2020 Vol. 11, No. 4
2020, 11(4): 391-398.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.001
Abstract:
α6/α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (α6β4*nAChRs, the asterisk denotes the possible presence of additional subunits) are mainly distributed in the hippocampus, peripheral ganglia and human adrenal chromaffin cells, and are closely related to neuropathic and inflammatory pain, stress, etc. Recombinant expression of rat α6/α3β4 nAChR on Xenopus laevis oocytes was detected by using the two-electrode voltage clamp to record inward currents elicited by acetylcholine at different concentrations in light of α and β subunits at different ratios, and the sensitivity of this receptor was verified by its antagonist α-conotoxin TxID. The results showed that α6β4 nAChR subtypes with different ratios of subunits were successfully expressed in the oocyte membrane, and had good sensitivity of ligand-gated ion channel function.
α6/α3β4 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (α6β4*nAChRs, the asterisk denotes the possible presence of additional subunits) are mainly distributed in the hippocampus, peripheral ganglia and human adrenal chromaffin cells, and are closely related to neuropathic and inflammatory pain, stress, etc. Recombinant expression of rat α6/α3β4 nAChR on Xenopus laevis oocytes was detected by using the two-electrode voltage clamp to record inward currents elicited by acetylcholine at different concentrations in light of α and β subunits at different ratios, and the sensitivity of this receptor was verified by its antagonist α-conotoxin TxID. The results showed that α6β4 nAChR subtypes with different ratios of subunits were successfully expressed in the oocyte membrane, and had good sensitivity of ligand-gated ion channel function.
2020, 11(4): 399-405.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.002
Abstract:
In order to understand the effect of WP-1 [(22E, 24R)-5, 8-epidioxy-5α, 8α-ergosta-6, 9(11), 22E-trien-3β-ol] isolated from Cytospora sp., an endophytic fungus from the mangrove plant Ceriops tagal on human cervical cancer HeLa cells, the proliferation and apoptosis of HeLa cells treated with WP-1 was determined and analyzed by using MTT colorimetry, clone formation, Hoechst 33258 staining and Western blot. It was found that with the increase of WP-1 concentration the survival rate of the HeLa cells decreased significantly, and that the WP-1 significantly inhibited the colony formation of cells. When treated with WP-1 at a concentration of 10 μmol·L−1 the HeLa cells showed chromatin condensation and nucleosome fragmentation, which were characteristic of apoptosis. Western blot analysis showed that with the increase of WP-1 dose, the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 were down-regulated in the HeLa cells, while the expressions of Cleaved Caspase-3 and Cleaved Caspase-9 were significantly up-regulated. The results show that WP-1 can inhibit the proliferation of HeLa cells and promote apoptosis of HeLa cells.
In order to understand the effect of WP-1 [(22E, 24R)-5, 8-epidioxy-5α, 8α-ergosta-6, 9(11), 22E-trien-3β-ol] isolated from Cytospora sp., an endophytic fungus from the mangrove plant Ceriops tagal on human cervical cancer HeLa cells, the proliferation and apoptosis of HeLa cells treated with WP-1 was determined and analyzed by using MTT colorimetry, clone formation, Hoechst 33258 staining and Western blot. It was found that with the increase of WP-1 concentration the survival rate of the HeLa cells decreased significantly, and that the WP-1 significantly inhibited the colony formation of cells. When treated with WP-1 at a concentration of 10 μmol·L−1 the HeLa cells showed chromatin condensation and nucleosome fragmentation, which were characteristic of apoptosis. Western blot analysis showed that with the increase of WP-1 dose, the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 were down-regulated in the HeLa cells, while the expressions of Cleaved Caspase-3 and Cleaved Caspase-9 were significantly up-regulated. The results show that WP-1 can inhibit the proliferation of HeLa cells and promote apoptosis of HeLa cells.
2020, 11(4): 406-414.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.003
Abstract:
Ten samples containing actinomycetes were collected from mangrove plants in the west coast of Hainan Island and cultured on 4 isolation mediums for isolation. The isolated actinomycetes associated with the mangrove plant samples were identified by 16S rRNA sequence analysis, and the antimicrobial activities of fermented products of the isolated actinomycetes were analyzed by using filter paper diffusion method. The results showed that a total of 63 actinomycetes were isolated from the 10 mangrove plant samples. The taxonomic status of 16 representative strains of the isolated actinomycetes was established. Among the 16 representative strains 13 strains belong to the genus Streptomyces, of which 4 strains are of potential novel species, and 3 strains belong to the genus Micromonospora. The test of antimicrobial activity showed that the fermented products of 16 representative strains of the isolated actinomycetes have antimicrobial activity against at least one indicator bacterium or fungus. Compound A was isolated from the crude fermented extract of strain HNM0645, which was identified as known compound K-252a by structure. The inhibitory rates of the compound A against yam anthracnose pathogens (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) were measured, and a toxicity regression equation was established by using Excel to calculate the EC50. The EC50 value of the compound A against the yam anthracnose pathogens was 286.61 μg·mL−1, indicating the compound A had some antifungal activity against the yam anthracnose pathogen. The compound A was found to have no significant antibacterial activity against the tested bacteria.
Ten samples containing actinomycetes were collected from mangrove plants in the west coast of Hainan Island and cultured on 4 isolation mediums for isolation. The isolated actinomycetes associated with the mangrove plant samples were identified by 16S rRNA sequence analysis, and the antimicrobial activities of fermented products of the isolated actinomycetes were analyzed by using filter paper diffusion method. The results showed that a total of 63 actinomycetes were isolated from the 10 mangrove plant samples. The taxonomic status of 16 representative strains of the isolated actinomycetes was established. Among the 16 representative strains 13 strains belong to the genus Streptomyces, of which 4 strains are of potential novel species, and 3 strains belong to the genus Micromonospora. The test of antimicrobial activity showed that the fermented products of 16 representative strains of the isolated actinomycetes have antimicrobial activity against at least one indicator bacterium or fungus. Compound A was isolated from the crude fermented extract of strain HNM0645, which was identified as known compound K-252a by structure. The inhibitory rates of the compound A against yam anthracnose pathogens (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) were measured, and a toxicity regression equation was established by using Excel to calculate the EC50. The EC50 value of the compound A against the yam anthracnose pathogens was 286.61 μg·mL−1, indicating the compound A had some antifungal activity against the yam anthracnose pathogen. The compound A was found to have no significant antibacterial activity against the tested bacteria.
2020, 11(4): 415-425.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.004
Abstract:
Transcriptome-based analysis of the strigolactone-deficient mutant d17 of rice (Oryza sativa L ssp. japonica) and its wild-type ZH11 (O. sativa L. ssp. japonica cv. Zhonghua11) were performed. A total of 248 and 441 differentially expressed genes were found in the roots and leaves of d17, which were enriched on the lipid metabolism pathway. Metabolomics analysis revealed that lipid and flavonoid contents were significantly different between the d17 mutant and ZH11. Further research found that the contents of lysophospholipid and flavonoids in the d17 was decreased significantly, and that the expression levels of related genes were decreased. Our results revealed that strigolactone was involved in regulating of flavonoids and lipid metabolism in rice, which provides references for further research on strigolactone in regulating of secondary metabolism and growth in rice.
Transcriptome-based analysis of the strigolactone-deficient mutant d17 of rice (Oryza sativa L ssp. japonica) and its wild-type ZH11 (O. sativa L. ssp. japonica cv. Zhonghua11) were performed. A total of 248 and 441 differentially expressed genes were found in the roots and leaves of d17, which were enriched on the lipid metabolism pathway. Metabolomics analysis revealed that lipid and flavonoid contents were significantly different between the d17 mutant and ZH11. Further research found that the contents of lysophospholipid and flavonoids in the d17 was decreased significantly, and that the expression levels of related genes were decreased. Our results revealed that strigolactone was involved in regulating of flavonoids and lipid metabolism in rice, which provides references for further research on strigolactone in regulating of secondary metabolism and growth in rice.
2020, 11(4): 426-436.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.005
Abstract:
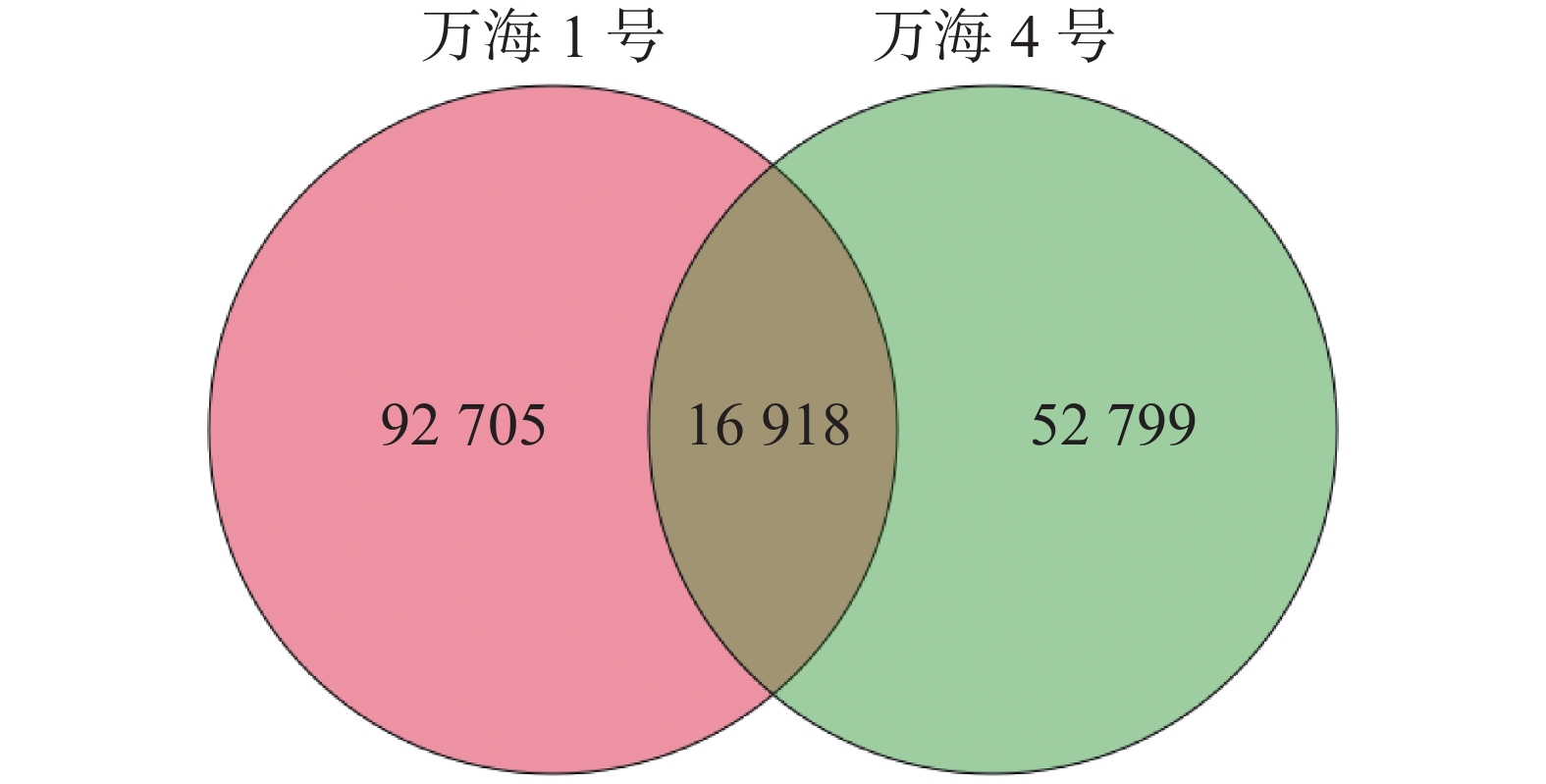
In order to further explore the physiological characteristics and metabolic process and also to provide scientific basis for the selection of excellent clones of Camellia vietnamensis in Hainan, mature leaves of two years old plants from two clones (Camellia vietnamensis ‘Wanghai1’ and ‘Wanhai4’ derived from two elite individuals of Camellia vietnamensis plants from Hainan were selected for transcriptome sequencing and analysis by using next-generation high-throughput Illumina transcriptome sequencing technology, and their differences in gene expression were compared. The results showed that among the specific genes of ‘Wanhai1’ there were 651 annotated to the path related to plant disease resistance, accounting for about 5.26%, and 510 annotated to the pathway related to fatty acid metabolism, accounting for about 4.12 %, and that among the specific genes in ‘Wanhai2’ there were 169 annotated to pathways such as sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis, brassinosteroid biosynthesis, steroid biosynthesis and monoterpenoid biosynthesis, which are related to plant secondary metabolism. The single-copy homologous genes of the two samples were mostly enriched to GO entries related to antioxidant capacity and KEGG entries related to amino acid anabolic metabolism, and their P levels were less than 0.05, showing a significant correlation between their genes and antioxidant capacity or amino acid anabolic metabolism. This might indicate that Clone ‘Wanhai1’ has higher stress resistance while Clone ‘Wanhai4’ accumulates more secondary metabolites.
In order to further explore the physiological characteristics and metabolic process and also to provide scientific basis for the selection of excellent clones of Camellia vietnamensis in Hainan, mature leaves of two years old plants from two clones (Camellia vietnamensis ‘Wanghai1’ and ‘Wanhai4’ derived from two elite individuals of Camellia vietnamensis plants from Hainan were selected for transcriptome sequencing and analysis by using next-generation high-throughput Illumina transcriptome sequencing technology, and their differences in gene expression were compared. The results showed that among the specific genes of ‘Wanhai1’ there were 651 annotated to the path related to plant disease resistance, accounting for about 5.26%, and 510 annotated to the pathway related to fatty acid metabolism, accounting for about 4.12 %, and that among the specific genes in ‘Wanhai2’ there were 169 annotated to pathways such as sesquiterpenoid and triterpenoid biosynthesis, brassinosteroid biosynthesis, steroid biosynthesis and monoterpenoid biosynthesis, which are related to plant secondary metabolism. The single-copy homologous genes of the two samples were mostly enriched to GO entries related to antioxidant capacity and KEGG entries related to amino acid anabolic metabolism, and their P levels were less than 0.05, showing a significant correlation between their genes and antioxidant capacity or amino acid anabolic metabolism. This might indicate that Clone ‘Wanhai1’ has higher stress resistance while Clone ‘Wanhai4’ accumulates more secondary metabolites.
2020, 11(4): 437-445.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.006
Abstract:
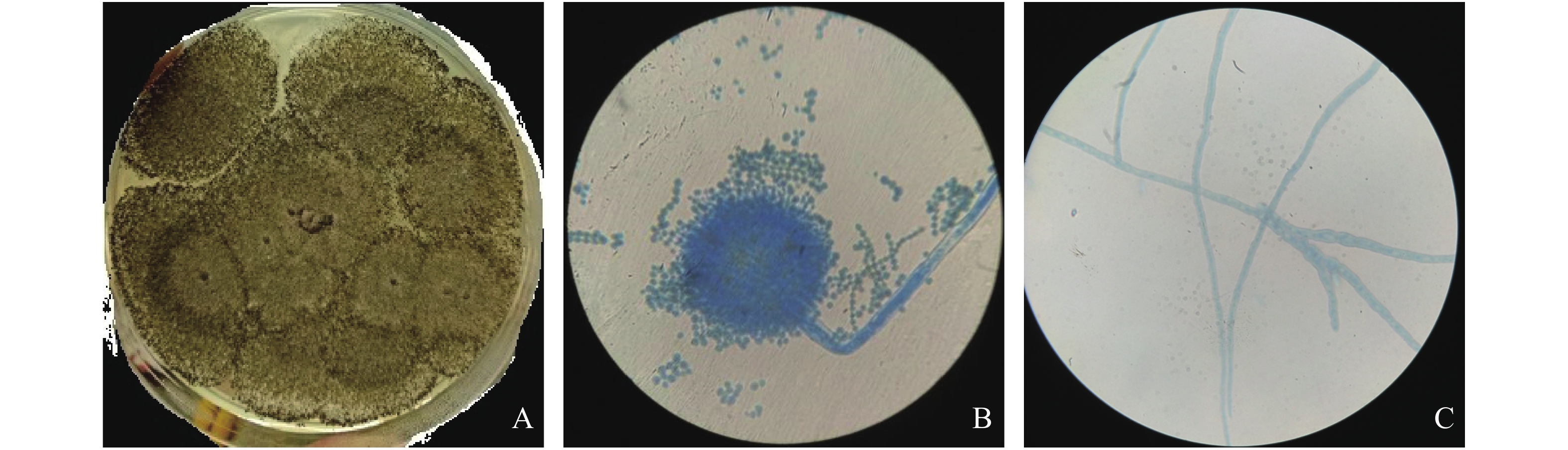
An attempt was made to study the effect of fermentation conditions on the bacteriostasis of endophytic fungus M2 extracted from Noni (Morinda citrifolia Linn.). A combination of traditional methods and ITS rDNA sequencing was used to identify the Noni endophytic fungus M2 with outstanding bacteriostatic effect. The endophytic fungus M2 was cultured and fermented under different conditions by using single factor experiment and orthogonal design to optimize its fermentation conditions. The Noni endophytic fungus M2 was initially identified as Aspergillus aculeatus, and its accession number was MK560191 in the NCBI database. The optimum medium for the endophytic fungus M2 was potato infusion 200 g from potato boiled for 30 min, glucose 20 g, sodium nitrate 5 g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.2 g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2 g, 1000 mL double distilled water. The optimum fermentation conditions were solution 60 mL in a 150 mL conical flask, temperature 25 ℃, initial culture medium pH 8 and rotation speed 170 r·min−1.
An attempt was made to study the effect of fermentation conditions on the bacteriostasis of endophytic fungus M2 extracted from Noni (Morinda citrifolia Linn.). A combination of traditional methods and ITS rDNA sequencing was used to identify the Noni endophytic fungus M2 with outstanding bacteriostatic effect. The endophytic fungus M2 was cultured and fermented under different conditions by using single factor experiment and orthogonal design to optimize its fermentation conditions. The Noni endophytic fungus M2 was initially identified as Aspergillus aculeatus, and its accession number was MK560191 in the NCBI database. The optimum medium for the endophytic fungus M2 was potato infusion 200 g from potato boiled for 30 min, glucose 20 g, sodium nitrate 5 g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.2 g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2 g, 1000 mL double distilled water. The optimum fermentation conditions were solution 60 mL in a 150 mL conical flask, temperature 25 ℃, initial culture medium pH 8 and rotation speed 170 r·min−1.
2020, 11(4): 446-454.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.007
Abstract:
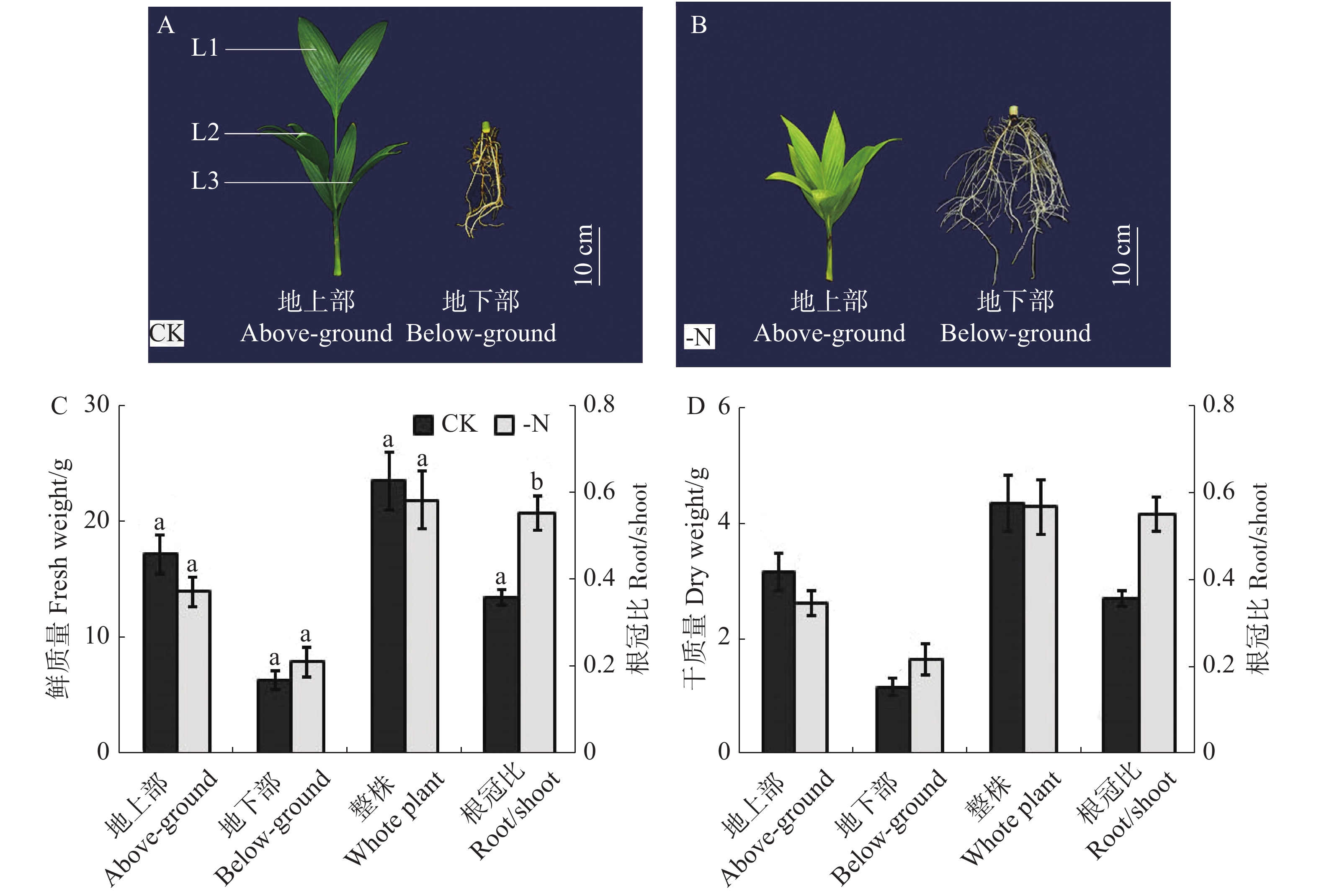
The growth and leaf microstructure of seedlings of arecanut (Areca catechu L.) under nitrogen deficiency were observed, and the biomass, chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and gas exchange index of the arecanut seedling leaves were determined to analyze the effect of nitrogen deficiency stress on photosynthetic characteristics of arecanut seedling leaves. The results showed that compared with the control the arecanut seedlings were shorter in the aboveground part, yellow in the leaves and lower in the biomass but without significant difference, while they were well developed in the root system in the underground part and had a significantly high ratio of root to crown. The contents of chlorophyll a, b in each leaf of the first three leaves from the top of the arecanut seedlings was significantly lower under the nitrogen deficiency stress than in the control, and the content of chlorophyll b decreased more significantly. The nitrogen deficiency stress reduced significantly leaf chlorophyll content, photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, the maximal photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm), actual photochemical efficiency Y (Ⅱ) and photochemical quenching coefficient qP but increased the intercellular CO2 concentration and the non-photochemical quenching coefficient NPQ significantly. The density of mesophyll cells in all the first three leaves of the arecanut seedlings was significantly lower in the nitrogen deficiency treatment than in the control. The results showed that nitrogen deficiency stress inhibited the synthesis of chlorophyll, and reduced the activity of PSII reaction center and the photosynthetic efficiency, leading to lower production of the biomass of the arecanut seedlings. Under nitrogen deficiency the arecanut seedlings regulate their biomass distribution between the aboveground and underground parts to maintain their balanced growth between the aboveground part and the root system, and at the same time they may reduce the proportion of chlorophyll b in the photosynthetic pigments and improve the thickness of leaves and the cells of the upper epidermis of the leaves to enhance their heat dissipation mechanism for their adaptation to the environment of high temperature and strong sunlight in the tropics.
The growth and leaf microstructure of seedlings of arecanut (Areca catechu L.) under nitrogen deficiency were observed, and the biomass, chlorophyll content, chlorophyll fluorescence parameters and gas exchange index of the arecanut seedling leaves were determined to analyze the effect of nitrogen deficiency stress on photosynthetic characteristics of arecanut seedling leaves. The results showed that compared with the control the arecanut seedlings were shorter in the aboveground part, yellow in the leaves and lower in the biomass but without significant difference, while they were well developed in the root system in the underground part and had a significantly high ratio of root to crown. The contents of chlorophyll a, b in each leaf of the first three leaves from the top of the arecanut seedlings was significantly lower under the nitrogen deficiency stress than in the control, and the content of chlorophyll b decreased more significantly. The nitrogen deficiency stress reduced significantly leaf chlorophyll content, photosynthetic rate, transpiration rate, stomatal conductance, the maximal photochemical efficiency (Fv/Fm), actual photochemical efficiency Y (Ⅱ) and photochemical quenching coefficient qP but increased the intercellular CO2 concentration and the non-photochemical quenching coefficient NPQ significantly. The density of mesophyll cells in all the first three leaves of the arecanut seedlings was significantly lower in the nitrogen deficiency treatment than in the control. The results showed that nitrogen deficiency stress inhibited the synthesis of chlorophyll, and reduced the activity of PSII reaction center and the photosynthetic efficiency, leading to lower production of the biomass of the arecanut seedlings. Under nitrogen deficiency the arecanut seedlings regulate their biomass distribution between the aboveground and underground parts to maintain their balanced growth between the aboveground part and the root system, and at the same time they may reduce the proportion of chlorophyll b in the photosynthetic pigments and improve the thickness of leaves and the cells of the upper epidermis of the leaves to enhance their heat dissipation mechanism for their adaptation to the environment of high temperature and strong sunlight in the tropics.
2020, 11(4): 455-460.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.008
Abstract:
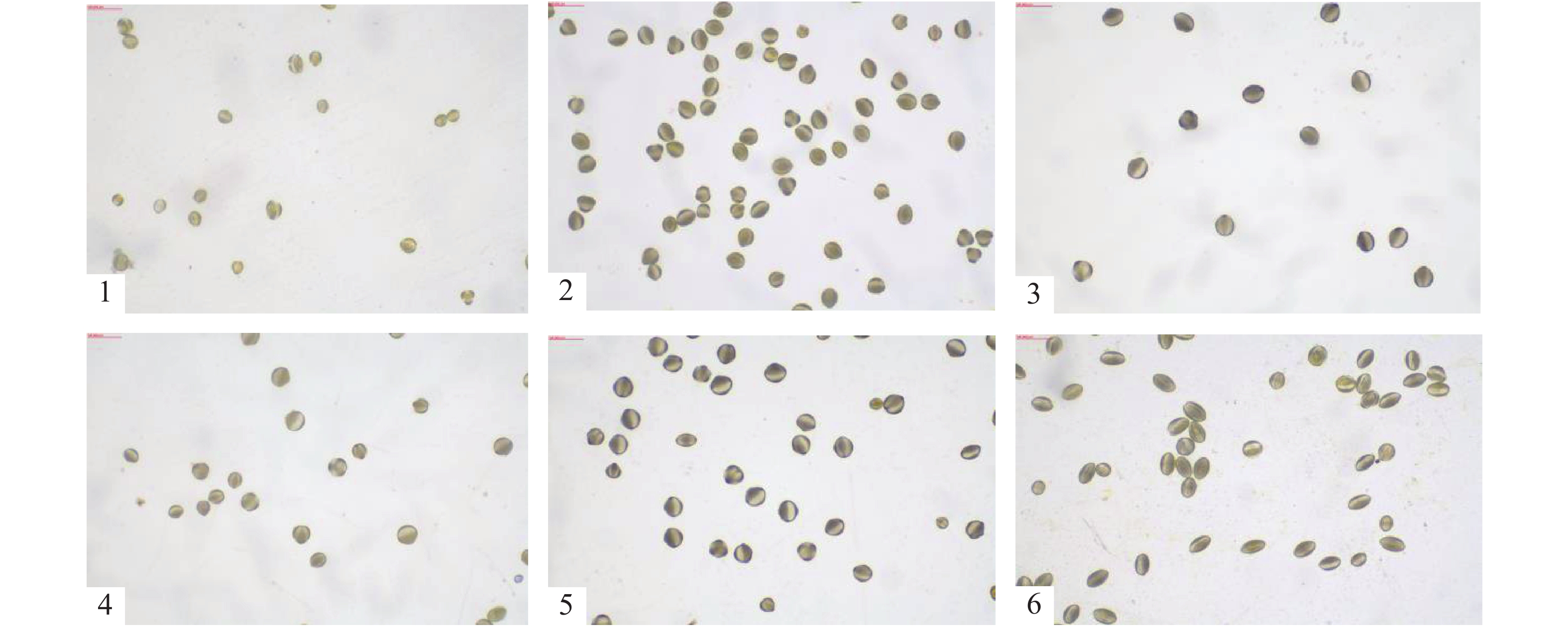
In order to study the pollen characteristics and in vitro germination under different conditions, 6 Gerbera jamesonii Bolus cultivars were observed in terms of pollen morphology, pollen quantity and pollen viability, and the pollen size, morphological index and pollen quantity were systematically analyzed by using SPSS23.0 software. The results showed that there were differences in pollen morphology, pollen quantity and pollen viability among the 6 Gerbera cultivars. The pollen grains of the cultivar ‘Linglong’ were the largest, and those of cultivar ‘Daxueju’ the smallest. The quantity of pollen of cultivar ‘Yunnan Hong’ was the highest, and that of cultivar ‘Linglong’ the lowest. The pollen viability at different flowering stages (flowers initially opened, half opened or fully opened) and temperatures (5, 15, 25, 35 ℃) determined by pollen germination in vitro ranged from 2.75% to 33.54% and from 0.37% to 34.62%, respectively. The systematic clustering showed that the length and diameter of pollen grain were clustered. Six Gerbera cultivars were divided into two categories at distance 25 between the categories. The first category includes cultivars ‘Daxueju’, ‘Lasi’, ‘xiangbin’, ‘Yunnan Hong’ and ‘Zixia’, while cultivar ‘Linglong’ in the second category was clustered into one group.
In order to study the pollen characteristics and in vitro germination under different conditions, 6 Gerbera jamesonii Bolus cultivars were observed in terms of pollen morphology, pollen quantity and pollen viability, and the pollen size, morphological index and pollen quantity were systematically analyzed by using SPSS23.0 software. The results showed that there were differences in pollen morphology, pollen quantity and pollen viability among the 6 Gerbera cultivars. The pollen grains of the cultivar ‘Linglong’ were the largest, and those of cultivar ‘Daxueju’ the smallest. The quantity of pollen of cultivar ‘Yunnan Hong’ was the highest, and that of cultivar ‘Linglong’ the lowest. The pollen viability at different flowering stages (flowers initially opened, half opened or fully opened) and temperatures (5, 15, 25, 35 ℃) determined by pollen germination in vitro ranged from 2.75% to 33.54% and from 0.37% to 34.62%, respectively. The systematic clustering showed that the length and diameter of pollen grain were clustered. Six Gerbera cultivars were divided into two categories at distance 25 between the categories. The first category includes cultivars ‘Daxueju’, ‘Lasi’, ‘xiangbin’, ‘Yunnan Hong’ and ‘Zixia’, while cultivar ‘Linglong’ in the second category was clustered into one group.
2020, 11(4): 461-469.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.009
Abstract:
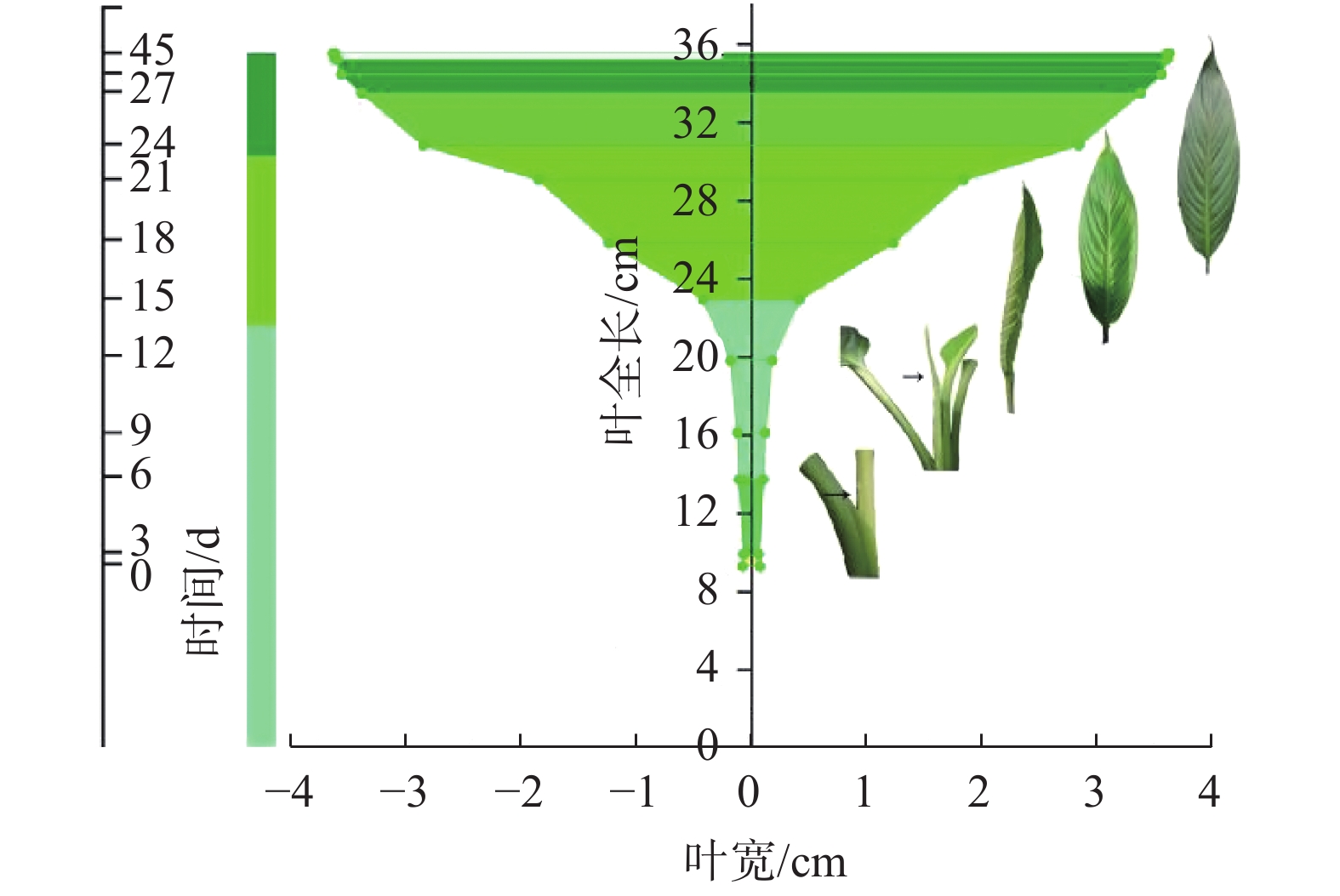
The leaf width, leaf length, leaf area, leaf vein number, leaf apex angle, fullleaf length and leaf SPAD of three Spathiphyllum cultivars, ‘Mojo’, ‘Sensation’ and ‘Queen’, with different leaf shapes were measured during the leaf growth stages, and the resultingdata were statistically analyzed to determine the quantitative leaf growth of the three cultivars, and fitted to the logistic equation as leaf growth models. A funnel-shaped plot presented a great change in a two-dimensional dynamic pattern of full leaf length and leaf width over time. Fully-expanded leaves were significantly different in leaf morphology among the three cultivars, and full leaf length, leaf length and leaf thickness were key characters that contributed to significant differences in leaf morphology among the cultivars. Full leaf length, leaf length, leaf width, leaf area were selected, based on which a Logistic growth model y=K/(1+ae−bt) was established. Fitting degree R2 of the Logistic growth equation for these four characters was above 0.97, and the coefficients between the measured and theoretical values were all above 0.99, which means the equation is suitable for fitting the growth of theSpathiphyllumleaves. Start-up growth stage, fast-growth stage and post-growth stage were deduced for Spathiphyllumleaf growth through the derivation of the Logistic growth equation combining with the leaf morphological changes. The coefficients of variation of the 8 main leaf characters of the three Spathiphyllum cultivars were distributed to a range between 18.07% and 88.85%, and the Shannon genetic diversity index H′ was 2.94−3.28, indicating a genetic diversity of the leaf characters inSpathiphyllum.
The leaf width, leaf length, leaf area, leaf vein number, leaf apex angle, fullleaf length and leaf SPAD of three Spathiphyllum cultivars, ‘Mojo’, ‘Sensation’ and ‘Queen’, with different leaf shapes were measured during the leaf growth stages, and the resultingdata were statistically analyzed to determine the quantitative leaf growth of the three cultivars, and fitted to the logistic equation as leaf growth models. A funnel-shaped plot presented a great change in a two-dimensional dynamic pattern of full leaf length and leaf width over time. Fully-expanded leaves were significantly different in leaf morphology among the three cultivars, and full leaf length, leaf length and leaf thickness were key characters that contributed to significant differences in leaf morphology among the cultivars. Full leaf length, leaf length, leaf width, leaf area were selected, based on which a Logistic growth model y=K/(1+ae−bt) was established. Fitting degree R2 of the Logistic growth equation for these four characters was above 0.97, and the coefficients between the measured and theoretical values were all above 0.99, which means the equation is suitable for fitting the growth of theSpathiphyllumleaves. Start-up growth stage, fast-growth stage and post-growth stage were deduced for Spathiphyllumleaf growth through the derivation of the Logistic growth equation combining with the leaf morphological changes. The coefficients of variation of the 8 main leaf characters of the three Spathiphyllum cultivars were distributed to a range between 18.07% and 88.85%, and the Shannon genetic diversity index H′ was 2.94−3.28, indicating a genetic diversity of the leaf characters inSpathiphyllum.
2020, 11(4): 470-478.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.010
Abstract:
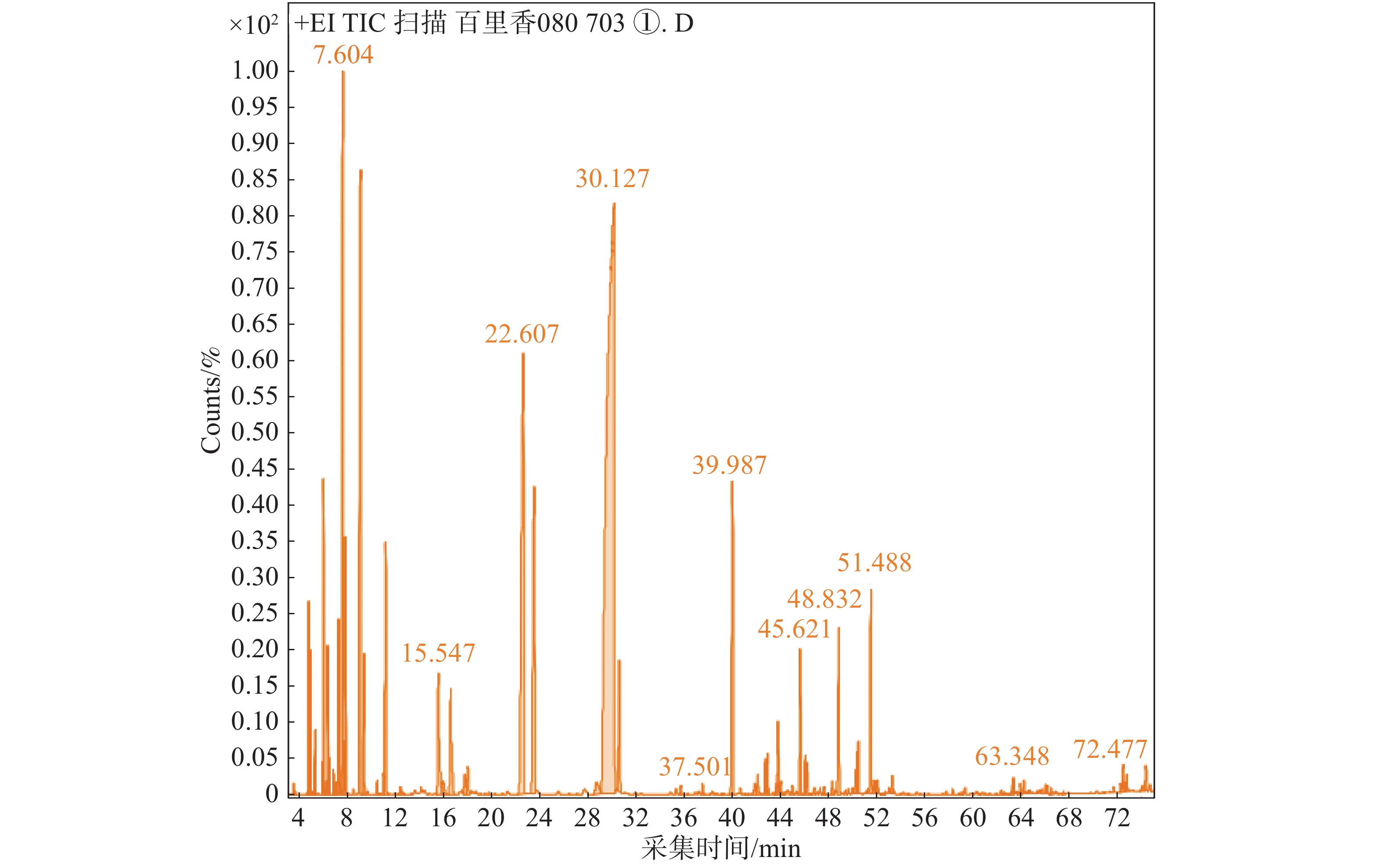
The content and the compositions of essential oils extracted with steam distillation from three species of thyme (Thymus vulgaris, Thymus citriodorus, Thymus serpyllum) were analyzed by using GC-MS method and compared. The results showed that the contents of essential oils extracted from the three Thymus species were 0.15−5.00 mL·kg−1, of which the essential oil content of T. serpyllum was the highest. There were 59 volatile components in the essential oils detected, including 23 terpenes, 13 alcohols, 7 esters, 4 phenols, 3 ketones, 5 alkanes, 2 ethers and 2 aldehydes. T. vulgaris and T. serpyllum were detected to contain 34 and 35 compounds in the essential oils, respectively, and their relative contents of thymol were the highest (37.45% and 40.17%, respectively), based on which they were grouped as the thymol type. T. citriodorus was identified to contain 29 compounds in the essential oil, and its relative content of cis-geraniol was the highest (36.01%), based on which it was listed as geraniol type, and had a strong aroma of Lemon. There are significant differences in type and content of components in the essential oil among the three Thymus species, which might provide some evidences for the development and utilization of the three Thymus species in Quanzhou, Fujiang.
The content and the compositions of essential oils extracted with steam distillation from three species of thyme (Thymus vulgaris, Thymus citriodorus, Thymus serpyllum) were analyzed by using GC-MS method and compared. The results showed that the contents of essential oils extracted from the three Thymus species were 0.15−5.00 mL·kg−1, of which the essential oil content of T. serpyllum was the highest. There were 59 volatile components in the essential oils detected, including 23 terpenes, 13 alcohols, 7 esters, 4 phenols, 3 ketones, 5 alkanes, 2 ethers and 2 aldehydes. T. vulgaris and T. serpyllum were detected to contain 34 and 35 compounds in the essential oils, respectively, and their relative contents of thymol were the highest (37.45% and 40.17%, respectively), based on which they were grouped as the thymol type. T. citriodorus was identified to contain 29 compounds in the essential oil, and its relative content of cis-geraniol was the highest (36.01%), based on which it was listed as geraniol type, and had a strong aroma of Lemon. There are significant differences in type and content of components in the essential oil among the three Thymus species, which might provide some evidences for the development and utilization of the three Thymus species in Quanzhou, Fujiang.
2020, 11(4): 479-486.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.011
Abstract:
An attempt was made to analyze the interspecific associations between the tree layer, shrub layer and herb layer within the Phoebe tavoyana (Meissn.) Hook f secondary forest communities in the low-altitude areas of Mount Wuzhishan in Hainan Province with a view to making clear the inherent laws between community succession and association for the conservation, restoration and reestablishment of the P. tavoyana natural secondary communities in the low-altitude areas of Mount Wuzhishan. Based on the quadrat survey the overall associations among the populations of 19 tree species, 15 shrub species and 10 herbaceous species within the 8 quadrat sampling sites of the P. tavoyana secondary forest communities which have been restored for the longest time duration were analyzed by using 2×2 contingency table, variance ratio method, chi-square test and Jaccard indexes. The analysis showed that the overall associations among the dominant populations were not significantly correlated at the tree and shrub layers in the P. tavoyana secondary forest communities. The Jaccard indexes were highly consistent with the results of the chi-square test. There were more species pairs with positive than negative correlation. The species pairs with significantly positive correlation were in the minority, while those with insignificantly positive correlation were in the majority. The overall associations among the dominant populations at the herb layer were significantly negatively correlated, with a small number of herbaceous species positively correlated and a large number of herbaceous species negatively correlated, which suggests fierce competition for sunlight and heat resources among the herbaceous species. It is concluded that the P. tavoyana secondary forest communities in the low-altitude areas of Mount Wuzhishan in Hainan are loosely structured.
An attempt was made to analyze the interspecific associations between the tree layer, shrub layer and herb layer within the Phoebe tavoyana (Meissn.) Hook f secondary forest communities in the low-altitude areas of Mount Wuzhishan in Hainan Province with a view to making clear the inherent laws between community succession and association for the conservation, restoration and reestablishment of the P. tavoyana natural secondary communities in the low-altitude areas of Mount Wuzhishan. Based on the quadrat survey the overall associations among the populations of 19 tree species, 15 shrub species and 10 herbaceous species within the 8 quadrat sampling sites of the P. tavoyana secondary forest communities which have been restored for the longest time duration were analyzed by using 2×2 contingency table, variance ratio method, chi-square test and Jaccard indexes. The analysis showed that the overall associations among the dominant populations were not significantly correlated at the tree and shrub layers in the P. tavoyana secondary forest communities. The Jaccard indexes were highly consistent with the results of the chi-square test. There were more species pairs with positive than negative correlation. The species pairs with significantly positive correlation were in the minority, while those with insignificantly positive correlation were in the majority. The overall associations among the dominant populations at the herb layer were significantly negatively correlated, with a small number of herbaceous species positively correlated and a large number of herbaceous species negatively correlated, which suggests fierce competition for sunlight and heat resources among the herbaceous species. It is concluded that the P. tavoyana secondary forest communities in the low-altitude areas of Mount Wuzhishan in Hainan are loosely structured.
2020, 11(4): 487-491.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.012
Abstract:
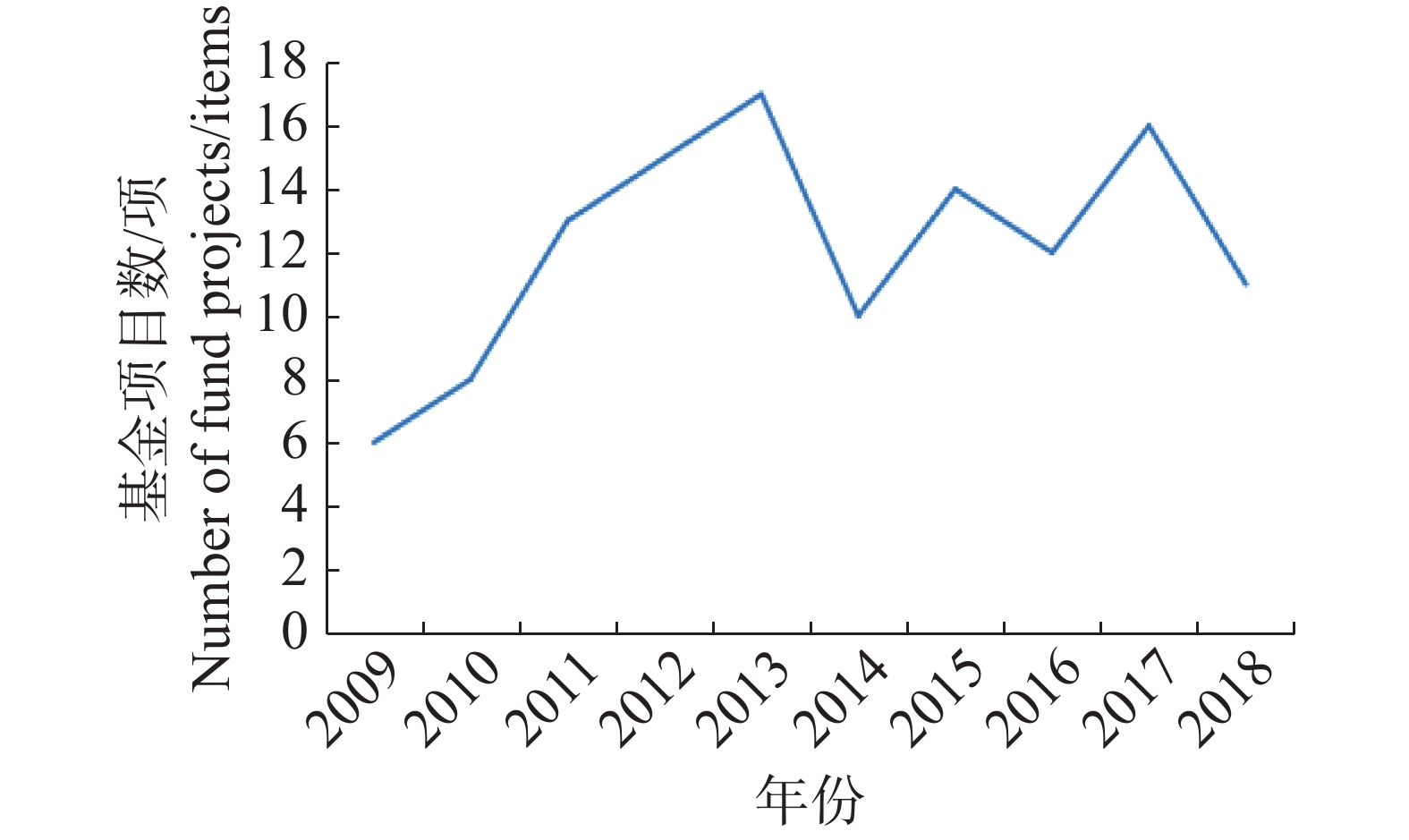
Based on the data obtained from the National Natural Science Foundation (NSFC) for research on banana from 2009 to 2018, the status of the NSFC projects for research on banana was analyzed. The results showed that 122 projects of research on banana were funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China in the past ten years, with a total funding of 56.02 million yuan. Of the total projects, 102 projects were mainly funded from the Department of Life Sciences under the NSFC, totaling 46.68 million yuan. Project chiefs Dr. Lu Wangjin and Dr. Zhang Xirui implemented the largest number of NSFC projects, 3 projects each. The top three institutions that received most projects were Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (28 projects), South China Agricultural University (21 projects), and Hainan University (16 projects). For the types of NSFC projects funded by the NSFC the general program (40 projects) accounted for 33%, Young Scientist Fund (52 projects) for 42%, and Fund for Less Developed Regions (26 projects) for 21%. At the same time, the changing trend of the NSFC projects funded for research on banana were analyzed, and some suggestions were made based on the current problems arising from the application for the NSFC projects.
Based on the data obtained from the National Natural Science Foundation (NSFC) for research on banana from 2009 to 2018, the status of the NSFC projects for research on banana was analyzed. The results showed that 122 projects of research on banana were funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China in the past ten years, with a total funding of 56.02 million yuan. Of the total projects, 102 projects were mainly funded from the Department of Life Sciences under the NSFC, totaling 46.68 million yuan. Project chiefs Dr. Lu Wangjin and Dr. Zhang Xirui implemented the largest number of NSFC projects, 3 projects each. The top three institutions that received most projects were Chinese Academy of Tropical Agricultural Sciences (28 projects), South China Agricultural University (21 projects), and Hainan University (16 projects). For the types of NSFC projects funded by the NSFC the general program (40 projects) accounted for 33%, Young Scientist Fund (52 projects) for 42%, and Fund for Less Developed Regions (26 projects) for 21%. At the same time, the changing trend of the NSFC projects funded for research on banana were analyzed, and some suggestions were made based on the current problems arising from the application for the NSFC projects.
2020, 11(4): 492-506.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.013
Abstract:
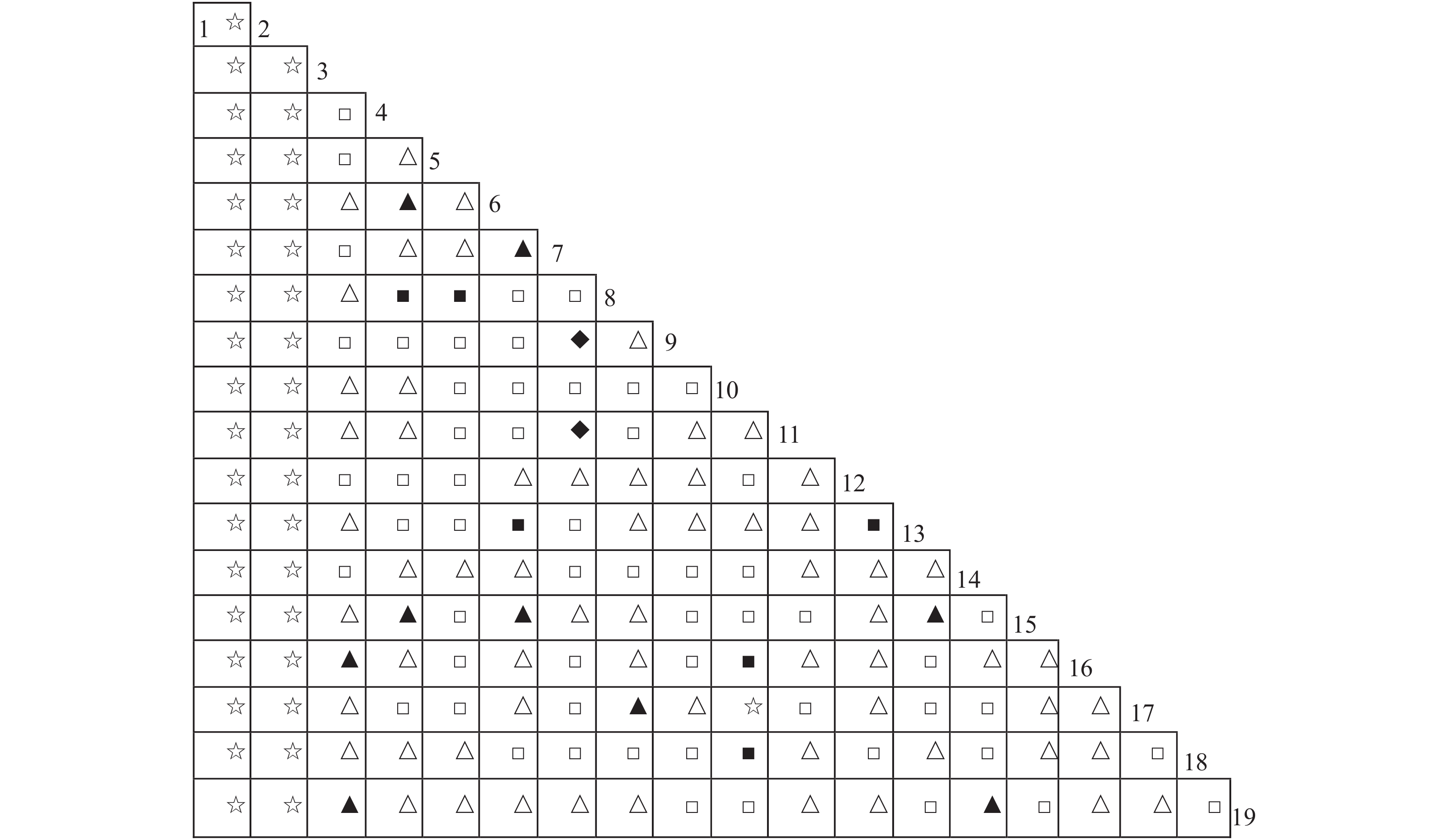
A survey of invasive plants at Danzhou Campus of Hainan University and its surrounding areas to observe the distribution and habitats of the invasive plants. In the survey 80 quadrats (2.3 ha each quadrat) were arranged in an area of 184.1 ha at the Campus and its surroundings, and 223 invasive plants were counted to observe their distribution frequency and diversity in the quadrats. The habitats of the invasive plants, quadrats and invasive plants were clustered by using the pheatmap function package in R language to calculate the similarity of the invasive plant species in different habitats or quadrats, and the probability of simultaneous appearance of different invasive plant species in the quadrats. The results showed that in the habitat clustering the invasive plant species had the highest similarity in the wasteland and vegetable field, followed by in the buildings and nurseries. As for the clustering of the quadrats, the quadrats were grouped into three modules: red, yellow and blue, where the invasive plant species were distributed in a given way and the main invasive plants were not the same. For the clustering of invasive plants, the invasive plants were grouped into gray, green, orange, green and purple modules, and they were related to the distribution frequency of each species to some extent. Moreover, the invasive plant species with similar characteristics tended to be distributed in the specific quadrats. This survey not only clarifies the distribution and habitats of each invasive plant species, but also provides reference for control and application of these invasive plants.
A survey of invasive plants at Danzhou Campus of Hainan University and its surrounding areas to observe the distribution and habitats of the invasive plants. In the survey 80 quadrats (2.3 ha each quadrat) were arranged in an area of 184.1 ha at the Campus and its surroundings, and 223 invasive plants were counted to observe their distribution frequency and diversity in the quadrats. The habitats of the invasive plants, quadrats and invasive plants were clustered by using the pheatmap function package in R language to calculate the similarity of the invasive plant species in different habitats or quadrats, and the probability of simultaneous appearance of different invasive plant species in the quadrats. The results showed that in the habitat clustering the invasive plant species had the highest similarity in the wasteland and vegetable field, followed by in the buildings and nurseries. As for the clustering of the quadrats, the quadrats were grouped into three modules: red, yellow and blue, where the invasive plant species were distributed in a given way and the main invasive plants were not the same. For the clustering of invasive plants, the invasive plants were grouped into gray, green, orange, green and purple modules, and they were related to the distribution frequency of each species to some extent. Moreover, the invasive plant species with similar characteristics tended to be distributed in the specific quadrats. This survey not only clarifies the distribution and habitats of each invasive plant species, but also provides reference for control and application of these invasive plants.
2020, 11(4): 507-516.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.014
Abstract:
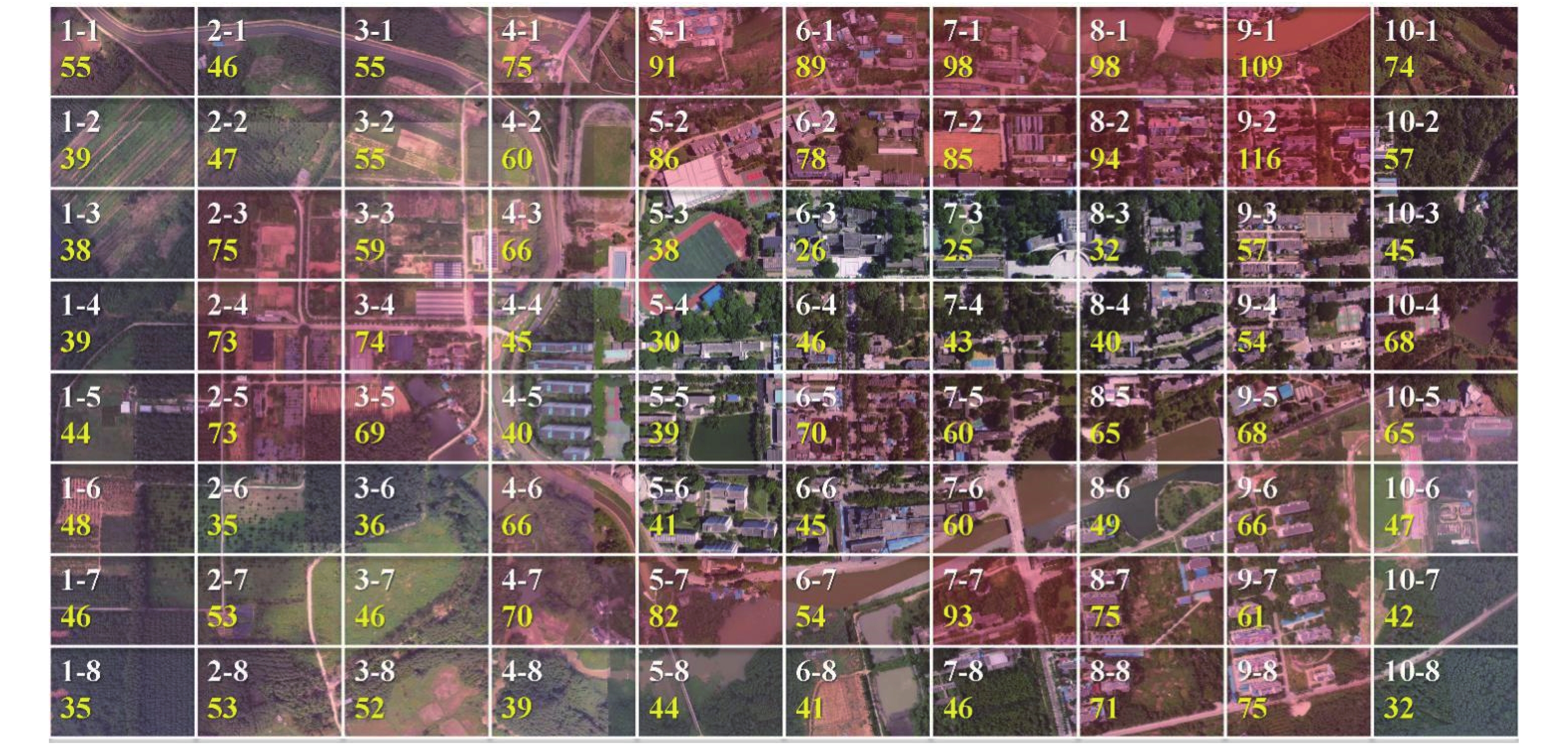
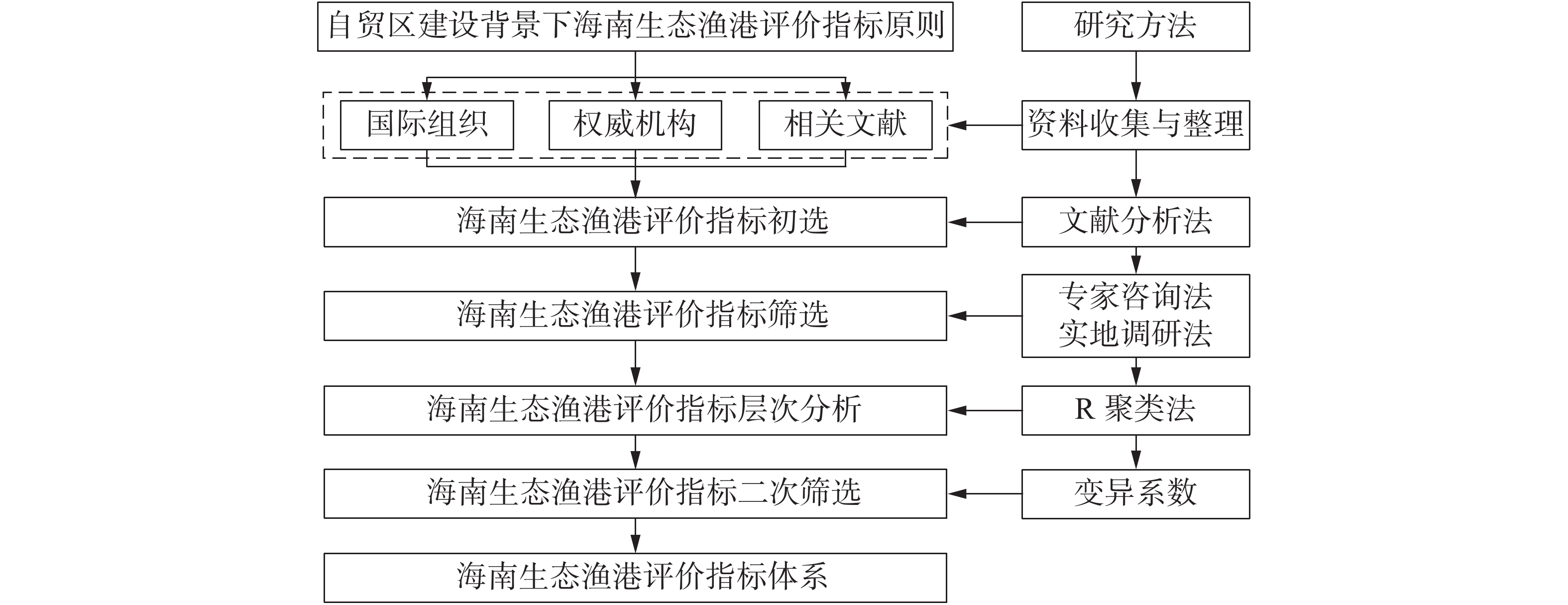
Under the background of Hainan free trade port (FTP) construction, the development of Hainan fishing port must meet the requirements of ecological construction. From the perspective of ecological civilization and green development, the evaluation indicators related to ecological fishing port (EFP) are obtained through primary selection and screening. By using clustering method and coefficient of variation analysis, the evaluation index system of ecological fishing port including target layer, criterion layer, factor layer and index layer is constructed. Based on the data obtained, this paper makes an empirical study on six fishing ports in Hainan. The results show that the constructed evaluation index system can accurately evaluate the ecology of each fishing port, which proves the rationality of the comprehensive evaluation system of Hainan Ecological fishing port under the background of free trade port construction.
Under the background of Hainan free trade port (FTP) construction, the development of Hainan fishing port must meet the requirements of ecological construction. From the perspective of ecological civilization and green development, the evaluation indicators related to ecological fishing port (EFP) are obtained through primary selection and screening. By using clustering method and coefficient of variation analysis, the evaluation index system of ecological fishing port including target layer, criterion layer, factor layer and index layer is constructed. Based on the data obtained, this paper makes an empirical study on six fishing ports in Hainan. The results show that the constructed evaluation index system can accurately evaluate the ecology of each fishing port, which proves the rationality of the comprehensive evaluation system of Hainan Ecological fishing port under the background of free trade port construction.
2020, 11(4): 517-522.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.015
Abstract:
Cerambycid beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) are an economically important group of insect pests which cause damages to forestry and fruit industry. They are numerous in species, widely distributed and hard to control due to their better protection mechanism and periodic outbreak, leading to serious infestation. Population control in the chemical ecology of cerambycid beetles has recently become a novel approach for integrated control of cerambycid beetles since the traditional insecticidal control of cerambycid beetles is less effective. Insect pheromones have the advantages of very low application rate, high efficiency, non-toxicity and no pollution, and can be used for target pest monitoring and trapping, which plays a key role in integrated pest control. The previous researches of cerambycid pheromones were reviewed, and an outlook for application of the cerambycid pheromones were made to provide reference for the integrated control of the cerambycid beetles.
Cerambycid beetles (Coleoptera: Cerambycidae) are an economically important group of insect pests which cause damages to forestry and fruit industry. They are numerous in species, widely distributed and hard to control due to their better protection mechanism and periodic outbreak, leading to serious infestation. Population control in the chemical ecology of cerambycid beetles has recently become a novel approach for integrated control of cerambycid beetles since the traditional insecticidal control of cerambycid beetles is less effective. Insect pheromones have the advantages of very low application rate, high efficiency, non-toxicity and no pollution, and can be used for target pest monitoring and trapping, which plays a key role in integrated pest control. The previous researches of cerambycid pheromones were reviewed, and an outlook for application of the cerambycid pheromones were made to provide reference for the integrated control of the cerambycid beetles.
2020, 11(4): 523-532.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.04.016
Abstract:
Areca nut is one of the most popular masticatories and has also been widely controversial. On the one hand, areca nut has been considered a healthful traditional food and medicine, while on the other hand, areca nut has been classified as carcinogenic to human beings (Group 1) by the International Agency for Cancer Research (IARC). In China the arecanut industry generated a total output value of nearly 100 billion yuan in 2019, and increasing public attention to public health and hygiene has also triggered public opinion crises against the arecanut industry. Therefore, we urgently need to fully understand the health benefits and disadvantages of arecanut with a view to establishing comprehensive management regulations and systems for arecanut in China. A review was made of the cultural traditions, patterns of use, health effects, and policies of areca nuts in the world, especially in Southeast Asian countries in order to provide references for the healthy development of the arecanut industry in China and the policy making by China’s regulatory authorities.
Areca nut is one of the most popular masticatories and has also been widely controversial. On the one hand, areca nut has been considered a healthful traditional food and medicine, while on the other hand, areca nut has been classified as carcinogenic to human beings (Group 1) by the International Agency for Cancer Research (IARC). In China the arecanut industry generated a total output value of nearly 100 billion yuan in 2019, and increasing public attention to public health and hygiene has also triggered public opinion crises against the arecanut industry. Therefore, we urgently need to fully understand the health benefits and disadvantages of arecanut with a view to establishing comprehensive management regulations and systems for arecanut in China. A review was made of the cultural traditions, patterns of use, health effects, and policies of areca nuts in the world, especially in Southeast Asian countries in order to provide references for the healthy development of the arecanut industry in China and the policy making by China’s regulatory authorities.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 898KB
PDF 898KB






 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS