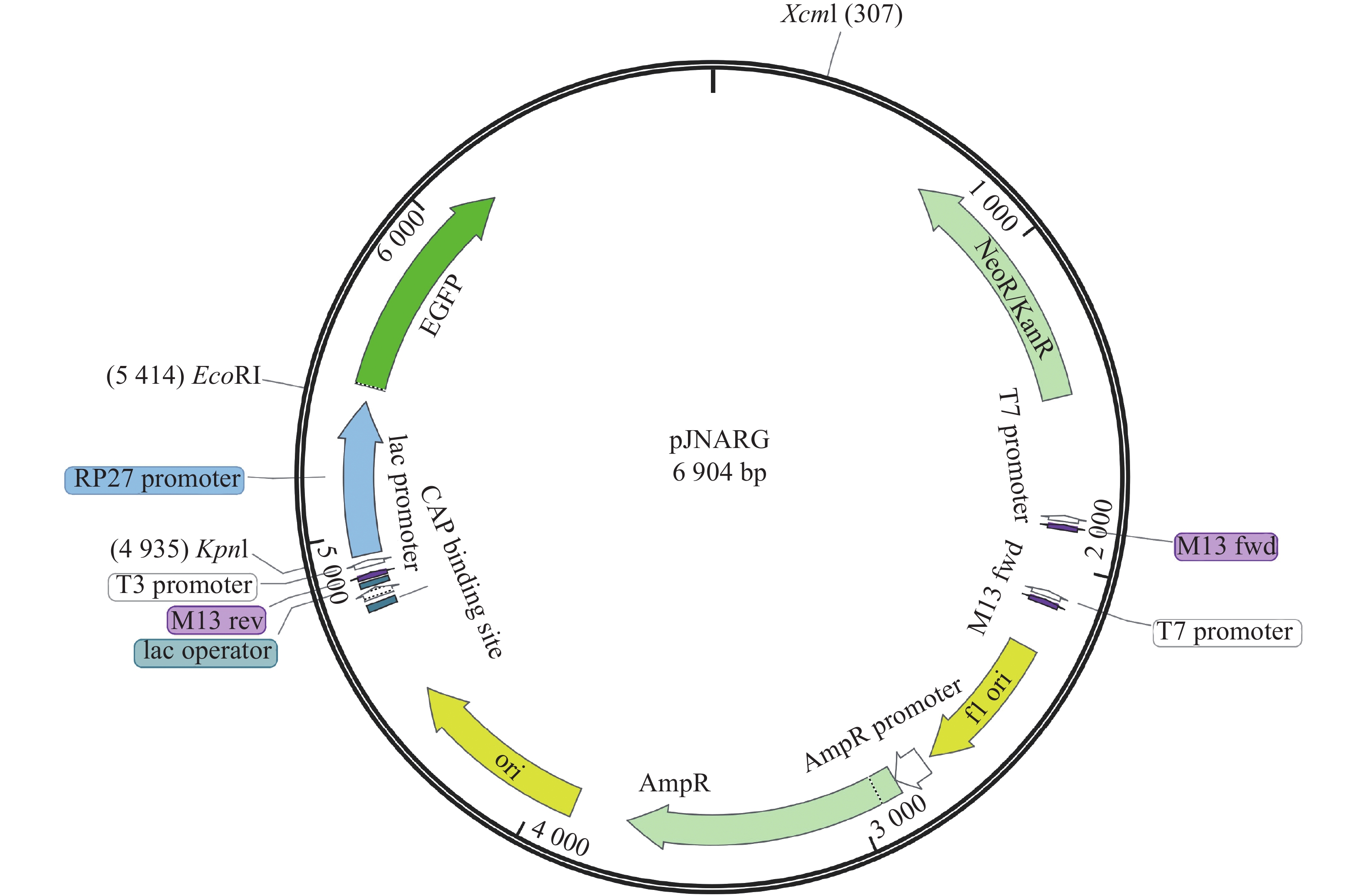
Our laboratory preliminarily identified WY172 and WY195 promoter sequences from the rubber tree powdery mildew fungus (Erysiphe quercicola), which could effectively drive GUS expression in both monocotyledonous rice and dicotyledonous tobacco. In order to investigate whether WY172 and WY195 have promoter activity in E. quercicola, the pJNARG vector was used as a backbone, linking WY172-GFP and WY195-GFP to construct recombinant expression vectors (WY172-GFP and WY195-GFP vectors). The recombinant vectors were introduced into Colletotrichum siamense infecting rubber trees by protoplast transformation method. Fluorescence microscopy showed that both WY172 and WY195 could stably drive the expression of GFP gene. And in different stages of C. siamense, WY172 and WY195 could play promoter roles to stably drive the expression of GFP. In addition, we changed the environmental conditions for the growth of anthracis and measured the GFP expression under different conditions. The results showed that the long light condition enhanced the activity of WY172 to drive GFP expression, and that the activity of WY195 was improved by the long light treatment and the low temperature treatment at 23°C. This indicates that WY172 and WY195 have stable promoter activities in C. siamense, and that their activities can be induced by changing light or temperature conditions.
Our laboratory preliminarily identified WY172 and WY195 promoter sequences from the rubber tree powdery mildew fungus (Erysiphe quercicola), which could effectively drive GUS expression in both monocotyledonous rice and dicotyledonous tobacco. In order to investigate whether WY172 and WY195 have promoter activity in E. quercicola, the pJNARG vector was used as a backbone, linking WY172-GFP and WY195-GFP to construct recombinant expression vectors (WY172-GFP and WY195-GFP vectors). The recombinant vectors were introduced into Colletotrichum siamense infecting rubber trees by protoplast transformation method. Fluorescence microscopy showed that both WY172 and WY195 could stably drive the expression of GFP gene. And in different stages of C. siamense, WY172 and WY195 could play promoter roles to stably drive the expression of GFP. In addition, we changed the environmental conditions for the growth of anthracis and measured the GFP expression under different conditions. The results showed that the long light condition enhanced the activity of WY172 to drive GFP expression, and that the activity of WY195 was improved by the long light treatment and the low temperature treatment at 23°C. This indicates that WY172 and WY195 have stable promoter activities in C. siamense, and that their activities can be induced by changing light or temperature conditions.
2023, 14(5): 514-520.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220035
Abstract:
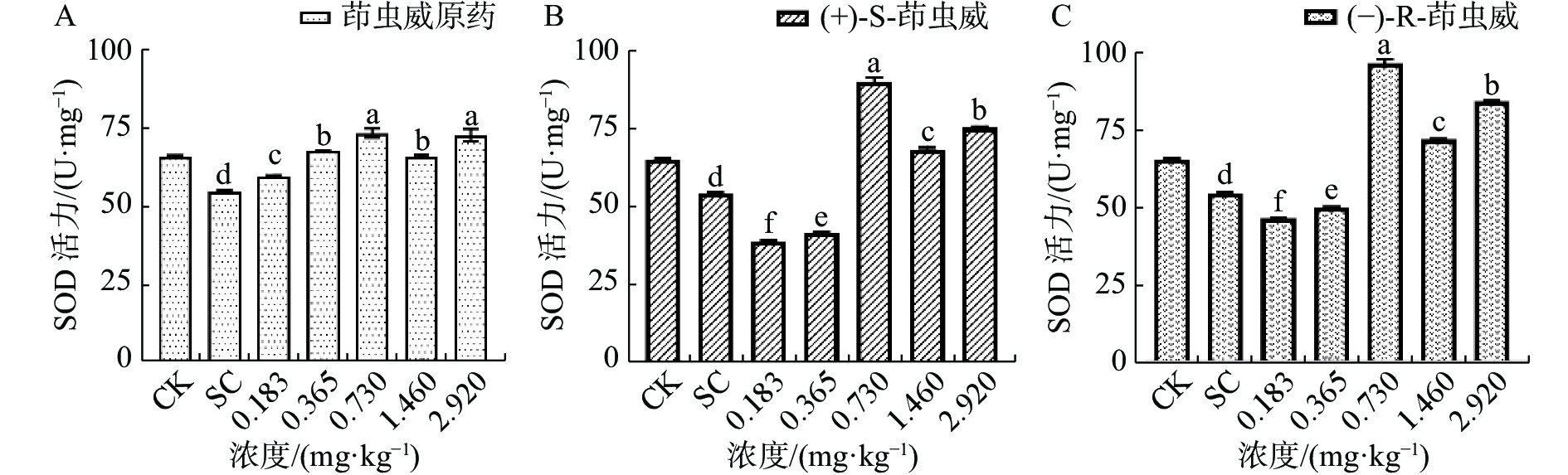
Indoxacarb belongs to oxadiazine insecticide, which blocks the insect sodium channel. Lepidopteran pests, such as Cotton Bollworm, Plutella xylostella, and Spodoptera litura, were effectively controlled by indoxacarb. The scholars have focused on the selective toxicity of indoxacarb isomers to non-target organisms. In this study the acute toxicity of indoxacarb and its isomers, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb, on the silkworm Bombyx mori was evaluated by spray method. Additionally, the toxic effects of indoxacarb and its isomers on the silkworm were evaluated by measuring the changes in the activities of antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD) in the silkworm. The results showed that the 96 h-LC50 of indoxacarb, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb to the silkworm were 0.379, 0.041 and 0.113 mg·kg−1 mulberry leaf, respectively. The (+)-S- indoxacarb and (−)-R- indoxacarb were highly toxic to the silkworm. The 96 h-LC50 of the (+)-S-indoxacarb was 2.750 folds higher than that of the (−)-R-indoxacarb, which suggested an enantioselective toxicity to the silkworms. The mixture of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb showed an antagonism effect with the co-toxicity coefficient being 12.868. The activities of SOD and CAT in the silkworm were significantly increased in the indoxacarb treatment groups, which induced oxidative stress in the silkworm. The activities of SOD significantly increased in the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb treatment groups with the concentrations of 0.730, 1.460, and 2.920 mg·kg−1 mulberry leaf. The activities of CAT significantly increased in the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb treatment groups with all the concentrations except the concentration of 0.183 mg·kg−1. The activities of POD were decreased in all the indoxacarb treatment groups. The effect of indoxacarb on SOD, CAT and POD was lower than the sum of the individual effects of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb, indicating that the mixture of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb produced antagonistic effects on inducing of oxidative stress in the silkworm. The toxic effects of indoxacarb, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb on silkworms were preliminarily evaluated, which provides reference for the application of indoxacarb in the field. This result suggests that the indoxacarb when sprayed in the field should be kept away from mulberry gardens to avoid harm to silkworms.
Indoxacarb belongs to oxadiazine insecticide, which blocks the insect sodium channel. Lepidopteran pests, such as Cotton Bollworm, Plutella xylostella, and Spodoptera litura, were effectively controlled by indoxacarb. The scholars have focused on the selective toxicity of indoxacarb isomers to non-target organisms. In this study the acute toxicity of indoxacarb and its isomers, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb, on the silkworm Bombyx mori was evaluated by spray method. Additionally, the toxic effects of indoxacarb and its isomers on the silkworm were evaluated by measuring the changes in the activities of antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and peroxidase (POD) in the silkworm. The results showed that the 96 h-LC50 of indoxacarb, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb to the silkworm were 0.379, 0.041 and 0.113 mg·kg−1 mulberry leaf, respectively. The (+)-S- indoxacarb and (−)-R- indoxacarb were highly toxic to the silkworm. The 96 h-LC50 of the (+)-S-indoxacarb was 2.750 folds higher than that of the (−)-R-indoxacarb, which suggested an enantioselective toxicity to the silkworms. The mixture of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb showed an antagonism effect with the co-toxicity coefficient being 12.868. The activities of SOD and CAT in the silkworm were significantly increased in the indoxacarb treatment groups, which induced oxidative stress in the silkworm. The activities of SOD significantly increased in the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb treatment groups with the concentrations of 0.730, 1.460, and 2.920 mg·kg−1 mulberry leaf. The activities of CAT significantly increased in the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb treatment groups with all the concentrations except the concentration of 0.183 mg·kg−1. The activities of POD were decreased in all the indoxacarb treatment groups. The effect of indoxacarb on SOD, CAT and POD was lower than the sum of the individual effects of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb, indicating that the mixture of the (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb produced antagonistic effects on inducing of oxidative stress in the silkworm. The toxic effects of indoxacarb, (+)-S-indoxacarb and (−)-R-indoxacarb on silkworms were preliminarily evaluated, which provides reference for the application of indoxacarb in the field. This result suggests that the indoxacarb when sprayed in the field should be kept away from mulberry gardens to avoid harm to silkworms.
2023, 14(5): 521-529.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230051
Abstract:
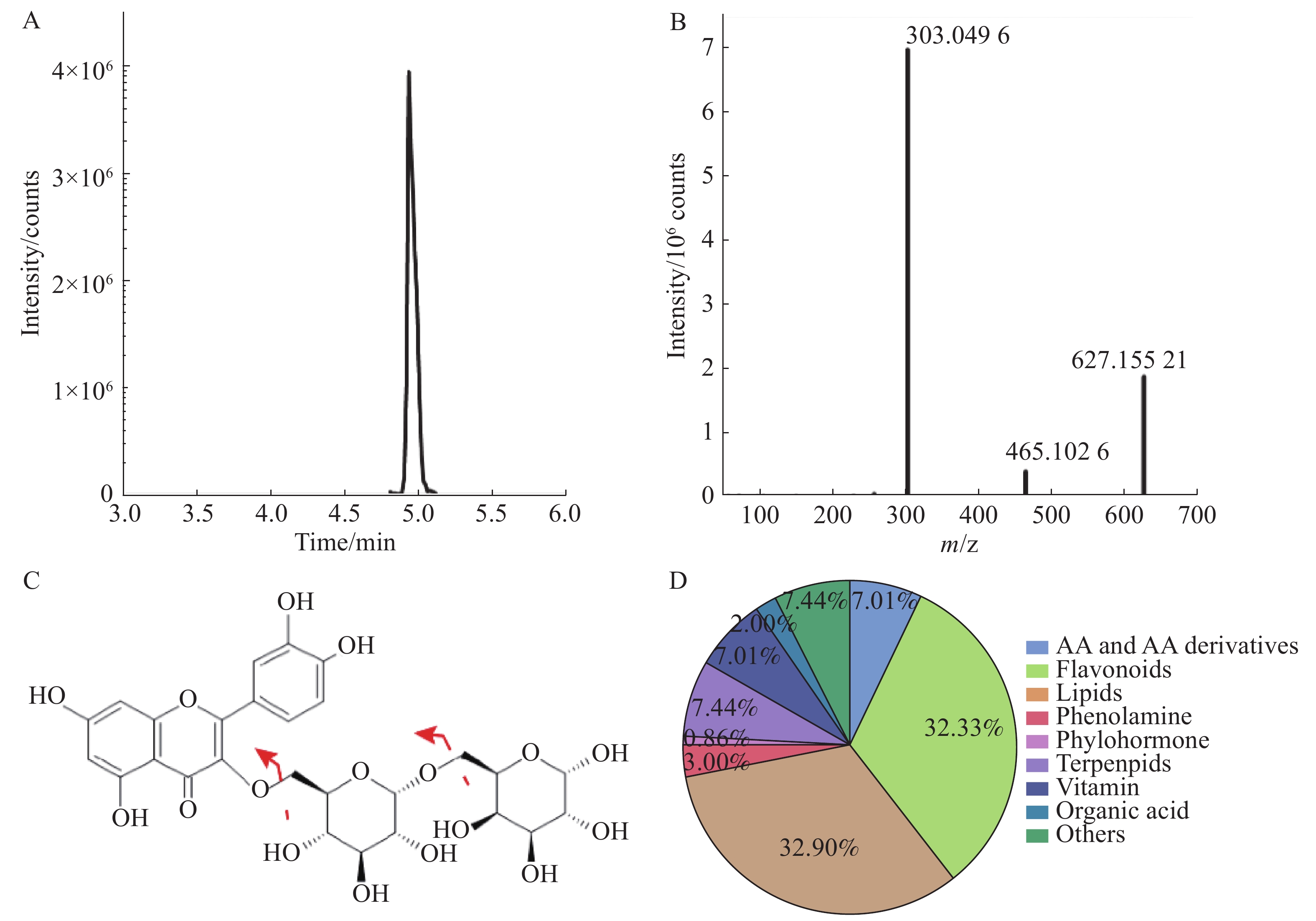
Grapes are vining plants of the genus Vitis, consisting of four major groups of Vitis species: Eurasian, American, East Asian, and hybrids selected from crosses of the three major groups. Twenty grape varieties from the Eurasian group (V. vinifera) and their hybrid populations were collected and analyzed by using a wide range of targeted metabolic assays, combined with multiple substance annotation methods to analyze the distribution and accumulation of nutrients in the grapes. A grape metabolic database was established containing 768 known metabolites, covering flavonoids, lipids, amino acids, vitamins, organic acids, terpenoids, polyphenols, phenolamines, and others. Metabolic analysis showed that there were differences in the accumulation of metabolites between the Eurasian group and the hybrids. The relative contents of total amino acids, vitamin B3 group, total fatty acids and four anthocyanins were higher in the hybrids than in the Eurasian group, while the relative contents of metabolites such as vitamin B6 and flavanols were higher in the Eurasian group.
Grapes are vining plants of the genus Vitis, consisting of four major groups of Vitis species: Eurasian, American, East Asian, and hybrids selected from crosses of the three major groups. Twenty grape varieties from the Eurasian group (V. vinifera) and their hybrid populations were collected and analyzed by using a wide range of targeted metabolic assays, combined with multiple substance annotation methods to analyze the distribution and accumulation of nutrients in the grapes. A grape metabolic database was established containing 768 known metabolites, covering flavonoids, lipids, amino acids, vitamins, organic acids, terpenoids, polyphenols, phenolamines, and others. Metabolic analysis showed that there were differences in the accumulation of metabolites between the Eurasian group and the hybrids. The relative contents of total amino acids, vitamin B3 group, total fatty acids and four anthocyanins were higher in the hybrids than in the Eurasian group, while the relative contents of metabolites such as vitamin B6 and flavanols were higher in the Eurasian group.
2023, 14(5): 530-535.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220070
Abstract:
Germplasm is the basic material for breeding and selection. It is of great significance to understand various characters of germplasm and fully exploit the utilization value of the germplasm. Jaboticaba (Plinia cauliflora) germplasm is characterized by a high diversity of plant phenotypes including long fruiting, ornamental and unique flavors. Twenty-three jaboticaba cultivars introduced for planting in Hainan were used as materials for the evaluation of 16 traits including stamen shape, tree height, stem diameter, etc. The average coefficient of variation for the phenotypic traits tested was 23.35%. The highest mean coefficient of variation was 32.52% for jaboticaba cultivar Kembuka, while the lowest mean coefficient of variation was 17.81% for cultivar Esca. The diversity index for descriptive traits of 23 jaboticaba cultivars was 0.287 - 0.855. All these results showed that the introduced jaboticaba planted in Hainan had a high genetic diversity in phenotypic traits.
Germplasm is the basic material for breeding and selection. It is of great significance to understand various characters of germplasm and fully exploit the utilization value of the germplasm. Jaboticaba (Plinia cauliflora) germplasm is characterized by a high diversity of plant phenotypes including long fruiting, ornamental and unique flavors. Twenty-three jaboticaba cultivars introduced for planting in Hainan were used as materials for the evaluation of 16 traits including stamen shape, tree height, stem diameter, etc. The average coefficient of variation for the phenotypic traits tested was 23.35%. The highest mean coefficient of variation was 32.52% for jaboticaba cultivar Kembuka, while the lowest mean coefficient of variation was 17.81% for cultivar Esca. The diversity index for descriptive traits of 23 jaboticaba cultivars was 0.287 - 0.855. All these results showed that the introduced jaboticaba planted in Hainan had a high genetic diversity in phenotypic traits.
2023, 14(5): 536-544.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220007
Abstract:
Coral reef degradation trends are becoming more and more pronounced, and restoration methods such as coral nurseries and engineered reef bodies that are currently used require laying materials such as grid plates as artificial substrates to facilitate the immobilization of transplanted corals, but there are few studies on the effects of the pore size of the skeletonized substrate on corals that are widely used. An attempt was made to established coral nurseries to explore the growth effects of four metal mesh plates of different pore sizes (A, B, C, D, aperture sizes of 1 cm×2 cm, 2.5 cm× 2.5 cm, 4.5 cm×4.5 cm, 6 cm×6 cm) on the growth of Acropora microphthalma. The results showed that the corals in groups C and D maintained 100% survival at the end of the experimental period, while the coral survival rates in groups A and B dropped to 80% and 87%. The main algae attached to the substrates in groups C and D were crustose coralline algae, and the dry weight of algae attached to the turf algae was significantly lower in groups C and D than in groups A and B. The average length of turf algae attached to the substrates was significantly lower in groups C and D than in groups A and B. The turf algae attached to the substrates of small aperture could obtain nutrients from the suspended matter in the water and lead to excessive growth, thus inhibiting coral growth and even death. Based on symbiotic algae density and photosynthetic physiology, corals in groups C and D had higher photosynthetic capacity, which ensured coral calcification growth. Therefore, the grid plate with large aperture (≥4.5 cm×4.5 cm) is more favorable for the growth of transplanted coral, and more suitable as the transplanted substrate of engineered reef.
Coral reef degradation trends are becoming more and more pronounced, and restoration methods such as coral nurseries and engineered reef bodies that are currently used require laying materials such as grid plates as artificial substrates to facilitate the immobilization of transplanted corals, but there are few studies on the effects of the pore size of the skeletonized substrate on corals that are widely used. An attempt was made to established coral nurseries to explore the growth effects of four metal mesh plates of different pore sizes (A, B, C, D, aperture sizes of 1 cm×2 cm, 2.5 cm× 2.5 cm, 4.5 cm×4.5 cm, 6 cm×6 cm) on the growth of Acropora microphthalma. The results showed that the corals in groups C and D maintained 100% survival at the end of the experimental period, while the coral survival rates in groups A and B dropped to 80% and 87%. The main algae attached to the substrates in groups C and D were crustose coralline algae, and the dry weight of algae attached to the turf algae was significantly lower in groups C and D than in groups A and B. The average length of turf algae attached to the substrates was significantly lower in groups C and D than in groups A and B. The turf algae attached to the substrates of small aperture could obtain nutrients from the suspended matter in the water and lead to excessive growth, thus inhibiting coral growth and even death. Based on symbiotic algae density and photosynthetic physiology, corals in groups C and D had higher photosynthetic capacity, which ensured coral calcification growth. Therefore, the grid plate with large aperture (≥4.5 cm×4.5 cm) is more favorable for the growth of transplanted coral, and more suitable as the transplanted substrate of engineered reef.
2023, 14(5): 545-551.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230022
Abstract:
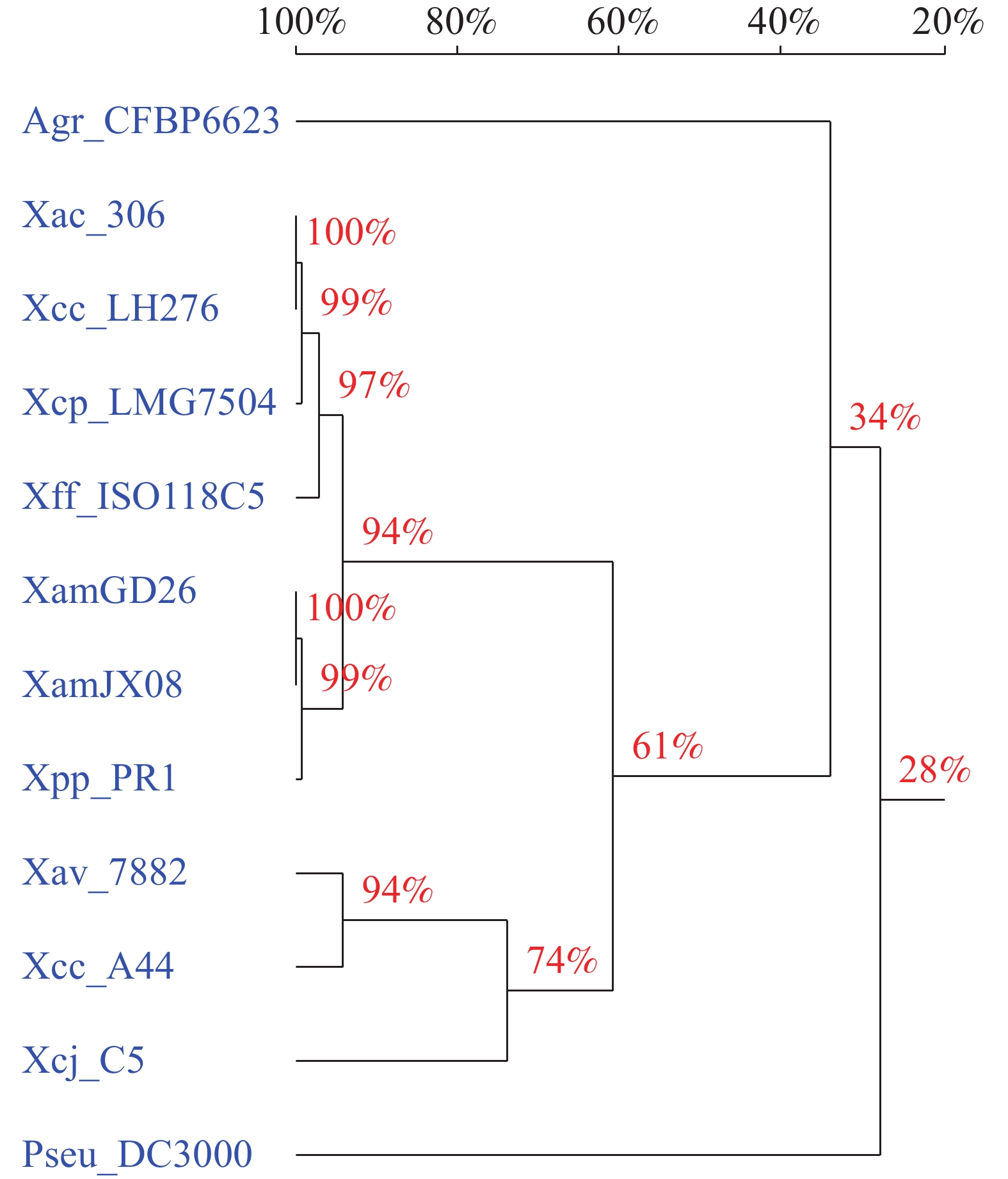
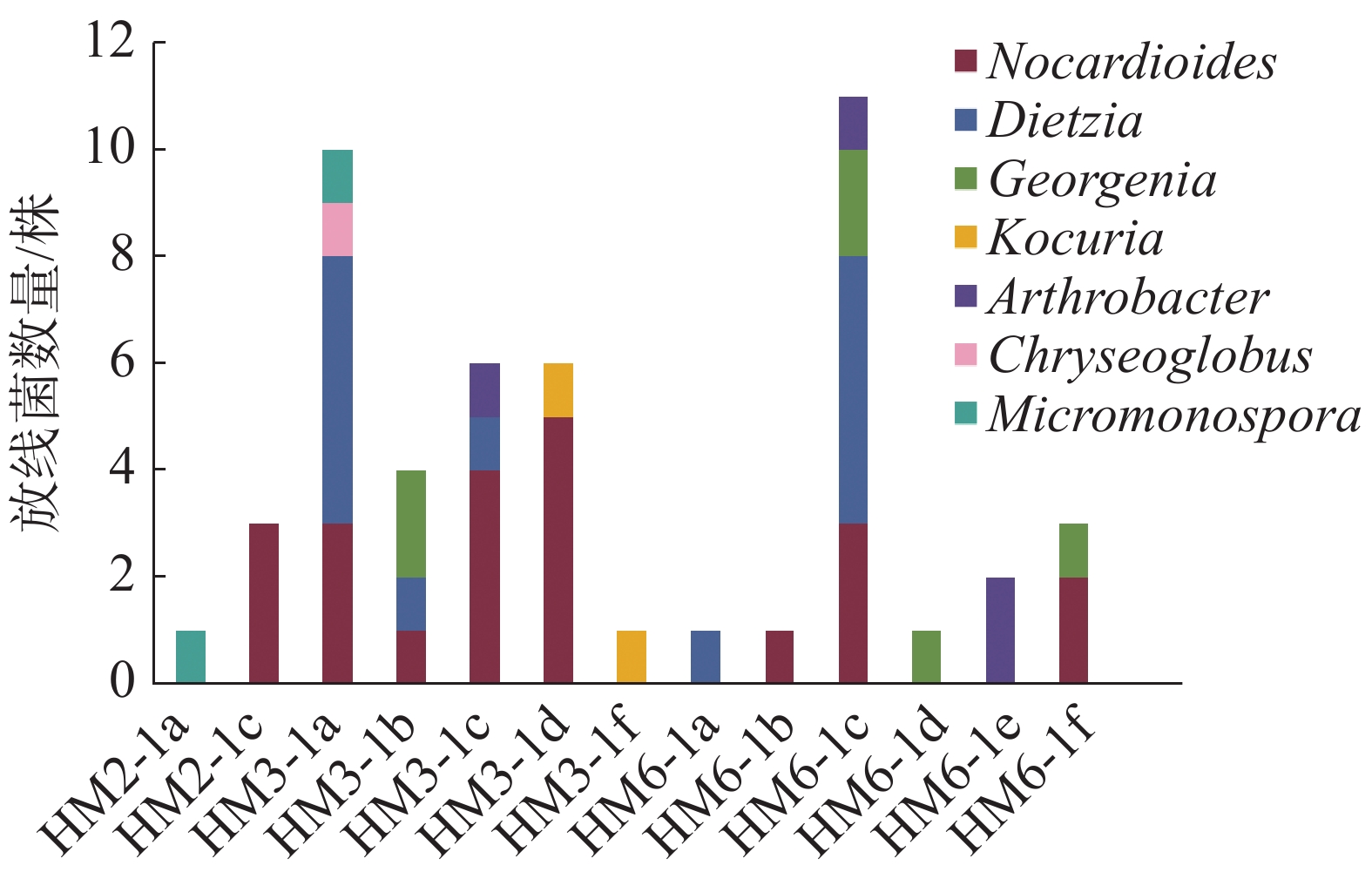
In order to explore the resources and potential bioactivity value of actinomycetes, actinomycetes were isolated from the deep-sea sediments in the cold seeps of South China Sea by serial dilution and spread plate technique and cultured. The strains of isolated actinomycetes were identified by using 16S rRNA gene sequencing, based on which a phylogenetic tree was constructed, and the diversity of actinomycetes were analyzed. The antibacterial activities of the crude extracts of the isolated actinomycetes were tested by using the K-B test for antibiotic susceptibility. The results showed that 50 isolated actinomyces belonged to 5 families and 7 genera, and that 5 strains of actinomycetes were preliminarily identified as potential new species. And the crude extracts of 7 strains showed different antibacterial activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Among the 7 strains, two strains of Micromonospora displayed the highest antibacterial activity. Micromonospora sp.LDBS3988 has the highest antibacterial activity, and Micromonospora sp.LDBS3949 has a broad-spectrum antibacterial activity.
In order to explore the resources and potential bioactivity value of actinomycetes, actinomycetes were isolated from the deep-sea sediments in the cold seeps of South China Sea by serial dilution and spread plate technique and cultured. The strains of isolated actinomycetes were identified by using 16S rRNA gene sequencing, based on which a phylogenetic tree was constructed, and the diversity of actinomycetes were analyzed. The antibacterial activities of the crude extracts of the isolated actinomycetes were tested by using the K-B test for antibiotic susceptibility. The results showed that 50 isolated actinomyces belonged to 5 families and 7 genera, and that 5 strains of actinomycetes were preliminarily identified as potential new species. And the crude extracts of 7 strains showed different antibacterial activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Among the 7 strains, two strains of Micromonospora displayed the highest antibacterial activity. Micromonospora sp.LDBS3988 has the highest antibacterial activity, and Micromonospora sp.LDBS3949 has a broad-spectrum antibacterial activity.
2023, 14(5): 552-559.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220047
Abstract:
Huguangyan Maar Lake is endowed with a special geographical environment and has a great potential for exploring thermotolerant fungal resources in special habitats. A thermotolerant fungus HS1-1 was collected from Huguangyan Maar Lake, observed morphologically and identified molecularly, and its physiological properties, enzyme production capacity and antibacterial activity were determined. The results showed that the strain of this fungus is identified as Aspergillus fumigatus. This fungus can grow at the temperatures of 15-50℃ and pH3-pH12, and has an optimum growth at the temperature of 40℃, a salt concentration of 1%-2%, and pH6-pH7. The fungus has a strong ability to utilize soluble starch, lactose and carboxymethyl cellulose, and has a certain inhibitory effect on five indicator bacteria, as determined by screening on four enzyme-producing media. This indicates that the fungus HS1-1 is high in thermotolerance and acid and base tolerance with some antibacterial activities. This study provides a theoretical basis for an in-depth understanding of the thermotolerant fungi of Huguangyan Marr Lake and their further development and utilization.
Huguangyan Maar Lake is endowed with a special geographical environment and has a great potential for exploring thermotolerant fungal resources in special habitats. A thermotolerant fungus HS1-1 was collected from Huguangyan Maar Lake, observed morphologically and identified molecularly, and its physiological properties, enzyme production capacity and antibacterial activity were determined. The results showed that the strain of this fungus is identified as Aspergillus fumigatus. This fungus can grow at the temperatures of 15-50℃ and pH3-pH12, and has an optimum growth at the temperature of 40℃, a salt concentration of 1%-2%, and pH6-pH7. The fungus has a strong ability to utilize soluble starch, lactose and carboxymethyl cellulose, and has a certain inhibitory effect on five indicator bacteria, as determined by screening on four enzyme-producing media. This indicates that the fungus HS1-1 is high in thermotolerance and acid and base tolerance with some antibacterial activities. This study provides a theoretical basis for an in-depth understanding of the thermotolerant fungi of Huguangyan Marr Lake and their further development and utilization.
2023, 14(5): 560-568.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220014
Abstract:
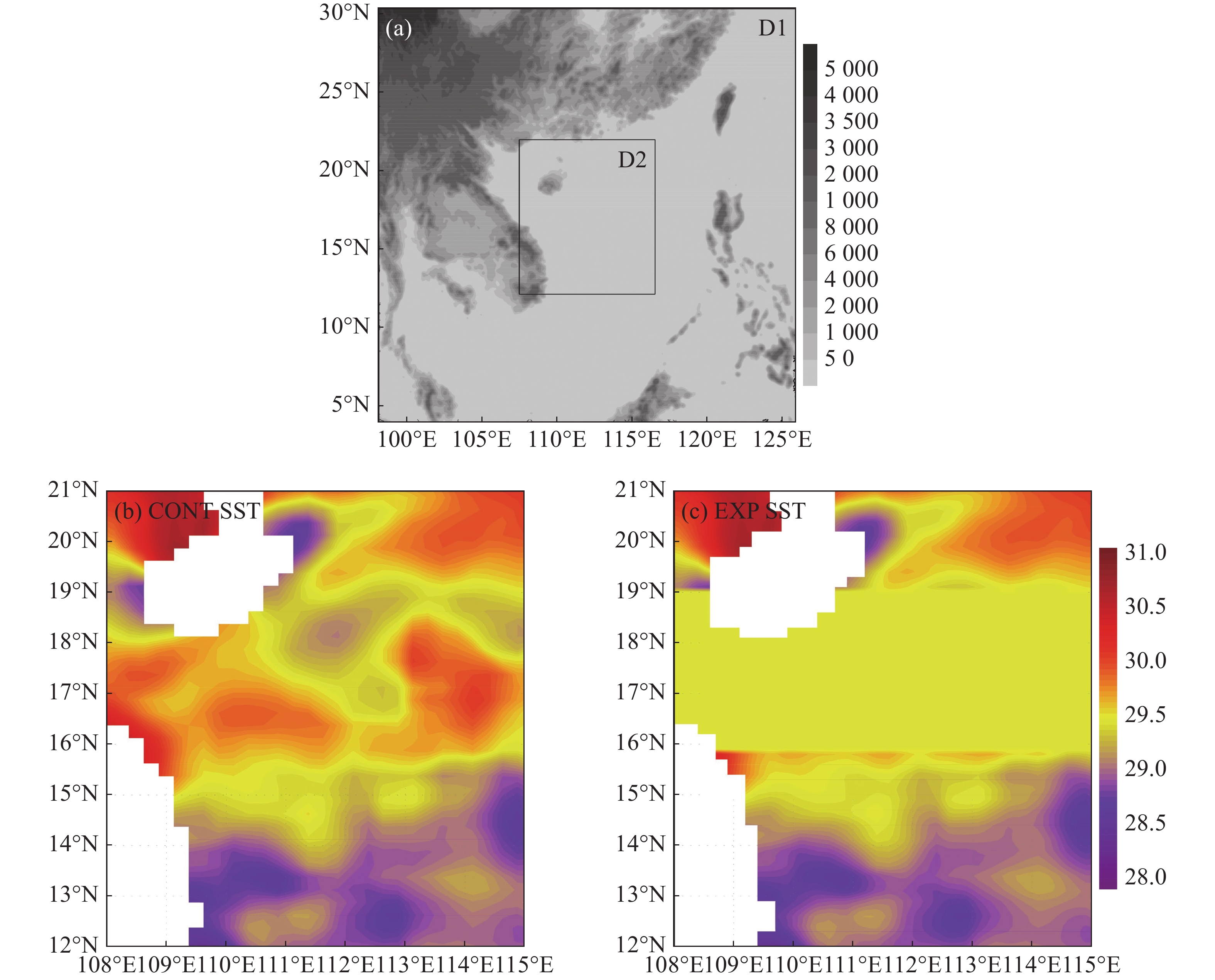
To investigate the impact of sea surface temperature gradients on severe convection, Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model is used to simulate a severe convection event occurred in the northeast of the South China Sea on 14 August 2010.The characteristics of water vapor transport, wind field and ground surface heat flux were analyzed during the development of severe convection by comparing a control run (CNTL) with a sensitivity experiment (EXP). Results show that ocean warm eddy and high SST gradient can stimulate convergence or divergence and enhance moisture transport by changing local thermal conditions, which cause release of latent heat providing energies for the evolution of severe convection. The precipitation regions correspond to the high SST center and the strong SST gradient area. The high (low) SST gradients can cause changes in sensible heat flux and latent heat flux, thus strengthening (inhibiting) precipitation.
To investigate the impact of sea surface temperature gradients on severe convection, Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) model is used to simulate a severe convection event occurred in the northeast of the South China Sea on 14 August 2010.The characteristics of water vapor transport, wind field and ground surface heat flux were analyzed during the development of severe convection by comparing a control run (CNTL) with a sensitivity experiment (EXP). Results show that ocean warm eddy and high SST gradient can stimulate convergence or divergence and enhance moisture transport by changing local thermal conditions, which cause release of latent heat providing energies for the evolution of severe convection. The precipitation regions correspond to the high SST center and the strong SST gradient area. The high (low) SST gradients can cause changes in sensible heat flux and latent heat flux, thus strengthening (inhibiting) precipitation.
2023, 14(5): 569-576.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230074
Abstract:
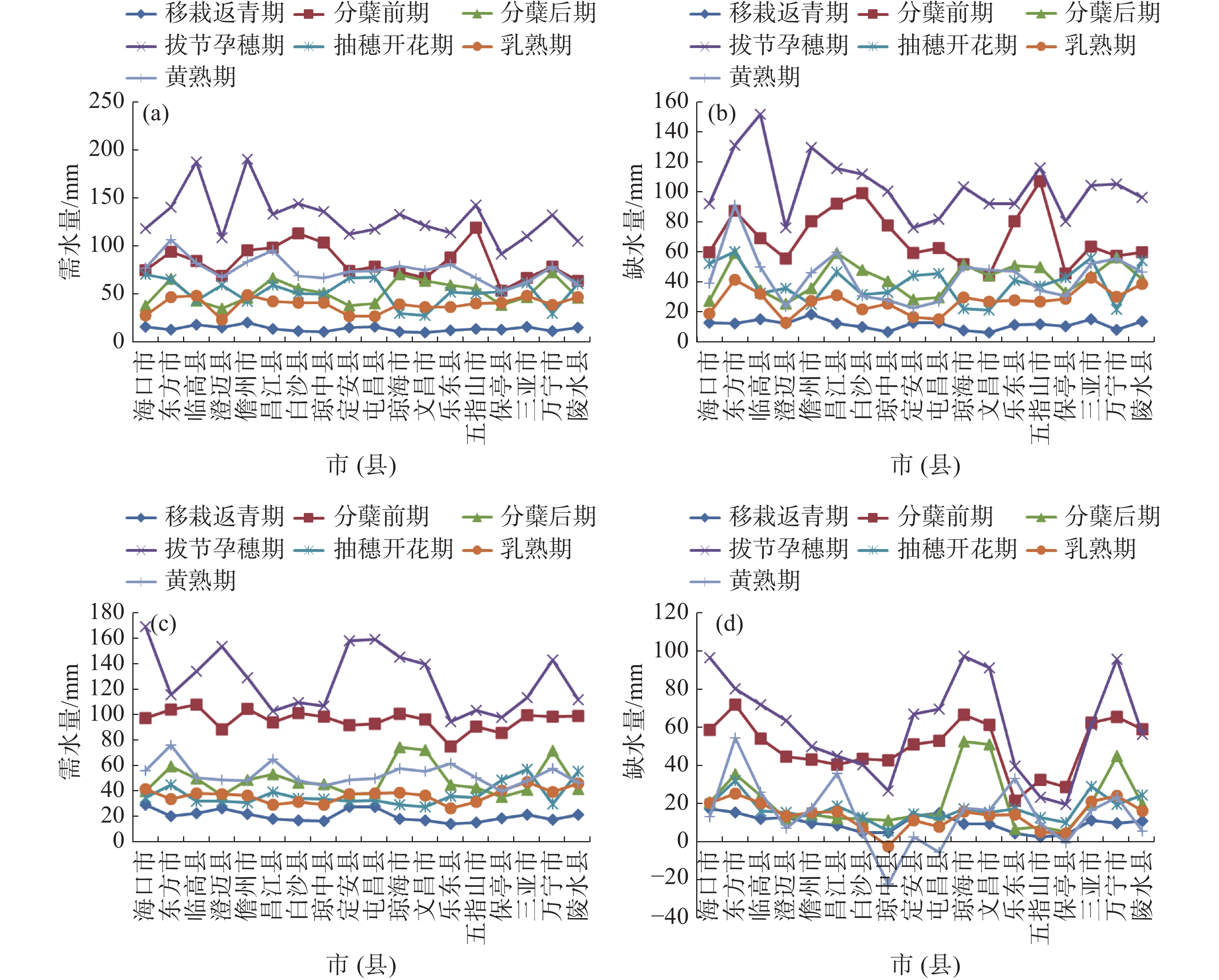
An attempt was made to grasp the spatial and temporal variation of water requirement and water deficit of rice in Hainan Island. Based on the daily meteorological data from 18 cities/counties in Hainan Island from 1971 to 2020 and the growth period data of early and late rice from 6 agro-meteorological stations in Hainan Island, the water requirement and deficit of early and late rice were calculated by using Penman-Monteith formula, crop coefficient method and the method recommended by the Soil Conservation Service of the United States Department of Agriculture, and their spatial-temporal variations were analyzed. The results showed that in the past 50 years the water requirements during the whole growth period of early and late rice in Hainan Island were 444.9 mm and 419.7 mm, respectively, while the water deficits during the whole growth period were 337.1 mm and 186.9 mm, respectively. The spatial distribution of water requirements and deficits during the whole growth period of early and late rice varied. All cities/counties were short of water during the whole growth period of early and late rice, and the water shortage was mainly distributed in the jointing-booting stage and pre-tillering stage. In recent 50 years the water requirement and water deficit during the whole growth period of early and late rice showed a decreasing trend and was mainly not significantly reduced at most cities/counties (accounting for 55.6 %~66.7%), which was generally beneficial to the rice cultivation in Hainan Island. However, the early rice was deficit of water during the whole growth period in Haikou, Dongfang, Lingao, Baisha, Qiongzhong and Dingan, and the late rice tended to increase its water deficit in Dongfang, Changjiang, Baisha, Qiongzhong, Dingan, Qionghai, Wenchang and Ledong, indicating the need to strengthen water management in paddy fields.
An attempt was made to grasp the spatial and temporal variation of water requirement and water deficit of rice in Hainan Island. Based on the daily meteorological data from 18 cities/counties in Hainan Island from 1971 to 2020 and the growth period data of early and late rice from 6 agro-meteorological stations in Hainan Island, the water requirement and deficit of early and late rice were calculated by using Penman-Monteith formula, crop coefficient method and the method recommended by the Soil Conservation Service of the United States Department of Agriculture, and their spatial-temporal variations were analyzed. The results showed that in the past 50 years the water requirements during the whole growth period of early and late rice in Hainan Island were 444.9 mm and 419.7 mm, respectively, while the water deficits during the whole growth period were 337.1 mm and 186.9 mm, respectively. The spatial distribution of water requirements and deficits during the whole growth period of early and late rice varied. All cities/counties were short of water during the whole growth period of early and late rice, and the water shortage was mainly distributed in the jointing-booting stage and pre-tillering stage. In recent 50 years the water requirement and water deficit during the whole growth period of early and late rice showed a decreasing trend and was mainly not significantly reduced at most cities/counties (accounting for 55.6 %~66.7%), which was generally beneficial to the rice cultivation in Hainan Island. However, the early rice was deficit of water during the whole growth period in Haikou, Dongfang, Lingao, Baisha, Qiongzhong and Dingan, and the late rice tended to increase its water deficit in Dongfang, Changjiang, Baisha, Qiongzhong, Dingan, Qionghai, Wenchang and Ledong, indicating the need to strengthen water management in paddy fields.
2023, 14(5): 577-584.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230071
Abstract:
Common agricultural wastes, cassava residues and sugarcane bagasse, were selected from Hainan as precursor materials to produce biochar through 650℃ pyrolysis with a single-factor experimental design, and the biochar was used to treat lateritic soil in the south of China at different rates (0, 0.1%, 0.5%, 1% and 5%) to observe the effect of the biochar on the physical properties such as bulk density, porosity, aggregates, etc, and chemical properties such as pH, cation exchange capacity (CEC), organic matter, available N, available P, available K, etc. The results showed that the biochar derived from sugarcane bagasse and cassava residues was higher in C content, much higher than in other elements, and was also higher in C/H and C/O ratios, which represent aromaticity and polarity. The biochar treatment resulted in significant improvement in the soil physical properties as compared with the control. Specifically, the bulk density of the lateritic soil significantly decreased, while the porosity and the content of macroaggregates (>0.25 mm) increased significantly. For the chemical properties of the lateritic soil, the pH, available N, available P, available K, organic matter, and CEC also increased significantly in the biochar treatment. Principal component analysis showed that the biochar derived from sugarcane bagasse had higher ameliorative effect on the lateritic soil than the biochar derived from cassava residues.
Common agricultural wastes, cassava residues and sugarcane bagasse, were selected from Hainan as precursor materials to produce biochar through 650℃ pyrolysis with a single-factor experimental design, and the biochar was used to treat lateritic soil in the south of China at different rates (0, 0.1%, 0.5%, 1% and 5%) to observe the effect of the biochar on the physical properties such as bulk density, porosity, aggregates, etc, and chemical properties such as pH, cation exchange capacity (CEC), organic matter, available N, available P, available K, etc. The results showed that the biochar derived from sugarcane bagasse and cassava residues was higher in C content, much higher than in other elements, and was also higher in C/H and C/O ratios, which represent aromaticity and polarity. The biochar treatment resulted in significant improvement in the soil physical properties as compared with the control. Specifically, the bulk density of the lateritic soil significantly decreased, while the porosity and the content of macroaggregates (>0.25 mm) increased significantly. For the chemical properties of the lateritic soil, the pH, available N, available P, available K, organic matter, and CEC also increased significantly in the biochar treatment. Principal component analysis showed that the biochar derived from sugarcane bagasse had higher ameliorative effect on the lateritic soil than the biochar derived from cassava residues.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 623KB
PDF 623KB









 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS