2023 Vol. 14, No. 4
2023, 14(4): 347-356.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.001
Abstract:
To explore the resources and diversity of halophytes in the coastal area of Hainan Island, a general survey of the distribution of halophytes was conducted by using plot sampling, and the species and diversity of the halophytes were analyzed. The results showed that a total of 125 species halophytes belonging to 92 genera and 50 families were recorded, including 123 species in 91 genera and 49 families of angiosperms, and 2 species in 1 genus and 1 family of pteridophytes. There were fewer families with multiple species, more families with single species, and most families with 2−9 species accounting for 52% of the total number of families. The number of genera with single species was the largest, accounting for 78.26% of the total species. In terms of life form, the halophytes in Hainan Island included 23 species in 17 genera and 14 families of trees, 32 species in 29 genera and 20 families of shrubs and small trees, 63 species in 46 genera and 22 families of herbs, and 7 species in 7 genera and 4 families of vines. The halophytes are divided into 6 and 11 areal types of species and genera, respectively, with their tropical distribution being dominant. The salt-secreting plants were richest in the halophytes with 63 species according to the salt regulation system of halophyte types. Wenchang city was relatively rich in species, with a high diversity index but uneven distribution. There were many species of herbs in cities and counties. The halophytes have various uses in Hainan Island. It is concluded that the halophytes in the coastal area of Hainan Island are rich in species and high in diversity.
To explore the resources and diversity of halophytes in the coastal area of Hainan Island, a general survey of the distribution of halophytes was conducted by using plot sampling, and the species and diversity of the halophytes were analyzed. The results showed that a total of 125 species halophytes belonging to 92 genera and 50 families were recorded, including 123 species in 91 genera and 49 families of angiosperms, and 2 species in 1 genus and 1 family of pteridophytes. There were fewer families with multiple species, more families with single species, and most families with 2−9 species accounting for 52% of the total number of families. The number of genera with single species was the largest, accounting for 78.26% of the total species. In terms of life form, the halophytes in Hainan Island included 23 species in 17 genera and 14 families of trees, 32 species in 29 genera and 20 families of shrubs and small trees, 63 species in 46 genera and 22 families of herbs, and 7 species in 7 genera and 4 families of vines. The halophytes are divided into 6 and 11 areal types of species and genera, respectively, with their tropical distribution being dominant. The salt-secreting plants were richest in the halophytes with 63 species according to the salt regulation system of halophyte types. Wenchang city was relatively rich in species, with a high diversity index but uneven distribution. There were many species of herbs in cities and counties. The halophytes have various uses in Hainan Island. It is concluded that the halophytes in the coastal area of Hainan Island are rich in species and high in diversity.
2023, 14(4): 357-363.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.002
Abstract:
Oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) is an important tropical palm with high oil production. Fatty acyl-ACP thioesterase (FAT) is the key enzyme for hydrolysis of acyl and ACP and termination of carbon chain extension. The oil palm FATA family mainly acts on eighteen-carbon chain fatty acids (18: X-ACP), but the specific hydrolysis substrates and preferences are unknown. In this study, the full-length sequence of the EgFATA gene was first cloned from oil palm fruit. Bioinformatics analysis indicated that the EgFATA coding region consists of 1155 bases and can encode 385 amino acids with a molecular weight of 91.89 kDa, and is most closely related to the alga PdFATA. A viral silencing vector for EgFATA was constructed and then infected the embryoids of oil palm, and RT-qPCR results showed that the expression of EgFATA was down regulated by 85%-90%. At the same time, fatty acid GC analysis of the silenced embryoids showed that the contents of stearic acid (C18:0), oleic acid (C18:1) and linoleic acid (C18:2) were significantly reduced. The aforesaid results indicated that EgFATA had catalytic effect on the hydrolysis of C18:0-ACP, C18:1-ACP and C18:2-ACP in the oil palm embryoids, with the highest catalytic activity observed in the hydrolysis of C18:1-ACP. This study initially explored the biological functions of EgFATA genes in oil palm, providing a theoretical basis for further exploration of the molecular mechanisms of EgFATA in regulation of lipid metabolism.
Oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) is an important tropical palm with high oil production. Fatty acyl-ACP thioesterase (FAT) is the key enzyme for hydrolysis of acyl and ACP and termination of carbon chain extension. The oil palm FATA family mainly acts on eighteen-carbon chain fatty acids (18: X-ACP), but the specific hydrolysis substrates and preferences are unknown. In this study, the full-length sequence of the EgFATA gene was first cloned from oil palm fruit. Bioinformatics analysis indicated that the EgFATA coding region consists of 1155 bases and can encode 385 amino acids with a molecular weight of 91.89 kDa, and is most closely related to the alga PdFATA. A viral silencing vector for EgFATA was constructed and then infected the embryoids of oil palm, and RT-qPCR results showed that the expression of EgFATA was down regulated by 85%-90%. At the same time, fatty acid GC analysis of the silenced embryoids showed that the contents of stearic acid (C18:0), oleic acid (C18:1) and linoleic acid (C18:2) were significantly reduced. The aforesaid results indicated that EgFATA had catalytic effect on the hydrolysis of C18:0-ACP, C18:1-ACP and C18:2-ACP in the oil palm embryoids, with the highest catalytic activity observed in the hydrolysis of C18:1-ACP. This study initially explored the biological functions of EgFATA genes in oil palm, providing a theoretical basis for further exploration of the molecular mechanisms of EgFATA in regulation of lipid metabolism.
2023, 14(4): 364-370.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.003
Abstract:
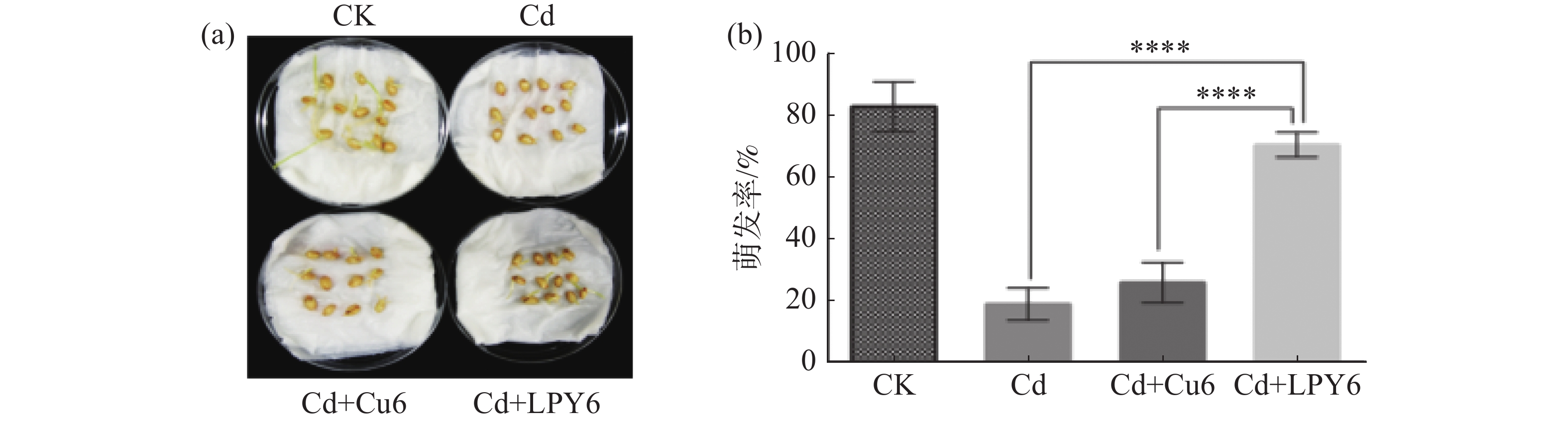
Soil cadmium pollution has attracted more attention in China, and calls for safe and effective remediation. Previously, we obtained a high cadmium-resistant strain Enterobacter cloacae LPY6 by domesticating E. cloacae Cu6. The strain LPY6 was used to treat seeds and plants of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in seed germination and pot experiments to analyze its potential and mechanism in alleviating the toxicity of cadmium to wheat growth. The seed germination and pot experiments found that LPY6 could reduce the toxic effects of cadmium on wheat seed germination and seedling growth, and decrease the cadmium levels in plants. In addition, LPY6 can also reduce the free cadmium contents in liquid media and in soils, suggesting LPY6 can adsorb or uptake cadmium from the soils and reduce the adsorption of available cadmium by plants. This indicates that LPY6 may be a potential strain for bioremediation of cadmium pollution.
Soil cadmium pollution has attracted more attention in China, and calls for safe and effective remediation. Previously, we obtained a high cadmium-resistant strain Enterobacter cloacae LPY6 by domesticating E. cloacae Cu6. The strain LPY6 was used to treat seeds and plants of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in seed germination and pot experiments to analyze its potential and mechanism in alleviating the toxicity of cadmium to wheat growth. The seed germination and pot experiments found that LPY6 could reduce the toxic effects of cadmium on wheat seed germination and seedling growth, and decrease the cadmium levels in plants. In addition, LPY6 can also reduce the free cadmium contents in liquid media and in soils, suggesting LPY6 can adsorb or uptake cadmium from the soils and reduce the adsorption of available cadmium by plants. This indicates that LPY6 may be a potential strain for bioremediation of cadmium pollution.
2023, 14(4): 371-378.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.004
Abstract:
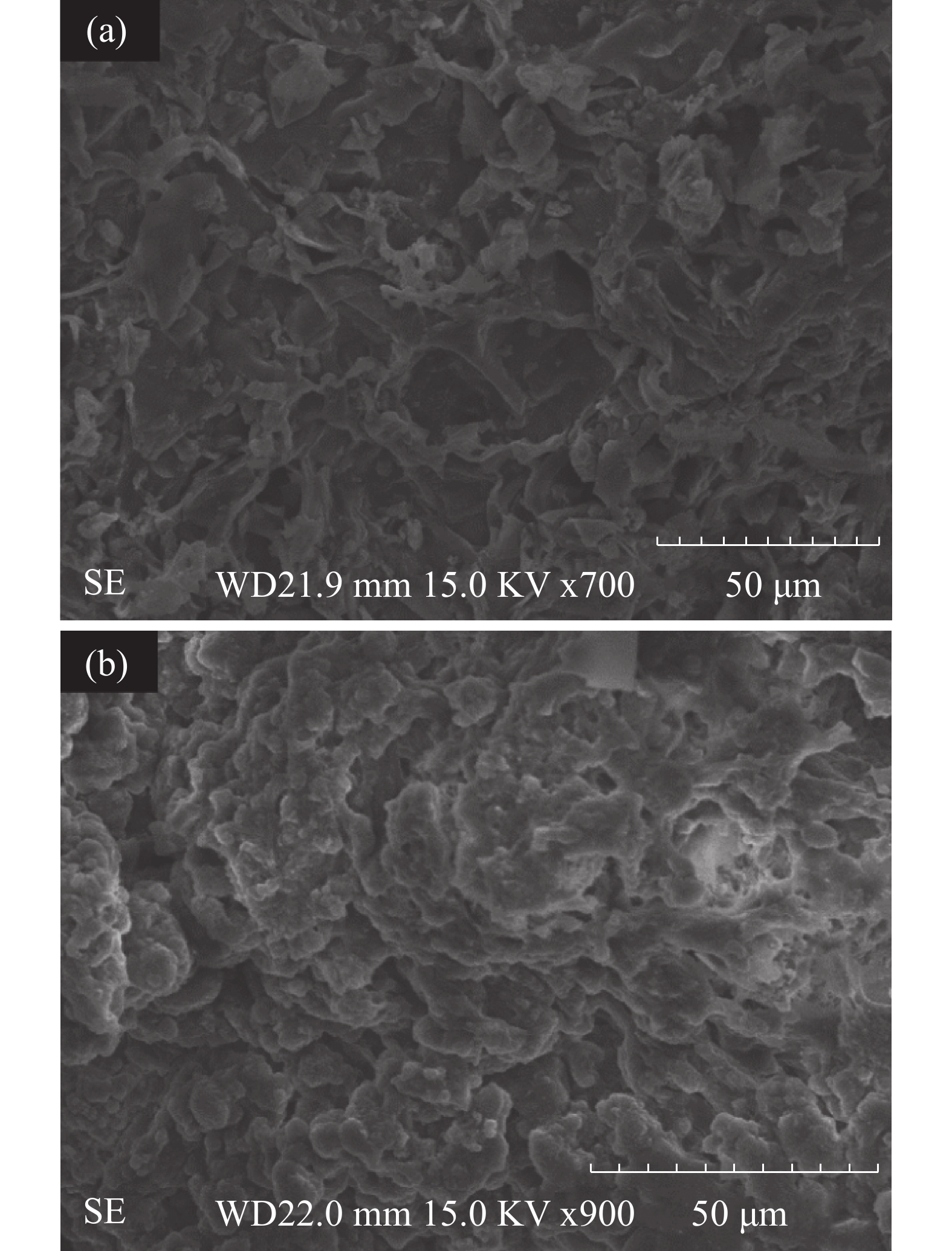
Activated carbon (AC) was prepared from sludge and betel nut, and then loaded with FeCl3 to prepare FeCl3-activated carbon (FAC). The physical and chemical properties of the prepared activated carbon before and after modification were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, specific surface area, FTIR infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results showed that the Fe3+ was successfully absorbed onto the surface of the activated carbons. Compared with AC, FAC increased to some extent its porous structure and surface area, and its functional groups changed significantly. FAC had a good adsorption capacity for methylene blue when pH value of the water was between 4 and 10. The adsorption isotherms of the two activated carbons fitted the Langmuir model, and the maximum adsorption capacities of FAC and AC were 341.30 and 133.33 mg·g−1, respectively. Moreover, the adsorption kinetic of the two activated carbons conformed to the second-order kinetic model. Thermodynamic calculation showed that AC and FAC are endothermic and spontaneous in adsorption process of dyes (methylene blue) in the water. Thus, FAC can be used as a biosorbent to remove dyes from contaminated wastewater.
Activated carbon (AC) was prepared from sludge and betel nut, and then loaded with FeCl3 to prepare FeCl3-activated carbon (FAC). The physical and chemical properties of the prepared activated carbon before and after modification were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, specific surface area, FTIR infrared spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results showed that the Fe3+ was successfully absorbed onto the surface of the activated carbons. Compared with AC, FAC increased to some extent its porous structure and surface area, and its functional groups changed significantly. FAC had a good adsorption capacity for methylene blue when pH value of the water was between 4 and 10. The adsorption isotherms of the two activated carbons fitted the Langmuir model, and the maximum adsorption capacities of FAC and AC were 341.30 and 133.33 mg·g−1, respectively. Moreover, the adsorption kinetic of the two activated carbons conformed to the second-order kinetic model. Thermodynamic calculation showed that AC and FAC are endothermic and spontaneous in adsorption process of dyes (methylene blue) in the water. Thus, FAC can be used as a biosorbent to remove dyes from contaminated wastewater.
2023, 14(4): 379-379.
Abstract:
2023, 14(4): 380-388.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.005
Abstract:
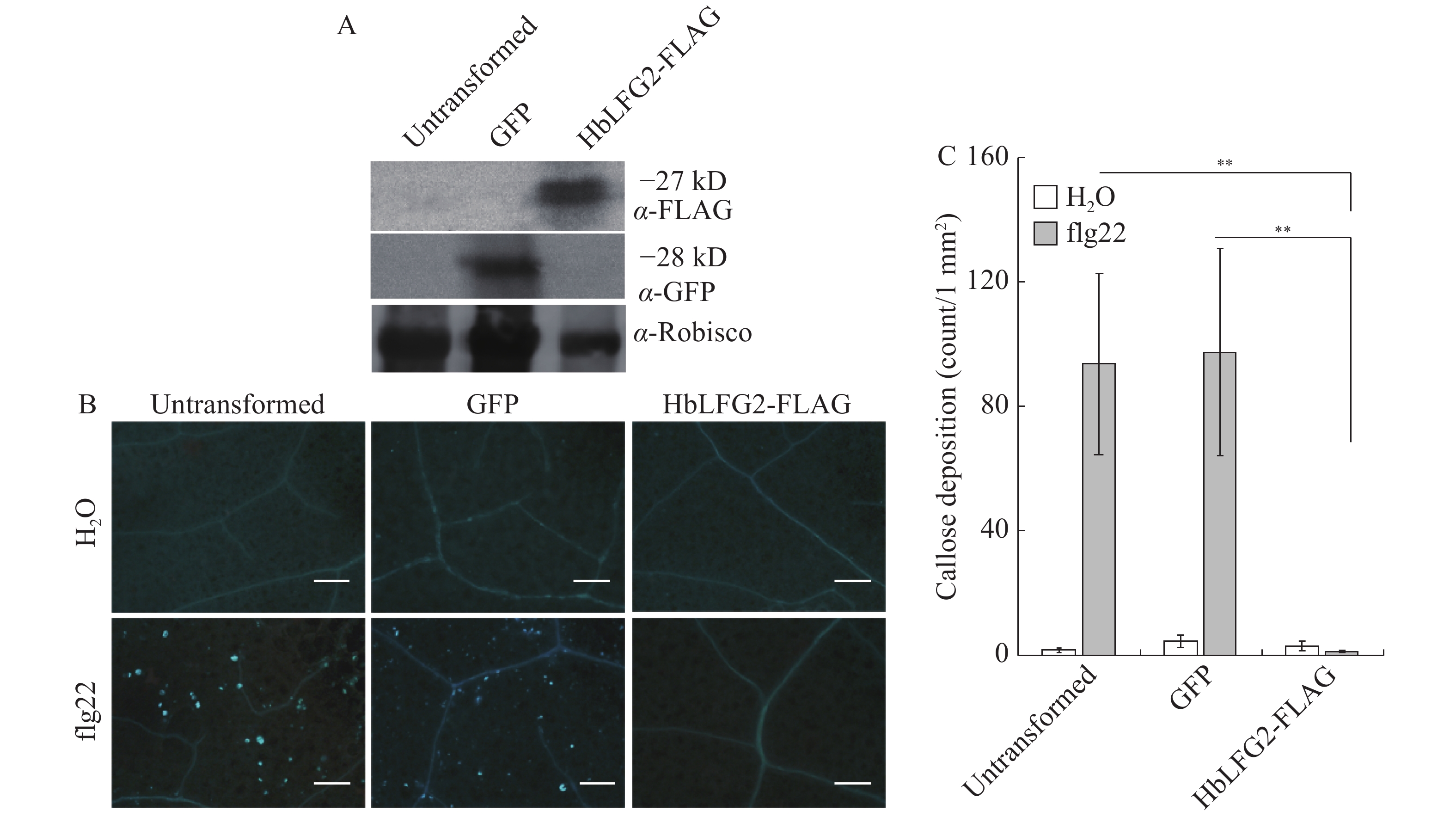
The rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) infected with powdery mildew fungus Erysiphe quercicola will have a significant loss in natural rubber yield. Previous studies suggest that LFG proteins confer susceptibility to plants, and that the mutations on LFGs can inhibit invasions of powdery mildew fungi in barley (Hordeum vulgare) and Arabidopsis thaliana. In H. brasiliensis, gene expressions of two putative LFG proteins including HbLFG1 and HbLFG2 respond to the pathogenic development of the powdery mildew. HbLFG1 negatively regulates plant immunity. However, the function of HbLFG2 was not known. In this context the function of HbLFG2 in plant immunity was investigated by using Agrobacterium mediated transformation in A. thaliana and Nicotiana tabacum. The results showed that constitutive expressions of HbLFG2 in A. thaliana and N. benthamiana inhibited reactive oxygen burst and callose deposition induced by bacteria flg22 (flagellin domain of a synthetic 22-amino-acid peptide). This function of HbLFG2 was similar to that of HbLFG1. Moreover, HbLFG2 could not inhibit the hypersensitive response induced by phytophthora elicitor INF1 or DTT (Dithiothreitol) but by Bax. It was different from HbLFG1. These results suggest that both HbLFG1 and HbLFG2 can inhibit plant immunity responses, but have different mechanisms for their functions.
The rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) infected with powdery mildew fungus Erysiphe quercicola will have a significant loss in natural rubber yield. Previous studies suggest that LFG proteins confer susceptibility to plants, and that the mutations on LFGs can inhibit invasions of powdery mildew fungi in barley (Hordeum vulgare) and Arabidopsis thaliana. In H. brasiliensis, gene expressions of two putative LFG proteins including HbLFG1 and HbLFG2 respond to the pathogenic development of the powdery mildew. HbLFG1 negatively regulates plant immunity. However, the function of HbLFG2 was not known. In this context the function of HbLFG2 in plant immunity was investigated by using Agrobacterium mediated transformation in A. thaliana and Nicotiana tabacum. The results showed that constitutive expressions of HbLFG2 in A. thaliana and N. benthamiana inhibited reactive oxygen burst and callose deposition induced by bacteria flg22 (flagellin domain of a synthetic 22-amino-acid peptide). This function of HbLFG2 was similar to that of HbLFG1. Moreover, HbLFG2 could not inhibit the hypersensitive response induced by phytophthora elicitor INF1 or DTT (Dithiothreitol) but by Bax. It was different from HbLFG1. These results suggest that both HbLFG1 and HbLFG2 can inhibit plant immunity responses, but have different mechanisms for their functions.
2023, 14(4): 389-398.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.006
Abstract:
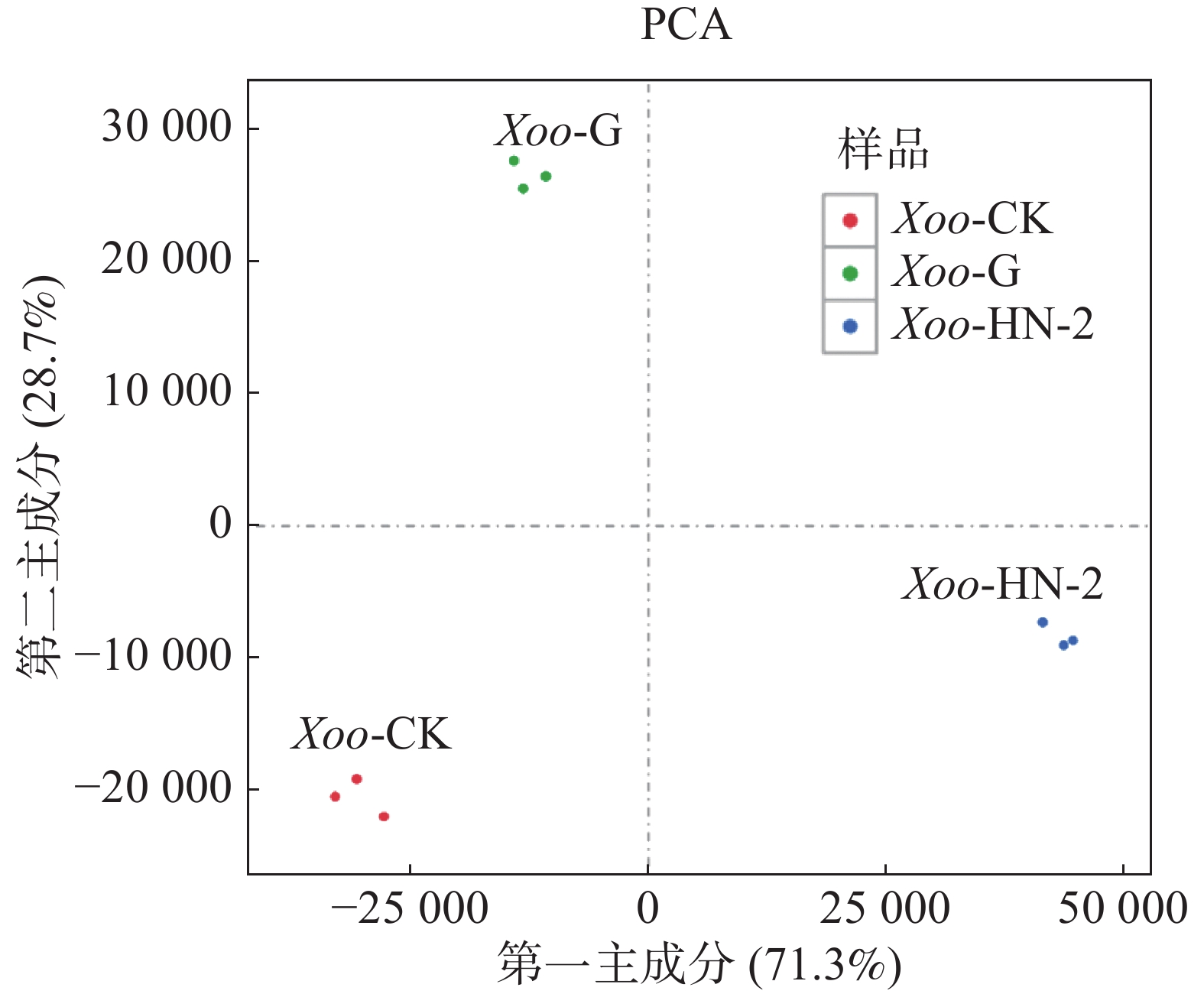
Bacterial blight of rice is a bacterial disease caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), and it occurs in a large area, causing serious damage, and is difficult to control. In our laboratory a Bacillus velezensis strain HN-2 with a strong biocontrol activity isolated from the paddy soil was found that its n-butanol extract has a strong inhibitory activity against Xoo. In order to study the inhibition mechanism of the n-butanol extract of the strain HN-2 on Xoo, Xoo was treated with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 and bacitracin, respectively and analyzed by using transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq)., and the transcriptome data was then analyzed by using GO database and KEGG database. Transcriptome data analysis results showed that a large number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Xoo after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 and bacitracin. A total of 1512 DEGs were obtained after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2, 871 DEGs were up-regulated and 641 down-regulated. GO enrichment analysis found that after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2, the DEGs in Xoo are mainly clustered in the cell process, metabolic process, macromolecular complex, catalytic activities, etc. KEGG cluster analysis found that after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 the ribosomal pathway in Xoo contained the largest number of DEGs while the other major metabolic pathways involved are starch and sucrose metabolism, benzoate degradation, glycerophospholipid metabolism, bacterial chemotaxis, etc. This suggests the n-butanol extract of HN-2 should have a main impact on the ribosomal pathway, and pathways of starch and sucrose metabolism and bacterial chemotaxis.
Bacterial blight of rice is a bacterial disease caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), and it occurs in a large area, causing serious damage, and is difficult to control. In our laboratory a Bacillus velezensis strain HN-2 with a strong biocontrol activity isolated from the paddy soil was found that its n-butanol extract has a strong inhibitory activity against Xoo. In order to study the inhibition mechanism of the n-butanol extract of the strain HN-2 on Xoo, Xoo was treated with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 and bacitracin, respectively and analyzed by using transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq)., and the transcriptome data was then analyzed by using GO database and KEGG database. Transcriptome data analysis results showed that a large number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Xoo after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 and bacitracin. A total of 1512 DEGs were obtained after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2, 871 DEGs were up-regulated and 641 down-regulated. GO enrichment analysis found that after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2, the DEGs in Xoo are mainly clustered in the cell process, metabolic process, macromolecular complex, catalytic activities, etc. KEGG cluster analysis found that after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 the ribosomal pathway in Xoo contained the largest number of DEGs while the other major metabolic pathways involved are starch and sucrose metabolism, benzoate degradation, glycerophospholipid metabolism, bacterial chemotaxis, etc. This suggests the n-butanol extract of HN-2 should have a main impact on the ribosomal pathway, and pathways of starch and sucrose metabolism and bacterial chemotaxis.
2023, 14(4): 399-404, 440.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.007
Abstract:
The principles, methods and steps of multi-omics, including metabonomics, transcriptomics and proteomics technologies, were described, and the current status, future research directions and the advantages of high sensitivity and high throughput of metabonomics, transcriptomics and proteomics technologies in the interaction between mycoviruses and host fungi were comprehensively analyzed in combination with their research cases in hypovirulent mycoviruses. This review is helpful for deep exploration of the effects of mycoviruses on host fungi and their molecular mechanisms, and provides methods and ideas to determine whether mycoviruses can be used as biological factors for control of plant fungal diseases.
The principles, methods and steps of multi-omics, including metabonomics, transcriptomics and proteomics technologies, were described, and the current status, future research directions and the advantages of high sensitivity and high throughput of metabonomics, transcriptomics and proteomics technologies in the interaction between mycoviruses and host fungi were comprehensively analyzed in combination with their research cases in hypovirulent mycoviruses. This review is helpful for deep exploration of the effects of mycoviruses on host fungi and their molecular mechanisms, and provides methods and ideas to determine whether mycoviruses can be used as biological factors for control of plant fungal diseases.
2023, 14(4): 405-411.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.008
Abstract:
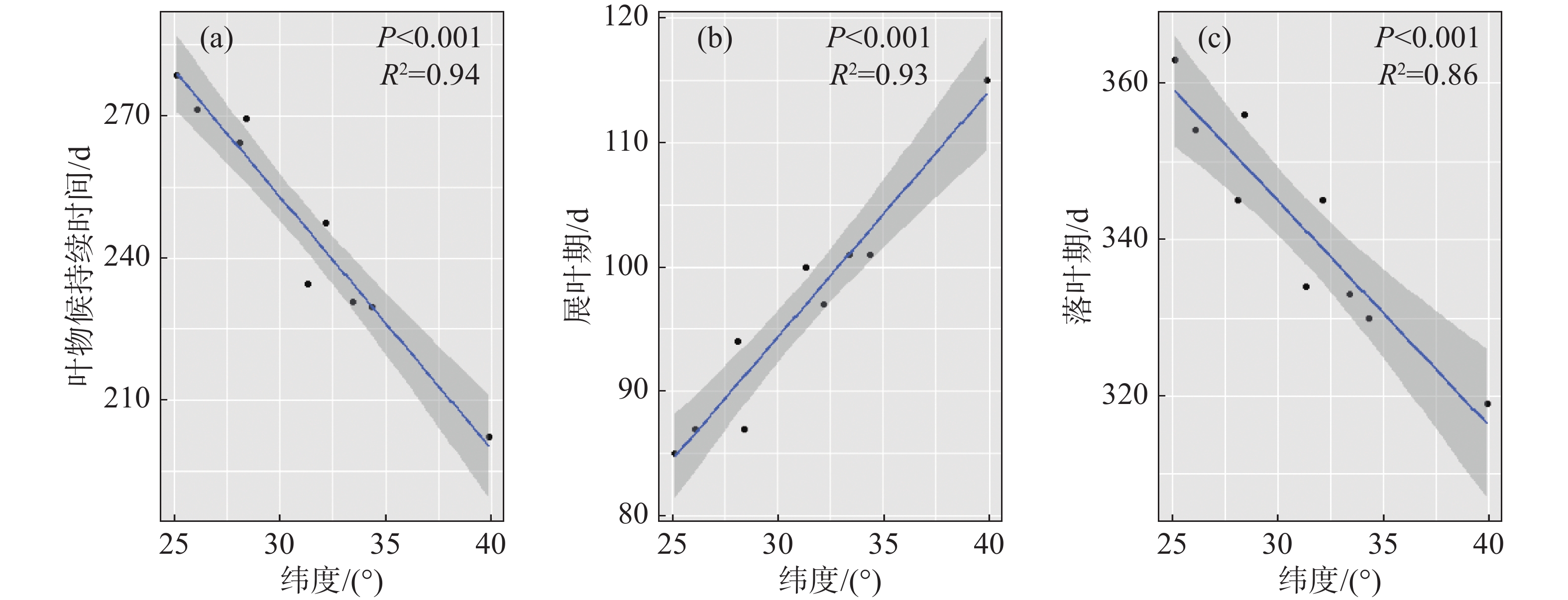
In the Northern Hemisphere, leaf phenology is often reported to have a high spatial variability due to environmental differences at different latitudes. The duration of plant leaf phenology has an important impact not only on the carbon sequestration capacity of plants, but also on their reproductive success and ability to adapt to climate change. However, previous studies on population differences in leaf phenology often were only focused on the differences in leaf unfolding or leaf discoloration stages among different populations, and less attention was paid to the duration of leaf phenology and its driving mechanism. In this study, linear regression models were established by using the phenological data of the leaves of paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera). recorded by China Phenology Observation Network to analyze the latitudinal differences in the duration of phenology of the leaves. The analysis showed that with the increase of latitude, the leaf-unfolding stage for paper mulberry gradually advances and the leaf-falling period gradually delays, indicating that the leaf phenology duration for paper mulberry tended to be shortened with the increase in latitude. The analysis of the importance of environmental factors by using random forest regression showed that the temperature before the leaf-unfolding stage was the most critical environmental factor controlling the leaf-unfolding stage and leaf duration of paper mulberry, and that the precipitation prior to leaf fall was the most critical environmental factor at the leaf fall season, indicating that the latitudinal patterns in leaf phenology duration are jointly shaped by temperature and precipitation. All these results show that the phenology of widely distributed plants has obvious latitudinal gradients in different populations, so as to adapt to different local environmental conditions and improve their own adaptability. Studying the phenological differentiation of different populations of the same species from the perspective of latitudinal differences is helpful to assess the changes in the distribution range and extinction risk of species in the future.
In the Northern Hemisphere, leaf phenology is often reported to have a high spatial variability due to environmental differences at different latitudes. The duration of plant leaf phenology has an important impact not only on the carbon sequestration capacity of plants, but also on their reproductive success and ability to adapt to climate change. However, previous studies on population differences in leaf phenology often were only focused on the differences in leaf unfolding or leaf discoloration stages among different populations, and less attention was paid to the duration of leaf phenology and its driving mechanism. In this study, linear regression models were established by using the phenological data of the leaves of paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera). recorded by China Phenology Observation Network to analyze the latitudinal differences in the duration of phenology of the leaves. The analysis showed that with the increase of latitude, the leaf-unfolding stage for paper mulberry gradually advances and the leaf-falling period gradually delays, indicating that the leaf phenology duration for paper mulberry tended to be shortened with the increase in latitude. The analysis of the importance of environmental factors by using random forest regression showed that the temperature before the leaf-unfolding stage was the most critical environmental factor controlling the leaf-unfolding stage and leaf duration of paper mulberry, and that the precipitation prior to leaf fall was the most critical environmental factor at the leaf fall season, indicating that the latitudinal patterns in leaf phenology duration are jointly shaped by temperature and precipitation. All these results show that the phenology of widely distributed plants has obvious latitudinal gradients in different populations, so as to adapt to different local environmental conditions and improve their own adaptability. Studying the phenological differentiation of different populations of the same species from the perspective of latitudinal differences is helpful to assess the changes in the distribution range and extinction risk of species in the future.
2023, 14(4): 412-423.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.009
Abstract:
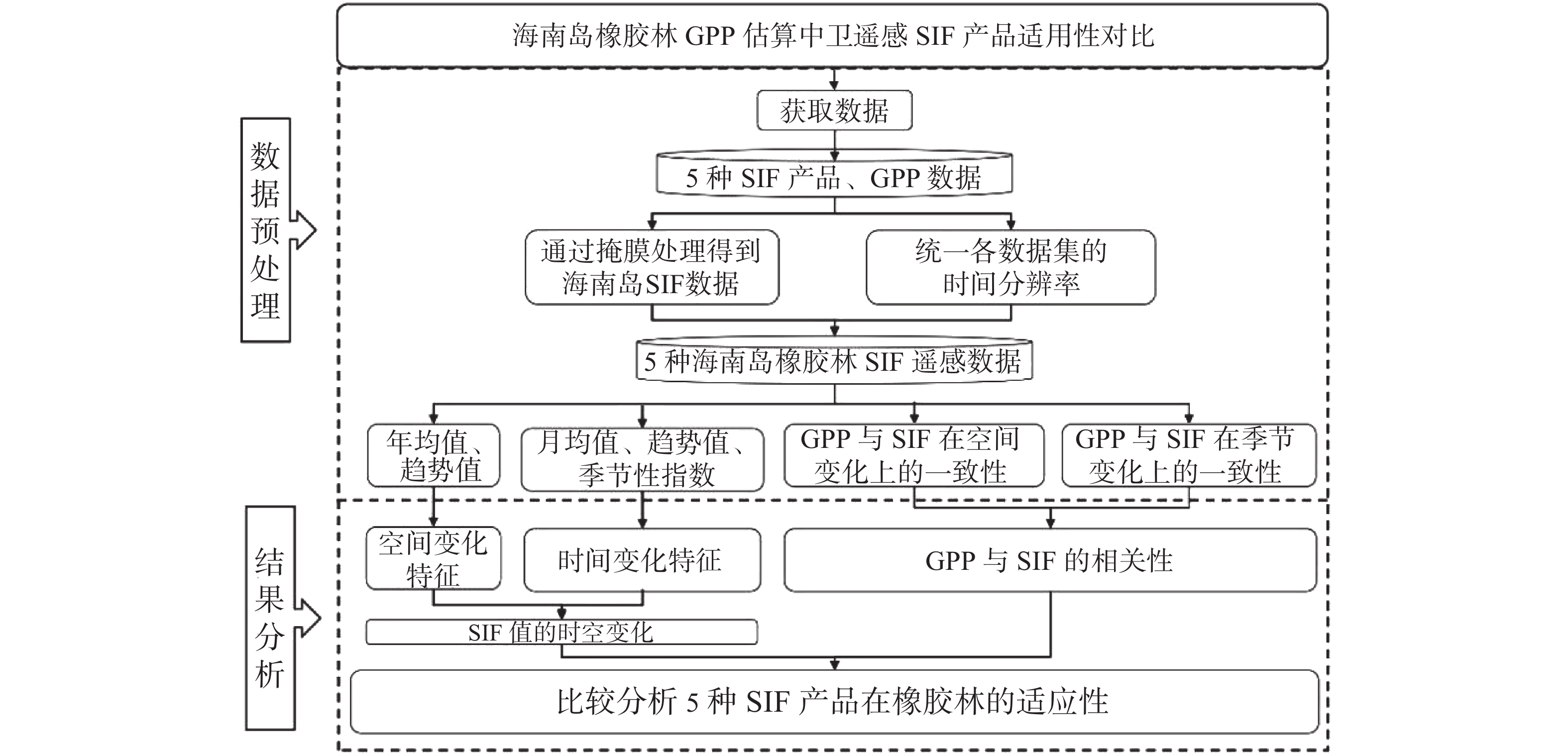
An attempt was made to explore the effect of different solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) products on the estimate of the gross primary production (GPP) of rubber plantations in Hainan Island. The light use efficiency (LUE) model based on localized eddy covariance flux data was used to estimate the GPP of the rubber plantations in Hainan Island. The LUE was used as a reference, and the differences of SIF products retrieved from remote sensing data of 5 satellites (CSIF, GOSIF, SIFOCO2-1696, SIF005, SIFLUE) were compared by using spatiotemporal consistency analysis. The effects of the 5 satellite-based SIF products on GPP estimates of rubber plantations in Hainan Island were evaluated. The results show that CSIF and GOSIF have better applicability in the analysis of spatiotemporal changes, but CSIF is not suitable for long-term trend analysis, and that both the CSIF and GOSIF have a high spatiotemporal consistency with GPP estimates of the rubber plantations in Hainan Island. The SIF005 followed the CSIF and GOSIF, while the data of the SIFOCO2-1696 product in Hainan Island in the past 20 years were seriously lost and the data of the SIFLUE product in the southern part of Hainan Island were also missed, indicated that the last two SIF products are not representative. All the results showed that the CSIF and GOSIF are better in GPP estimate of rubber plantations in Hainan Island, followed by the SIF005, while the SIFOCO2-1696 and SIFLUE are relatively unsuitable for GPP estimate.
An attempt was made to explore the effect of different solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence (SIF) products on the estimate of the gross primary production (GPP) of rubber plantations in Hainan Island. The light use efficiency (LUE) model based on localized eddy covariance flux data was used to estimate the GPP of the rubber plantations in Hainan Island. The LUE was used as a reference, and the differences of SIF products retrieved from remote sensing data of 5 satellites (CSIF, GOSIF, SIFOCO2-1696, SIF005, SIFLUE) were compared by using spatiotemporal consistency analysis. The effects of the 5 satellite-based SIF products on GPP estimates of rubber plantations in Hainan Island were evaluated. The results show that CSIF and GOSIF have better applicability in the analysis of spatiotemporal changes, but CSIF is not suitable for long-term trend analysis, and that both the CSIF and GOSIF have a high spatiotemporal consistency with GPP estimates of the rubber plantations in Hainan Island. The SIF005 followed the CSIF and GOSIF, while the data of the SIFOCO2-1696 product in Hainan Island in the past 20 years were seriously lost and the data of the SIFLUE product in the southern part of Hainan Island were also missed, indicated that the last two SIF products are not representative. All the results showed that the CSIF and GOSIF are better in GPP estimate of rubber plantations in Hainan Island, followed by the SIF005, while the SIFOCO2-1696 and SIFLUE are relatively unsuitable for GPP estimate.
2023, 14(4): 424-432.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.010
Abstract:
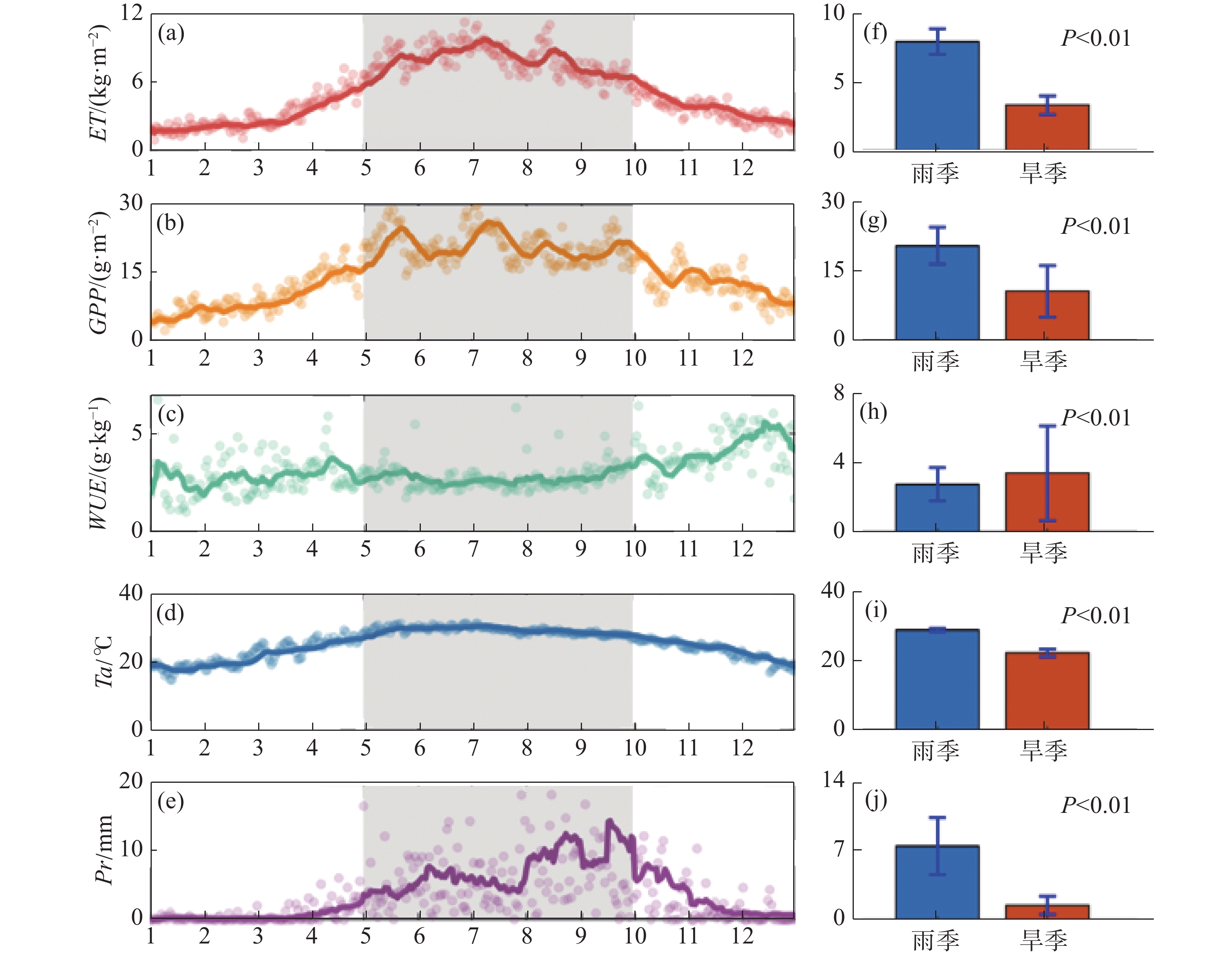
Water use efficiency (WUE), a critical element of carbon and hydrological cycle, plays a key role in land-atmosphere feedback. The seasonal differences of rubber plantation ecosystems in WUE from 2010 to 2019 were analyzed by using the EC-LUE model and the Penman-Monteith model based on the data of gross primarily productivity (GPP) and evapotranspiration (ET). Furthermore, the impact of each factor on the change of WUE was quantitatively evaluated. The factors were then classified into two groups: atmospheric (temperature, atmospheric pressure, water vapor deficit, net radiation, and solar radiation) and biophysical (fraction of photosynthetically active radiation, soil heat flux, aerodynamic resistance, and canopy resistance). The results showed that the rubber plantation ecosystems had a lower WUE(3.52 g·kg−1) in the rainy season than in the dry season (4.73 g·kg−1) from 2010 to 2019, and that both GPP and ET curves were clearly unimodal, with their peaks all in the rainy season. Solar radiation tended to reduce the increase of WUE in the dry season, indicating a negative contribution, although this suppression was counteracted by other atmospheric factors, showing a positive contribution. Surface impedance, which tended to encourage the growth of WUE in the dry season, had the highest contribution to WUE change, accounting for 33.29% of the total. The WUE change in rubber plantations from rainy to drought seasons were primarily governed by biophysical parameters, which might serve as a reference for a further study of the ecohydrological and carbon-water cycle activities in rubber plantations.
Water use efficiency (WUE), a critical element of carbon and hydrological cycle, plays a key role in land-atmosphere feedback. The seasonal differences of rubber plantation ecosystems in WUE from 2010 to 2019 were analyzed by using the EC-LUE model and the Penman-Monteith model based on the data of gross primarily productivity (GPP) and evapotranspiration (ET). Furthermore, the impact of each factor on the change of WUE was quantitatively evaluated. The factors were then classified into two groups: atmospheric (temperature, atmospheric pressure, water vapor deficit, net radiation, and solar radiation) and biophysical (fraction of photosynthetically active radiation, soil heat flux, aerodynamic resistance, and canopy resistance). The results showed that the rubber plantation ecosystems had a lower WUE(3.52 g·kg−1) in the rainy season than in the dry season (4.73 g·kg−1) from 2010 to 2019, and that both GPP and ET curves were clearly unimodal, with their peaks all in the rainy season. Solar radiation tended to reduce the increase of WUE in the dry season, indicating a negative contribution, although this suppression was counteracted by other atmospheric factors, showing a positive contribution. Surface impedance, which tended to encourage the growth of WUE in the dry season, had the highest contribution to WUE change, accounting for 33.29% of the total. The WUE change in rubber plantations from rainy to drought seasons were primarily governed by biophysical parameters, which might serve as a reference for a further study of the ecohydrological and carbon-water cycle activities in rubber plantations.
2023, 14(4): 433-440.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.011
Abstract:
It has been demonstrated that exosomes derived from macrophages can be used as adjuvants to enhance cellular immune response. An attempt was made to explore whether exosomes derived from lipopolysaccharide-activated chicken macrophages could be used as immune adjuvants for the potential prevention and control of epidemic diseases in Wenchang chicken. The exosomes were extracted by ultracentrifugation and identified by transmission electron microscopy and particle size analysis. Subsequently, the exosomes were labeled with PKH67 dye and co-incubated with bone marrow-derived dendritic cells from Wenchang chicken. The uptake and activation of the exosomes by the dendritic cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope. The results showed that the exosomes derived from chicken macrophage HD 11 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharides were ingested by amphioxus-derived dendritic cells and promoted the activation of dendritic cells.
It has been demonstrated that exosomes derived from macrophages can be used as adjuvants to enhance cellular immune response. An attempt was made to explore whether exosomes derived from lipopolysaccharide-activated chicken macrophages could be used as immune adjuvants for the potential prevention and control of epidemic diseases in Wenchang chicken. The exosomes were extracted by ultracentrifugation and identified by transmission electron microscopy and particle size analysis. Subsequently, the exosomes were labeled with PKH67 dye and co-incubated with bone marrow-derived dendritic cells from Wenchang chicken. The uptake and activation of the exosomes by the dendritic cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope. The results showed that the exosomes derived from chicken macrophage HD 11 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharides were ingested by amphioxus-derived dendritic cells and promoted the activation of dendritic cells.
2023, 14(4): 441-450.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.012
Abstract:
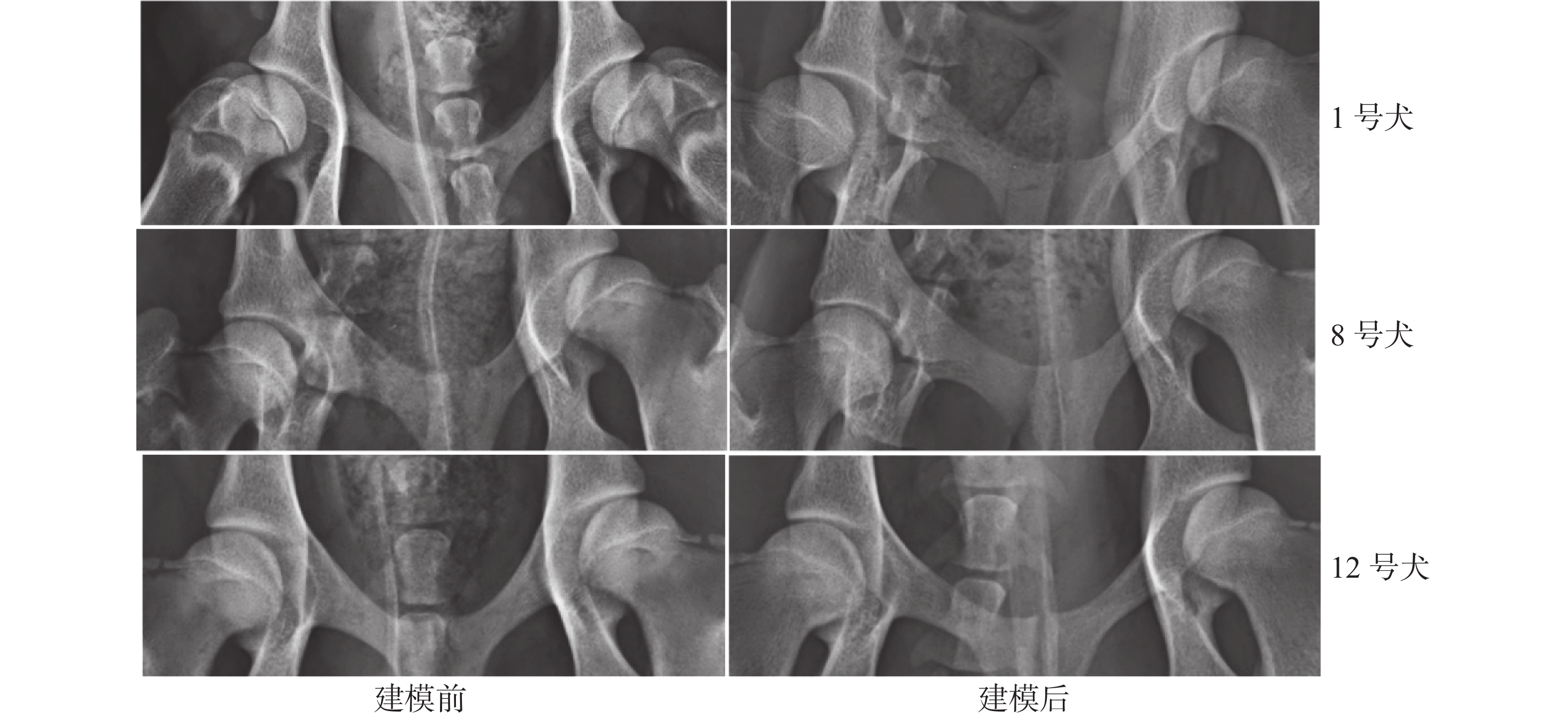
An attempt was made to study the therapeutic effect of alendronate sodium and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on canine Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (LCPD) to provide a new way for the clinical treatment of avascular necrosis of canine femoral head. Twelve 6-month-old dogs with similar body weight were selected to establish the LCPD model by liquid nitrogen freezing, and the modeling results were evaluated and staged by X-ray film and Ficat-Arlet classification system. According to the clinical diagnostic criteria, nine dogs with the stages Ⅰ−Ⅱ of avascular necrosis of the femoral head were randomly divided into three groups, A, B and C. Group A was treated with alendronate sodium orally; Group B received intra-articular injection of calcium gluconate activated platelet rich plasma; Group C served as a control group without any treatment. Three months after treatment, X-ray films were taken and the femoral head of the affected limb was dissected to evaluate the therapeutic effect. If the X-ray film shows no phase Ⅲ and Ⅳ pathological features and anatomical results, and the surface of the femoral head is smooth without collapse, it is considered that the treatment is effective, otherwise it is ineffective. The results showed that the two dogs in Group A had effective treatment while one did not have effective treatment. All the three dogs in Group B were treated effectively, and the three dogs in Group C were not effectively treated. This indicated that both alendronate sodium and PRP can effectively treat canine LCPD, but there was no significant difference in treatment effect between alendronate sodium and PRP (P=0.267).
An attempt was made to study the therapeutic effect of alendronate sodium and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on canine Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease (LCPD) to provide a new way for the clinical treatment of avascular necrosis of canine femoral head. Twelve 6-month-old dogs with similar body weight were selected to establish the LCPD model by liquid nitrogen freezing, and the modeling results were evaluated and staged by X-ray film and Ficat-Arlet classification system. According to the clinical diagnostic criteria, nine dogs with the stages Ⅰ−Ⅱ of avascular necrosis of the femoral head were randomly divided into three groups, A, B and C. Group A was treated with alendronate sodium orally; Group B received intra-articular injection of calcium gluconate activated platelet rich plasma; Group C served as a control group without any treatment. Three months after treatment, X-ray films were taken and the femoral head of the affected limb was dissected to evaluate the therapeutic effect. If the X-ray film shows no phase Ⅲ and Ⅳ pathological features and anatomical results, and the surface of the femoral head is smooth without collapse, it is considered that the treatment is effective, otherwise it is ineffective. The results showed that the two dogs in Group A had effective treatment while one did not have effective treatment. All the three dogs in Group B were treated effectively, and the three dogs in Group C were not effectively treated. This indicated that both alendronate sodium and PRP can effectively treat canine LCPD, but there was no significant difference in treatment effect between alendronate sodium and PRP (P=0.267).
2023, 14(4): 451-457.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.013
Abstract:
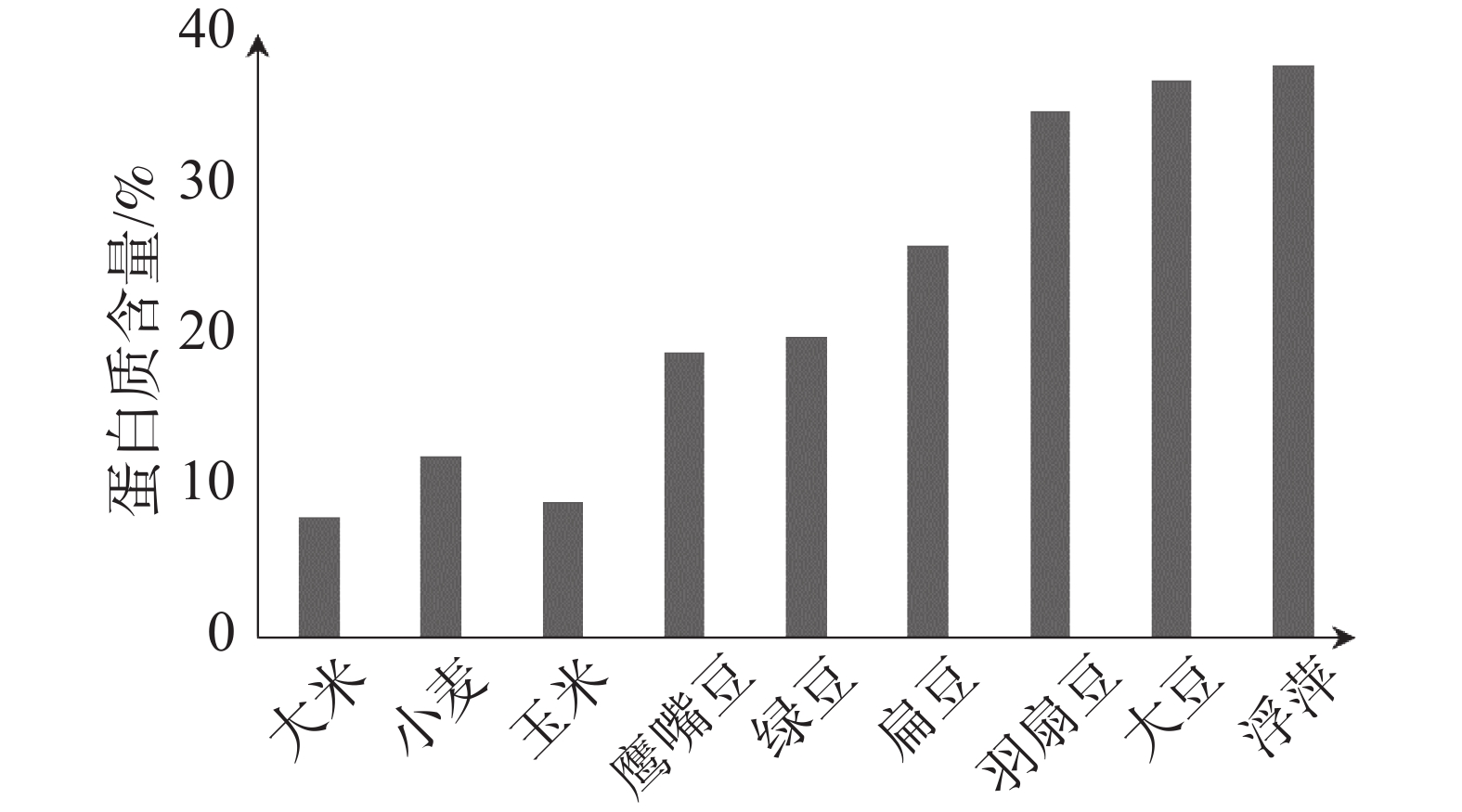
Leaf meal of giant duckweed (Lemna polyrhiza) variety DW2602 was used as a feed supplement in the conventional tilapia feed at a rate of 0, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and 30%, respectively, and fed to tilapia fingerlings at the feeding rate of 2.5%, 3%, and 4% of tilapia body weight for 40 days. The growth indexes of the tilapia fingerlings fed with the giant duckweed leaf meal as feed supplement, such as weight gain, specific growth rate, condition factor, viscerosomatic index, etc. were determined. The results indicated that the tilapia fingerlings fed with the tilapia feed supplemented with the giant duckweed leaf meal increased their crude protein content by 4.3%, reduced their crude oil by 0.9%, and enhanced their sulfur-containing amino acids (methionine and cysteine) by 0.1% as compared to those fed only with the conventional feed, and that no obvious change was measured in their lysine content. The giant duckweed leaf meal used as feed supplement promoted the growth of tilapia (P < 0.05). The conventional feed supplemented with 20% of giant duckweed leaf meal at a feeding rate of 3% of the tilapia body weight significantly promoted the growth of tilapia, and increased tilapia weight gain by 57.5% and the specific growth rate by 30.3% and reduced the condition factor and viscerosomatic index by 6.4% and 5.5%, respectively, as compared to the 100% conventional feed. This indicates that supplement of giant duckweed leaf meal in the conventional tilapia feed at a given rate promotes the growth of tilapia.
Leaf meal of giant duckweed (Lemna polyrhiza) variety DW2602 was used as a feed supplement in the conventional tilapia feed at a rate of 0, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and 30%, respectively, and fed to tilapia fingerlings at the feeding rate of 2.5%, 3%, and 4% of tilapia body weight for 40 days. The growth indexes of the tilapia fingerlings fed with the giant duckweed leaf meal as feed supplement, such as weight gain, specific growth rate, condition factor, viscerosomatic index, etc. were determined. The results indicated that the tilapia fingerlings fed with the tilapia feed supplemented with the giant duckweed leaf meal increased their crude protein content by 4.3%, reduced their crude oil by 0.9%, and enhanced their sulfur-containing amino acids (methionine and cysteine) by 0.1% as compared to those fed only with the conventional feed, and that no obvious change was measured in their lysine content. The giant duckweed leaf meal used as feed supplement promoted the growth of tilapia (P < 0.05). The conventional feed supplemented with 20% of giant duckweed leaf meal at a feeding rate of 3% of the tilapia body weight significantly promoted the growth of tilapia, and increased tilapia weight gain by 57.5% and the specific growth rate by 30.3% and reduced the condition factor and viscerosomatic index by 6.4% and 5.5%, respectively, as compared to the 100% conventional feed. This indicates that supplement of giant duckweed leaf meal in the conventional tilapia feed at a given rate promotes the growth of tilapia.
2023, 14(4): 458-466.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.014
Abstract:
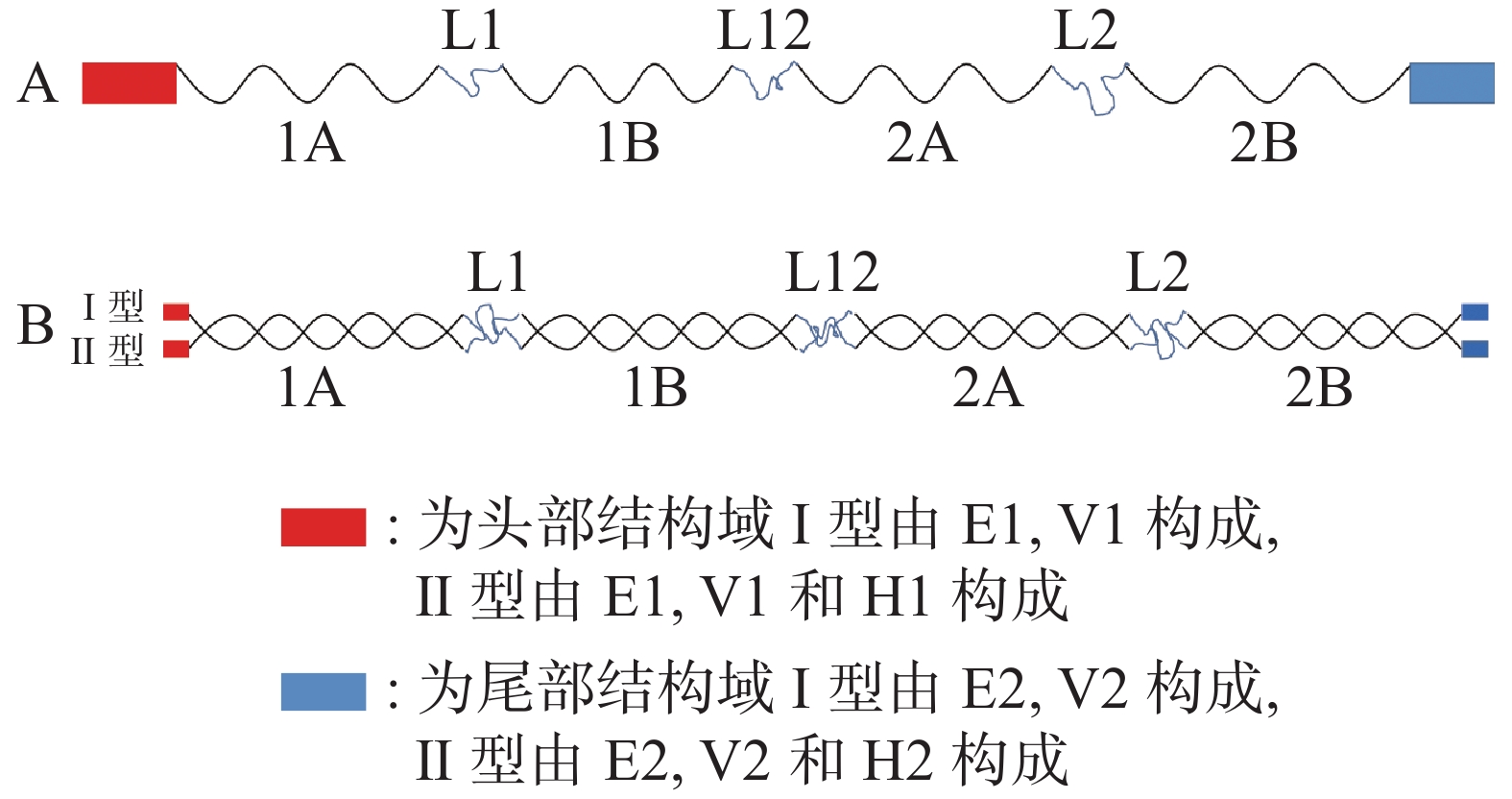
The structural features of keratins, the three degradation methods for keratins including physical, chemical and biological degradation, and the utilization of degradation products were reviewed, and the three degradation methods were compared. Compared with the physical and chemical degradation methods, the biological degradation approach, especially the enzymatic hydrolysis method, has the advantages of environmental friendliness, low-cost, and high-value degradation products which can be effectively utilized in the sectors of medicine, industry and aquaculture. The recent research and application of keratinase from the perspectives of classification, developmental evolution relationship and degradation methods and modes were overviewed. At present, the existing research on keratinases needs to improve. For example, most of the selected keratinases are unable to degrade keratin alone without disruption of the keratin disulfide bond in a reducing environment. Or multiple different keratinases are used simultaneously to complete the degradation process. These shortcomings and deficiencies prevent the large-scale industrial application of keratinase. It is still the focus of future research to screen and purify more efficient keratinases tolerant of high temperature, acid and alkali to explore the molecular mechanism of keratin degradation by keratinases, and to make full use of keratinases for targeted cleavage of keratin to obtain high-purity and high-value-added degradation products.
The structural features of keratins, the three degradation methods for keratins including physical, chemical and biological degradation, and the utilization of degradation products were reviewed, and the three degradation methods were compared. Compared with the physical and chemical degradation methods, the biological degradation approach, especially the enzymatic hydrolysis method, has the advantages of environmental friendliness, low-cost, and high-value degradation products which can be effectively utilized in the sectors of medicine, industry and aquaculture. The recent research and application of keratinase from the perspectives of classification, developmental evolution relationship and degradation methods and modes were overviewed. At present, the existing research on keratinases needs to improve. For example, most of the selected keratinases are unable to degrade keratin alone without disruption of the keratin disulfide bond in a reducing environment. Or multiple different keratinases are used simultaneously to complete the degradation process. These shortcomings and deficiencies prevent the large-scale industrial application of keratinase. It is still the focus of future research to screen and purify more efficient keratinases tolerant of high temperature, acid and alkali to explore the molecular mechanism of keratin degradation by keratinases, and to make full use of keratinases for targeted cleavage of keratin to obtain high-purity and high-value-added degradation products.



 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 747KB
PDF 747KB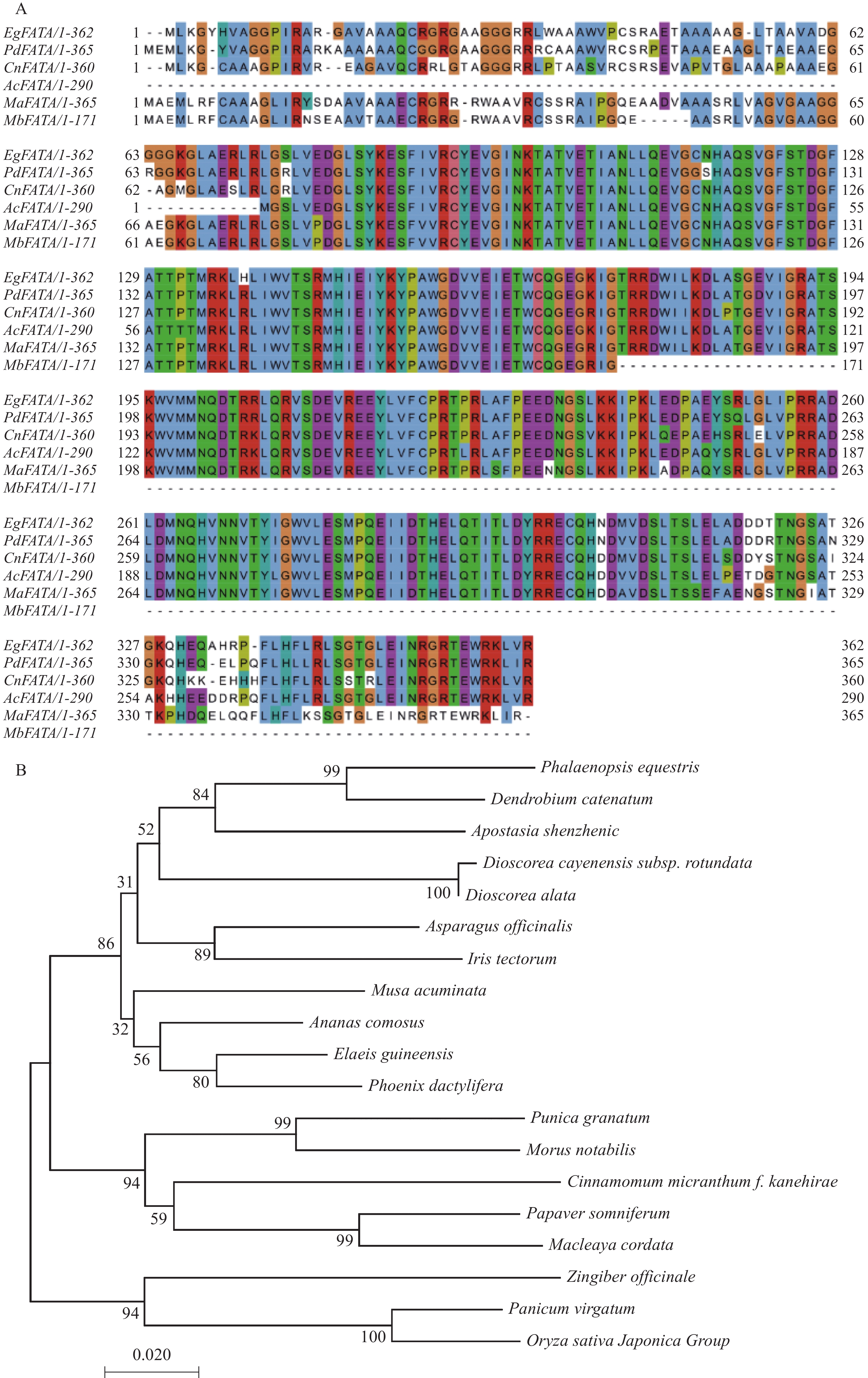







 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS