2022 Vol. 13, No. 6
2022, 13(6): 541-549.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.001
Abstract:
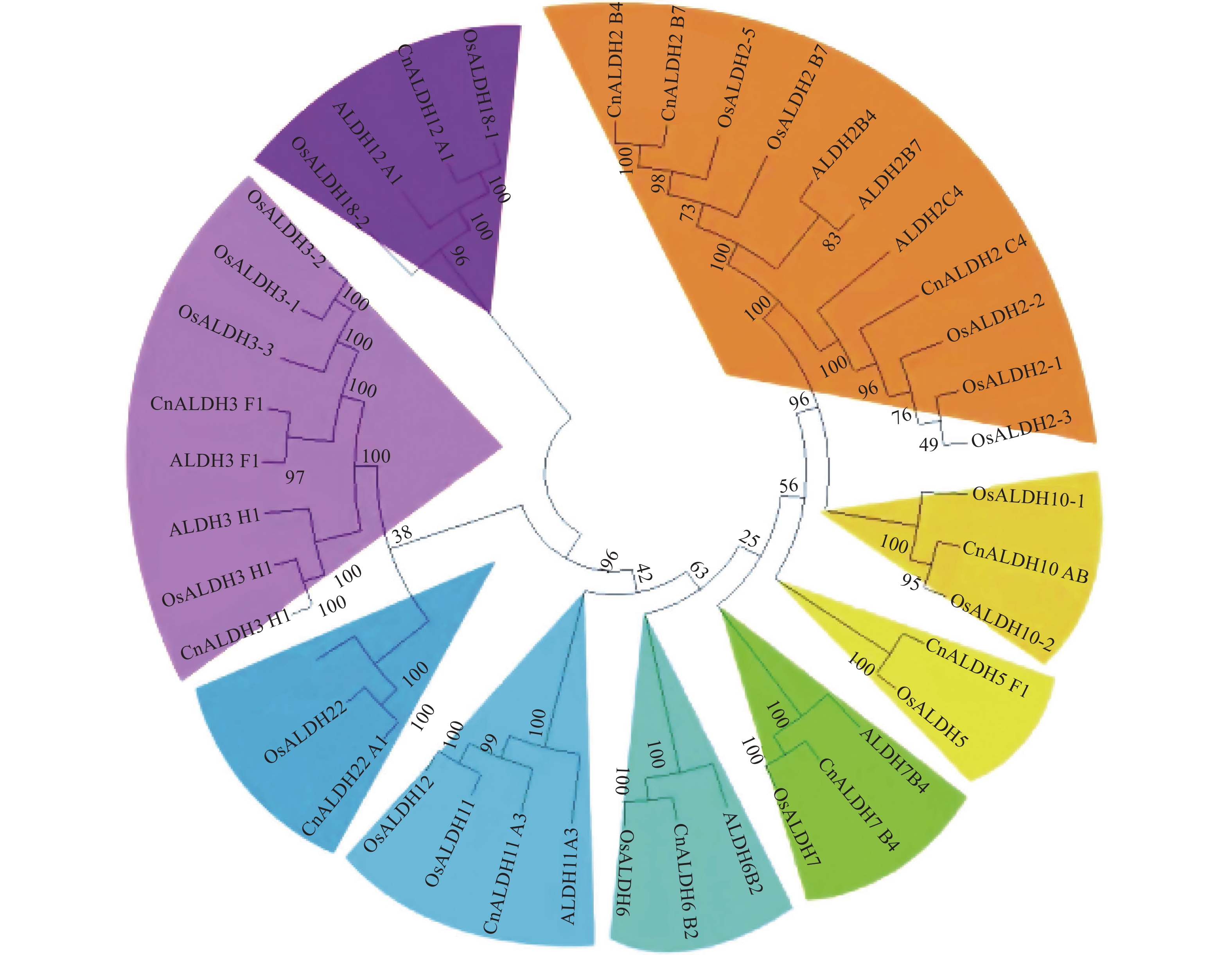
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), which dehydrogenates aldehydes into carboxylic acids, plays an important role in plant stress, development and fragrance synthesis. The protein sequences of OsALDH gene were downloaded and compared with the protein database of coconut, and 12 CnALDH genes were identified, which belonged to 9 subfamilies. The results showed that the isoelectric points of amino acids encoded by ALDH ranged from 5.35 to 8.68, and most of them were distributed in chloroplasts. Expression profile analysis showed that all ALDH gene family members were highly expressed in coconut young leaves except CnALDH12_A1 and CnALDH22_A1. CnALDH10_A8 showed constitutive expression in different tissues and at different periods, suggesting that CnALDH10_A8 is an indispensable gene involved in some basic functions in coconut.
Aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), which dehydrogenates aldehydes into carboxylic acids, plays an important role in plant stress, development and fragrance synthesis. The protein sequences of OsALDH gene were downloaded and compared with the protein database of coconut, and 12 CnALDH genes were identified, which belonged to 9 subfamilies. The results showed that the isoelectric points of amino acids encoded by ALDH ranged from 5.35 to 8.68, and most of them were distributed in chloroplasts. Expression profile analysis showed that all ALDH gene family members were highly expressed in coconut young leaves except CnALDH12_A1 and CnALDH22_A1. CnALDH10_A8 showed constitutive expression in different tissues and at different periods, suggesting that CnALDH10_A8 is an indispensable gene involved in some basic functions in coconut.
2022, 13(6): 550-557.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.002
Abstract:
Xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (XTH) is a key enzyme in plant cell wall remodeling and plays an important role in plant growth and development. Previously, we screened the differentially expressed gene XTH23 related to the male sterility in Hevea brasiliensis by transcriptome sequencing. The HbXTH23 gene expression in different organic tissues and male flowers at different development stages was then analyzed by using qRT-PCR, and the location of specific expression of HbXTH23 gene in the male flowers was analyzed by using mRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (mRNA-FISH). The qRT-PCR results showed that HbXTH23 gene expression was significantly higher in male flowers of male sterile varieties (MS) than in male flowers of male fertile varieties (MF), and also significantly higher than in other tissues, and was almost not expressed in latex. HbXTH23 gene expression in MF at the three stages, microspore mother cell, tetrad and mononuclear microspore, presented a rising trend, and the expression in MS increased first and then decreased. And the highest difference in expression between MF and MS was at the tetrad stage. The results obtained by mRNA - FISH showed that HbXTH23 gene was mainly expressed in filaments (style) and the anther wall. It was speculated that the abnormal expression in the filaments (style) and anther wall may be one of the causes of male flower sterility. The open reading frame of HbXTH23 was 861 bp, and encoded a polypeptide of 286 amino acids with a relative molecular weight of 31.95 kDa and a theoretical isoelectric point of 7.62. The grand average hydropathy (GRAVY) score of the protein was −0.288, and the hydropathy values of amino acids in the sequence were mostly distributed below zero, which indicated that the protein was hydrophilic (hydrophobic). Subcellular localization predicted that HbXTH23 protein existed in cell wall and cytoplasm. It had a signal peptide, and the shear site of the signal peptide was located between the 26th and 27th amino acids. HbXTH23 was closely related to Mucuna pruriens and Nicotiana attenuata protein. Thes study can provide a scientific basis for the further study of the molecular mechanism of male sterility and the breeding of Hevea brasiliensis.
Xyloglucan endotransglucosylase/hydrolase (XTH) is a key enzyme in plant cell wall remodeling and plays an important role in plant growth and development. Previously, we screened the differentially expressed gene XTH23 related to the male sterility in Hevea brasiliensis by transcriptome sequencing. The HbXTH23 gene expression in different organic tissues and male flowers at different development stages was then analyzed by using qRT-PCR, and the location of specific expression of HbXTH23 gene in the male flowers was analyzed by using mRNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (mRNA-FISH). The qRT-PCR results showed that HbXTH23 gene expression was significantly higher in male flowers of male sterile varieties (MS) than in male flowers of male fertile varieties (MF), and also significantly higher than in other tissues, and was almost not expressed in latex. HbXTH23 gene expression in MF at the three stages, microspore mother cell, tetrad and mononuclear microspore, presented a rising trend, and the expression in MS increased first and then decreased. And the highest difference in expression between MF and MS was at the tetrad stage. The results obtained by mRNA - FISH showed that HbXTH23 gene was mainly expressed in filaments (style) and the anther wall. It was speculated that the abnormal expression in the filaments (style) and anther wall may be one of the causes of male flower sterility. The open reading frame of HbXTH23 was 861 bp, and encoded a polypeptide of 286 amino acids with a relative molecular weight of 31.95 kDa and a theoretical isoelectric point of 7.62. The grand average hydropathy (GRAVY) score of the protein was −0.288, and the hydropathy values of amino acids in the sequence were mostly distributed below zero, which indicated that the protein was hydrophilic (hydrophobic). Subcellular localization predicted that HbXTH23 protein existed in cell wall and cytoplasm. It had a signal peptide, and the shear site of the signal peptide was located between the 26th and 27th amino acids. HbXTH23 was closely related to Mucuna pruriens and Nicotiana attenuata protein. Thes study can provide a scientific basis for the further study of the molecular mechanism of male sterility and the breeding of Hevea brasiliensis.
2022, 13(6): 558-561.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.003
Abstract:
Wenchang Chicken is a local excellent broiler breed in Hainan, which has the advantages of strong adaptability, heat resistance and good meat quality. At present, there is a problem with high abdominal fat rate in Wenchang Chickens. Excessive fat deposition is undesirable since it decreases feed efficiency, and affects human health. Adiponectin, which is secreted by mature adipose cells, plays an important role in lipid metabolism. CDH13 is the third type of receptor for adiponectin, and the function of chicken CDH13 has not yet been reported. Therefore, the expression pattern of CDH13 in different tissues and during the growth and development of the abdominal adipose tissue of Wenchang Chickens was determined by using the RT-qPCR. The results showed that the gene CDH13 had higher mRNA abundance in the heart, ileum, adipose tissue, cerebellum and gizzard, and that adiponectin had similar trend of transcriptional levels to CDH13. The gene CDH13 was stably and highly expressed during the growth and development of abdominal adipose tissue, and its expression level was the highest at the age of the fourth week in the fattening period.
Wenchang Chicken is a local excellent broiler breed in Hainan, which has the advantages of strong adaptability, heat resistance and good meat quality. At present, there is a problem with high abdominal fat rate in Wenchang Chickens. Excessive fat deposition is undesirable since it decreases feed efficiency, and affects human health. Adiponectin, which is secreted by mature adipose cells, plays an important role in lipid metabolism. CDH13 is the third type of receptor for adiponectin, and the function of chicken CDH13 has not yet been reported. Therefore, the expression pattern of CDH13 in different tissues and during the growth and development of the abdominal adipose tissue of Wenchang Chickens was determined by using the RT-qPCR. The results showed that the gene CDH13 had higher mRNA abundance in the heart, ileum, adipose tissue, cerebellum and gizzard, and that adiponectin had similar trend of transcriptional levels to CDH13. The gene CDH13 was stably and highly expressed during the growth and development of abdominal adipose tissue, and its expression level was the highest at the age of the fourth week in the fattening period.
2022, 13(6): 562-568.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.004
Abstract:
The exosomes of antigen presenting cells (Antigen presenting cell, APC) participate in the immune response process, and can activate the adaptive immune response after carrying the antigen. As a kind of antigen-presenting cells, the related functions of poultry macrophage-derived exosomes are still unknown. The S1 protein of chicken infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) was used as the model antigen, the S1 protein was stably expressed in HD11 cells through the lentiviral expression system, and then the exosomes were separated and purified from the cell culture supernatant by ultracentrifugation. The protein immunoblot analysis, electron microscopy and particle size analysis detection showed that stable S1 protein expression can be detected in the exosomes secreted by the recombinant HD11 cells. Recombinant exosomes harboring IBV S1 protein were successfully constructed, which can provide a reference for the functional study of avian macrophage-derived exosomes in immune response and the development of poultry exosome vector vaccines.
The exosomes of antigen presenting cells (Antigen presenting cell, APC) participate in the immune response process, and can activate the adaptive immune response after carrying the antigen. As a kind of antigen-presenting cells, the related functions of poultry macrophage-derived exosomes are still unknown. The S1 protein of chicken infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) was used as the model antigen, the S1 protein was stably expressed in HD11 cells through the lentiviral expression system, and then the exosomes were separated and purified from the cell culture supernatant by ultracentrifugation. The protein immunoblot analysis, electron microscopy and particle size analysis detection showed that stable S1 protein expression can be detected in the exosomes secreted by the recombinant HD11 cells. Recombinant exosomes harboring IBV S1 protein were successfully constructed, which can provide a reference for the functional study of avian macrophage-derived exosomes in immune response and the development of poultry exosome vector vaccines.
2022, 13(6): 569-574.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.005
Abstract:
Seedlings of Vitex quinata were raised in different sizes of non-woven bags and different substrates in an experiment of a randomized block design with two factors to determine the effects of container sizes and substrates on their growth. The results showed that the container sizes and substrates had significant effects on the container seedling growth of V. quinate. The container sizes had significant effects on the height-diameter ratio, root diameter and root biomass, and highly significant effects on the seedling height, ground diameter, main root length, root volume, leaf biomass, total biomass and quality index, but no significant effects on the stem biomass and root shoot ratio. The substrates had highly significant effects on seedling height, underground diameter, taproot length, root volume, stem biomass, root biomass, total biomass and quality index, but no significant effects on height-diameter ratio, root diameter, leaf biomass and root-shoot ratio. The interaction of container sizes and substrates had significant effects on seedling height, taproot length, root volume and leaf biomass, but no significant effects on other indexes. Comprehensive evaluation of all the treatments by using a membership function showed that the combination of the container with diameter 16 cm × height 16 cm and the substrate with the mixture of yellow soil∶peat∶perlite = 4∶4∶2 had the highest average membership function value (0.97), which indicates this combination is the most suitable treatment for container seedling growth of V. quinata.
Seedlings of Vitex quinata were raised in different sizes of non-woven bags and different substrates in an experiment of a randomized block design with two factors to determine the effects of container sizes and substrates on their growth. The results showed that the container sizes and substrates had significant effects on the container seedling growth of V. quinate. The container sizes had significant effects on the height-diameter ratio, root diameter and root biomass, and highly significant effects on the seedling height, ground diameter, main root length, root volume, leaf biomass, total biomass and quality index, but no significant effects on the stem biomass and root shoot ratio. The substrates had highly significant effects on seedling height, underground diameter, taproot length, root volume, stem biomass, root biomass, total biomass and quality index, but no significant effects on height-diameter ratio, root diameter, leaf biomass and root-shoot ratio. The interaction of container sizes and substrates had significant effects on seedling height, taproot length, root volume and leaf biomass, but no significant effects on other indexes. Comprehensive evaluation of all the treatments by using a membership function showed that the combination of the container with diameter 16 cm × height 16 cm and the substrate with the mixture of yellow soil∶peat∶perlite = 4∶4∶2 had the highest average membership function value (0.97), which indicates this combination is the most suitable treatment for container seedling growth of V. quinata.
2022, 13(6): 575-581.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.006
Abstract:
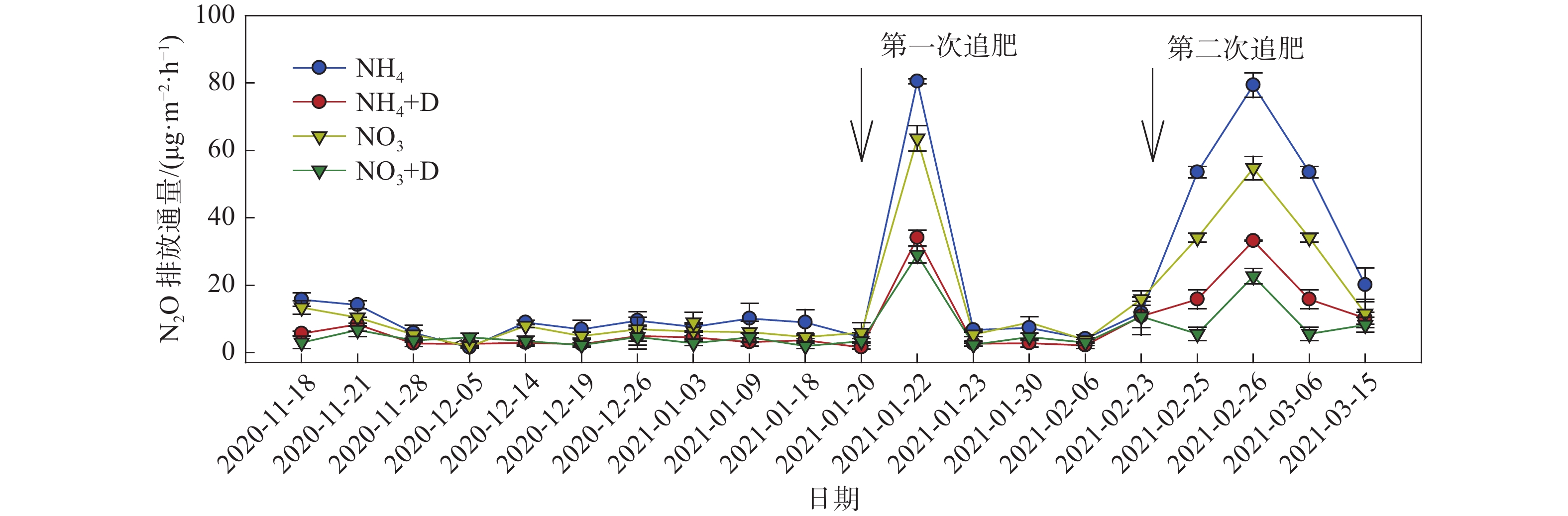
Chili peppers were applied with nitrogen fertilizer combined with nitrification inhibitors to analyze nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from chili pepper fields in Hainan, the tropical area in China, by static box-gas chromatography method. The results showed that the variation of N2O emission flux from the chili pepper fields ranged from 1.51 to 80.53 μg·m−2·h−1. The soil N2O emission flux was higher in the NH4 treatment than in the NO3 treatment. The maximum peak value of N2O emission in the NH4 treatment was 80.53 μg·m−1 m−2·h−1, and the Compared with the single treatment with nitrogen fertilizer, both the NH4 and the NO3 combined with dicyandiamide (DCD) treatment significantly reduced the cumulative N2O emissions by 59% and 49%, respectively, and their effects on the cumulative N2O emissions were not significantly different. The chili pepper in the NH4 treatment and the NO3 treatment yielded 18.06 and 11.41 tons/ha, respectively, with the yield in the former treatment increasing by 58.28%, indicating a significant difference in yield between the two treatments. After applying with DCD, there was no significant difference of peper yield between the NH4+DCD and the NO3+DCD treatments. Together, these results indicated that the application of ammonium nitrogen fertilizer combined with DCD can significantly reduce N2O emissions from the vegetable fields while maintaining high peper yield.
Chili peppers were applied with nitrogen fertilizer combined with nitrification inhibitors to analyze nitrous oxide (N2O) emissions from chili pepper fields in Hainan, the tropical area in China, by static box-gas chromatography method. The results showed that the variation of N2O emission flux from the chili pepper fields ranged from 1.51 to 80.53 μg·m−2·h−1. The soil N2O emission flux was higher in the NH4 treatment than in the NO3 treatment. The maximum peak value of N2O emission in the NH4 treatment was 80.53 μg·m−1 m−2·h−1, and the Compared with the single treatment with nitrogen fertilizer, both the NH4 and the NO3 combined with dicyandiamide (DCD) treatment significantly reduced the cumulative N2O emissions by 59% and 49%, respectively, and their effects on the cumulative N2O emissions were not significantly different. The chili pepper in the NH4 treatment and the NO3 treatment yielded 18.06 and 11.41 tons/ha, respectively, with the yield in the former treatment increasing by 58.28%, indicating a significant difference in yield between the two treatments. After applying with DCD, there was no significant difference of peper yield between the NH4+DCD and the NO3+DCD treatments. Together, these results indicated that the application of ammonium nitrogen fertilizer combined with DCD can significantly reduce N2O emissions from the vegetable fields while maintaining high peper yield.
2022, 13(6): 582-588.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.007
Abstract:
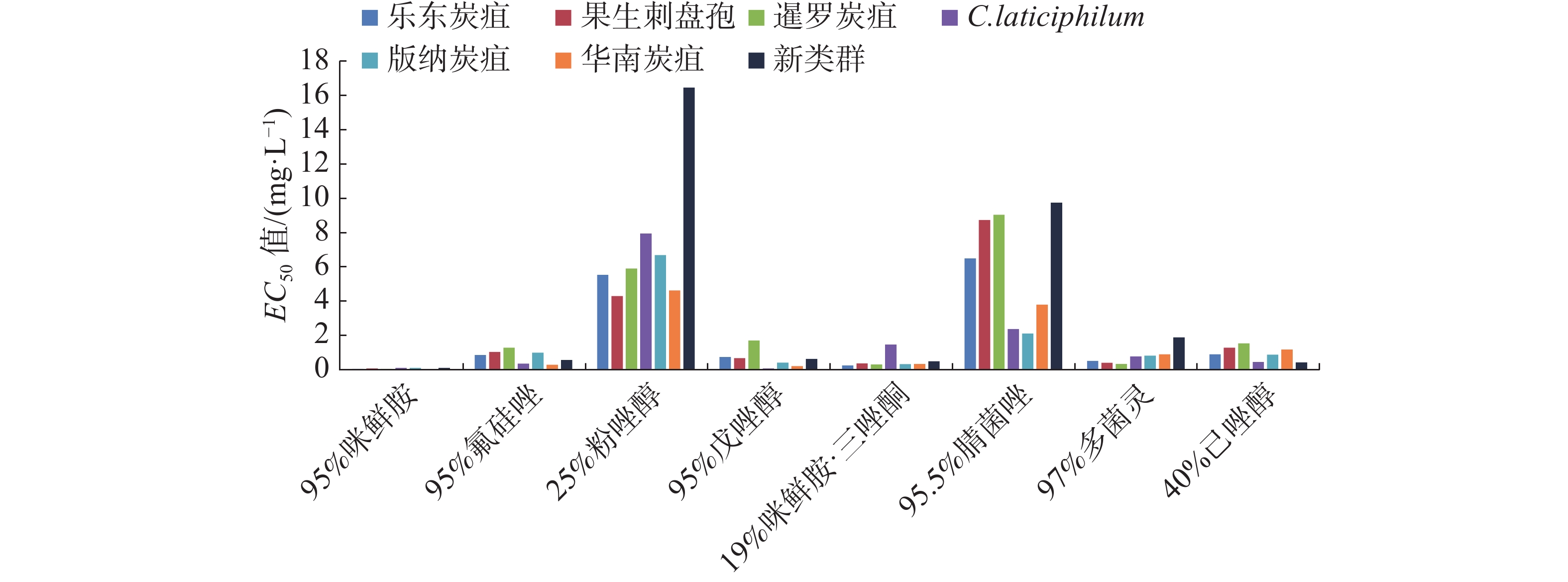
In order to understand the sensitivity of various Colletotrichum spp. to different fungicides in different species complexes in various rubber planting areas in China, the sensitivity of C. ledongense, C. fructicola and C. siamense in the C. glocosporioides species complex and C. bannanense, C. laticiphilum, new species groups, and C. australisinense in the C. acutalum species complex to 8 fungicides were determined by growth rate method, based on which two fungicides were mixed at different ratios to evaluate their effectiveness. The results showed that 17 strains of Colletotrichum spp. from rubber anthracnose were the most sensitive to prochloraz, with EC50 values of 0.001 1 − 0.218 7 mg·L−1, averaging 0.085 3 mg·L−1. The fungicides prochloraz, carbendazim, flusilazole, tebuconazole, hexazolol and the mixtures of prochloraz and triadimefon had a significant inhibitory activity against the mycelial growth of Colletotrichum spp, the pathogenic fungi from the rubber anthracnose. Nitridazole and fenoxazole had a poor inhibitory effect on the mycelial growth of the pathogenic fungi. Most ergosterol biological inhibitors represented by triazole had a significant inhibitory effect on the mycelial growth of the pathogenic fungi. The new species groups had a poor sensitivity to fenoxazole, nitridazole and carbendazim. The mixtures of prochloraz and tebuconazole at the respective mix ratios of 7∶3 and 4∶6 had the best inhibitory effect on C. siamense and C. australisinense which were dominant species from the rubber anthracnose.
In order to understand the sensitivity of various Colletotrichum spp. to different fungicides in different species complexes in various rubber planting areas in China, the sensitivity of C. ledongense, C. fructicola and C. siamense in the C. glocosporioides species complex and C. bannanense, C. laticiphilum, new species groups, and C. australisinense in the C. acutalum species complex to 8 fungicides were determined by growth rate method, based on which two fungicides were mixed at different ratios to evaluate their effectiveness. The results showed that 17 strains of Colletotrichum spp. from rubber anthracnose were the most sensitive to prochloraz, with EC50 values of 0.001 1 − 0.218 7 mg·L−1, averaging 0.085 3 mg·L−1. The fungicides prochloraz, carbendazim, flusilazole, tebuconazole, hexazolol and the mixtures of prochloraz and triadimefon had a significant inhibitory activity against the mycelial growth of Colletotrichum spp, the pathogenic fungi from the rubber anthracnose. Nitridazole and fenoxazole had a poor inhibitory effect on the mycelial growth of the pathogenic fungi. Most ergosterol biological inhibitors represented by triazole had a significant inhibitory effect on the mycelial growth of the pathogenic fungi. The new species groups had a poor sensitivity to fenoxazole, nitridazole and carbendazim. The mixtures of prochloraz and tebuconazole at the respective mix ratios of 7∶3 and 4∶6 had the best inhibitory effect on C. siamense and C. australisinense which were dominant species from the rubber anthracnose.
2022, 13(6): 589-594.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.008
Abstract:
In order to clarify the pathogen species of anthracnose disease infecting Lagetstroemia speciosa to provide a theoretical basis for further study on its pathogenesis, diagnosis and control, the leaves of L. speciosa infected with anthracnose disease were sampled and isolated, and the isolates were determined in terms of pathogenicity and morphological characteristics and analyzed by using ITS, ACT, GAPDH and CHS sequence analysis. The isolates were identified as Colletotrichum aenigma, a pathogen causing anthracnose disease of L. speciosa. Biological characteristics tests showed that the pathogen had optimum mycelial growth when cultured at 30 ℃ on the PDA medium with pH 8. Dark culture was conducive to mycelial growth of the pathogen, and the mycelia of the pathogen grew fast on both the PDA and PSA media.
In order to clarify the pathogen species of anthracnose disease infecting Lagetstroemia speciosa to provide a theoretical basis for further study on its pathogenesis, diagnosis and control, the leaves of L. speciosa infected with anthracnose disease were sampled and isolated, and the isolates were determined in terms of pathogenicity and morphological characteristics and analyzed by using ITS, ACT, GAPDH and CHS sequence analysis. The isolates were identified as Colletotrichum aenigma, a pathogen causing anthracnose disease of L. speciosa. Biological characteristics tests showed that the pathogen had optimum mycelial growth when cultured at 30 ℃ on the PDA medium with pH 8. Dark culture was conducive to mycelial growth of the pathogen, and the mycelia of the pathogen grew fast on both the PDA and PSA media.
2022, 13(6): 595-604.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.009
Abstract:
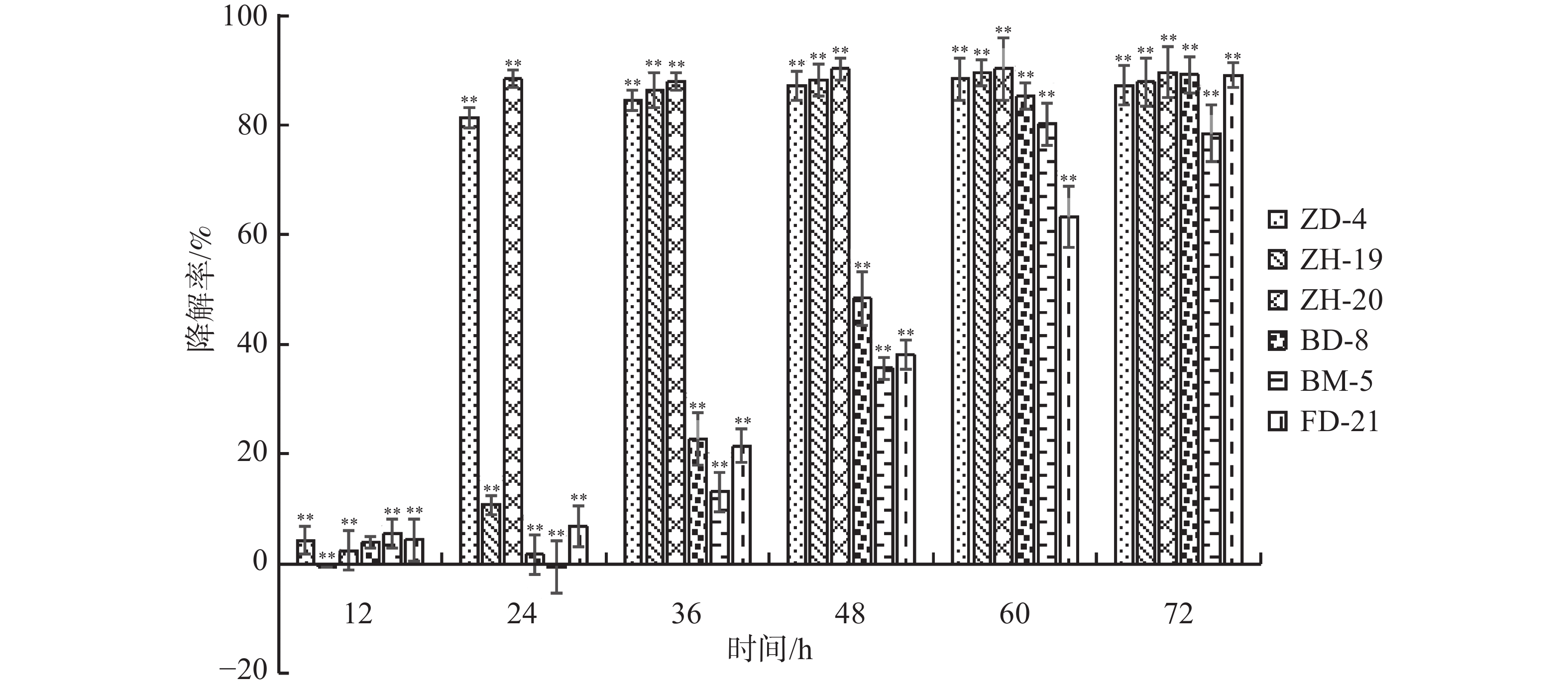
In order to explore the use of beneficial microorganisms to degrade root autotoxic substances, alleviate the biological obstacles of continuous cropping of vanilla (Vanilla planifolia Andr.), and reserve beneficial microbial resources, microbial strains degrading phenolic acids which are autotoxic substances in the rhizosphere of vanilla plantations were screened by using the traditional isolation and culture method. Degrading activity of the isolated microbial strains against the phenolic acids in culture medium and continuous cropping soil and their plate inhibition ability against pathogenic agents were determined, and 6 microbial strains were isolated from the rhizosphere of vanilla plantations with continuous cropping, which were labelled fungi BM-5, FD-21 and BD-8, and bacteria ZD-4, ZH-19 and ZH-20. The fungal strain FD-21 when cultured in shake flasks for 72 h, had degradation rates of 78.87%, 89.5% and 93.62% for p-benzoic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid and salicylic acid, respectively, but it had degradation rates of 43.5%, 34.2% and 67.28%, respectively, when thermostatically cultured for 7 days after its inoculation of the continuous cropping soil. The plate bacteriostatic effect test showed that the 6 strains had a certain antagonistic effect on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae, a pathogen of vanilla soil-borne Fusarium wilt disease. The bacterial strains ZH-19 and ZH-20 had the highest inhibition rates against F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae, which were 82.87% and 82.94%, respectively, and the fungal strain FD-21 had an inhibition rate of 45.49% against F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae. 16S rRNA and ITS sequence alignment showed that the bacterial strain ZD-4 was identified as Bacillus subtilis, the bacterial strain ZH-19 as Bacillus anthracis, the bacterial strain ZH-20 as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the fungal strain BM-5 as Talaromyces sp., the fungal strain FD-21 as Penicillium sp., the fungal strain BD-8 as Penicillium citrinum. This indicates that the screened microbial strains can degrade autotoxic phenolic acids secreted by the vanilla roots and have an antagonistic effect on F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae.
In order to explore the use of beneficial microorganisms to degrade root autotoxic substances, alleviate the biological obstacles of continuous cropping of vanilla (Vanilla planifolia Andr.), and reserve beneficial microbial resources, microbial strains degrading phenolic acids which are autotoxic substances in the rhizosphere of vanilla plantations were screened by using the traditional isolation and culture method. Degrading activity of the isolated microbial strains against the phenolic acids in culture medium and continuous cropping soil and their plate inhibition ability against pathogenic agents were determined, and 6 microbial strains were isolated from the rhizosphere of vanilla plantations with continuous cropping, which were labelled fungi BM-5, FD-21 and BD-8, and bacteria ZD-4, ZH-19 and ZH-20. The fungal strain FD-21 when cultured in shake flasks for 72 h, had degradation rates of 78.87%, 89.5% and 93.62% for p-benzoic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid and salicylic acid, respectively, but it had degradation rates of 43.5%, 34.2% and 67.28%, respectively, when thermostatically cultured for 7 days after its inoculation of the continuous cropping soil. The plate bacteriostatic effect test showed that the 6 strains had a certain antagonistic effect on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. vanillae, a pathogen of vanilla soil-borne Fusarium wilt disease. The bacterial strains ZH-19 and ZH-20 had the highest inhibition rates against F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae, which were 82.87% and 82.94%, respectively, and the fungal strain FD-21 had an inhibition rate of 45.49% against F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae. 16S rRNA and ITS sequence alignment showed that the bacterial strain ZD-4 was identified as Bacillus subtilis, the bacterial strain ZH-19 as Bacillus anthracis, the bacterial strain ZH-20 as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, the fungal strain BM-5 as Talaromyces sp., the fungal strain FD-21 as Penicillium sp., the fungal strain BD-8 as Penicillium citrinum. This indicates that the screened microbial strains can degrade autotoxic phenolic acids secreted by the vanilla roots and have an antagonistic effect on F. oxysporum f. sp. vanillae.
2022, 13(6): 605-613.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.010
Abstract:
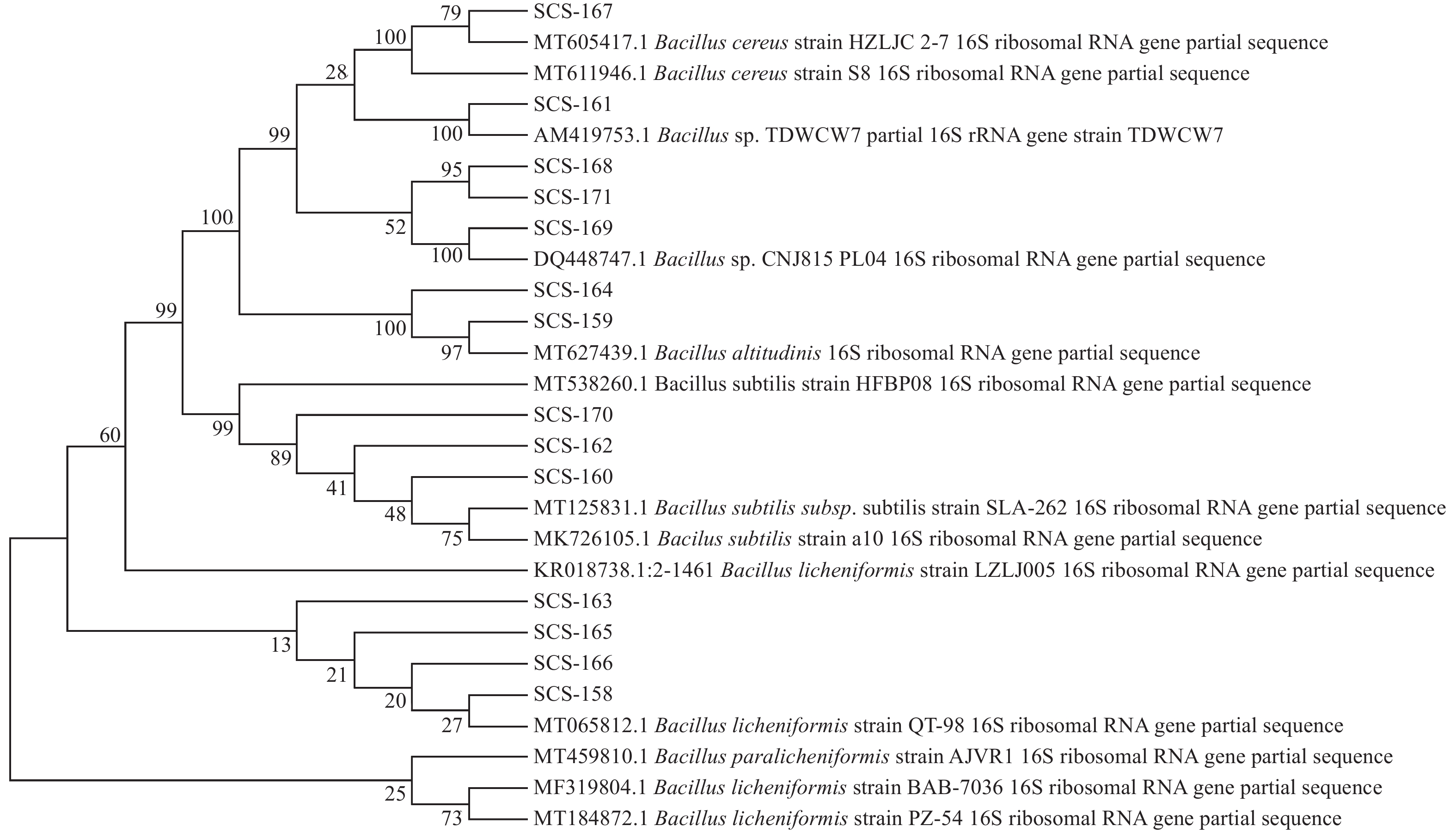
Fourteen strains of Bacillus spp, named SCS-158 to SCS-171, were selected to determine their bacteriostatic effect against 40 strains of aquatic pathogens (bacterial indicators) by the streak plate method. The results show that the whole bacterial solutions of 14 Bacillus strains cultured for 24h had the highest bacteriostatic rate, up to 20.00%, of which those of the strains SCS-160, SCS-162 and SCS-170 had an inhibitory effect on all the strains of Aeromonas vickerii tested. Of the 14 Bacillus strains 10 strains had an inhibitory effect on the bacterial indicator Staphylococcus albicans 18QW206. The 24 h cultured supernatant and the 48 h cultured whole bacterial solution had a lower inhibitory effect on the bacterial indicator S. albicans 18QW206 as compared with the 24 h cultured whole bacterial solution. The inhibitory effect of the 24 h cultured supernatant of the strain SCS-162 decreased most obviously, with the diameter of the inhibition zone dropping by 28.55%, while the diameter of the inhibition zone of the strain SCS-164 dropped the least by 5.35%. In addition, the inhibition zone of the 48 h cultured whole bacterial solution of the strain SCS-160 decreased the most by 42.86%, while that of the strain SCS-163 dropped the least by 4.19%. These results indicate that Bacillus spp. had bacteriostatic effect on the aquatic pathogens.
Fourteen strains of Bacillus spp, named SCS-158 to SCS-171, were selected to determine their bacteriostatic effect against 40 strains of aquatic pathogens (bacterial indicators) by the streak plate method. The results show that the whole bacterial solutions of 14 Bacillus strains cultured for 24h had the highest bacteriostatic rate, up to 20.00%, of which those of the strains SCS-160, SCS-162 and SCS-170 had an inhibitory effect on all the strains of Aeromonas vickerii tested. Of the 14 Bacillus strains 10 strains had an inhibitory effect on the bacterial indicator Staphylococcus albicans 18QW206. The 24 h cultured supernatant and the 48 h cultured whole bacterial solution had a lower inhibitory effect on the bacterial indicator S. albicans 18QW206 as compared with the 24 h cultured whole bacterial solution. The inhibitory effect of the 24 h cultured supernatant of the strain SCS-162 decreased most obviously, with the diameter of the inhibition zone dropping by 28.55%, while the diameter of the inhibition zone of the strain SCS-164 dropped the least by 5.35%. In addition, the inhibition zone of the 48 h cultured whole bacterial solution of the strain SCS-160 decreased the most by 42.86%, while that of the strain SCS-163 dropped the least by 4.19%. These results indicate that Bacillus spp. had bacteriostatic effect on the aquatic pathogens.
2022, 13(6): 614-621.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.011
Abstract:
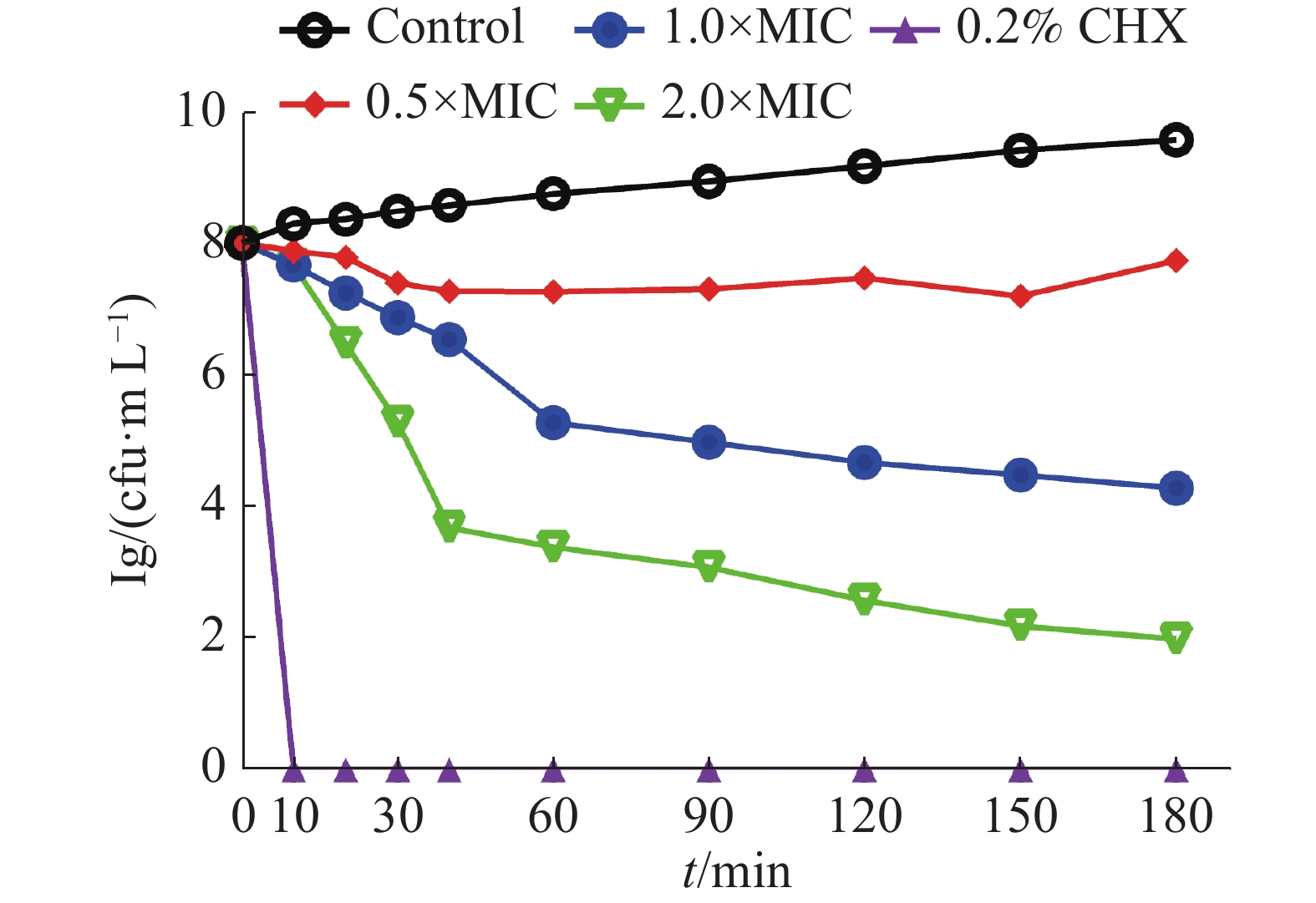
Objective The present study aimed to evaluate the antibacterial effect of p-methoxybezaldehyde on Streptococcus mutans, and to clarify its probable mechanism. Methods Determining the antibacterial and antibiofilm activity of p-methoxybezaldehyde against Streptococcus mutans by time-kill curve, cell membrane integrity, bacterial hydrophobicity, biofilm quantification and RT-qPCR experiments. Results The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of p-methoxybezaldehyde against Streptococcus mutans were 4 g·L−1 and 8 g·L−1. The result showed that the contents of protein and nucleic acid gradually increased with the increase of p-methoxybezaldehyde concentration. Confocal laser scanning microscopy revealed S. mutans at 1 × MIC concentration of p-methoxybezaldehyde, resulting in changed membrane integrity in contrast to control groups. Conclusion The antibiofilm activity of p-methoxybezaldehyde against S. mutans was determined by the crystal violet method. p-methoxybezaldehyde exerts S. mutans antibiofilm activity by changing the hydrophobicity of S. mutans and down-regulating gene expression.These results indicate the potential of p-methoxybezaldehyde as a natural antibacterial agent to be further developed as potential anti-caries agents.
2022, 13(6): 622-627.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.012
Abstract:
In order to evaluate the effect of physcion, a new veterimary additive, on the performance of laying hens, and to assess its alternative to antibiotics in livestock and poultry industry 2 250 laying hens aged 31 weeks were randomly divided into 4 physcion treatment groups (400, 800, 1 000, 1 200 mg·kg−1), an oregano oil control group and a blank control group. They were fed with diets supplemented with physion or oregano oil or with basal diet for 14 days in a run and their daily performance and production performance were observed and determined. The results showed that all the physcion treatment groups had a significantly lower culling rate than the blank control group and the oregano oil control group, giving a dose response of physcion on the laying hens to a given extent. Moreover, the 400 mg·kg−1 and 1 000 mg·kg−1 physcion treatment groups had the significantly higher average egg weight than the blank control group (P<0.05), and the 800 mg·kg−1 physcion treatment group had a significantly higher qualified egg rate than the blank control group (P<0.05). With prolonging administration of physion to the laying hens, the qualified egg rate was also observed to increase gradually in the 400 mg/kg, 800 mg/kg, and 1 000 mg·kg−1 physion treatment groups, a significant difference between the laying hens prior to and after administration (P<0.05). Compared to the blank control group, both 800 mg·kg−1 and 1 200 mg·kg−1 physcion treatment groups had a higher egg-laying rate (P<0.05). No statistical difference was found in various indexes between the physcion treatment groups and the oregano oil group. Based on the aforementioned evidence, physcion is a promising feed additive to enhance production performance and reduce culling rate of laying hens, and is a new alternative to antibiotics.
In order to evaluate the effect of physcion, a new veterimary additive, on the performance of laying hens, and to assess its alternative to antibiotics in livestock and poultry industry 2 250 laying hens aged 31 weeks were randomly divided into 4 physcion treatment groups (400, 800, 1 000, 1 200 mg·kg−1), an oregano oil control group and a blank control group. They were fed with diets supplemented with physion or oregano oil or with basal diet for 14 days in a run and their daily performance and production performance were observed and determined. The results showed that all the physcion treatment groups had a significantly lower culling rate than the blank control group and the oregano oil control group, giving a dose response of physcion on the laying hens to a given extent. Moreover, the 400 mg·kg−1 and 1 000 mg·kg−1 physcion treatment groups had the significantly higher average egg weight than the blank control group (P<0.05), and the 800 mg·kg−1 physcion treatment group had a significantly higher qualified egg rate than the blank control group (P<0.05). With prolonging administration of physion to the laying hens, the qualified egg rate was also observed to increase gradually in the 400 mg/kg, 800 mg/kg, and 1 000 mg·kg−1 physion treatment groups, a significant difference between the laying hens prior to and after administration (P<0.05). Compared to the blank control group, both 800 mg·kg−1 and 1 200 mg·kg−1 physcion treatment groups had a higher egg-laying rate (P<0.05). No statistical difference was found in various indexes between the physcion treatment groups and the oregano oil group. Based on the aforementioned evidence, physcion is a promising feed additive to enhance production performance and reduce culling rate of laying hens, and is a new alternative to antibiotics.
2022, 13(6): 628-633.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.013
Abstract:
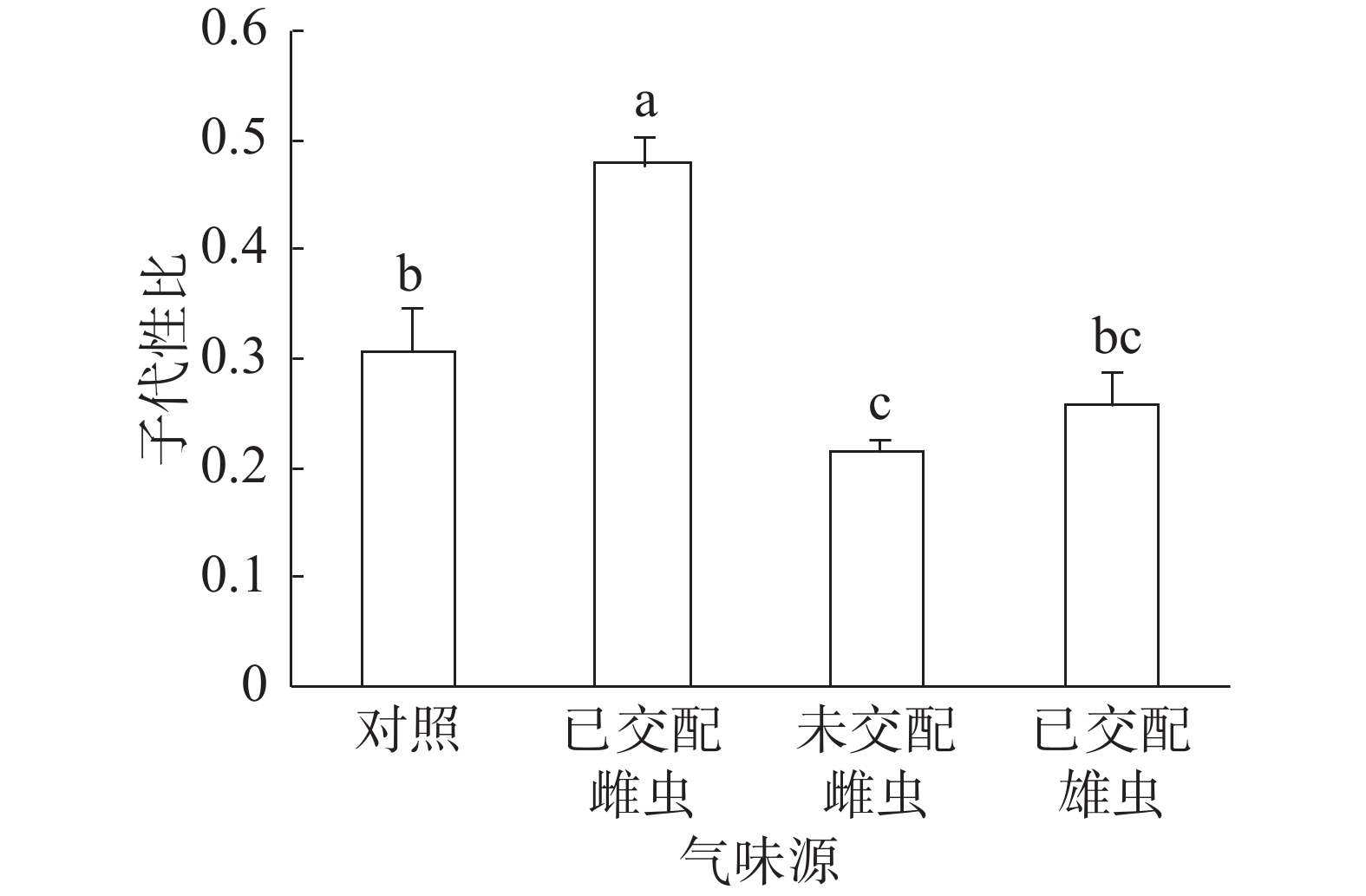
To explore the effects of odors from conspecific adults on sex ratio adjustment during mating by bean flower thrips, Megalurothrips usitatus, one of main pests on Vigna unguiculata . In this paper, a pair of newly emerged male and female of the been flower thrips was exposed for 24 hours to the odors from 6 mated females, 6 virgin females, 6 mated males and no adult as control, respectively. Then the focal female was transferred to a glass tube containing a section of a young cowpea pod for her feeding and oviposition. The pod was replaced daily until the focal female died. The pod containing eggs was transferred to a new glass tube for the offsprings’ growth. Oviposition days of the focal females were recorded, and their adult offspring were sexed and counted. Sex ratios of offspring were calculated as proportion of males. The results showed that the number of female offspring per focal female for the treatment with the odor from mated females was 22.80, being significantly less than those for other treatments. The sex ratios of adult offspring produced by the thrips treated with the odors from mated and virgin females were 0.48 and 0.22, respectively, which both were significantly different from that of control (0.31). The odor from mated males, however, showed no significant effect on offspring sex ratio. The daily sex ratio at the last oviposition day for the focal females treated with the odor from mated females reached 1.00, suggesting that their sperms had been depleted. The oviposition days of the focal females did not differ among all treatments. Our research revealed that the bean flower thrips during mating can use olfactory cues to assess mating status of conspecific females, and then control the number of sperms transferred into spermathecae, thereby adjusting sex ratio of their offspring.
To explore the effects of odors from conspecific adults on sex ratio adjustment during mating by bean flower thrips, Megalurothrips usitatus, one of main pests on Vigna unguiculata . In this paper, a pair of newly emerged male and female of the been flower thrips was exposed for 24 hours to the odors from 6 mated females, 6 virgin females, 6 mated males and no adult as control, respectively. Then the focal female was transferred to a glass tube containing a section of a young cowpea pod for her feeding and oviposition. The pod was replaced daily until the focal female died. The pod containing eggs was transferred to a new glass tube for the offsprings’ growth. Oviposition days of the focal females were recorded, and their adult offspring were sexed and counted. Sex ratios of offspring were calculated as proportion of males. The results showed that the number of female offspring per focal female for the treatment with the odor from mated females was 22.80, being significantly less than those for other treatments. The sex ratios of adult offspring produced by the thrips treated with the odors from mated and virgin females were 0.48 and 0.22, respectively, which both were significantly different from that of control (0.31). The odor from mated males, however, showed no significant effect on offspring sex ratio. The daily sex ratio at the last oviposition day for the focal females treated with the odor from mated females reached 1.00, suggesting that their sperms had been depleted. The oviposition days of the focal females did not differ among all treatments. Our research revealed that the bean flower thrips during mating can use olfactory cues to assess mating status of conspecific females, and then control the number of sperms transferred into spermathecae, thereby adjusting sex ratio of their offspring.
2022, 13(6): 634-643.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.014
Abstract:
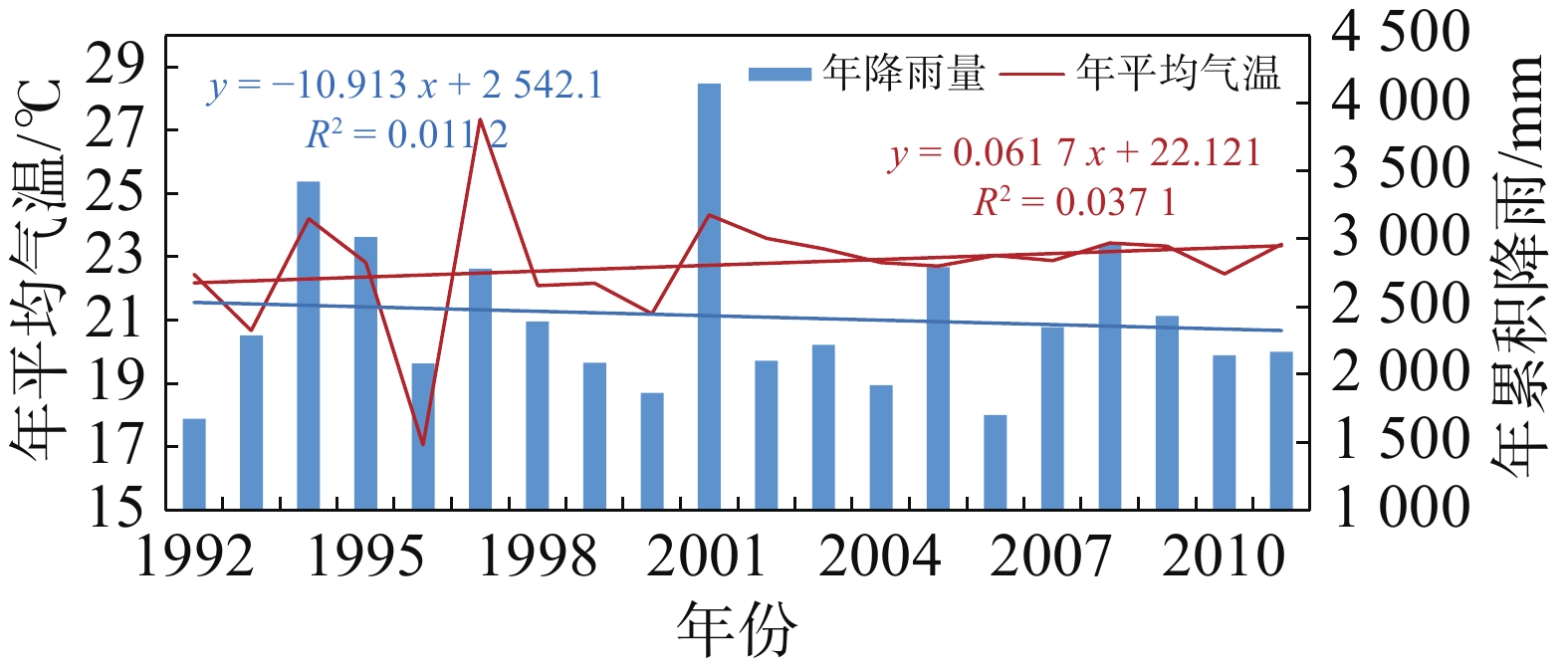
The data on mangrove area under infestation by two typical insect pests, Oligochroa cantonella and Hyblaea puera, in mangroves and the climate data in Fangchenggang in the years from 2015 to 2019 were collected and analyzed by using the Pearson correlation method to reveal and compare the key meteorological factors and the time durations associated with occurrence of these two insect pests on monthly and ten-day scales. The results showed that the occurrence of the two insect pests in the study area was significantly affected by the rainfall and relative humidity in late May (pest occurrence period). O. cantonella occurrence was negatively correlated with the temperature in late May, whereas H. puera occurrence was positively correlated with the temperature in late May. Moreover, the occurrence of O. cantonella was also affected by relative humidity and wind speed in the pre-occurrence periods (early and late March), and the occurrence of H. puera was affected by rainfall in the pre-occurrence periods (early and late February). The relationship between the occurrence of the two pest insects and the meteorological factors in Fangchenggang was then established, which is helpful for forecasting and early warning of occurrence and infestation of pest insects.
The data on mangrove area under infestation by two typical insect pests, Oligochroa cantonella and Hyblaea puera, in mangroves and the climate data in Fangchenggang in the years from 2015 to 2019 were collected and analyzed by using the Pearson correlation method to reveal and compare the key meteorological factors and the time durations associated with occurrence of these two insect pests on monthly and ten-day scales. The results showed that the occurrence of the two insect pests in the study area was significantly affected by the rainfall and relative humidity in late May (pest occurrence period). O. cantonella occurrence was negatively correlated with the temperature in late May, whereas H. puera occurrence was positively correlated with the temperature in late May. Moreover, the occurrence of O. cantonella was also affected by relative humidity and wind speed in the pre-occurrence periods (early and late March), and the occurrence of H. puera was affected by rainfall in the pre-occurrence periods (early and late February). The relationship between the occurrence of the two pest insects and the meteorological factors in Fangchenggang was then established, which is helpful for forecasting and early warning of occurrence and infestation of pest insects.
2022, 13(6): 644-650.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.015
Abstract:
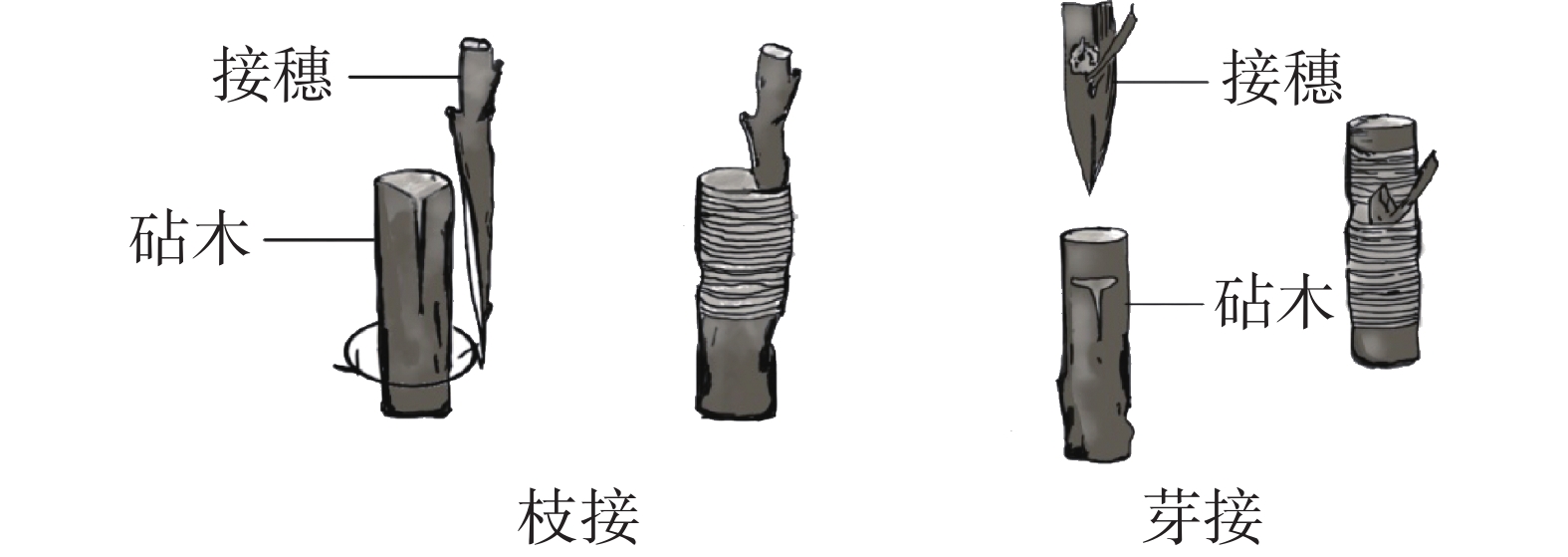
The plant height of trees is an important trait that affects the fruit yield and ornamental quality of plants. The physical dwarfing cultivation, spraying of growth retarders, and the dwarfing effects of genes and viruses on plants were reviewed based on the literature, and at the same time the application of dwarfing in garden development and fruit industry was summarized in order to provide reference for further optimization of arbor dwarfing and its application in gardening.
The plant height of trees is an important trait that affects the fruit yield and ornamental quality of plants. The physical dwarfing cultivation, spraying of growth retarders, and the dwarfing effects of genes and viruses on plants were reviewed based on the literature, and at the same time the application of dwarfing in garden development and fruit industry was summarized in order to provide reference for further optimization of arbor dwarfing and its application in gardening.
2022, 13(6): 651-658.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.06.016
Abstract:
Plant diseases restrict the development of agriculture in production, safety and economy. Monitoring plant health status and preventing plant diseases from occurrence are very important for sustainable agricultural development. With the interaction, connection and collision between agriculture and modern information technology, agriculture gradually tends to be modern, intelligent and digital. Computer vision has been widely used in detecting plant diseases in recent years, which is more rapid and accurate than traditional methods. The computer vision in recognition of plant diseases was reviewed from the aspects of image acquisition, image preprocessing, image segmentation, image feature extraction and disease recognition and classification, and its key points were summarized. Problems arising from and outlook on the image recognition of plant diseases based on computer vision were put forward to provide some reference for the application and research of computer vision in recognition of plant diseases in the future.
Plant diseases restrict the development of agriculture in production, safety and economy. Monitoring plant health status and preventing plant diseases from occurrence are very important for sustainable agricultural development. With the interaction, connection and collision between agriculture and modern information technology, agriculture gradually tends to be modern, intelligent and digital. Computer vision has been widely used in detecting plant diseases in recent years, which is more rapid and accurate than traditional methods. The computer vision in recognition of plant diseases was reviewed from the aspects of image acquisition, image preprocessing, image segmentation, image feature extraction and disease recognition and classification, and its key points were summarized. Problems arising from and outlook on the image recognition of plant diseases based on computer vision were put forward to provide some reference for the application and research of computer vision in recognition of plant diseases in the future.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 7673KB
PDF 7673KB








 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS