2024 Vol. 15, No. 6
2024, 15(6): 655-663.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240109
Abstract:
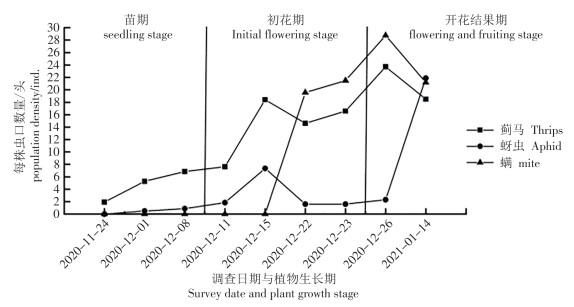
Pest surveys were made by using both visual observation and color plates attraction to investigate the occurrence and population dynamics of major pests, including thrips, in pepper fields of Sanya’s main winter vegetable production regions in Hainan. Our findings reveal that thrips was the main pest in both conventionally treated and untreated pepper fields. Untreated chili fields harbored a diverse array of pests, spanning six orders,eight families, and 14 species, with thrips, aphids, Polyphagotarsonemus latus(Banks), and Bemisia tabaci(Gennadius) being the most prevalent. Notably, Thrips palmi Karny was dominant throughout the growth cycle in the untreated pepper field, while Frankliniella intonsa(Trybom) prevailed during the middle to late flowering stages. These dominances, expressed as indices, were 0.795 5, 0.762 8, 0.542 1, and 0.076 9, respectively at the seedling stage and the prophase and the middle and late stages of flowering and fruiting, with a minor presence of Megalurothrips usitatus(Bagnll). Infestation peaks emerge during the initial and second flowering stages of peppers, while Polyphagotarsonemus latus(Banks) outbreaks occur during flowering. In conventionally pesticidetreated pepper fields, thrips remain the major pest, dominating the entire growth cycle. Their population dominance indices, ranging from 0.412 6 to 0.6707, were higher than those of T.palmi and M.usitatus. During flowering and fruiting, multiple population peaks occur, particularly during the initial flowering, first and second flowering phases, and late flowering and fruiting periods. The second flowering stage marked the climax of the pest outbreak, with a stunning count of 55 thrips per plant, significantly surpassing other growth phases. In conclusion, notable disparities exist in pest species, occurrence trends, and prevailing species between untreated and conventionally treated pepper fields. Regardless of management approach, thrips emerge as the primary menace, and their emergence patterns align closely with pepper’s flowering cycle. Two distinct pest outbreaks accompany the peak flowering seasons. This research sheds light on the infestation trends of primary chili pepper pests in Sanya, Hainan’s key winter vegetable production hub, and delves into the dynamics of prevalent thrip species. This insight offers invaluable theoretical direction for forecasting chili pest infestations in Hainan’s tropical regions and devising effective prevention and control strategies.
Pest surveys were made by using both visual observation and color plates attraction to investigate the occurrence and population dynamics of major pests, including thrips, in pepper fields of Sanya’s main winter vegetable production regions in Hainan. Our findings reveal that thrips was the main pest in both conventionally treated and untreated pepper fields. Untreated chili fields harbored a diverse array of pests, spanning six orders,eight families, and 14 species, with thrips, aphids, Polyphagotarsonemus latus(Banks), and Bemisia tabaci(Gennadius) being the most prevalent. Notably, Thrips palmi Karny was dominant throughout the growth cycle in the untreated pepper field, while Frankliniella intonsa(Trybom) prevailed during the middle to late flowering stages. These dominances, expressed as indices, were 0.795 5, 0.762 8, 0.542 1, and 0.076 9, respectively at the seedling stage and the prophase and the middle and late stages of flowering and fruiting, with a minor presence of Megalurothrips usitatus(Bagnll). Infestation peaks emerge during the initial and second flowering stages of peppers, while Polyphagotarsonemus latus(Banks) outbreaks occur during flowering. In conventionally pesticidetreated pepper fields, thrips remain the major pest, dominating the entire growth cycle. Their population dominance indices, ranging from 0.412 6 to 0.6707, were higher than those of T.palmi and M.usitatus. During flowering and fruiting, multiple population peaks occur, particularly during the initial flowering, first and second flowering phases, and late flowering and fruiting periods. The second flowering stage marked the climax of the pest outbreak, with a stunning count of 55 thrips per plant, significantly surpassing other growth phases. In conclusion, notable disparities exist in pest species, occurrence trends, and prevailing species between untreated and conventionally treated pepper fields. Regardless of management approach, thrips emerge as the primary menace, and their emergence patterns align closely with pepper’s flowering cycle. Two distinct pest outbreaks accompany the peak flowering seasons. This research sheds light on the infestation trends of primary chili pepper pests in Sanya, Hainan’s key winter vegetable production hub, and delves into the dynamics of prevalent thrip species. This insight offers invaluable theoretical direction for forecasting chili pest infestations in Hainan’s tropical regions and devising effective prevention and control strategies.
2024, 15(6): 664-671.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240089
Abstract:
Mortality rates of 1-6 instar larvae and pupae of Spodoptera frugiperda under low temperature conditions were measured in the laboratory to explore the cold resistance of the larvae and pupae of S. frugiperda(J. E. Smith). The linear regression equation was fitted and the discriminating temperatures at each developmental stage were calculated. The discriminating temperatures for 1-6 instar larvae and pupae were-7.80 ℃,-9.70 ℃,-9.61 ℃,-8.78 ℃,-8.29 ℃,-8.05 ℃ and-9.51 ℃, respectively. The expression of Hsp70gene(GenBank accession number: NC_064223.1) and Hsp90 gene(GenBank accession number: MN832694) of S. frugiperda reared at room temperature and treated at low temperature was analyzed by using quantitative realtime PCR. The results showed that the expression levels of Hsp70 gene and Hsp90 gene of S. frugiperda reared at room temperature and treated at low temperature were different at different developmental stages. After low temperature treatment, the expression level of Hsp70 gene in the first instar larvae was significantly reduced(P < 0.05), while the expression levels in 2nd-6th instar larvae and pupae were significantly increased(P < 0.01). The expression level of Hsp90 gene in 1st-6th instar larvae was significantly increased(P < 0.01), and the expression level in pupae was significantly decreased(P < 0.01).
Mortality rates of 1-6 instar larvae and pupae of Spodoptera frugiperda under low temperature conditions were measured in the laboratory to explore the cold resistance of the larvae and pupae of S. frugiperda(J. E. Smith). The linear regression equation was fitted and the discriminating temperatures at each developmental stage were calculated. The discriminating temperatures for 1-6 instar larvae and pupae were-7.80 ℃,-9.70 ℃,-9.61 ℃,-8.78 ℃,-8.29 ℃,-8.05 ℃ and-9.51 ℃, respectively. The expression of Hsp70gene(GenBank accession number: NC_064223.1) and Hsp90 gene(GenBank accession number: MN832694) of S. frugiperda reared at room temperature and treated at low temperature was analyzed by using quantitative realtime PCR. The results showed that the expression levels of Hsp70 gene and Hsp90 gene of S. frugiperda reared at room temperature and treated at low temperature were different at different developmental stages. After low temperature treatment, the expression level of Hsp70 gene in the first instar larvae was significantly reduced(P < 0.05), while the expression levels in 2nd-6th instar larvae and pupae were significantly increased(P < 0.01). The expression level of Hsp90 gene in 1st-6th instar larvae was significantly increased(P < 0.01), and the expression level in pupae was significantly decreased(P < 0.01).
2024, 15(6): 672-682.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240130
Abstract:
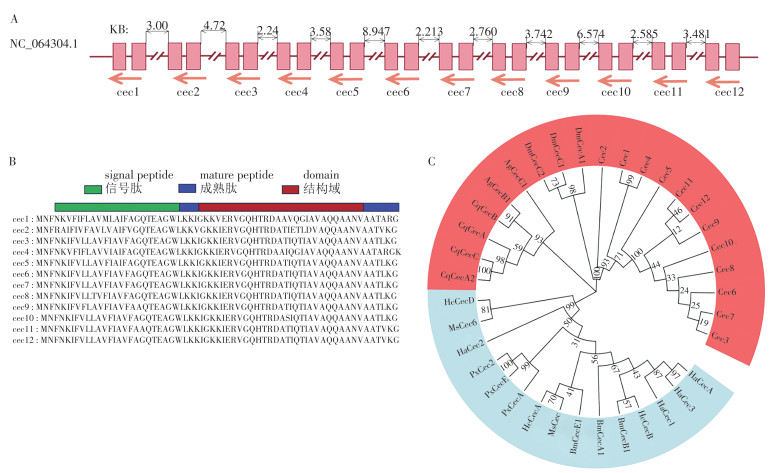
The antimicrobial peptide(AMP) genes of Bactrocera dorsalis were identified at the genome level to explore potential AMPs for the control of B. dorsalis. The composition, structural features, and phylogenetic relationships of AMPs across different insect species were analyzed by using bioinformatics methods based on chromosome-level genomic data. Furthermore, expression profiles of AMPs at different developmental stages in six adult parts were examined by employing qRT-PCRe. A total of 29 AMP genes were identified, including 12cecropins, 11 defensins, 4 attacins, and 2 diptericins. The genomic and protein structures indicate that B. dorsalis AMP molecules and structures exhibit genetic diversity mechanisms, including gene duplication. The expression profiles of AMPs at different developmental stages revealed that most AMPs are highly expressed during the pupal and adult stages. The expression characteristics of different types of AMPs varied significantly in different body parts, and apart from the hemolymph, individual genes were also expressed in the head and integument.These findings provide a database and information for further research on the functions of B. dorsalis AMPs.
The antimicrobial peptide(AMP) genes of Bactrocera dorsalis were identified at the genome level to explore potential AMPs for the control of B. dorsalis. The composition, structural features, and phylogenetic relationships of AMPs across different insect species were analyzed by using bioinformatics methods based on chromosome-level genomic data. Furthermore, expression profiles of AMPs at different developmental stages in six adult parts were examined by employing qRT-PCRe. A total of 29 AMP genes were identified, including 12cecropins, 11 defensins, 4 attacins, and 2 diptericins. The genomic and protein structures indicate that B. dorsalis AMP molecules and structures exhibit genetic diversity mechanisms, including gene duplication. The expression profiles of AMPs at different developmental stages revealed that most AMPs are highly expressed during the pupal and adult stages. The expression characteristics of different types of AMPs varied significantly in different body parts, and apart from the hemolymph, individual genes were also expressed in the head and integument.These findings provide a database and information for further research on the functions of B. dorsalis AMPs.
2024, 15(6): 683-690.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240077
Abstract:
A peptide sequence was identified from antimicrobial proteins in Trichoderma viride based on the denovo mass spectrometry determination. Through BLASTp database searching, it was found that this peptide sequence is encoded by a alkaline proteinase gene, and the target gene fragment was amplified using homologybased cloning. Bioinformatics analysis reveals that the TvALP gene(GenBank number KJ659907) has a complete open reading frame of 1 230 bp and encodes a protein composed of 409 amino acids. This protein has a predicted molecular weight of about 43 kD, and an isoelectric point of 7.96, and contains a signal peptide composed of 20amino acids. According to classification, the protein belongs to the peptidase inhibitor_I9 superfamily and is a member of the subtilisin serine protease S8 family. The sequenced plasmid was ligated into the prokaryotic expression vector pET30a using double digestion, and the expression was induced in the host bacterium BL21(DE3)pLysS. The result showed a specific protein band at 45 kD, which was consistent with the predicted size of the target protein, indicating that the expression plasmid pET30a-ΔTvALP(“Δ” Signaling peptide excision) was successfully expressed in the host bacterium BL21(DE3)pLysS. After sonication, the protein formed inclusion bodies. However, after in vitro renaturation, no active protein was obtained for antibacterial mechanism research.
A peptide sequence was identified from antimicrobial proteins in Trichoderma viride based on the denovo mass spectrometry determination. Through BLASTp database searching, it was found that this peptide sequence is encoded by a alkaline proteinase gene, and the target gene fragment was amplified using homologybased cloning. Bioinformatics analysis reveals that the TvALP gene(GenBank number KJ659907) has a complete open reading frame of 1 230 bp and encodes a protein composed of 409 amino acids. This protein has a predicted molecular weight of about 43 kD, and an isoelectric point of 7.96, and contains a signal peptide composed of 20amino acids. According to classification, the protein belongs to the peptidase inhibitor_I9 superfamily and is a member of the subtilisin serine protease S8 family. The sequenced plasmid was ligated into the prokaryotic expression vector pET30a using double digestion, and the expression was induced in the host bacterium BL21(DE3)pLysS. The result showed a specific protein band at 45 kD, which was consistent with the predicted size of the target protein, indicating that the expression plasmid pET30a-ΔTvALP(“Δ” Signaling peptide excision) was successfully expressed in the host bacterium BL21(DE3)pLysS. After sonication, the protein formed inclusion bodies. However, after in vitro renaturation, no active protein was obtained for antibacterial mechanism research.
2024, 15(6): 691-699.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230126
Abstract:
Leaves of virus-free seedlings of Passiflora edulis ‘Qinmi 9’ and suspected diseased P. edulis plants were collected for extraction of nucleic acids. P. edulis virus detection primers were designed according to the conserved regions of P. edulis woodiness virus, P. edulis mottle virus, East Asian Passiflora virus, Telosma mosaic virus, P. edulis leaf distortion virus, Euphorbia leaf curl virus, Papaya leaf curl Guangdong virus and Cucumber mosaic virus., and the virus species in different samples were identified by using PCR method. No suspected virus fragments were amplified from the virus-free seedlings of P. edulis. A total of five possible virus fragments were amplified from suspected infected P. edulis seedling samples in the field. They were identified by sequencing as East Asian P. edulis virus,Telosma mosaic virus and Euphorbia leaf curl virus, Papaya leaf curl Guangdong virus. Sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis showed that the PCR products had a high homology with the virus strains from Taiwan Province of China, the Republic of Korea, Fujian Province of China and other regions. The ‘Qinmi 9’ plant planted locally in Zhanjiang was confirmed to carry the virus EAPV, TeMV, EuLCV, PaLCuGDV. This is also the first time that viruses EAPV, PaLCuGV and EuLCV were detected in P. edulis in Guangdong, China.
Leaves of virus-free seedlings of Passiflora edulis ‘Qinmi 9’ and suspected diseased P. edulis plants were collected for extraction of nucleic acids. P. edulis virus detection primers were designed according to the conserved regions of P. edulis woodiness virus, P. edulis mottle virus, East Asian Passiflora virus, Telosma mosaic virus, P. edulis leaf distortion virus, Euphorbia leaf curl virus, Papaya leaf curl Guangdong virus and Cucumber mosaic virus., and the virus species in different samples were identified by using PCR method. No suspected virus fragments were amplified from the virus-free seedlings of P. edulis. A total of five possible virus fragments were amplified from suspected infected P. edulis seedling samples in the field. They were identified by sequencing as East Asian P. edulis virus,Telosma mosaic virus and Euphorbia leaf curl virus, Papaya leaf curl Guangdong virus. Sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis showed that the PCR products had a high homology with the virus strains from Taiwan Province of China, the Republic of Korea, Fujian Province of China and other regions. The ‘Qinmi 9’ plant planted locally in Zhanjiang was confirmed to carry the virus EAPV, TeMV, EuLCV, PaLCuGDV. This is also the first time that viruses EAPV, PaLCuGV and EuLCV were detected in P. edulis in Guangdong, China.
2024, 15(6): 700-708.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240125
Abstract:
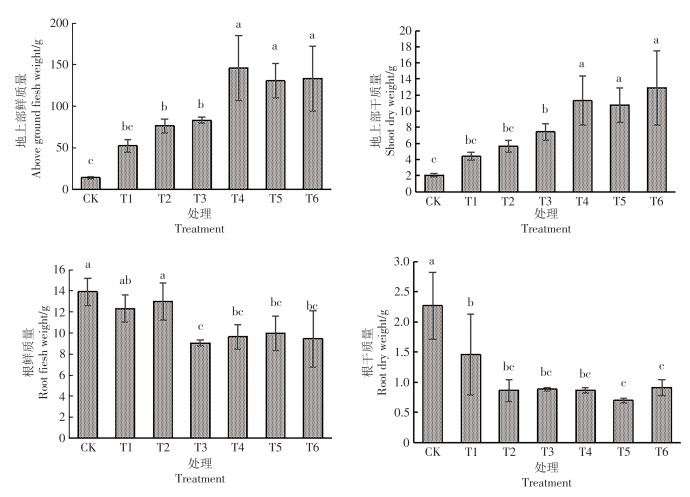
In order to study the effect of nutrient solution concentration on the vegetable value and ornamental value of hydroponic vegetable sweetpotato, the vegetable sweetpotato ‘Haida 7791’ was used for hydroponic culture with Japanese garden formula as the basic nutrient solution formula, and clear water as the control. Seven treatments were designed: control treatment(CK) and treatments T1, T2, T3, T4, T5 and T6, in which ‘Haida 7791’ was treated with 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, and 2.5 times the concentration of the basic nutrient solution,respectively, to study the effects of different nutrient solution concentrations on its vegetable value and ornamental value. The results show that an increase in the concentration of the basic nutrient solution within a certain range significantly promoted plant growth and increased the dry and fresh weight of the aboveground part.The yield increased gradually with the nutrient solution concentration. The yield and total yield of the three harvests showed that the treatments T4-T6 yielded higher. In terms of vegetable quality, CK had the best vitamin C and soluble sugar content, and the lowest nitrate nitrogen content. T4 was the highest in chlorophyll content,and CK was the highest in root activity. In terms of top heart leaf color, treatments with low concentrations of the basic nutrient solution was more conducive to the accumulation of anthocyanin, among which CK was the highest in relative content of anthocyanin. The total content of chlorophyll in top heart leaf was the highest in T4. The leaf color parameters was consistent with the relative content of anthocyanin and chlorophyll content. In summary, in terms of vegetable value, T4 had high biomass and high yield, while CK was the highest in soluble sugar content and vitamin C content, the lowest in nitrate nitrogen content and hence the best in nutritional quality. Combined with the performance of yield and quality, it can be considered to use 1.5 times the concentration of the basic nutrient solution at the early and middle stages of growth, and change to clear water at the late stage of growth(before harvest). In terms of ornamental value, CK was the highest in anthocyanin content and reddest in top heart leaf vein, and T4 was the highest in chlorophyll content. Consumers can choose freely vegetable sweetpotato plants cultured in CK and T4 according to their preferences for red or green.
In order to study the effect of nutrient solution concentration on the vegetable value and ornamental value of hydroponic vegetable sweetpotato, the vegetable sweetpotato ‘Haida 7791’ was used for hydroponic culture with Japanese garden formula as the basic nutrient solution formula, and clear water as the control. Seven treatments were designed: control treatment(CK) and treatments T1, T2, T3, T4, T5 and T6, in which ‘Haida 7791’ was treated with 0, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2, and 2.5 times the concentration of the basic nutrient solution,respectively, to study the effects of different nutrient solution concentrations on its vegetable value and ornamental value. The results show that an increase in the concentration of the basic nutrient solution within a certain range significantly promoted plant growth and increased the dry and fresh weight of the aboveground part.The yield increased gradually with the nutrient solution concentration. The yield and total yield of the three harvests showed that the treatments T4-T6 yielded higher. In terms of vegetable quality, CK had the best vitamin C and soluble sugar content, and the lowest nitrate nitrogen content. T4 was the highest in chlorophyll content,and CK was the highest in root activity. In terms of top heart leaf color, treatments with low concentrations of the basic nutrient solution was more conducive to the accumulation of anthocyanin, among which CK was the highest in relative content of anthocyanin. The total content of chlorophyll in top heart leaf was the highest in T4. The leaf color parameters was consistent with the relative content of anthocyanin and chlorophyll content. In summary, in terms of vegetable value, T4 had high biomass and high yield, while CK was the highest in soluble sugar content and vitamin C content, the lowest in nitrate nitrogen content and hence the best in nutritional quality. Combined with the performance of yield and quality, it can be considered to use 1.5 times the concentration of the basic nutrient solution at the early and middle stages of growth, and change to clear water at the late stage of growth(before harvest). In terms of ornamental value, CK was the highest in anthocyanin content and reddest in top heart leaf vein, and T4 was the highest in chlorophyll content. Consumers can choose freely vegetable sweetpotato plants cultured in CK and T4 according to their preferences for red or green.
2024, 15(6): 709-717.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240064
Abstract:
The variations in nutritional composition and physicochemical properties among different banana varieties are crucial for their processing purposes. However, inadequate understanding of the nutritional composition and physicochemical properties of many banana varieties currently restricts the potential for in-depth processing and utilization of diverse banana varieties. To delve into the potential application value of bananas, a ripening time series experiment was conducted for deep analysis of the physicochemical characteristics and nutritional value of eight different banana varieties at three stages of ripening. Principal component analysis(PCA) of multi-components of banana fruits found that there was a significant change in soluble sugar content among varieties as ripeness increased, with the Lady Finger variety being the highest in soluble sugar content(22.75%) at the third ripening stage(S3), while the Pome variety being the highest in starch content(54.77%) at the first ripening stage(S1). Starch content decreased with ripeness, and was still 7.96% in the Pome variety at full ripeness. Moreover, the contents of pectin and titrable acidity were closely related to soluble sugar, and the contents of fat, protein, titrable acidity, and vitamin C were observed significantly different in varieties at different ripening stages. PCA analysis revealed significant differences in the composition of banana fruits of different varieties at different ripening stages, providing a scientific basis for selecting suitable varieties and ripening stages for processing.
The variations in nutritional composition and physicochemical properties among different banana varieties are crucial for their processing purposes. However, inadequate understanding of the nutritional composition and physicochemical properties of many banana varieties currently restricts the potential for in-depth processing and utilization of diverse banana varieties. To delve into the potential application value of bananas, a ripening time series experiment was conducted for deep analysis of the physicochemical characteristics and nutritional value of eight different banana varieties at three stages of ripening. Principal component analysis(PCA) of multi-components of banana fruits found that there was a significant change in soluble sugar content among varieties as ripeness increased, with the Lady Finger variety being the highest in soluble sugar content(22.75%) at the third ripening stage(S3), while the Pome variety being the highest in starch content(54.77%) at the first ripening stage(S1). Starch content decreased with ripeness, and was still 7.96% in the Pome variety at full ripeness. Moreover, the contents of pectin and titrable acidity were closely related to soluble sugar, and the contents of fat, protein, titrable acidity, and vitamin C were observed significantly different in varieties at different ripening stages. PCA analysis revealed significant differences in the composition of banana fruits of different varieties at different ripening stages, providing a scientific basis for selecting suitable varieties and ripening stages for processing.
2024, 15(6): 718-727.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240117
Abstract:
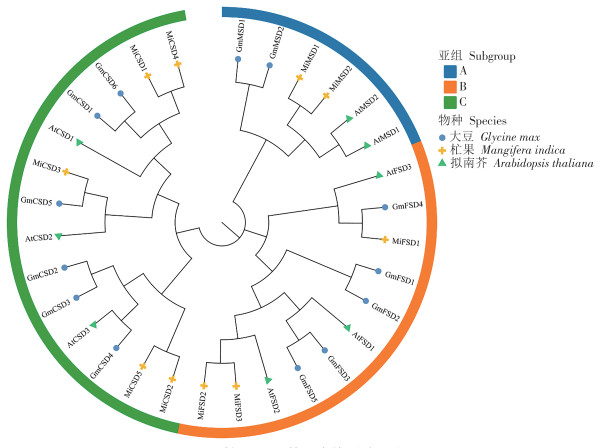
Superoxide dismutase(SOD) is an important enzyme in the plant antioxidant system, playing a crucial role in plant growth and development. An attempt was made to analyze the gene function of MiSOD and its expression patterns in different tissues and under enhanced UV-B irradiation. Members of the MiSOD gene family from multiple aspects such as protein characteristics, phylogenetic relationships, gene structure, and promoter cis acting elements were identified by using the mango genome and bioinformatics methods, and the expression patterns of MiSOD gene family members were identified by using the transcriptome analysis. A total of 10 SOD genes were identified in the mango fruit, and most of the MiSOD proteins belong to stable proteins and acidic proteins. The phylogenetic analysis of multiple species SOD proteins showed that SOD was clustered into three subgroups according to protein types. Gene structure analysis shows that the SOD gene contains 5-8introns, and genes from the same evolutionary branch have more similar structures. The conserved motifs and domains of their proteins are also the same. Ten MiSOD are distributed on 7 chromosomes and 1 fragment,containing 3 segmental duplication genes. The analysis of cis acting elements showed that the promoters of MiSOD members contain growth and development elements, hormone response elements, and stress response related elements. The expression pattern of MiSOD genes varies in different tissues of ‘Alphonso’ mango.MiCSD3, MiFSD1, 2, 3 have low expression levels in different tissues; the expression level of MiCSD4 is highest in the flesh, leaves, bark, and peel; the expression level of MiMSD1 is highest in the seeds, and the expression level of MiCSD1 is highest in the roots and flowers. Compared with the control, there was no significant difference in the MiSOD genes in the flesh of “Tainong-1” mango under enhanced UV-B irradiation. In summary, members of the MiSOD gene family may exert different functions by sensing different types of signals, thereby forming different expression patterns. SOD may not play a key role in the response of ‘Tainong-1’ mango to UV-B stress.This study lays the foundation for further investigating the response mechanism of MiSOD genes to different signals.
Superoxide dismutase(SOD) is an important enzyme in the plant antioxidant system, playing a crucial role in plant growth and development. An attempt was made to analyze the gene function of MiSOD and its expression patterns in different tissues and under enhanced UV-B irradiation. Members of the MiSOD gene family from multiple aspects such as protein characteristics, phylogenetic relationships, gene structure, and promoter cis acting elements were identified by using the mango genome and bioinformatics methods, and the expression patterns of MiSOD gene family members were identified by using the transcriptome analysis. A total of 10 SOD genes were identified in the mango fruit, and most of the MiSOD proteins belong to stable proteins and acidic proteins. The phylogenetic analysis of multiple species SOD proteins showed that SOD was clustered into three subgroups according to protein types. Gene structure analysis shows that the SOD gene contains 5-8introns, and genes from the same evolutionary branch have more similar structures. The conserved motifs and domains of their proteins are also the same. Ten MiSOD are distributed on 7 chromosomes and 1 fragment,containing 3 segmental duplication genes. The analysis of cis acting elements showed that the promoters of MiSOD members contain growth and development elements, hormone response elements, and stress response related elements. The expression pattern of MiSOD genes varies in different tissues of ‘Alphonso’ mango.MiCSD3, MiFSD1, 2, 3 have low expression levels in different tissues; the expression level of MiCSD4 is highest in the flesh, leaves, bark, and peel; the expression level of MiMSD1 is highest in the seeds, and the expression level of MiCSD1 is highest in the roots and flowers. Compared with the control, there was no significant difference in the MiSOD genes in the flesh of “Tainong-1” mango under enhanced UV-B irradiation. In summary, members of the MiSOD gene family may exert different functions by sensing different types of signals, thereby forming different expression patterns. SOD may not play a key role in the response of ‘Tainong-1’ mango to UV-B stress.This study lays the foundation for further investigating the response mechanism of MiSOD genes to different signals.
2024, 15(6): 728-736.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240093
Abstract:
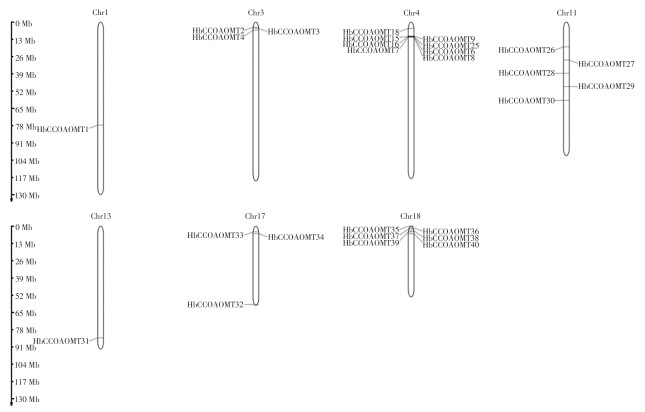
To further understand the role of the HbCCoAOMT gene in the growth, development, and stress resistance of the rubber tree(Hevea brasiliensis), the HbCCoAOMT family genes were identified and analyzed by examining the whole genome sequencing data of H. brasiliensis. A total of 40 members of the HbCCoAOMT family were identified, and their distribution on chromosomes, domain characteristics, and tissue expression profiles were analyzed. The results revealed that HbCCoAOMT members were only distributed in 7 chromosomes: 1, 3, 4,11, 13, 17, and 18 out of the18 chromosones in rubber trees. Expression pattern analysis indicated that 12members were expressed in all the five tissues. The HbCCoAOMT enzyme activity assay showed the enzyme activity was highest in the stems of H. brasiliensis. Moreover, HbCCoAOMT1, which had the highest expression abundance, was successfully cloned from H. brasiliensis. The CDS length of HbCCoAOMT1 is 746 bp, encoding 241 amino acids. HbCCoAOMT1 was inserted into the prokaryotic expression vector p ET28a, and the recombinant HbCCoAOMT1 protein was successfully expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3). Analysis of the HbCCoAOMT1 promoter region showed that HbCCoAOMT1 contains various hormone-and stress-related cisacting elements.
To further understand the role of the HbCCoAOMT gene in the growth, development, and stress resistance of the rubber tree(Hevea brasiliensis), the HbCCoAOMT family genes were identified and analyzed by examining the whole genome sequencing data of H. brasiliensis. A total of 40 members of the HbCCoAOMT family were identified, and their distribution on chromosomes, domain characteristics, and tissue expression profiles were analyzed. The results revealed that HbCCoAOMT members were only distributed in 7 chromosomes: 1, 3, 4,11, 13, 17, and 18 out of the18 chromosones in rubber trees. Expression pattern analysis indicated that 12members were expressed in all the five tissues. The HbCCoAOMT enzyme activity assay showed the enzyme activity was highest in the stems of H. brasiliensis. Moreover, HbCCoAOMT1, which had the highest expression abundance, was successfully cloned from H. brasiliensis. The CDS length of HbCCoAOMT1 is 746 bp, encoding 241 amino acids. HbCCoAOMT1 was inserted into the prokaryotic expression vector p ET28a, and the recombinant HbCCoAOMT1 protein was successfully expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3). Analysis of the HbCCoAOMT1 promoter region showed that HbCCoAOMT1 contains various hormone-and stress-related cisacting elements.
2024, 15(6): 737-744.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240068
Abstract:
The integument somatic embryos of rubber tree of clone RRIM 600 were cultured in an intermittent immersion bioreactor RITA®, and the suitable conditions for somatic embryo culture of rubber tree were established. The types of hormones were screened and the culture conditions were optimized. The experimental results showed that the best condition for intermittent immersion culture of RRIM 600 rubber integument primordium-derived somatic embryos were: MS + 1.0 mg·L-1 6-BA + 0.1 mg·L-1 NAA + 50 g·L-1 sucrose as the medium, with the intermittent immersion frequency of nutrient solution being 1 min/6 h, and the inoculation density being 15 individual embryos/container. Compared with solid culture, the intermittent immersion culture under this condition increased significantly the plant height, stem diameter, root length, root number and fresh weight per plant of somatic embryo regeneration plants by 30%, 91.7%, 34.8%, 53.3% and 97.2%, respectively.The coordination ability of SOD, CAT and POD in regenerated plants was higher under this condition, which was an effective way to improve the efficiency of regeneration plant formation from primary somatic embryos of rubber tree. All these results showed that the use of intermittent immersion culture method RITA® could shorten the formation cycle of somatic embryo regeneration plants and improve the growth quality of somatic embryo plants of rubber tree.
The integument somatic embryos of rubber tree of clone RRIM 600 were cultured in an intermittent immersion bioreactor RITA®, and the suitable conditions for somatic embryo culture of rubber tree were established. The types of hormones were screened and the culture conditions were optimized. The experimental results showed that the best condition for intermittent immersion culture of RRIM 600 rubber integument primordium-derived somatic embryos were: MS + 1.0 mg·L-1 6-BA + 0.1 mg·L-1 NAA + 50 g·L-1 sucrose as the medium, with the intermittent immersion frequency of nutrient solution being 1 min/6 h, and the inoculation density being 15 individual embryos/container. Compared with solid culture, the intermittent immersion culture under this condition increased significantly the plant height, stem diameter, root length, root number and fresh weight per plant of somatic embryo regeneration plants by 30%, 91.7%, 34.8%, 53.3% and 97.2%, respectively.The coordination ability of SOD, CAT and POD in regenerated plants was higher under this condition, which was an effective way to improve the efficiency of regeneration plant formation from primary somatic embryos of rubber tree. All these results showed that the use of intermittent immersion culture method RITA® could shorten the formation cycle of somatic embryo regeneration plants and improve the growth quality of somatic embryo plants of rubber tree.
2024, 15(6): 745-755.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240007
Abstract:
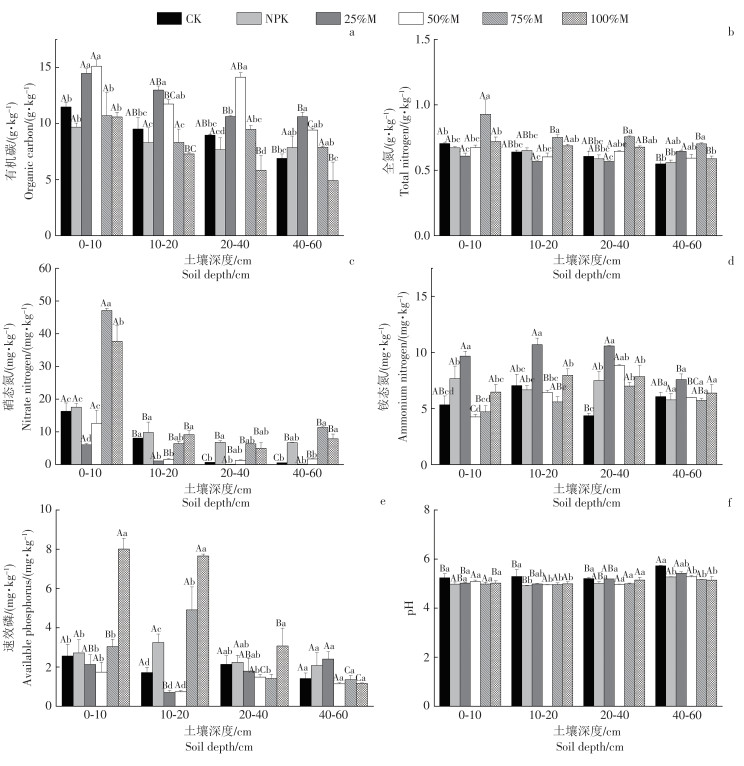
The effects of different proportions of organic fertilizer replacing chemical nitrogen fertilizer on soil nutrient and enzyme activity in rubber plantations is of great significance for selecting a reasonable substitution ratio and the sustainable development of natural rubber. The rubber plantations in Zhubijiang Farm, Baisha Li Autonomous County, Hainan Province was selected as the subject, and six different treatments were set up from June 2022 using the principle of equal nitrogen application: no fertilizer treatment(CK), Conventional fertilizer treatment(NPK), organic fertilizer replacing 25% chemical nitrogen treatment(25% M), organic fertilizer replacing 50% chemical nitrogen treatment(50% M), organic fertilizer replacing 75% chemical nitrogen treatment(75% M), organic fertilizer replacing 100% chemical nitrogen treatment(100% M). Soil samples of 0 ~10 cm, 10 ~ 20 cm, 20 ~ 40 cm and 40 ~ 60 cm were collected after fertilization for 4 months, and the characteristics of soil nutrients and enzyme activities were analyzed. The results showed that 1) compared with the NPK treatment, the 25% M and 50% M treatments significantly increased the soil organic carbon(SOC)content in 0 ~ 10 cm, 10 ~ 20 cm, 20 ~ 40 cm and 40 ~ 60 cm soil layers. The 75% M treatment significantly increased soil total N(TN) content in all soil layers at 0 ~ 10 cm and 10 ~ 20 cm. The 75% M and 100% M significantly increased the content of soil nitrate-N(NO3--N) in 0 ~ 10 cm soil layer. The 25% M treatment significantly increased the content of soil NH4+-N in 0 ~ 10 cm, 10 ~ 20 cm, and 20 ~ 40 cm soil layers. The 100% M treatment significantly increased the content of soil available P(AvP) in 0 ~ 10 cm and 10 ~ 20 cm soil layers. 2) Compared with the CK treatment, the 75% M treatment significantly increased activities of C(β-1,4-glucosidase, BG), N(L-leucine aminopeptidase, LAP; β-1, 4-N-Acetyl Glucosaminase(AP)), P(Acid phosphatase, AP) cycling enzymes in the 10 ~ 20 cm and 40 ~ 60 cm soil layers. The pH, SOC, soil water content(SWC), TN, AvP, NH4+-N and NO3--N were the main factors affecting the activities of C, N and P cycle.3) Random forest model showed that compared with the NPK treatment, the 50% M, 75% M and 100% M treatments significantly increased the rubber yield per plant by 11.9%, 16.4% and 11.8%, respectively. In summary, the 75% substitution ratio of organic fertilizer is effective on increasing the soil TN content and soil C,N, and P cycle-related enzyme activity, thereby improving the rubber plantation soil environment, better increasing the individual rubber yield, promoting the sustainable development of rubber production.
The effects of different proportions of organic fertilizer replacing chemical nitrogen fertilizer on soil nutrient and enzyme activity in rubber plantations is of great significance for selecting a reasonable substitution ratio and the sustainable development of natural rubber. The rubber plantations in Zhubijiang Farm, Baisha Li Autonomous County, Hainan Province was selected as the subject, and six different treatments were set up from June 2022 using the principle of equal nitrogen application: no fertilizer treatment(CK), Conventional fertilizer treatment(NPK), organic fertilizer replacing 25% chemical nitrogen treatment(25% M), organic fertilizer replacing 50% chemical nitrogen treatment(50% M), organic fertilizer replacing 75% chemical nitrogen treatment(75% M), organic fertilizer replacing 100% chemical nitrogen treatment(100% M). Soil samples of 0 ~10 cm, 10 ~ 20 cm, 20 ~ 40 cm and 40 ~ 60 cm were collected after fertilization for 4 months, and the characteristics of soil nutrients and enzyme activities were analyzed. The results showed that 1) compared with the NPK treatment, the 25% M and 50% M treatments significantly increased the soil organic carbon(SOC)content in 0 ~ 10 cm, 10 ~ 20 cm, 20 ~ 40 cm and 40 ~ 60 cm soil layers. The 75% M treatment significantly increased soil total N(TN) content in all soil layers at 0 ~ 10 cm and 10 ~ 20 cm. The 75% M and 100% M significantly increased the content of soil nitrate-N(NO3--N) in 0 ~ 10 cm soil layer. The 25% M treatment significantly increased the content of soil NH4+-N in 0 ~ 10 cm, 10 ~ 20 cm, and 20 ~ 40 cm soil layers. The 100% M treatment significantly increased the content of soil available P(AvP) in 0 ~ 10 cm and 10 ~ 20 cm soil layers. 2) Compared with the CK treatment, the 75% M treatment significantly increased activities of C(β-1,4-glucosidase, BG), N(L-leucine aminopeptidase, LAP; β-1, 4-N-Acetyl Glucosaminase(AP)), P(Acid phosphatase, AP) cycling enzymes in the 10 ~ 20 cm and 40 ~ 60 cm soil layers. The pH, SOC, soil water content(SWC), TN, AvP, NH4+-N and NO3--N were the main factors affecting the activities of C, N and P cycle.3) Random forest model showed that compared with the NPK treatment, the 50% M, 75% M and 100% M treatments significantly increased the rubber yield per plant by 11.9%, 16.4% and 11.8%, respectively. In summary, the 75% substitution ratio of organic fertilizer is effective on increasing the soil TN content and soil C,N, and P cycle-related enzyme activity, thereby improving the rubber plantation soil environment, better increasing the individual rubber yield, promoting the sustainable development of rubber production.
2024, 15(6): 756-763.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240112
Abstract:
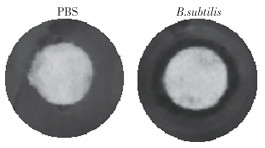
Infection of Aeromonas veronii(A. veronii), a kind of zoonotic multidrug-resistant bacteria, is mainly treated or prevented with antibiotics. However, the extensive use of antibiotics can lead to the emergence of new drug-resistant mutant strains. Bacillus subtilis(B. subtilis), as a common probiotic, which can inhibit various species of pathogenic bacteria. The antibacterial ability of B. subtilis against A. veronii was detected and its therapeutic effect on A. veronii intestinal infection evaluated. Filter paper method showed that B. subtilis possessed an obvious inhibitory effect on A. veronii C4, and TEM showed that it caused the dilatation and damage of A. veronii C4 cells. In addition, B. subtilis reduced the intracellular cytotoxicity of A. veronii C4. In a mouse model with damaged intestinal barrier, B. subtilis showed higher efficiency than the clinical antibiotic on A.veronii C4 infections, contributing to their natural ability of intestinal barrier repair and the antibacterial ability against A. veronii C4. B.subtilis can thus be used as a biocontrol agent for the treatment of A. veronii infection,which is of great significance for curbing the development of drug-resistance.
Infection of Aeromonas veronii(A. veronii), a kind of zoonotic multidrug-resistant bacteria, is mainly treated or prevented with antibiotics. However, the extensive use of antibiotics can lead to the emergence of new drug-resistant mutant strains. Bacillus subtilis(B. subtilis), as a common probiotic, which can inhibit various species of pathogenic bacteria. The antibacterial ability of B. subtilis against A. veronii was detected and its therapeutic effect on A. veronii intestinal infection evaluated. Filter paper method showed that B. subtilis possessed an obvious inhibitory effect on A. veronii C4, and TEM showed that it caused the dilatation and damage of A. veronii C4 cells. In addition, B. subtilis reduced the intracellular cytotoxicity of A. veronii C4. In a mouse model with damaged intestinal barrier, B. subtilis showed higher efficiency than the clinical antibiotic on A.veronii C4 infections, contributing to their natural ability of intestinal barrier repair and the antibacterial ability against A. veronii C4. B.subtilis can thus be used as a biocontrol agent for the treatment of A. veronii infection,which is of great significance for curbing the development of drug-resistance.
2024, 15(6): 764-769.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240049
Abstract:
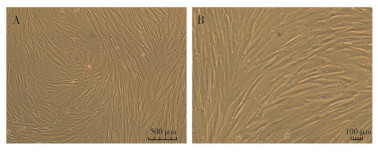
Myxomatous mitral valve disease(MMVD) is one of the most common heart diseases in mammals,which can lead to heart failure and sudden death in clinical practice. The extracellular matrix remodeling caused by mitral stromal cells(MVICs) activation is the key pathological change in the development of MMVD.Therefore, this study intended to establish a separation and culture system for primary MVICs of Wuzhishan pig to obtain stable cultured MVICs, providing cell materials for in vitro research on MMVD. The results showed that the mitral valve cells of Wuzhishan pig isolated by the present method were CD31 negative and Vimentin positive, which were consistent with the characteristics of MVIC. Compared with the medium with different serum concentrations, the complete medium containing 10% FBS serum was more favorable to the proliferation activity of MVICs cells, and could support the stable culture of MVICs in vitro for at least 20 generations. The primary MVICs of Wuzhishan pig obtained in this study can provide an in vitro research platform for the study of the pathological mechanism of mitral valve disease and the further development of targeted drugs.
Myxomatous mitral valve disease(MMVD) is one of the most common heart diseases in mammals,which can lead to heart failure and sudden death in clinical practice. The extracellular matrix remodeling caused by mitral stromal cells(MVICs) activation is the key pathological change in the development of MMVD.Therefore, this study intended to establish a separation and culture system for primary MVICs of Wuzhishan pig to obtain stable cultured MVICs, providing cell materials for in vitro research on MMVD. The results showed that the mitral valve cells of Wuzhishan pig isolated by the present method were CD31 negative and Vimentin positive, which were consistent with the characteristics of MVIC. Compared with the medium with different serum concentrations, the complete medium containing 10% FBS serum was more favorable to the proliferation activity of MVICs cells, and could support the stable culture of MVICs in vitro for at least 20 generations. The primary MVICs of Wuzhishan pig obtained in this study can provide an in vitro research platform for the study of the pathological mechanism of mitral valve disease and the further development of targeted drugs.
2024, 15(6): 770-779.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230129
Abstract:
In recent years, the growth environment of mangroves has been seriously threatened and has become one of the most endangered ecosystems in the world. To clarify the current situation of mangroves and formulate more effective protection measures, digital orthophotos of Hainan Province were used to interpret the area and distribution areas of mangroves in Xincun Port, Lingshui, Hainan, and a survey was made of the species of mangroves in Xincun Port by using a sampling method. At the same time, the diversity of main biological indicators, and the distribution characteristics of natural and artificial populations of mangroves on the south and north bamks of Xincun Port were analyzed. The results indicate there are a total of 12 species of mangroves, including 8 species on the south shore,with the dominant species being Rhizophora apiculata; and 6 species on the north shore, with the dominant species being Laguncularia racemos. A national second-level protected plant(Lumnitzera littorea) has been transplanted and its growth condition is good. On both the north and south shores, natural forests have shown adaptability to high tide levels, but the growth status of mangroves on the south shore is better than that on the north shore. However, the trees in plantation forests on both shores are relatively short. In terms of species diversity, the biodiversity of natural forests is higher on the south shore than on the north shore. However, in terms of plantation forests, the biodiversity is slightly higher on the north shore than on the south shore. On the south shore mainly grows a natural forest, where it is more suitable to plant Sonneratia apetala or prune the trees to have loose canopy to increase species diversity,while the plantation forests on the north shore are mostly of native species. Planting multi-species at a two-layer pattern can increase species diversity more effectively. At the same time, taking into account the characteristics of biological invasion and different tide levels, a suggestion was made on planting Sonneratia apetala at high tide levels. This study clarified the species distribution and ecological characteristics of the mangroves in Xincun Port,Lingshui, which might provide valuable survey data for the mangrove protection and restoration projects in the area,facilitating optimization of the mangrove protection strategy, and hence the ecological protection and sustainable development of mangroves in Xincun Port.
In recent years, the growth environment of mangroves has been seriously threatened and has become one of the most endangered ecosystems in the world. To clarify the current situation of mangroves and formulate more effective protection measures, digital orthophotos of Hainan Province were used to interpret the area and distribution areas of mangroves in Xincun Port, Lingshui, Hainan, and a survey was made of the species of mangroves in Xincun Port by using a sampling method. At the same time, the diversity of main biological indicators, and the distribution characteristics of natural and artificial populations of mangroves on the south and north bamks of Xincun Port were analyzed. The results indicate there are a total of 12 species of mangroves, including 8 species on the south shore,with the dominant species being Rhizophora apiculata; and 6 species on the north shore, with the dominant species being Laguncularia racemos. A national second-level protected plant(Lumnitzera littorea) has been transplanted and its growth condition is good. On both the north and south shores, natural forests have shown adaptability to high tide levels, but the growth status of mangroves on the south shore is better than that on the north shore. However, the trees in plantation forests on both shores are relatively short. In terms of species diversity, the biodiversity of natural forests is higher on the south shore than on the north shore. However, in terms of plantation forests, the biodiversity is slightly higher on the north shore than on the south shore. On the south shore mainly grows a natural forest, where it is more suitable to plant Sonneratia apetala or prune the trees to have loose canopy to increase species diversity,while the plantation forests on the north shore are mostly of native species. Planting multi-species at a two-layer pattern can increase species diversity more effectively. At the same time, taking into account the characteristics of biological invasion and different tide levels, a suggestion was made on planting Sonneratia apetala at high tide levels. This study clarified the species distribution and ecological characteristics of the mangroves in Xincun Port,Lingshui, which might provide valuable survey data for the mangrove protection and restoration projects in the area,facilitating optimization of the mangrove protection strategy, and hence the ecological protection and sustainable development of mangroves in Xincun Port.
2024, 15(6): 780-790.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240009
Abstract:
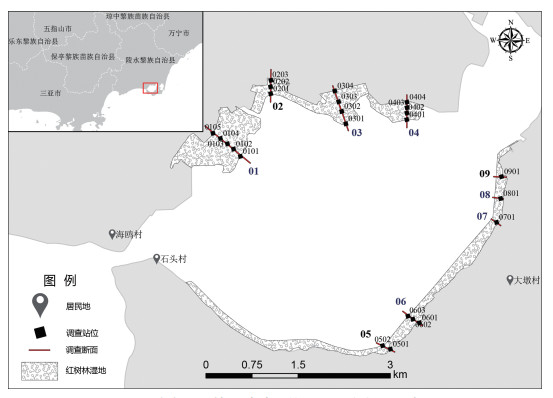
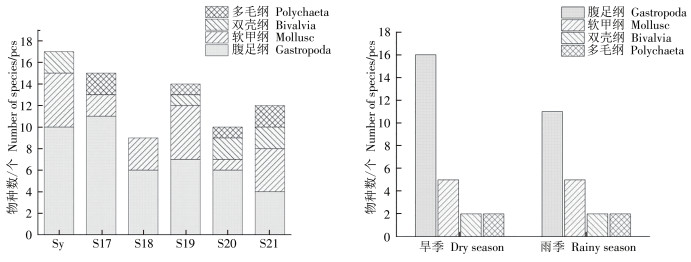
Due to the influence of human activities such as pond aquaculture, the mangrove forests in Lingshui,Hainan Province have been seriously encroached. Since 2016, Lingshui has started to implement the ecological restoration project of mangrove wetlands by returning the ponds for aquaculture to the forests. In order to understand the characteristics of macrobenthic community changes and their relationship with environmental factors during mangrove restoration, surveys were made of benthic macrofauna in mangrove forests at five different restoration stages(2017—2021) and one natural mangrove area in December 2022(dry season) and June 2023(rainy season), respectively. A total of 30 species of benthic macrofauna belonging to 4 classes, 9orders and 18 families were collected and identified. The main dominant species in both natural and restored mangrove forests are gastropods and mollusks, such as the pearl-banded crab snail, the longitudinal-banded beach snail, the mangrove fiddler crab, etc. The number of species, habitat density, biomass and diversity index of mangrove macrobenthos in the mangrove restoration area showed an increasing trend with the increase of the restoration period, indicating that the community structure of benthic macrofauna was becoming more and more stable and the quality of mangrove habitats has been improved in the return-pond-to-forest restoration project.Moreover, in terms of seasonal distribution, the number of macrobenthic species and habitat density were higher in the dry season than in the rainy season; whereas the number of dominant species, biomass, and diversity indices were lower in the dry season than in the rainy season. Correlation analysis showed that pH and total nitrogen content of the sediment were the main environmental factors affecting the distribution of mangrove macrobenthos. All the results showed that the mangrove restoration project of returning ponds to forests had improved to some extent the eco-environment quality of the mangrove restoration area and that the community structure of the benthic macrofauna was obviously correlated with the restoration time, but it will take a long time to recover to the level of natural mangrove forests. These results can provide basic information for conservation of mangrove benthos microfauna diversity and ecological restoration of the mangroves.
Due to the influence of human activities such as pond aquaculture, the mangrove forests in Lingshui,Hainan Province have been seriously encroached. Since 2016, Lingshui has started to implement the ecological restoration project of mangrove wetlands by returning the ponds for aquaculture to the forests. In order to understand the characteristics of macrobenthic community changes and their relationship with environmental factors during mangrove restoration, surveys were made of benthic macrofauna in mangrove forests at five different restoration stages(2017—2021) and one natural mangrove area in December 2022(dry season) and June 2023(rainy season), respectively. A total of 30 species of benthic macrofauna belonging to 4 classes, 9orders and 18 families were collected and identified. The main dominant species in both natural and restored mangrove forests are gastropods and mollusks, such as the pearl-banded crab snail, the longitudinal-banded beach snail, the mangrove fiddler crab, etc. The number of species, habitat density, biomass and diversity index of mangrove macrobenthos in the mangrove restoration area showed an increasing trend with the increase of the restoration period, indicating that the community structure of benthic macrofauna was becoming more and more stable and the quality of mangrove habitats has been improved in the return-pond-to-forest restoration project.Moreover, in terms of seasonal distribution, the number of macrobenthic species and habitat density were higher in the dry season than in the rainy season; whereas the number of dominant species, biomass, and diversity indices were lower in the dry season than in the rainy season. Correlation analysis showed that pH and total nitrogen content of the sediment were the main environmental factors affecting the distribution of mangrove macrobenthos. All the results showed that the mangrove restoration project of returning ponds to forests had improved to some extent the eco-environment quality of the mangrove restoration area and that the community structure of the benthic macrofauna was obviously correlated with the restoration time, but it will take a long time to recover to the level of natural mangrove forests. These results can provide basic information for conservation of mangrove benthos microfauna diversity and ecological restoration of the mangroves.
2024, 15(6): 791-799.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240027
Abstract:
In the nearshore mariculture area in Qinglan Port, Hainan, three materials, polyethylene(PE),polyamide(PA), and polymethyl methacrylate(PMMA), were employed as sea-hanging panels in the mariculture area and microbial biofilms were collected from the macrofoulers on the panels for high-throughput sequencing and analysis. A comparative analysis of the characteristics of eukaryotic microbial communities in the initial attachment areas(IAA) of three macrofouler, including Hydroides elegans, Balanus amphitrite and Membranipora savartii, showed that the microbial community structures in the initial attachment areas of the same species of a macrofouler on the three materials exhibited high similarity. The dominant taxa in the eukaryotic microbial communities varied among different macrofouler IAAs, with Ulva(43.02%-93.31%) dominating in H. elegans,Picochlorum(10.74%-60.86%) in B. amphitrite, and Monhystrella(12.08%-34.78%) in M. savartii. The alpha diversity of the eukaryotic microbial community in M. savartii IAA was the highest. Co-occurrence network analysis indicated that mutualistic symbiosis was the predominant interspecies relationship in the eukaryotic microbial community. Functional prediction analysis revealed higher abundances of taxa associated with biosynthesis, degradation/utilization/assimilation, generation of precursor metabolite and energy production in the eukaryotic microbial communities of IAAs. This study contributes to a better understanding of the correlation between the attachment of large fouling animals and the underlying microbial community, providing reference data for anti-fouling work in mariculture.
In the nearshore mariculture area in Qinglan Port, Hainan, three materials, polyethylene(PE),polyamide(PA), and polymethyl methacrylate(PMMA), were employed as sea-hanging panels in the mariculture area and microbial biofilms were collected from the macrofoulers on the panels for high-throughput sequencing and analysis. A comparative analysis of the characteristics of eukaryotic microbial communities in the initial attachment areas(IAA) of three macrofouler, including Hydroides elegans, Balanus amphitrite and Membranipora savartii, showed that the microbial community structures in the initial attachment areas of the same species of a macrofouler on the three materials exhibited high similarity. The dominant taxa in the eukaryotic microbial communities varied among different macrofouler IAAs, with Ulva(43.02%-93.31%) dominating in H. elegans,Picochlorum(10.74%-60.86%) in B. amphitrite, and Monhystrella(12.08%-34.78%) in M. savartii. The alpha diversity of the eukaryotic microbial community in M. savartii IAA was the highest. Co-occurrence network analysis indicated that mutualistic symbiosis was the predominant interspecies relationship in the eukaryotic microbial community. Functional prediction analysis revealed higher abundances of taxa associated with biosynthesis, degradation/utilization/assimilation, generation of precursor metabolite and energy production in the eukaryotic microbial communities of IAAs. This study contributes to a better understanding of the correlation between the attachment of large fouling animals and the underlying microbial community, providing reference data for anti-fouling work in mariculture.
2024, 15(6): 800-811.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240107
Abstract:
Tropical high-efficiency agriculture is a key leading industry in Hainan Province. To develop tropical high-efficiency agriculture in Hainan Province, it is important to integrate distinctive crop germplasm resources and traditional agricultural culture of Hainan Province. In this study, the traditional stereoscopic planting model "kapok-rice agroforestry system", which is mainly practiced in Hainan Province, was systematically reviewed and summarized with an emphasis on its traditional farming techniques and rich germplasm resources. The biodiversity value, rice and kapok product quality, and yield in this traditional agroforestry system were then analyzed. We also discussed the paths and methods for the development of current tropical high-efficiency agriculture model based on the traditional skills and updated high yield and high quality techniques of kapok-rice agroforestry system. Four strategies were proposed, 1) to explore the detailed resource recycling processes and underlying mechanisms; 2) to establish the 'kapok rice' brand based on the unique traditional rice landraces;3) to reveal the scientific basis of traditional agricultural skills and increase the cultural and economic values of both rice and kapok flowers through applying Chinese Important Agricultural Heritage; 4) to systematically build up integrated development strategies of agriculture, historical culture, ecology, tourism, and natural education.
Tropical high-efficiency agriculture is a key leading industry in Hainan Province. To develop tropical high-efficiency agriculture in Hainan Province, it is important to integrate distinctive crop germplasm resources and traditional agricultural culture of Hainan Province. In this study, the traditional stereoscopic planting model "kapok-rice agroforestry system", which is mainly practiced in Hainan Province, was systematically reviewed and summarized with an emphasis on its traditional farming techniques and rich germplasm resources. The biodiversity value, rice and kapok product quality, and yield in this traditional agroforestry system were then analyzed. We also discussed the paths and methods for the development of current tropical high-efficiency agriculture model based on the traditional skills and updated high yield and high quality techniques of kapok-rice agroforestry system. Four strategies were proposed, 1) to explore the detailed resource recycling processes and underlying mechanisms; 2) to establish the 'kapok rice' brand based on the unique traditional rice landraces;3) to reveal the scientific basis of traditional agricultural skills and increase the cultural and economic values of both rice and kapok flowers through applying Chinese Important Agricultural Heritage; 4) to systematically build up integrated development strategies of agriculture, historical culture, ecology, tourism, and natural education.
2024, 15(6): 812-822.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240103
Abstract:
An attempt was made to identify chemical constituents and their biological activities of Sarcophyton crassocaule, a soft coral, collected off the Xisha Islands in the South China Sea. Using silica gel column chromatography, thin-layer chromatography, Sephadex-20 gel column chromatography, and semi-preparative highperformance liquid chromatography(Semi-Prep HPLC), the ethyl acetate fraction of S. crassocaule was separated and purified, from which 11 compounds were yielded. The physical and chemical properties and spectroscopic data of these compounds were compared with those in the literature. The 11 compounds were identified assarsolilide A( 1 ); trochelioid A( 2 );(1R*,2R*,7R*,8R*,15R*,3E,11E)-7,8: 1,15-diepoxycembra-3,11-dien-16,2-olide( 3 );(+)-7α,8β-dihydroxy-deepoxy-sarcophine( 4 ); 1,15β-epoxy-deoxysarcophine( 5 );(-)-isosarcophine( 6 ); cherbonolide A( 7 );sarcomililatin A( 8 ); trocheliolide A( 9 ); lobophytin B( 10 );(+)-sarcophine( 11 ). Compounds 1~11 are diterpenoids.Compound 3 was identified in S. crassocaule for the first time. The anti-inflammatory activity test showed that sarcomililatin A( 8 ) could inhibit the production of NO in RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS, with the IC50 value of(35.60 ±3.10) μmol·L-1, while the other compounds did not exhibit significant anti-inflammatory activity.
An attempt was made to identify chemical constituents and their biological activities of Sarcophyton crassocaule, a soft coral, collected off the Xisha Islands in the South China Sea. Using silica gel column chromatography, thin-layer chromatography, Sephadex-20 gel column chromatography, and semi-preparative highperformance liquid chromatography(Semi-Prep HPLC), the ethyl acetate fraction of S. crassocaule was separated and purified, from which 11 compounds were yielded. The physical and chemical properties and spectroscopic data of these compounds were compared with those in the literature. The 11 compounds were identified assarsolilide A( 1 ); trochelioid A( 2 );(1R*,2R*,7R*,8R*,15R*,3E,11E)-7,8: 1,15-diepoxycembra-3,11-dien-16,2-olide( 3 );(+)-7α,8β-dihydroxy-deepoxy-sarcophine( 4 ); 1,15β-epoxy-deoxysarcophine( 5 );(-)-isosarcophine( 6 ); cherbonolide A( 7 );sarcomililatin A( 8 ); trocheliolide A( 9 ); lobophytin B( 10 );(+)-sarcophine( 11 ). Compounds 1~11 are diterpenoids.Compound 3 was identified in S. crassocaule for the first time. The anti-inflammatory activity test showed that sarcomililatin A( 8 ) could inhibit the production of NO in RAW264.7 cells induced by LPS, with the IC50 value of(35.60 ±3.10) μmol·L-1, while the other compounds did not exhibit significant anti-inflammatory activity.
2024, 15(6): 823-830.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240092
Abstract:
Acanthaster cf. solaris disaster outbreak is one of the main causes of coral reef degradation in the South China Sea, so it is of great significance to develop a disaster prevention and control method for A. cf. solaris. An indoor research platform for A. cf. solaris behavior was set up, and it was found that Pocillopora damicornis had a higher effect on inducing aggregation of A. cf. solaris than Galaxea fascicularis and Porites lutea(P < 0.05). At the same time, a sustained-release agent was prepared from coral mucus by using hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and other reagents. It was found that the sustained-release agent with lower hardness and faster sustainedrelease rate had a significant effect on inducing A. cf. solaris aggregation(P < 0.01). In summary, a preparation method for a sustained-release agent from coral mucus was developed, and it was proved that the coral mucus of P. damicornis could significantly induce A. cf. solaris population aggregation, which provides a scientific basis for the analysis of A. cf. solaris population aggregation mechanism and the innovative development of disaster prevention and control method.
Acanthaster cf. solaris disaster outbreak is one of the main causes of coral reef degradation in the South China Sea, so it is of great significance to develop a disaster prevention and control method for A. cf. solaris. An indoor research platform for A. cf. solaris behavior was set up, and it was found that Pocillopora damicornis had a higher effect on inducing aggregation of A. cf. solaris than Galaxea fascicularis and Porites lutea(P < 0.05). At the same time, a sustained-release agent was prepared from coral mucus by using hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose and other reagents. It was found that the sustained-release agent with lower hardness and faster sustainedrelease rate had a significant effect on inducing A. cf. solaris aggregation(P < 0.01). In summary, a preparation method for a sustained-release agent from coral mucus was developed, and it was proved that the coral mucus of P. damicornis could significantly induce A. cf. solaris population aggregation, which provides a scientific basis for the analysis of A. cf. solaris population aggregation mechanism and the innovative development of disaster prevention and control method.


 Abstract
Abstract PDF 2918KB
PDF 2918KB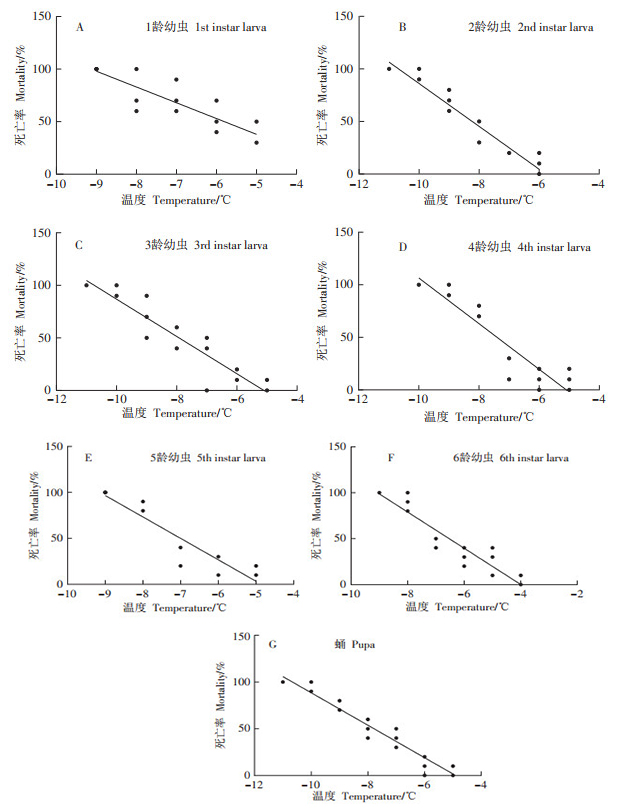











 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS