-
入侵植物是指由于自然因素或人类活动等原因有意或无意的传播,亦或是引入到异域的植物,其通过与本土物种的竞争,建立繁殖种群,从而影响当地的生物多样性和生态环境,造成经济损失[1]。众所周知,入侵植物的危害极大,一方面抢夺水资源、营养物质,影响本土物种的生长繁殖;另一方面还会改变当地的生物多样性、生态系统的初级生产力以及营养循环速率。如果大肆蔓延,会造成水体平衡破坏、土壤结构改变,对环境造成无法挽回的危害[2-4]。迄今为止,《中国入侵植物名录》共收录了94科450属806种,其中恶性入侵类34种,严重入侵类69种[1]。就全国范围来看,中国东南地区入侵情况较为严重,主要是因为该地的年均温度和年降水量适宜入侵植物的生长繁殖[5]。海南岛地处东南,气候适宜,雨水丰沛,据调查,现有外来入侵植物52科161属227种[6]。但由于研究时间较早,收录情况存在不足,数据仍有待完善。谢薇等[7]通过踏查及样本采集,研究了海南大学儋州校区的入侵植物分布情况,结果表明,现有入侵植物51科152属211种,其中恶性入侵类19种,严重入侵类30种。然而该研究只反映了原产地、分布频度和性状等情况,对其生长环境和分布格局等未进行深入研究。因此,笔者以校园入侵植物的分布格局为重点,对每种植物的生长特性及彼此关联进行调查,旨在明确入侵植物的分布情况和生活习性,为采取相应防治措施和应用提供参考。
HTML
-
海南大学儋州校区及其周边,地理位置为19.199°~19.513°N,109.481°~109.504°E。该地区属于热带湿润季风气候,光照时间长,年均温适宜,年降水量充沛,且位于城郊,包括居民区、教学区、经济林区等多种不同环境,适合入侵植物的生长和繁殖。
-
将海南大学儋州校区及其周边共计184.1 hm2区域平均划分为80块样地(每块样地2.3 hm2),进行实地踏查。根据《中国入侵植物名录》记载的种类,统计各个样地的分布情况。调查内容:分布频度(分布频度=某种入侵植物在80块样地中出现的次数/80×100%)、生长环境、性状、原产地和用途。
-
将在80块样地或7种生长环境内分布/未分布的物种标记为1/0,制作物种分布矩阵,使用R语言中的pheatmap函数包对物种和样地进行聚类并绘制出聚类热图。
不同生长环境中入侵物种相似度=在需要计算的生长环境中入侵物种同时出现的次数/在需要计算的生长环境中各入侵物种同时或各自出现的次数。不同样地中入侵物种相似度=在需要计算的样地中入侵物种同时出现的次数/在需要计算的样地中各入侵物种同时或各自出现的次数。不同物种在样地中同时出现的概率=需要计算的入侵物种在80块样地中同时出现的次数/需要计算的物种在80块样地中同时或各自出现的次数。
1.1. 调查区域
1.2. 调查方法
1.3. 聚类分析
-
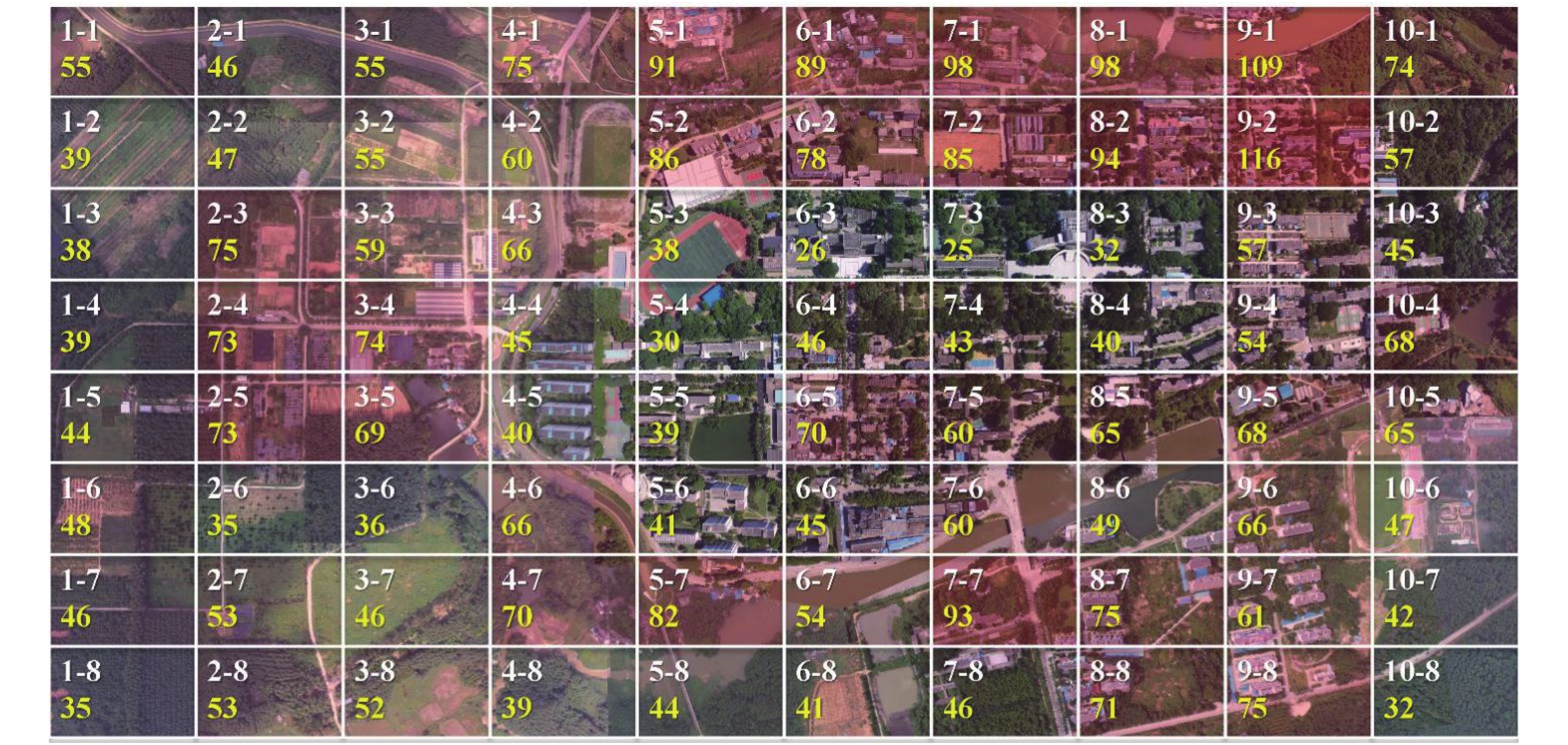
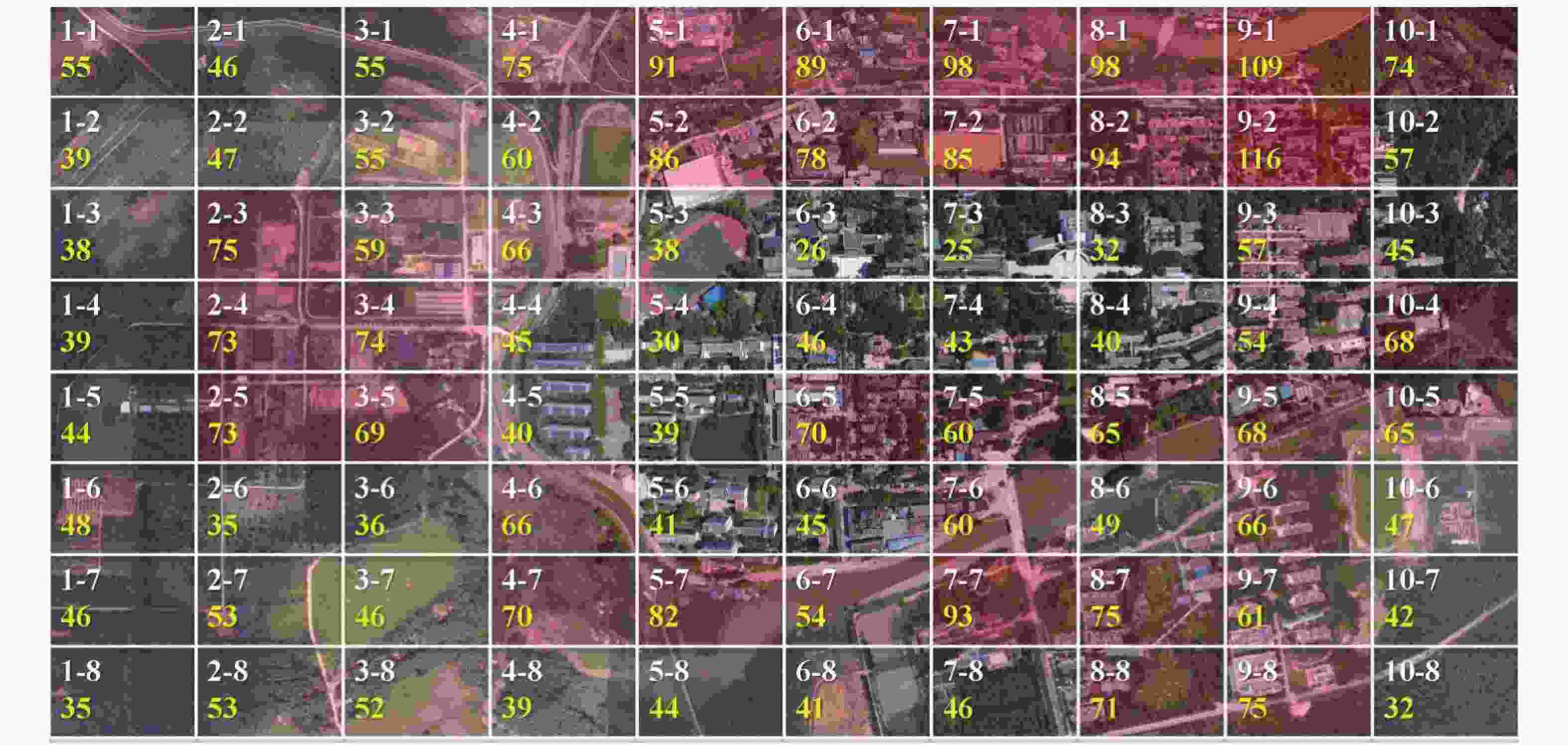
由图1可知,样地9-2,9-1,7-1和8-1的入侵植物物种数较多,依次为116,109,98和98种。其中,样地9-2的数量最多,占总入侵植物物种数的52.02%;而样地7-3,6-3和5-4的入侵植物物种数较少,分别只有25,26和30种。
-
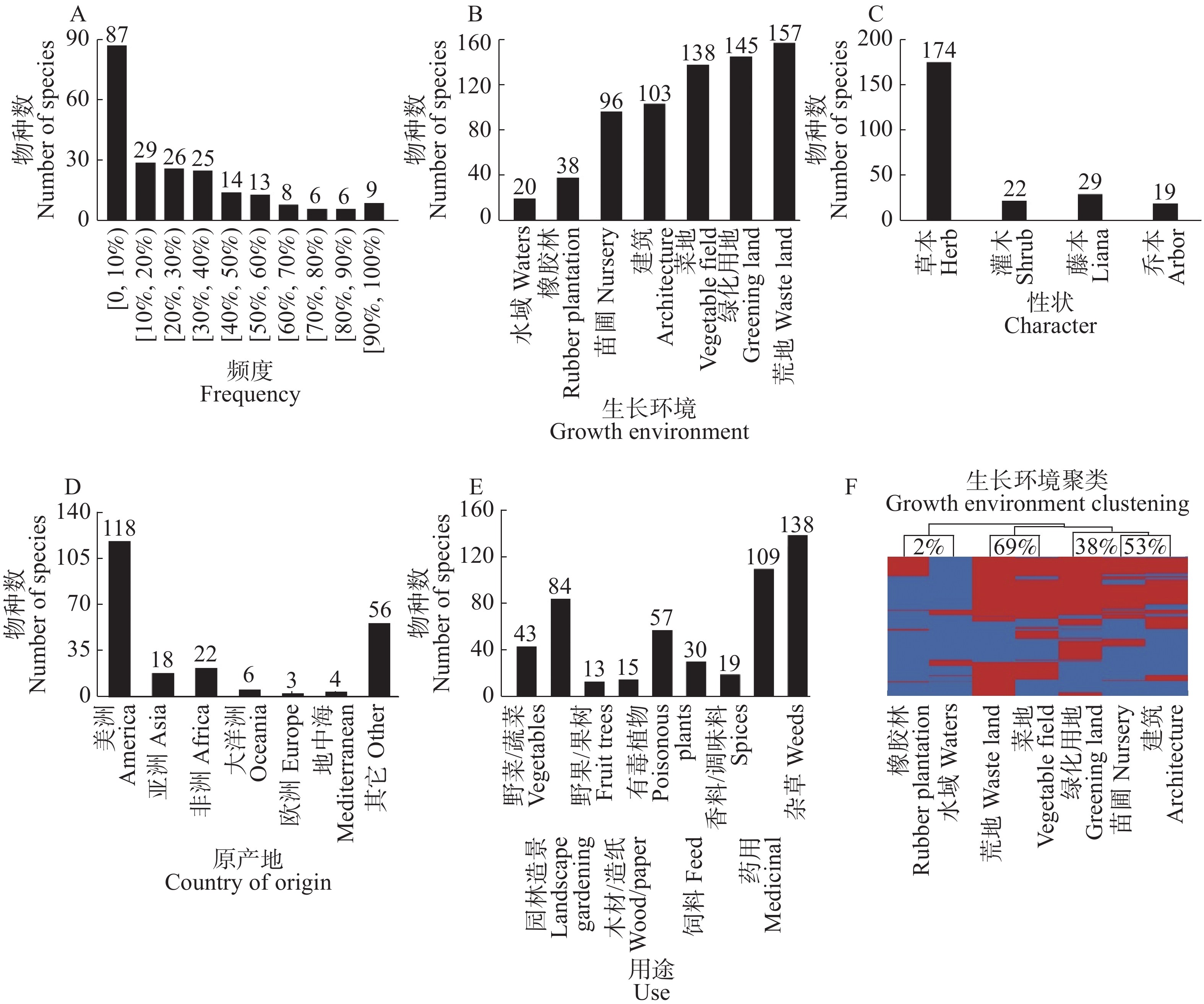
由图2A可知,分布频度为0~10%的入侵物种数最多,为87种,随频度的不断增加,物种数大体呈递减趋势。从表1可知,个别入侵植物的分布频度极高,其中,白花鬼针草(Bidens pilosa var. radiata)、两耳草(Paspalum conjugatum)、一点红(Emilia sonchifolia)、小蓬草(Conyza canadensis)、酢浆草(Oxalis corniculata)、含羞草(Mimosa pudica)、黄花稔(Sida acuta)、光叶丰花草(Spermacoce remota)和苦味叶下珠(Phyllanthus amarus) 的频度高达90%~100%。
序号
Code物种
Plant species拉丁文名
Latin name频度/%
Frequency生长环境
Habitat植物用途
Plant uses1 苹 Marsilea quadrifolia L. 2.50 C,H,S J,s,y,z 2 草胡椒 Peperomia pellucida (L.) Kunth 18.75 C,H,J,L z 3 蒌叶 Piper betle L. 0.00 H c,x,y 4 皱子白花菜 Cleome rutidosperma DC. 57.50 C,H,J,L,P z 5 芥菜 Brassica juncea (L.) Czern. et Coss. 36.25 C,H c,x,y 6 弯曲碎米荠 Cardamine flexuosa With. 5.00 C,H y,z 7 落地生根 Bryophyllum pinnatum (L. f.) Oken 26.25 H,J,L j,y,z 8 大叶落地生根 Bryophyllum daigremontianum Berger 10.00 J,L j 9 鹅肠菜 Myosoton aquaticum (L.) Moench 27.50 C,H,J,S c,s,y,z 10 土人参 Talinum paniculatum (Jacq.) Gaertn. 21.25 C,H,J c,y 11 大花马齿苋 Portulaca grandiflora Hook. 7.50 J,L j,y,z 12 马齿苋 Portulaca oleracea L. 48.75 C,H,J,L,P c,d,s,y,z 13 毛马齿苋 Portulaca pilosa L. 37.50 H,J,L,P y,z 14 珊瑚藤 Antigonon leptopus Hook. & Arn. 3.75 J j 15 萹蓄 Polygonum aviculare L. 0.00 C,H y,z 16 垂序商陆 Phytolacca americana L. 2.50 C,H d,y,z 17 土荆芥 Chenopodium ambrosioides L. 0.00 H d,y,z 18 繁穗苋 Amaranthus paniculatus L. 23.75 C,H,J,L,P c,z 19 凹头苋 Amaranthus lividus L. 36.25 C,H,J,L,P s,y,z 20 刺苋 Amaranthus spinosus L. 17.50 C,H,L,P c,y,z 21 苋 Amaranthus tricolor L. 25.00 C,H,L,P c,j,y,z 22 莲子草 Alternanthera sessilis (L.) DC. 55.00 C,H,J,L,P,S c,s,y,z 23 锦绣苋 Alternanthera bettzickiana (Regel) Nichols. 21.25 C,H,J,L j,y 24 鸡冠花 Celosia cristata L. 1.25 L,P j,y 25 青葙 Celosia argentea L. 50.00 C,H,J,L,P c,j,s,y,z 26 银花苋 Gomphrena celosioides Mart. 33.75 C,H,J,L,P z 27 千日红 Gomphrena globosa L. 1.25 L,P j,y 28 土牛膝 Achyranthes aspera L. 50.00 C,H,J,L,P y,z 29 落葵薯 Anredera cordifolia (Tenore) Steenis 21.25 C,H,J,L,P c,y,z 30 落葵 Basella alba L. 53.75 C,H,J,L,P c,y,z 31 红花酢浆草 Oxalis corymbosa DC. 48.75 C,H,L,P j,y,z 32 酢浆草 Oxalis corniculata L. 93.75 C,H,J,L,P,X d,y,z 33 紫叶酢浆草 Oxalis triangularis A. Saint-Hilaire 8.75 L j 34 凤仙花 Impatiens balsamina L. 3.75 J,L d,j,y 35 苏丹凤仙花 Impatiens walleriana Hook. f. 3.75 L,P j 36 倒挂金钟 Fuchsia hybrida Hort. ex Sieb. et Voss. 1.25 P j 37 毛草龙 Ludwigia octovalvis (Jacq.) Raven 21.25 C,H,L,S z 38 草龙 Ludwigia hyssopifolia (G. Don) Exell 5.00 C,H,S y,z 39 粉绿狐尾藻 Myriophyllum aquaticum (Vell.) Verdc. 1.25 S J,z 40 紫茉莉 Mirabilis jalapa L. 8.75 H,L,X d、j、y 41 叶子花 Bougainvillea spectabilis Willd. 65.00 H,J,L,P j 42 龙珠果 Passiflora foetida L. 6.25 H,J,L g,y,z 43 鸡蛋果 Passiflora edulis Sims 7.50 J,L g,j,s,y 44 苦瓜 Momordica charantia L. 3.75 C c,g,y 45 佛手瓜 Sechium edule (Jacq.) Swartz 12.50 C,J c 46 四季秋海棠 Begonia cucullata Willdenow 2.50 P j 47 仙人掌 Opuntia stricta (Haw.) Haw. var. dillenii (Ker-Gawl.) 27.50 H,L,P g,j,y 48 量天尺 Hylocereus undatus (Haw.) Britt. et Rose 37.50 C,J,P c,g,j,s 49 木麒麟 Pereskia aculeata Mill. 27.50 C,H,J,L,X c,g,j 50 窿缘桉 Eucalyptus exserta F. V. Muell. 1.25 L j,m,x 51 番石榴 Psidium guajava L. 36.25 C,H,J,L,P g,y 52 蒲桃 Syzygium jambos (L.) Alston 1.25 L g,j,m 53 桉 Eucalyptus robusta Smith 10.00 X j,m,x,y 54 野牡丹 Melastoma candidum D. Don 27.50 H,L,P,X j 55 黄麻 Corchorus capsularis L. 3.75 C c,z 56 长蒴黄麻 Corchorus olitorius L. 8.75 C,H z 57 蛇婆子 Waltheria indica L. 0.00 H z 58 木棉 Bombax malabaricum DC. 12.50 L c,j,m,y 59 地桃花 Urena lobata L. 52.50 C,H,L,P y,z 60 赛葵 Malvastrum coromandelianum (L.) Gurcke 68.75 C,H,J,L,P,X y,z 61 黄葵 Abelmoschus moschatus Medikus 2.50 C j,m,x,y 62 黄花稔 Sida acuta Burm. f. 90.00 C,H,J,L,P,X y,z 63 蓖麻 Ricinus communis L. 13.75 C,H d,y 64 猩猩草 Euphorbia cyathophora Murr. 5.00 H d,j,z 65 白苞猩猩草 Euphorbia heterophylla L. 45.00 C,H,J,L,P,X d,z 66 一品红 Euphorbia pulcherrima Willd. et Kl. 5.00 L,P d,j,y 67 飞扬草 Euphorbia hirta L. 80.00 C,H,J,L,P,X d,y,z 68 火殃勒 Euphorbia antiquorum L. 12.50 L d,j,y 69 匍匐大戟 Euphorbia prostrata Ait. 16.25 C,H,J,L z 70 绿玉树 Euphorbia tirucalli L. 2.50 H,L d,j 71 地锦 Euphorbia humifusa Willd. ex Schlecht. 8.75 C,H,J,L,P y,z 72 麻疯树 Jatropha curcas L. 3.75 C,H d,y 73 木薯 Manihot esculenta Crantz 65.00 C,H,J,L,P,X c,d,j,s,y 74 红雀珊瑚 Pedilanthus tithymaloides (L.) Poit. 20.00 H,L d,j,y 75 苦味叶下珠 Phyllanthus amarus Schumacher & Thonning 96.25 C,H,J,L,P z 76 含羞草 Mimosa pudica L. 95.00 C,H,J,L,P,X d,j,y,z 77 光荚含羞草 Mimosa sepiaria Benth. 55.00 C,H,J,L,P,X z 78 巴西含羞草 Mimosa diplotricha C. Wright ex Sauvalle 71.25 C,H,J,L,P d,z 79 无刺含羞草 Mimosa diplotricha C. Wright ex Sauvalle var. inermis
(Adelbert) Veldkamp37.50 C,H,J,L,P d,z 80 银合欢 Leucaena leucocephala (Lam.) de Wit 52.50 C,H,J,L,P d,j,m,s,z 81 台湾相思 Acacia confusa Merr. 5.00 L d,j,m,x 82 大叶相思 Acacia auriculiformis A. Cunn. ex Benth. 1.25 L,X d,j,m 83 含羞草决明 Cassia mimosoides L. 23.75 C,H,L,P d,z 84 翅荚决明 Cassia alata L. 5.00 C,H,J j,z 85 望江南 Cassia occidentalis L. 3.75 C,H d,y,z 86 黄槐决明 Cassia surattensis Burm. 1.25 L j 87 金凤花 Caesalpinia pulcherrima (L.) Sw. 20.00 L d,j 88 酸豆 Tamarindus indica L. 17.50 C,H,L g,m,x,y 89 蔓花生 Arachis duranensis Krapov. & W. C. Greg. 21.25 C,H,J,L,P j,z 90 毛蔓豆 Calopogonium mucunoides Desv. 62.50 C,H,J,L,P,X z 91 三裂叶野葛 Pueraria phaseoloides (Roxb.) Benth. 27.50 C,H,J s,z 92 木豆 Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp. 18.75 C,H,L,P c,s,y 93 距瓣豆 Centrosema pubescens Benth. 76.25 C,H,J,L,P,X s,z 94 蝶豆 Clitoria ternatea L. 2.50 C,H d,j 95 猪屎豆 Crotalaria pallida Ait. 23.75 C,H d,y,z 96 菜豆 Phaseolus vulgaris L. 27.50 C c,d 97 扁豆 Lablab purpureus (L.) Sweet 20.00 C,H c,y 98 田菁 Sesbania cannabina (Retz.) Poir. 0.00 H d,s,z 99 紫花大翼豆 Macroptilium atropurpureum (DC.) Urban 15.00 C,H,P z 100 大翼豆 Macroptilium lathyroides (Linn.) Urban 1.25 H s,z 101 木麻黄 Casuarina equisetifolia Forst. 3.75 H,L j,m,s,y 102 小叶冷水花 Pilea microphylla (L.) Liebm. 65.00 C,H,J,L,S j,z 103 乌蔹莓 Cayratia japonica (Thunb.) Gagnep. 1.25 X y,z 104 龙眼 Dimocarpus longan Lour. 48.75 C,H,J,L,P,X g,j,m,y 105 倒地铃 Cardiospermum halicacabum L. 7.50 C,H,J,P d,y,z 106 杧果 Mangifera indica L. 36.25 C,H,J,L,P d,g,j,m,x,y 107 南美天胡荽 Hydrocotyle verticillata Thunb. 5.00 L,S j 108 天胡荽 Hydrocotyle sibthorpioides Lam. 50.00 C,H,J,L y,z 109 刺芹 Eryngium foetidum L. 13.75 C,H,J,L c,x,y,z 110 芫荽 Coriandrum sativum L. 27.50 C c,x,y 111 茴香 Foeniculum vulgare Mill. 31.25 C c,x,y 112 长春花 Catharanthus roseus (L.) G. Don 36.25 C,H,J,L d,j,y 113 夹竹桃 Nerium indicum Mill. 7.50 L d,j 114 糖胶树 Alstonia scholaris (L.) R. Br. 30.00 H,L,P d,j,y 115 阔叶丰花草 Spermacoce alata Aubl. 57.50 C,H,J,L,P,X z 116 丰花草 Spermacoce pusilla Wallich 42.50 C,H,J,L,P,X z 117 光叶丰花草 Spermacoce remota Lam. 97.50 C,H,J,L,P,X z 118 墨苜蓿 Richardia scabra L. 37.50 C,H,J,L,P z 119 耳草 Hedyotis auricularia L. 63.75 C,H,L,X y,z 120 伞房花耳草 Hedyotis corymbosa (L.) Lam. 80.00 C,H,J,L,P,X y,z 121 臭鸡矢藤 Paederia foetida L. 33.75 C,H,L x,y,z 122 万寿菊 Tagetes erecta L. 5.00 L,P j 123 孔雀草 Tagetes patula L. 2.50 L,P j 124 飞机草 Eupatorium odoratum L. 77.50 C,H,J,L,P,X d,y,z 125 藿香蓟 Ageratum conyzoides L. 81.25 C,H,J,L,P,X x,y,z 126 假臭草 Praxelis clematidea R. M. King & H. Rob. 67.50 C,H,J,L,P,X x,z 127 银胶菊 Parthenium hysterophorus L. 36.25 C,H,J,L,P z 128 薇甘菊 Mikania micrantha Kunth 26.25 C,H,J,L,P,X z 129 南美蟛蜞菊 Sphagneticola trilobata (L.) Pruski 82.50 C,H,J,L,P,S,X j,z 130 小蓬草 Conyza canadensis (L.) Cronq. 92.50 C,H,J,L,P,X s,y,z 131 金腰箭 Synedrella nodiflora (L.) Gaertn. 87.50 C,H,J,L,P,X z 132 羽芒菊 Tridax procumbens L. 32.50 C,H,J,L,P z 133 地胆草 Elephantopus scaber L. 17.50 C,H,L,X y,z 134 白花地胆草 Elephantopus tomentosus L. 17.50 C,H,L,X y,z 135 鬼针草 Bidens pilosa L. 43.75 C,H,J,L,P,X c,s,y,z 136 白花鬼针草 Bidens pilosa L. var. radiata Sch.-Bip. 90.00 C,H,J,L,P,X c,s,y,z 137 菊芹 Erechtites valerianifolius (Wolf) DC. 8.75 C,H,L,P z 138 茼蒿 Chrysanthemum coronarium L. 13.75 C c,j 139 秋英 Cosmos bipinnatus Cav. 0.00 L j 140 黄秋英 Cosmos sulphureus Cav. 1.25 L j 141 鳢肠 Eclipta prostrata (L.) L. 46.25 C,H,J,L,P,S y,z 142 一点红 Emilia sonchifolia (L.) DC. 91.25 C,H,J,L,P d,y,z 143 匙叶鼠麴草 Gamochaeta pensylvanica (Willdenow) Cabrera 45.00 C,H,J,L,P z 144 非洲菊 Gerbera jamesonii Bolus 2.50 P j 145 莴苣 Lactuca sativa L. 31.25 C c 146 肿柄菊 Tithonia diversifolia A. Gray 0.00 H j,z 147 钻叶紫菀 Aster subulatus Michx. 1.25 H z 148 野茼蒿 Crassocephalum crepidioides (Benth.) S. Moore 0.00 C,H,J,L,P c,y,z 149 鱼眼草 Dichrocephala auriculata (Thunb.) Druce 2.50 H,L y,z 150 白花丹 Plumbago zeylanica L. 1.25 H d,j,y,z 151 车前 Plantago asiatica L. 28.75 C,H,J,L,P y,z 152 半边莲 Lobelia chinensis Lour. 0.00 L d,y,z 153 洋金花 Datura metel L. 0.00 H d,z 154 喀西茄 Solanum khasianum C. B. Clarke 1.25 H d,z 155 假烟叶树 Solanum verbascifolium L. 17.50 H,J d,y,z 156 牛茄子 Solanum capsicoides Allioni 8.75 H z 157 水茄 Solanum torvum Swartz 22.50 C,H,J c,d,y,z 158 少花龙葵 Solanum americanum Mill. 72.50 C,H,J,L,P,X c,d,g,y,z 159 夜香树 Cestrum nocturnum L. 5.00 L d,j 160 碧冬茄 Petunia hybrida Vilm. 3.75 L,P j 161 苦蘵 Physalis angulata L. 6.25 C,H y,z 162 小酸浆 Physalis minima L. 40.00 C,H,P z 163 鸳鸯茉莉 Brunfelsia acuminata Bentham 3.75 L j 164 辣椒 Capsicum annuum L. 38.75 C,J c,d,x,y 165 番茄 Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. 31.25 C,H,J c,d,g 166 烟草 Nicotiana tabacum L. 1.25 J d,y,z 167 五爪金龙 Ipomoea cairica (L.) Sweet 18.75 H,J,L d,j,y,z 168 蕹菜 Ipomoea aquatica Forsk. 22.50 C,H,S c,s,y,z 169 番薯 Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. 56.25 C,H,J,P c,s 170 小心叶薯 Ipomoea obscura (L.) Ker-Gawl. 45.00 C,H,J,L z 171 三裂叶薯 Ipomoea triloba L. 58.75 C,H z 172 茑萝 Quamoclit pennata (Desr.) Bojer 3.75 H,J,L d,j 173 野甘草 Soparia dulcis L. 75.00 C,H,J,L,P z 174 独脚金 Striga asiatica (L.) O. Kuntze 1.25 L y,z 175 炮仗花 Pyrostegia venusta (Ker-Gawl.) Miers 11.25 J,L j 176 火焰树 Spathodea campanulata Beauv. 13.75 L,P j 177 黄脉爵床 Sanchezia nobilis Hook. f. 11.25 L j 178 爵床 Rostellularia procumbens (L.) Nees 1.25 J,L j,y,z 179 穿心莲 Andrographis paniculata (Burm. f.) Nees 3.75 C,L d,y 180 小驳骨 Gendarussa vulgaris Nees 10.00 C,L y 181 山牵牛 Thunbergia grandiflora (Rottl. ex Willd.) Roxb. 1.25 J,L j 182 翼叶山牵牛 Thunbergia alata Bojer et Sims 2.50 H,L j,z 183 马缨丹 Lantana camara L. 33.75 C,H,L,P,X d,j,y,z 184 假马鞭 Stachytarpheta jamaicensis (L.) Vahl. 2.50 H,X y,z 185 马鞭草 Verbena officinalis L. 5.00 H d,y,z 186 假连翘 Duranta repens L. 45.00 H,L d,j,y 187 吊球草 Hyptis rhomboidea Mart. et Gal. 0.00 H z 188 短柄吊球草 Hyptis brevipes Poit. 3.75 C,H z 189 皱叶留兰香 Mentha crispata Schrad.ex Willd. 28.75 C c,x 190 罗勒 Ocimum basilicum L. 37.50 C,H,J c,x,y 191 紫苏 Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt. 11.25 C c,x,y 192 一串红 Salvia splendens Ker-Gawl. 5.00 L,P j 193 黄花蔺 Limnocharis flava (L.) Buch enau 3.75 C,H,S z 194 吊竹梅 Tradescantia zebrina Bosse 2.50 L j 195 美人蕉 Canna indica L. 7.50 L j,m,y 196 萱草 Hemerocallis fulva (L.) L. 1.25 C c,d,j 197 凤眼蓝 Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms 10.00 S c,j,s,y,z 198 芋 Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott 31.25 C,H,S c,d 199 浮萍 Lemna minor L. 3.75 C,S s,y,z 200 葱莲 Zephyranthes candida (Lindl.) Herb. 1.25 L d,j 201 韭莲 Zephyranthes grandiflora Lindl. 16.25 L d,j 202 风车草 Cyperus alternifolius L. subsp. Flabelliformis (Rottb.) KüKenth. 1.25 H,S j 203 香附子 Cyperus rotundus L. 33.75 C,H,J,L,P y,z 204 水蜈蚣 Kyllinga brevifolia Rottb. 53.75 C,H,J,L,P,S y,z 205 牧地狼尾草 Pennisetum setosum (Swartz) Rich. 16.25 H,J,P z 206 象草 Pennisetum purpureum Schum. 47.50 C,H,S s,z 207 两耳草 Paspalum conjugatum Berg. 91.25 C,H,J,L,P,X z 208 牛筋草 Eleusine indica (L.) Gaertn. 82.50 C,H,J,L,P s,y,z 209 红毛草 Rhynchelytrum repens (Willd.) Hubb. 10.00 H,L,P z 210 地毯草 Axonopus compressus (Sw.) Beauv. 77.50 C,H,J,L,P j,z 211 白茅 Imperata cylindrica (L.) Beauv. 37.50 C,H,J,L,P z 212 柠檬草 Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf 1.25 C,J c,x,y,z 213 大黍 Panicum maximum Jacq. 65.00 C,H,J,L,P s,z 214 稗 Echinochloa crusgalli (L.) Beauv. 25.00 C,H,L,P,S z 215 棕叶狗尾草 Setaria palmifolia (Koen.) Stapf 6.25 L y,z 216 莠狗尾草 Setaria geniculata (Lam.) Beauv. 16.25 C,H,J,P z 217 薏苡 Coix lacryma-jobi L. 7.50 C,H z 218 龙爪茅 Dactyloctenium aegyptium (L.) Beauv. 43.75 C,H,J,L,P z 219 虮子草 Leptochloa panicea (Retz.) Ohwi 37.50 C,H,J,L,P,S s,z 220 虎尾草 Chloris virgata Sw. 40.00 C,H,J,L,P s,z 221 弓果黍 Cyrtococcum patens (L.) A. Camus 31.25 H,X z 222 五节芒 Miscanthus floridulus (Lab.) Warb. ex K. Schum. et Laut. 16.25 C,H,J,L m,s,z 223 芦苇 Phragmites australis (Cav.) Trin. ex Steud. 0.00 H j,m,s,y,z 注:C,H,J,L,P,S和X分别代表菜地、荒地、建筑、绿化用地、苗圃、水域和橡胶林;c,d,g,j,m,s,x,y和z分别代表野菜(蔬菜)、有毒、野果(果树)、园林造景、木材(造纸)、饲料、香料(调味料)、药用和杂草。
Notes: C, H, J, P, S, L and X represent vegetable fields, waste land, buildings, green land, nursery, waters and rubber plantations, respectively, and c, d, g, m, j, z, s, x and y represent wild vegetables (vegetables), poisonous plants, wild fruits (fruit trees), wood (paper pulp), landscaping, feed, spices (seasonings), medicinal plants and weeds, respectively.Table 1. The frequency, habitat and uses of invasive plants
-
从图2C可知,入侵植物以草本居多,有174种占比78.03%,其次为藤本(29种,13.00%)、灌木(22种,9.87%)和乔木(19种,8.52%)。由图2D可知,有118种入侵植物来源于美洲,占比最大,为52.91%,除去56种原产地不详的植物,剩下来源于非洲(22种,9.87%)、亚洲(18种,8.07%)、大洋洲(6种,2.69%)、地中海(4种,1.79%)和欧洲(3种,1.35%)。由图2E可知,入侵植物用途可分为:野菜/蔬菜、园林造景、野果/果树、木材/造纸、有毒、饲料、香料/调味料、药用和杂草,其中以杂草居多,有138种,药用次之,野果/果树最少。入侵植物的用途并不单一,有70.40%的物种同时拥有2种及以上的用途,其中,拥有2种用途的物种数最多,为70种。
-
从图2B可知,入侵植物的生长环境可分为水域、橡胶林、苗圃、建筑、菜地、绿化用地和荒地7类。其中,157种入侵植物出现在荒地,占比最大,为70.40%,其次为绿化用地(65.02%)和菜地(61.88%),水域中入侵植物物种数最少,只有20种,占总数的8.97%。根据图2F的聚类分析结果显示,7种生长环境可分为3支,其中,荒地和菜地的相似度最高,为69%,其次为建筑、苗圃和绿化用地(38%)。而橡胶林和水域的相似度最低,只有2%。
-
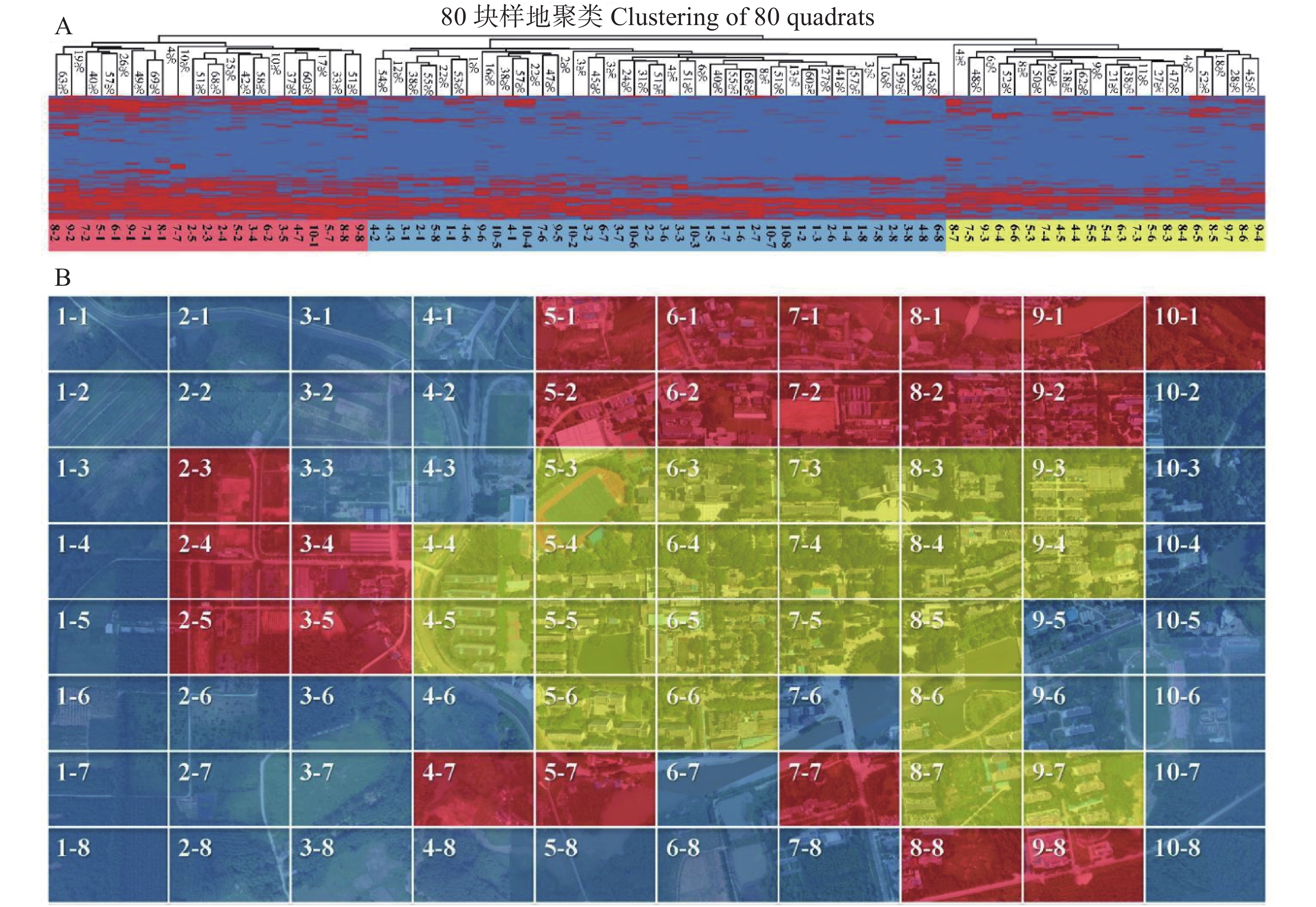
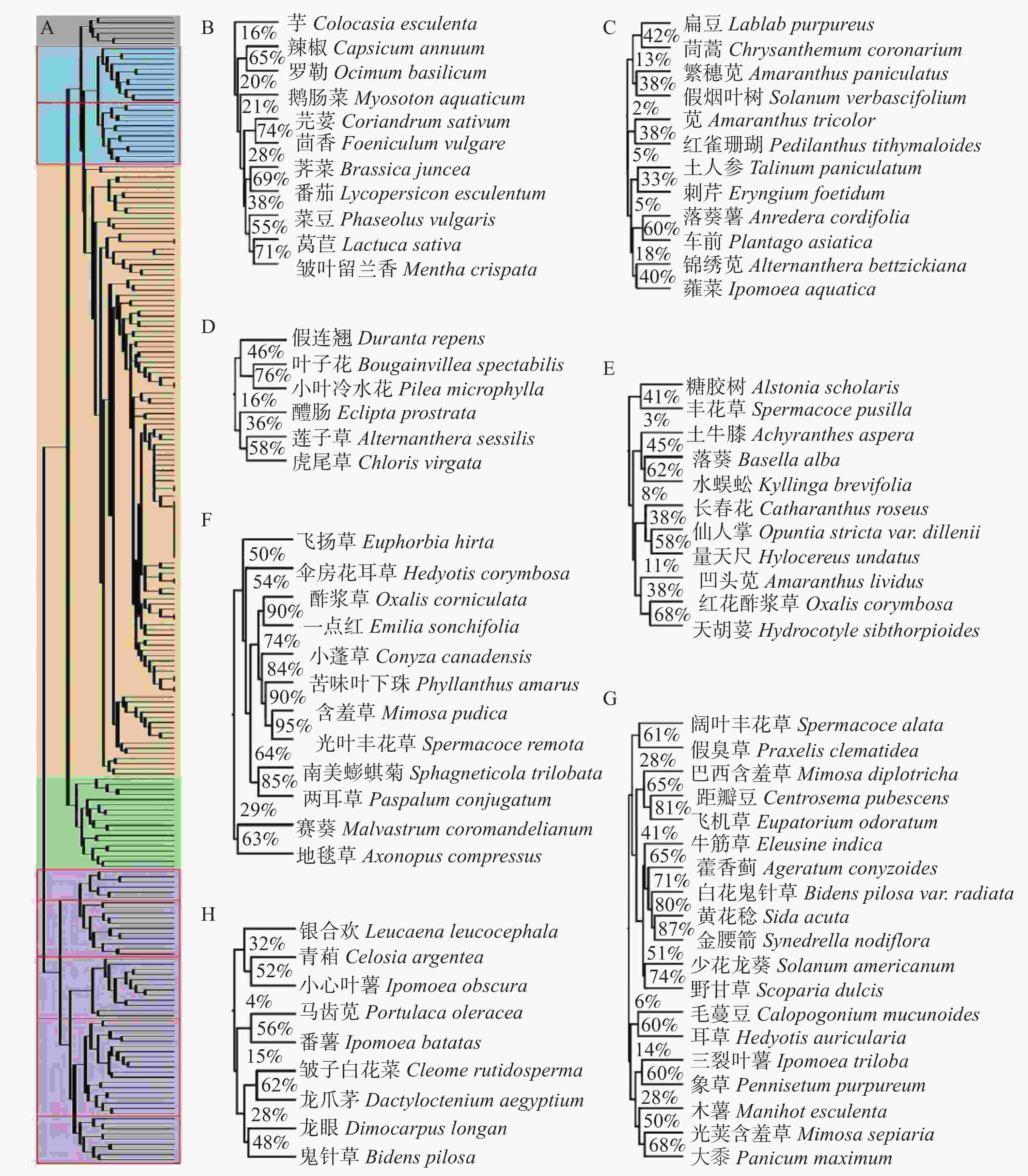
从图3A可知,以物种相似度对80块样地进行聚类的结果可分为3大模块,分别为黄色、红色和蓝色模块。从图3B中可以看出,黄色和红色模块各由21块样地组成,黄色模块位于地图中央,红色模块位于周边。蓝色模块范围最广,共有38块样地,位于四周。
从图3A可知,在黄色模块中,样地4-4和5-5的入侵物种相似度最高,为62%,且有4%的物种在黄色模块内同时出现,分别为酢浆草、苦味叶下珠、小叶冷水花(Pilea microphylla)、光叶丰花草、伞房花耳草(Hedyotis corymbosa)和地毯草(Axonopus compressus)。还有一些物种只在黄色模块中出现,为鸡冠花(Celosia cristata)、倒挂金钟(Fuchsia hybrida)、窿缘桉(Eucalyptus exserta)、蒲桃(Syzygium jambos)、黄槐决明(Cassia surattensis)、鱼眼草(Dichrocephala auriculata)、烟草(Nicotiana tabacum)、独脚金(Striga asiatica)和风车草(Cyperus alternifolius subsp. Flabelliformis)。在红色模块中,入侵物种相似度最高的为样地7-1和8-1(69%),其次为样地2-3和2-4(68%),且有4%的物种在红色模块中同时出现,为酢浆草、黄花稔、苦味叶下珠、含羞草、藿香蓟(Ageratum conyzoides)、小蓬草、一点红和少花龙葵(Solanum americanum)。所有物种中,有23种入侵植物只在红色模块中出现,如弯曲碎米荠(Cardamine flexuosa)、草龙(Ludwigia hyssopifolia)、长蒴黄麻(Corchorus olitorius)、麻疯树(Jatropha curcas)、蝶豆(Clitoria ternatea)、大翼豆(Macroptilium lathyroides)、黄花蔺(Limnocharis flava)、浮萍(Lemna minor)和薏苡(Coix lacryma-jobi)等。在蓝色模块中,样地1-6和2-7的物种相似度最高,为68%。其中,只有白花鬼针草同时存在于蓝色模块。且粉绿狐尾藻(Myriophyllum aquaticum)、大叶相思(Acacia auriculiformis)、翼叶山牵牛(Thunbergia alata)和葱莲(Zephyranthes candida)等只在蓝色模块中出现。
-
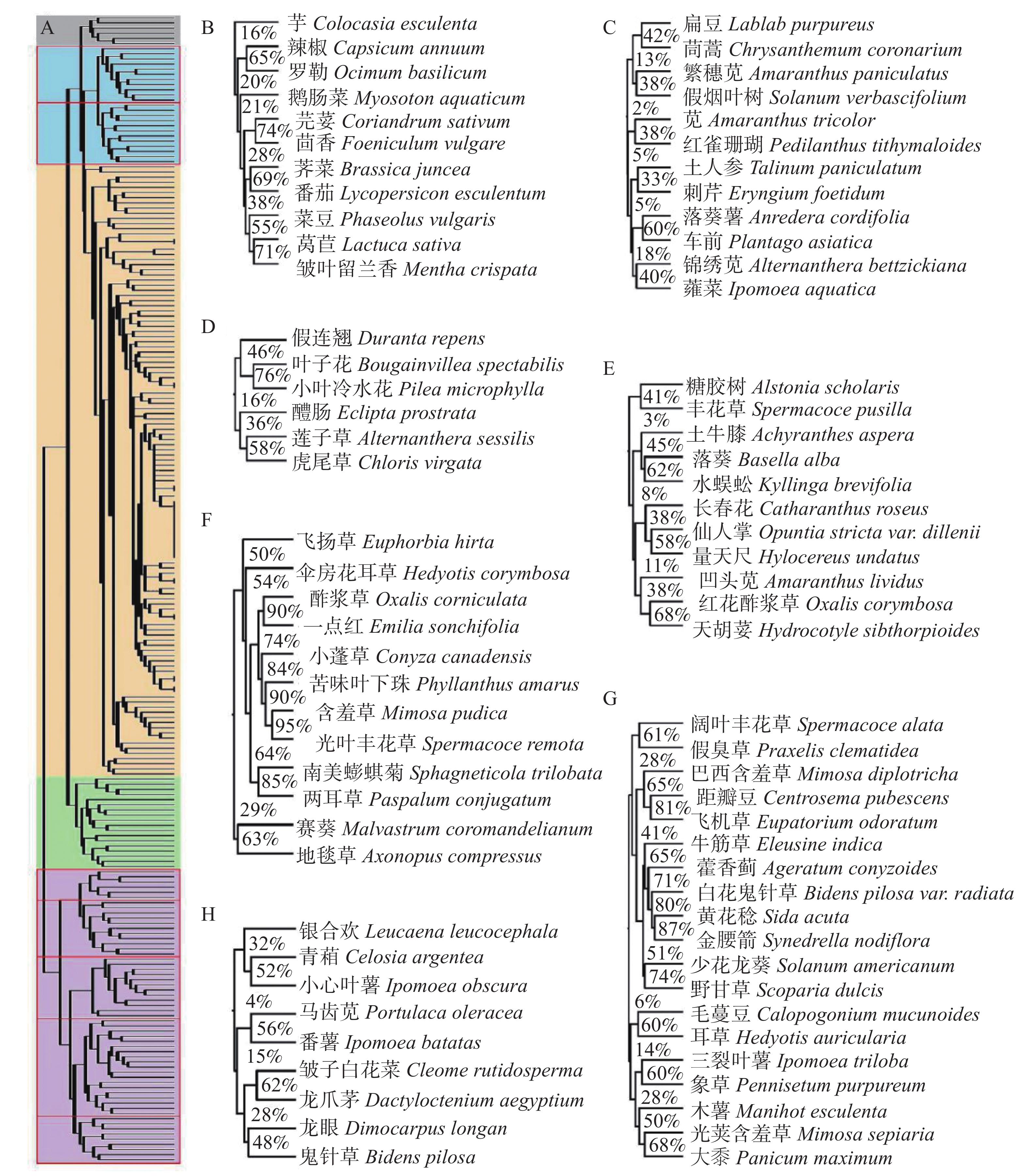
由图4A可知,以样地相似度对223种入侵植物进行聚类的结果可分为5大模块,分别为橙色、紫色、绿色、青色和灰色模块。橙色模块的入侵植物物种数最多,但分布频度却最低,中位数只有3.75%。紫色模块的物种数排名第2,分布频度最高,中位数达到62.50%。除此之外,绿色、青色和灰色模块的分布频度中位数依次为36.25%、27.50%和26.25%。
橙色模块中,119种入侵植物囊括7种生长环境,且该模块中有54.62%的物种可分布于绿化用地,51.26%可分布于荒地。紫色模块中,南美蟛蜞菊(Sphagneticola trilobata)在7种生长环境下均可生存,且该模块的入侵植物分布广泛,用途多样。其中,D和E部分多为园林造景植物及伴生杂草。由图4D、4E结果可知,这两部分入侵植物各自同时存在的概率分别为16%和3%。F和G部分多为顽固杂草和高频入侵植物,由图4F、4G结果可知,含羞草和光叶丰花草同时出现的概率高达95%,且酢浆草和一点红也达到了90%。而黄花稔和金腰箭(Synedrella nodiflora)也有87%。且F和G部分中的入侵植物各自同时存在的概率分别为29%和6%。H部分多为饲料来源及杂草,由图4H结果可知,且这9种入侵植物同时存在的概率为4%。绿色模块中,入侵植物的生长环境不包括水域,故没有水生植物,且只有该模块的入侵植物不分布于样地7-3和8-3中。青色和灰色模块中,没有生长环境位于橡胶林的植物,且在青色模块中,B部分为蔬菜类,主要分布于菜地。由图4B、4C结果可知,芋(Colocasia esculenta)、辣椒(Capsicum annuum)、罗勒(Ocimum basilicum)、鹅肠菜(Myosoton aquaticum)、芫荽(Coriandrum sativum)、茴香(Foeniculum vulgare)、芥菜(Brassica juncea)、番茄(Lycopersicon esculentum)、菜豆(Phaseolus vulgaris)、莴苣(Lactuca sativa)和皱叶留兰香(Mentha crispata)同时出现的概率为16%,且芫荽和茴香相似度较高,达到74%(图4B)。C部分多为杂草,集中分布于居民区,且同时出现的概率为2%。
2.1. 入侵植物的多样性分析
2.2. 入侵植物分布频度分析
2.3. 入侵植物的性状、原产地和用途分析
2.4. 入侵植物的生长环境分析
2.5. 80块样地聚类分析
2.6. 入侵植物聚类分析
-
本文收录的物种均来自于《中国入侵植物名录》,其把入侵植物分为7个等级,分别为1级恶性入侵类、2级严重入侵类、3级局部入侵类、4级一般入侵类、5级有待观察类、6级建议排除类和7级中国国产类[1]。统计的223种入侵植物中,有一些植物没有明显危害,且用途广泛。如量天尺(Hylocereus undatus)和番石榴(Psidium guajava)等,属于5级有待观察类,即入侵时间短,无法判断今后发展的植物。而番茄、辣椒、苦瓜(Momordica charantia)、莴苣、杧果(Mangifera indica)和龙眼(Dimocarpus longan)等属于果蔬类,是6级建议排除类,因为其不具备入侵特性,仅因为有文献记载才归入入侵植物行列[1]。
根据物种相似度对80块样地进行聚类,由图1,3可知,红色模块的入侵植物物种数普遍较高,可能是因为该区域多为居民区,包括菜地、苗圃和荒地,人流量较大,导致人为干扰严重。且荒地及路边等地,各物种关联较低,干扰较弱,便于入侵植物的传入与传播[8]。其主要入侵物种为酢浆草、黄花稔、苦味叶下珠、含羞草、藿香蓟、小蓬草、一点红和少花龙葵等。蓝色模块和黄色模块的人为管理比较合适,故入侵物种数相对较少,其分别为橡胶林和校园内部,且橡胶林中最为严重的入侵植物为弓果黍(Cyrtococcum patens)。统计得知,苹(Marsilea quadrifolia)、弯曲碎米荠、垂序商陆(Phytolacca americana)、草龙、长蒴黄麻、麻疯树、蝶豆、黄花蔺和薏苡等只在红色模块中出现,可能是因为该类植物多生长于荒地和菜地,与红色模块的地形相符。而大叶相思、山牵牛(Thunbergia grandiflora)、翼叶山牵牛、葱莲、鸡冠花、窿缘桉、蒲桃、黄槐决明、鱼眼草和独脚金等多生长于绿化用地,故只出现在蓝色模块或黄色模块。根据样地相似度对物种进行聚类可知,5大模块的分布频度与物种相似度有一定的关系。聚成一支的入侵植物分布频度相对较近,但反之并不成立。如灰色模块和青色模块的频度虽然相近,但分布特性差异较大。可能是因为这两大模块的入侵植物生长环境和生活习性存在差异。蓝色模块与其他模块的分布特性相似度差异最大,主要是因为该模块多为顽固杂草和高频入侵植物,其生长速度快、范围广,故需要重点防治。
笔者发现,物种的聚类有一定的规律可言,如辣椒、罗勒、芥菜、番茄、菜豆和莴苣等多为蔬菜,且多分布于菜地中,需要人为种植,基本无逸生现象。因为具有相似的用途和生长环境,最终聚为一支。而菜豆和扁豆(Lablab purpureus)虽均属于蝶形花科(Papilionoideae),但相似度很低,可能是因为菜豆只能人为种植,不能野外自行生长。而扁豆则可以成为杂草,有逸生现象,具有在野外独自生存的能力,不需要人为栽培,故两者的相似度差异较大。
-
80块样地中,菜地和荒地的入侵物种数较多,且较为集中的位于红色区域。可采用化学治理的方法,对于已经被入侵植物大量覆盖且严重影响的地区,如荒地中的白花鬼针草和大黍(Panicum maximum)等,可采用灭生性除草剂对其展开治理。而对于其他地区,如莎草科(Cyperaceae)的入侵植物,可使用二甲四氯钠类选择性除草剂[9]。除此之外,绿化用地的入侵植物也居多,可使用割草机进行治理,主要应用于田间除草、绿化带及园林景观修剪等,不仅提高了除草效率,而且节省了人力物力资源。橡胶林分布范围广,可选择草甘膦除草剂,不仅高效、低毒,而且施药次数少、残留量低,对橡胶树无害,是较为理想的除草药剂[10]。但近年来,单一施用草甘膦除草剂造成“绿色荒漠”现象,物种多样性急剧减少,故可以使用套种经济作物的方法,使其与入侵植物竞争,争夺营养物质,从而抑制入侵植物的生长繁殖。
在223种入侵植物中,白花鬼针草、两耳草、一点红、小蓬草、酢浆草、含羞草、黄花稔、光叶丰花草和苦味叶下珠,其分布频度都达到了90%。这些入侵植物已形成较稳定的种群,是危害程度较大的物种。其均为草本植物,且原产地多为美洲。因此,可根据此类植物的生活特性施用相应的化学除草剂或生长抑制剂,再根据其在美洲的生境,制定适宜的防治措施[11]。若情况严重,直接采用灭生性除草剂进行防治。对于聚众分布的入侵植物,特别是顽固杂草,直接施用除草剂统一进行防除。最后,需要增强防护意识,尽量降低入侵植物的危害。同时对一些存在于样地外,还未入侵到校内的植物,如土荆芥等,加强防范措施。
-
入侵植物具有适应性强、繁殖速度快和天敌少等特点,虽然在经济、生态和人畜健康等多方面造成了危害,但是也可以发展成为对人类有利的经济植物。应用如下:(1)牲畜饲料。大多数入侵植物的生长繁殖都较为迅速,可以成为很好的饲料来源。如禾本科(Gramineae)的象草(Pennisetum purpureum)、大黍和芦苇(Phragmites australis)等;(2)水果、蔬菜和调味剂。如番茄、茼蒿和莴苣等可作为蔬菜,杧果、龙眼和番石榴等可作为水果,而芥菜、辣椒和酸豆(Tamarindus indica)等可作为调味料[12];(3)药用。某些入侵植物具有较高的药用价值,如少花龙葵有清凉散热的功效,可用于治疗喉咙疼痛,而青葙(Celosia argentea)的种子可药用,具有明目、清热的功效[13];(4)环境美化。如炮仗花(Pyrostegia venusta)缠绕墙壁建筑生长,成为园林景观。叶子花(Bougainvillea spectabilis)也常见于南方的绿化公园[14]。木棉(Bombax malabaricum)和火焰树(Spathodea campanulata)等可用作行道树,且地毯草等可用作草坪草;(5)芳香公园。香料植物给人营造一种嗅觉美的舒适感受,可以使人置身于大自然,舒缓疲惫。且具有杀灭细菌和净化空气的功能,可用于打造芳香植物公园。如茄科(Solanaceae)的夜香树(Cestrum nocturnum)会给游览者营造一种香远益清的氛围[15];(6)木材/造纸。如银合欢(Leucaena leucocephala)的木质坚硬,为良好的薪炭材;五节芒(Miscanthus floridulus)的秆可作造纸原料(中国植物志);(7)有毒。如垂序商陆的根或浆果部位有毒性,可致呕吐、腹泻,严重时会导致死亡;紫茉莉的种子和根部有毒,会造成唇口麻木,听力减退[16];(8)生态监控。当某个区域入侵植物大量爆发时,可作为当地生态环境恶化的指示性植物[8]。








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: