2021 Vol. 12, No. 2
2021, 12(2): 139-146.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.001
Abstract:
Large-scale outbreaks of coral diseases have been seriously threatening the health of coral reef ecosystems. Lysozyme is one of the important effectors in the innate immune response of invertebrates. A lysozyme gene, PdLYZ, was cloned from Pocillopora damicornis. The recombinant protein of PdLYZ (rPdLYZ) was expressed and purified in vitro, and its bacteriostatic activities against the Gram-positive bacteria Streptococcus mutans and Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli were determined. The effect of high temperature on the bacteriostatic activity of rPdLYZ against the pathogenic bacteria Vibrio coralliilyticus was further explored. The identified PdLYZ was comprised of 215 amino acid residues and predicted to contain one lysozyme-like superfamily domain (Ile31-Gly214), and its sequence was 25.54%−49.15% similar to those of lysozymes from other organisms. Results showed that rPdLYZ had lytic activities against E. coli, S. mutans and V. coralliilyticus. The rPdLYZ inhibited the growth of V. coralliilyticus at the early stage under high temperature. These results suggest that PdLYZ be involved in the immune defense of corals, and this study provides a theoretical reference for further understanding of the immune mechanism of corals.
Large-scale outbreaks of coral diseases have been seriously threatening the health of coral reef ecosystems. Lysozyme is one of the important effectors in the innate immune response of invertebrates. A lysozyme gene, PdLYZ, was cloned from Pocillopora damicornis. The recombinant protein of PdLYZ (rPdLYZ) was expressed and purified in vitro, and its bacteriostatic activities against the Gram-positive bacteria Streptococcus mutans and Gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli were determined. The effect of high temperature on the bacteriostatic activity of rPdLYZ against the pathogenic bacteria Vibrio coralliilyticus was further explored. The identified PdLYZ was comprised of 215 amino acid residues and predicted to contain one lysozyme-like superfamily domain (Ile31-Gly214), and its sequence was 25.54%−49.15% similar to those of lysozymes from other organisms. Results showed that rPdLYZ had lytic activities against E. coli, S. mutans and V. coralliilyticus. The rPdLYZ inhibited the growth of V. coralliilyticus at the early stage under high temperature. These results suggest that PdLYZ be involved in the immune defense of corals, and this study provides a theoretical reference for further understanding of the immune mechanism of corals.
2021, 12(2): 147-153.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.002
Abstract:
Benzo [α] pyrene (Benzo (a) pyrene, BaP) is a toxic environmental pollutant that exists widely in the environment. Corals are the cornerstones of coral reef ecosystems with important values. Three typical reef-building corals in the South China Sea, Pocillopora damicornis, Montipora digitata, Acropora formosa, and Acropora formosa, were selected and treated with BaP at the concentrations of 1 μg·L−1, 12.5 μg·L−1, 25 μg·L−1, 50 μg·L−1, 100 μg·L−1, respectively, with the DMSO solvent as control. Samples were collected on the initial 0th day; the 3rd, 5th, and 7th day after exposure to the BaP stress at different concentrations. The photosynthetic and respiratory metabolism rate, the density of the symbiotic zooxanthellae and the change of chlorophyll a content of the coral-zooxanthellae symbiont were measured, and “Logistic model” was used to fit the median effective concentration (EC50) of BaP for the symbiotic zooxanthellae. The results showed that the EC50 of BaP on the 7th day was 47.00 μg·L−1 for M. digitata, 22.15 μg·L−1 for P. damicornis, and 5.38 μg·L−1 for A. formosa. Comprehensive analysis of various physiological indicators showed that A. formosa was most sensitive to BaP among the three corals which were tolerant to BaP in the order of M. digitata > P. damicornis > A. formosa.
Benzo [α] pyrene (Benzo (a) pyrene, BaP) is a toxic environmental pollutant that exists widely in the environment. Corals are the cornerstones of coral reef ecosystems with important values. Three typical reef-building corals in the South China Sea, Pocillopora damicornis, Montipora digitata, Acropora formosa, and Acropora formosa, were selected and treated with BaP at the concentrations of 1 μg·L−1, 12.5 μg·L−1, 25 μg·L−1, 50 μg·L−1, 100 μg·L−1, respectively, with the DMSO solvent as control. Samples were collected on the initial 0th day; the 3rd, 5th, and 7th day after exposure to the BaP stress at different concentrations. The photosynthetic and respiratory metabolism rate, the density of the symbiotic zooxanthellae and the change of chlorophyll a content of the coral-zooxanthellae symbiont were measured, and “Logistic model” was used to fit the median effective concentration (EC50) of BaP for the symbiotic zooxanthellae. The results showed that the EC50 of BaP on the 7th day was 47.00 μg·L−1 for M. digitata, 22.15 μg·L−1 for P. damicornis, and 5.38 μg·L−1 for A. formosa. Comprehensive analysis of various physiological indicators showed that A. formosa was most sensitive to BaP among the three corals which were tolerant to BaP in the order of M. digitata > P. damicornis > A. formosa.
2021, 12(2): 154-160.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.003
Abstract:
Aeromonas veronii is a gram-negative pathogen that infects humans terrestial and aquatic animals. In gram-negative bacteria, ExsA can activate the type Ⅲ secretion system and mediate cytotoxicity to the hosts. Our previous genomic analysis showed that A. veronii had two copies of exsA gene, suggesting that its virulence regulation might be mediated by exsA gene. In this study, the homologous recombination double exchange technology was applied to construct the Aeromonas veronii ΔexsA1 mutant strains, and the challenge experiment was carried out by means of intraperitoneal injection. The results showed that the virulence of A. veronii without exsA1 was decreased significantly. After tilapia fish was inoculated with the ΔexsA1 attenuated strains and the wild strains, respectively, the accumulation level of immunoglobulin M (IgM) in the serum of fish was increased and reached its peak at the 4th day. The immune protection rate of ΔexsA1 attenuated strains against tilapia was 70% under the lethal dose of A. veronii wild strains. These results indicated that ΔexsA1 attenuated strains could induce the immune response of tilapia, which may lay a foundation for the further development of A. veronii as a live attenuated vaccine.
Aeromonas veronii is a gram-negative pathogen that infects humans terrestial and aquatic animals. In gram-negative bacteria, ExsA can activate the type Ⅲ secretion system and mediate cytotoxicity to the hosts. Our previous genomic analysis showed that A. veronii had two copies of exsA gene, suggesting that its virulence regulation might be mediated by exsA gene. In this study, the homologous recombination double exchange technology was applied to construct the Aeromonas veronii ΔexsA1 mutant strains, and the challenge experiment was carried out by means of intraperitoneal injection. The results showed that the virulence of A. veronii without exsA1 was decreased significantly. After tilapia fish was inoculated with the ΔexsA1 attenuated strains and the wild strains, respectively, the accumulation level of immunoglobulin M (IgM) in the serum of fish was increased and reached its peak at the 4th day. The immune protection rate of ΔexsA1 attenuated strains against tilapia was 70% under the lethal dose of A. veronii wild strains. These results indicated that ΔexsA1 attenuated strains could induce the immune response of tilapia, which may lay a foundation for the further development of A. veronii as a live attenuated vaccine.
2021, 12(2): 161-166.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.004
Abstract:
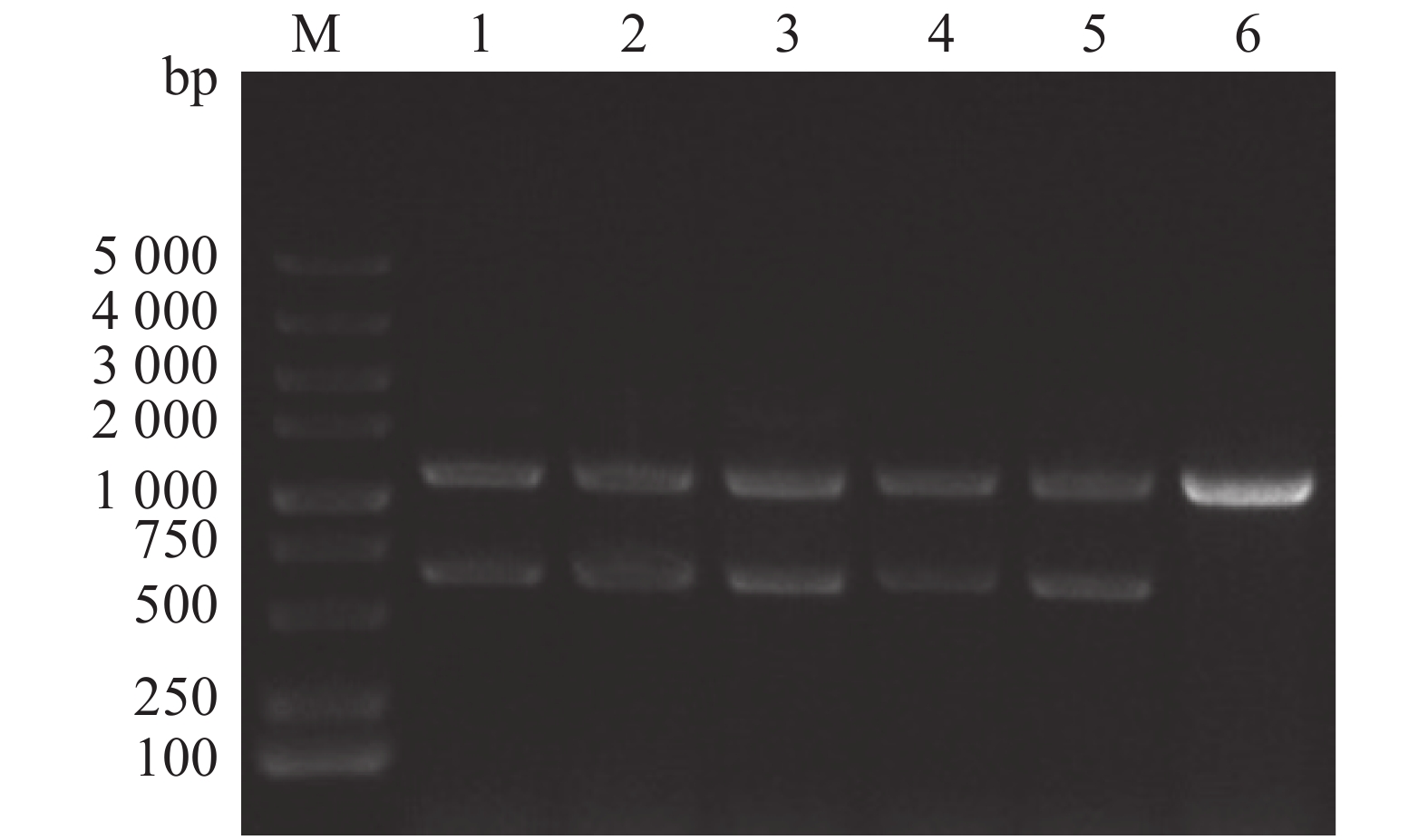
Aeromonas veronii is a common merman comorbid pathogen. To study the function of the flrB gene in Aeromonas veronii, the upstream and downstream homology arms of the flrB gene were amplified and integrated to the pRE112 plasmid, and the recombinant plasmid was transformed into E. coli WM3064 by electroporation, and then was conjugated into the wild-type A. veronii. After screened under sucrose pressure, the knockout strains were verified by PCR and sequencing. The flrB gene knockout strain is tested for growth curve and biofilm formation. The biofilm test showed that the knockout of flrB reduced the formation of biofilm, but did not affect the growth of A. veronii. This revealed that the flrB gene could promote biofilm formation of A. veronii, which lays a foundation for further revealing the function and mechanism of this gene.
Aeromonas veronii is a common merman comorbid pathogen. To study the function of the flrB gene in Aeromonas veronii, the upstream and downstream homology arms of the flrB gene were amplified and integrated to the pRE112 plasmid, and the recombinant plasmid was transformed into E. coli WM3064 by electroporation, and then was conjugated into the wild-type A. veronii. After screened under sucrose pressure, the knockout strains were verified by PCR and sequencing. The flrB gene knockout strain is tested for growth curve and biofilm formation. The biofilm test showed that the knockout of flrB reduced the formation of biofilm, but did not affect the growth of A. veronii. This revealed that the flrB gene could promote biofilm formation of A. veronii, which lays a foundation for further revealing the function and mechanism of this gene.
2021, 12(2): 167-175.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.005
Abstract:
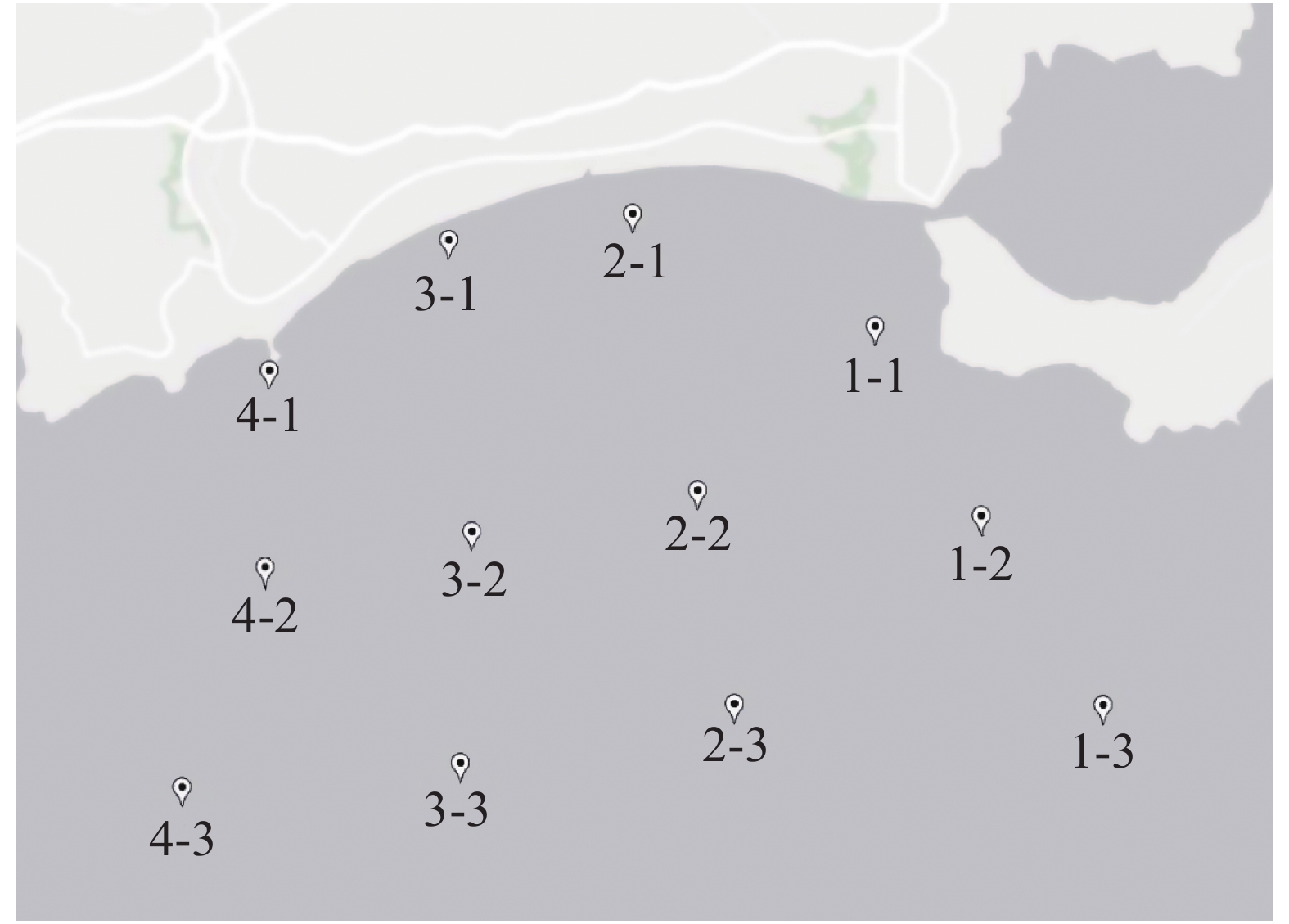
The species, community structure and diversity index of phytoplankton and seawater quality in the coastal waters of Lingshui Bay were investigated in the spring and autumn of 2019. The results showed that there were 81 species of phytoplankton in 6 phyla and 53 species in 3 phyla identified in spring and autumn, respectively, most of which were diatoms. There are 7 dominant species of phytoplankton although different in spring and autumn. The average cell density of phytoplankton in spring and autumn was 8.56×103 cells·m−3 and 22.81×103 cells·m−3, respectively. The average diversity index and uniformity of phytoplankton in the sea waters were 2.99 and 0.76 in spring, and 3.03 and 0.79 in autumn. Redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that the ecological environment in Lingshui Bay was excellent. The phytoplankton was significantly positively correlated with salinity and nitrite-nitrogen in spring, and with nitrite-nitrogen in autumn, indicating that the main factors affecting phytoplankton in Lingshui Bay are salinity and nitrite-nitrogen content. The phytoplankton community structure in Lingshui Bay was closely related to the nutrients in the sea water. The control of discharge of sewage in Lingshui Bay should be strengthened to enhance the protection of the coastal waters of Lingshui Bay.
The species, community structure and diversity index of phytoplankton and seawater quality in the coastal waters of Lingshui Bay were investigated in the spring and autumn of 2019. The results showed that there were 81 species of phytoplankton in 6 phyla and 53 species in 3 phyla identified in spring and autumn, respectively, most of which were diatoms. There are 7 dominant species of phytoplankton although different in spring and autumn. The average cell density of phytoplankton in spring and autumn was 8.56×103 cells·m−3 and 22.81×103 cells·m−3, respectively. The average diversity index and uniformity of phytoplankton in the sea waters were 2.99 and 0.76 in spring, and 3.03 and 0.79 in autumn. Redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that the ecological environment in Lingshui Bay was excellent. The phytoplankton was significantly positively correlated with salinity and nitrite-nitrogen in spring, and with nitrite-nitrogen in autumn, indicating that the main factors affecting phytoplankton in Lingshui Bay are salinity and nitrite-nitrogen content. The phytoplankton community structure in Lingshui Bay was closely related to the nutrients in the sea water. The control of discharge of sewage in Lingshui Bay should be strengthened to enhance the protection of the coastal waters of Lingshui Bay.
2021, 12(2): 176-184.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.006
Abstract:
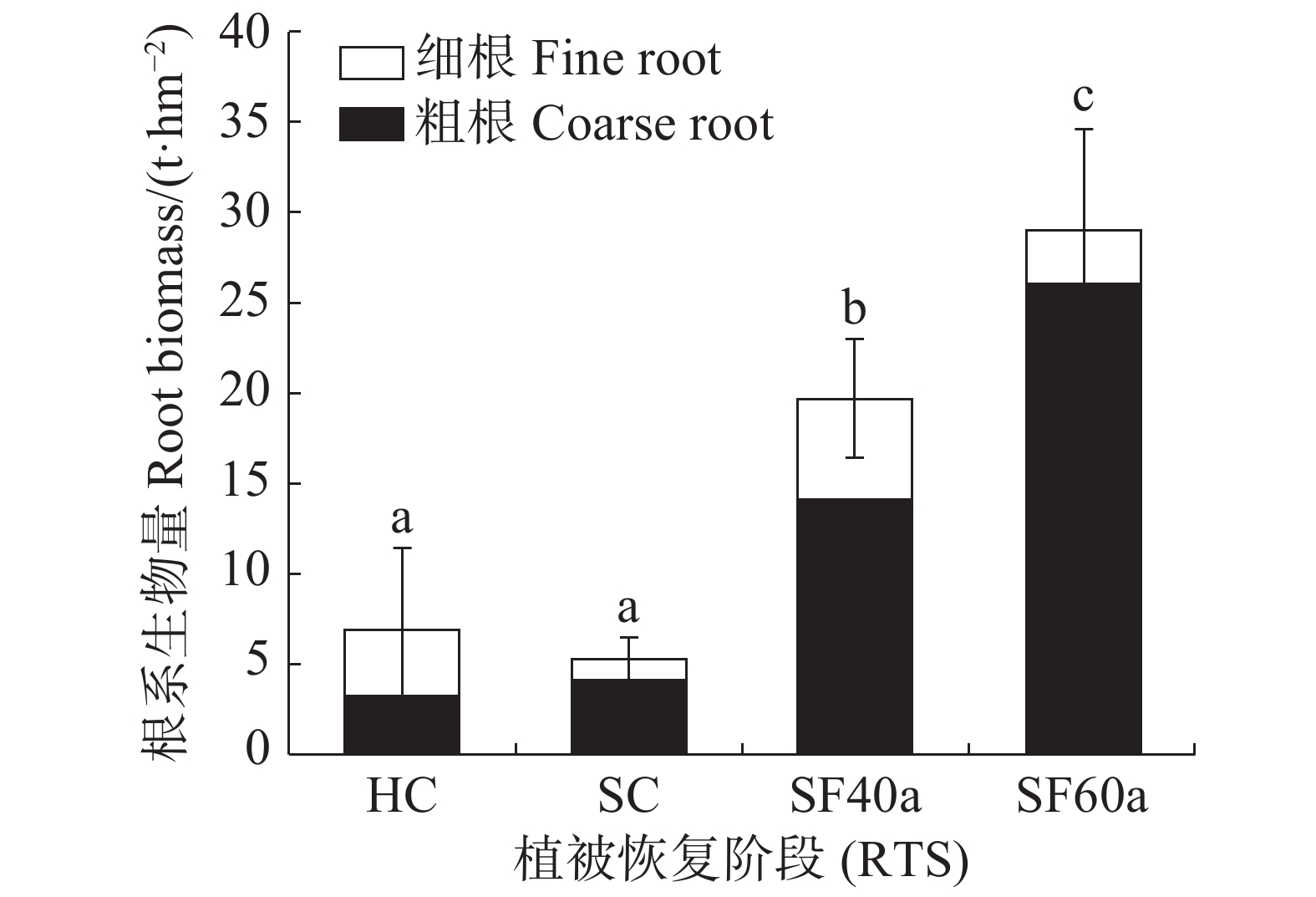
Plant root biomass in tropical regions plays an important role in predicting the change of soil carbon pool under climate change and understanding the ecological process of secondary succession of tropical rain forest. Four vegetation communities at different restoration stages (herb community, shrub community, secondary forest with 40 years, secondary forest with 60 years) were selected in Ganshiling Natural Reserve, and their root samples in the soil 0~100 cm deep were collected by the average-tree-specific sampling method. The root biomass and the structure and vertical distribution of underground roots with different diameters were analyzed. The results show that the total root biomass of plants at different succession stages ranged from 5.23 t·hm−2 to 28.98 t·hm−2 in the tropical lowland rain forest in Ganshiling Natural Reserve, and that vegetation restoration succession (forward) significantly increased root biomass at various vegetation stages except the root biomass at the succession stage from the herb to shrub, which decreased and was not significantly different. The root biomass of the woody plant community consisted mainly of thick roots (>2 mm), which accounted for 89.76% of the total root biomass, whereas that of herbaceous plant community consisted mainly of fine root (≤2 mm), which accounted for 53.53% of the total root biomass. With the restoration of vegetation in Ganshiling Natural Reserve the proportion of the thick roots in root biomass gradually increased, while the proportion of the fine root in root biomass gradually decreased. About 80% of the root biomass in the tropical lowland rain forest was mainly produced in the soil layer between 0~20 cm. With the increase of the soil depth in the soil profile the root biomass decreased significantly. The root biomass in the herb community showed a vertical change with exponential regression in the soil profile, while the root biomass in the woody and shrub communities at the restoration succession stages had a vertical change with power function regression. The tree height and D2h were best fitted to the root biomass in the root biomass model, and the root biomass could be estimated according to the tree height and D2h in Ganshiling Natural Reserve. This study can provide a reference for estimating the root biomass and productivity of the tropical lowland rain forest in China, and it also lays a foundation for further study of carbon distribution and soil carbon pool change of the plant communities in the tropical lowland rain forest in Ganshiling.
Plant root biomass in tropical regions plays an important role in predicting the change of soil carbon pool under climate change and understanding the ecological process of secondary succession of tropical rain forest. Four vegetation communities at different restoration stages (herb community, shrub community, secondary forest with 40 years, secondary forest with 60 years) were selected in Ganshiling Natural Reserve, and their root samples in the soil 0~100 cm deep were collected by the average-tree-specific sampling method. The root biomass and the structure and vertical distribution of underground roots with different diameters were analyzed. The results show that the total root biomass of plants at different succession stages ranged from 5.23 t·hm−2 to 28.98 t·hm−2 in the tropical lowland rain forest in Ganshiling Natural Reserve, and that vegetation restoration succession (forward) significantly increased root biomass at various vegetation stages except the root biomass at the succession stage from the herb to shrub, which decreased and was not significantly different. The root biomass of the woody plant community consisted mainly of thick roots (>2 mm), which accounted for 89.76% of the total root biomass, whereas that of herbaceous plant community consisted mainly of fine root (≤2 mm), which accounted for 53.53% of the total root biomass. With the restoration of vegetation in Ganshiling Natural Reserve the proportion of the thick roots in root biomass gradually increased, while the proportion of the fine root in root biomass gradually decreased. About 80% of the root biomass in the tropical lowland rain forest was mainly produced in the soil layer between 0~20 cm. With the increase of the soil depth in the soil profile the root biomass decreased significantly. The root biomass in the herb community showed a vertical change with exponential regression in the soil profile, while the root biomass in the woody and shrub communities at the restoration succession stages had a vertical change with power function regression. The tree height and D2h were best fitted to the root biomass in the root biomass model, and the root biomass could be estimated according to the tree height and D2h in Ganshiling Natural Reserve. This study can provide a reference for estimating the root biomass and productivity of the tropical lowland rain forest in China, and it also lays a foundation for further study of carbon distribution and soil carbon pool change of the plant communities in the tropical lowland rain forest in Ganshiling.
2021, 12(2): 185-191.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.007
Abstract:
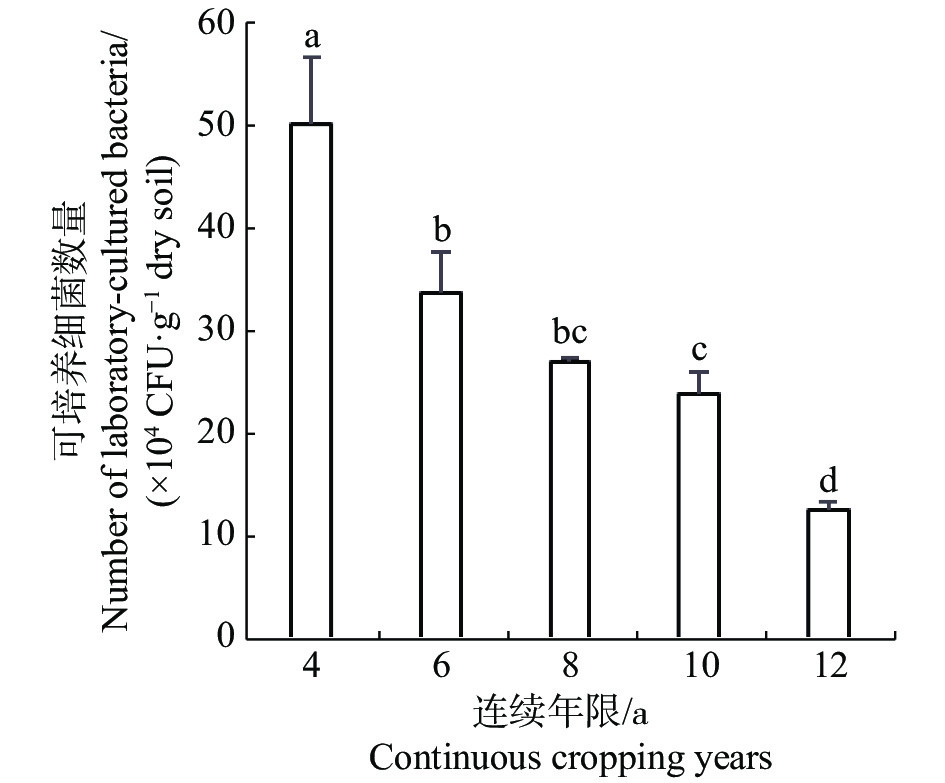
Pineapple is one of the most important cash crops in China. Long-term continuous cropping causes a serious obstruction to continuous cropping and gives a serious impact to the development of pineapple industry in China. The soil samples (from Qiong Hai city of Hainan)in the pineapple orchards for different consecutive cropping years (4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 years) were collected to analyze the changes in soil nutrients and the number of culturable microorganisms in the pineapple orchards. The results show that the soil acidification in the pineapple orchards becomes more and more serious with the continuous cropping years. The contents of organic matter and alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen in soil decreased. The content of available potassium in the soil decreased firstly and then increased. The content of available phosphorus in the soil increased with the continuous cropping years and showed a high enrichment effect. The soil contents of exchangeable calcium and magnesium were mostly accumulated in the pineapple orchards for 8 and 10 years of continuous cropping. The number of culturable bacteria and actinomycetes in the soil decreased gradually with the increase of continuous cropping years, while the number of culturable fungi in the soil increased gradually. Redundancy analysis showed that the number of culturable bacteria was positively correlated with the content of available phosphorus and pH. The number of culturable fungi and actinomycetes was positively correlated with the contents of alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, organic matter and available potassium in the soil. Thus, the long-term continuous cropping of pineapple changes the proportion of soil nutrients in the pineapple orchards, resulting in the imbalance of the number of culturable microorganisms in the soil, thus affecting the growth of pineapple.
Pineapple is one of the most important cash crops in China. Long-term continuous cropping causes a serious obstruction to continuous cropping and gives a serious impact to the development of pineapple industry in China. The soil samples (from Qiong Hai city of Hainan)in the pineapple orchards for different consecutive cropping years (4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 years) were collected to analyze the changes in soil nutrients and the number of culturable microorganisms in the pineapple orchards. The results show that the soil acidification in the pineapple orchards becomes more and more serious with the continuous cropping years. The contents of organic matter and alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen in soil decreased. The content of available potassium in the soil decreased firstly and then increased. The content of available phosphorus in the soil increased with the continuous cropping years and showed a high enrichment effect. The soil contents of exchangeable calcium and magnesium were mostly accumulated in the pineapple orchards for 8 and 10 years of continuous cropping. The number of culturable bacteria and actinomycetes in the soil decreased gradually with the increase of continuous cropping years, while the number of culturable fungi in the soil increased gradually. Redundancy analysis showed that the number of culturable bacteria was positively correlated with the content of available phosphorus and pH. The number of culturable fungi and actinomycetes was positively correlated with the contents of alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, organic matter and available potassium in the soil. Thus, the long-term continuous cropping of pineapple changes the proportion of soil nutrients in the pineapple orchards, resulting in the imbalance of the number of culturable microorganisms in the soil, thus affecting the growth of pineapple.
2021, 12(2): 192-201.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.008
Abstract:
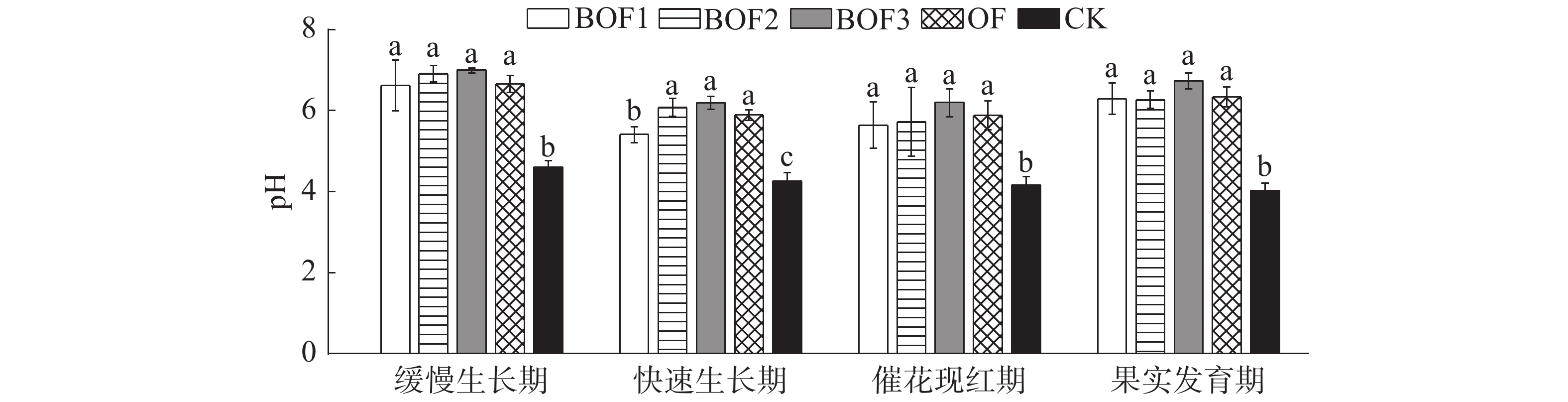
Pineapples in the plantation under long-term continuous cropping were applied with organic or biological organic fertilizers (OF, BOF1, BOF2, BOF3) prepared from bacteria (Bacillus subtilis HL2) as a biocontrol agent, carriers (rapeseed cake, peat soil, coconut bran) and common organic fertilizer by secondary fermentation technology, and chemical fertilizer as control (CK) to analyze the effects of the organic, bio-organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil nutrients, yield and economic benefits of the pineapple plantation under continuous cropping. In the whole growth period of pineapple, the treatments with organic and bio-organic fertilizers increased the soil pH, the soil contents of organic matter and available phosphorus, and yield and economic benefit of pineapples in the pineapple plantation under continuous cropping by 26.99%~67.41%, 13.65%~150.32%, 4.96%~70.9% and 31.21%~66.83%, 25.31%~55.88%, respectively as compared with CK. The BOF1 treatment increased the content of soil available potassium in the pineapple plantation under continuous cropping by 9.04% to 37.38%. Organic fertilizer (OF), bio-organic fertilizers (BOF1, BOF2, BOF3) and inorganic fertilizer all improved soil nutrient content, and increased pineapple yield and economic benefits, especially the bio-organic fertilizer BOF1 which was much better than other fertilizers. Regression analysis of yield data and evaluation indexes of soil physical and chemical indicators showed that pineapple yield has a certain correlation with soil nutrients.
Pineapples in the plantation under long-term continuous cropping were applied with organic or biological organic fertilizers (OF, BOF1, BOF2, BOF3) prepared from bacteria (Bacillus subtilis HL2) as a biocontrol agent, carriers (rapeseed cake, peat soil, coconut bran) and common organic fertilizer by secondary fermentation technology, and chemical fertilizer as control (CK) to analyze the effects of the organic, bio-organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil nutrients, yield and economic benefits of the pineapple plantation under continuous cropping. In the whole growth period of pineapple, the treatments with organic and bio-organic fertilizers increased the soil pH, the soil contents of organic matter and available phosphorus, and yield and economic benefit of pineapples in the pineapple plantation under continuous cropping by 26.99%~67.41%, 13.65%~150.32%, 4.96%~70.9% and 31.21%~66.83%, 25.31%~55.88%, respectively as compared with CK. The BOF1 treatment increased the content of soil available potassium in the pineapple plantation under continuous cropping by 9.04% to 37.38%. Organic fertilizer (OF), bio-organic fertilizers (BOF1, BOF2, BOF3) and inorganic fertilizer all improved soil nutrient content, and increased pineapple yield and economic benefits, especially the bio-organic fertilizer BOF1 which was much better than other fertilizers. Regression analysis of yield data and evaluation indexes of soil physical and chemical indicators showed that pineapple yield has a certain correlation with soil nutrients.
2021, 12(2): 202-209.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.009
Abstract:
Areca nut is an important pillar industry in Hainan Province, and arecanut yellow leaf disease occurring seriously in Hainan has led to the decline of areca nut yield and quality, and seriously affects the development of areca nut industry in Hainan Province. It was found that earthworm castings as vermicompost could reduce yellowing of arecanut leaves when applied to the rhisosphere, but its mechanism in reducing leaf yellowing resulting from arecanut leaf yellow disease was not clear. Therefore, an experiment was made at a Longgun arecanut plantation in Wanning County, Hainan Province by using earthworm castings as manure to observe the microbial diversity in the rhizosphere of arecanut plants in the arecanut plantation. Three treatments were arranged: earthworm castings (TLG1), earthworm castings + chemical fertilizer (urea) (TLG2) and the blank control (TLG3). After 10 months of treatment, samples were collected from the rhizosphere in the arecanut plantation to analyze the dynamic changes of soil bacterial diversity and microbial interaction network in different treatments by using Illumina Miseq high-throughput sequencing to reveal the correlation between microbial diversity and soil physical and chemical properties. The results showed that the treatments with the earthworm castings and the earthworm manure + urea increased significantly the microbial diversity in the rhizosphere of the aracanut plants, as compared with the control. The treatments of the earthworm castings and the earthworm castings + urea increased significantly Acidothermus, Occalatibacter and Conexibater at the genus level in the rhizosphere (P < 0.05), and reduced significantly Candidatus Solibacter (P < 0.05). The microbial interaction network analysis showed that a special bacteria (s_unclassified_G_norank_F_norank_O_Chloroplast), belonging to the phylum Cyanobacteria, and a species of bacteria (S_uncultured_ bacterium_ G_ norank_ F_ LWQ8), belonging to the phylum Patescibacteria, were found in the top 50 abundant species in the treatments with the earthworm castings and the earthworm castings + urea, respectively. This experiment showed that exogenous earthworm castings could significantly enhance the diversity and abundance of soil microorganisms in the rhizosphere of arecanut plants in the arecanut plantation, and significantly increase the stability of microbial interaction network in the rhizosphere. Moreover, the available potassium and other physical and chemical factors had a significant impact on microbial groups. The results of this experiment might provide some reference for further understanding of the mechanism of the earthworm castings in reducing leaf yellowing resulting from the yellow leaf disease.
Areca nut is an important pillar industry in Hainan Province, and arecanut yellow leaf disease occurring seriously in Hainan has led to the decline of areca nut yield and quality, and seriously affects the development of areca nut industry in Hainan Province. It was found that earthworm castings as vermicompost could reduce yellowing of arecanut leaves when applied to the rhisosphere, but its mechanism in reducing leaf yellowing resulting from arecanut leaf yellow disease was not clear. Therefore, an experiment was made at a Longgun arecanut plantation in Wanning County, Hainan Province by using earthworm castings as manure to observe the microbial diversity in the rhizosphere of arecanut plants in the arecanut plantation. Three treatments were arranged: earthworm castings (TLG1), earthworm castings + chemical fertilizer (urea) (TLG2) and the blank control (TLG3). After 10 months of treatment, samples were collected from the rhizosphere in the arecanut plantation to analyze the dynamic changes of soil bacterial diversity and microbial interaction network in different treatments by using Illumina Miseq high-throughput sequencing to reveal the correlation between microbial diversity and soil physical and chemical properties. The results showed that the treatments with the earthworm castings and the earthworm manure + urea increased significantly the microbial diversity in the rhizosphere of the aracanut plants, as compared with the control. The treatments of the earthworm castings and the earthworm castings + urea increased significantly Acidothermus, Occalatibacter and Conexibater at the genus level in the rhizosphere (P < 0.05), and reduced significantly Candidatus Solibacter (P < 0.05). The microbial interaction network analysis showed that a special bacteria (s_unclassified_G_norank_F_norank_O_Chloroplast), belonging to the phylum Cyanobacteria, and a species of bacteria (S_uncultured_ bacterium_ G_ norank_ F_ LWQ8), belonging to the phylum Patescibacteria, were found in the top 50 abundant species in the treatments with the earthworm castings and the earthworm castings + urea, respectively. This experiment showed that exogenous earthworm castings could significantly enhance the diversity and abundance of soil microorganisms in the rhizosphere of arecanut plants in the arecanut plantation, and significantly increase the stability of microbial interaction network in the rhizosphere. Moreover, the available potassium and other physical and chemical factors had a significant impact on microbial groups. The results of this experiment might provide some reference for further understanding of the mechanism of the earthworm castings in reducing leaf yellowing resulting from the yellow leaf disease.
2021, 12(2): 210-218.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.010
Abstract:
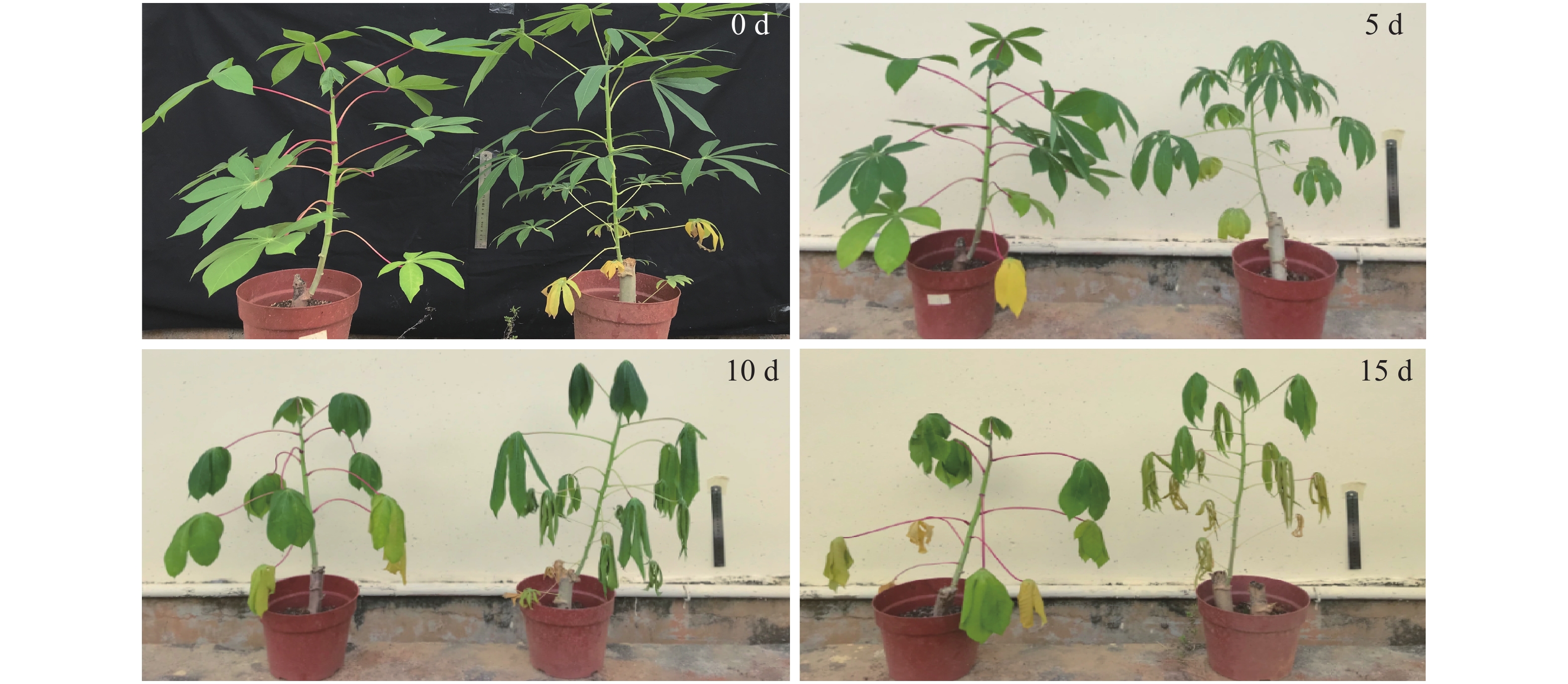
An attempt was made to analyze the drought resistance of sexual tetraploid cassava. Sexual tetraploid cassava was treated under different levels of drought with its maternal parent as control, and their leaves were sampled and analyzed in terms of leaf morphology, physiology, biochemistry and proteomics. Comparison of the leaf morphology and leaf physiological and biochemical indicators such as the contents of MDA and proline and SOD activity showed that the sexual tetraploid cassava had higher drought resistance than the cassava SC5. The leaves of cassava SC5 and its sexual tetraploid plants under drought stress were run on two-dimensional protein electrophoresis and analyzed by using Delta 2D software., and 34 protein spots with an average differential expression of at least 2.0 fold change in expression were obtained from the leaves under drought stress, of which 18 were up-regulated and 16 down-regulated. The different protein spots were analyzed by using mass spectrometry and matched to the NCBI database, and 29 protein spots were matched to the NCBI database entries. These 29 proteins are mainly related to photosynthesis, inorganic ion transport and metabolism, carbohydrate and metabolism, binding, detoxification and antioxidants, etc. Moreover, the ribulose bishosphate carboxylase and the oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 1 of the Photosystem II (PSII) in response to drought stress were up-regulated in expression, which implies that the sexual tetraploid cassava is more effective than the SC5 in maintaining the normal structure and function of the photosynthesis system, and hence respond more quickly to drought stress.
An attempt was made to analyze the drought resistance of sexual tetraploid cassava. Sexual tetraploid cassava was treated under different levels of drought with its maternal parent as control, and their leaves were sampled and analyzed in terms of leaf morphology, physiology, biochemistry and proteomics. Comparison of the leaf morphology and leaf physiological and biochemical indicators such as the contents of MDA and proline and SOD activity showed that the sexual tetraploid cassava had higher drought resistance than the cassava SC5. The leaves of cassava SC5 and its sexual tetraploid plants under drought stress were run on two-dimensional protein electrophoresis and analyzed by using Delta 2D software., and 34 protein spots with an average differential expression of at least 2.0 fold change in expression were obtained from the leaves under drought stress, of which 18 were up-regulated and 16 down-regulated. The different protein spots were analyzed by using mass spectrometry and matched to the NCBI database, and 29 protein spots were matched to the NCBI database entries. These 29 proteins are mainly related to photosynthesis, inorganic ion transport and metabolism, carbohydrate and metabolism, binding, detoxification and antioxidants, etc. Moreover, the ribulose bishosphate carboxylase and the oxygen-evolving enhancer protein 1 of the Photosystem II (PSII) in response to drought stress were up-regulated in expression, which implies that the sexual tetraploid cassava is more effective than the SC5 in maintaining the normal structure and function of the photosynthesis system, and hence respond more quickly to drought stress.
2021, 12(2): 219-227.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.011
Abstract:
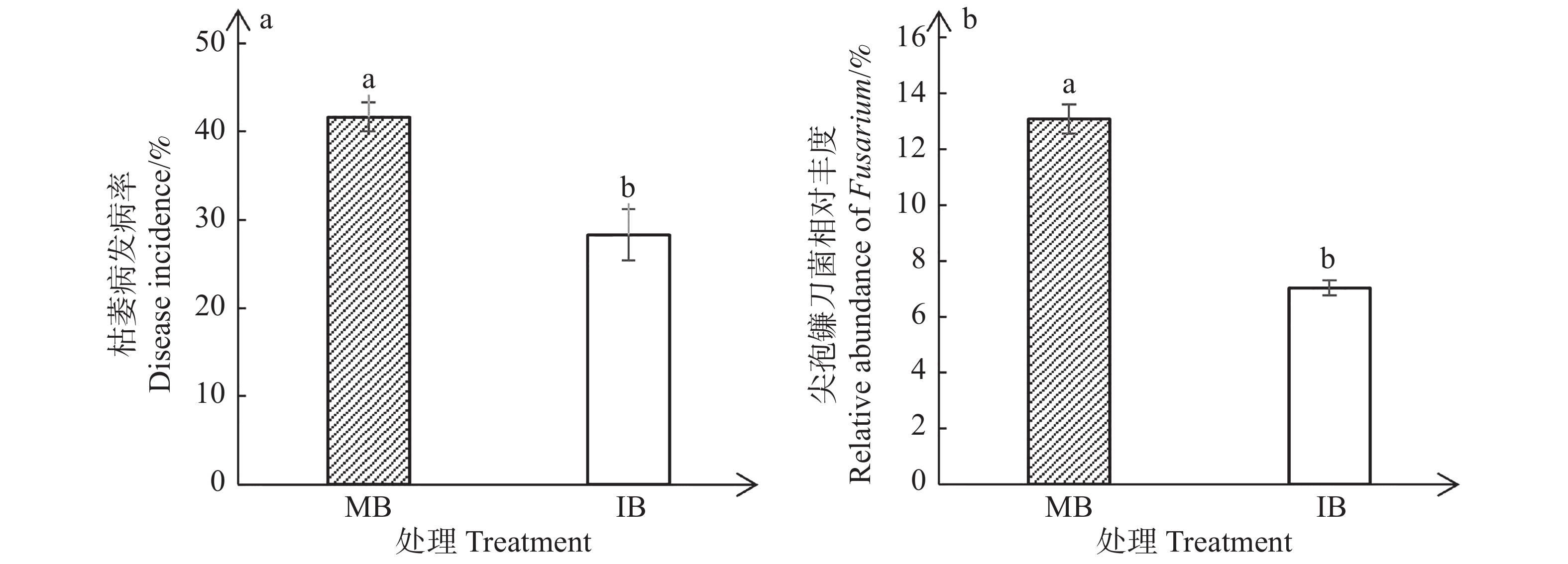
An attempt was made to explore the changes of soil microbial community in continuous cropping banana orchards after banana was intercropped with white clover (Trifolium repens L) and the effect of the intercropping on the incidence of banana Fusarium wilt. Banana was intercropped with white clover in continuous cropping banana orchards, with monoculture of banana as control. The soil microbial community structure and composition among different treatments in the banana orchards were detected by using high-throughput sequencing and their differences were analyzed. Compared with the monoculture of banana, intercropping of banana with white clover reduced the disease incidence of banana Fusarium wilt by 13.34%, increased the pH value by 0.54, and increased the content of soil available potassium by 7.21 mg·kg−1. Compared with the monoculture of banana, the intercropping of banana with white clover significantly increased soil microbial diversity, and formed a unique community structure. Moreover, the intercropping of banana with white clover changed the community composition of soil microorganisms, significantly decreased the relative abundance of Fusarium oxysporum, and increased the relative abundance of GP16 and Davidiella. It is concluded that the intercropping of banana with white clover in continuous cropping banana orchards significantly reduced the number of F. oxysporum, increased soil pH and microbial diversity, changed the community structure of microorganisms, and then reduced the incidence of banana Fusarium wilt disease.
An attempt was made to explore the changes of soil microbial community in continuous cropping banana orchards after banana was intercropped with white clover (Trifolium repens L) and the effect of the intercropping on the incidence of banana Fusarium wilt. Banana was intercropped with white clover in continuous cropping banana orchards, with monoculture of banana as control. The soil microbial community structure and composition among different treatments in the banana orchards were detected by using high-throughput sequencing and their differences were analyzed. Compared with the monoculture of banana, intercropping of banana with white clover reduced the disease incidence of banana Fusarium wilt by 13.34%, increased the pH value by 0.54, and increased the content of soil available potassium by 7.21 mg·kg−1. Compared with the monoculture of banana, the intercropping of banana with white clover significantly increased soil microbial diversity, and formed a unique community structure. Moreover, the intercropping of banana with white clover changed the community composition of soil microorganisms, significantly decreased the relative abundance of Fusarium oxysporum, and increased the relative abundance of GP16 and Davidiella. It is concluded that the intercropping of banana with white clover in continuous cropping banana orchards significantly reduced the number of F. oxysporum, increased soil pH and microbial diversity, changed the community structure of microorganisms, and then reduced the incidence of banana Fusarium wilt disease.
2021, 12(2): 228-235.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.012
Abstract:
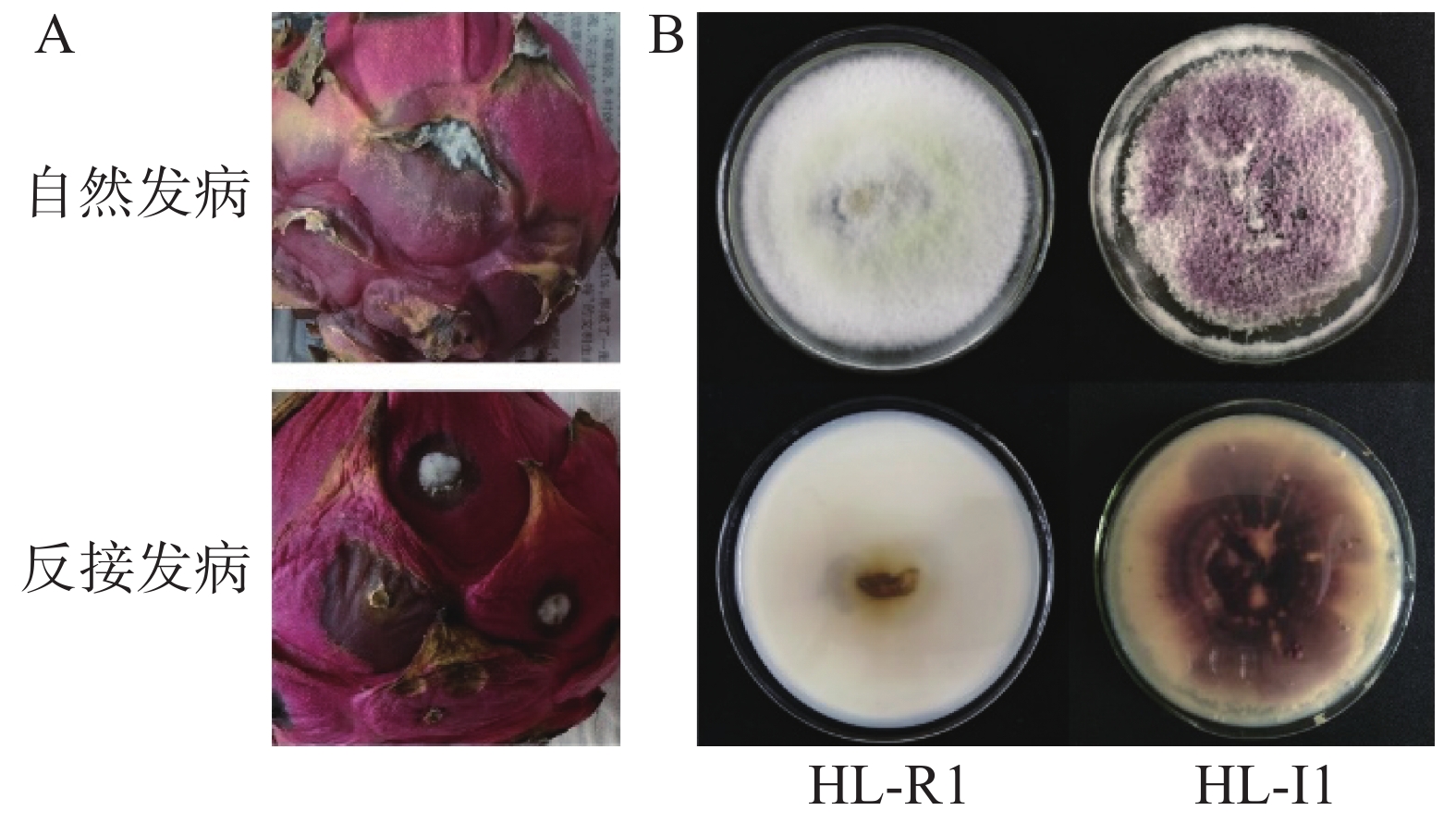
Postharvest pathogens were isolated from naturally diseased pitaya fruits in Haikou, Hainan, and the plant extracts with antimicrobial activity against the pathogens were screened by antimicrobial zone method. An orthogonal experiment was designed to test the effect of combination of the two existing antagonistic bacteria in the laboratory and the plant extracts on inhibition of the isolates. The isolates were identified based on their morphology and molecular biology. The isolates strains HL-R1 and HL-I1 were identified as Fusarium equiseti and Fusarium oxysporum, respectively. The two pathogens were treated with combinations of the two antagonistic bacteria and the plant extracts from banana peel, pomegranate peel, citrus peel, dragon peel, wampee peel, ginger and garlic to observe the control effect of the combinations against the pathogens. The combination of the extract of wampee peel or ginger and the antagonistic bacteria had better antimicrobial activities among the combinations. The results showed that the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of these two plant extracts, wampee peel and ginger, against the two pathogens were 62.50 g·L−1, with the diameter of pathogen inhibition zone being ≥ 22.35 mm or higher. The orthogonal experiment showed that the mycelial growth inhibition rate of F. equiseti and F. oxysporum treated with these two combinations were 59.19% and 53.11%, respectively.
Postharvest pathogens were isolated from naturally diseased pitaya fruits in Haikou, Hainan, and the plant extracts with antimicrobial activity against the pathogens were screened by antimicrobial zone method. An orthogonal experiment was designed to test the effect of combination of the two existing antagonistic bacteria in the laboratory and the plant extracts on inhibition of the isolates. The isolates were identified based on their morphology and molecular biology. The isolates strains HL-R1 and HL-I1 were identified as Fusarium equiseti and Fusarium oxysporum, respectively. The two pathogens were treated with combinations of the two antagonistic bacteria and the plant extracts from banana peel, pomegranate peel, citrus peel, dragon peel, wampee peel, ginger and garlic to observe the control effect of the combinations against the pathogens. The combination of the extract of wampee peel or ginger and the antagonistic bacteria had better antimicrobial activities among the combinations. The results showed that the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of these two plant extracts, wampee peel and ginger, against the two pathogens were 62.50 g·L−1, with the diameter of pathogen inhibition zone being ≥ 22.35 mm or higher. The orthogonal experiment showed that the mycelial growth inhibition rate of F. equiseti and F. oxysporum treated with these two combinations were 59.19% and 53.11%, respectively.
2021, 12(2): 236-243.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.013
Abstract:
Endophytes were isolated from healthy Oncidium hybridum leaves. An endophyte strain WB75 was identified as a potential biocontrol agent via plate confrontation analysis by using Colletotrichum gloeosporioides as reference pathogen which causes O. hybridum anthracnose. The plate confrontation showed the endophyte strain WB75 had an inhibition rate of 58.79% against C. gloeosporioides, and that its fermentation broth and autoclaved fermentation broth had inhibition rates of 77.69% and 41.26% against C. gloeosporioides, respectively. It was speculated that the endophyte strain WB75 had poor thermal stability. The antagonism of the endophyte strain WB75 against other pathogens were detected by using the plant confrontation, and these pathogens included 12 strains of 8 species of pathogens, Colletotrichum tropicicola, Fusarium delphinoides, Fusarium solani, Paraconiothyrium thysanolaenae, Fusarium oxysporum, Curvularia aeragrostidis, Guignardia mangiferae, Muyocopron alcornii, which were isolated from different parts of O. hybridum. The plate confrontation showed that the inhibition rates of the endophyte strain WB75 against the 12 strains of pathogens ranged from 38.42 to 91.53%. The endophyte strain WB75 was identified as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens through its physiological-biochemical characteristics and the sequence analysis of its 16s rDNA, and gyrA and gyrB genes. It is concluded that B. amyloliquefaciens is a species of bacteria with potential biocontrol activity against Oncidium hybridum anthracnose.
Endophytes were isolated from healthy Oncidium hybridum leaves. An endophyte strain WB75 was identified as a potential biocontrol agent via plate confrontation analysis by using Colletotrichum gloeosporioides as reference pathogen which causes O. hybridum anthracnose. The plate confrontation showed the endophyte strain WB75 had an inhibition rate of 58.79% against C. gloeosporioides, and that its fermentation broth and autoclaved fermentation broth had inhibition rates of 77.69% and 41.26% against C. gloeosporioides, respectively. It was speculated that the endophyte strain WB75 had poor thermal stability. The antagonism of the endophyte strain WB75 against other pathogens were detected by using the plant confrontation, and these pathogens included 12 strains of 8 species of pathogens, Colletotrichum tropicicola, Fusarium delphinoides, Fusarium solani, Paraconiothyrium thysanolaenae, Fusarium oxysporum, Curvularia aeragrostidis, Guignardia mangiferae, Muyocopron alcornii, which were isolated from different parts of O. hybridum. The plate confrontation showed that the inhibition rates of the endophyte strain WB75 against the 12 strains of pathogens ranged from 38.42 to 91.53%. The endophyte strain WB75 was identified as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens through its physiological-biochemical characteristics and the sequence analysis of its 16s rDNA, and gyrA and gyrB genes. It is concluded that B. amyloliquefaciens is a species of bacteria with potential biocontrol activity against Oncidium hybridum anthracnose.
2021, 12(2): 244-252.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.014
Abstract:
A novel sequencing batch reactor (SBR) based on falling aeration was designed and built for wastewater treatment with anionic surfactants without the decanterto realize micro-dynamic aeration to reduce energy consumption. The starting process, operation effect and influencing factors of the SBR were investigated, and the degradation characteristics of anionic surfactants were discussed. Activated sludge was analyzed in terms of biodegradation kinetics, and characterized by using SEM, FT-IR and UV-Vis. The results showed that the COD, TN and NH4+-N concentrations of the effluent from the novel SBR reactor were 10, 4.0 and 3.4 mg·L−1, respectively after the sludge were activated for 150 days, with their removal rates being 94.0%, 88.2% and 86.9%, respectively. The novel SBR process was 21.2% higher in removal rates of TN than compared with the traditional SBR process. The circulating upflow air velocity of the SBR process was controlled at 4.52 m·h−1 (Reflux ratio R=1.8∶1; hydraulic retention time T=3 days). The degradation rate of typical pollutant anionic surfactant in the novel SBR reactor was 81.3%. The degradation process conforms to the first-order biodegeneration kinetic equation.
A novel sequencing batch reactor (SBR) based on falling aeration was designed and built for wastewater treatment with anionic surfactants without the decanterto realize micro-dynamic aeration to reduce energy consumption. The starting process, operation effect and influencing factors of the SBR were investigated, and the degradation characteristics of anionic surfactants were discussed. Activated sludge was analyzed in terms of biodegradation kinetics, and characterized by using SEM, FT-IR and UV-Vis. The results showed that the COD, TN and NH4+-N concentrations of the effluent from the novel SBR reactor were 10, 4.0 and 3.4 mg·L−1, respectively after the sludge were activated for 150 days, with their removal rates being 94.0%, 88.2% and 86.9%, respectively. The novel SBR process was 21.2% higher in removal rates of TN than compared with the traditional SBR process. The circulating upflow air velocity of the SBR process was controlled at 4.52 m·h−1 (Reflux ratio R=1.8∶1; hydraulic retention time T=3 days). The degradation rate of typical pollutant anionic surfactant in the novel SBR reactor was 81.3%. The degradation process conforms to the first-order biodegeneration kinetic equation.
2021, 12(2): 253-260.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.015
Abstract:
In order to maintain the dynamic balance of substances and energy in cells fungi have formed some complex mechanisms during the evolution process to regulate the metabolism and circulation of intracellular materials, and one of the important pathways is autophagy. Autophagy is a highly conserved process in eukaryotes, and it encapsulates the damaged organelles or proteins in the cell by forming autophagosome vesicles with a double membrane structure and then transports them to vacuoles for degradation. In the past two decades fungal autophagy has been well documented. The analysis of autophagy-related proteins has gradually revealed some molecular and regulatory mechanisms in the process of autophagy. The functional analysis of autophagy genes in filamentous fungi has showed that autophagy plays a very important role in vegetative growth, sporulation, spore germination, formation of infective structure and pathogenicity of filamentous fungi. A review is made of the molecular and regulatory mechanisms of autophagy in fungi as well as the research progress of autophagy genes in filamentous fungi.
In order to maintain the dynamic balance of substances and energy in cells fungi have formed some complex mechanisms during the evolution process to regulate the metabolism and circulation of intracellular materials, and one of the important pathways is autophagy. Autophagy is a highly conserved process in eukaryotes, and it encapsulates the damaged organelles or proteins in the cell by forming autophagosome vesicles with a double membrane structure and then transports them to vacuoles for degradation. In the past two decades fungal autophagy has been well documented. The analysis of autophagy-related proteins has gradually revealed some molecular and regulatory mechanisms in the process of autophagy. The functional analysis of autophagy genes in filamentous fungi has showed that autophagy plays a very important role in vegetative growth, sporulation, spore germination, formation of infective structure and pathogenicity of filamentous fungi. A review is made of the molecular and regulatory mechanisms of autophagy in fungi as well as the research progress of autophagy genes in filamentous fungi.
2021, 12(2): 261-270.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.02.016
Abstract:
Scuba diving is considered as an ecotourism activity with high economic value, which has little impact on coral reefs in the early days. However, as diving tourism has become increasingly popular recently many studies have shown that the coral reef degradation is exacerbating in the diving areas around the world for the reason that the times of diving each year in some intensive diving areas greatly exceed the ecological carrying capacity of coral reefs. A review was made of the researches on the ecological carrying capacity of coral reefs for diving tourism and the main factors of diving tourism affecting coral reefs, and the impacts of diving activities on corals, coral fishes, benthic communities and coral reef ecosystem were summarized. Some suggestions for future research were made based on the review. It is highly advisable to identify the ecological carrying capacity of coral reefs in different areas for diving tourism, combine indoor simulation with the field monitoring and observation, and make a systematic research on the impact of tourism on the coral reef system other marine organisms.
Scuba diving is considered as an ecotourism activity with high economic value, which has little impact on coral reefs in the early days. However, as diving tourism has become increasingly popular recently many studies have shown that the coral reef degradation is exacerbating in the diving areas around the world for the reason that the times of diving each year in some intensive diving areas greatly exceed the ecological carrying capacity of coral reefs. A review was made of the researches on the ecological carrying capacity of coral reefs for diving tourism and the main factors of diving tourism affecting coral reefs, and the impacts of diving activities on corals, coral fishes, benthic communities and coral reef ecosystem were summarized. Some suggestions for future research were made based on the review. It is highly advisable to identify the ecological carrying capacity of coral reefs in different areas for diving tourism, combine indoor simulation with the field monitoring and observation, and make a systematic research on the impact of tourism on the coral reef system other marine organisms.



 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML
 PDF 2035KB
PDF 2035KB










 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS