2022 Vol. 13, No. 5
2022, 13(5): 429-439.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.002
Abstract:
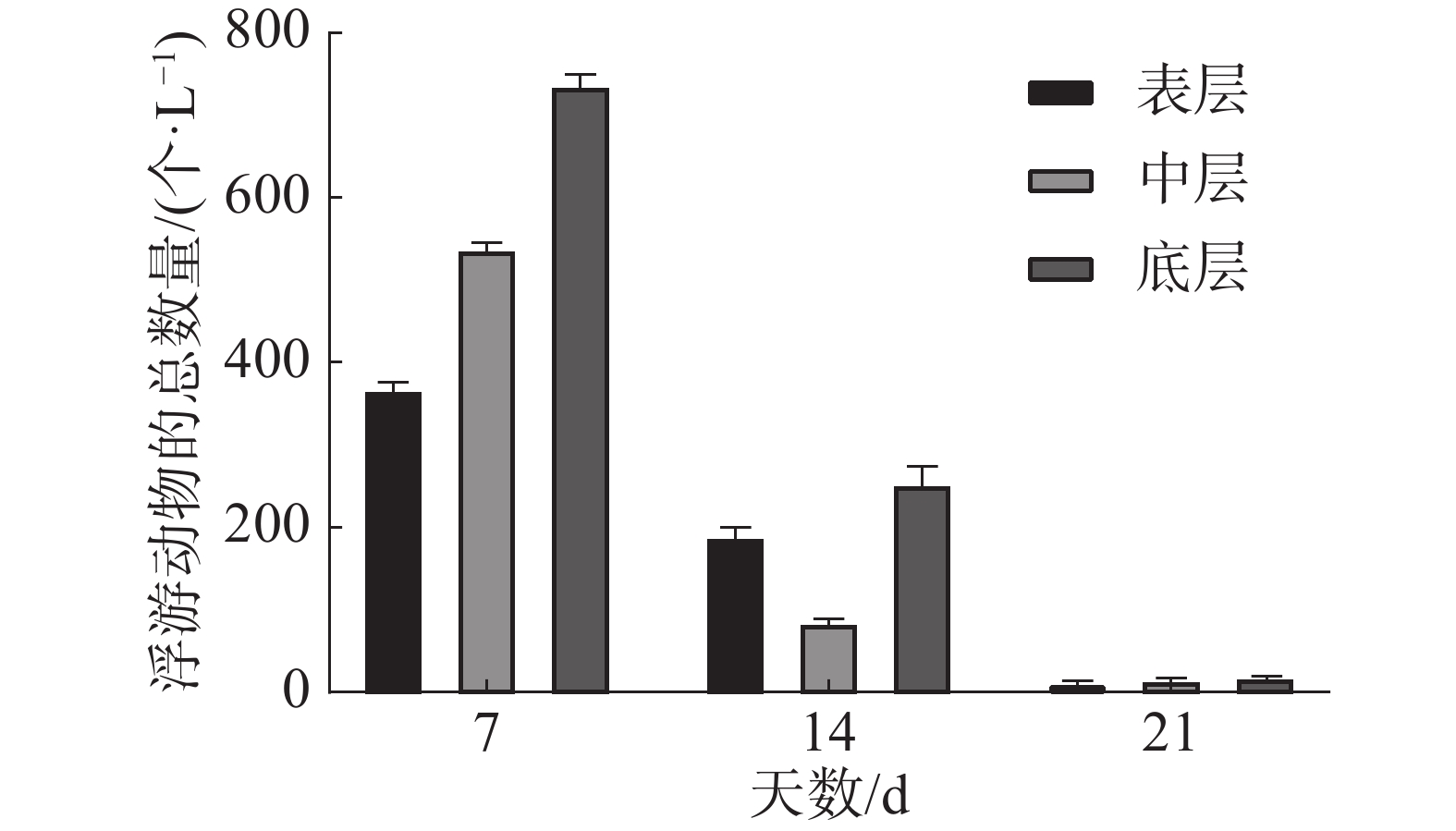
A combination of sand filtration, storage precipitation and chlorine-containing disinfectant was used to treat the aquaculture water for intensive culture of Litopenaeus vannamei in high level ponds. The differences of plankton in the offshore seawater, sand filtrated water and treated water were compared, and the temporal and spatial changes of plankton in the aquaculture water were analyzed. The results showed that there were many species of plankton in the offshore water, including 33 species belonging to 27 genera and 9 phyla. There were 17 species of plankton in the treated water, belonging to 15 genera and 5 phyla, second to those in the offshore water. There were 16 species of plankton in the sand filtrated water, belonging to 5 phyla 15 genera. The number of zooplankton was significantly higher in the treated water than in the offshore water and the sand filtrated water (P < 0.05). The zooplankton density in the offshore seawater was the second highest, with an average of (26.45±14.30) ·L−1. The zooplankton density in the sand filtrated water was the lowest, with an average of (6.31±1.45) ·L−1. The number of phytoplankton was significantly higher in the treated water than in the offshore seawater and the sand filtrated water (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between the two (P > 0.05). In the vertical direction, the change in total number of phytoplankton increased from the surface layer to the middle layer and then to the bottom layer, and the distribution of the total number of phytoplankton was higher in the surface layer than in middle layer and the bottom layer, but with no significant difference (P > 0.05). In the horizontal direction, there was significant difference in the distribution of the total number of phytoplankton in the horizontal direction (P < 0.05). These results might provide reference for the directional regulation of plankton in shrimp aquaculture ponds and shrimp disease control.
A combination of sand filtration, storage precipitation and chlorine-containing disinfectant was used to treat the aquaculture water for intensive culture of Litopenaeus vannamei in high level ponds. The differences of plankton in the offshore seawater, sand filtrated water and treated water were compared, and the temporal and spatial changes of plankton in the aquaculture water were analyzed. The results showed that there were many species of plankton in the offshore water, including 33 species belonging to 27 genera and 9 phyla. There were 17 species of plankton in the treated water, belonging to 15 genera and 5 phyla, second to those in the offshore water. There were 16 species of plankton in the sand filtrated water, belonging to 5 phyla 15 genera. The number of zooplankton was significantly higher in the treated water than in the offshore water and the sand filtrated water (P < 0.05). The zooplankton density in the offshore seawater was the second highest, with an average of (26.45±14.30) ·L−1. The zooplankton density in the sand filtrated water was the lowest, with an average of (6.31±1.45) ·L−1. The number of phytoplankton was significantly higher in the treated water than in the offshore seawater and the sand filtrated water (P < 0.05), but there was no significant difference between the two (P > 0.05). In the vertical direction, the change in total number of phytoplankton increased from the surface layer to the middle layer and then to the bottom layer, and the distribution of the total number of phytoplankton was higher in the surface layer than in middle layer and the bottom layer, but with no significant difference (P > 0.05). In the horizontal direction, there was significant difference in the distribution of the total number of phytoplankton in the horizontal direction (P < 0.05). These results might provide reference for the directional regulation of plankton in shrimp aquaculture ponds and shrimp disease control.
2022, 13(5): 440-450.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.003
Abstract:
MD-2-related Lipid-recognition proteins (ML) are a class of proteins that play an important role in the innate immunity and lipid recognition and metabolism. Two ML family genes PmML1 and PmML2 were cloned from shrimps (Penaeus monodon) by using PCR and RACE methods for bioinformatics analysis, and their expression profiles in various tissues of the shrimps were analyzed by using the quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The results showed that the open reading frame (ORF) length of PmML1 was 462 bp, encoding 153 amino acids and that the ORF length of PmML2 was 471 bp, encoding 156 amino acids. There is a typical ML family protein structural domain in these two genes. Multiple alignments revealed that the ML domain and the cysteine position in the PmML1 and PmML2 were relatively conserved. Alignment of the amino acid sequences showed that the similarity between PmML1 and PmML2 was only 42.37%. Moreover, the similarity between PmML1 and the MjML4 of Marsupenaeus japonicus was the highest (91.5%), and the similarity between PmML2 and the ML protein of Litopenaeus vannamei was the highest (88.46%). Phylogenetic analysis showed that PmML1 and PmML2 were found in two different branches, indicating that the evolution of two genes is relatively independent, which proved that two genes were identified different. Furthermore, the qRT-PCR results showed that PmML1 expressed highest in the eye stalk, followed by in the intestine, stomach, heart, gill, muscle and hepatopancreas, and the lowest expression level was in the blood cells. PmML2 expressed highest in the eye stalk, followed by in the intestine, gill, stomach, blood cells, heart, hepatopancreas and muscle, and the lowest expression level was in the muscle. As the eyestalk is an important neuroendocrine regulatory organ, it is speculated that PmML1 and PmML2 may play a role in the neuroendocrine regulation in P. monodon. This result might provide basic data for further study of ML family genes and their biological functions in shrimps.
MD-2-related Lipid-recognition proteins (ML) are a class of proteins that play an important role in the innate immunity and lipid recognition and metabolism. Two ML family genes PmML1 and PmML2 were cloned from shrimps (Penaeus monodon) by using PCR and RACE methods for bioinformatics analysis, and their expression profiles in various tissues of the shrimps were analyzed by using the quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). The results showed that the open reading frame (ORF) length of PmML1 was 462 bp, encoding 153 amino acids and that the ORF length of PmML2 was 471 bp, encoding 156 amino acids. There is a typical ML family protein structural domain in these two genes. Multiple alignments revealed that the ML domain and the cysteine position in the PmML1 and PmML2 were relatively conserved. Alignment of the amino acid sequences showed that the similarity between PmML1 and PmML2 was only 42.37%. Moreover, the similarity between PmML1 and the MjML4 of Marsupenaeus japonicus was the highest (91.5%), and the similarity between PmML2 and the ML protein of Litopenaeus vannamei was the highest (88.46%). Phylogenetic analysis showed that PmML1 and PmML2 were found in two different branches, indicating that the evolution of two genes is relatively independent, which proved that two genes were identified different. Furthermore, the qRT-PCR results showed that PmML1 expressed highest in the eye stalk, followed by in the intestine, stomach, heart, gill, muscle and hepatopancreas, and the lowest expression level was in the blood cells. PmML2 expressed highest in the eye stalk, followed by in the intestine, gill, stomach, blood cells, heart, hepatopancreas and muscle, and the lowest expression level was in the muscle. As the eyestalk is an important neuroendocrine regulatory organ, it is speculated that PmML1 and PmML2 may play a role in the neuroendocrine regulation in P. monodon. This result might provide basic data for further study of ML family genes and their biological functions in shrimps.
2022, 13(5): 451-456.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.004
Abstract:
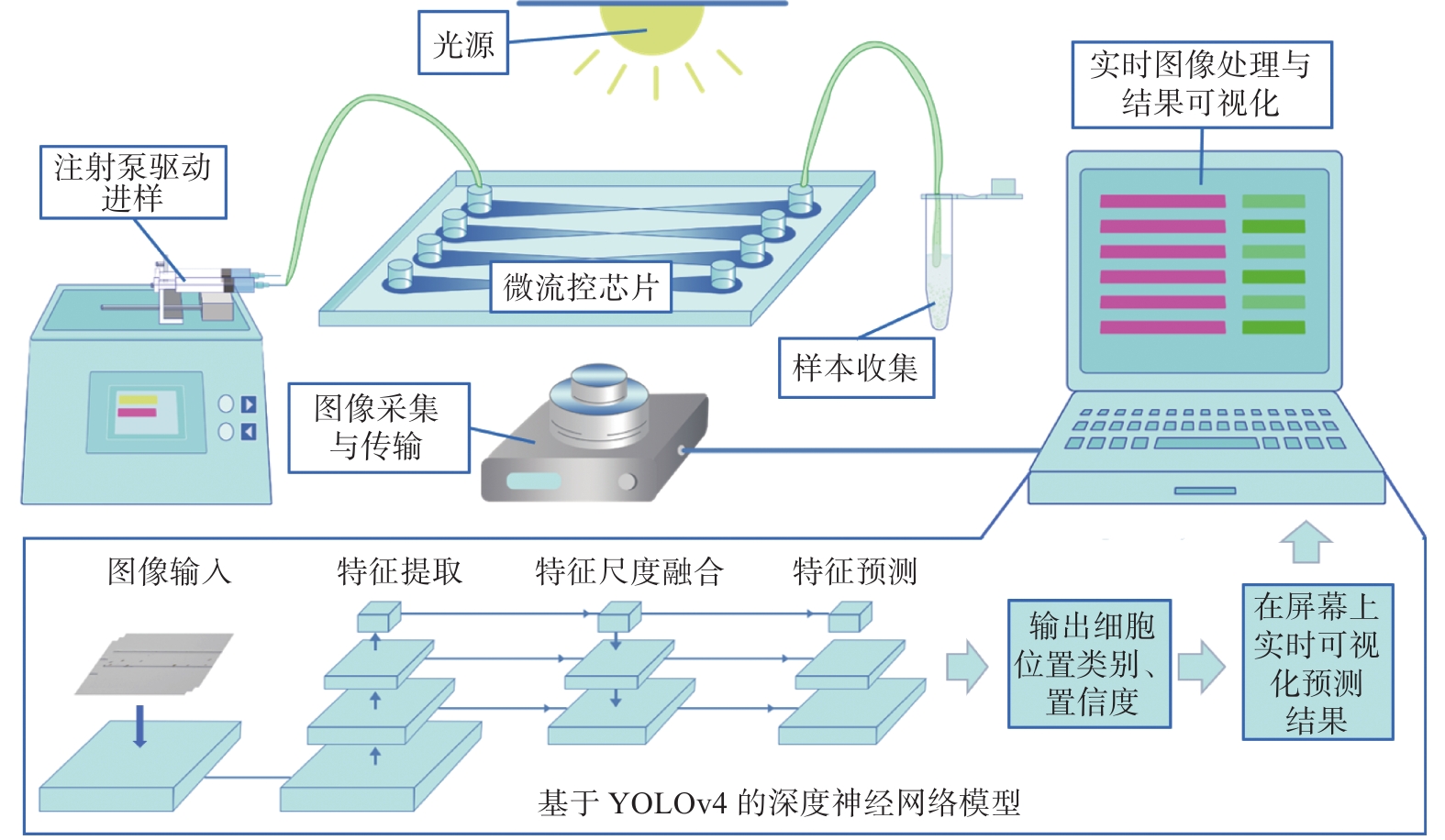
Measuring the species and density of Symbiodinium is important for predicting coral bleaching. At present, the rapid detection method of microalgae cells has great limitations. Manual microscopic inspection is time-consuming and laborious, while benchtop automated instruments are not suitable for large-scale real-time detection during field sampling. This research combines microfluidics, microscopic image processing and a deep learning neural network to proposes a deep neural network-based method for the microfluidic detection of in vivo Symbiodinium. The results of the detection of solution samples mixed with polymethylmethacrylate microspheres, normal and bleached methanogens cells show the neural network model trained using bright-field microscopic images is generalized to microfluidic on-chip cell detection, and is able to identify different physiological states of Symbiodinium cells and other objects with an average precision of 93.9%, demonstrating the feasibility, accuracy and sensitivity of the method.
Measuring the species and density of Symbiodinium is important for predicting coral bleaching. At present, the rapid detection method of microalgae cells has great limitations. Manual microscopic inspection is time-consuming and laborious, while benchtop automated instruments are not suitable for large-scale real-time detection during field sampling. This research combines microfluidics, microscopic image processing and a deep learning neural network to proposes a deep neural network-based method for the microfluidic detection of in vivo Symbiodinium. The results of the detection of solution samples mixed with polymethylmethacrylate microspheres, normal and bleached methanogens cells show the neural network model trained using bright-field microscopic images is generalized to microfluidic on-chip cell detection, and is able to identify different physiological states of Symbiodinium cells and other objects with an average precision of 93.9%, demonstrating the feasibility, accuracy and sensitivity of the method.
2022, 13(5): 457-463.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.005
Abstract:
Elysia leucolegnote are sacoglossan sea slugs, belonging to the family Elysiidae and the genus Elysia. They are distributed in mangroves throughout China, Thailand and the Philippines. Photosynthetic sea slugs are famous for their ability of photosynthesis. Stolen chloroplasts are called kleptoplasts. However, there has been no important breakthrough in the molecular mechanism research of kleptoplasts. In this context whole genome survey analysis of E. leucolegnote was conducted to find the clue about the regulation of photosynthesis and maintenance of chloroplast activities by high-throughput sequencing technology. The high-throughput sequencing produced 25 Gb high-quality data in E. leucolegnote, with a total sequencing depth of about 30x. According to 17-mer analysis, the predicted genome size was 724.8 Mb, the genome duplication rate was 52.8%, the heterozygosity was 1.55%, and the model fitting value was 99.38%. The 19-mer analysis predicted that the genome size was 730.8 Mb, with the genome duplication rate of 35.1%, the heterozygosity of 1.68%, and the model fitting value of 99.72%. A draft genome of E. leucolegnote Ker was obtained by preliminary assembly with a total length of 628 Mb. These results showed that E. leucolegnote is a highly heterozygous species with a genome size of more than 700 Mb.
Elysia leucolegnote are sacoglossan sea slugs, belonging to the family Elysiidae and the genus Elysia. They are distributed in mangroves throughout China, Thailand and the Philippines. Photosynthetic sea slugs are famous for their ability of photosynthesis. Stolen chloroplasts are called kleptoplasts. However, there has been no important breakthrough in the molecular mechanism research of kleptoplasts. In this context whole genome survey analysis of E. leucolegnote was conducted to find the clue about the regulation of photosynthesis and maintenance of chloroplast activities by high-throughput sequencing technology. The high-throughput sequencing produced 25 Gb high-quality data in E. leucolegnote, with a total sequencing depth of about 30x. According to 17-mer analysis, the predicted genome size was 724.8 Mb, the genome duplication rate was 52.8%, the heterozygosity was 1.55%, and the model fitting value was 99.38%. The 19-mer analysis predicted that the genome size was 730.8 Mb, with the genome duplication rate of 35.1%, the heterozygosity of 1.68%, and the model fitting value of 99.72%. A draft genome of E. leucolegnote Ker was obtained by preliminary assembly with a total length of 628 Mb. These results showed that E. leucolegnote is a highly heterozygous species with a genome size of more than 700 Mb.
2022, 13(5): 464-471.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.006
Abstract:
To understand the occurrence and characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the coastal coral reef ecosystem of Hainan Island, a survey was made in the seawater of the coral reef ecosystems along the east coast of Hainan Island, and the sea water at different depths was sampled at 8 survey sites to analyze its abundances of ARGs of sulfonamides (sul1 and sul2), quinolones (qnrB and qnrS), and chloramphenicol (cmlA1-01, cmlA1-02, and cmx(A)), and its correlation between ARGs abundances and environmental conditions including salinity, nutrient (NH3−-N, NO2−-N, NO3−-N, and PO43−-P), and metal (Hg, As, Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, and Cr) ion content by using real-time PCR-based absolute quantification. The results showed that the detection rates of 7 ARGs in the 3 types of sulfonamide, quinolone and chloramphenicol in the seawater at the 8 survey sites were 100%, and that sul2 (3.96×107−1.65×109 copies·L−1) was the most abundant in the seawater in all the coral reef ecosystems. Moreover, the absolute abundances of five ARGs (sul1, qnrS, cmlA1-01, cmlA1-02, and cmx(A)) were negatively correlated with salinity. Meanwhile, the absolute abundances of both cmlA1-01 and qnrS were positively correlated with the NO2−-N content, and sul1 and qnrB were positively correlated with Cu and Cr, respectively. These results suggest that there should be many types of ARG pollutions in the coral reef ecosystems along the east coast of Hainan Island. Salinity, nutrients and metal ions may be the main environmental factors driving the spread of ARGs in the coral reef area.
To understand the occurrence and characteristics of antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) in the coastal coral reef ecosystem of Hainan Island, a survey was made in the seawater of the coral reef ecosystems along the east coast of Hainan Island, and the sea water at different depths was sampled at 8 survey sites to analyze its abundances of ARGs of sulfonamides (sul1 and sul2), quinolones (qnrB and qnrS), and chloramphenicol (cmlA1-01, cmlA1-02, and cmx(A)), and its correlation between ARGs abundances and environmental conditions including salinity, nutrient (NH3−-N, NO2−-N, NO3−-N, and PO43−-P), and metal (Hg, As, Cu, Pb, Zn, Cd, and Cr) ion content by using real-time PCR-based absolute quantification. The results showed that the detection rates of 7 ARGs in the 3 types of sulfonamide, quinolone and chloramphenicol in the seawater at the 8 survey sites were 100%, and that sul2 (3.96×107−1.65×109 copies·L−1) was the most abundant in the seawater in all the coral reef ecosystems. Moreover, the absolute abundances of five ARGs (sul1, qnrS, cmlA1-01, cmlA1-02, and cmx(A)) were negatively correlated with salinity. Meanwhile, the absolute abundances of both cmlA1-01 and qnrS were positively correlated with the NO2−-N content, and sul1 and qnrB were positively correlated with Cu and Cr, respectively. These results suggest that there should be many types of ARG pollutions in the coral reef ecosystems along the east coast of Hainan Island. Salinity, nutrients and metal ions may be the main environmental factors driving the spread of ARGs in the coral reef area.
2022, 13(5): 472-477.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.007
Abstract:
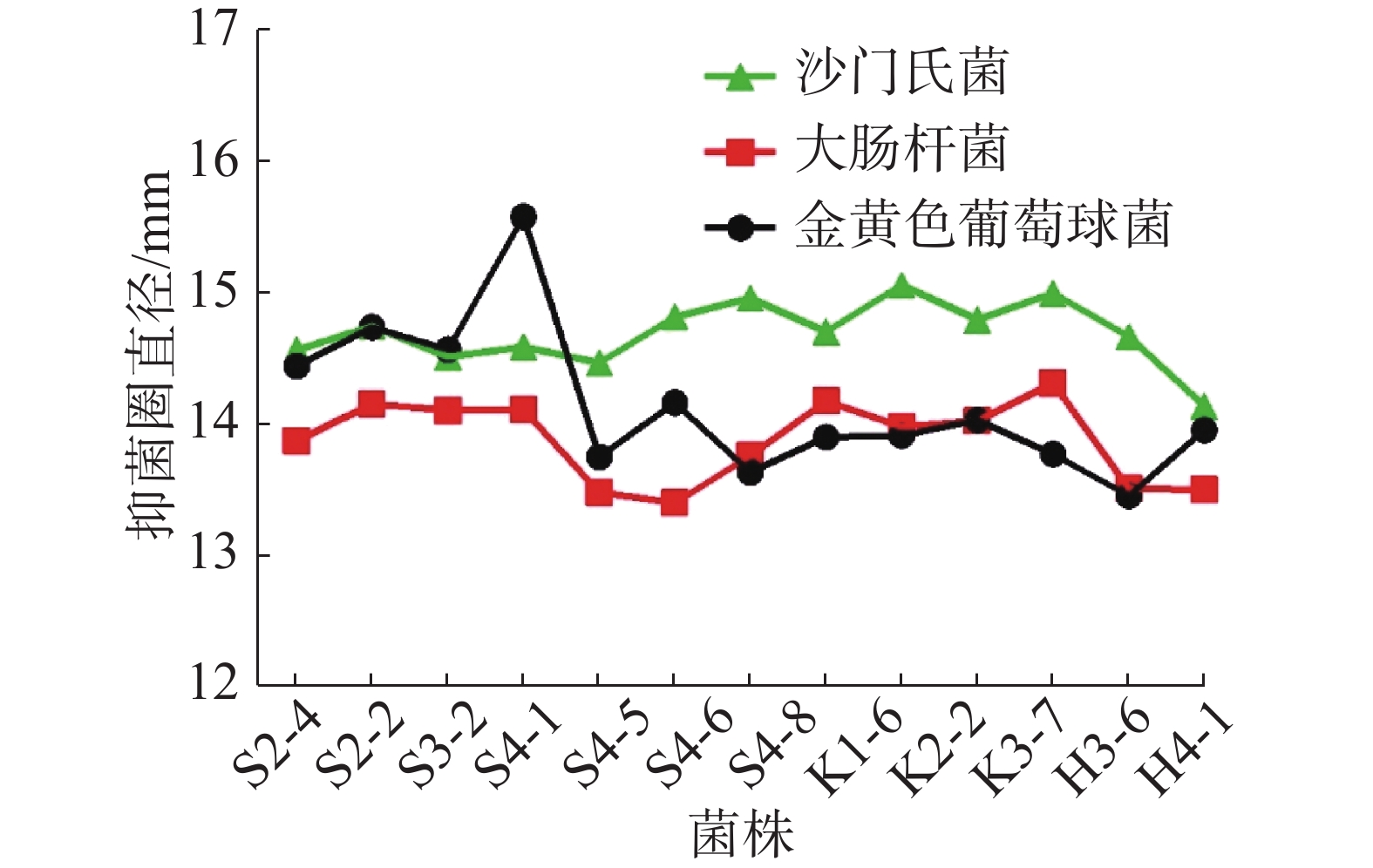
Lactic acid bacteria were isolated from the intestinal mucosa and contents of Wenchang Chicken in Hainan to obtain the strains of lactic acid bacteria with bacteriostatic activity. The isolates were determined and identified by morphological observation, Gram staining, hydrogen peroxide test, and 16S rRNA gene sequencing, and their acid and bile tolerance were tested by using the acid tolerance test and the bile salt tolerance test to screen the lactic acid bacteria with bacteriostatic activity from the intestinal tracts of tropical animals. A total of 17 strains of lactic acid bacteria were selected from the isolates, including 13 strains of Lactobacillus plantarum and 4 strains of Enterococcus faecalis. Of the 17 strains isolated, the strains of L. plantarum showed a high inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, and had some tolerance to acid and bile, while the strains of Enterococcus faecalis had low bacteriostatic effect. Comprehensive evaluation showed that the strain S4-1 of L. plantarum showed a higher bacteriostatic effect. The strain S4-1 of L. plantarum isolated from Wenchang Chicken in Hainan can hence be used as a follow-up study for the development of probiotic preparations for livestock intestines.
Lactic acid bacteria were isolated from the intestinal mucosa and contents of Wenchang Chicken in Hainan to obtain the strains of lactic acid bacteria with bacteriostatic activity. The isolates were determined and identified by morphological observation, Gram staining, hydrogen peroxide test, and 16S rRNA gene sequencing, and their acid and bile tolerance were tested by using the acid tolerance test and the bile salt tolerance test to screen the lactic acid bacteria with bacteriostatic activity from the intestinal tracts of tropical animals. A total of 17 strains of lactic acid bacteria were selected from the isolates, including 13 strains of Lactobacillus plantarum and 4 strains of Enterococcus faecalis. Of the 17 strains isolated, the strains of L. plantarum showed a high inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, and had some tolerance to acid and bile, while the strains of Enterococcus faecalis had low bacteriostatic effect. Comprehensive evaluation showed that the strain S4-1 of L. plantarum showed a higher bacteriostatic effect. The strain S4-1 of L. plantarum isolated from Wenchang Chicken in Hainan can hence be used as a follow-up study for the development of probiotic preparations for livestock intestines.
2022, 13(5): 478-487.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.008
Abstract:
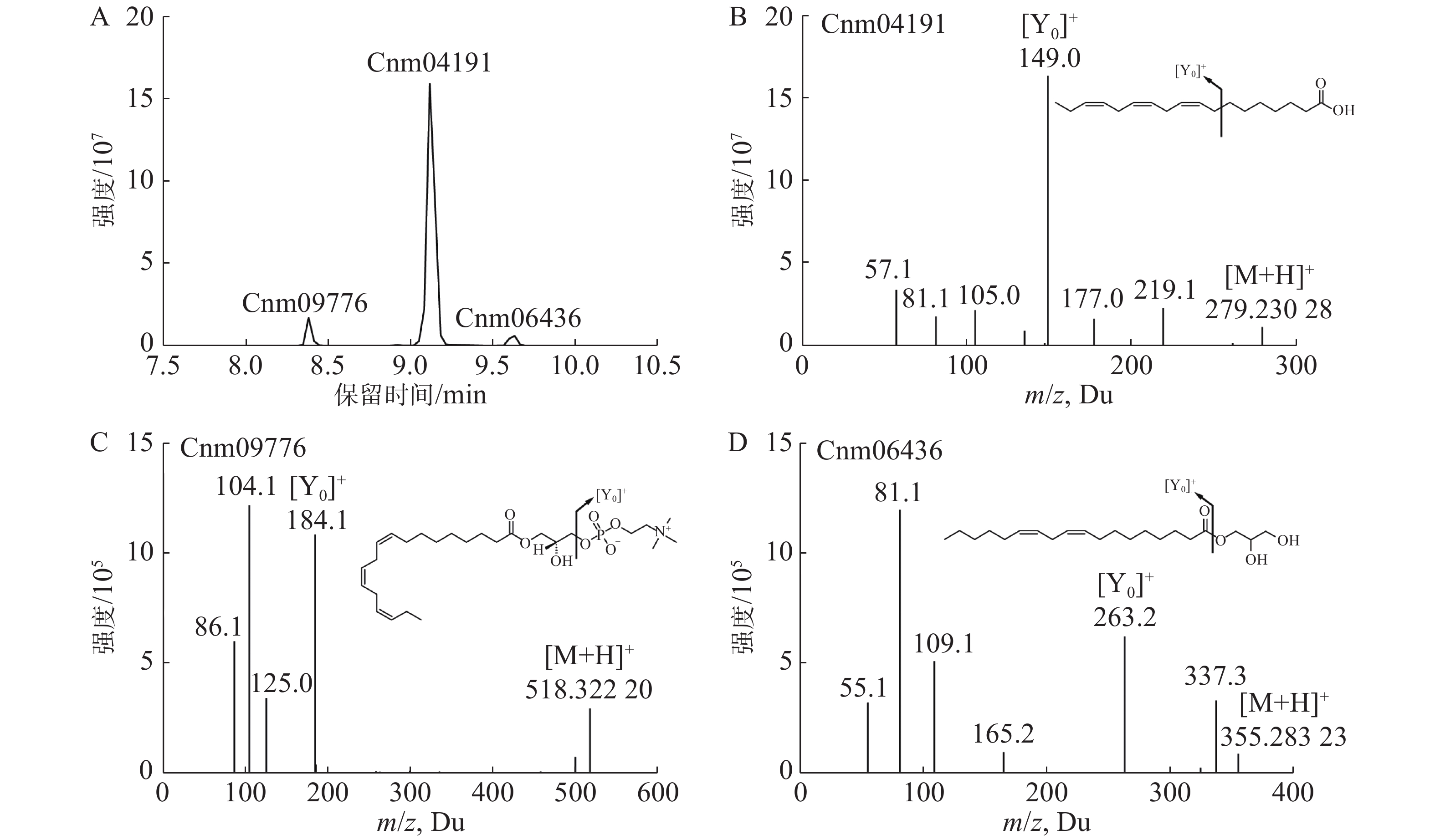
Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.), as an important oil crop, is one of the sources of high-quality vegetable oil in the world. In order to explore the differences of lipid species and their contents in different types of coconuts, non-targeted metabolomics method was used to analyze the metabolites in coconut meat tissue of tall and dwarf coconuts in Hainan. A total of 12 579 metabolic signals were detected, among which 564 metabolites were identified, including fatty acids, amino acids, and flavonoids, etc. Quantitative analysis showed that the lipid content of tall coconut was generally higher than that of dwarf coconut, and that the lipid content of green dwarf coconut was the lowest. Glycerolipids, sphingolipids and fatty acylides were the main differentiating substances in different types of coconuts. Transcriptome data showed that the differential genes in three types of coconuts were mainly involved in fatty acid metabolism, α-linolenic acid metabolism, lignin metabolism and phenylpropane metabolism. The differential genes were divided into 20 modules based on expression patterns, among which "Melightyellow" module was highly correlated with differential accumulation of fatty acids. Analysis of the cis-elements in the promoter regions of lipid pathway structural genes in the module showed that there were multiple MYB family transcription factors binding sites and a large number of hormone signal response elements. These results suggested that MYB transcription factors may play an important role in the regulation of lipid synthesis, and that hormones may be involved in the regulation of lipid synthesis as signaling molecules. In this study, the molecular mechanism of lipid differences in meat tissues of different coconut varieties was analyzed through a combination strategy, and a synthetic regulatory network of transcription factors-structural genes-metabolites was further constructed. This study not only provided resources for the subsequent analysis of the molecular mechanism of lipid synthesis regulation, but also provided a basis for the breeding of high-fat coconut varieties.
Coconut (Cocos nucifera L.), as an important oil crop, is one of the sources of high-quality vegetable oil in the world. In order to explore the differences of lipid species and their contents in different types of coconuts, non-targeted metabolomics method was used to analyze the metabolites in coconut meat tissue of tall and dwarf coconuts in Hainan. A total of 12 579 metabolic signals were detected, among which 564 metabolites were identified, including fatty acids, amino acids, and flavonoids, etc. Quantitative analysis showed that the lipid content of tall coconut was generally higher than that of dwarf coconut, and that the lipid content of green dwarf coconut was the lowest. Glycerolipids, sphingolipids and fatty acylides were the main differentiating substances in different types of coconuts. Transcriptome data showed that the differential genes in three types of coconuts were mainly involved in fatty acid metabolism, α-linolenic acid metabolism, lignin metabolism and phenylpropane metabolism. The differential genes were divided into 20 modules based on expression patterns, among which "Melightyellow" module was highly correlated with differential accumulation of fatty acids. Analysis of the cis-elements in the promoter regions of lipid pathway structural genes in the module showed that there were multiple MYB family transcription factors binding sites and a large number of hormone signal response elements. These results suggested that MYB transcription factors may play an important role in the regulation of lipid synthesis, and that hormones may be involved in the regulation of lipid synthesis as signaling molecules. In this study, the molecular mechanism of lipid differences in meat tissues of different coconut varieties was analyzed through a combination strategy, and a synthetic regulatory network of transcription factors-structural genes-metabolites was further constructed. This study not only provided resources for the subsequent analysis of the molecular mechanism of lipid synthesis regulation, but also provided a basis for the breeding of high-fat coconut varieties.
2022, 13(5): 488-495.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.009
Abstract:
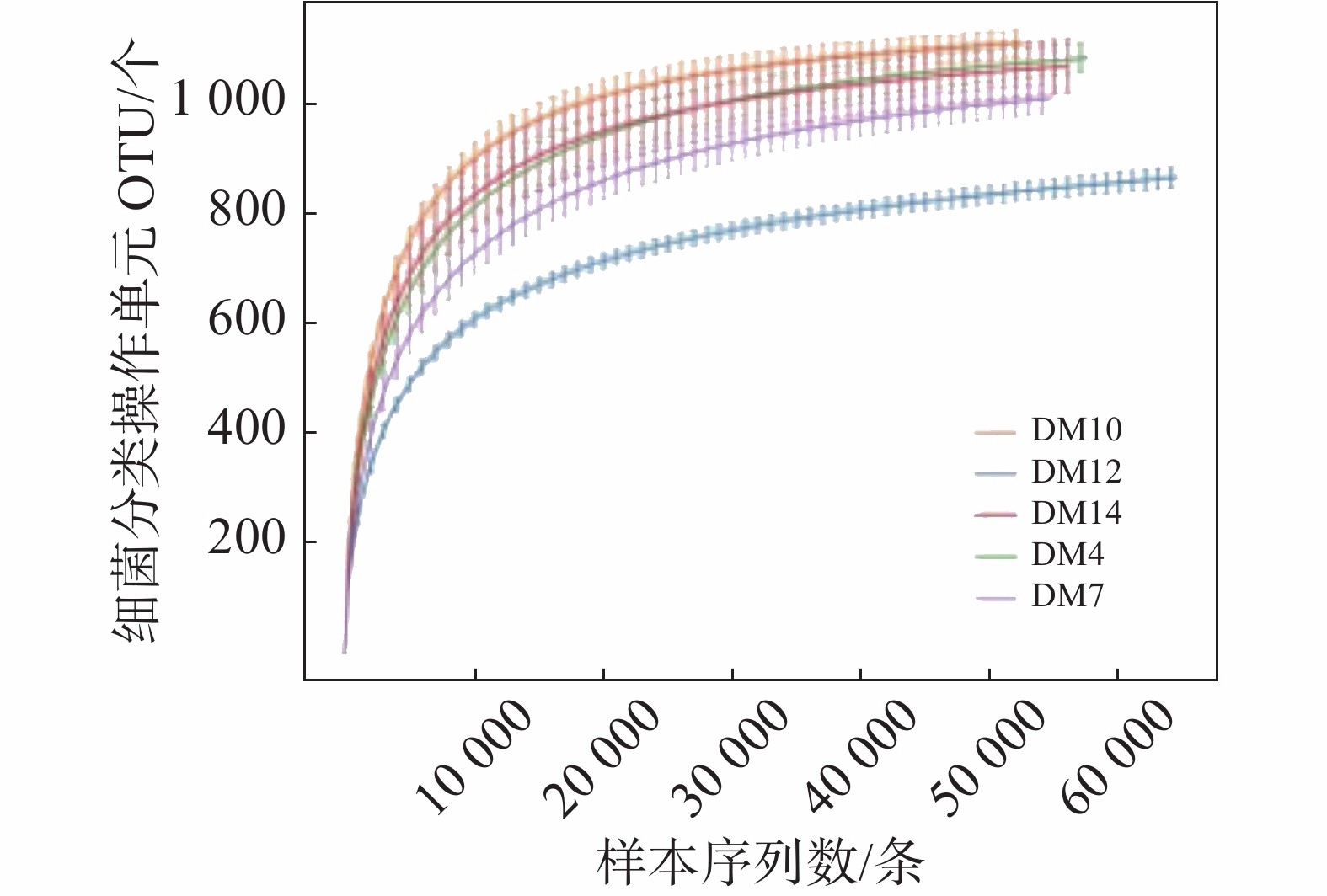
An attempt was made to understand the main bacterial community structure and bacterial diversity in the rhizosphere of Nauclea officinalis to clarify the relationship between its community structure and bacterial diversity and soil physicochemical properties for further isolation and screening of rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria in different planting areas. Fifteen rhizosphere soil samples from 5 planting areas under N. officinalis were analyzed by high-throughput sequencing technology. Multiple comparisons and correlation analysis were performed on the data using Excel, DPS and SPSS20.0 software. The results showed that the average sequence length of the 15 soil samples was 414−418 bp. The average operational taxonomic unit (OTU) numbers of samples DM4, DM7, DM10, DM12 and DM14 were 1084, 1012, 1109, 870 and 997, respectively, and 1223 bacterial taxa were obtained. The sample community structure analysis showed that there were 10 dominant bacterial phyla, such as Rokuacteria, WPS-2, Gemmatimonadetes. The dominant genera were Bacillus, Acidobacter, Streptomyces, Burkholderia, Gammaproteobacteria, Acidophilus, and the unidentified genera Candidatus, Udaeobacter, and AD3. The diversity analysis of the bacteria from the samples showed that the species abundance and diversity of the bacteria were higher in the samples form Wuzhishan city than in the samples from Qiongzhong county. The sample correlation analysis showed that soil physicochemical properties were related to dominant bacteria. For instance, organic matter, available potassium, available phosphorus and alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen were negatively correlated significantly with Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, and positively significantly with Planctomycetes. Humidity, organic matter, available potassium were positively significantly while the temperature and pH were negatively significantly with the species abundance and diversity of the bacteria. The composition of the main community structure in the N. officinalis plantations in Wuzhishan and Qiongzhong is generally the same, but different in abundance ratios. The bacterial community abundance and bacterial diversity were different in these two areas, indicating that the bacterial community abundance and bacterial diversity are different in different planting areas. Moreover, the bacterial community abundance and bacterial diversity in the samples from Wuzhishan were higher than those from Qiongzhong. The soil physicochemical properties had an impact on the main phyla, bacterial community abundance and bacterial diversity of rhizosphere bacteria.
An attempt was made to understand the main bacterial community structure and bacterial diversity in the rhizosphere of Nauclea officinalis to clarify the relationship between its community structure and bacterial diversity and soil physicochemical properties for further isolation and screening of rhizosphere growth-promoting bacteria in different planting areas. Fifteen rhizosphere soil samples from 5 planting areas under N. officinalis were analyzed by high-throughput sequencing technology. Multiple comparisons and correlation analysis were performed on the data using Excel, DPS and SPSS20.0 software. The results showed that the average sequence length of the 15 soil samples was 414−418 bp. The average operational taxonomic unit (OTU) numbers of samples DM4, DM7, DM10, DM12 and DM14 were 1084, 1012, 1109, 870 and 997, respectively, and 1223 bacterial taxa were obtained. The sample community structure analysis showed that there were 10 dominant bacterial phyla, such as Rokuacteria, WPS-2, Gemmatimonadetes. The dominant genera were Bacillus, Acidobacter, Streptomyces, Burkholderia, Gammaproteobacteria, Acidophilus, and the unidentified genera Candidatus, Udaeobacter, and AD3. The diversity analysis of the bacteria from the samples showed that the species abundance and diversity of the bacteria were higher in the samples form Wuzhishan city than in the samples from Qiongzhong county. The sample correlation analysis showed that soil physicochemical properties were related to dominant bacteria. For instance, organic matter, available potassium, available phosphorus and alkali-hydrolyzable nitrogen were negatively correlated significantly with Firmicutes and Proteobacteria, and positively significantly with Planctomycetes. Humidity, organic matter, available potassium were positively significantly while the temperature and pH were negatively significantly with the species abundance and diversity of the bacteria. The composition of the main community structure in the N. officinalis plantations in Wuzhishan and Qiongzhong is generally the same, but different in abundance ratios. The bacterial community abundance and bacterial diversity were different in these two areas, indicating that the bacterial community abundance and bacterial diversity are different in different planting areas. Moreover, the bacterial community abundance and bacterial diversity in the samples from Wuzhishan were higher than those from Qiongzhong. The soil physicochemical properties had an impact on the main phyla, bacterial community abundance and bacterial diversity of rhizosphere bacteria.
2022, 13(5): 496-501.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.010
Abstract:
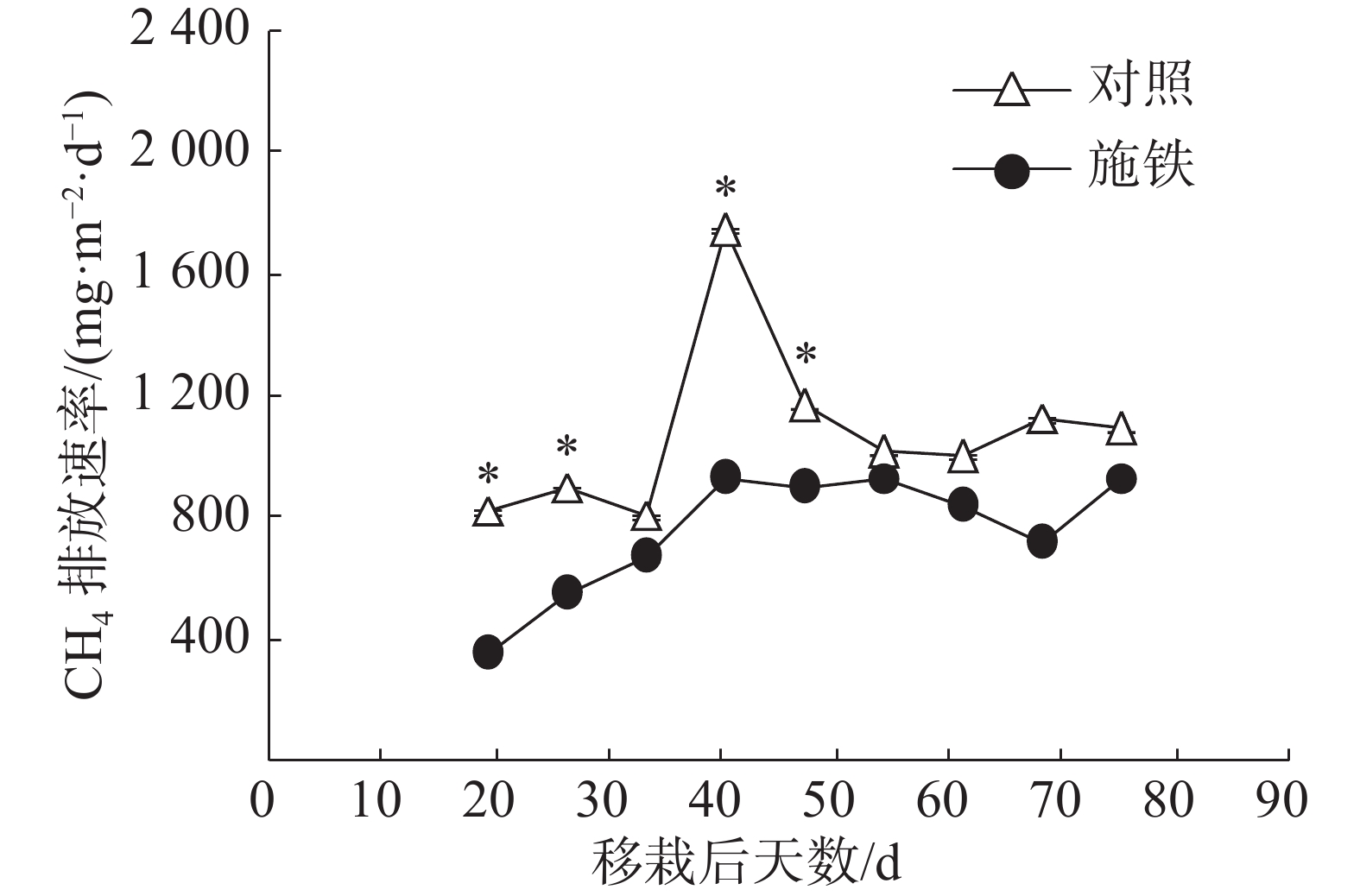
In order to explore the effect of Fe amendment on methane emission from Oryza rufipogon paddy soil, a comparison experiment was conducted in concrete ponds using a Oryza rufipogon population with higher capacity to form iron plaque on roots. The 11-day-old seedlings were transplanted to the rice paddy soil which was previously treated with or without addition of ferrihydrite at a rate of 0.7 g Fe/kg dry weight soil and already planted 6 growing seasons of rice under continuous flooding regime. Methane emission rate, Fe2+ concentration in soil pore water, root biomass and iron plaque on roots were measured. The experimental results showed that the methane emission in the Fe-amended pond during the period of 19-75 days after transplanting was reduced by up to 29.51%, comparing to control. Methane suppression observed by Fe amendment occurred only in the early growing season. There was a significant difference in Fe2+ concentration in soil pore water between two treatments only at 19 days after transplanting over the investigation period. The difference in both root biomass and amount of iron plaque per plant between Fe-amended treatment and control increased with age of plants. The present study suggests that Fe amendment can effectively mitigate methane emission from Oryza rufipogon plants with potential to have much more iron plaque on roots.
In order to explore the effect of Fe amendment on methane emission from Oryza rufipogon paddy soil, a comparison experiment was conducted in concrete ponds using a Oryza rufipogon population with higher capacity to form iron plaque on roots. The 11-day-old seedlings were transplanted to the rice paddy soil which was previously treated with or without addition of ferrihydrite at a rate of 0.7 g Fe/kg dry weight soil and already planted 6 growing seasons of rice under continuous flooding regime. Methane emission rate, Fe2+ concentration in soil pore water, root biomass and iron plaque on roots were measured. The experimental results showed that the methane emission in the Fe-amended pond during the period of 19-75 days after transplanting was reduced by up to 29.51%, comparing to control. Methane suppression observed by Fe amendment occurred only in the early growing season. There was a significant difference in Fe2+ concentration in soil pore water between two treatments only at 19 days after transplanting over the investigation period. The difference in both root biomass and amount of iron plaque per plant between Fe-amended treatment and control increased with age of plants. The present study suggests that Fe amendment can effectively mitigate methane emission from Oryza rufipogon plants with potential to have much more iron plaque on roots.
2022, 13(5): 502-508.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.011
Abstract:
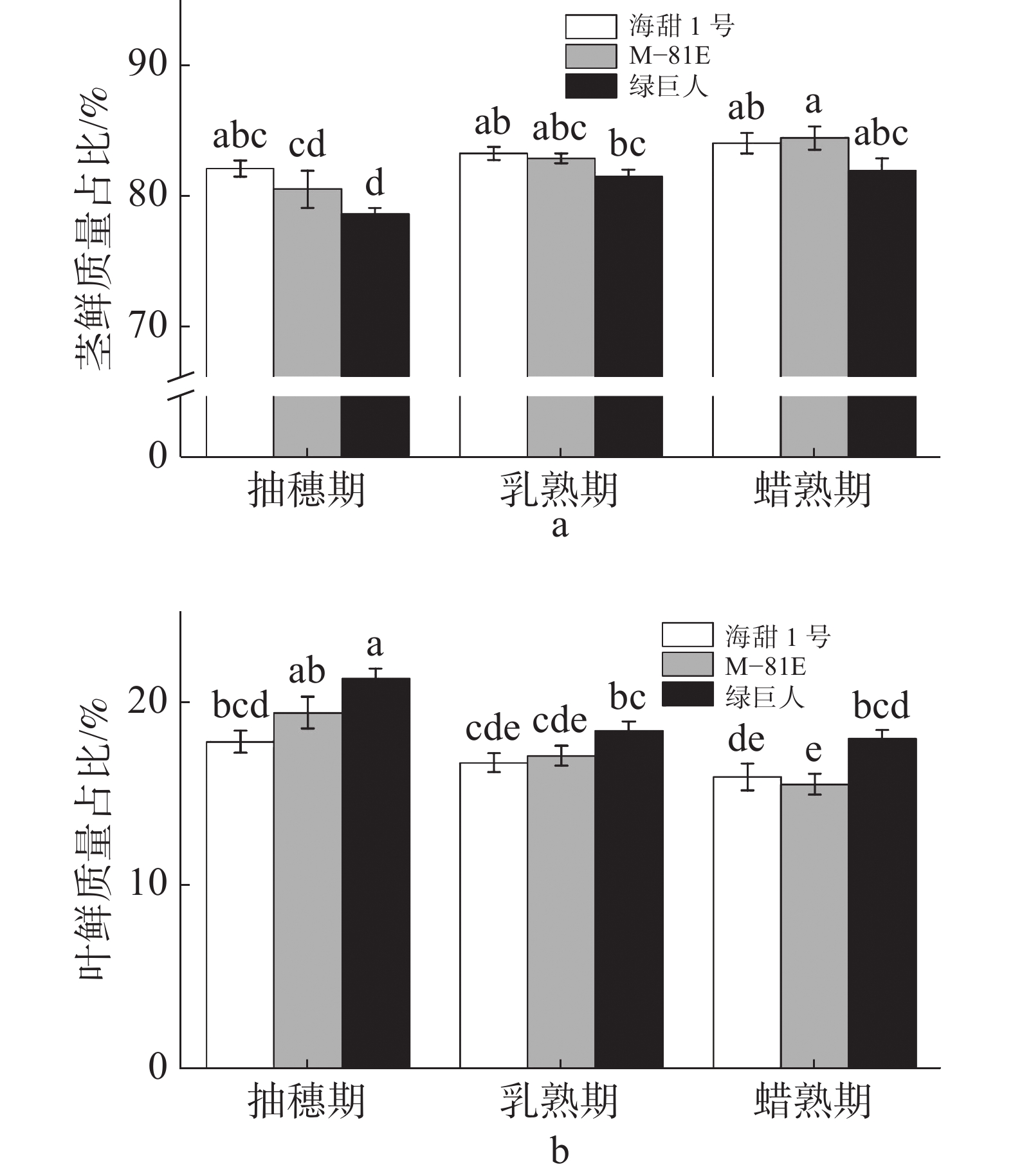
In order to study the effects of cutting at different periods on agronomic traits and nutritional quality of sweet sorghum, sweet sorghum varieties ‘Haitian 1’, ‘M-81E’ and ‘Green Hulk’ were planted in Dongfang, Hainan and cut at three growth stages. Agronomic traits including plant height, stem diameter, fresh weight per plant, dry weight per plant and yield, as well as nutritional quality parameters including crude protein, acid neutral fiber and soluble sugar were systematically determined at the heading, milk and dough stages to provide reference for the planting and harvesting of these sorghum varieties. The results showed that the plant heights of ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘M-81E’ was maximum at the milk stage, which were 317.76 cm and 294.06 cm, respectively, and that the plant heights of ‘Green Hulk’ was maximum at the dough stage, which was 354.06 cm. The fresh weight per plant and plot yield of ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘Green Hulk’ increased significantly from the heading stage to the milk stage, maximum at the milk stage, and were 1996.71g and 2240.97 g at the heading stage, and 28.99 kg and 32.13 kg at the dough stage, respectively. The fresh weight per plant and plot yield of ‘M-81E’ decreased gradually from the heading stage to the dough stage, maximum at the heading stage, and were 1667.55 g and 24.11 kg, respectively. The dry weight per plant and dry matter content of ‘Haitian 1’, ‘M-81E’ and ‘Green Hulk’ were increasing from the heading stage to the dough stage. From the heading stage to the dough stage, ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘Green Hulk’ increased first and then decreased in the contents of neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber while ‘M-81E’ showed a decreasing trend. All the three varieties increased in soluble sugar and crude ash contents from the heading stage to the dough stage, and tended to decrease in crude protein content from the heading stage to the dough stage. ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘M-81E’ had a maximum relative feeding value at the dough stage, which were 117.20 and 142.55, respectively, and ‘Green Hulk’ had a maximum feeding value (95.43) at the heading stage. The results showed that there is a significant difference in the effects of cutting at different growth stages on the agronomic traits and nutritional quality of sweet sorghum. Based on the agronomic traits and nutritional quality parameters of the three varieties, the optimum harvesting stage was between milky and dough stages for ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘Green Hulk’, and the optimum harvesting stage was between the heading and the milky stage for ‘M-81E’.
In order to study the effects of cutting at different periods on agronomic traits and nutritional quality of sweet sorghum, sweet sorghum varieties ‘Haitian 1’, ‘M-81E’ and ‘Green Hulk’ were planted in Dongfang, Hainan and cut at three growth stages. Agronomic traits including plant height, stem diameter, fresh weight per plant, dry weight per plant and yield, as well as nutritional quality parameters including crude protein, acid neutral fiber and soluble sugar were systematically determined at the heading, milk and dough stages to provide reference for the planting and harvesting of these sorghum varieties. The results showed that the plant heights of ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘M-81E’ was maximum at the milk stage, which were 317.76 cm and 294.06 cm, respectively, and that the plant heights of ‘Green Hulk’ was maximum at the dough stage, which was 354.06 cm. The fresh weight per plant and plot yield of ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘Green Hulk’ increased significantly from the heading stage to the milk stage, maximum at the milk stage, and were 1996.71g and 2240.97 g at the heading stage, and 28.99 kg and 32.13 kg at the dough stage, respectively. The fresh weight per plant and plot yield of ‘M-81E’ decreased gradually from the heading stage to the dough stage, maximum at the heading stage, and were 1667.55 g and 24.11 kg, respectively. The dry weight per plant and dry matter content of ‘Haitian 1’, ‘M-81E’ and ‘Green Hulk’ were increasing from the heading stage to the dough stage. From the heading stage to the dough stage, ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘Green Hulk’ increased first and then decreased in the contents of neutral detergent fiber and acid detergent fiber while ‘M-81E’ showed a decreasing trend. All the three varieties increased in soluble sugar and crude ash contents from the heading stage to the dough stage, and tended to decrease in crude protein content from the heading stage to the dough stage. ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘M-81E’ had a maximum relative feeding value at the dough stage, which were 117.20 and 142.55, respectively, and ‘Green Hulk’ had a maximum feeding value (95.43) at the heading stage. The results showed that there is a significant difference in the effects of cutting at different growth stages on the agronomic traits and nutritional quality of sweet sorghum. Based on the agronomic traits and nutritional quality parameters of the three varieties, the optimum harvesting stage was between milky and dough stages for ‘Haitian 1’ and ‘Green Hulk’, and the optimum harvesting stage was between the heading and the milky stage for ‘M-81E’.
2022, 13(5): 509-513.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.012
Abstract:
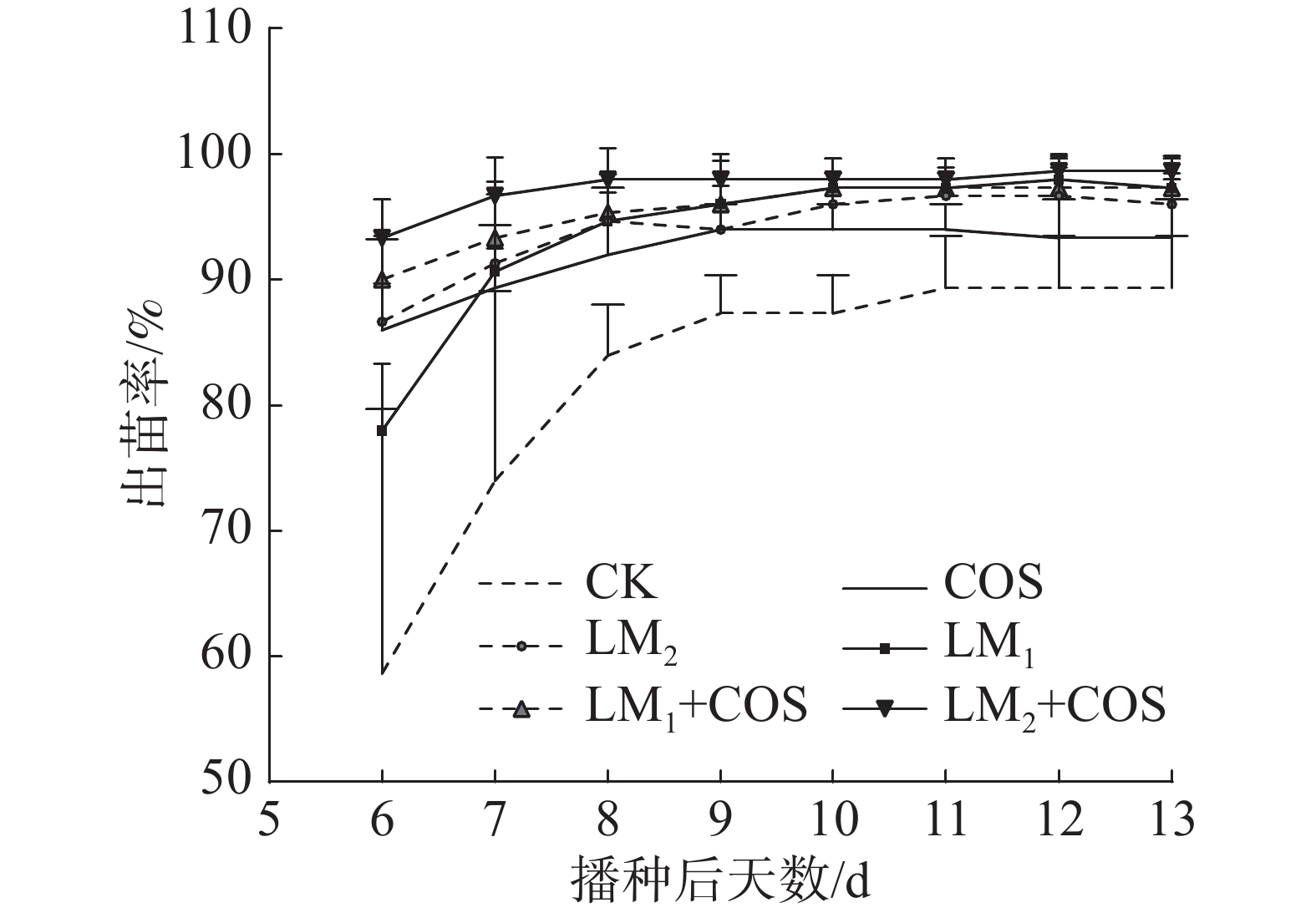
To explore the effect of Streptomyces 30702 and chitososaccharides on seed germination and seedling growth in Pepper, 3 concentration levels of Streptomyces and 2 concentration levels of chitooligosaccharides were conducted to soak seeds and then cultivate seedlings in hole tray and study seedling quality and physiology. The result showed that after treatment with Streptomyces and chitooligosaccharides, emergence rate , plant height, stem thickness, root length, leaf area, seedling strongness index, total dry weight, soluble sugar and soluble protein were significantly improved, while wilting index was significantly reduced, the extent of influence increased as the using concentration of Streptomyces , Among them compound treatment of Streptomyces 1.2 × 107 cfu·mL−1 and chitosaccharide 100 g·L−1 grew best, wilting index lowest. After the principal component analysis, the compound treatment had the highest comprehensive score. Through interaction analysis, Streptomyces and chitooligosaccharides interacted significantly, except for the total dry weight and seedling strongness index. In a word, Streptomyces 30702 promotes seed to germinate and grow stronger than chitooligosaccharides, interact with chitooligosaccharides in pepper.
To explore the effect of Streptomyces 30702 and chitososaccharides on seed germination and seedling growth in Pepper, 3 concentration levels of Streptomyces and 2 concentration levels of chitooligosaccharides were conducted to soak seeds and then cultivate seedlings in hole tray and study seedling quality and physiology. The result showed that after treatment with Streptomyces and chitooligosaccharides, emergence rate , plant height, stem thickness, root length, leaf area, seedling strongness index, total dry weight, soluble sugar and soluble protein were significantly improved, while wilting index was significantly reduced, the extent of influence increased as the using concentration of Streptomyces , Among them compound treatment of Streptomyces 1.2 × 107 cfu·mL−1 and chitosaccharide 100 g·L−1 grew best, wilting index lowest. After the principal component analysis, the compound treatment had the highest comprehensive score. Through interaction analysis, Streptomyces and chitooligosaccharides interacted significantly, except for the total dry weight and seedling strongness index. In a word, Streptomyces 30702 promotes seed to germinate and grow stronger than chitooligosaccharides, interact with chitooligosaccharides in pepper.
2022, 13(5): 514-518.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.013
Abstract:
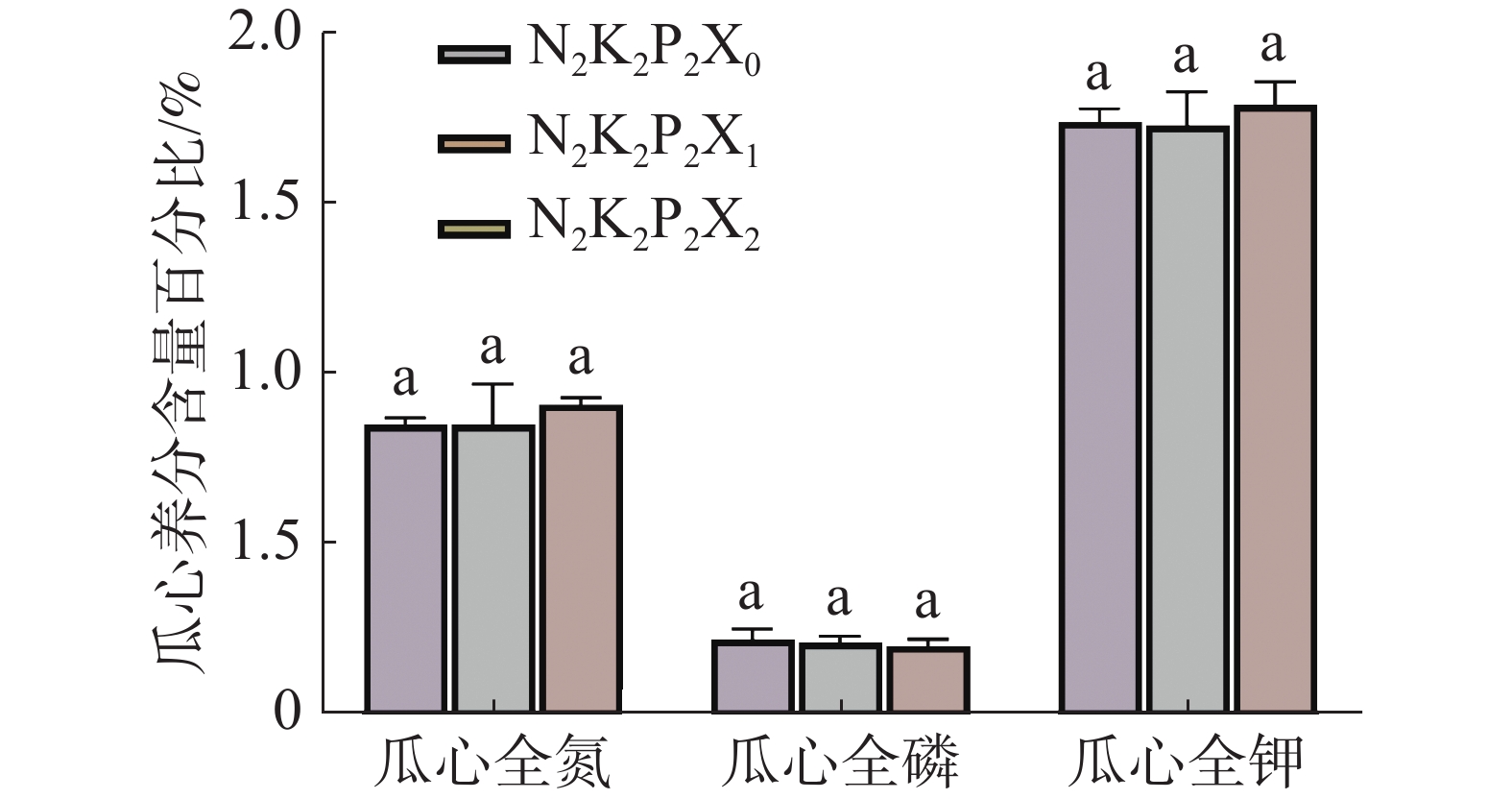
A field fertilizer experiment was made to analyze the effect of magnesium on the yield and quality of Hami melon (Cucumis melo L.). Hami melon was treated with no magnesium (T1), magnesium at a rate of 30 kg/ha (T2) and magnesium at a rate of 60 kg/ha (T3) to observe their yield and quality. The results showed Hami melon yield higher and then lower with the increase of magnesium. Hami melon yielded the highest in the T2 (4805.79 kg/ha), an 8.81% increase as compared with the T1. The contents of VC and sugar of Hami melon increased first and then decreased with the increase of magnesium, and were 19.63% and 3.69% higher than those of the T1. Application of magnesium at different rates had significant effects on the pH and nutrient contents of the soil in the Hami melon field. The pH and the contents of organic matter, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, exchangeable calcium and exchangeable magnesium in the soil in the T2 increased by 2.63%, 63.41%, 58.76%, 18.04%, 64.09%, 75.81% and 207.71% compared with those of the soil before the experiment. Therefore, magnesium fertilizer application at a suitable rate can improve not only the yield and quality of Hami melon, but also the soil and fertility.
A field fertilizer experiment was made to analyze the effect of magnesium on the yield and quality of Hami melon (Cucumis melo L.). Hami melon was treated with no magnesium (T1), magnesium at a rate of 30 kg/ha (T2) and magnesium at a rate of 60 kg/ha (T3) to observe their yield and quality. The results showed Hami melon yield higher and then lower with the increase of magnesium. Hami melon yielded the highest in the T2 (4805.79 kg/ha), an 8.81% increase as compared with the T1. The contents of VC and sugar of Hami melon increased first and then decreased with the increase of magnesium, and were 19.63% and 3.69% higher than those of the T1. Application of magnesium at different rates had significant effects on the pH and nutrient contents of the soil in the Hami melon field. The pH and the contents of organic matter, alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, exchangeable calcium and exchangeable magnesium in the soil in the T2 increased by 2.63%, 63.41%, 58.76%, 18.04%, 64.09%, 75.81% and 207.71% compared with those of the soil before the experiment. Therefore, magnesium fertilizer application at a suitable rate can improve not only the yield and quality of Hami melon, but also the soil and fertility.
2022, 13(5): 519-523.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.014
Abstract:
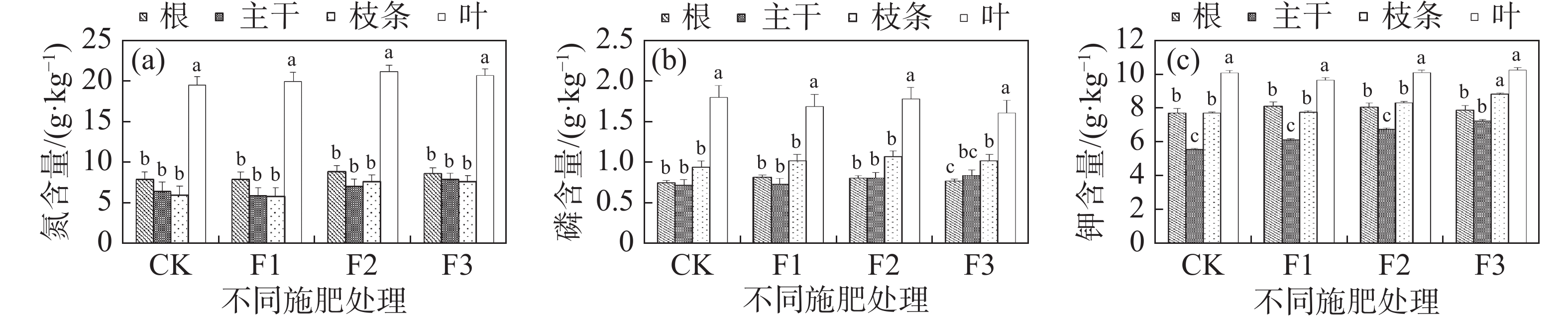
Research and analysis of the plant nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium ecological stoichiometry can reflect the distribution status and mutual correlation of the nutrients in different organs of the plant, and determine the nutrient-limiting factors of the plant in the different environments. Young rubber plants transplanted were treated with fertilizer at four different rates in an experiment with random complete block design and three replicates each treatment and then sampled, and the contents of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and their ecological stoichiometric characteristics in different organs of the young rubber plants collected were determined and analyzed to explore the characteristics of the distribution and utilization of soil nutrients in the young rubber plants under fertilizer treatment. The results showed that with the increase of fertilizer application rate the contents of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in all the organs of the young rubber plants increased except phosphorus content in the leaves and potassium content in the trunk that decreased slightly, and that the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium were mainly distributed in the leaves, accounting for more than 30%. The first limiting factor affecting the growth of the young rubber plants is nitrogen. In normal rubber production young rubber plants can be applied with formula fertilizer formulated with nitrogen at an appropriately higher ratio and phosphorus and potassium at a lower ratio on the basis of the existing fertilizer formula, and at the same time organic fertilizer should be applied to improve the soil organic nitrogen content.
Research and analysis of the plant nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium ecological stoichiometry can reflect the distribution status and mutual correlation of the nutrients in different organs of the plant, and determine the nutrient-limiting factors of the plant in the different environments. Young rubber plants transplanted were treated with fertilizer at four different rates in an experiment with random complete block design and three replicates each treatment and then sampled, and the contents of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and their ecological stoichiometric characteristics in different organs of the young rubber plants collected were determined and analyzed to explore the characteristics of the distribution and utilization of soil nutrients in the young rubber plants under fertilizer treatment. The results showed that with the increase of fertilizer application rate the contents of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in all the organs of the young rubber plants increased except phosphorus content in the leaves and potassium content in the trunk that decreased slightly, and that the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium were mainly distributed in the leaves, accounting for more than 30%. The first limiting factor affecting the growth of the young rubber plants is nitrogen. In normal rubber production young rubber plants can be applied with formula fertilizer formulated with nitrogen at an appropriately higher ratio and phosphorus and potassium at a lower ratio on the basis of the existing fertilizer formula, and at the same time organic fertilizer should be applied to improve the soil organic nitrogen content.
2022, 13(5): 524-531.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.015
Abstract:
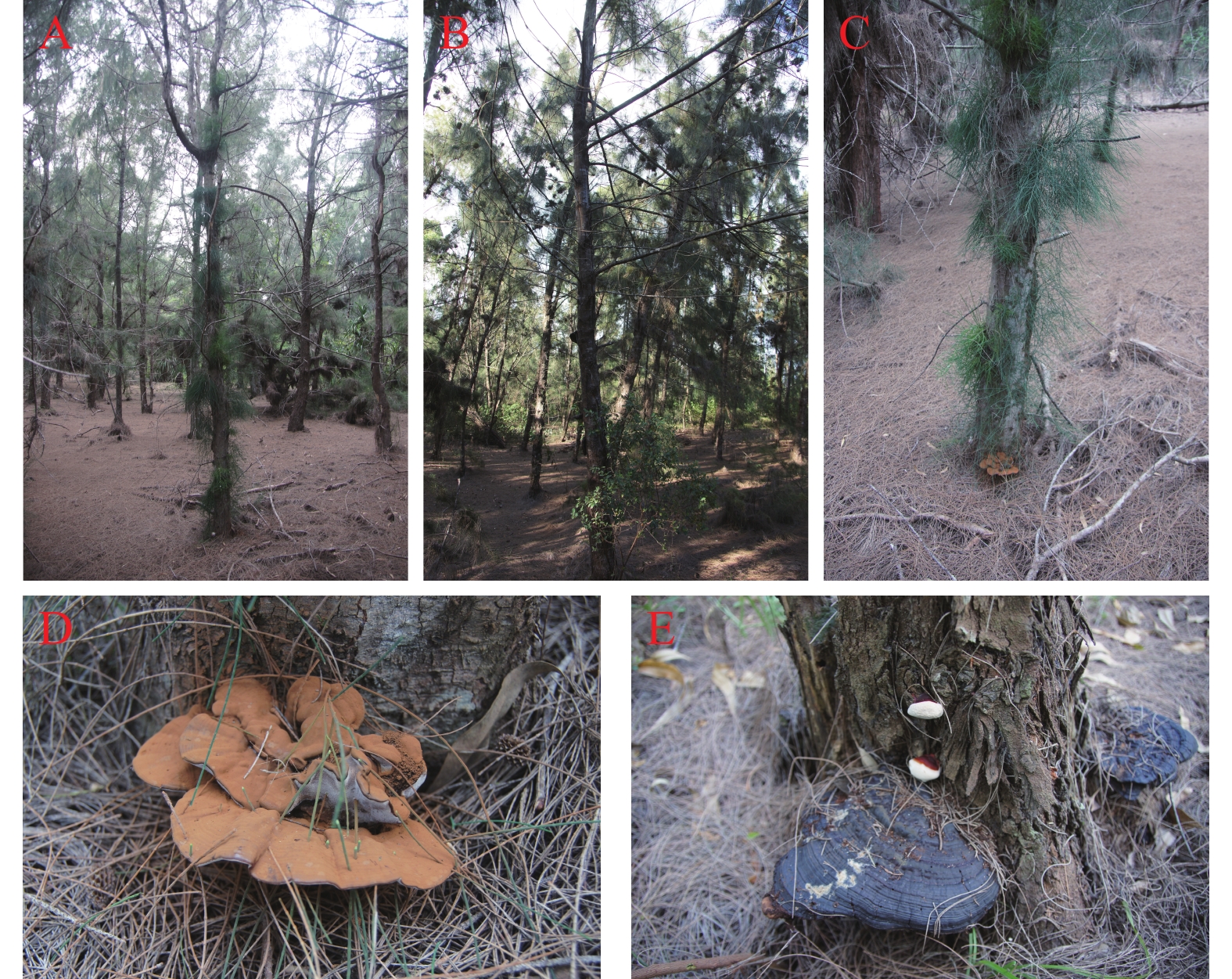
A new stem rot caused by Ganoderma sp. was found on Casuarina equisetifolia growing in Qizi Bay, Changjiang County, Hainan Province. A representative strain HNCJ201801001 was isolated from basidiocarps of the pathogen by tissue isolation method. The pathogenicity determination, basidiocarp induction and morphological identification of the strain were carried out, a phylogenetic tree using rDNA-ITS and LSU genes was constructed for analysis of the strain, and the biological characteristics of the strain were determined. According to the results of morphological and molecular detection, the pathogen of C. equisetifolia stem rot in Qizi Bay, Changjiang County, Hainan Province was identified as Ganoderma boninense. The biological characteristics of G. boninense were determined and the results showed that the growth of G. boninense was optimum when cultured at temperature 28 ℃, pH5.0 in dark. Dark condition was more conducive to mycelial growth of G. boninense, and G. boninense grew better on PDA and PSA mediums than on the other mediums.
A new stem rot caused by Ganoderma sp. was found on Casuarina equisetifolia growing in Qizi Bay, Changjiang County, Hainan Province. A representative strain HNCJ201801001 was isolated from basidiocarps of the pathogen by tissue isolation method. The pathogenicity determination, basidiocarp induction and morphological identification of the strain were carried out, a phylogenetic tree using rDNA-ITS and LSU genes was constructed for analysis of the strain, and the biological characteristics of the strain were determined. According to the results of morphological and molecular detection, the pathogen of C. equisetifolia stem rot in Qizi Bay, Changjiang County, Hainan Province was identified as Ganoderma boninense. The biological characteristics of G. boninense were determined and the results showed that the growth of G. boninense was optimum when cultured at temperature 28 ℃, pH5.0 in dark. Dark condition was more conducive to mycelial growth of G. boninense, and G. boninense grew better on PDA and PSA mediums than on the other mediums.
2022, 13(5): 532-539.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.05.016
Abstract:
Biological control plays an important role in agricultural production, and insect natural enemies has an incalculable role in biocontrol. The rearing and releasing of insect natural enemies is an important means of sustainable pest management. Literature was reviewed to summarize the production of the main insect natural enemy species and its problems in China. The insect natural enemy species were limited, small in production scale, low in mechanization level and poor in support service, and farmers were poorly aware of the importance of biocontrol. In this context a countermeasure was suggested based on the review to provide reference for production and application of the insect natural enemies. The countermeasure include promotion of the publicity and guidance of biocontrol, introduction of more insect natural enemy species, improvement of rearing and production techniques and technical facilities, enhancement of packaging, transport and services of the insect natural enemies, boosting of quality inspection and test, reducing of production cost for the insect natural enemies, strengthening of researches on necessary techniques for the application of the insect natural enemies in the field.
Biological control plays an important role in agricultural production, and insect natural enemies has an incalculable role in biocontrol. The rearing and releasing of insect natural enemies is an important means of sustainable pest management. Literature was reviewed to summarize the production of the main insect natural enemy species and its problems in China. The insect natural enemy species were limited, small in production scale, low in mechanization level and poor in support service, and farmers were poorly aware of the importance of biocontrol. In this context a countermeasure was suggested based on the review to provide reference for production and application of the insect natural enemies. The countermeasure include promotion of the publicity and guidance of biocontrol, introduction of more insect natural enemy species, improvement of rearing and production techniques and technical facilities, enhancement of packaging, transport and services of the insect natural enemies, boosting of quality inspection and test, reducing of production cost for the insect natural enemies, strengthening of researches on necessary techniques for the application of the insect natural enemies in the field.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 1895KB
PDF 1895KB







 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS