2024 Vol. 15, No. 5
2024, 15(5): 509-519.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230128
Abstract:
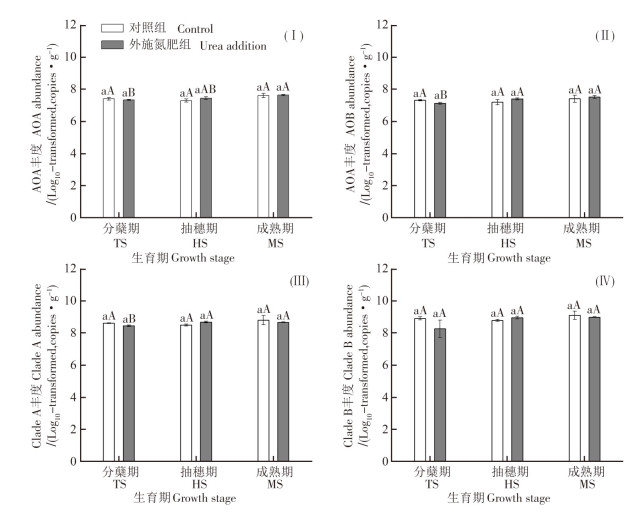
In order to reveal the differences in response and sensitivity of comamox Nitrospira and incomplete nitrifiers to nitrogen addition in acidic rice fields, a pot experiment was conducted to investigate the impact of urea fertilization, in conjunction with growth stage, on complete nitrifiers, and to compare their responsiveness to nitrogen(N) fertilization with that of incomplete nitrifiers in acidic paddy soils. The research results revealed that irrespective of fertilization conditions, comammox Nitrospira(Clade A: 3.24×108-7.24×108 copies·g-1, Clade B: 2.14×108-1.48×109 copies · g-1) rather than ammonia-oxidizing archaea(AOA: 2.00×107-4.37×107 copies·g-1) and nitriteoxidizing bacteria(AOB: 1.35×107-3.31×107 copies·g-1), were the dominant ammonia oxidizers across tillering,heading, and maturity stages. Neither urea fertilization(Clade A: P = 0.762, Clade B: P = 0.398) nor growth stage(Clade A: P = 0.264, Clade B: P = 0.237), nor their interaction(Clade A: P = 0.316, Clade B: P = 0.294),significantly influenced comammox Nitrospira clades A and B, as their populations remained consistent across the fertilizer treatments and seasons. It is plausible that the environmental factors governing comammox bacterial abundance in urea-fertilized and unfertilized soils may vary. In the absence of urea, the abundance of comammox Nitrospira clades A(R =-0.73, P = 0.027) and B(R =-0.75, P = 0.019) exhibited a negative correlation with soil N, suggesting that increased ammonia, ammonification, and organic N may not be conducive to comammox bacterial growth and activity in unfertilized soils. Conversely, in the presence of urea, comammox bacteria,especially clade A, were notably influenced by soil pH and redox potential(Eh). Notably, urea application had the potential to alter the interplay between complete and incomplete nitrifiers, as evidenced by the absence of a positive mode of population co-variation of clade B with AOA and AOB following urea application.
In order to reveal the differences in response and sensitivity of comamox Nitrospira and incomplete nitrifiers to nitrogen addition in acidic rice fields, a pot experiment was conducted to investigate the impact of urea fertilization, in conjunction with growth stage, on complete nitrifiers, and to compare their responsiveness to nitrogen(N) fertilization with that of incomplete nitrifiers in acidic paddy soils. The research results revealed that irrespective of fertilization conditions, comammox Nitrospira(Clade A: 3.24×108-7.24×108 copies·g-1, Clade B: 2.14×108-1.48×109 copies · g-1) rather than ammonia-oxidizing archaea(AOA: 2.00×107-4.37×107 copies·g-1) and nitriteoxidizing bacteria(AOB: 1.35×107-3.31×107 copies·g-1), were the dominant ammonia oxidizers across tillering,heading, and maturity stages. Neither urea fertilization(Clade A: P = 0.762, Clade B: P = 0.398) nor growth stage(Clade A: P = 0.264, Clade B: P = 0.237), nor their interaction(Clade A: P = 0.316, Clade B: P = 0.294),significantly influenced comammox Nitrospira clades A and B, as their populations remained consistent across the fertilizer treatments and seasons. It is plausible that the environmental factors governing comammox bacterial abundance in urea-fertilized and unfertilized soils may vary. In the absence of urea, the abundance of comammox Nitrospira clades A(R =-0.73, P = 0.027) and B(R =-0.75, P = 0.019) exhibited a negative correlation with soil N, suggesting that increased ammonia, ammonification, and organic N may not be conducive to comammox bacterial growth and activity in unfertilized soils. Conversely, in the presence of urea, comammox bacteria,especially clade A, were notably influenced by soil pH and redox potential(Eh). Notably, urea application had the potential to alter the interplay between complete and incomplete nitrifiers, as evidenced by the absence of a positive mode of population co-variation of clade B with AOA and AOB following urea application.
2024, 15(5): 520-530.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240046
Abstract:
Investigating the spatial distribution characteristics of phosphorus in farmland plow layer soil can help understand the accumulation status of soil phosphorus, providing a basis for the judicial application of phosphorus fertilizer in farmland. From the main farmlands in Hainan Island 2 386 soil samples were collected from the plow layer(0-20 cm) and their soil indexes such as total phosphorus content, available phosphorus content, organic matter content, etc., in the soil were determined. The spatial autocorrelation of the total phosphorus and available phosphorus in the soil was analyzed by using geostatistical methods, and ordinary kriging interpolation was used to predict the spatial distribution of total phosphorus and available phosphorus in the plow layer soil of the main farmlands in Hainan Island. The results indicate that the plow layer soil in the main farmlands of Hainan Island has relatively high and highly variable contents of total phosphorus and available phosphorus. The range of total phosphorus content in the soil is between 0.06 to 4.61 g·kg-1, with 40%of the soil samples exceeding the first level(> 1 g·kg-1), with a mean of 1.02 g·kg-1 and a coefficient of variation of 64%; the range of available phosphorus content in the soil is between 3.16 to 478.88 mg·kg-1, with 72% of the soil samples exceeding the first level(> 40 mg·kg-1), with a mean of 106.51 mg·kg-1 and a high coefficient of variation of 91%. The Nugget/Sill ratios of total phosphorus content and available phosphorus content are 0.918and 0.928, respectively, indicating weak spatial autocorrelation mainly influenced by random factors. The kriging interpolation prediction map shows that the plow layer soil has higher total phosphorus content in the soil, mainly between 0.8 to 4.61 g·kg-1 in the north and south of Hainan Island, and relatively lower total phosphorus content,mainly ranging from 0.4 to 0.8 g·kg-1 in the east and west. The overall available phosphorus content in the soil is relatively high, with the available phosphorus content in the north ranging from 3.16 to 478.88 mg·kg-1,exhibiting uneven distribution, with the highest available phosphorus content reaching around 400 mg·kg-1 in Haikou City and Chengmai County. In the south the available phosphorus content in the soil is concentrated in between 90 to 240 mg·kg-1, while in the east and west it is relatively lower, concentrated in between 20 to 90 mg·kg-1. Overall, the contents of total phosphorus and available phosphorus in the plow layer soil of the main farmlands in Hainan Island are at a relatively high level, highly influenced by fertilizer application. The water bodies surrounding the main farmlands face significant pollution risks, indicating the need to control the application of phosphorus fertilizers in agricultural production.
Investigating the spatial distribution characteristics of phosphorus in farmland plow layer soil can help understand the accumulation status of soil phosphorus, providing a basis for the judicial application of phosphorus fertilizer in farmland. From the main farmlands in Hainan Island 2 386 soil samples were collected from the plow layer(0-20 cm) and their soil indexes such as total phosphorus content, available phosphorus content, organic matter content, etc., in the soil were determined. The spatial autocorrelation of the total phosphorus and available phosphorus in the soil was analyzed by using geostatistical methods, and ordinary kriging interpolation was used to predict the spatial distribution of total phosphorus and available phosphorus in the plow layer soil of the main farmlands in Hainan Island. The results indicate that the plow layer soil in the main farmlands of Hainan Island has relatively high and highly variable contents of total phosphorus and available phosphorus. The range of total phosphorus content in the soil is between 0.06 to 4.61 g·kg-1, with 40%of the soil samples exceeding the first level(> 1 g·kg-1), with a mean of 1.02 g·kg-1 and a coefficient of variation of 64%; the range of available phosphorus content in the soil is between 3.16 to 478.88 mg·kg-1, with 72% of the soil samples exceeding the first level(> 40 mg·kg-1), with a mean of 106.51 mg·kg-1 and a high coefficient of variation of 91%. The Nugget/Sill ratios of total phosphorus content and available phosphorus content are 0.918and 0.928, respectively, indicating weak spatial autocorrelation mainly influenced by random factors. The kriging interpolation prediction map shows that the plow layer soil has higher total phosphorus content in the soil, mainly between 0.8 to 4.61 g·kg-1 in the north and south of Hainan Island, and relatively lower total phosphorus content,mainly ranging from 0.4 to 0.8 g·kg-1 in the east and west. The overall available phosphorus content in the soil is relatively high, with the available phosphorus content in the north ranging from 3.16 to 478.88 mg·kg-1,exhibiting uneven distribution, with the highest available phosphorus content reaching around 400 mg·kg-1 in Haikou City and Chengmai County. In the south the available phosphorus content in the soil is concentrated in between 90 to 240 mg·kg-1, while in the east and west it is relatively lower, concentrated in between 20 to 90 mg·kg-1. Overall, the contents of total phosphorus and available phosphorus in the plow layer soil of the main farmlands in Hainan Island are at a relatively high level, highly influenced by fertilizer application. The water bodies surrounding the main farmlands face significant pollution risks, indicating the need to control the application of phosphorus fertilizers in agricultural production.
2024, 15(5): 531-546.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240025
Abstract:
Evaluating and screening of salt-tolerant rice germplasm materials is of a great scientific and practical significance to conserve and utilize Shanlan upland rice in Hainan. Potting experiments were made and 40accessions of Shanlan upland rice, 3 accessions of common upland rice and 3 accessions of common paddy rice were selected for treatment under salt stress at the germination stage and the whole growth stage. They were treated with 0.6% NaCl solution at the germination stage and 4g kg-1 at the whole growth stage. The 25 growth indexes related to the salt tolerance of rice were determined, and their salt tolerance at the whole growth stage was analyzed by using correlation analysis, grey relational analysis and comprehensive evaluation to screen salt tolerance indexes. The results showed that single plant yield, flag leaf area, total number of grains per panicle,seed set rate and effective panicle number varied significantly between rice accessions(P < 0.05), and were highly sensitive to salt stress. Comprehensive evaluation of the salt tolerance of 46 accessions of rice at the whole growth stage showed that 46 accessions can be divided into 4 categories: 9 accessions with high salt tolerance that could complete the growth period under salt stress; 3 accessions with high salt tolerance that could enter the reproductive growth stage but cannot form yield; 16 accessions with general salt tolerance that died before entering the reproductive growth; 18 accessions with poor salt tolerance that died after 35 days of salt stress.Through principal component analysis and membership function analysis, the comprehensive measurement value(D value) of salt resistance was obtained, and the Shanlan upland rice ‘WMS02’ and the common upland rice ‘Huangyedao’ were selected as materials with high salt resistance. Correlation analysis and grey relational analysis showed the penultimate leaf area and plant height at the tillering stage were identified as effective indexes for the identification of early stage salt tolerance.
Evaluating and screening of salt-tolerant rice germplasm materials is of a great scientific and practical significance to conserve and utilize Shanlan upland rice in Hainan. Potting experiments were made and 40accessions of Shanlan upland rice, 3 accessions of common upland rice and 3 accessions of common paddy rice were selected for treatment under salt stress at the germination stage and the whole growth stage. They were treated with 0.6% NaCl solution at the germination stage and 4g kg-1 at the whole growth stage. The 25 growth indexes related to the salt tolerance of rice were determined, and their salt tolerance at the whole growth stage was analyzed by using correlation analysis, grey relational analysis and comprehensive evaluation to screen salt tolerance indexes. The results showed that single plant yield, flag leaf area, total number of grains per panicle,seed set rate and effective panicle number varied significantly between rice accessions(P < 0.05), and were highly sensitive to salt stress. Comprehensive evaluation of the salt tolerance of 46 accessions of rice at the whole growth stage showed that 46 accessions can be divided into 4 categories: 9 accessions with high salt tolerance that could complete the growth period under salt stress; 3 accessions with high salt tolerance that could enter the reproductive growth stage but cannot form yield; 16 accessions with general salt tolerance that died before entering the reproductive growth; 18 accessions with poor salt tolerance that died after 35 days of salt stress.Through principal component analysis and membership function analysis, the comprehensive measurement value(D value) of salt resistance was obtained, and the Shanlan upland rice ‘WMS02’ and the common upland rice ‘Huangyedao’ were selected as materials with high salt resistance. Correlation analysis and grey relational analysis showed the penultimate leaf area and plant height at the tillering stage were identified as effective indexes for the identification of early stage salt tolerance.
2024, 15(5): 547-557.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240055
Abstract:
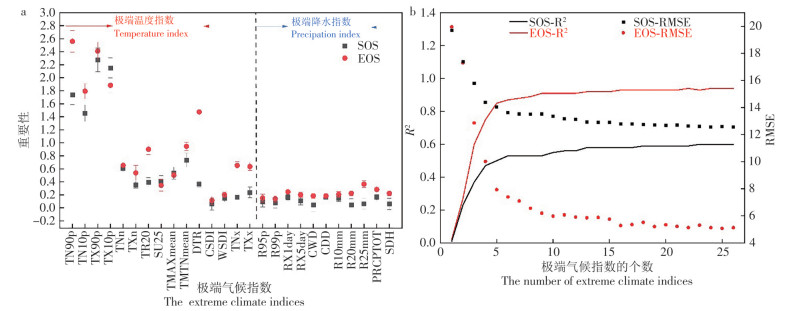
With the intensification of climate change, the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events have increased, and their impacts on ecosystem structure and function far exceeds those of gradual trend changes. As an important component of terrestrial ecosystems, the phenological response of tropical forests to climate change has always been a research hotspot. However, due to their high plant diversity and evergreen characteristics, scientific findings have not been consolidated. This study focuses on monoculture rubber plantations with distinct phenological characteristics as an entry point. Extreme weather events sensitive to phenological responses were selected by fitting multi-curves pixel-by-pixel to rubber plantations phenology and employing machine learning techniques to reveal the spatiotemporal distribution patterns of spring phenology(Start of growing Season, SOS), autumn phenology(End of growing Season, EOS), and extreme weather events during 2003—2018. The impacts of climate extreme indices on phenology were analyzed based on partial correlation analysis. The results show that the SOS of rubber plantations in Hainan Island advanced by an average of 0.73 d·a-1, while the EOS was delayed by 0.60 d·a-1. A few extreme cold events showed an increasing trend, while extremely hot events showed the opposite trend. The days of extreme daytime and night-time temperatures were the main factors affecting SOS and EOS; the number of days with low day-time temperature(TN10p) and the number of days with low night-time temperature(TX10p) were positively correlated with SOS, while the number of days with warm day-time temperature(TN90p) and the number of days with warm night-time temperature(TX90p) were negatively correlated with SOS; TN10p, TN90p, and TX90p were positively correlated with EOS, but TX10p was negatively correlated with EOS. The responses of SOS and EOS to extreme weather events with different intensities and frequencies exhibited obvious east-west differences in space. All these findings showed that it can enhance our understanding of the response of tropical forest structure and function to climate change when extreme weather factors are considered.
With the intensification of climate change, the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events have increased, and their impacts on ecosystem structure and function far exceeds those of gradual trend changes. As an important component of terrestrial ecosystems, the phenological response of tropical forests to climate change has always been a research hotspot. However, due to their high plant diversity and evergreen characteristics, scientific findings have not been consolidated. This study focuses on monoculture rubber plantations with distinct phenological characteristics as an entry point. Extreme weather events sensitive to phenological responses were selected by fitting multi-curves pixel-by-pixel to rubber plantations phenology and employing machine learning techniques to reveal the spatiotemporal distribution patterns of spring phenology(Start of growing Season, SOS), autumn phenology(End of growing Season, EOS), and extreme weather events during 2003—2018. The impacts of climate extreme indices on phenology were analyzed based on partial correlation analysis. The results show that the SOS of rubber plantations in Hainan Island advanced by an average of 0.73 d·a-1, while the EOS was delayed by 0.60 d·a-1. A few extreme cold events showed an increasing trend, while extremely hot events showed the opposite trend. The days of extreme daytime and night-time temperatures were the main factors affecting SOS and EOS; the number of days with low day-time temperature(TN10p) and the number of days with low night-time temperature(TX10p) were positively correlated with SOS, while the number of days with warm day-time temperature(TN90p) and the number of days with warm night-time temperature(TX90p) were negatively correlated with SOS; TN10p, TN90p, and TX90p were positively correlated with EOS, but TX10p was negatively correlated with EOS. The responses of SOS and EOS to extreme weather events with different intensities and frequencies exhibited obvious east-west differences in space. All these findings showed that it can enhance our understanding of the response of tropical forest structure and function to climate change when extreme weather factors are considered.
2024, 15(5): 558-566.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240036
Abstract:
In order to construct a reliable and stable mouse model of allergic asthma, 12 5-week-old female BALB/c mice were selected and randomly divided into a model group and a control group of 6 mice each. Each mouse in the model group was sensitized with an intraperitoneal injection of 1 mg-mL-1 feline and canine fusion allergen Fel d 1-Can f 1/aluminum hydroxide complexes, and injected with 1 mg-mL-1 feline and canine fusion allergen Fel d 1-Can f 1 via the trachea. The control group was given an equal volume of PBS. A number of indices were employed to ascertain the efficacy of the constructed allergic asthma model, including serum specific IgE levels, airway reactivity levels, allergen-induced stress allergic reactions, ear prick tests, the degree of inflammatory infiltration in lung tissues, the number of polymucous cuprocytes in lung tissues, and the degree of collagen fiber deposition. The results demonstrated that mice exposed to Fel d 1-Can f 1 exhibited a notable elevation in serum-specific IgE levels, a substantial increase in airway responsiveness, a significant decline in allergen-induced body temperature, and an expansion in the area of ear dye. Furthermore, the study revealed that the mice exhibited leakage and a significant enhancement in the net intensity of leakage, as well as a significant increase in inflammatory infiltration of the lungs, an increase in the number of multilocular cup cells, and an aggravation in the degree of collagen fiber deposition, when compared to the control group. In conclusion, a mouse model of allergic asthma was successfully constructed, which will provide model conditions for the development and evaluation of allergy-control vaccines for cats and dogs.
In order to construct a reliable and stable mouse model of allergic asthma, 12 5-week-old female BALB/c mice were selected and randomly divided into a model group and a control group of 6 mice each. Each mouse in the model group was sensitized with an intraperitoneal injection of 1 mg-mL-1 feline and canine fusion allergen Fel d 1-Can f 1/aluminum hydroxide complexes, and injected with 1 mg-mL-1 feline and canine fusion allergen Fel d 1-Can f 1 via the trachea. The control group was given an equal volume of PBS. A number of indices were employed to ascertain the efficacy of the constructed allergic asthma model, including serum specific IgE levels, airway reactivity levels, allergen-induced stress allergic reactions, ear prick tests, the degree of inflammatory infiltration in lung tissues, the number of polymucous cuprocytes in lung tissues, and the degree of collagen fiber deposition. The results demonstrated that mice exposed to Fel d 1-Can f 1 exhibited a notable elevation in serum-specific IgE levels, a substantial increase in airway responsiveness, a significant decline in allergen-induced body temperature, and an expansion in the area of ear dye. Furthermore, the study revealed that the mice exhibited leakage and a significant enhancement in the net intensity of leakage, as well as a significant increase in inflammatory infiltration of the lungs, an increase in the number of multilocular cup cells, and an aggravation in the degree of collagen fiber deposition, when compared to the control group. In conclusion, a mouse model of allergic asthma was successfully constructed, which will provide model conditions for the development and evaluation of allergy-control vaccines for cats and dogs.
2024, 15(5): 567-576.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240040
Abstract:
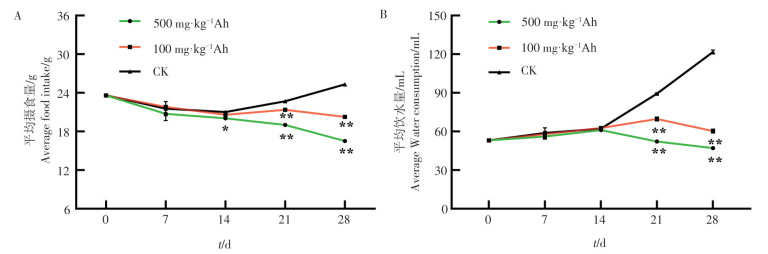
An attempt was made to understand the effects of arecoline on gut microbiota composition and neurotransmitters contents in SD rats based on the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Three groups of SD rats were administered with arecoline hydrobromide(Ah) solution dissolved in 0.9% Na Cl aqueous solution by gavage for 28 days, and the ratios of weight of Ah/rat were 500, 100 and 0(control group) mg·kg-1 after administration. Then the composition of intestinal microbes in colon, the contents of short-chain fatty acids in feces and the contents of neurotransmitters in the cerebral cortex and serum were determined and analyzed. The results showed that the Ah,when administered to SD rats, increased relative abundance of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, and the contents of acetic acid and propionic acid in the gut, and the contents of excitatory neurotransmitters like DA and 5-HT in the cerebral cortex, and reduced the content of GABA which is inhibitory neurotransmitters. These results indicate that arecolineAh regulates the physiological metabolism and behavior of SD rats through microbiota-gut-brain axis,leading to symptoms such as hyperactivity, loss of appetite, and weight loss in SD rats.
An attempt was made to understand the effects of arecoline on gut microbiota composition and neurotransmitters contents in SD rats based on the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Three groups of SD rats were administered with arecoline hydrobromide(Ah) solution dissolved in 0.9% Na Cl aqueous solution by gavage for 28 days, and the ratios of weight of Ah/rat were 500, 100 and 0(control group) mg·kg-1 after administration. Then the composition of intestinal microbes in colon, the contents of short-chain fatty acids in feces and the contents of neurotransmitters in the cerebral cortex and serum were determined and analyzed. The results showed that the Ah,when administered to SD rats, increased relative abundance of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, and the contents of acetic acid and propionic acid in the gut, and the contents of excitatory neurotransmitters like DA and 5-HT in the cerebral cortex, and reduced the content of GABA which is inhibitory neurotransmitters. These results indicate that arecolineAh regulates the physiological metabolism and behavior of SD rats through microbiota-gut-brain axis,leading to symptoms such as hyperactivity, loss of appetite, and weight loss in SD rats.
2024, 15(5): 577-585.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240038
Abstract:
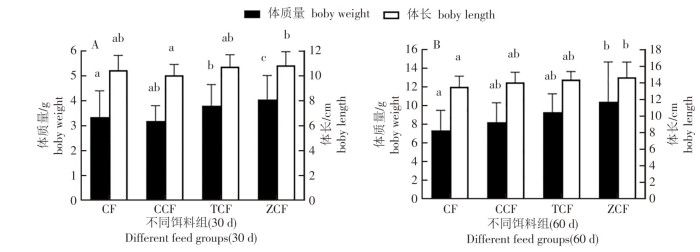
An attempt was made to analyze the effects of biological feeds on the cultivation of Mastacembelus armatus. Bloodworms(Chironomidae), yellow mealworms(Tenebrio molitor), and superworms(Zophobas atratus)were added to the compound feed(CF) to feed Mastacembelus armatus and the fish growth and its contents of animo acids and fatty acids in muscle were observed and determined. The results showed that after 30 days of feeding, the fish body mass was significantly higher in the CF + superworms group than in the other three groups(P < 0.05), with the lowest body mass observed in the control group without supplementation of any worms. After 60 days of feeding, the CF+ superworms group still had a significantly higher fish body mass compared to the other three groups(P < 0.05). Amino acid testing showed the total amino acids in the fish muscle were significantly higher in the CF+ yellow mealworms group than in the other three groups(P < 0.05). The CF+superworms group was significantly higher in flavor amino acids content than the other three groups(P < 0.05).There were no significant differences in EPA and DHA levels among all the groups, but the contents of saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids in the fish were all significantly higher in the CF+ superworms than in the other three groups. The experimental results indicate that the feed for M. armatus added with super worms produced the best results in terms of weight gain, condition factor, and flavor amino acid content in the fish.
An attempt was made to analyze the effects of biological feeds on the cultivation of Mastacembelus armatus. Bloodworms(Chironomidae), yellow mealworms(Tenebrio molitor), and superworms(Zophobas atratus)were added to the compound feed(CF) to feed Mastacembelus armatus and the fish growth and its contents of animo acids and fatty acids in muscle were observed and determined. The results showed that after 30 days of feeding, the fish body mass was significantly higher in the CF + superworms group than in the other three groups(P < 0.05), with the lowest body mass observed in the control group without supplementation of any worms. After 60 days of feeding, the CF+ superworms group still had a significantly higher fish body mass compared to the other three groups(P < 0.05). Amino acid testing showed the total amino acids in the fish muscle were significantly higher in the CF+ yellow mealworms group than in the other three groups(P < 0.05). The CF+superworms group was significantly higher in flavor amino acids content than the other three groups(P < 0.05).There were no significant differences in EPA and DHA levels among all the groups, but the contents of saturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, and polyunsaturated fatty acids in the fish were all significantly higher in the CF+ superworms than in the other three groups. The experimental results indicate that the feed for M. armatus added with super worms produced the best results in terms of weight gain, condition factor, and flavor amino acid content in the fish.
2024, 15(5): 586-598.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230109
Abstract:
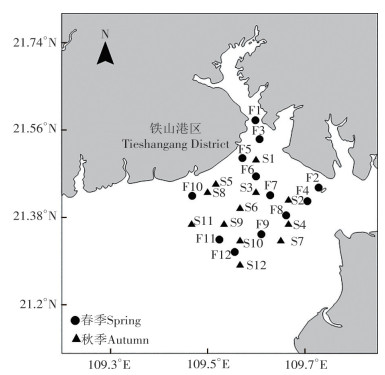
In March 2021 and September 2021, a survey of macrobenthos was carried out in Tieshangang seawaters of Beihai city. Samples from 24 stations were collected in the seawaters, and used for species identification, and the density, biomass and Bray-curtis similarity coefficient of macrobenthos species and sediment quality were analyzed. The abundance/biomass curve(ABC curve) of macrobenthos were plotted and the disturbance of macrobenthos was analyzed. The results showed that a total of 42 species of macrobenthos were collected, including 19 of annelidas, 11 of arthropods, 6 of mollusks, 2 of echinoderms and chordates, and 1 of neoglyphs and cnidarians each. The average density and average biomass of macrobenthic animals were 141 ind·m-2 and 96.95 g·m-2. The dominant species were Ruditapes philippinarum and Xenophthalmus pinnotheroides in spring and Branchiostoma belcheri in autumn. The average value of Shannon-Wiener index(H')was 1.73 in spring and 1.25 in autumn. The standard index of each evaluation factor of sediment was less than 1.The ABC analysis showed that all the stations were not disturbed except for F06 station, which was moderately disturbed in spring. All stations were undisturbed in autumn. In general, the macrobenthos community in the survey seawaters was stable. The cluster analysis and MDS analysis showed that the community similarity of each station was low in spring and in autumn.
In March 2021 and September 2021, a survey of macrobenthos was carried out in Tieshangang seawaters of Beihai city. Samples from 24 stations were collected in the seawaters, and used for species identification, and the density, biomass and Bray-curtis similarity coefficient of macrobenthos species and sediment quality were analyzed. The abundance/biomass curve(ABC curve) of macrobenthos were plotted and the disturbance of macrobenthos was analyzed. The results showed that a total of 42 species of macrobenthos were collected, including 19 of annelidas, 11 of arthropods, 6 of mollusks, 2 of echinoderms and chordates, and 1 of neoglyphs and cnidarians each. The average density and average biomass of macrobenthic animals were 141 ind·m-2 and 96.95 g·m-2. The dominant species were Ruditapes philippinarum and Xenophthalmus pinnotheroides in spring and Branchiostoma belcheri in autumn. The average value of Shannon-Wiener index(H')was 1.73 in spring and 1.25 in autumn. The standard index of each evaluation factor of sediment was less than 1.The ABC analysis showed that all the stations were not disturbed except for F06 station, which was moderately disturbed in spring. All stations were undisturbed in autumn. In general, the macrobenthos community in the survey seawaters was stable. The cluster analysis and MDS analysis showed that the community similarity of each station was low in spring and in autumn.
2024, 15(5): 599-607.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240003
Abstract:
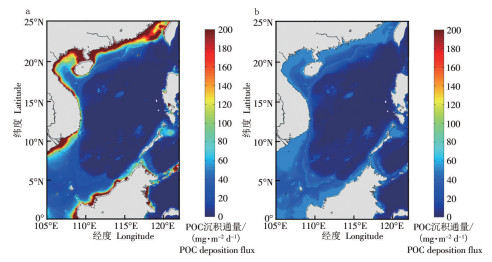
This study is based on the monthly particulate organic carbon(POC) flux data of the euphotic layer and ETOPO5 water depth data inverted from MODIS(Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, MODIS)from 2009 to 2018 were used for POC vertical migration formula inversion and empirical threshold linear fitting to present the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of POC sedimentation flux in the South China Sea from a macro perspective. MATLAB is used for data preprocessing such as synthesis analysis, error analysis and quality control of data, and the Martin curve is compared to carry out correlation verification analysis in non-shore areas(water depth greater than 100 m), and empirical thresholds and linear fitting are used to correct offshore areas(water depth less than 100 m). The results showed that there are obvious seasonal changes in POC deposition flux in the study area. The seasonal average values of POC deposition flux are 13.03 mg C·m-2·d-1 in spring and 14.25 mg C·m-2·d-1 in summer, 15.15 mg C·m-2·d-1 in autumn, and 17.99 mg C·m-2·d-1 in winter, with higher values in winter and autumn than in spring and summer. The overall distribution trend is that the POC deposition flux is higher in the insider than the outside of the bay, higher in the near shore than in the ocean basin, and higher in the shallow sea than in the deep sea. When the depth is less than or equal to 50 m, greater than 50 m,less than or equal to 100 m, and greater than 100 m, the average POC deposition flux is 46.39, 14.28, and 8.04 mg C·m-2·d-1, respectively. The total POC deposition flux in the study area throughout the year is approximately 19.04(15.72-22.36) TgC·a-1. These results are of great significance for understanding the carbon storage potential of the South China Sea, and at the same time provide a certain reference for research on blue carbon economic value accounting.
This study is based on the monthly particulate organic carbon(POC) flux data of the euphotic layer and ETOPO5 water depth data inverted from MODIS(Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer, MODIS)from 2009 to 2018 were used for POC vertical migration formula inversion and empirical threshold linear fitting to present the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of POC sedimentation flux in the South China Sea from a macro perspective. MATLAB is used for data preprocessing such as synthesis analysis, error analysis and quality control of data, and the Martin curve is compared to carry out correlation verification analysis in non-shore areas(water depth greater than 100 m), and empirical thresholds and linear fitting are used to correct offshore areas(water depth less than 100 m). The results showed that there are obvious seasonal changes in POC deposition flux in the study area. The seasonal average values of POC deposition flux are 13.03 mg C·m-2·d-1 in spring and 14.25 mg C·m-2·d-1 in summer, 15.15 mg C·m-2·d-1 in autumn, and 17.99 mg C·m-2·d-1 in winter, with higher values in winter and autumn than in spring and summer. The overall distribution trend is that the POC deposition flux is higher in the insider than the outside of the bay, higher in the near shore than in the ocean basin, and higher in the shallow sea than in the deep sea. When the depth is less than or equal to 50 m, greater than 50 m,less than or equal to 100 m, and greater than 100 m, the average POC deposition flux is 46.39, 14.28, and 8.04 mg C·m-2·d-1, respectively. The total POC deposition flux in the study area throughout the year is approximately 19.04(15.72-22.36) TgC·a-1. These results are of great significance for understanding the carbon storage potential of the South China Sea, and at the same time provide a certain reference for research on blue carbon economic value accounting.
2024, 15(5): 608-614.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230121
Abstract:
Sugarcane ring spot is a common disease in sugarcane, which is more common in Guangdong and Guangxi, China. One fungal strain, YLES 1, was isolated from sugarcane diseased leaves in the regions of Guangxi province. The pathogenicity of this strain was determined according to Koch’s postulates, confirming that it is a pathogen causing sugarcane ring spot disease. This fungus has similar morphological characteristics to Epicoccum. Sequence analyses based on concatenated data sets of the internal transcribed spacer(ITS) region of the ribosomal DNA(rDNA), large subunit rDNA(LSU) and β-tubulin(Tu) of the isolate showed that the strain YLES 1 was E. sorginum. The results indicated that E. sorginum was a pathogen of sugarcane ring spot disease.The biological characteristic analysis showed that the optimal temperature for the growth of the strain YLES 1was 28 ℃, that the optimal pH for mycelial growth and spore production was 7-9, that the optimal carbon source for growth and spore production was sucrose, and that the optimal nitrogen source was yeast extract. Moreover, dark conditions were conducive to the growth of YLES 1.
Sugarcane ring spot is a common disease in sugarcane, which is more common in Guangdong and Guangxi, China. One fungal strain, YLES 1, was isolated from sugarcane diseased leaves in the regions of Guangxi province. The pathogenicity of this strain was determined according to Koch’s postulates, confirming that it is a pathogen causing sugarcane ring spot disease. This fungus has similar morphological characteristics to Epicoccum. Sequence analyses based on concatenated data sets of the internal transcribed spacer(ITS) region of the ribosomal DNA(rDNA), large subunit rDNA(LSU) and β-tubulin(Tu) of the isolate showed that the strain YLES 1 was E. sorginum. The results indicated that E. sorginum was a pathogen of sugarcane ring spot disease.The biological characteristic analysis showed that the optimal temperature for the growth of the strain YLES 1was 28 ℃, that the optimal pH for mycelial growth and spore production was 7-9, that the optimal carbon source for growth and spore production was sucrose, and that the optimal nitrogen source was yeast extract. Moreover, dark conditions were conducive to the growth of YLES 1.
2024, 15(5): 615-622.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240029
Abstract:
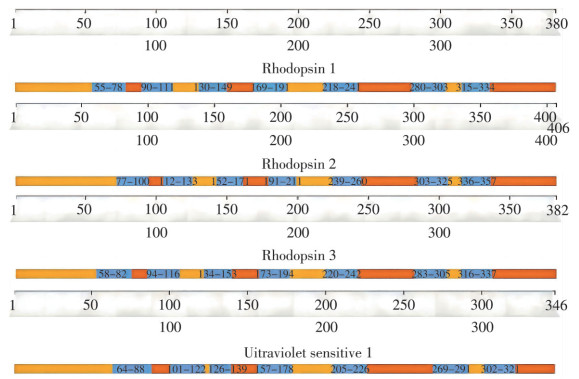
Megalurothrips usitatus is an important thrips pest of legume crops, with obvious phototaxis(color),and the light environment can affect its behavior and physiology. Four visual genes were cloned and their sequence data were uploaded to NCBI for searching. Moreover, the expression changes of the visual genes at different ages and genders were detected by real-time PCR. The results indicate that all four visual genes belong to the G protein coupled receptor family members. There were significant differences in expression levels of four visual genes among different age groups of M. usitatus(P < 0.05), and their expression levels fluctuated in different age groups. There is a significant difference in the expression level of visual genes between female and male adults(P < 0.05), and the expression level of visual genes in males is higher than that in females at all ages.This study clarified the molecular characteristics of the visual genes of M. usitatus and revealed the patterns of changes during their development, which has important guiding significance for precision control of thrips in the field using methods such as blue sticky insect plates or changing the light environment.
Megalurothrips usitatus is an important thrips pest of legume crops, with obvious phototaxis(color),and the light environment can affect its behavior and physiology. Four visual genes were cloned and their sequence data were uploaded to NCBI for searching. Moreover, the expression changes of the visual genes at different ages and genders were detected by real-time PCR. The results indicate that all four visual genes belong to the G protein coupled receptor family members. There were significant differences in expression levels of four visual genes among different age groups of M. usitatus(P < 0.05), and their expression levels fluctuated in different age groups. There is a significant difference in the expression level of visual genes between female and male adults(P < 0.05), and the expression level of visual genes in males is higher than that in females at all ages.This study clarified the molecular characteristics of the visual genes of M. usitatus and revealed the patterns of changes during their development, which has important guiding significance for precision control of thrips in the field using methods such as blue sticky insect plates or changing the light environment.
2024, 15(5): 623-631.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230140
Abstract:
Neonicotinoids that act on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors(nAChRs) are common tools for crop pest control, but they have serious negative effects on pollinators such as Apis mellifera. In this study, the nAChR α1 subunit gene was cloned from A. mellifera and systematically analyzed. The interaction mechanism between the nAChR α1 subtype and neonicotinoids(imidacloprid, clothianidin, and dinotefuran) was investigated by using the two-electrode voltage clamp technique. Sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis showed that the nAChR α1 subunit of A. mellifera had typical domain characteristics in the nAChR subunit family genes, and was most distantly related to the α1 subunit of Hemiptera insects and most closely related to the α1 subunit of bees from Hymenoptera. The combination of A. mellifera nAChR α1 subunit and Rattus norvegicus nAChR β2 subunit was co-expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Electrophysiological results showed that imidacloprid had the highest agonistic efficiency and lowest agonistic affinity, that clothianidin had the lowest agonistic efficiency and that dinotefuran had the highest agonistic affinity for Amα1/rβ2 nAChR, indicating that the α1 subunit of A. mellifera nAChRs is one of the targets of neonicotinoids and the sensitivity of Amα1/rβ2 nAChR to different neonicotinoids is different. All these results have important theoretical significance for the development of novel highly selective insecticides for target insects.
Neonicotinoids that act on insect nicotinic acetylcholine receptors(nAChRs) are common tools for crop pest control, but they have serious negative effects on pollinators such as Apis mellifera. In this study, the nAChR α1 subunit gene was cloned from A. mellifera and systematically analyzed. The interaction mechanism between the nAChR α1 subtype and neonicotinoids(imidacloprid, clothianidin, and dinotefuran) was investigated by using the two-electrode voltage clamp technique. Sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree analysis showed that the nAChR α1 subunit of A. mellifera had typical domain characteristics in the nAChR subunit family genes, and was most distantly related to the α1 subunit of Hemiptera insects and most closely related to the α1 subunit of bees from Hymenoptera. The combination of A. mellifera nAChR α1 subunit and Rattus norvegicus nAChR β2 subunit was co-expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Electrophysiological results showed that imidacloprid had the highest agonistic efficiency and lowest agonistic affinity, that clothianidin had the lowest agonistic efficiency and that dinotefuran had the highest agonistic affinity for Amα1/rβ2 nAChR, indicating that the α1 subunit of A. mellifera nAChRs is one of the targets of neonicotinoids and the sensitivity of Amα1/rβ2 nAChR to different neonicotinoids is different. All these results have important theoretical significance for the development of novel highly selective insecticides for target insects.
2024, 15(5): 632-638.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230138
Abstract:
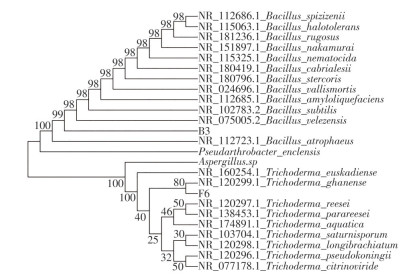
A strain of Trichoderma and a strain of Bacillus were screened from the rhizosphere soil of dragon fruit(Hylocereus undulates Britt.&Rose) using nitrogen fixation, phosphorus solubilization, potassium solubilization,and IAA production media. The growth promoting effect of their fermentation broth on dragon fruit was determined through pot experiments. The results showed that strains F6(Trichoderma ghanense) and B3(Bacillus velezensis) were screened from the rhizosphere soil of dragon fruit, which had the ability to dissolve phosphorus and potassium, fix nitrogen, and produce IAA. Among them, F6 had the highest ability to fix nitrogen and produce IAA, while B3 had the highest ability to dissolve phosphorus and potassium. Inoculation with microbial agents significantly improved the agronomic traits of dragon fruit. The combined microbial agents(B3+F6) had the most significant effect, increasing the fresh weight by 33.09% and the dry weight by 23.11%. Inoculation with microbial agents can improve soil fertility, significantly increase the contents of available phosphorus, available potassium, and organic matter in the soil. Compared with CK treatment, inoculation with a single strain B3 or F6increased the available phosphorus content by 14.49% and 9.9%, the available potassium content by 10.4% and 16.47%, and the alkaline nitrogen content by 25.85% and 14.35%, respectively, whereas the inoculation of the mixed strains B3+F6 increased the contents of available phosphorus, available potassium, and organic matter by 37.02%, 12.64%, and 16.77%, respectively. Correlation analysis between soil physicochemical properties and growth promoting indicators of dragon fruit shows that under the inoculation with the combined microbial agents the content of soil available potassium is significantly positively correlated with the fresh weight and dry weight of dragon fruit above ground, as well as the accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in dragon fruit. It can hence be concluded that inoculation with the combined microbial agents(B3+F6) has a significant improvement effect on the fresh and dry weight of the above ground parts of dragon fruit, as well as the root system of dragon fruit. The combined microbial agents have a synergistic effect on the accumulation of nutritional elements, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, in dragon fruit, and also has the effect of improving soil fertility.
A strain of Trichoderma and a strain of Bacillus were screened from the rhizosphere soil of dragon fruit(Hylocereus undulates Britt.&Rose) using nitrogen fixation, phosphorus solubilization, potassium solubilization,and IAA production media. The growth promoting effect of their fermentation broth on dragon fruit was determined through pot experiments. The results showed that strains F6(Trichoderma ghanense) and B3(Bacillus velezensis) were screened from the rhizosphere soil of dragon fruit, which had the ability to dissolve phosphorus and potassium, fix nitrogen, and produce IAA. Among them, F6 had the highest ability to fix nitrogen and produce IAA, while B3 had the highest ability to dissolve phosphorus and potassium. Inoculation with microbial agents significantly improved the agronomic traits of dragon fruit. The combined microbial agents(B3+F6) had the most significant effect, increasing the fresh weight by 33.09% and the dry weight by 23.11%. Inoculation with microbial agents can improve soil fertility, significantly increase the contents of available phosphorus, available potassium, and organic matter in the soil. Compared with CK treatment, inoculation with a single strain B3 or F6increased the available phosphorus content by 14.49% and 9.9%, the available potassium content by 10.4% and 16.47%, and the alkaline nitrogen content by 25.85% and 14.35%, respectively, whereas the inoculation of the mixed strains B3+F6 increased the contents of available phosphorus, available potassium, and organic matter by 37.02%, 12.64%, and 16.77%, respectively. Correlation analysis between soil physicochemical properties and growth promoting indicators of dragon fruit shows that under the inoculation with the combined microbial agents the content of soil available potassium is significantly positively correlated with the fresh weight and dry weight of dragon fruit above ground, as well as the accumulation of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in dragon fruit. It can hence be concluded that inoculation with the combined microbial agents(B3+F6) has a significant improvement effect on the fresh and dry weight of the above ground parts of dragon fruit, as well as the root system of dragon fruit. The combined microbial agents have a synergistic effect on the accumulation of nutritional elements, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, in dragon fruit, and also has the effect of improving soil fertility.
2024, 15(5): 639-649.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230083
Abstract:
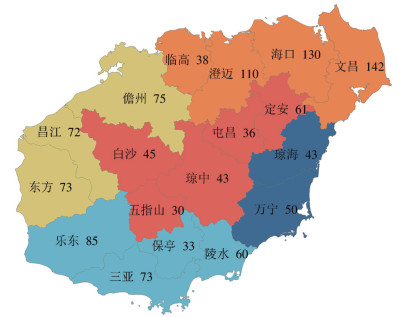
Based on the nutrient requirements of major crops in Hainan Island, combined with the current planting structure characteristics and the characteristics of phosphorus fertilizer application in crop systems, the phosphorus fertilizer demand and reducing potential in this region were evaluated, and the structural characteristics of phosphorus fertilizer products applied in farmland and existing problems were identified.Through field surveys, information on the phosphorus fertilizer application intensity and phosphorus fertilizer product structure of major crops such as grains, vegetables, and fruits in Hainan Island was collected to clarify the phosphorus balance status in the major crops in Hainan Island. At the same time, the recommended phosphorus fertilizer rates for the major crops were evaluated, and the phosphorus fertilizer reducing targets for the major crops were determined by analyzing the total reasonable demand for phosphorus fertilizer in Hainan Island. The results show that the average phosphorus fertilizer application intensity for farmland crops in Hainan Island was 95.68 kg·hm-2(as P), which was 62.17% higher than the national average. Among them, the average input of chemical phosphorus fertilizer were 87.59 kg·hm-2, and the average input of organic phosphorus fertilizer was 8.09 kg·hm-2, with an organic substitution ratio of 8.46%. The overall phosphorus surplus of crops in Hainan Island was relatively high, with 30.00 kg·hm-2 for grain crops, 94.64 kg·hm-2 for vegetable crops, and 155.00 kg·hm-2 for fruit crops. As of 2021, the annual average phosphorus fertilizer consumption in Hainan Island was 242,800 tons(as P2O5), and the overall P fertilizer reducing potential was 59.90%. High-phosphorus balanced compound fertilizers are the main phosphorus fertilizer products used, accounting for 78.46% of the total phosphorus input.Currently, Hainan Island has a serious problem of excessive application of phosphorus fertilizer, with high phosphorus surplus and environmental risks, while the organic substitution ratio was low, indicating significant potential for reducing phosphorus fertilizer usage. These results provide important reference for the scientific application of phosphorus fertilizer in Hainan Island.
Based on the nutrient requirements of major crops in Hainan Island, combined with the current planting structure characteristics and the characteristics of phosphorus fertilizer application in crop systems, the phosphorus fertilizer demand and reducing potential in this region were evaluated, and the structural characteristics of phosphorus fertilizer products applied in farmland and existing problems were identified.Through field surveys, information on the phosphorus fertilizer application intensity and phosphorus fertilizer product structure of major crops such as grains, vegetables, and fruits in Hainan Island was collected to clarify the phosphorus balance status in the major crops in Hainan Island. At the same time, the recommended phosphorus fertilizer rates for the major crops were evaluated, and the phosphorus fertilizer reducing targets for the major crops were determined by analyzing the total reasonable demand for phosphorus fertilizer in Hainan Island. The results show that the average phosphorus fertilizer application intensity for farmland crops in Hainan Island was 95.68 kg·hm-2(as P), which was 62.17% higher than the national average. Among them, the average input of chemical phosphorus fertilizer were 87.59 kg·hm-2, and the average input of organic phosphorus fertilizer was 8.09 kg·hm-2, with an organic substitution ratio of 8.46%. The overall phosphorus surplus of crops in Hainan Island was relatively high, with 30.00 kg·hm-2 for grain crops, 94.64 kg·hm-2 for vegetable crops, and 155.00 kg·hm-2 for fruit crops. As of 2021, the annual average phosphorus fertilizer consumption in Hainan Island was 242,800 tons(as P2O5), and the overall P fertilizer reducing potential was 59.90%. High-phosphorus balanced compound fertilizers are the main phosphorus fertilizer products used, accounting for 78.46% of the total phosphorus input.Currently, Hainan Island has a serious problem of excessive application of phosphorus fertilizer, with high phosphorus surplus and environmental risks, while the organic substitution ratio was low, indicating significant potential for reducing phosphorus fertilizer usage. These results provide important reference for the scientific application of phosphorus fertilizer in Hainan Island.
2024, 15(5): 650-654.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230130
Abstract:
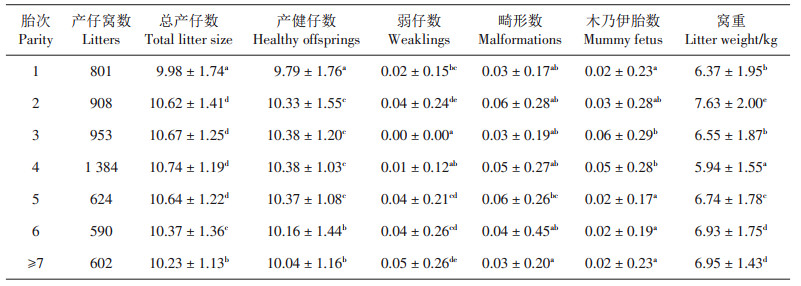
In order to determine the litter performance of Duroc×Luchuan(Dulu) binary sows and the coat color of their crossbred offspring with Chuanxiang black pigs, a total of 5 862 litters wtih effective breeding was recorded at three Chuanxiang×Duroc×Luchuan(Chuandulu) ternary commercial pig production farms in Hainan Province from January 2022 to June 2023. The litter performance of sows was compared according to parity and pig farm, and the coat color traits of ternary commercial pigs were counted. The results showed that there were significant differences in total litter size, healthy litter size and litter weight among different farms(P <0.05). Comparison of litter sizes revealed no significant difference in total litter size and number of healthy piglets born in litters 2, 3, 4 and 5(P > 0.05). The indicators of the first parity were significantly lower than those of other parities(P < 0.05), and the indicators of the 6th parity and above were also significantly different from those of other parities(P < 0.05). The 4th parity was significantly lower in litter weight than the other parities, while the 2nd parity was significantly higher in litter weight than the other parities(P < 0.05). The piglets born in the experimental group were mainly black in coat color, with a few being red, and very few being white in coat color,and the average proportion of piglets with black coat color reached 98.79%. In conclusion, there were significant differences in the litter performance of sows among different farms, sows with 2-5 parities were highly fertile, and piglets at birth were significantly different in litter weights; the vast majority of Chuandulu ternary commercial pigs were black in coat color.
In order to determine the litter performance of Duroc×Luchuan(Dulu) binary sows and the coat color of their crossbred offspring with Chuanxiang black pigs, a total of 5 862 litters wtih effective breeding was recorded at three Chuanxiang×Duroc×Luchuan(Chuandulu) ternary commercial pig production farms in Hainan Province from January 2022 to June 2023. The litter performance of sows was compared according to parity and pig farm, and the coat color traits of ternary commercial pigs were counted. The results showed that there were significant differences in total litter size, healthy litter size and litter weight among different farms(P <0.05). Comparison of litter sizes revealed no significant difference in total litter size and number of healthy piglets born in litters 2, 3, 4 and 5(P > 0.05). The indicators of the first parity were significantly lower than those of other parities(P < 0.05), and the indicators of the 6th parity and above were also significantly different from those of other parities(P < 0.05). The 4th parity was significantly lower in litter weight than the other parities, while the 2nd parity was significantly higher in litter weight than the other parities(P < 0.05). The piglets born in the experimental group were mainly black in coat color, with a few being red, and very few being white in coat color,and the average proportion of piglets with black coat color reached 98.79%. In conclusion, there were significant differences in the litter performance of sows among different farms, sows with 2-5 parities were highly fertile, and piglets at birth were significantly different in litter weights; the vast majority of Chuandulu ternary commercial pigs were black in coat color.


 Abstract
Abstract PDF 1656KB
PDF 1656KB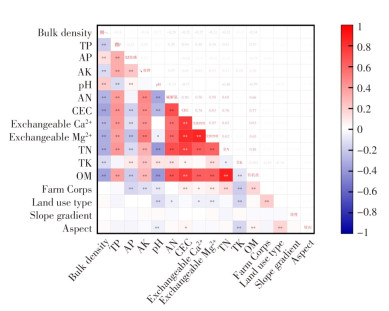


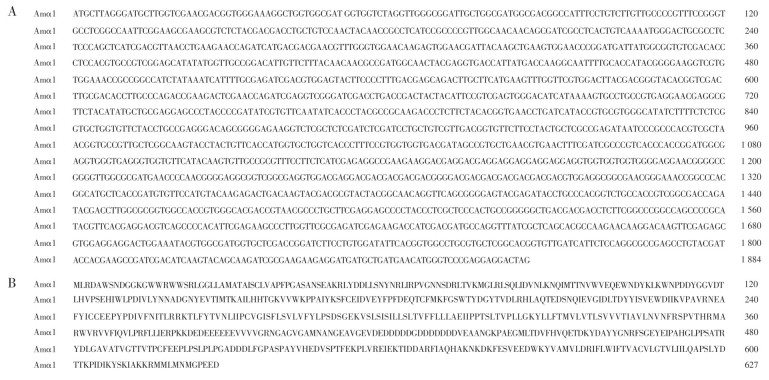





 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS