2021 Vol. 12, No. 1
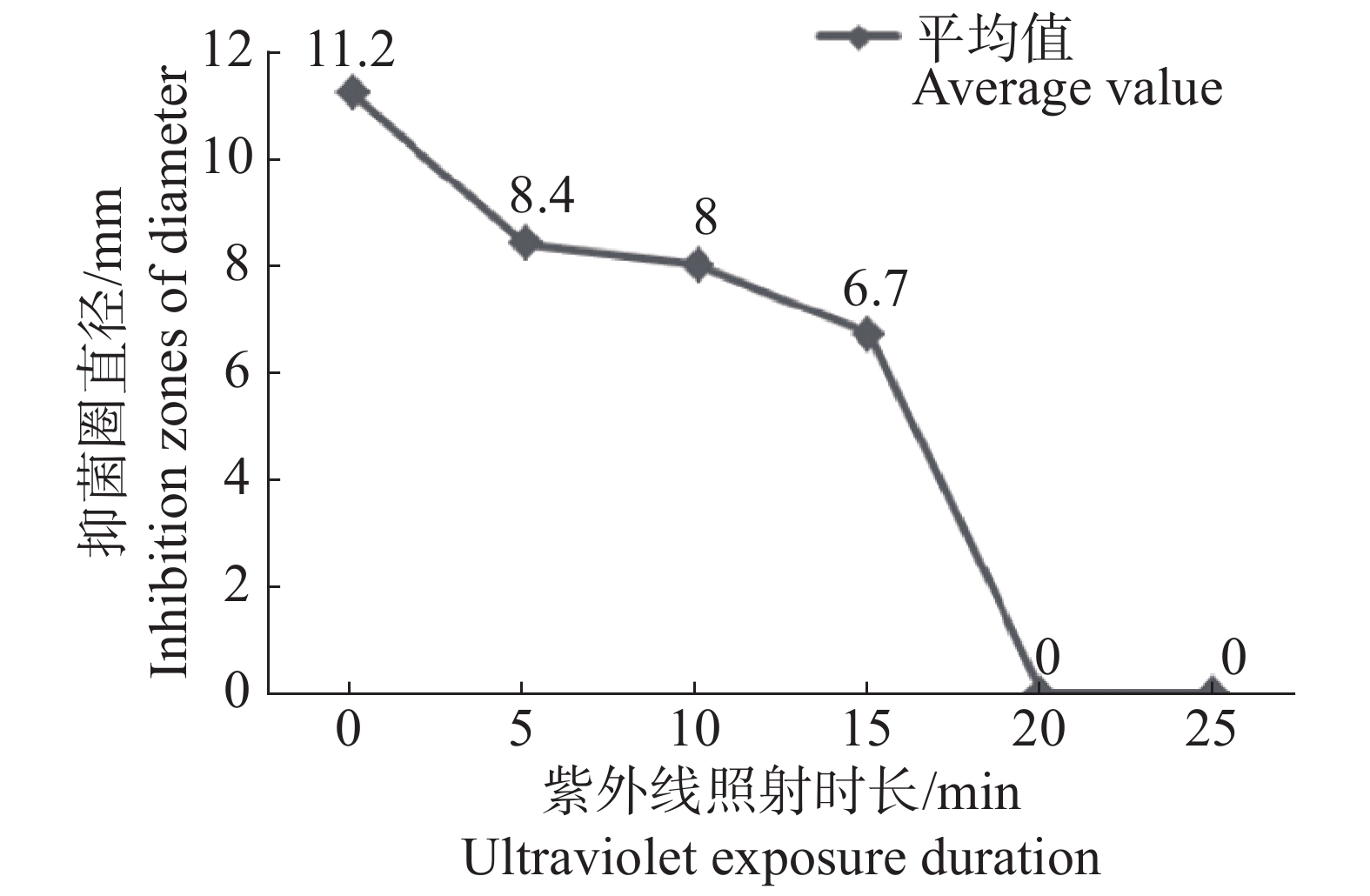
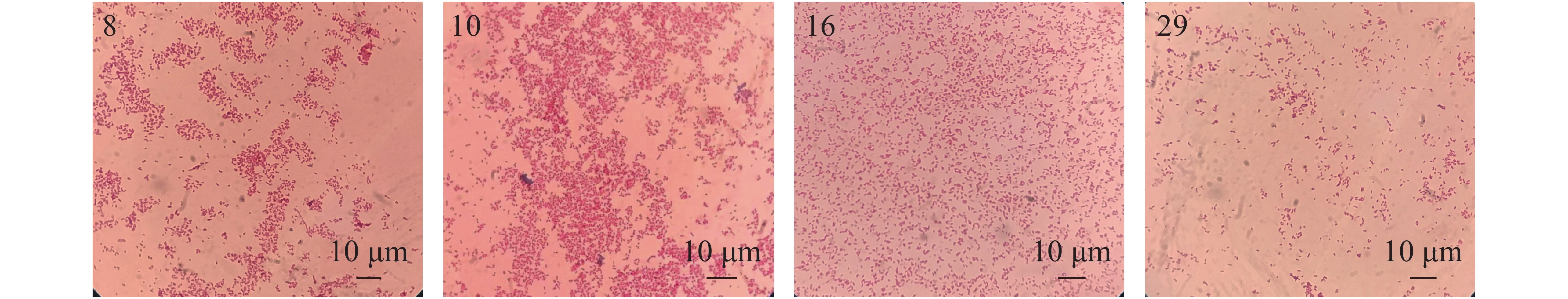
The effective components of noni (Morinda citrifolia) fruit were extracted by traditional water decocting method and used to test their bacteriostatic effect on Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolated from Litopenaeus vannamei. V. parahaemolyticus is the causative agent of acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease that causes serious loss in aquaculture of Litopenaeus vannamei. Diameter of inhibition zones, minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC), minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) and bacteriostatic rate were determined, based on which the antibacterial effects of the noni fruit extract on V. parahaemolyticus in vitro were discussed. The results showed that the noni fruit extract inhibited the growth of V. parahaemolyticus at the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 25.00 g·L−1 and the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of 50.00 g·L−1. The bacteriostatic effect of the noni fruit extract on V. parahaemolyticus decreased or even disappeared with the increase of duration of exposure of the noni fruit extract to ultraviolet. Only when boiled for 15 min or more for extraction could M. citrifolia have a better bacteriostatic effect on the growth of V. parahaemolyticus.
Dof (DNA binding with one finger) transcription factor is a unique transcription factor in plants, which plays an important role in plant growth and development. Based on the litchi fruit development transcriptome database the basic physicochemical properties, subcellular localization, protein conserved domain, and evolutionary relationships of the Dof gene family in the fruits of litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) was analyzed by using bioinformatics methods, and the expression profile of the Dof gene family in the litchi pulp at the fruit development. stage were determined. The results showed that LcDof gene famliy in litchi contained 19 family members, with LcDof encoded protein ranging from 157 to 497 aa, and that the corresponding relative molecular weight was 17.70−54.35 kDa, with the isoelectric point (pI) ranging from 4.49 to 9.42. All subcellular localizations of LcDof family members were predicted to be located in the nucleus. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the LxDof gene family was divided into 5 groups (Group Ⅰ−Group Ⅴ), and that the expression patterns of LcDof genes were different at different fruit development stages, of which LcDof7, LcDof9, LcDof12 and LcDof15 were expressed higher at different pulp development stages, while LcDof3, LcDof10, LcDof16, LcDof17 and LcDof19 were expressed low.
In recent years the economy has developed rapidly in Sanya City, Hainan Province. With the rapid development of tourism, Gulf port construction, aquaculture and other industries, the ecological environment of the coastal waters in Sanya Bay has attracted much attention. In order to understand the relationship between the phytoplankton community structure and environmental factors in Sanya Bay, a sampling survey of phytoplankton and seawater quality at 12 survey stations near the coast of Sanya Bay was made in April and September 2019. The results showed that there are a total number of 82 species of phytoplankton identified in Spring, and a total number of 85 species identified in Autumn, in which diatoms and dinoflagellates were predominant in species composition and cell abundance. There were 4 and 9 dominant species in Spring and Autumn, respectively. Chaetoceros sp, Chaetoceros indicus, Neoceratium tripos and Guinardia flaccida were dominant species in Spring, and Chaetoceros sp was the first dominant species. Thalassionema nitzschioides, Skeletonema tropicum, Hemiaulus hauckii, Asterionella japonica, Leptocylindrus danicus, Chaetoceros lorenzianus and Chaetoceros diversus were dominant species in Autumn, and Thalassionema nitzschioides was the first dominant species. The average Shannon-Wiener diversity index, Pielou evenness index and Margalef diversity index were 3.33, 3.27, 2.26 in Spring, respectively, and 4.05, 0.79, 3.09 in Autumn, respectively. The redundancy analysis showed that the main factors affecting the phytoplankton structure were total phosphorus, ammonia nitrogen and water temperature in Spring, and total nitrogen, salinity and conductivity in Autumn.
Asplenium nidus, commonly called bird’s nest fern, now unique in the rainforest, is referred to as a “Hanging Garden” plant. In order to reveal the genetic diversity and genetic relationship of the natural population of A. nidus, and promote the effective conservation and utilization of wild A. nidus resources, 96 samples were collected from 6 populations of A. nidus in Hainan Island, and clustered by using UPGMA cluster analysis based on SRAP markers. The results showed that a total of 184 loci were amplified by 10 pairs of primers in A. nidus, of which 174 were polymorphic loci with the percentage of polymorphic loci or bands (PPB) being 94.57%. The PPB varied greatly in the populations, with an average of 85.15% based on SRAP markers. The populations of A. nidus had a relatively higher genetic variation, and each population had a high level of genetic diversity. POPGENE analysis showed that the percentage of genetic differentiation within the population was 86.94%, while the percentage of genetic differentiation between populations was 13.06%, which proved that there was a certain level of genetic differentiation among the populations. The average genetic similarity of the 6 populations of A nidus was 0.9224, and the average genetic distance was 0.0809. The genetic distance of the populations between BW and EXL was the closest, which was 0.0508, and the genetic distance between LMS2 and LMS3 was the longest, which was 0.1166. UPGMA cluster analysis showed the genetic distance of the wild populations of A. nidus in BW and EXL are geographically close, and hence were clustered together, indicating that the gene flow of A nidus in these two locations was smooth. The A nidus populations in LMS1 and LMS3 in the same area were clustered together. The genetic distance between the population in LMS2 and other populations in LiMushan area was the highest, and the genetic differentiation was also the most significant. This shows that SRAP markers have abundant polymorphisms among the populations of A nidus and are of great significance for revealing the genetic relationship of A nidus. When compared with the wild habitat, the population of A. nidus in each area was found to be damaged to different degrees. It is recommended to focus on in-situ conservation of A nidus. The LMS3 area, where the genetic diversity of the A nidus population is higher, can be selected to establish a higher-level nature reserve or Hainan tropical rainforest national park to facilitate expansion and rehabilitation of the population and habitat of A nidus for conservation of tropical rainforest and sustainable development of plant diversity.
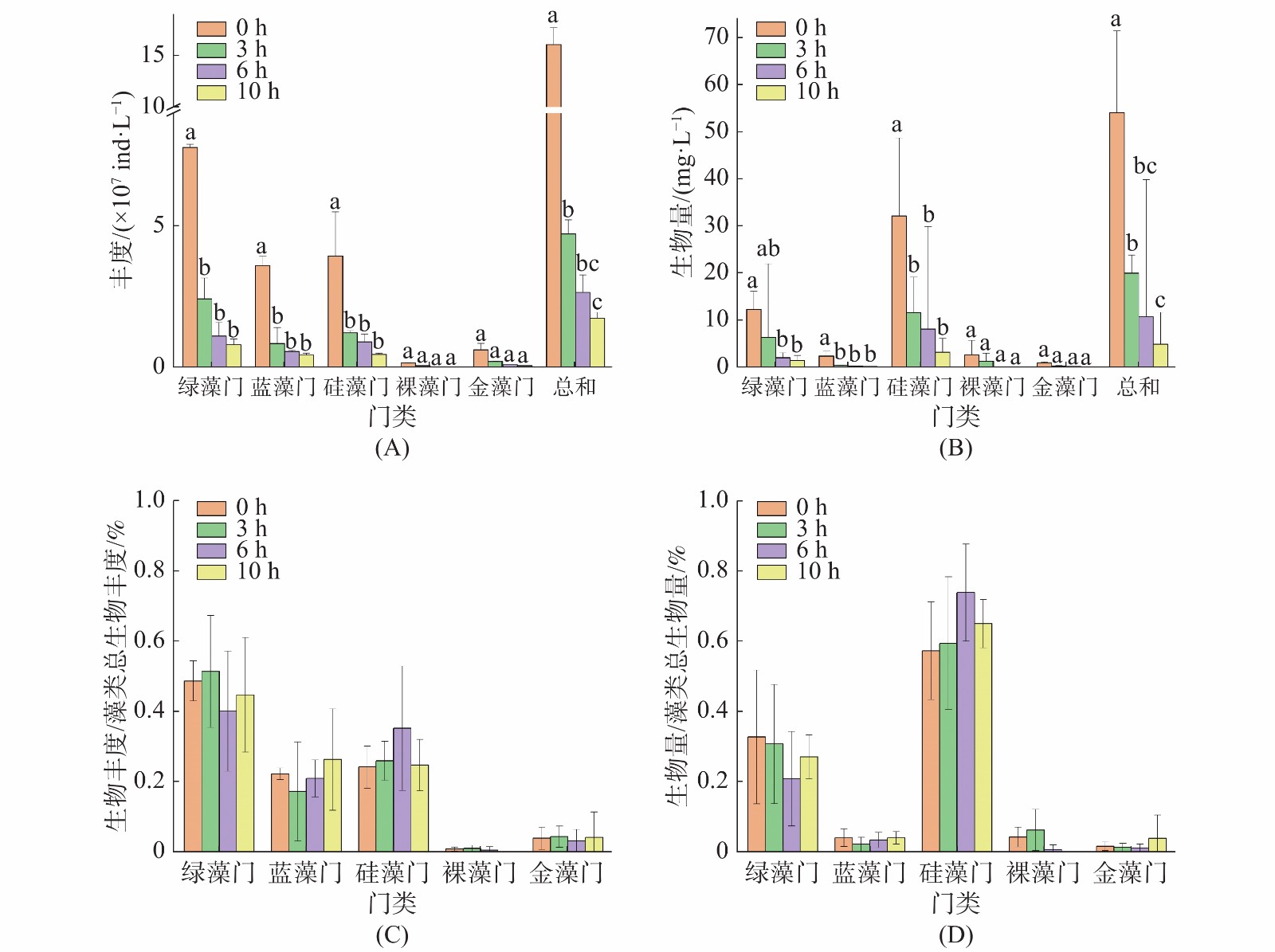
Polyculture model can improve the economic benefits of aquaculture and reduce the pollution of aquarium water. Using shellfish to ingest microalgae is an important link in this model. Due to incomplete development of filter-feeding structures, juveniles of shellfish have high filter-feeding selectivity for phytoplankton. Besides, the filter-feeding of shellfish will cause the sedimentation of suspended solids, which is helpful to improve water quality. In order to study the filter-feeding selection effect on phytoplankton and biodeposition effect of juvenile short necked clam (Ruditapes philippinarum), samples of phytoplankton in the ponds culturing juvenile short necked clam were collected at 0 h, 3 h, 6 h and 10 h after feeding for analysis of their changes in the species and density of phytoplankton. Water transparency, suspended solids, and chlorophyll-a content were measured to observe the change of water color. The results showed that about 50 species of phytoplankton were observed during the survey, mainly including Bacillariophyta, Chlorophyta, and Cyanophyta among others. Comparison of the species and biomass of phytoplankton before and after filtering showed that the juveniles of the short necked clam had a significant filter-feeding selection on the species in the phylum Bacillariophyta. Cyclotella meneghiniana is expected to be a high-quality and efficient juvenile bait. After 10 hours of feeding, the mean biomass of C. meneghiniana decreased by 94.02%, accounting for 39.97% of the mean total loss of phytoplankton. And the suspended solids settled rapidly due to filtering by the juveniles, reducing the cell density of phytoplankton. The water color changed significantly after filtering. The suspended solids decreased by 85.6%, the chlorophyll-a content decreased by 72.9%, and the transparency of the water body increased by 96.7%, which proved that the juvenile short necked clam can improve water quality via filter feeding.
In order to assess the distribution characteristics and pollution status of antibiotics in Wanning and Lingshui mariculture areas in Hainan province, Lc-ms /MS was used to detect four classes of 40 antibiotics including sulfonamides, tetracycline, chloramphenicol and quinolones in seawater. The results showed that 13 sample point concentration of antibiotic residues in the range of 10.28−156.63 ng∙L−1, and two quinolones, three tetracyclines, one chloramphenicol were detected. Among the 6 antibiotics, the content of oxytetracycline in seawater was the highest, with a mean of 16.20 ng∙L−1, followed by tetracycline, doxycycline, thiamphenicol and ciprofloxacin, with mean values of 5.39, 4.10, 1.84 and 0.18 ng∙L−1 respectively, and the lowest was Danofloxacin with a mean value of 0.13 ng∙L−1. The risk assessment of residual antibiotics in water was carried out by using the RQs risk assessment method. The results showed that there were certain ecological risks in the environment of the sampling areas of Mariculture in Wanning and Lingshui, Hainan. In particular, oxytetracycline in the fishing port of Lingshui New Village had medium risks to the relevant sensitive species and affected the growth of phytoplankton such as algae. It is recommended to control the use of these antibiotics in the process of mariculture to reduce ecological risks, and to conduct long-term observation on the ecological risks of antibiotics in mariculture areas.
In order to reveal abundance distribution patterns of evergreen and deciduous trees in the same community and the major ecologic process of the community establishment by plant species of two leading plant life forms, a community ecological survey was conducted at the permanent plot with an area of 2 ha at the broadleaf evergreen forest in Dagan Mountain, Jiangxi Province. The distribution features of the plants of two different life forms were quantified by using the cumulative empirical distribution function, and fitted by using 6 distribution models. The goodness of fit of the 6 models were tested by using Akaike information criterion (AIC) and Kolmogorov-Smimov Test. The results showed that the top three evergreen tree species arranged by the importance value are Castanopsis fargesii, Cyclobalanopsis glauca and Rhododendron latoucheae in the broadleaf evergreen forest in Dagang Mountain, while the three deciduous tree species arranged by the importance value are Alniphyllum fortune, Sapium discolor and Vernicia montana. The distribution curves of the plant species of the two life forms in Dagang Mountain were all in a S shape and were not significantly different. The pure statistical model and the neutral theoretical model except the niche models were acceptable. Neutral processes play an important role in the formation of species-abundance distribution patterns of two plant life forms.
Soil samples collected from a banana plantation in Hongxing Farm, Lingao, Hainan, were potted, and fresh harvested foliage (leaves and pseudostems) collected from the banana plantation were grounded and returned to the potted soil for indoor culture to analyze the difference of soil microbial communities in the potted soil for revelation of the effects of soil returning of the fresh harvested foliage on soil microorganism. Three treatments were arranged: soil without banana foliage (control, CK); soil mulched with banana foliage (F); soil mixed with banana foliage (T). The results showed that the relative abundance of fungal phylum Basidiomcota in the T and F treatments increased by 1.3% and 2.8%, respectively, as compared with the CK, while the relative abundance of bacterial phylum Acidobacteria increased by 5.1% and 1.1%, respectively, and that of Actinobacteria increased by 1.9%, 3.2%, respectively. The relative abundance of Fusarium between treatments was in the order of CK>F>T. The bacterial community richness (SChao1) and diversity (HShannon) between the treatments were in the order of T>F>CK, and no difference was observed in fungal communities between the treatments. Cluster analysis showed that the structure of soil microbial community in the treatment T was significantly different from that of CK. Principal coordinate analysis and OTU distribution showed that the structure of soil microbial community in the treatment T was similar to that in the treatment F. It is concluded that the treatment T increased the richness and diversity of soil bacterial community, changed the structure of soil microbial community, improved the relative abundance of microorganisms that have a decomposition function, and significantly reduced the relative abundance of pathogen Fusarium.
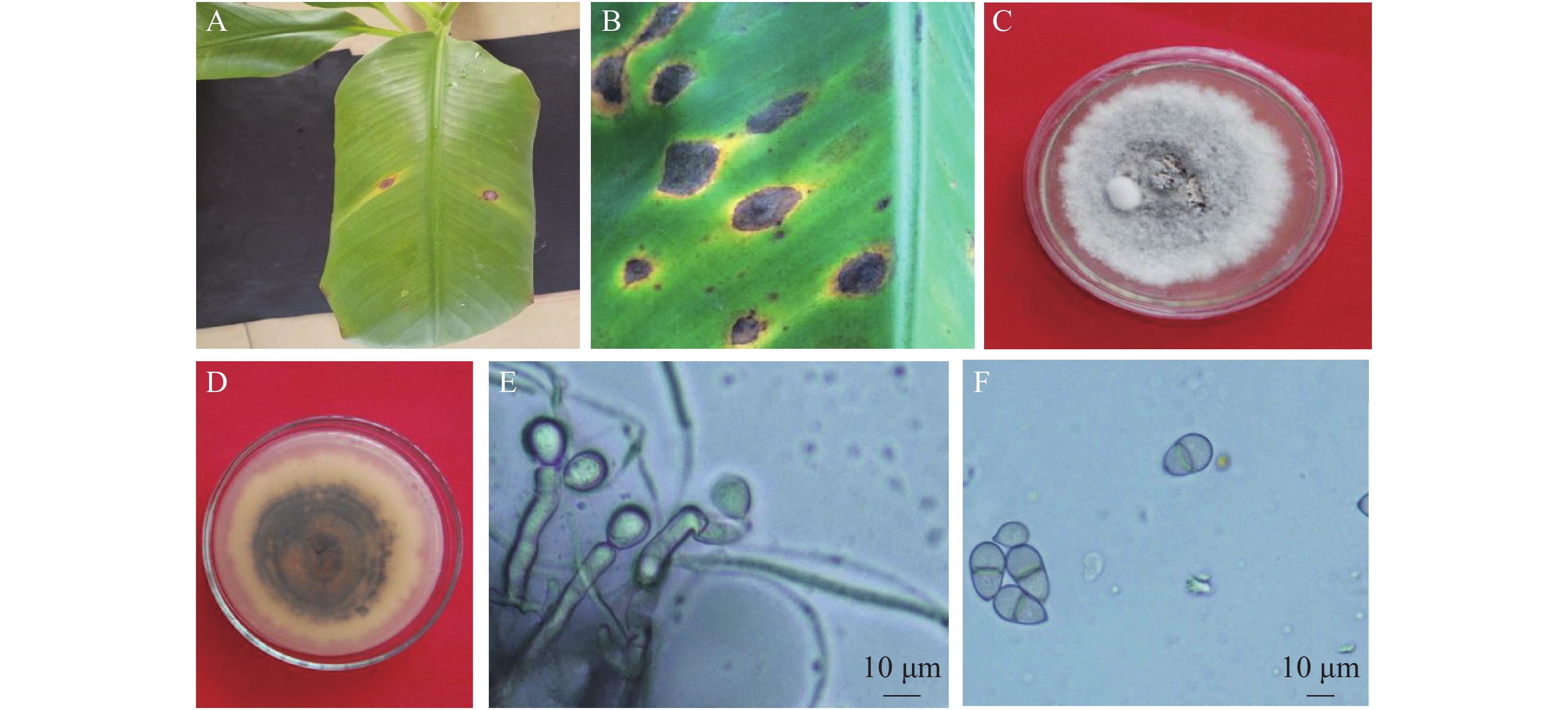
An attempt was made to have a good understanding of Cordana leaf spot of banana in Hainnan province for prevention and control. Fungi were isolated through routine tissue separation and identified based on pathogenicity test, morphological characteristics, analysis of fungal rDNA-ITS sequence and phylogeny. The isolated fungi were cultured to observe their mycelial growth on different mediums under different conditions of temperature, pH, carbon source, nitrogen source, light and ventilation. The results showed that necrotic spots with concentric rings surrounded by a bright yellow halo were observed on the infected leaves three days after inoculation, which was similar to the symptoms and signs on the leaves infected in the field. The colonies of the six strains of the fungi were grayish-white, and circular with concentric rings and irregular edge. The conidia of the six strains were obovate with single septum. The rDNA-ITS sequence length of the six strains was 575 bp (representing the accession number of strain CATAS-CM01: MN960387), which shared 100% sequence similarity to each other among the fungi isolated and 99.28%−99.65% sequence similarity to those of Neocordana musae ex-types in Genbank. Phylogenetic analysis showed that CATAS-CM01 was gathered on the same branch of several sequences of N. musae. Based on the morphological characteristics and analysis of ITS sequence and phylogenetic relationship the six pathogenic strains were identified as Neocordana musae. The analysis of the biological characteristics of the fungi isolated showed that the optimal culture media, temperature and pH for its mycelia growth were PDA and OA, 30 ℃ and 6, respectively. The optimal C-source and N-source for the mycelia growth of the fungi were lactobiose and yeast extract, respectively. Successive light and shaking were favorable for the growth of mycelia. The lethal temperature for the mycelia growth was 60℃ for 10 min
Twelve plant essential oils were tested to observe their inhibitory effect on Gilbertella persicaria that causes fruit rot of pitaya or dragon fruit in order to clarify the sensitivity of G.persicaria to plant essential oils during the storage of pitaya. The results showed that all the tested 12 plant essential oils had an inhibitory effect on G. persicaria. The top 5 plant essential oils with higher antifungal activities are oregano essential oil, citronella essential oil, cinnamon essential oil, mustard essential oil and clove essential oil, which had the EC50 values of 94.1, 122.9, 174.0, 254.3 and 261.1 μg·mL−1, respectively. Pitaya fruits were treated with these 5 essential oils at a concentration of 1 000 μL·L−1 by dipping, and inoculated with the fungi G.persicaria to observe the control effect of the essential oils on the fungi. The results showed the mustard essential oil had the control rate of 100% against G. persicaria and caused no damage to the surface of the fruit, while the oregano essential oil had a control rate of 91.96% against G. persicaria, but caused serious damage to the fruit surface, which is not suitable for application in production.
Powdery mildew fungi complete its infection process on living host plants through the establishment of haustoria which secretes a plethora of effectors into plant cells. A previous study showed that 133 potential effectors of Oidium heveae have been predicted by genome and transcriptome sequencing. However, the biological function of these effectors are still unknown. In this study, an effector gene, named OhEF 2, was cloned and transformed into Arabidopsis, and the transgenic plants of OhEF 2 gene in Arabidopsis Col-0 background were constructed and inoculated with O. heveae. Inoculation assay showed that OhEF 2 obviously enhanced the susceptibility of Arabidopsis to O. heveae. However, OhEF 2 did not increase the virulence of Pseudomonas syringae DC 3000, suggesting that OhEF 2 probably plays a role only in the process of powdery mildew infection. Further study showed that OhEF 2 decreased the callose deposition and PR1 gene expression triggered by O. heveae in Arabidopsis, which lays a foundation for the future study of OhEF 2 virulence mechanisms in host plants.
The acute toxicity of four new insecticides and seven conventional insecticides to natural enemy Trichogramma chilonis was measured with the method of film residue in a tube, and safety assessment was conducted according to the field recommended dosages. Results showed that among the four new insecticides, Spinetoram had exhibited a medium risk on T. chilonis adults while Cyantraniliprole、Triflumezopyrim and flubendiamide exhibited relative safety; Among the seven conventional insecticides, Chlorpyrifos had exhibited a high risk on T. chilonis adults while Abamectin, Imidacloprid and Nitenpyram was defined as a medium risk, Chlorantraniliprole, Indoxacarb, and Emamectin benzoate exhibited relative safety. Our results provided a valuable reference to the applications of chemical control and nature enemy control of insect pests.
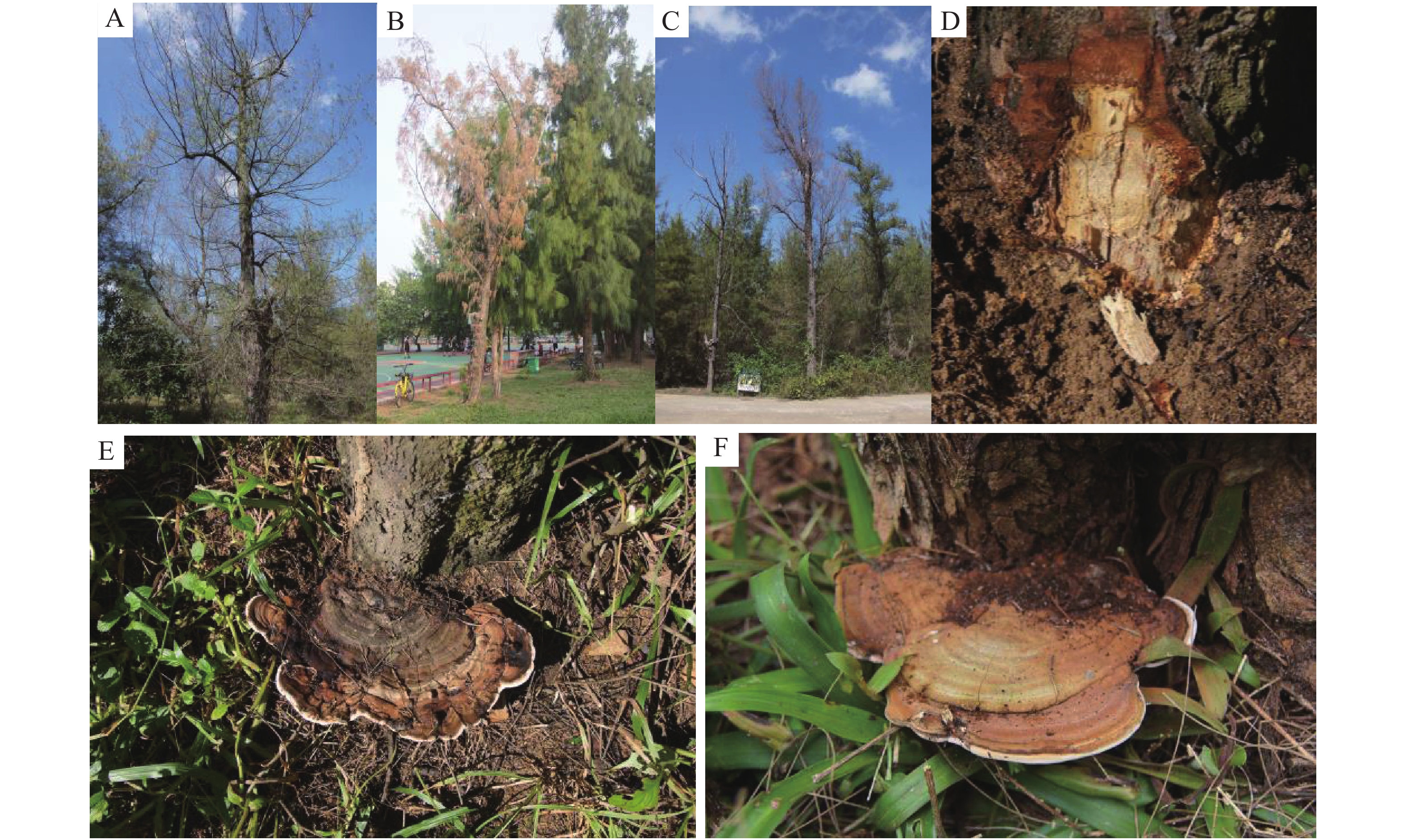
A Ganoderma stem rot disease was found to infect Casuarina equisetifolia in 2018 in Wanning City, Hainan Province. In order to clarify the pathogen species and biological characteristics of the disease, 10 strains with the same morphology were isolated from basidiocarps by using the conventional tissue separation method. MMHJF001, a representative strain with excellent growth, was selected for pathogenicity determination, morphological identification, sequence analysis of rDNA-ITS and SSU, phylogenetic tree construction, and biological characteristics determination. The results showed that the pathogen causing the stem rot of C. equisetifolia was Ganoderma australe (Fr.) Pat. The optimum temperature for mycelial growth of the pathogen is 28 ℃, and the optimum pH is 7.0. Dark conditions are conducive to mycelial growth of the pathogen, and the pathogen grows better on the plant extract media from Acacia auriculiformis, Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) and Hevea brasiliensis.
A total of 10 strains of Aeromonas spp. were isolated from sick Siamese crocodile in Hainan, including 5 strains of Aeromonas hydrophila, 3 strains of Aeromonas dhakensis, 1 strain of Aeromonas veronii and 1 strain of Aeromonas jandaei, and tested for virulence genes, antibiotic resistance genes, and antibiotic susceptibility. The results showed that aerosol genes, enterotoxin genes and protease genes had a higher detection rate, of which two virulence genes, lip and ela, had a detection rate of up to 100% and the genes resistant to quinolones, tetracyclines, sulfonamides, β-lactams, and aminoglycoside had a detection rate of higher than 50%. Antibiotic susceptibility testing showed that Aeromonas spp.were more sensitive to quinolone, tetracycline, aminoglycoside, chloramphenicol and carbapenem antibiotics, and more resistant to β-lactam, sulfonamides and glycopeptide antibiotics.
In order to reveal the pollution situation of salmonella in fresh livestock and poultry meats in Meilan district of Haikou City, Hainan Province a total of 50 samples of pork, chicken and duck meats from inside and outside of the market were collected for salmonella isolation, Kindy-Bauer antibiotic sensitivity test and antibiotic resistance gene analysis. The results showed that 4 strains of salmonella were isolated from the 50 samples with a detection rate of 8%. The 4salmonella isolates exhibited different levels of sensitivity to 15 antibiotics: 100% resistant to penicillin, ampicillin, tetracycline and kitasamycin, 75% resistant to chloramphenicol, amoxicillin and sulfisoxazole and upto 50% resistant to doxycycline, erythromycin, kanamycin, norfloxacin and streptomycin but not sensitive to ciprofloxacin. Meanwhile, the detection rate of the 4 salmonella isolates for sulfonamide resistance gene sul2 and quinolone resistance gene qurB gene was 0, and the detection rate for tetracycline resistance tetA gene was 50%. It is concluded that the fresh meats of livestock and poultry in Haikou infected with salmonella was not popular, but these isolates had a wide resistance to multi-antibiotics. It is necessary to strengthen the supervision of food safety and reduce the abuse of antibiotics.
Drosera peltata is not only a common insectivore plant in nature, but also an important medicinal material. It is widely used as an anti-inflammatory drug in China to treat injuries, arthritis, neurodermatitis and other diseases. D. peltata has a potential development value, and its clinical application and other aspects have gradually attracted the attention of scholars from all walks of life. The advances in research and development of D. peltata are reviewed in terms of chemical composition, medicine value and application in a view to providing reference for its follow-up research and development.
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR-Cas) has been widely used as a tool in recent years for gene editing in animal and plant gene editing. The proven Class2 CRISPR-Cas systems, such as CRISPR-Cas12 and CRISPR-Cas14, have been discovered through bioinformatics mining. Bioinformatics has become an important tool for discovering of new CRISPR-Cas systems and their subtypes. Two methods for bioinformatics mining of Cas enzymes are reviewed. One method is to create a hidden Markov model (HMM) using known Cas enzymes to predict similar Cas enzymes, and the other method is to analyze the possible upstream and downstream Cas enzymesbased on the recognition of the marker sequence Cas1 or CRISPR. The limitations of these two methods are discussed. Furthermore, methods for further analysis of Cas protein and CRISPR sequences are also reviewed, including Cas protein homology, phylogenetic analysis, and analysis of CRISPR sequence spacers, protospacers&protospacer adjacent motifs (PAM).
Fungi are one class of important plant pathogens, which accounts for two thirds of all plant diseases. The rapid and accurate early detection technologies for plant fungal diseases are the key to disease prediction and prevention of disease prevalence. The detection principle, application status and existing problems of common early detection technologies for fungal diseases were reviewed. The detection system of fluorescence quantitative PCR and its application prospect in the prediction model for rubber tree anthracnose were summarized, which provides reference for the early detection and prediction of rubber tree anthracnose.
Thrips palmi Karny is a small but highly productive invasive pest insect and causes damages to the host plants mainly through direct feeding, oviposition and/or indirect transmission of a virus. T. palmi has been found distributed in 13 provinces of China, and infects a variety of crops, leading to slow plant growth of the crops and abnormal growth of melon and fruit and hence heavy economic losses. A review of T. palmi was made in morphological identification characteristics, ecological characteristics, occurrence hazards, drug resistance status and comprehensive control techniques in combination with our recent research. The purpose of this review is to enable technicians and growers of fruits and vegetables to have a deeper understanding of T. palmi so that they can prevent and control T. palmi more effectively to avoid more serious economic losses and to maintain the healthy development of fruit and vegetable sectors in China for high-quality production of fruits and vegetables and hence good economic benefits.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 632KB
PDF 632KB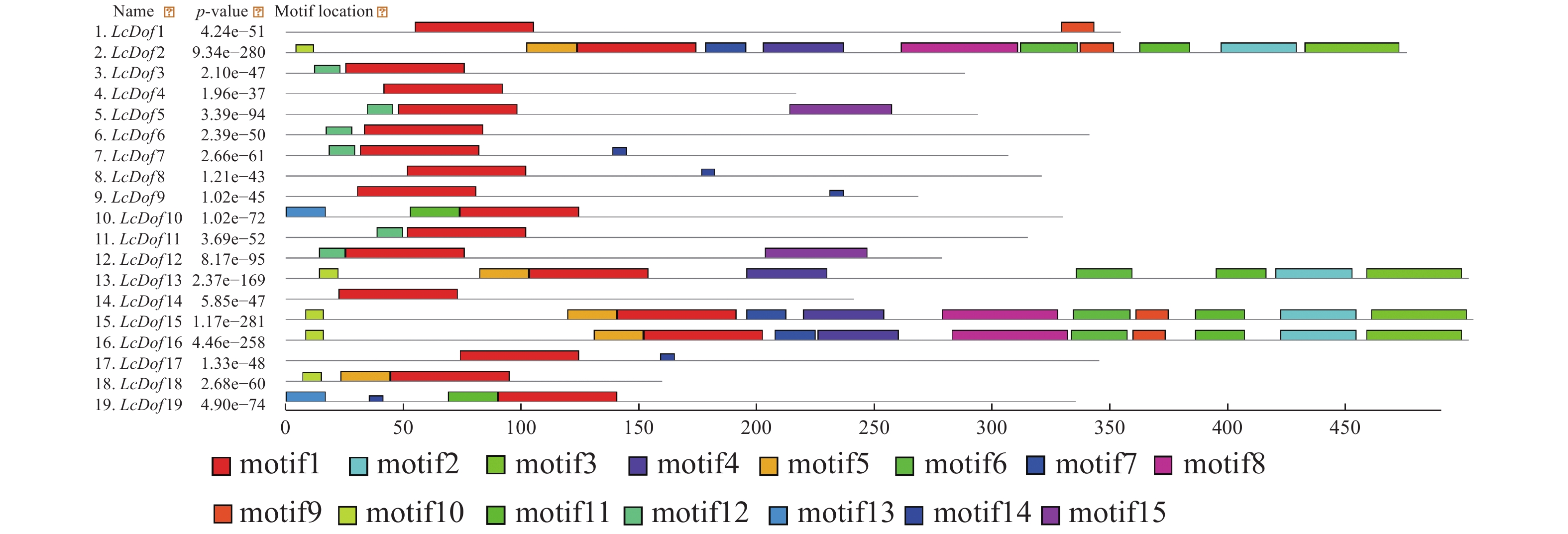














 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS