2025 Vol. 16, No. 1
2025, 16(1): 13-20.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240110
Abstract:
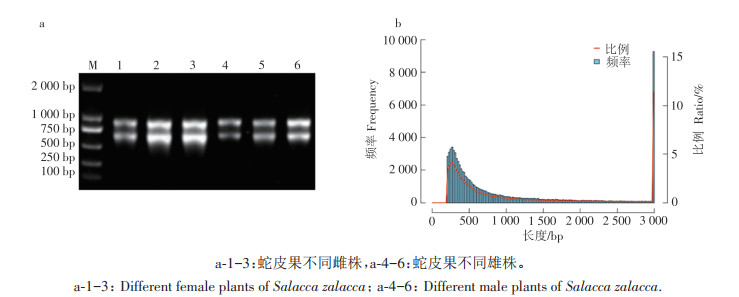
Salacca zalacca(Arecaceae: Salaccinae) is a palm species characteristic of tropical regions, known for its dioecious nature with distinct male and female individuals. Early sex determination is crucial for optimizing the ratio of male to female seedlings in S. zalacca plantations. An attempt was made to obtain molecular markers for early sex differentiation. Leaves from three female and three male S. zalacca trees from Hainan Province were collected for transcriptome sequencing analysis, and 19 differentially expressed genes(DEGs) showing significant variations between male and female genotypes were identified. Further validation using an expanded cohort of seven female and seven male S. zalacca individuals confirmed that the Unigene0079610(GOLS1) gene exhibits stable differential expression patterns between the sexes. Consequently, the GOLS1 gene can serve as a robust molecular marker for sex identification in S. zalacca. Molecular signatures relevant to sex determination in S.zalacca were delineated through large-scale transcriptome screening, based on which a rapid detection protocol for the GOLS1 gene was established. These results provide a viable technological approach for the sex identification of S. zalacca nursery stock and offer a foundational framework for sex determination methods in other horticultural crops.
Salacca zalacca(Arecaceae: Salaccinae) is a palm species characteristic of tropical regions, known for its dioecious nature with distinct male and female individuals. Early sex determination is crucial for optimizing the ratio of male to female seedlings in S. zalacca plantations. An attempt was made to obtain molecular markers for early sex differentiation. Leaves from three female and three male S. zalacca trees from Hainan Province were collected for transcriptome sequencing analysis, and 19 differentially expressed genes(DEGs) showing significant variations between male and female genotypes were identified. Further validation using an expanded cohort of seven female and seven male S. zalacca individuals confirmed that the Unigene0079610(GOLS1) gene exhibits stable differential expression patterns between the sexes. Consequently, the GOLS1 gene can serve as a robust molecular marker for sex identification in S. zalacca. Molecular signatures relevant to sex determination in S.zalacca were delineated through large-scale transcriptome screening, based on which a rapid detection protocol for the GOLS1 gene was established. These results provide a viable technological approach for the sex identification of S. zalacca nursery stock and offer a foundational framework for sex determination methods in other horticultural crops.
2025, 16(1): 21-30.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240031
Abstract:
The yield of banana(Musa AA) was predicted based on machine learning algorithm, and an optimal prediction model and yield influencing factors were clarified so as to provide technical support for the integrated nutrient management and yield prediction of banana(Musa AA) in Chengmai County, Hainan Province. The input variables were screened by correlation analysis and stepwise regression analysis, and then yield prediction models of banana(Musa AA) were established by random forest(RF), support vector machine(SVM), K-nearest neighbor(KNN) and artificial neural network(ANN). The models were interpreted by Shapley Additive exPlanations(SHAP) method to reveal the dominant factors affecting the yield of banana(Musa AA), and the impact of the dominant factors on yield was quantitatively analyzed. The results showed that the ANN model was the best for yield prediction with R2 being 0.98, and root-mean-square error(RMSE) and mean absolute error(MAE) being 0.16 kg·plant and 0.10 kg·plant, respectively, and that the prediction value of this model was basically of no deviation. The error of the ANN model had converged at about 100 samples, and even smaller cost could also achieve good prediction effect. The SVM model had only slightly lower prediction performance than the ANN model but had the risk of underfitting, while the KNN and RF models had lower prediction performance with overfitting, and the errors had not converged under the current sample size. The ANN model prediction results were explained by the SHAP method as follows: The leading factors affecting the yield of banana(Musa AA) were available potassium, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, exchangeable calcium and exchangeable magnesium.When the content of available potassium was greater than 100 mg·kg-1, the content of alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen was greater than 100 mg·kg-1, the content of exchangeable calcium was greater than 600 mg·kg-1, and the content of exchangeable magnesium was greater than 60 mg·kg-1, the yield of banana(Musa AA) was promoted. When the content of exchangeable calcium and magnesium in soil was deficient, the content of available manganese and available zinc in soil should be increased to alleviate the stress of nutrient deficiency in the banana plantations.
The yield of banana(Musa AA) was predicted based on machine learning algorithm, and an optimal prediction model and yield influencing factors were clarified so as to provide technical support for the integrated nutrient management and yield prediction of banana(Musa AA) in Chengmai County, Hainan Province. The input variables were screened by correlation analysis and stepwise regression analysis, and then yield prediction models of banana(Musa AA) were established by random forest(RF), support vector machine(SVM), K-nearest neighbor(KNN) and artificial neural network(ANN). The models were interpreted by Shapley Additive exPlanations(SHAP) method to reveal the dominant factors affecting the yield of banana(Musa AA), and the impact of the dominant factors on yield was quantitatively analyzed. The results showed that the ANN model was the best for yield prediction with R2 being 0.98, and root-mean-square error(RMSE) and mean absolute error(MAE) being 0.16 kg·plant and 0.10 kg·plant, respectively, and that the prediction value of this model was basically of no deviation. The error of the ANN model had converged at about 100 samples, and even smaller cost could also achieve good prediction effect. The SVM model had only slightly lower prediction performance than the ANN model but had the risk of underfitting, while the KNN and RF models had lower prediction performance with overfitting, and the errors had not converged under the current sample size. The ANN model prediction results were explained by the SHAP method as follows: The leading factors affecting the yield of banana(Musa AA) were available potassium, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, exchangeable calcium and exchangeable magnesium.When the content of available potassium was greater than 100 mg·kg-1, the content of alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen was greater than 100 mg·kg-1, the content of exchangeable calcium was greater than 600 mg·kg-1, and the content of exchangeable magnesium was greater than 60 mg·kg-1, the yield of banana(Musa AA) was promoted. When the content of exchangeable calcium and magnesium in soil was deficient, the content of available manganese and available zinc in soil should be increased to alleviate the stress of nutrient deficiency in the banana plantations.
2025, 16(1): 31-42.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240133
Abstract:
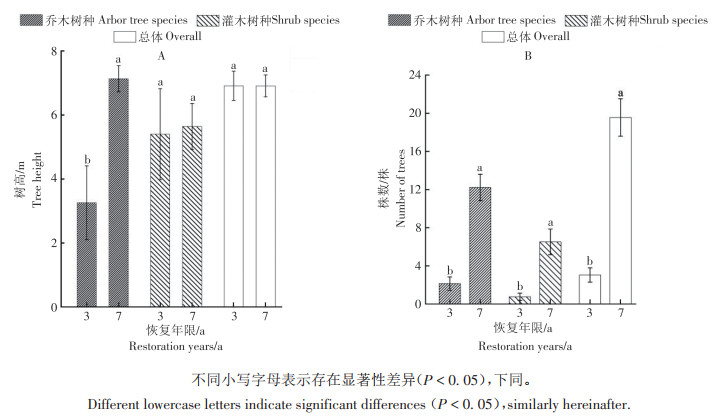
To explore the changes in the characteristics of the understory vegetation community after natural recovery of rubber plantations which were withdrawn from operation, to provide scientific basis for the disposal of rubber plantations returned to natural forests in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. A quadrat survey was made to assess the stand structure, growth status, species composition, species diversity and community similarity of the rubber plantation understory vegetation community by using a space-for-time substitution approach in different restoration years(0, 3, 7 a). The results show that the rubber plantations can form a vertical structure of trees, shrubs and grasses in 3 years and 7 years with an increase in restoration year. The species in the tree, shrub and herb layers of the understory of the rubber plantations are good in growth condition, and the trees in the tree layer are in good condition. The number of tree plants in the tree layer was maximum after 7 years of restoration.As the restoration years increase, the species composition of the understory plants in the rubber plantation tends to be more complex, and the community structure is stable; the species diversity in the shrub and herb layers tends to increase and then decrease, and the species diversity in the tree layer increases. In different restoration years, the dominant species in the tree, shrub, and herb layers of the understory of the rubber plantations changed greatly. In the three different restoration years, the community similarity between the tree and shrub layers under the rubber plantations is low, while the community similarity in the herb layer was high. Generally speaking, the understory plants of naturally restored rubber plantations are in good growth conditions, species diversity increases, stand structures tend to become complex, and the community structure is stable.
To explore the changes in the characteristics of the understory vegetation community after natural recovery of rubber plantations which were withdrawn from operation, to provide scientific basis for the disposal of rubber plantations returned to natural forests in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. A quadrat survey was made to assess the stand structure, growth status, species composition, species diversity and community similarity of the rubber plantation understory vegetation community by using a space-for-time substitution approach in different restoration years(0, 3, 7 a). The results show that the rubber plantations can form a vertical structure of trees, shrubs and grasses in 3 years and 7 years with an increase in restoration year. The species in the tree, shrub and herb layers of the understory of the rubber plantations are good in growth condition, and the trees in the tree layer are in good condition. The number of tree plants in the tree layer was maximum after 7 years of restoration.As the restoration years increase, the species composition of the understory plants in the rubber plantation tends to be more complex, and the community structure is stable; the species diversity in the shrub and herb layers tends to increase and then decrease, and the species diversity in the tree layer increases. In different restoration years, the dominant species in the tree, shrub, and herb layers of the understory of the rubber plantations changed greatly. In the three different restoration years, the community similarity between the tree and shrub layers under the rubber plantations is low, while the community similarity in the herb layer was high. Generally speaking, the understory plants of naturally restored rubber plantations are in good growth conditions, species diversity increases, stand structures tend to become complex, and the community structure is stable.
2025, 16(1): 43-57.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240016
Abstract:
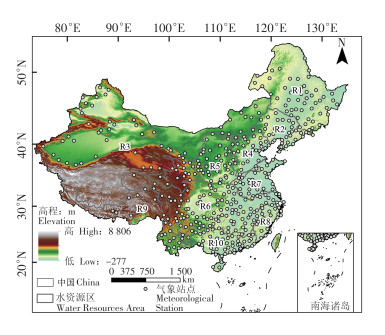
With the continued impact of global warming, extreme climate risks have increased significantly, directly affecting different stages of vegetation growth. Data from ten first-level water resources areas in China were collected and organized, including daily temperature(maximum, minimum, average temperature) and precipitation data sets of 443 stations in China from 1960 to 2020 as well as monthly/yearly GIMMS-NDVI data from 1982 to 2015 to quantify 27 extreme climate indices and characterize vegetation growth conditions. The data were analyzed by using trend analysis, geostatistical analysis and other methods to clarify the differences in extreme climate change trends and vegetation response sensitivities between regions. The results showed that except for the Songhua River Basin, the vegetation NDVI in all the water resource area under study in China from 1982 to 2015 tended to show an upward trend, with the most obvious increase trend in the Huang-Huai-Hai region. The extreme high temperature index mostly shows an upward trend. The extreme precipitation index shows an upward trend in the eastern and central parts of the study area and a downward trend in the northeast. The impact of extreme temperature on NDVI is stronger than that of extreme precipitation. The extreme temperature index that has the greatest impact on NDVI is different in different water resource areas. Among them, the index with the greatest influence is the maximum temperature(TMAXmean) in the Songhua River Basin and Liao River Basin. The index with the greatest influence in the Northwest River Basin,Yellow River Basin and Southeast River Basin is the number of warm night days(TN90P). The index with the greatest influence in the Haihe River Basin, Huaihe River Basin, Yangtze River Basin and Pearl River Basin is minimum temperature(TMINmean), and the index with the greatest impact in the Southwest River Basin is the extremely high daily minimum temperature(TNx). NDVI responds to extreme climate with a 1-3 month response Time, in which vegetation in the southwest and southeast regions has a response time of 2-3 months to extreme climate.
With the continued impact of global warming, extreme climate risks have increased significantly, directly affecting different stages of vegetation growth. Data from ten first-level water resources areas in China were collected and organized, including daily temperature(maximum, minimum, average temperature) and precipitation data sets of 443 stations in China from 1960 to 2020 as well as monthly/yearly GIMMS-NDVI data from 1982 to 2015 to quantify 27 extreme climate indices and characterize vegetation growth conditions. The data were analyzed by using trend analysis, geostatistical analysis and other methods to clarify the differences in extreme climate change trends and vegetation response sensitivities between regions. The results showed that except for the Songhua River Basin, the vegetation NDVI in all the water resource area under study in China from 1982 to 2015 tended to show an upward trend, with the most obvious increase trend in the Huang-Huai-Hai region. The extreme high temperature index mostly shows an upward trend. The extreme precipitation index shows an upward trend in the eastern and central parts of the study area and a downward trend in the northeast. The impact of extreme temperature on NDVI is stronger than that of extreme precipitation. The extreme temperature index that has the greatest impact on NDVI is different in different water resource areas. Among them, the index with the greatest influence is the maximum temperature(TMAXmean) in the Songhua River Basin and Liao River Basin. The index with the greatest influence in the Northwest River Basin,Yellow River Basin and Southeast River Basin is the number of warm night days(TN90P). The index with the greatest influence in the Haihe River Basin, Huaihe River Basin, Yangtze River Basin and Pearl River Basin is minimum temperature(TMINmean), and the index with the greatest impact in the Southwest River Basin is the extremely high daily minimum temperature(TNx). NDVI responds to extreme climate with a 1-3 month response Time, in which vegetation in the southwest and southeast regions has a response time of 2-3 months to extreme climate.
2025, 16(1): 71-78.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230023
Abstract:
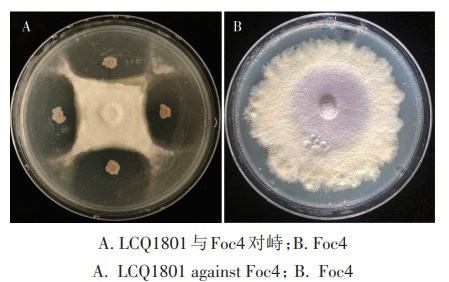
To develop biological organic fertilizer for preventing and controling Fusarium wilt of banana, a bio-control bacterial strain LCQ1801 was isolated from the soil of rubber plantation in Chengmai, Hainan and its inhibition activity against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense race 4(Foc4), the causal agent of banana Fusarium wilt was determined by using plate dual culture. The results indicated that LCQ1801 had obviously antagonistic effect on Foc4,and the inhibition rate was 65.9%. The LCQ1801 was identified as Bacillus velezensis by morphological observation,physiological and biochemical tests, combined with 16S rDNA sequencing analysis. Foc4 was cocultured with LCQ1801 bacterial liquid and filtrate, respectively. The result found that LCQ1801 bacterial fluid and filtrate caused abnormal growth or rupture of Foc4 hyphae and affected spore germination. At the same time, LCQ1801 was cultured on different substrates by using plate assay and culture flask culture. The plate assay indicated that the growth of LCQ1801 in the animal substrates of sheep dung, pig dung and cow dung was better than that in chicken dung. The growth of LCQ1801 in the plant substrates of wheat bran, corn flour, soybean meal and rice straw was better than that in the plant substrates of bagasse and coconut coir. Culture flask culture test showed that the number of viable bacteria of LCQ1801 in cow dung and sheep dung reached 16.8 billions·g-1 and 24.0 billions·g-1, respectively. The number of viable bacteria of LCQ1801 in rice straw, soybean meal and corn flour reached 32.2 billions·g-1, 24.9 billions·g-1 and 21.7 billions·g-1, respectively. LCQ1801 hardly grew in the substrate of coconut coir in both culture styles. This study provides strain materials and technical support for biological control of Fusarium wilt of banana.
To develop biological organic fertilizer for preventing and controling Fusarium wilt of banana, a bio-control bacterial strain LCQ1801 was isolated from the soil of rubber plantation in Chengmai, Hainan and its inhibition activity against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense race 4(Foc4), the causal agent of banana Fusarium wilt was determined by using plate dual culture. The results indicated that LCQ1801 had obviously antagonistic effect on Foc4,and the inhibition rate was 65.9%. The LCQ1801 was identified as Bacillus velezensis by morphological observation,physiological and biochemical tests, combined with 16S rDNA sequencing analysis. Foc4 was cocultured with LCQ1801 bacterial liquid and filtrate, respectively. The result found that LCQ1801 bacterial fluid and filtrate caused abnormal growth or rupture of Foc4 hyphae and affected spore germination. At the same time, LCQ1801 was cultured on different substrates by using plate assay and culture flask culture. The plate assay indicated that the growth of LCQ1801 in the animal substrates of sheep dung, pig dung and cow dung was better than that in chicken dung. The growth of LCQ1801 in the plant substrates of wheat bran, corn flour, soybean meal and rice straw was better than that in the plant substrates of bagasse and coconut coir. Culture flask culture test showed that the number of viable bacteria of LCQ1801 in cow dung and sheep dung reached 16.8 billions·g-1 and 24.0 billions·g-1, respectively. The number of viable bacteria of LCQ1801 in rice straw, soybean meal and corn flour reached 32.2 billions·g-1, 24.9 billions·g-1 and 21.7 billions·g-1, respectively. LCQ1801 hardly grew in the substrate of coconut coir in both culture styles. This study provides strain materials and technical support for biological control of Fusarium wilt of banana.
2025, 16(1): 79-86.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240001
Abstract:
In order to clarify the pathogen causing the leaf spot disease on Areca catechu and its biological characteristics near Huangzhutang Village, Longgun Town, Wanning City, Hainan Province, leaves infected with the leaf spot disease were collected from the plants of Areca catechu in the arecanut plantation in the village. The pathogen causing the leaf spot disease was isolated by using tissue isolation method and purified, and its pathogenicity was determined. Identification of the pathogen was carried out through morphological characteristics and phylogenetic analysis based on multiple genes(ITS, TEF1, CAL, HIS, and TUB). The biological characteristics of the pathogen under different culture conditions were also studied. Results showed that the pathogen causing the leaf spot disease on A. catechu was Diaporthe yunnanensis. The optimal conditions for the pathogen growth were found to be PDA medium, 28 ℃, and pH 6, and light condition is favorable for the growth of the pathogen. This study can provide a theoretic basis for further research on the pathogenicity mechanism of the pathogen, in vitro fungicide screening and development of techniques for prevention and control of the pathogen.
In order to clarify the pathogen causing the leaf spot disease on Areca catechu and its biological characteristics near Huangzhutang Village, Longgun Town, Wanning City, Hainan Province, leaves infected with the leaf spot disease were collected from the plants of Areca catechu in the arecanut plantation in the village. The pathogen causing the leaf spot disease was isolated by using tissue isolation method and purified, and its pathogenicity was determined. Identification of the pathogen was carried out through morphological characteristics and phylogenetic analysis based on multiple genes(ITS, TEF1, CAL, HIS, and TUB). The biological characteristics of the pathogen under different culture conditions were also studied. Results showed that the pathogen causing the leaf spot disease on A. catechu was Diaporthe yunnanensis. The optimal conditions for the pathogen growth were found to be PDA medium, 28 ℃, and pH 6, and light condition is favorable for the growth of the pathogen. This study can provide a theoretic basis for further research on the pathogenicity mechanism of the pathogen, in vitro fungicide screening and development of techniques for prevention and control of the pathogen.
2025, 16(1): 87-97.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240019
Abstract:
Fusarium wilt of banana is one of the major diseases infecting banana. Effectors produced by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cubense(Foc) play an important role during its infection of banana. Previously, a candidate effector FoSSP80 in Foc was screened. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that the FoSSP80 contained a signal peptide without transmembrane structural domains. Furthermore, the FoSSP80 was confirmed to have a secretory function by using the yeast secretion system. Transient expression of FoSSP80 in Nicotiana benthamiana led to inhibition of programmed cell death(PCD) induced by BAX. Moreover, FoSSP80 inhibited the accumulation of reactive oxygen species(ROS) and the callose deposition. The knockout mutant ΔFoSSP80 did not show significant differences in colony morphology, growth rate, and conidial production and pathogenicity compared with the wild-type and complement strains. These results suggested that FoSSP80 is a typical secretory protein and can inhibit plant defense responses.
Fusarium wilt of banana is one of the major diseases infecting banana. Effectors produced by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cubense(Foc) play an important role during its infection of banana. Previously, a candidate effector FoSSP80 in Foc was screened. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that the FoSSP80 contained a signal peptide without transmembrane structural domains. Furthermore, the FoSSP80 was confirmed to have a secretory function by using the yeast secretion system. Transient expression of FoSSP80 in Nicotiana benthamiana led to inhibition of programmed cell death(PCD) induced by BAX. Moreover, FoSSP80 inhibited the accumulation of reactive oxygen species(ROS) and the callose deposition. The knockout mutant ΔFoSSP80 did not show significant differences in colony morphology, growth rate, and conidial production and pathogenicity compared with the wild-type and complement strains. These results suggested that FoSSP80 is a typical secretory protein and can inhibit plant defense responses.
2025, 16(1): 98-106.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240023
Abstract:
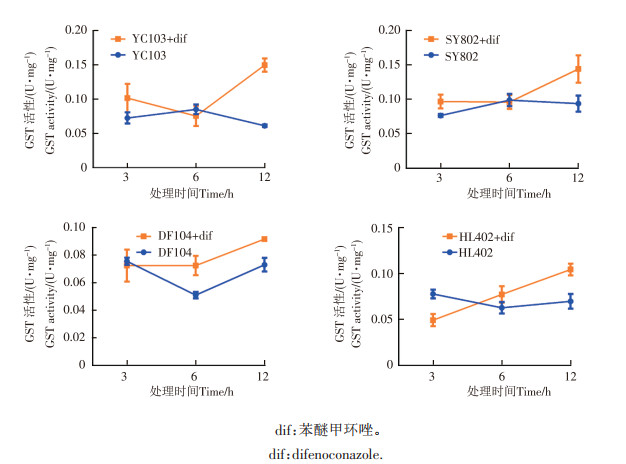
In order to explore the biochemical mechanism of metabolic resistance of Lasiodiplodia theobromae from mango to difenoconazole, some physiological and biochemical indexes of L. theobromae resistant to difenoconazole were determined. The sensitivity of 23 strains of L. theobromae to difenoconazole was tested by using the mycelial growth rate method. The sensitivity test showed that 9 of the 23 isolates were resistant to difenoconazole, with EC50 values being from 5.61 to 28.70 μg·mL-1 Metabolic enzyme inhibitors, diethyl maleate(DEM), piperonylbutoxide(PBO) and triphenyl phosphate(TPP) were selected to mix with difenoconazole to determine their synergistic effect. The results indicated that metabolic enzyme inhibitors all had synergistic effect on resistant isolates when treated with the combination of difenoconazole and DEM, PBO or TPP. After difenoconazole treatment, the enzyme activities of cytochrome P450(P450), glutathione-S-transferase(GST) and carboxylesterase(CarE) were increased. And the enzyme activity of difenoconazole-resistant isolates was significantly higher than sensitive isolates when treated for 12 h. Additionally, UPLC-MS/MS analysis revealed that difenoconazole residual amount of the sensitive isolates increased significantly compared with that of resistant isolates. These results indicate that GST, P450 and CarE may be related to the metabolic resistance of L.theobromae to difenoconazole. The results would provide new insights into the mechanism of pesticide resistance and lay foundation for in-depth analysis of the molecular mechanism of metabolic resistance to difenoconazole.
In order to explore the biochemical mechanism of metabolic resistance of Lasiodiplodia theobromae from mango to difenoconazole, some physiological and biochemical indexes of L. theobromae resistant to difenoconazole were determined. The sensitivity of 23 strains of L. theobromae to difenoconazole was tested by using the mycelial growth rate method. The sensitivity test showed that 9 of the 23 isolates were resistant to difenoconazole, with EC50 values being from 5.61 to 28.70 μg·mL-1 Metabolic enzyme inhibitors, diethyl maleate(DEM), piperonylbutoxide(PBO) and triphenyl phosphate(TPP) were selected to mix with difenoconazole to determine their synergistic effect. The results indicated that metabolic enzyme inhibitors all had synergistic effect on resistant isolates when treated with the combination of difenoconazole and DEM, PBO or TPP. After difenoconazole treatment, the enzyme activities of cytochrome P450(P450), glutathione-S-transferase(GST) and carboxylesterase(CarE) were increased. And the enzyme activity of difenoconazole-resistant isolates was significantly higher than sensitive isolates when treated for 12 h. Additionally, UPLC-MS/MS analysis revealed that difenoconazole residual amount of the sensitive isolates increased significantly compared with that of resistant isolates. These results indicate that GST, P450 and CarE may be related to the metabolic resistance of L.theobromae to difenoconazole. The results would provide new insights into the mechanism of pesticide resistance and lay foundation for in-depth analysis of the molecular mechanism of metabolic resistance to difenoconazole.
2025, 16(1): 107-114.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240078
Abstract:
An attempt was made to identify pathogens causing stem rot of Acacia mangium in Hainan and their biological characteristics to provide scientific theoretical basis for the occurrence and prevention of stem rot of A.mangium. The pathogens causing stem rot of A. mangium in Hainan were isolated and cultured by conventional tissue isolation method, and the representative strain HNBSMZXS20211011001 was obtained after purification.The pathogenicity of the isolated strain was tested by using Koch’s method and induced basidiocarp in the field.The results were consistent with the symptoms of plant disease in the field. The verification of Koch’s method was hence completed. According to the morphological characteristics of basidiocarps and basidiospores and molecular phylogenetic analysis of ITS, SSU, LSU and TEF1-α sequences, the Amauroderma pathogen causing stem rot of A. mangium in Hainan was identified as Amauroderma subresinosum. The colony of the pathogen cultured in PDA medium at 28 ℃ in darkness was round. At the early stage of growth, the colony was white and dense in the center, sparse and transparent on the edge, and it was light yellow in the late stage of growth. The biological characteristics of the strain showed that the pathogen had an optimum growth when cultured on PDA medium at 28 ℃ in darkness and pH5.
An attempt was made to identify pathogens causing stem rot of Acacia mangium in Hainan and their biological characteristics to provide scientific theoretical basis for the occurrence and prevention of stem rot of A.mangium. The pathogens causing stem rot of A. mangium in Hainan were isolated and cultured by conventional tissue isolation method, and the representative strain HNBSMZXS20211011001 was obtained after purification.The pathogenicity of the isolated strain was tested by using Koch’s method and induced basidiocarp in the field.The results were consistent with the symptoms of plant disease in the field. The verification of Koch’s method was hence completed. According to the morphological characteristics of basidiocarps and basidiospores and molecular phylogenetic analysis of ITS, SSU, LSU and TEF1-α sequences, the Amauroderma pathogen causing stem rot of A. mangium in Hainan was identified as Amauroderma subresinosum. The colony of the pathogen cultured in PDA medium at 28 ℃ in darkness was round. At the early stage of growth, the colony was white and dense in the center, sparse and transparent on the edge, and it was light yellow in the late stage of growth. The biological characteristics of the strain showed that the pathogen had an optimum growth when cultured on PDA medium at 28 ℃ in darkness and pH5.
2025, 16(1): 115-124.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240026
Abstract:
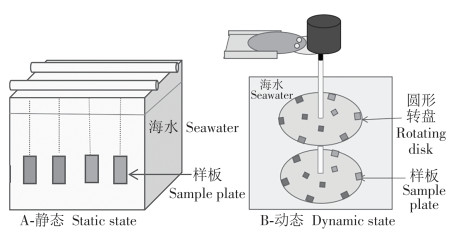
To reveal the impact of hydrodynamic changes on eukaryotic microbial communities in marine fouling,outdoor microcosm experiments were conducted by employing environmental microbial high-throughput sequencing technology to investigate the compositional structure and functional characteristics of eukaryotic microbial communities under different hydrodynamic conditions. There were 146 genus of eukaryotic microorganisms belonging to 18 phylum detected. Clustering analysis reveals significant differences in the microbial community structures between dynamic and static sample groups. The dominant phyla and genera in eukaryotic microbial communities varied under different materials and hydrodynamic conditions. Specifically, in the static group, the phylum Nematoda was dominant, with the genus Mononchus being the most abundant. In the dynamic group the dominant microbial phylum on the surface of the weak hydrodynamic group was Chlorophyta on the materials of fiber reinforced plastics and aluminum alloy, while it was Nematoda in the transferred group.The dominant microbial phylum on the surfaces of the strong hydrodynamic group on all the three materials was Haptophyta, but the community richness and diversity were lower in the strong hydrodynamic group. Cluster analysis revealed significant differences in microbial community structure between dynamic and static sample groups. Moreover, there were differences in metabolic pathways among communities under different hydrodynamic conditions, indicating that changes in hydrodynamic conditions also altered the correlations among species in the eukaryotic microbial community.
To reveal the impact of hydrodynamic changes on eukaryotic microbial communities in marine fouling,outdoor microcosm experiments were conducted by employing environmental microbial high-throughput sequencing technology to investigate the compositional structure and functional characteristics of eukaryotic microbial communities under different hydrodynamic conditions. There were 146 genus of eukaryotic microorganisms belonging to 18 phylum detected. Clustering analysis reveals significant differences in the microbial community structures between dynamic and static sample groups. The dominant phyla and genera in eukaryotic microbial communities varied under different materials and hydrodynamic conditions. Specifically, in the static group, the phylum Nematoda was dominant, with the genus Mononchus being the most abundant. In the dynamic group the dominant microbial phylum on the surface of the weak hydrodynamic group was Chlorophyta on the materials of fiber reinforced plastics and aluminum alloy, while it was Nematoda in the transferred group.The dominant microbial phylum on the surfaces of the strong hydrodynamic group on all the three materials was Haptophyta, but the community richness and diversity were lower in the strong hydrodynamic group. Cluster analysis revealed significant differences in microbial community structure between dynamic and static sample groups. Moreover, there were differences in metabolic pathways among communities under different hydrodynamic conditions, indicating that changes in hydrodynamic conditions also altered the correlations among species in the eukaryotic microbial community.
2025, 16(1): 125-133.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240035
Abstract:
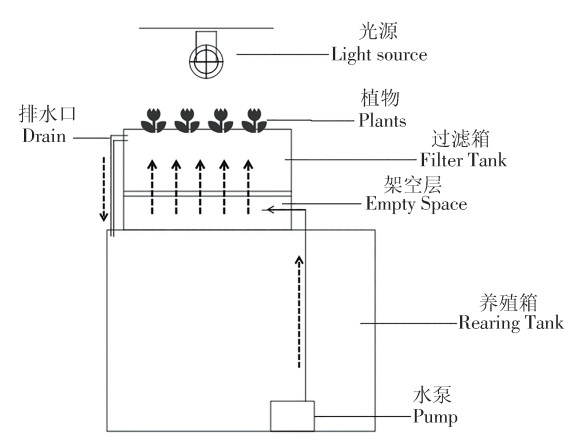
Four different species of plant were compared in terms of their effects on nitrogen transformation during the microbial biofilm forming period and post-forming period in the bog filtration system in order to provide a scientific basis for the construction of an effective bog filtration system for treating aquaculture wastewater. The results showed that all the treatment groups reached a peak in concentration of ammonia nitrogen in on the 5th day and then declined, initially increased and then decreased in the concentration of nitrite, and gradually increased in the concentration of nitrate before slightly decreasing. All experimental groups have lower concentrations of nitrate compared to the control group. MC group had the highest biomass growth(fresh weight increase of(56.87 ± 1.81) g, plant height increase of(30.7 ± 4.12) cm, root length increase of(7.70 ± 2.52) cm)and had the best effect on inorganic nitrogen transformation and absorption of nitrate(with a 71.1% lower concentration of nitrate on the 30th day compared to the control group). In the post-biofilm-forming expermient,MC group had the fastest ammonia nitrogen removal time(84 hours) and a nitrate removal rate of 25.6%, higher than the other treatment groups. In conclusion, the MC group exhibited the best performance in the transformation and absorption of nitrogen, providing an efficient filtration method for recirculating water treatment in aquaculture and offering valuable guidance for plant selection in bog filtration systems.
Four different species of plant were compared in terms of their effects on nitrogen transformation during the microbial biofilm forming period and post-forming period in the bog filtration system in order to provide a scientific basis for the construction of an effective bog filtration system for treating aquaculture wastewater. The results showed that all the treatment groups reached a peak in concentration of ammonia nitrogen in on the 5th day and then declined, initially increased and then decreased in the concentration of nitrite, and gradually increased in the concentration of nitrate before slightly decreasing. All experimental groups have lower concentrations of nitrate compared to the control group. MC group had the highest biomass growth(fresh weight increase of(56.87 ± 1.81) g, plant height increase of(30.7 ± 4.12) cm, root length increase of(7.70 ± 2.52) cm)and had the best effect on inorganic nitrogen transformation and absorption of nitrate(with a 71.1% lower concentration of nitrate on the 30th day compared to the control group). In the post-biofilm-forming expermient,MC group had the fastest ammonia nitrogen removal time(84 hours) and a nitrate removal rate of 25.6%, higher than the other treatment groups. In conclusion, the MC group exhibited the best performance in the transformation and absorption of nitrogen, providing an efficient filtration method for recirculating water treatment in aquaculture and offering valuable guidance for plant selection in bog filtration systems.
2025, 16(1): 134-151.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240042
Abstract:
Three common submerged plants, Hydrilla verticillata, Elodea nuttallii and Ceratophyllum demersum,collected in Hainan Province were cultured in aquaculture effluent prepared to explore their effects under different factors such as temperature, illumination intensity and plant density on the purification efficiency of simulated tilapia aquaculture effluent in an indoor static water culture experiment. The submerged plants with the best purification efficiency for the effluent treatment were screened. The results showed C. demersum had best comprehensive removal efficiency, with removal rates of NH4+-N, PO43--P, NO2--N and NO3--N being upto 67.11%,78.92%, 96.89% and 75.04%, respectively. H. verticillata and E. nuttallii had best purification efficiency at the plant density of 6.4 g·L-1, while the comprehensive purification efficiency of C. demersum at the plant densities of 6.4 and 4.4 g·L-1 were similar. E. nuttallii and C. demersum reduced the removal rates of NH4+-N by 26.54% and 62.36%, respectively, at the illumination intensity of 6 000 lx as against those at 18 000 lx, and. meanwhile H.verticillata completely lost the water purification ability, indicating that high light intensity might inhibit the growth of plants and reduce the efficiency of water purification.
Three common submerged plants, Hydrilla verticillata, Elodea nuttallii and Ceratophyllum demersum,collected in Hainan Province were cultured in aquaculture effluent prepared to explore their effects under different factors such as temperature, illumination intensity and plant density on the purification efficiency of simulated tilapia aquaculture effluent in an indoor static water culture experiment. The submerged plants with the best purification efficiency for the effluent treatment were screened. The results showed C. demersum had best comprehensive removal efficiency, with removal rates of NH4+-N, PO43--P, NO2--N and NO3--N being upto 67.11%,78.92%, 96.89% and 75.04%, respectively. H. verticillata and E. nuttallii had best purification efficiency at the plant density of 6.4 g·L-1, while the comprehensive purification efficiency of C. demersum at the plant densities of 6.4 and 4.4 g·L-1 were similar. E. nuttallii and C. demersum reduced the removal rates of NH4+-N by 26.54% and 62.36%, respectively, at the illumination intensity of 6 000 lx as against those at 18 000 lx, and. meanwhile H.verticillata completely lost the water purification ability, indicating that high light intensity might inhibit the growth of plants and reduce the efficiency of water purification.
2025, 16(1): 152-162.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240097
Abstract:
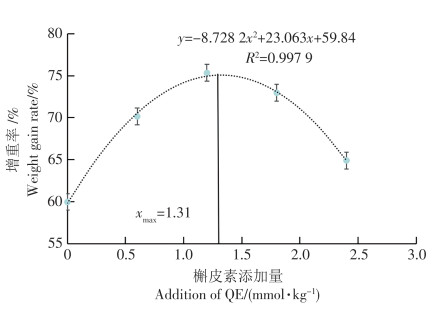
An attempt was made to investigate the effects of quercetin(QE) added in the diet on the growth performance, serum and liver antioxidant capacity, and intestinal microflora of Epinephelus akaara. The QE was added to the basal feed at the respective concentrations of 0(FM), 0.60(QE1), 0.12(QE2), 0.18(QE3) and 0.24(QE4) mmol · kg-1, and used to feed E. akaara with its initial weight(150 ± 5.17) g for 56 days. The growth performance, and the antioxidant enzyme activities of serum and liver were measured, and the intestinal flora structure were analyzed by using high-throughput sequencing. The results showed that the growth rate(WGR)tended to increase and then decrease with the increase of QE in the diet, but was significantly higher than that of the control group(P < 0.05), and was the highest in the QE2 group. Compared with the FM group,supplementation of QE in the feed significantly increased the activities of serum glutathione peroxidase(GPX)activity(P < 0.05) and reduced the content of malondialdehyde(MDA)(P < 0.05). An appropriate addition of QE significantly increased the activities of liver enzymes such as SOD, CAT, and GPX(P < 0.05), and reduced the content of MDA in the liver(P < 0.05). Compared with the FM group, the number of operational taxonomic units(OTUs) in each QE addition group showed an upward trend, and increased significantly in the QE3 and QE4groups(P < 0.05). Alpha diversity showed that compared to the control group, the QE3 and QE4 groups showed a significantly upward trend in the ACE, Chao1, Shannon index, and a significantly downward trend in the Simpson index(P < 0.05). Beta diversity analysis showed significant differences between the QE3 and QE4 groups and the FM group(P < 0.05). Compared with the FM group, the relative abundance of Fusobacteriota in each group with QE addition was significantly reduced(P < 0.05); the relative abundance of genera Staphylococcus and Desulfovibrio decreased significantly(P < 0.05), while the relative abundance of genus Turicibacter increased significantly(P < 0.05). In summary, adding of QE at a rate of 1.2-2.4 mmol·kg-1 to the diet can improve the growth performance and antioxidant enzyme activity of E. akaara, and enhance its intestinal microbial diversity and intestinal microbiota composition.
An attempt was made to investigate the effects of quercetin(QE) added in the diet on the growth performance, serum and liver antioxidant capacity, and intestinal microflora of Epinephelus akaara. The QE was added to the basal feed at the respective concentrations of 0(FM), 0.60(QE1), 0.12(QE2), 0.18(QE3) and 0.24(QE4) mmol · kg-1, and used to feed E. akaara with its initial weight(150 ± 5.17) g for 56 days. The growth performance, and the antioxidant enzyme activities of serum and liver were measured, and the intestinal flora structure were analyzed by using high-throughput sequencing. The results showed that the growth rate(WGR)tended to increase and then decrease with the increase of QE in the diet, but was significantly higher than that of the control group(P < 0.05), and was the highest in the QE2 group. Compared with the FM group,supplementation of QE in the feed significantly increased the activities of serum glutathione peroxidase(GPX)activity(P < 0.05) and reduced the content of malondialdehyde(MDA)(P < 0.05). An appropriate addition of QE significantly increased the activities of liver enzymes such as SOD, CAT, and GPX(P < 0.05), and reduced the content of MDA in the liver(P < 0.05). Compared with the FM group, the number of operational taxonomic units(OTUs) in each QE addition group showed an upward trend, and increased significantly in the QE3 and QE4groups(P < 0.05). Alpha diversity showed that compared to the control group, the QE3 and QE4 groups showed a significantly upward trend in the ACE, Chao1, Shannon index, and a significantly downward trend in the Simpson index(P < 0.05). Beta diversity analysis showed significant differences between the QE3 and QE4 groups and the FM group(P < 0.05). Compared with the FM group, the relative abundance of Fusobacteriota in each group with QE addition was significantly reduced(P < 0.05); the relative abundance of genera Staphylococcus and Desulfovibrio decreased significantly(P < 0.05), while the relative abundance of genus Turicibacter increased significantly(P < 0.05). In summary, adding of QE at a rate of 1.2-2.4 mmol·kg-1 to the diet can improve the growth performance and antioxidant enzyme activity of E. akaara, and enhance its intestinal microbial diversity and intestinal microbiota composition.


 Abstract
Abstract PDF 7543KB
PDF 7543KB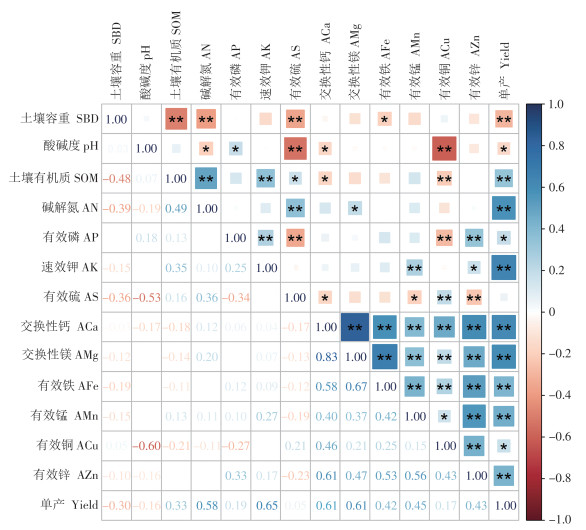








 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS