2020 Vol. 11, No. 3
2020, 11(3): 331-340.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.011
Abstract:
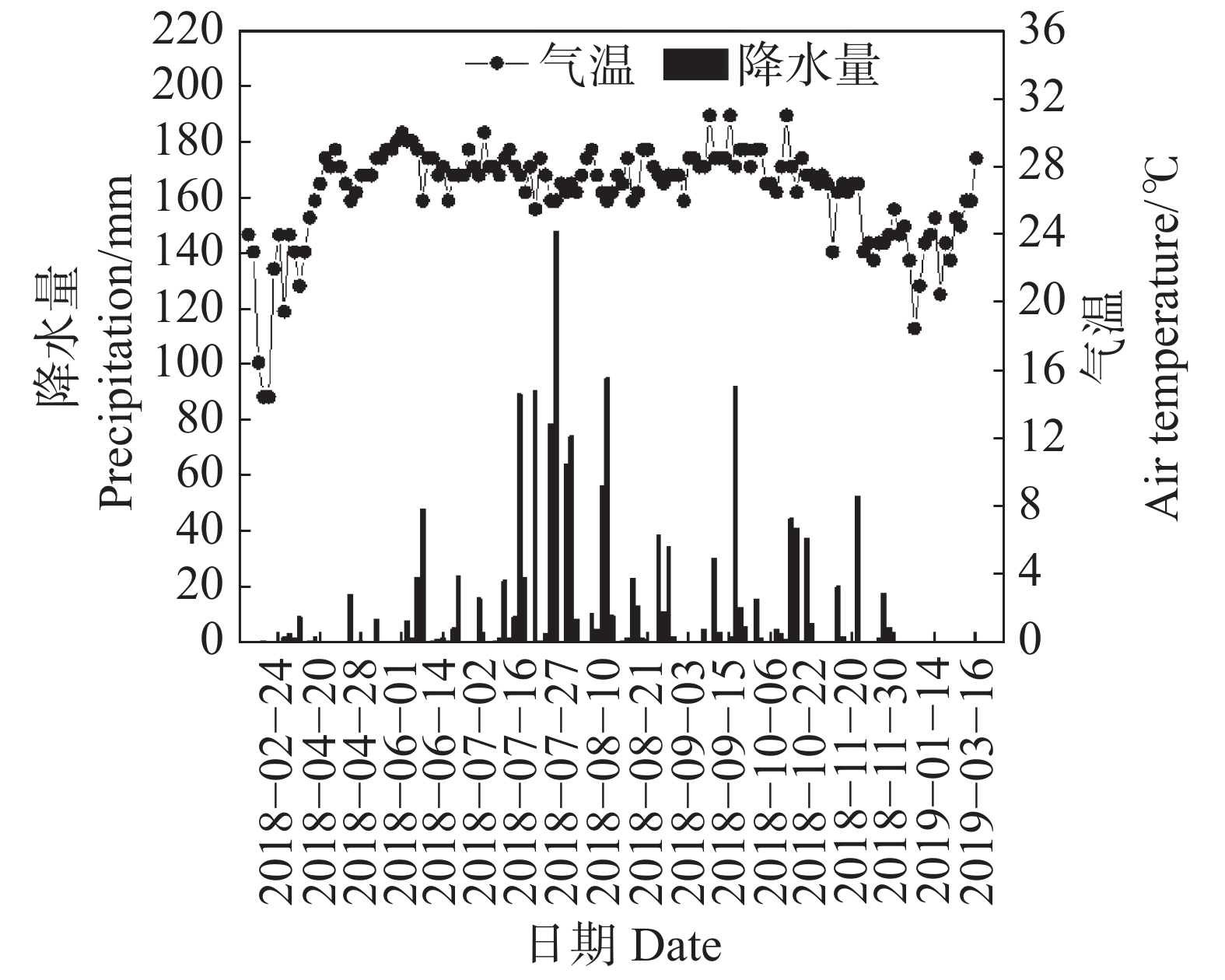
An attempt was made to explore the N2O emission characteristics of pineapple (Ananas comosus) soil under different fertilizer treatments to screen out an optimum fertilizer application approach which reduces N2O emissions and gives high pineapple yield. A fertilizer application trial was arranged in a pineapple field in the tropical region, and five treatments were arranged in the trial: no fertilizer (CK), conventional fertilizer (NPK), single application of fertilizer at a reduced rate (INF), combined application of inorganic fertilizer + organic fertilizer (INF+M), combined application of inorganic fertilizer + organic fertilizer + slow-control fertilizer (INF+M+S). The soil N2O emissions were monitored by using static black box-gas chromatography, and the relationship of soil temperature, soil moisture, nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen with N2O emissions and pineapple yield was analyzed under different treatments. The results showed that the INF+M+S, INF+M and INF treatments increased pineapple yield by 16.77%, 6.66% and 6.53%, respectively, when compared with the NPK treatment. During the whole pineapple growth stage, the N2O cumulative emission and average flux detected in the treatments were increased in the order of NPK> INF> INF+M> INF+M+S> CK and were significantly different between the treatments. The emission intensity was increased in the order of NPK>INF>INF+M>INF+M+S>CK and was significantly different between the treatments. The INF+M+S treatment had a significantly lower emission coefficient than all the other treatments. The soil N2O emission flux was significantly positively correlated with soil ammonium nitrogen content and soil nitrate nitrogen content. The INF+M+S treatment increased pineapple yield significantly and reduced the N2O emission in the pineapple field at the whole growth stage, and it can hence be used as an optimum approach for fertilizer application to pineapple.
An attempt was made to explore the N2O emission characteristics of pineapple (Ananas comosus) soil under different fertilizer treatments to screen out an optimum fertilizer application approach which reduces N2O emissions and gives high pineapple yield. A fertilizer application trial was arranged in a pineapple field in the tropical region, and five treatments were arranged in the trial: no fertilizer (CK), conventional fertilizer (NPK), single application of fertilizer at a reduced rate (INF), combined application of inorganic fertilizer + organic fertilizer (INF+M), combined application of inorganic fertilizer + organic fertilizer + slow-control fertilizer (INF+M+S). The soil N2O emissions were monitored by using static black box-gas chromatography, and the relationship of soil temperature, soil moisture, nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen with N2O emissions and pineapple yield was analyzed under different treatments. The results showed that the INF+M+S, INF+M and INF treatments increased pineapple yield by 16.77%, 6.66% and 6.53%, respectively, when compared with the NPK treatment. During the whole pineapple growth stage, the N2O cumulative emission and average flux detected in the treatments were increased in the order of NPK> INF> INF+M> INF+M+S> CK and were significantly different between the treatments. The emission intensity was increased in the order of NPK>INF>INF+M>INF+M+S>CK and was significantly different between the treatments. The INF+M+S treatment had a significantly lower emission coefficient than all the other treatments. The soil N2O emission flux was significantly positively correlated with soil ammonium nitrogen content and soil nitrate nitrogen content. The INF+M+S treatment increased pineapple yield significantly and reduced the N2O emission in the pineapple field at the whole growth stage, and it can hence be used as an optimum approach for fertilizer application to pineapple.
2020, 11(3): 257-265.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.001
Abstract:
Haiwei Bay is one of the important fishing ports in Hainan Province. Phytoplanton and sea water were sampled in 12 sampling stations in the seawaters near Haiwei Bay in July (summer) and September (autumn), 2018 to analyze the structure of phytoplankton community and the quality of seawater which had important effects on fishery resources. The results showed that there were a total number of 119 species of phytoplankton identified in July, and a total number of 114 species identified in September, in which diatoms and dinoflagellates were predominant in the species composition and the cell abundance. There were 7 and 10 dominant species in July and September, respectively. Interestingly, Chaetoceros curvisetus, Chaetoceros sp and Pseudo-nitzschia pungens were dominant both in July and September. The average cell density was 6.15×106 cells·m−3 in July, which was 10 times more than that in September. The seawaters in Haiwei Bay was rich in phytoplankton species. The average Shannon-Wiener diversity index, Pielou evenness index and Margalef diversity index were 5.3, 3.27, 0.56 in July, respectively, and 5.52, 4.19, 0.76 in September, respectively. All these indexes showed that the ecological environment in the seawaters was good. The redundancy analysis showed that the phytoplankton were positively significantly correlated with reactive silicate and total nitrogen, and negatively significantly with nitrite in July, while the main factor affecting the phytoplankton was pH in September, indicating that the main environmental factors for phytoplankton were silicate, total nitrogen and pH in the seawaters. The results showed the structure of phytoplankton community in Haiwei Bay was closely correlated with the seawater nutrients.
Haiwei Bay is one of the important fishing ports in Hainan Province. Phytoplanton and sea water were sampled in 12 sampling stations in the seawaters near Haiwei Bay in July (summer) and September (autumn), 2018 to analyze the structure of phytoplankton community and the quality of seawater which had important effects on fishery resources. The results showed that there were a total number of 119 species of phytoplankton identified in July, and a total number of 114 species identified in September, in which diatoms and dinoflagellates were predominant in the species composition and the cell abundance. There were 7 and 10 dominant species in July and September, respectively. Interestingly, Chaetoceros curvisetus, Chaetoceros sp and Pseudo-nitzschia pungens were dominant both in July and September. The average cell density was 6.15×106 cells·m−3 in July, which was 10 times more than that in September. The seawaters in Haiwei Bay was rich in phytoplankton species. The average Shannon-Wiener diversity index, Pielou evenness index and Margalef diversity index were 5.3, 3.27, 0.56 in July, respectively, and 5.52, 4.19, 0.76 in September, respectively. All these indexes showed that the ecological environment in the seawaters was good. The redundancy analysis showed that the phytoplankton were positively significantly correlated with reactive silicate and total nitrogen, and negatively significantly with nitrite in July, while the main factor affecting the phytoplankton was pH in September, indicating that the main environmental factors for phytoplankton were silicate, total nitrogen and pH in the seawaters. The results showed the structure of phytoplankton community in Haiwei Bay was closely correlated with the seawater nutrients.
2020, 11(3): 266-273.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.002
Abstract:
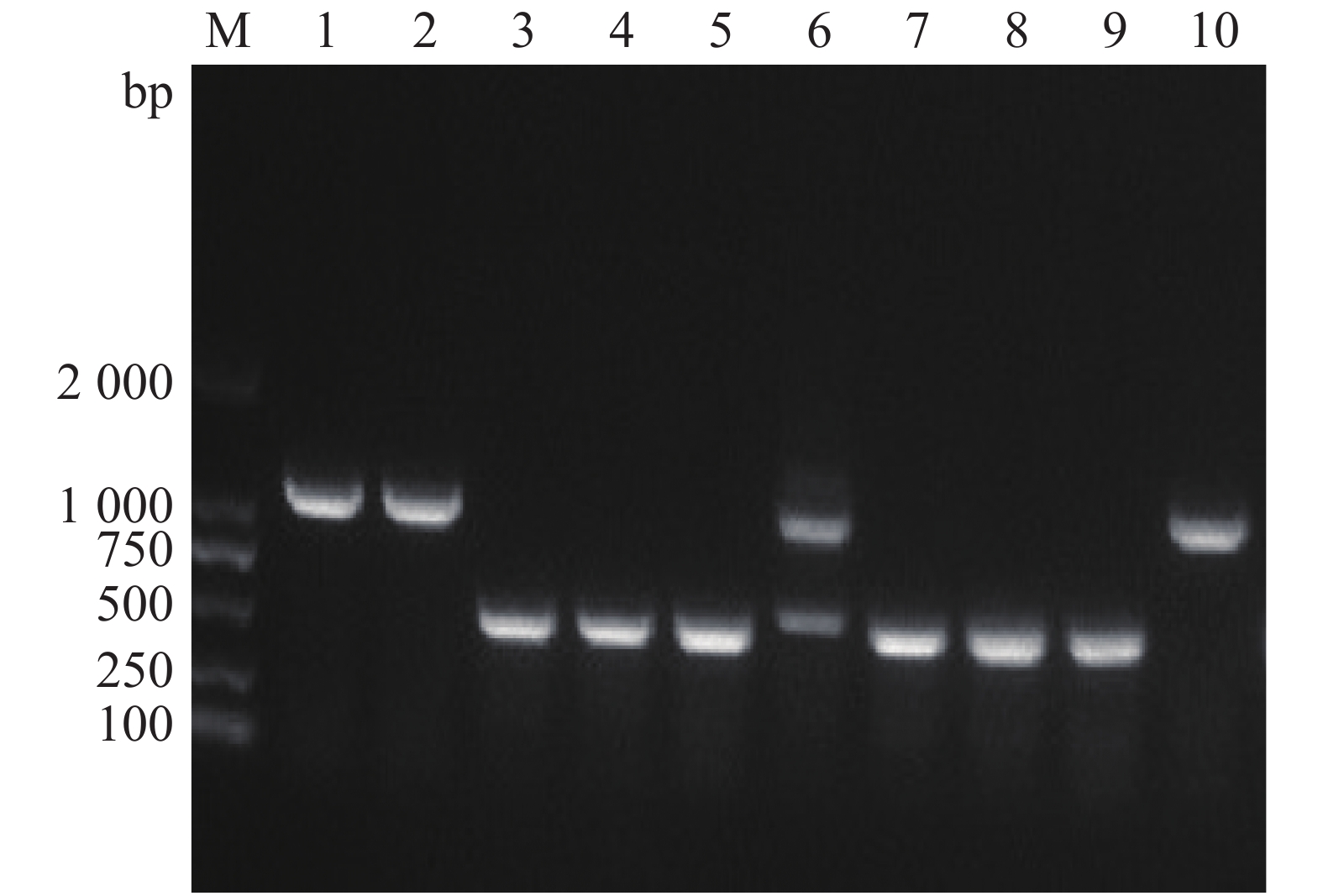
Vibrio coralliilyticus is pathogenic to many species of marine animals. HapR is a global regulator in Vibrio quorum sensing system. Our previous experiment showed that the pathogenicity of V. coralliilyticus was closely related to its inoculating concentration when Acropora species were infected with V. coralliilyticus under an artificial condition. Therefore, quorum sensing system of V. coralliilyticus is presumed to be essentially associated with its virulence. In this study, a deletion mutant strain △hapR-Vc450 and a complementary strain ChapR-Vc450 were successfully constructed in V. coralliilyticus. Phenotypic observation showed that loss of hapR resulted in change of colony morphology but not in the motility and flagellar structure of V. coralliilyticus. The loss of hapR caused lower maximum growth of V. coralliilyticus, but obvious formation of biofilm. When Acropora species was artificially infected with V. coralliilyticus, the deletion mutant strain and the complementary strain of V. coralliilyticus increased their virulence as compared with the wild type. This may be due to the fact that hapR has a similar function in V. coralliilyticus like in V. cholera, inhibiting cascade activation of virulence genes, and that the loss of hapR would activate the colonization and virulence of the genes through quorum sensing system.
Vibrio coralliilyticus is pathogenic to many species of marine animals. HapR is a global regulator in Vibrio quorum sensing system. Our previous experiment showed that the pathogenicity of V. coralliilyticus was closely related to its inoculating concentration when Acropora species were infected with V. coralliilyticus under an artificial condition. Therefore, quorum sensing system of V. coralliilyticus is presumed to be essentially associated with its virulence. In this study, a deletion mutant strain △hapR-Vc450 and a complementary strain ChapR-Vc450 were successfully constructed in V. coralliilyticus. Phenotypic observation showed that loss of hapR resulted in change of colony morphology but not in the motility and flagellar structure of V. coralliilyticus. The loss of hapR caused lower maximum growth of V. coralliilyticus, but obvious formation of biofilm. When Acropora species was artificially infected with V. coralliilyticus, the deletion mutant strain and the complementary strain of V. coralliilyticus increased their virulence as compared with the wild type. This may be due to the fact that hapR has a similar function in V. coralliilyticus like in V. cholera, inhibiting cascade activation of virulence genes, and that the loss of hapR would activate the colonization and virulence of the genes through quorum sensing system.
2020, 11(3): 274-280.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.003
Abstract:
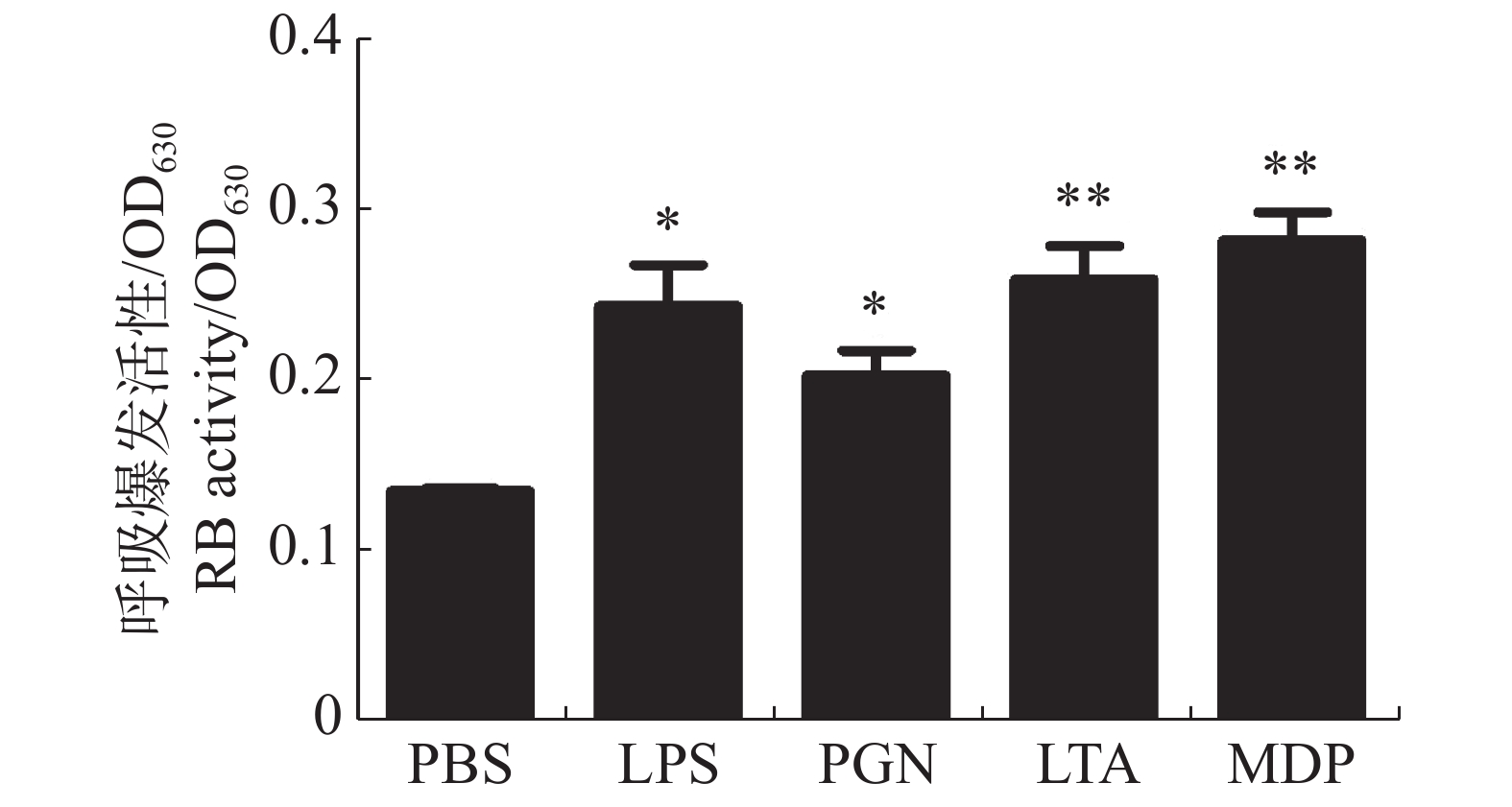
In order to study the effects of pathogen-associated molecular patterns on the immunologic function of the head kidney macrophages (HKMs) from large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea), the head kidney macrophages from L. crocea were extracted and then incubated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), peptidoglycan (PGN), lipoteichoic acid (LTA), muramyl dipeptide (MDP), respectively, and their respiratory burst activity, antioxidant enzyme (SOD & CAT) activity, lysozyme activity and expression of immune-related cellular inflammatory factors (TNFα, IL1β, IL8, IL10, CXCL9, MYD88, TLR3, and TLR8) were detected. The results showed that the LPS, PGN, LTA, and MDP increased the respiratory burst activity and lysozyme activity of HKMs from L. crocea, but reduced the activities of the two antioxidant enzymes SOD and CAT. The expression levels of TNFα, IL1β, IL8, IL10, CXCL9, MYD88, TLR3, and TLR8 were significantly up-regulated under the LPS and LTA stimulation, and other six immune-related cellular inflammatory factors except IL8 and CXCL9 were significantly up-regulated under the PGN and MDP stimulation. These results suggested that the four pathogen-associated molecular patterns, LPS, PGN, LTA and MDP, have significant effect on the non-specific immunity and the expression of immune-related cellular inflammatory factors of HKMs from L. crocea.
In order to study the effects of pathogen-associated molecular patterns on the immunologic function of the head kidney macrophages (HKMs) from large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea), the head kidney macrophages from L. crocea were extracted and then incubated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), peptidoglycan (PGN), lipoteichoic acid (LTA), muramyl dipeptide (MDP), respectively, and their respiratory burst activity, antioxidant enzyme (SOD & CAT) activity, lysozyme activity and expression of immune-related cellular inflammatory factors (TNFα, IL1β, IL8, IL10, CXCL9, MYD88, TLR3, and TLR8) were detected. The results showed that the LPS, PGN, LTA, and MDP increased the respiratory burst activity and lysozyme activity of HKMs from L. crocea, but reduced the activities of the two antioxidant enzymes SOD and CAT. The expression levels of TNFα, IL1β, IL8, IL10, CXCL9, MYD88, TLR3, and TLR8 were significantly up-regulated under the LPS and LTA stimulation, and other six immune-related cellular inflammatory factors except IL8 and CXCL9 were significantly up-regulated under the PGN and MDP stimulation. These results suggested that the four pathogen-associated molecular patterns, LPS, PGN, LTA and MDP, have significant effect on the non-specific immunity and the expression of immune-related cellular inflammatory factors of HKMs from L. crocea.
2020, 11(3): 281-287.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.004
Abstract:
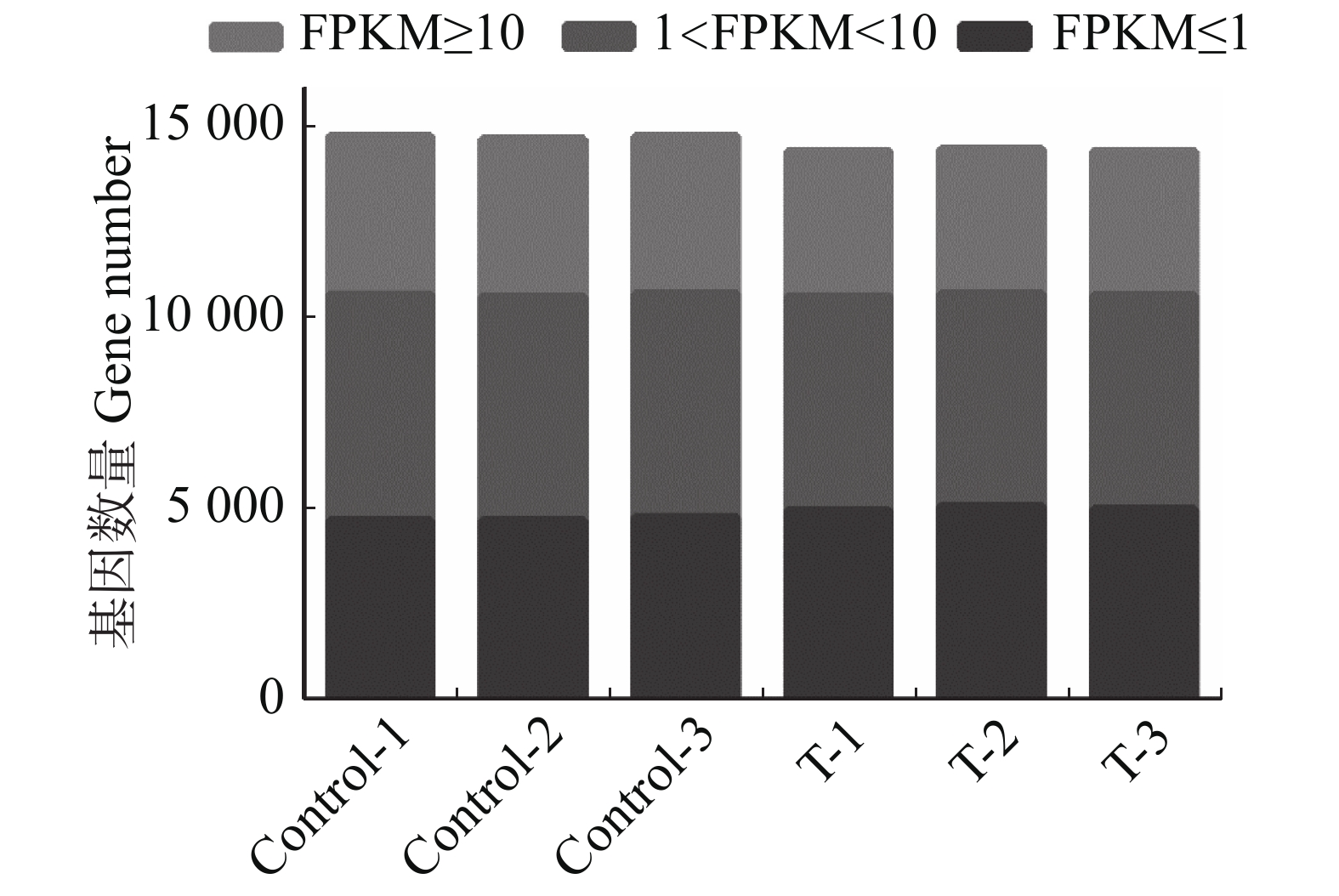
Transcriptomes of Aedes aegypti larvae before and after administration of tenvermectin were sequenced with RNA-Seq to investigate the gene expression differences of A. aegypti at the transcriptome level before and after the treatment. The gene expression differences of A. aegypti before and after the treatment were then analyzed, and verified by real-time quantitative PCR. The results showed that, compared with the control group, there were 2 647 genes that were significantly different in expression in the larvae of A. aegypti treated with tenvermectin, of which 697 were up-regulated and 1 950 down-regulated. Gene ontology analysis showed that the sequenced genes were mainly annotated into such functional groups as cellular process, metabolic process, membrane, and binding and catalytic activity. The differential gene KEGG pathway is mainly enriched in medicine metabolism, immune response, biosynthesis, digestion and absorption. Six genes including three upregulated genes GST-1, TS11 and CarE2 and three downregulated genes CP, CP19 and GCW were randomly selected from the genes of the larvae treated, and verified by using real-time quantitative PCR, and the results were consistent with the RNA Seq results. RNA Seq was used to screen out the genes that had different expression of A. aegypti before and after treatment with tenvermectin, which provides insight into understanding of the toxicological mechanism of tenvermectin in A. aegypti and finding of the medicine resistance related genes from A. aegypti.
Transcriptomes of Aedes aegypti larvae before and after administration of tenvermectin were sequenced with RNA-Seq to investigate the gene expression differences of A. aegypti at the transcriptome level before and after the treatment. The gene expression differences of A. aegypti before and after the treatment were then analyzed, and verified by real-time quantitative PCR. The results showed that, compared with the control group, there were 2 647 genes that were significantly different in expression in the larvae of A. aegypti treated with tenvermectin, of which 697 were up-regulated and 1 950 down-regulated. Gene ontology analysis showed that the sequenced genes were mainly annotated into such functional groups as cellular process, metabolic process, membrane, and binding and catalytic activity. The differential gene KEGG pathway is mainly enriched in medicine metabolism, immune response, biosynthesis, digestion and absorption. Six genes including three upregulated genes GST-1, TS11 and CarE2 and three downregulated genes CP, CP19 and GCW were randomly selected from the genes of the larvae treated, and verified by using real-time quantitative PCR, and the results were consistent with the RNA Seq results. RNA Seq was used to screen out the genes that had different expression of A. aegypti before and after treatment with tenvermectin, which provides insight into understanding of the toxicological mechanism of tenvermectin in A. aegypti and finding of the medicine resistance related genes from A. aegypti.
2020, 11(3): 288-295.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.005
Abstract:
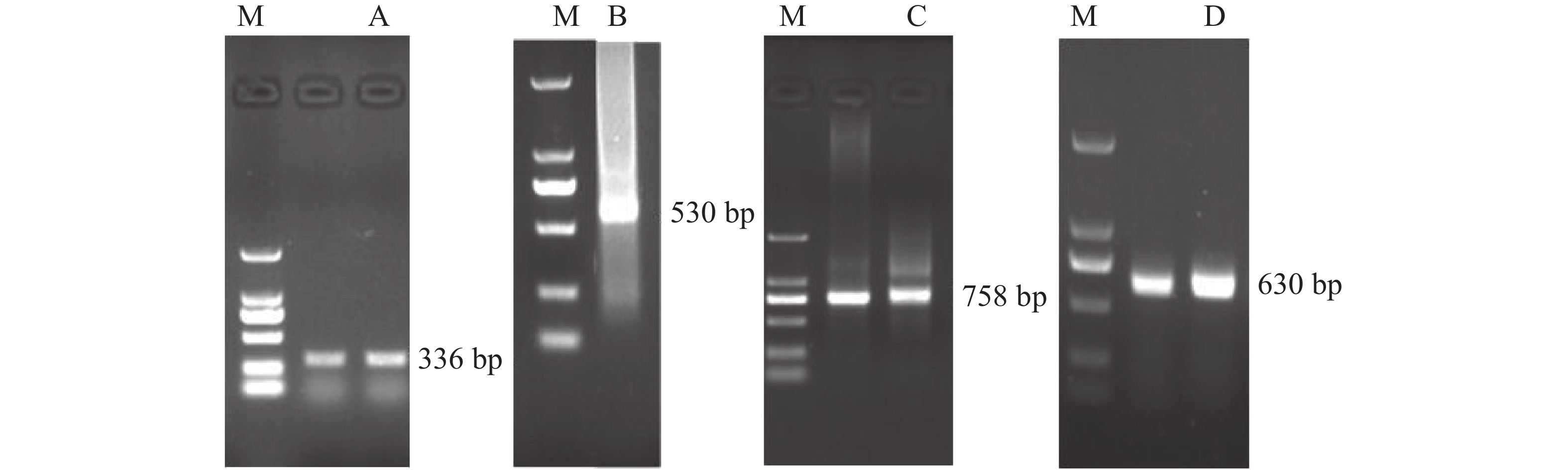
In order to characterize the key genes which control the petal senescence, a gene encoding an response regulator (RR), OnRR10 gene (GenBank accession number: MN337795), was isolated from the petals of Oncidium with RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends). The gene is 630 bp in length and encodes a protein of 209 amino acids in size. Protein secondary structure analysis showed that the OnRR10 protein is a hydrophilic protein and is localized in the nucleus. Homologous sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis showed that the OnRR10 belongs to the YesN family. In Orchidaceae, OnRR10 protein is closely related to the ORR10 gene of Phalaenopsis equestris. Real-time quantitative analysis showed that the expression level of the OnRR10 gene was the highest at the bud swelling stage and flower initial senescence stage of Oncidium during the flower development, and that the expression of the OnRR10 gene was not regulated by the circadian clock, but increased rapidly in a short time under the 6-BA (6-Benzylaminopurine) treatment. These results implicated that the OnRR10 gene may be involved in the petal senescence through cytokine effect.
In order to characterize the key genes which control the petal senescence, a gene encoding an response regulator (RR), OnRR10 gene (GenBank accession number: MN337795), was isolated from the petals of Oncidium with RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends). The gene is 630 bp in length and encodes a protein of 209 amino acids in size. Protein secondary structure analysis showed that the OnRR10 protein is a hydrophilic protein and is localized in the nucleus. Homologous sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis showed that the OnRR10 belongs to the YesN family. In Orchidaceae, OnRR10 protein is closely related to the ORR10 gene of Phalaenopsis equestris. Real-time quantitative analysis showed that the expression level of the OnRR10 gene was the highest at the bud swelling stage and flower initial senescence stage of Oncidium during the flower development, and that the expression of the OnRR10 gene was not regulated by the circadian clock, but increased rapidly in a short time under the 6-BA (6-Benzylaminopurine) treatment. These results implicated that the OnRR10 gene may be involved in the petal senescence through cytokine effect.
2020, 11(3): 296-300, 323.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.006
Abstract:
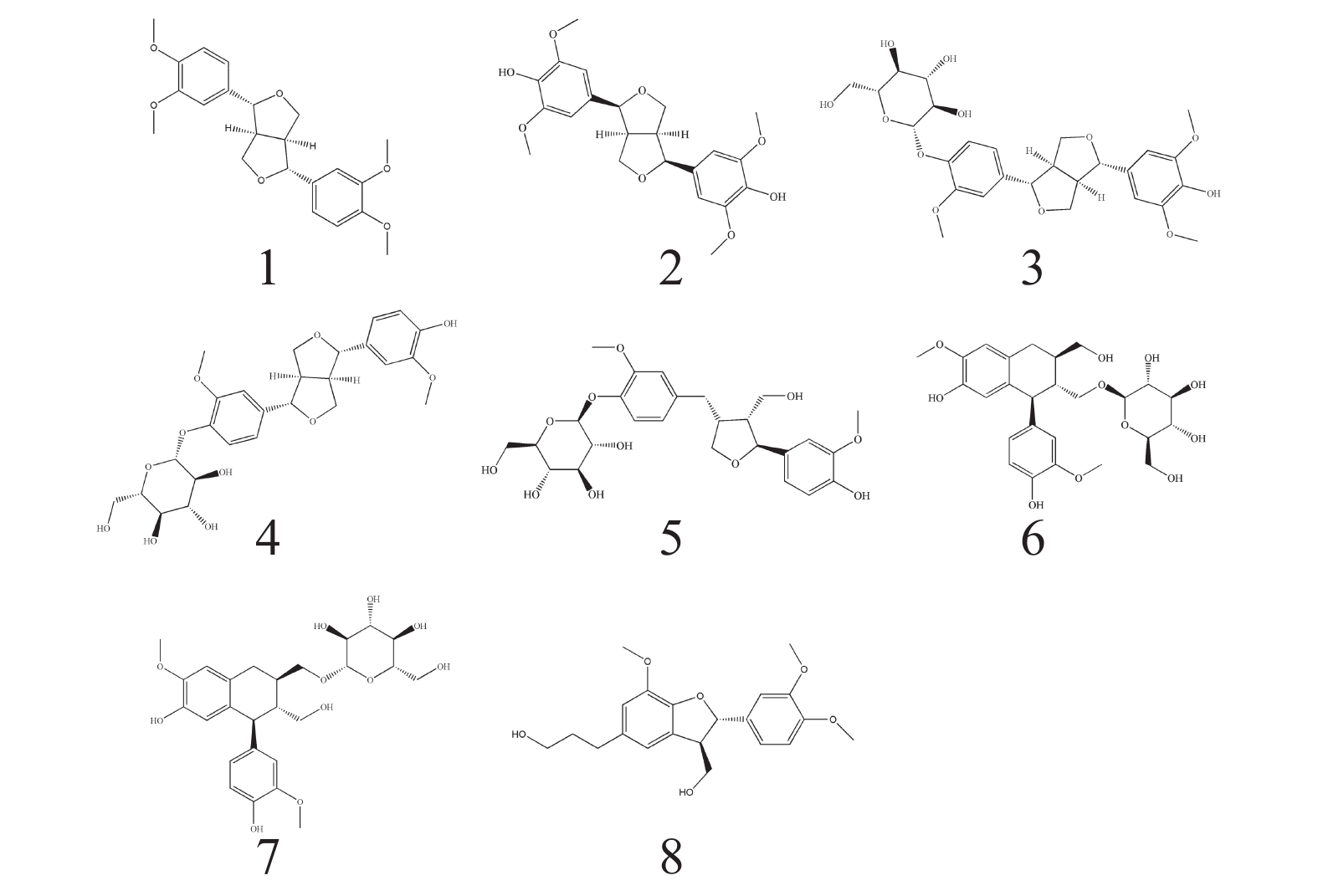
Flowers of Camellia nitidissima Chi were extracted, and their chemical constituents were then isolated and purified by silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 gel, C18 reversed silica gel, and semi-preparative HPLC. The structures of their chemical constituents were determined by using iH-NMR, 13C-NMR and ESI-MS spectra. Eight lignans were identified from the extracts of the flowers, and their structures were elucidated from the spectra as: eudesmin (1), (+)-diasyringaresinol (2), (+)-isoeucommin A (3), Pinoresinol 4-O-glucoside (4), 7S, 8R, 8′R-(-)-lariciresinol-4′-O-D-glucopyranoside (5), (+)-Isolariciresinol 9-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6), (+)-Isolariciresinol 9′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (7), and 3′, 4-O-dimethylcedrusin (8). All these chemical compounds were isolated from C. nitidissima Chi for the first time.
Flowers of Camellia nitidissima Chi were extracted, and their chemical constituents were then isolated and purified by silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 gel, C18 reversed silica gel, and semi-preparative HPLC. The structures of their chemical constituents were determined by using iH-NMR, 13C-NMR and ESI-MS spectra. Eight lignans were identified from the extracts of the flowers, and their structures were elucidated from the spectra as: eudesmin (1), (+)-diasyringaresinol (2), (+)-isoeucommin A (3), Pinoresinol 4-O-glucoside (4), 7S, 8R, 8′R-(-)-lariciresinol-4′-O-D-glucopyranoside (5), (+)-Isolariciresinol 9-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (6), (+)-Isolariciresinol 9′-O-β-D-glucopyranoside (7), and 3′, 4-O-dimethylcedrusin (8). All these chemical compounds were isolated from C. nitidissima Chi for the first time.
2020, 11(3): 301-309.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.007
Abstract:
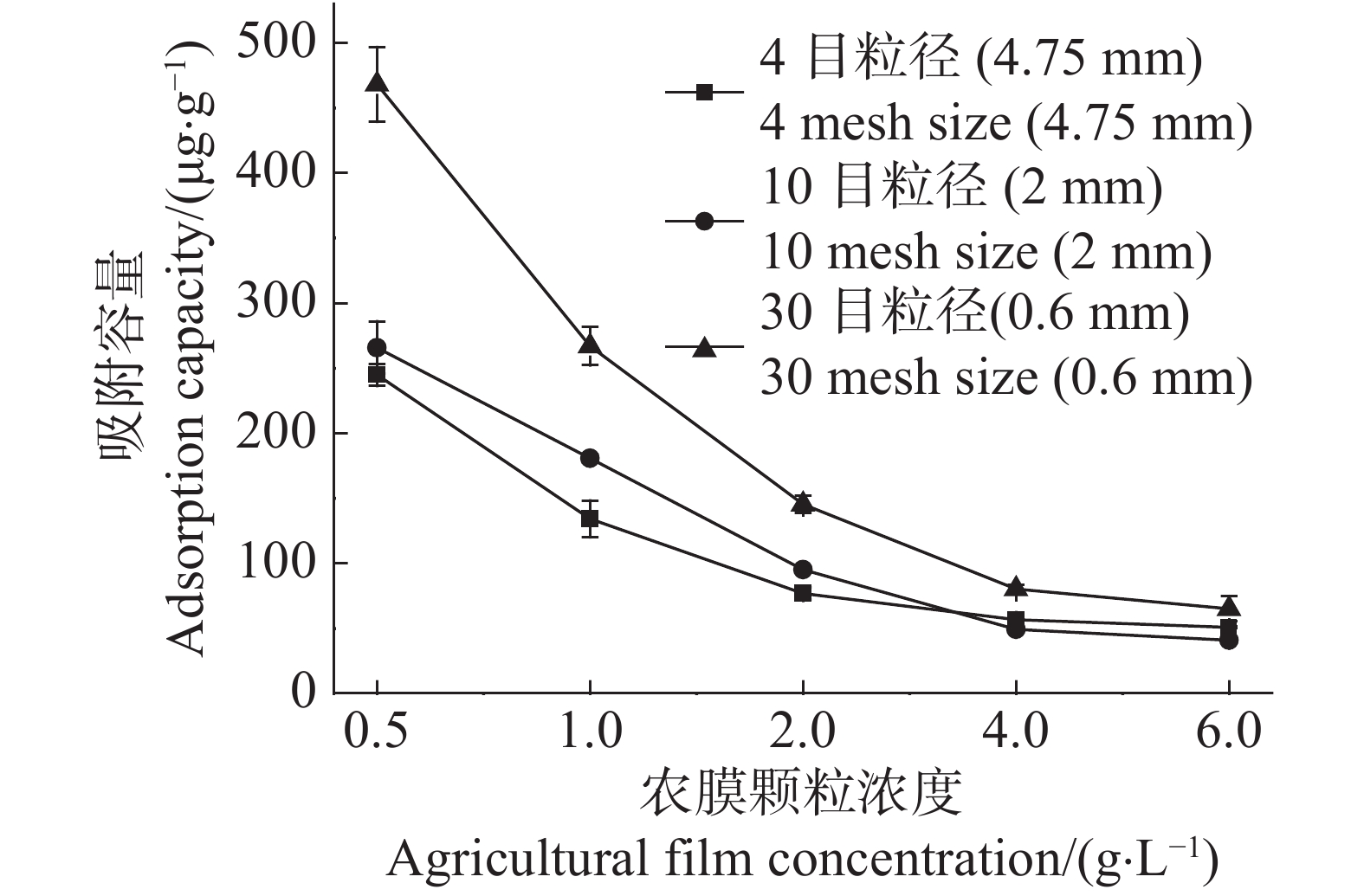
The wide application of agricultural film makes the problem of residual pollution of agricultural film impossible to be ignored, and the impact of agricultural film particles on the migration and transformation of pollutants in the soil environment is rarely studied. Agricultural film with three different particle sizes (4 mesh, 10 mesh, 30 mesh)were used to study the effects of agricultural film concentration, initial pH, adsorption time, initial Cd2+ concentration and aging methods on Cd2+ adsorption, and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) and adsorption model fitting were used to explore the Cd2+ adsorption characteristics of three different particle sizes of agricultural films under different aging methods. The results showed that the adsorption capacity of agricultural film particles for Cd2+ was inversely proportional to the particle size.The pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm adsorption model better fitted the adsorption process of Cd2+ by the agricultural films. The agricultural film particles treated with nitric acid aging reduced its adsorption capacity of Cd2+ by 50.10% and the hydrogen peroxide aging treatment increased its adsorption capacity of Cd2+ by 21.36% as against the control(agricultural film particles without aging). These results can provide a reference for exploration of the migration process and mechanism of Cd2+ in soil through agricultural film particles and the prevention and control of residual agricultural film.
The wide application of agricultural film makes the problem of residual pollution of agricultural film impossible to be ignored, and the impact of agricultural film particles on the migration and transformation of pollutants in the soil environment is rarely studied. Agricultural film with three different particle sizes (4 mesh, 10 mesh, 30 mesh)were used to study the effects of agricultural film concentration, initial pH, adsorption time, initial Cd2+ concentration and aging methods on Cd2+ adsorption, and Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) and adsorption model fitting were used to explore the Cd2+ adsorption characteristics of three different particle sizes of agricultural films under different aging methods. The results showed that the adsorption capacity of agricultural film particles for Cd2+ was inversely proportional to the particle size.The pseudo-second-order kinetic model and Langmuir isotherm adsorption model better fitted the adsorption process of Cd2+ by the agricultural films. The agricultural film particles treated with nitric acid aging reduced its adsorption capacity of Cd2+ by 50.10% and the hydrogen peroxide aging treatment increased its adsorption capacity of Cd2+ by 21.36% as against the control(agricultural film particles without aging). These results can provide a reference for exploration of the migration process and mechanism of Cd2+ in soil through agricultural film particles and the prevention and control of residual agricultural film.
2020, 11(3): 310-313.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.008
Abstract:
Soilborne diseases occur seriously in the field of muskmelon (Cucumis melo L) in winter and spring in Hainan in recent years, which severely affects the yield of muskmelon. The pathogens were isolated from the stem tissue of the muskmelon seedlings infected with the soilborne diseases, and identified as Fusarium oxysporum f.sp melonis by morphology and rDNA ITS sequence. Nine rootstock varieties of muskmelon were inoculated with the spores solution of F. oxysporum f. sp. melonis with Meinong muskmelon variety as the control to determine their resistance to muskmelon wilt caused by F. oxysporum f.sp melonis to select resistant rootstocks. The results showed that the control Meinong muskmelon variety had an incidence of muskmelon Fusarium wilt of 83.33%, while the rootstock varieties Guangzhen 1, Lianda, Xiali, and Yongzhan had no incidence of Fusarium wilt, and can hence be used as candidates for disease-resistant root stocks for muskmelon.
Soilborne diseases occur seriously in the field of muskmelon (Cucumis melo L) in winter and spring in Hainan in recent years, which severely affects the yield of muskmelon. The pathogens were isolated from the stem tissue of the muskmelon seedlings infected with the soilborne diseases, and identified as Fusarium oxysporum f.sp melonis by morphology and rDNA ITS sequence. Nine rootstock varieties of muskmelon were inoculated with the spores solution of F. oxysporum f. sp. melonis with Meinong muskmelon variety as the control to determine their resistance to muskmelon wilt caused by F. oxysporum f.sp melonis to select resistant rootstocks. The results showed that the control Meinong muskmelon variety had an incidence of muskmelon Fusarium wilt of 83.33%, while the rootstock varieties Guangzhen 1, Lianda, Xiali, and Yongzhan had no incidence of Fusarium wilt, and can hence be used as candidates for disease-resistant root stocks for muskmelon.
2020, 11(3): 314-323.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.009
Abstract:
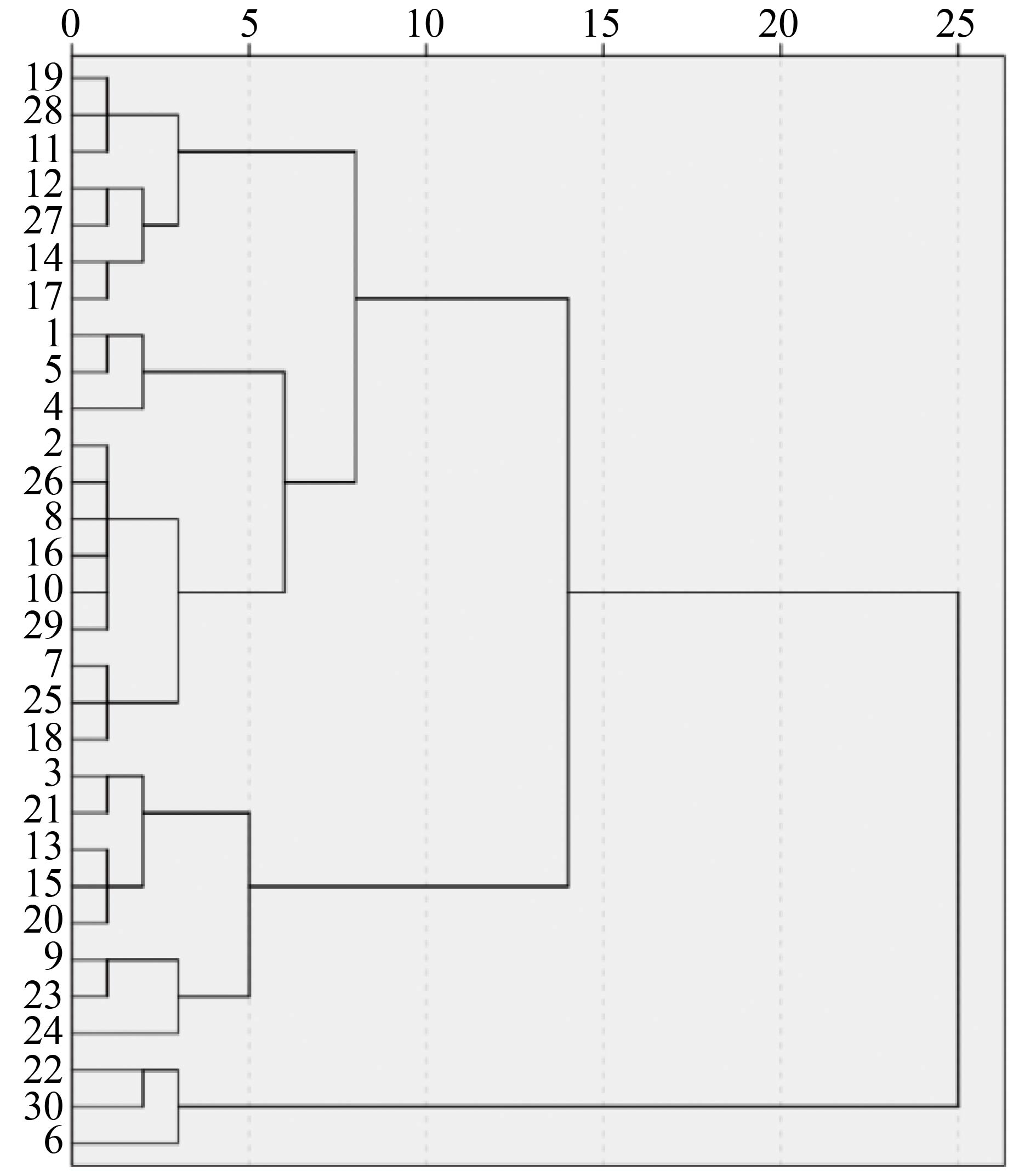
Thirty rice varieties/lines with different salt tolerance were treated with NaCl at concentrations of 0 (CK), 0.3% and 0.5% at the seedling stage, and their salt tolerance index was determined, based on which their salt tolerance was analyzed and evaluated by using correlation analysis, principal component analysis and membership function. The results showed that the growth related indexes of the 30 varieties/lines above ground under salt stress, such as fresh weight (FW), dry weight (DW), net photosynthetic rate (Pn), water use efficiency (WUE) and chlorophyll content (TC), declined to some extents, while the indexes related to physiological metabolism, such as malondialdehyde (MDA) content, soluble sugar (SS) content, soluble protein (SP) content, free proline (Pro) content, peroxidase (POD) activity, etc, were elevated. These rice varieties/lines had higher variation in coefficients of salt tolerance of all the indexes, except Pro content, under the 0.5% NaCl treatment than under the 0.3% NaCl treatment, indicating that these varieties/lines under the 0.5% NaCl treatment displayed the highest difference in salt tolerance among all the treatments. All the indexes of the rice under the 0.5% NaCl treatment were used for correlation analysis to select the salt tolerance indexes of high significance from all the indexes for evaluation, based on which D value was calculated by using the membership function. The results showed that 5 lines, 14-57, 14-6, 14-36, W01, and 14-58-2, were highly tolerant of salt and that anther 5 lines, 16-8, 50188-2, 16-9, 15-18-2, and 14- 58-1, were low in salt tolerance. The stepwise regression analysis showed that the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), water use efficiency (WUE) and fresh weight (FW) of the leaves were the three most important indexes for evaluation of the salt tolerance of rice, based on which the estimation accuracy of salt tolerance of each rice variety/line were more than 90%. According to the comprehensive evaluation results, the 30 rice varieties/lines were divided into three categories, salt tolerant, moderately salt tolerant and salt sensitive, by using system clustering.
Thirty rice varieties/lines with different salt tolerance were treated with NaCl at concentrations of 0 (CK), 0.3% and 0.5% at the seedling stage, and their salt tolerance index was determined, based on which their salt tolerance was analyzed and evaluated by using correlation analysis, principal component analysis and membership function. The results showed that the growth related indexes of the 30 varieties/lines above ground under salt stress, such as fresh weight (FW), dry weight (DW), net photosynthetic rate (Pn), water use efficiency (WUE) and chlorophyll content (TC), declined to some extents, while the indexes related to physiological metabolism, such as malondialdehyde (MDA) content, soluble sugar (SS) content, soluble protein (SP) content, free proline (Pro) content, peroxidase (POD) activity, etc, were elevated. These rice varieties/lines had higher variation in coefficients of salt tolerance of all the indexes, except Pro content, under the 0.5% NaCl treatment than under the 0.3% NaCl treatment, indicating that these varieties/lines under the 0.5% NaCl treatment displayed the highest difference in salt tolerance among all the treatments. All the indexes of the rice under the 0.5% NaCl treatment were used for correlation analysis to select the salt tolerance indexes of high significance from all the indexes for evaluation, based on which D value was calculated by using the membership function. The results showed that 5 lines, 14-57, 14-6, 14-36, W01, and 14-58-2, were highly tolerant of salt and that anther 5 lines, 16-8, 50188-2, 16-9, 15-18-2, and 14- 58-1, were low in salt tolerance. The stepwise regression analysis showed that the net photosynthetic rate (Pn), water use efficiency (WUE) and fresh weight (FW) of the leaves were the three most important indexes for evaluation of the salt tolerance of rice, based on which the estimation accuracy of salt tolerance of each rice variety/line were more than 90%. According to the comprehensive evaluation results, the 30 rice varieties/lines were divided into three categories, salt tolerant, moderately salt tolerant and salt sensitive, by using system clustering.
2020, 11(3): 324-330.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.010
Abstract:
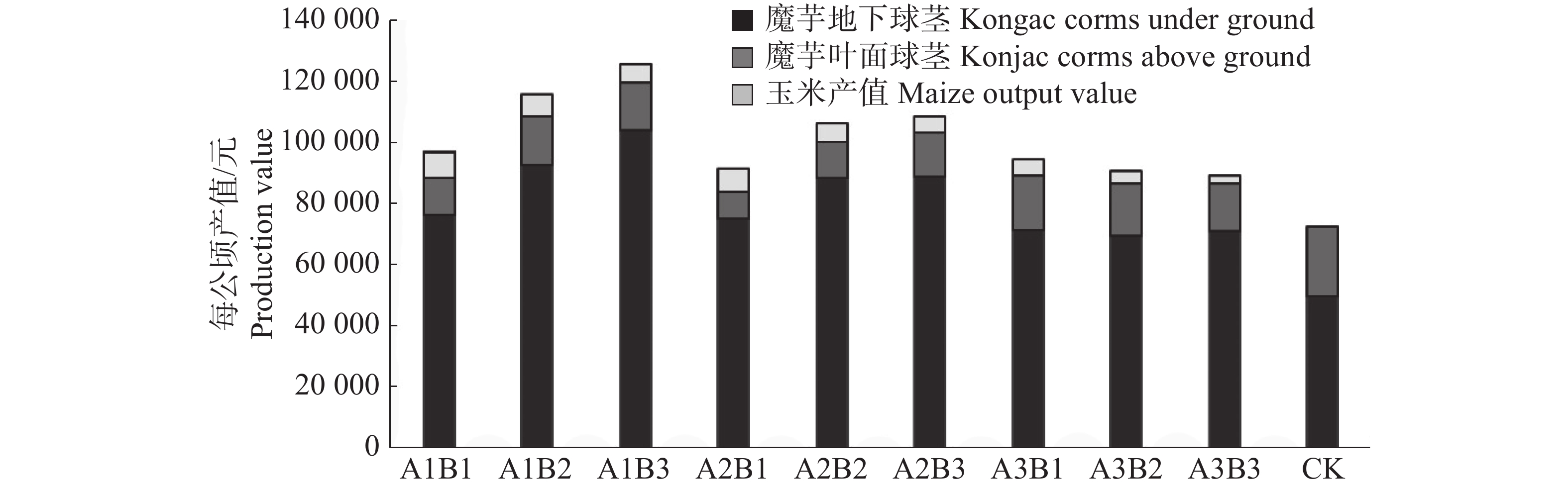
Konjac (Amorphophallus kongjac) was intercropped with maize to observe the effects of different sowing dates and planting densities of maize on the agronomic traits and yields konjac. Konjac was intercropped with maize at three sowing dates (A1: Konjac seedlings at an emergence rate of 10%; A2: Konjac seedlings at an emergence rate of 50%; A3: Konjac seedlings at an emergence rate of 90%), and at three planting densities (B1: 41 700 plants·hm−2; B2: 20 800 plants·hm−2; B3: 13 900 plants·hm−2). The agronomic traits of konjac at the end of the konjac leaf expansion, the yields of konjac and maize and land outputs were determined. The results showed that with the delay of maize sowing dates, the plant heights, petiole diameters and yield of underground corms of konjac, and maize yield decreased. With the decrease of maize planting densities, the leaf diameter and the yield of underground corms of konjac increased, while the konjac plant heights and maize yield decreased. Different maize sowing dates and planting densities had significant interaction effects on both konjac petiole diameter and the yield of underground corm. The maize densities used in different sowing dates did not have significant effect on the leaf diameters, plant heights, yield of aboveground corm of konjac, and yield of maize. When solely planted, kongjac was the highest in leaf diameters, petiole diameters and aboveground corm yield, but the lowest in plant heights and underground corm yield. The land had a higher output value when konjac was intercropped with maize at a density of 13,900 plants/ha at the maize sowing date when konjac had an emergence rate of 10%.
Konjac (Amorphophallus kongjac) was intercropped with maize to observe the effects of different sowing dates and planting densities of maize on the agronomic traits and yields konjac. Konjac was intercropped with maize at three sowing dates (A1: Konjac seedlings at an emergence rate of 10%; A2: Konjac seedlings at an emergence rate of 50%; A3: Konjac seedlings at an emergence rate of 90%), and at three planting densities (B1: 41 700 plants·hm−2; B2: 20 800 plants·hm−2; B3: 13 900 plants·hm−2). The agronomic traits of konjac at the end of the konjac leaf expansion, the yields of konjac and maize and land outputs were determined. The results showed that with the delay of maize sowing dates, the plant heights, petiole diameters and yield of underground corms of konjac, and maize yield decreased. With the decrease of maize planting densities, the leaf diameter and the yield of underground corms of konjac increased, while the konjac plant heights and maize yield decreased. Different maize sowing dates and planting densities had significant interaction effects on both konjac petiole diameter and the yield of underground corm. The maize densities used in different sowing dates did not have significant effect on the leaf diameters, plant heights, yield of aboveground corm of konjac, and yield of maize. When solely planted, kongjac was the highest in leaf diameters, petiole diameters and aboveground corm yield, but the lowest in plant heights and underground corm yield. The land had a higher output value when konjac was intercropped with maize at a density of 13,900 plants/ha at the maize sowing date when konjac had an emergence rate of 10%.
2020, 11(3): 341-346.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.012
Abstract:
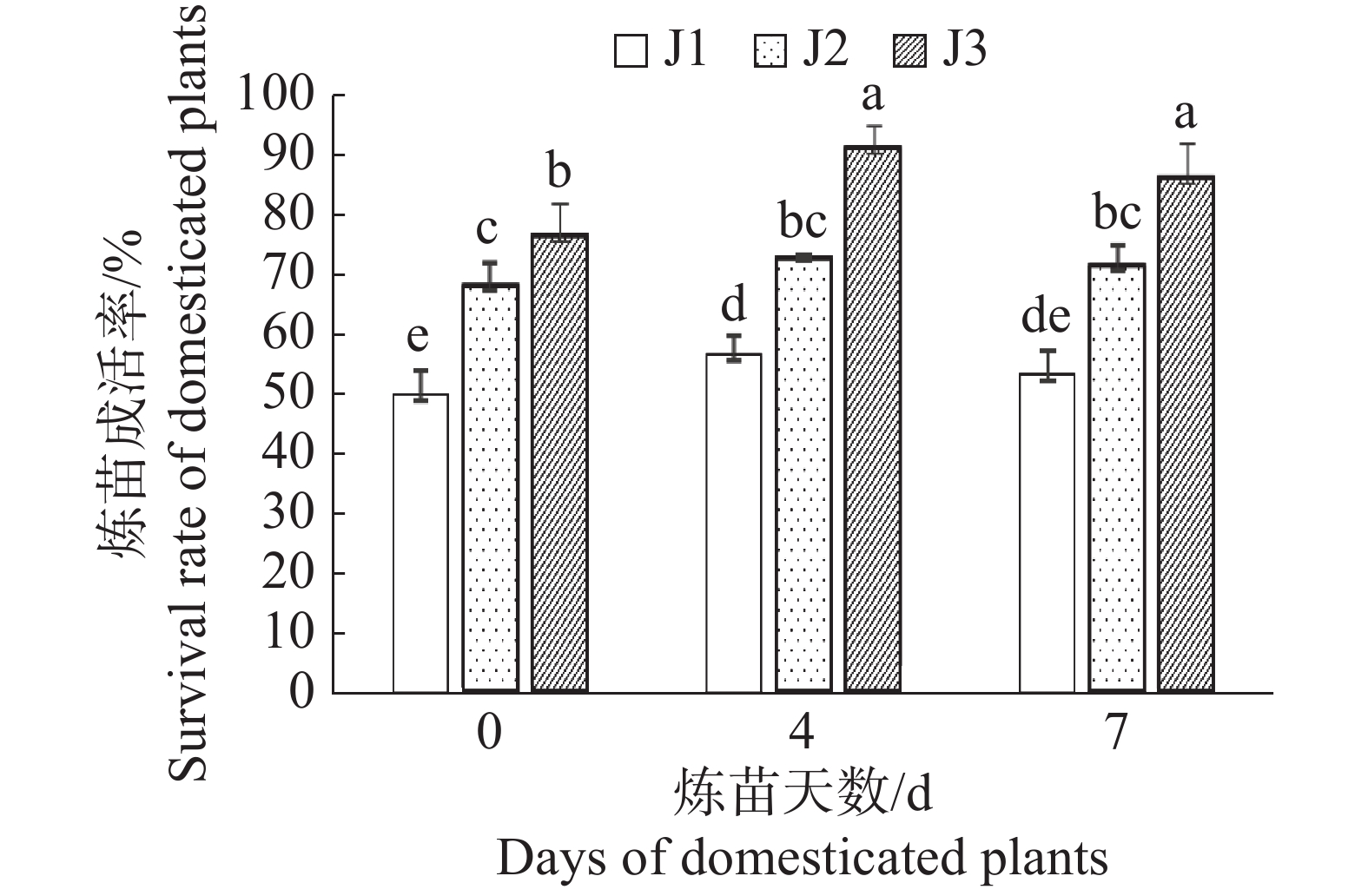
Gerbera hybrida haploids were propagated via tissue culture to observe the effects of culture medium, domestication and substrates on their rooting and transplanting success. The results showed that proliferation medium before rooting of tissue cultured plants of G. hybrida haploid had a significant effect on rooting culture. The optimum combination of rooting medium was an improved MS medium +KT 0.15 mg·L−1 for proliferation medium followed by 1/2MS +IBA 0.6 mg·L−1+ NAA 0.1 mg·L−1 for rooting medium. After 20 days of indoor culture the rooted tissue cultured plants were transferred to the shed for domestication for 4 days and then transferred onto the mixed substrate of humus: laterite: perlite with a volume ratio of 4∶1∶0.5 for further hardening off, based on which the tissue cultured plants were the highest in domestication and transplanting survival rate.
Gerbera hybrida haploids were propagated via tissue culture to observe the effects of culture medium, domestication and substrates on their rooting and transplanting success. The results showed that proliferation medium before rooting of tissue cultured plants of G. hybrida haploid had a significant effect on rooting culture. The optimum combination of rooting medium was an improved MS medium +KT 0.15 mg·L−1 for proliferation medium followed by 1/2MS +IBA 0.6 mg·L−1+ NAA 0.1 mg·L−1 for rooting medium. After 20 days of indoor culture the rooted tissue cultured plants were transferred to the shed for domestication for 4 days and then transferred onto the mixed substrate of humus: laterite: perlite with a volume ratio of 4∶1∶0.5 for further hardening off, based on which the tissue cultured plants were the highest in domestication and transplanting survival rate.
2020, 11(3): 347-352.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.013
Abstract:
Microalgae Nostoc sp., Anabaena sp., Lyngbya sp.and Chlorella sp. were cultured in the effluent from the natural rubber processing factories to observe their effect on the treatment of the effluent. The total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) removed from the effluent at different treatment stages was determined, and the cell density, pH value and conductivity of the effluent were measured after adding of nutrient solution into the effluent treated with the microalgae at the late log phase. The results show that Chlorella sp. was most adaptable in treatment of the effluent among the 4 species of microalgae. The higher the concentrations of the TN and TP and the COD in the effluent, the better the removal efficiency. Chlorella sp. could effectively remove TN, TP and COD from the effluent in the order of the original effluent> the anaerobically fermented effluent> the treated effluent, and its removal rates of TN, TP and COD from the effluent in the Rubber Processing Factory were 89.21%%, 70.00% and 49.33%, respectively. Adding of nutrient solution in the effluent cultured at the late log phase prolonged effectively the culture time of Chlorella sp in the effluent.
Microalgae Nostoc sp., Anabaena sp., Lyngbya sp.and Chlorella sp. were cultured in the effluent from the natural rubber processing factories to observe their effect on the treatment of the effluent. The total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP) and chemical oxygen demand (COD) removed from the effluent at different treatment stages was determined, and the cell density, pH value and conductivity of the effluent were measured after adding of nutrient solution into the effluent treated with the microalgae at the late log phase. The results show that Chlorella sp. was most adaptable in treatment of the effluent among the 4 species of microalgae. The higher the concentrations of the TN and TP and the COD in the effluent, the better the removal efficiency. Chlorella sp. could effectively remove TN, TP and COD from the effluent in the order of the original effluent> the anaerobically fermented effluent> the treated effluent, and its removal rates of TN, TP and COD from the effluent in the Rubber Processing Factory were 89.21%%, 70.00% and 49.33%, respectively. Adding of nutrient solution in the effluent cultured at the late log phase prolonged effectively the culture time of Chlorella sp in the effluent.
2020, 11(3): 353-360, 367.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.014
Abstract:
Building a complete sponge system in the city can effectively solve the problems of urban rainwater drainage and effective utilization of rainwater resources. Urban parks are an important part of a city under the concept of sponge city and play an indispensable role in the drainage and utilization of urban rainwater. However, the traditional urban parks are only focused on their landscape effect but not on the rainwater drainage and storage capacity inf their green space. A survey was made of urban parks in Haikou and the rainwater management in the urban parks, and the existing problems arising from the traditional urban parks were analyzed, based on which were put forward a rainwater management strategy for establishment of urban parks in a sponge way to provide reference for construction and promotion of sponge-type urban parks in the future.
Building a complete sponge system in the city can effectively solve the problems of urban rainwater drainage and effective utilization of rainwater resources. Urban parks are an important part of a city under the concept of sponge city and play an indispensable role in the drainage and utilization of urban rainwater. However, the traditional urban parks are only focused on their landscape effect but not on the rainwater drainage and storage capacity inf their green space. A survey was made of urban parks in Haikou and the rainwater management in the urban parks, and the existing problems arising from the traditional urban parks were analyzed, based on which were put forward a rainwater management strategy for establishment of urban parks in a sponge way to provide reference for construction and promotion of sponge-type urban parks in the future.
2020, 11(3): 361-367.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.015
Abstract:
Compared to traditional chemical and physical methods, the whole-cell biosensor has an irreplaceable advantage in the monitoring and evaluation of environmental toxicology. The Ciliata is the best in the whole-cell living biosensor because of its easy culture, large size for easy observation, eukaryotic and no cell wall. The monitoring performance of the Ciliata in heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and nanoparticle pollutants (NP) was described, and the metabolic mechanism of the Ciliata in exposure to these pollutants and the possibility of using the Ciliata organism as a standard whole-cell living biosensor chip to monitor early environmental pollution were discussed. In summary, the Ciliata Bio-toxicity Assessment System is an ideal early monitoring and evaluation system for environmental pollutants, but the research on the Ciliata is still at a relatively early stage, and a lot of research work needs to be done.
Compared to traditional chemical and physical methods, the whole-cell biosensor has an irreplaceable advantage in the monitoring and evaluation of environmental toxicology. The Ciliata is the best in the whole-cell living biosensor because of its easy culture, large size for easy observation, eukaryotic and no cell wall. The monitoring performance of the Ciliata in heavy metals, persistent organic pollutants (POPs) and nanoparticle pollutants (NP) was described, and the metabolic mechanism of the Ciliata in exposure to these pollutants and the possibility of using the Ciliata organism as a standard whole-cell living biosensor chip to monitor early environmental pollution were discussed. In summary, the Ciliata Bio-toxicity Assessment System is an ideal early monitoring and evaluation system for environmental pollutants, but the research on the Ciliata is still at a relatively early stage, and a lot of research work needs to be done.
2020, 11(3): 368-390.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.03.016
Abstract:
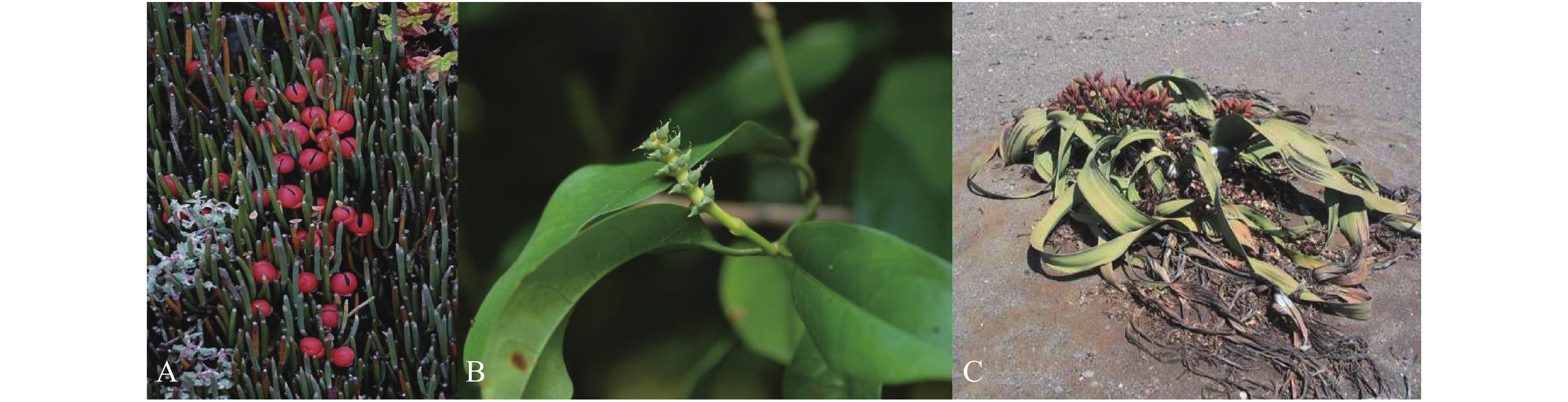
The correlation between Gnetales and Angiosperms was reviewed in classical taxonomy, chemotaxonomy, palaeobotany, and molecular biology, and the position of Gnetales in Angiosperm evolution was discussed based on the analysis of the two key chemical constituents isolated from the Gnetales and basal Angiosperms: quinoline alkaloids and stilbenes. We recognized the theory of Gnetales being the sister groups of Angiosperms, and suggested that Angiosperms originated from Gnetales
The correlation between Gnetales and Angiosperms was reviewed in classical taxonomy, chemotaxonomy, palaeobotany, and molecular biology, and the position of Gnetales in Angiosperm evolution was discussed based on the analysis of the two key chemical constituents isolated from the Gnetales and basal Angiosperms: quinoline alkaloids and stilbenes. We recognized the theory of Gnetales being the sister groups of Angiosperms, and suggested that Angiosperms originated from Gnetales


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 997KB
PDF 997KB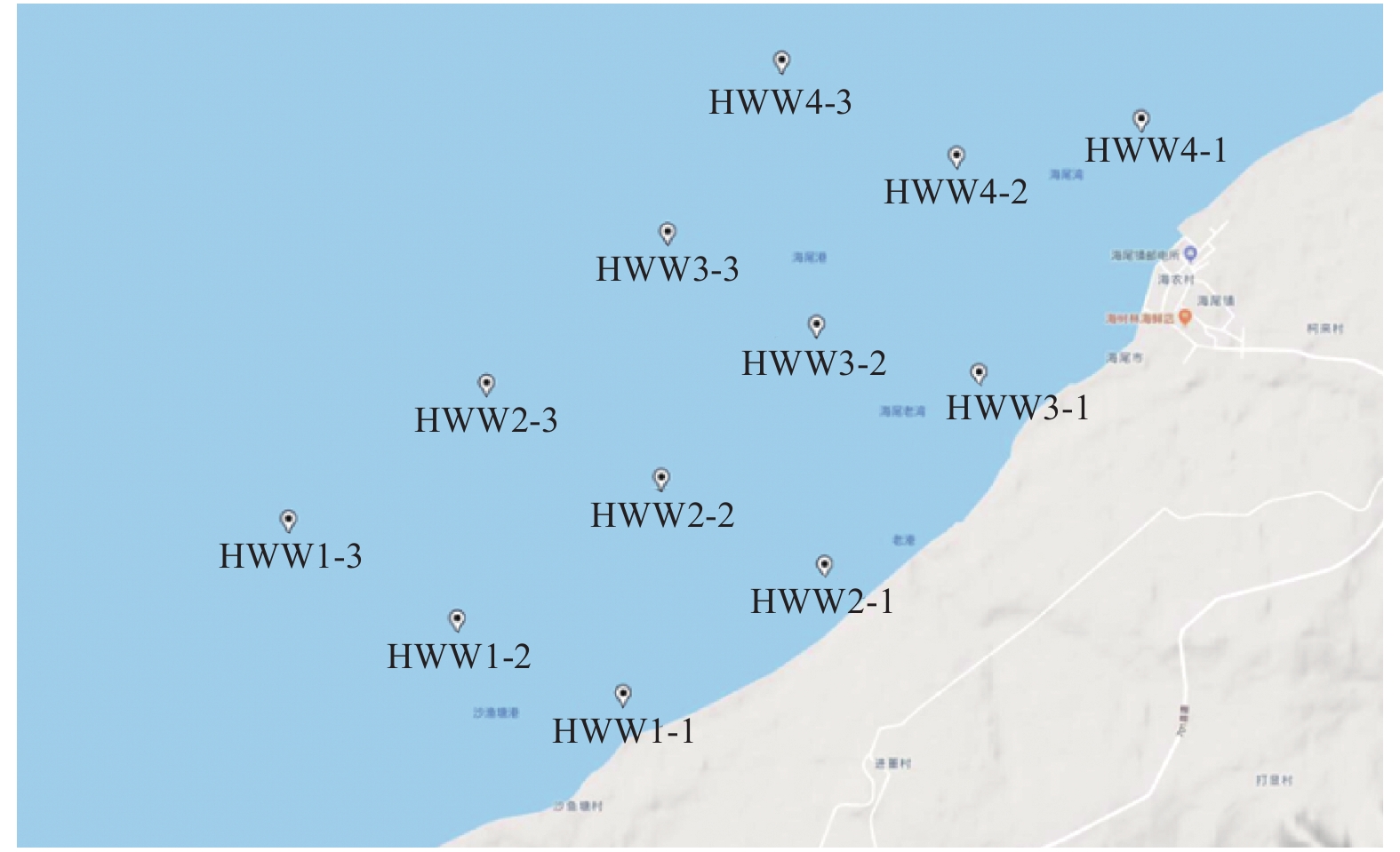










 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS