-
海南省冬春季种植的薄皮甜瓜上市早、糖度高、品质优,年均播种面积3 000~4 000 hm2,因经济效益好、栽培周期短,已成为当地农民增收的主要产业之一。近年来随着复种指数的提高,连作障碍严重,土传病害频发,减产问题十分突出。为了明确该病的病原种类及其分类地位,笔者在病菌分离的基础上,从致病性、形态学和分子生物学等方面进行了鉴定分析,并接种不同砧木品种进行抗性试验,以期筛选出抗性好的砧木品种,促进薄皮甜瓜产业的健康发展。
HTML
-
本实验病株采自海南省海口市永兴镇薄皮甜瓜产区,抗病砧木品种见表1。
代号 Code 品种 Variety 来源 Source CK 美浓 农友种苗(中国)有限公司 1 银光 北京育正泰种子有限公司 2 厦利 厦门好利得种苗有限公司 3 广砧1号 广西绿海种业公司 4 大白 海南富友种苗有限公司 5 连大 海南琼研瓜菜良种有限公司 6 砧8 农友种苗(中国)有限公司 7 大正 江苏正大种子有限公司 8 壮士 农友种苗(中国)有限公司 9 甬砧 宁波市农科院蔬菜研究所 Table 1. Disease-resistant varieties of thin-skinned muskmelon and their sources
-
田间采集的病枝用75%酒精进行表面消毒30 s,灭菌水冲洗干净,超净台晾干后剪取病健交界组织块0.1~0.5 cm2,放置在PDA平板上,27 ℃培养3~5 d,挑取新长的菌丝到空白PDA平板上进行纯化培养。
-
观察在PDA上纯化培养的病原菌菌落形态,显微镜观察菌丝形态。
-
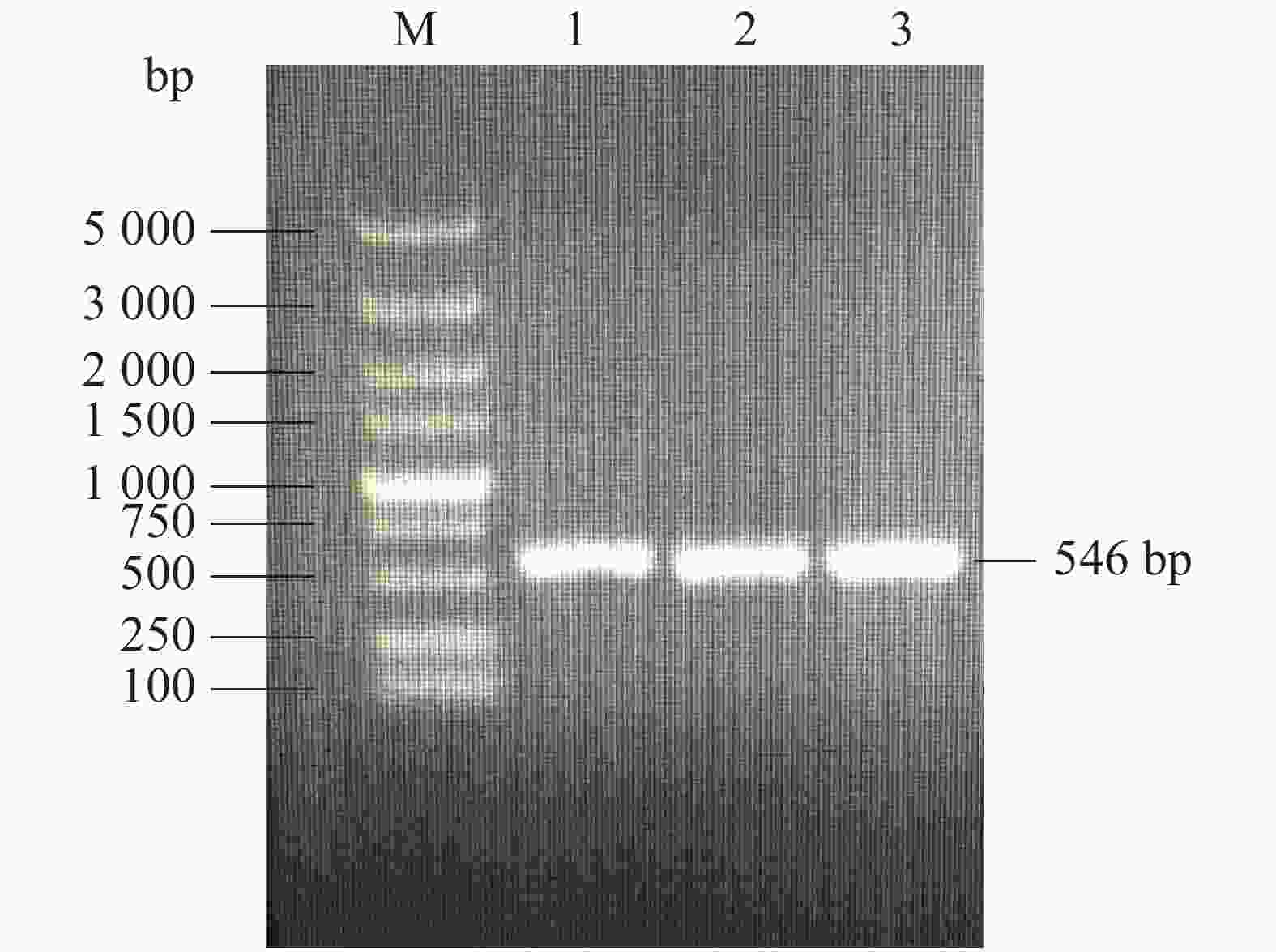
提取PDA平板上的病原真菌DNA,采用真菌通用引物ITS1,ITS4进行PCR扩增。PCR扩增体系25 μL,包括DNA模板1 μL,引物各1 μL,MIX 12.5 μL,ddH2O 9.5 μL。PCR扩增条件:95 ℃预变性5 min,94 ℃变性45 s,55 ℃退火45 s,72 ℃延伸45 s,共30个循环;最后72 ℃延伸10 min,4 ℃保存。取5 μL PCR产物1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,送样至广州华大科技有限公司进行测序,在NCBI进行BLAST比较。
-
将分离的真菌在PDA培养基上大量扩繁,放入生化培养箱27 ℃黑暗培养,待菌丝长满培养皿后,将其移出置室内自然光照刺激其产孢。1周后,用无菌水洗出孢子,镜检,用血细胞计数板计算孢子含量,按每盆1×107个·mL−1的孢子量加入无菌土壤。播种薄皮甜瓜‘美浓’种子,观察出苗及发病情况。
-
枯萎病病菌接种以‘美浓’自根苗为对照(CK),筛选出对枯萎病抗性较强的砧木品种,具体方法如下:(1)接种体准备:将枯萎病病原菌接种于装有米粒饭的三角瓶中。25 ℃培养10~15 d备用;(2)接种方法:用2 L蒸馏水洗培养皿上的孢子,血球计数板镜检记数,达到5×106个·mL−1,将不同砧木品种幼苗(子叶期,即一叶一心时)拔起植株并用清水清洗根部,轻微伤根部后在菌悬液蘸根15 min,然后定植营养钵(12 cm×15 cm)中,正常管理,每个处理定植24株;(3)发病株鉴定:定植后约50 d即初果期,根据薄皮甜瓜枯萎病田间典型表现症状(发病初期:病株叶片下而上逐渐萎蔫、似缺水状,中午更明显,早晚尚能恢复,数日后整株叶片严重萎蔫下垂、不能再恢复正常,整株死亡),将病茎纵割,维管束呈黄褐色鉴定为发病株。
1.1. 实验材料
1.2. 病原菌的分离纯化
1.3. 病原菌的形态观察
1.4. 病原菌的分子鉴定
1.5. 病原菌接种实验
1.6. 抗病砧木筛选方法
-
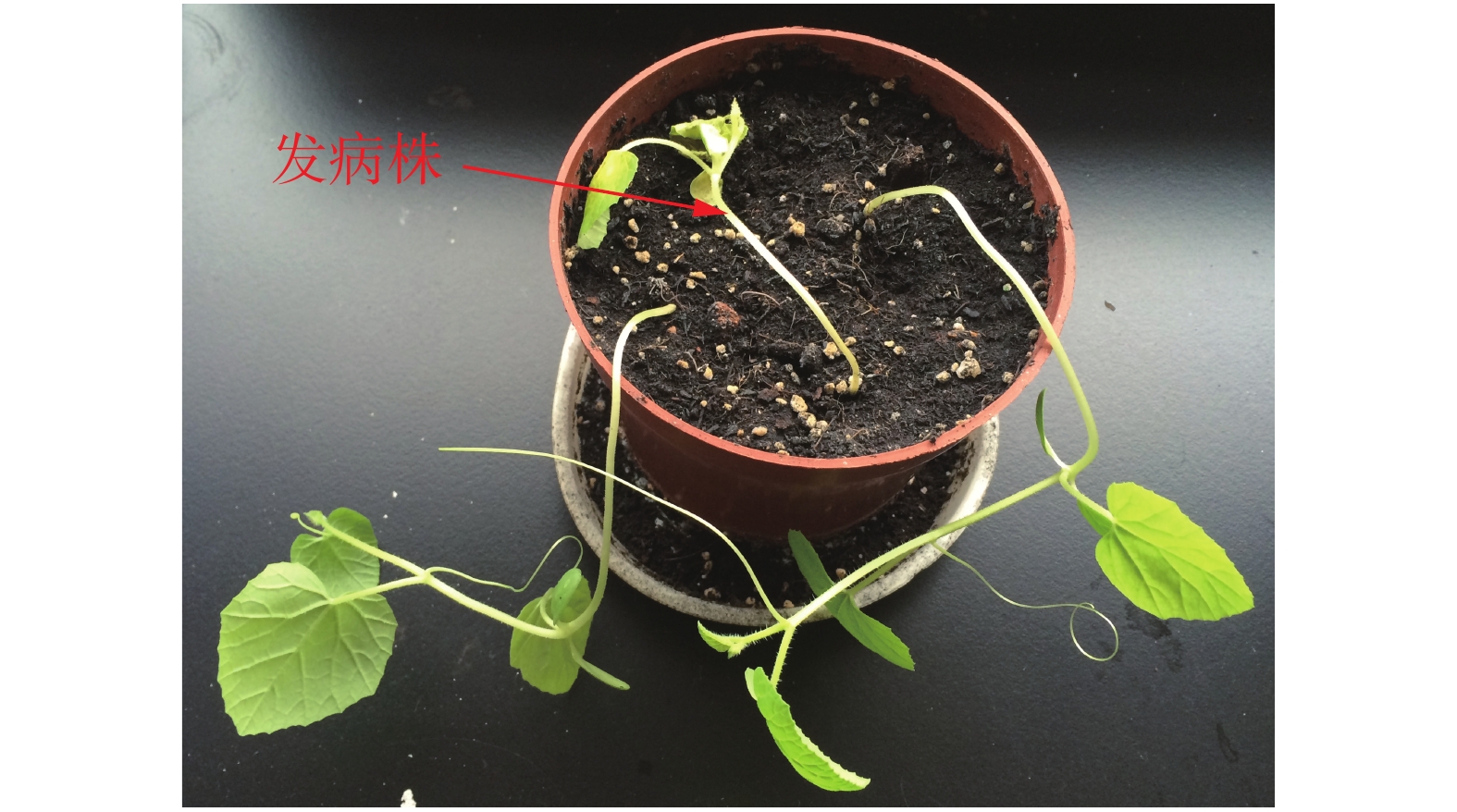
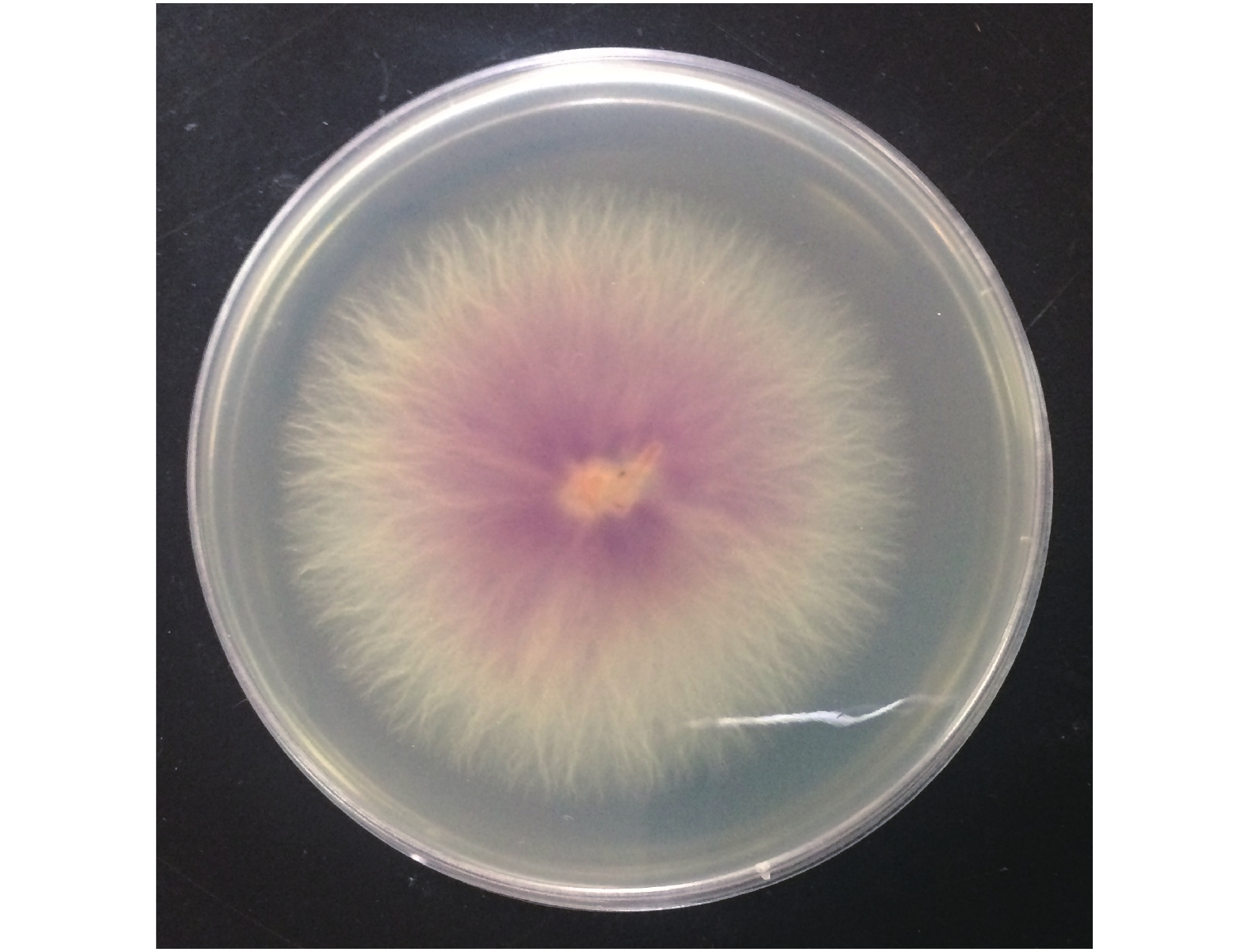
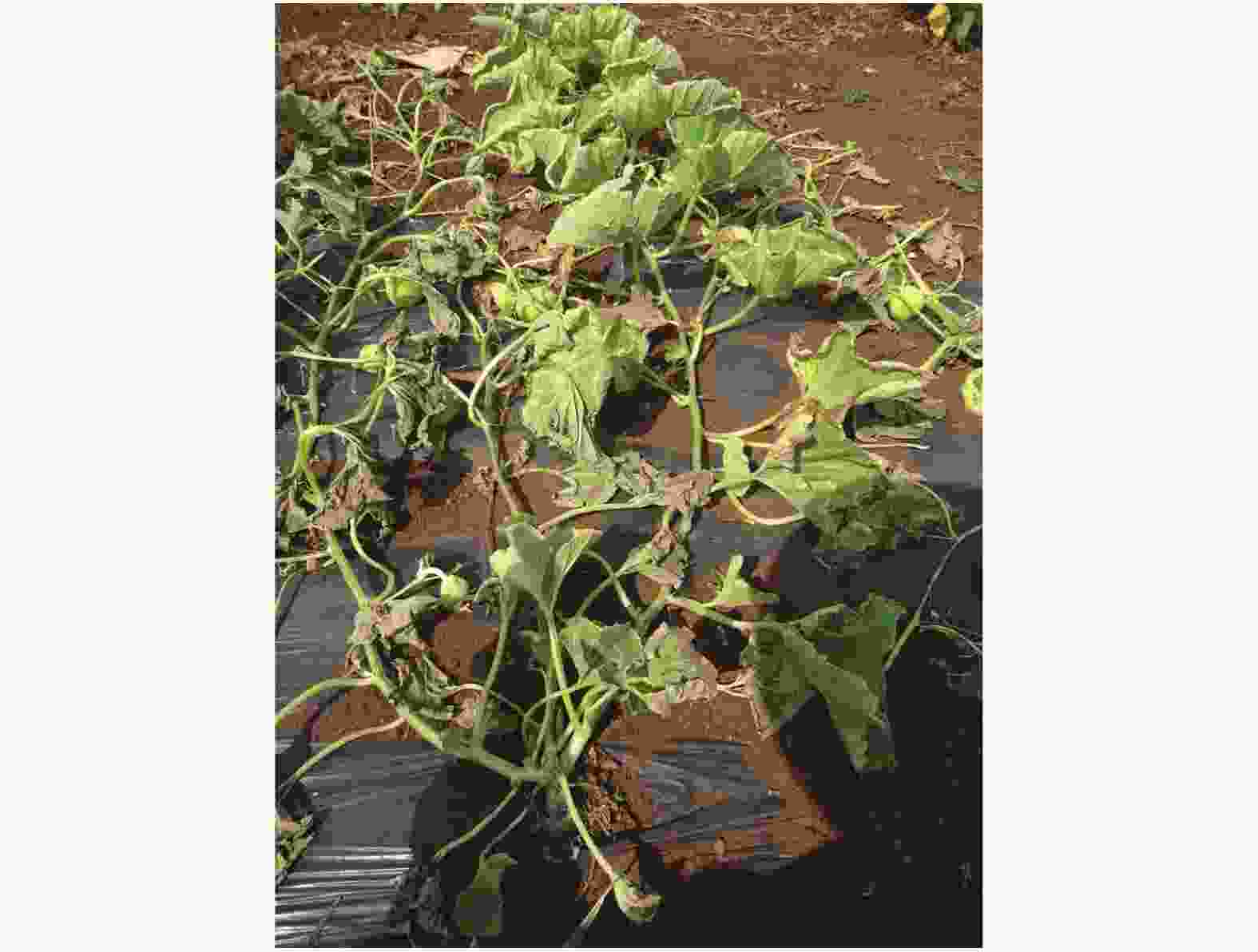
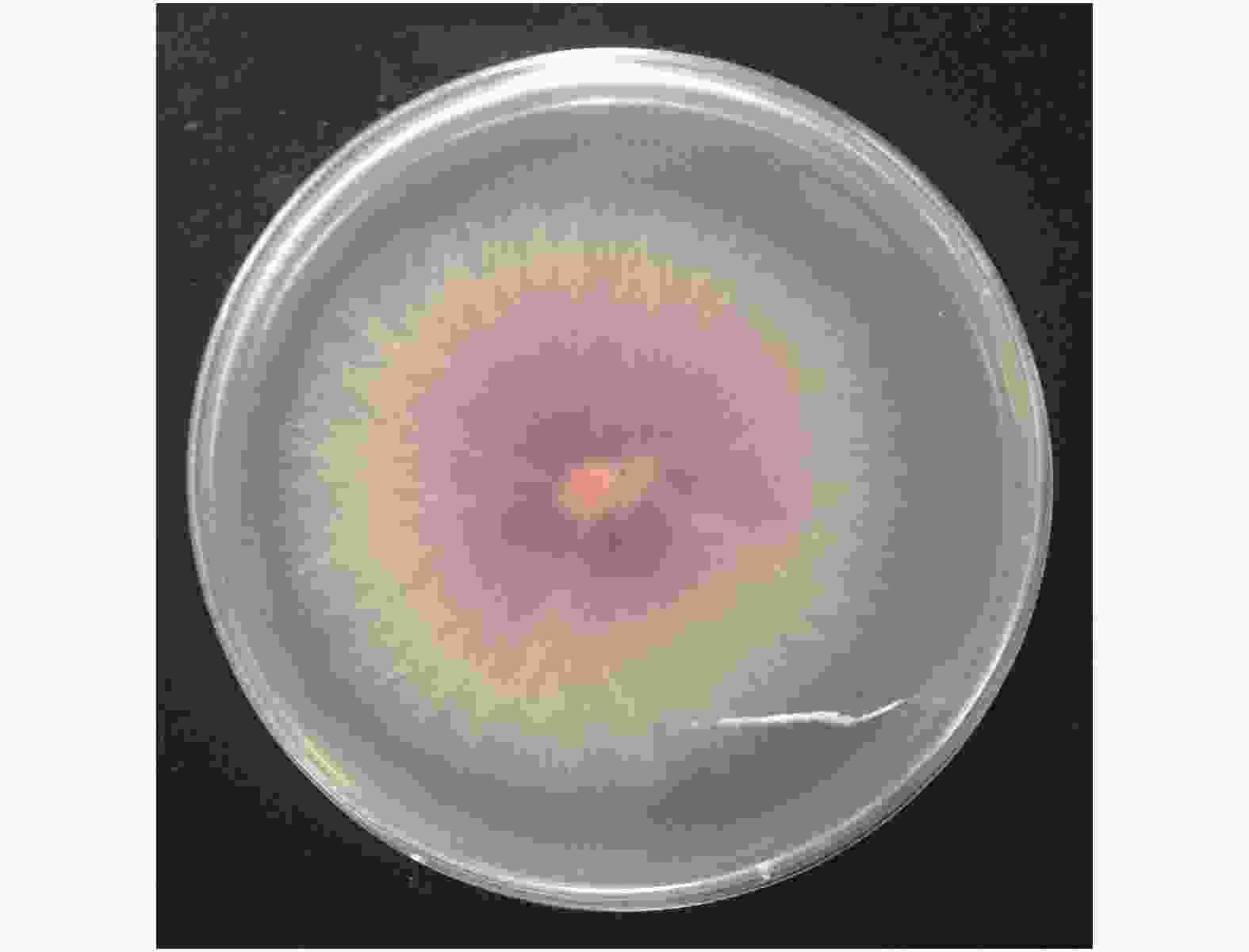
薄皮甜瓜枯萎病是由真菌引致的植物病害,症状包括严重的点斑、凋萎或叶、花、果、茎或整株植物的死亡。生长迅速的甜瓜的幼嫩组织常被侵袭,导致植株不能正常结实(图1)。病原菌为土传病害,从幼嫩的根部侵入植株,向上延伸发展。病害后期植株茎杆内部略呈现褐色(图2)。
-
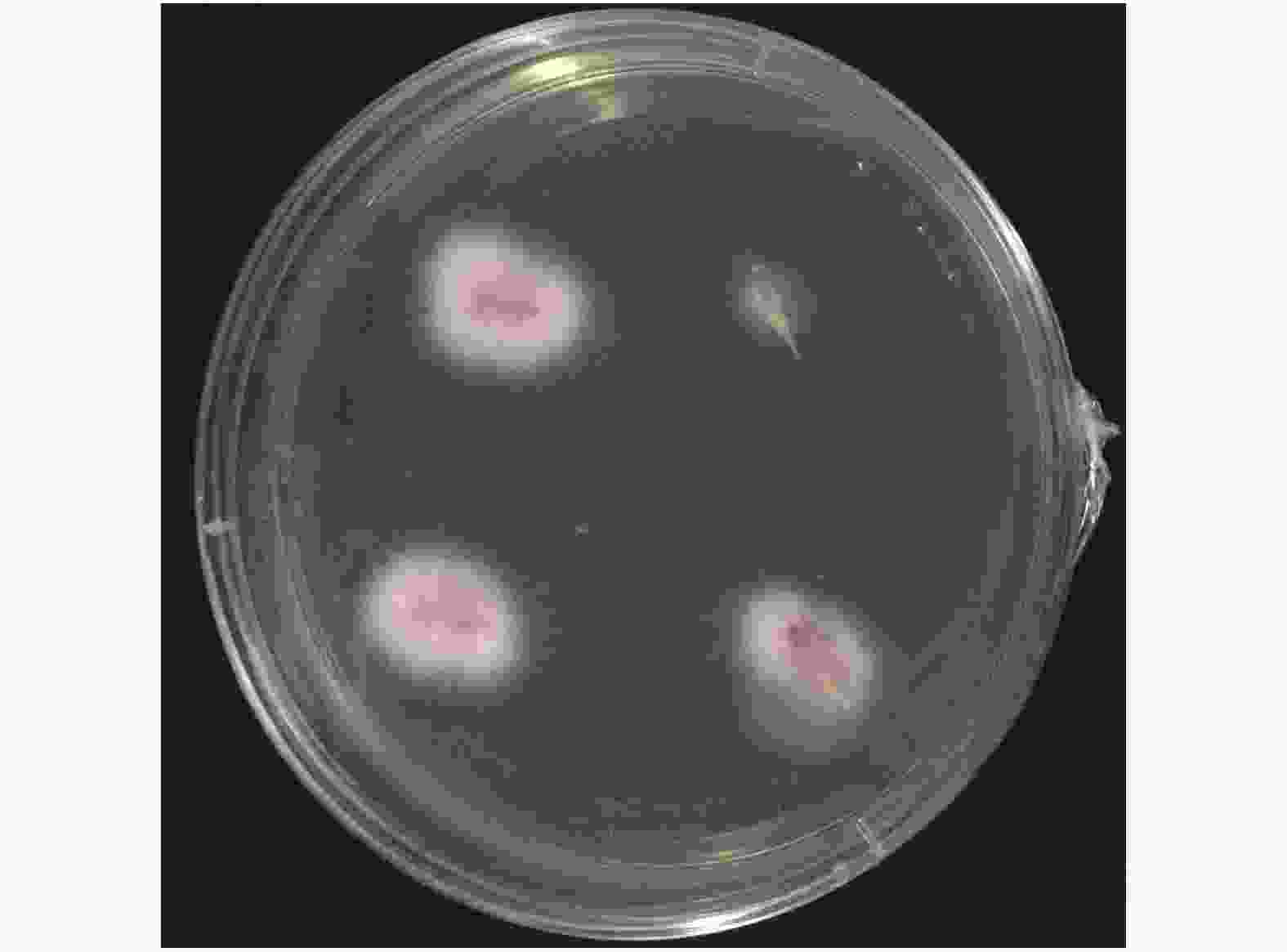
甜瓜枯萎病病原菌在PDA培养基上生长缓慢,外部菌丝为灰白色,中间菌丝在培养基里的呈现淡粉色(图3)。提取病原菌丝DNA进行ITS序列扩增(图4),测序结果546 bp碱基与 Fusarium oxysporum f. sp.(GenBank: GU247453.1)相似度达到99%。
-
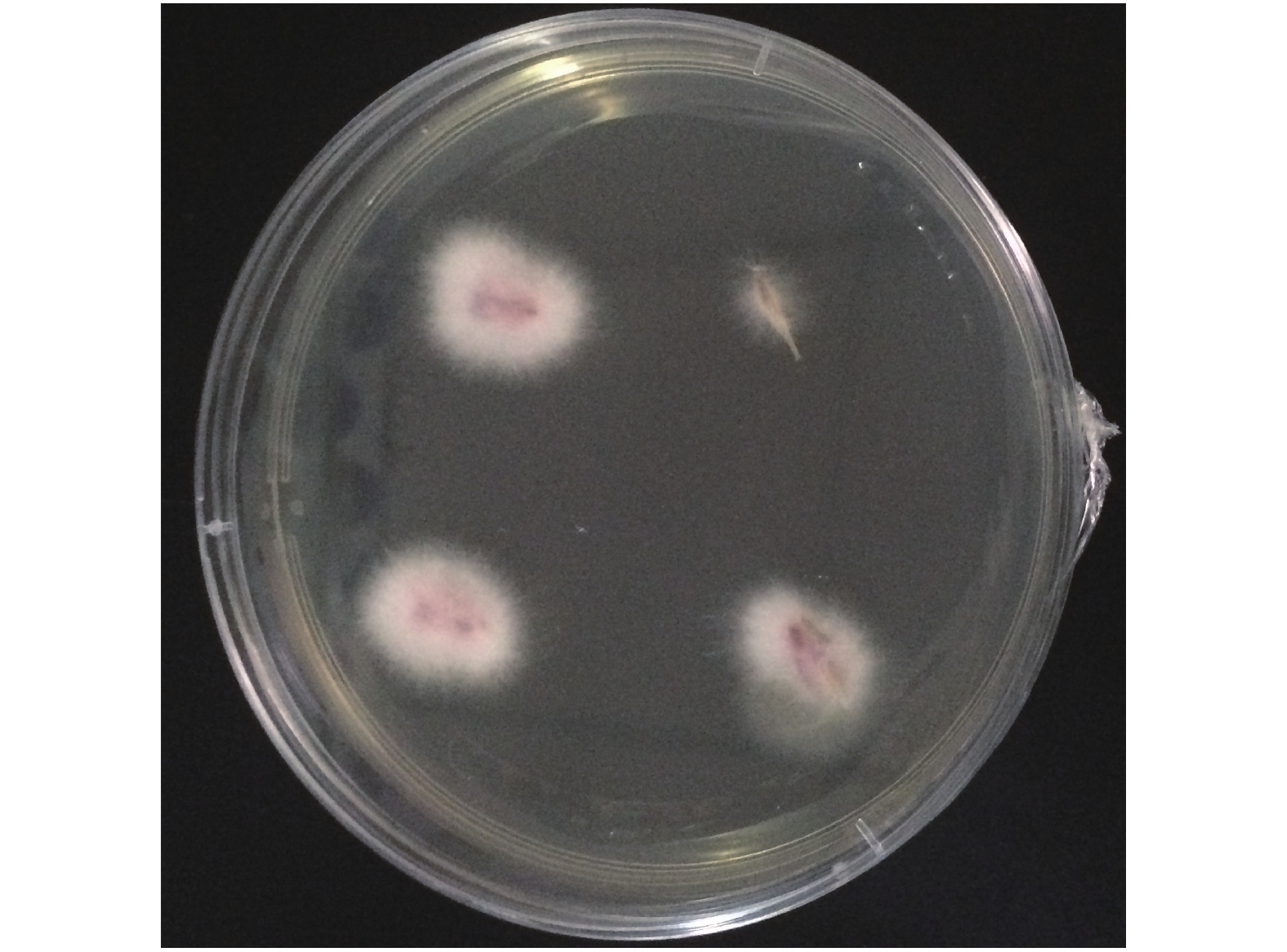
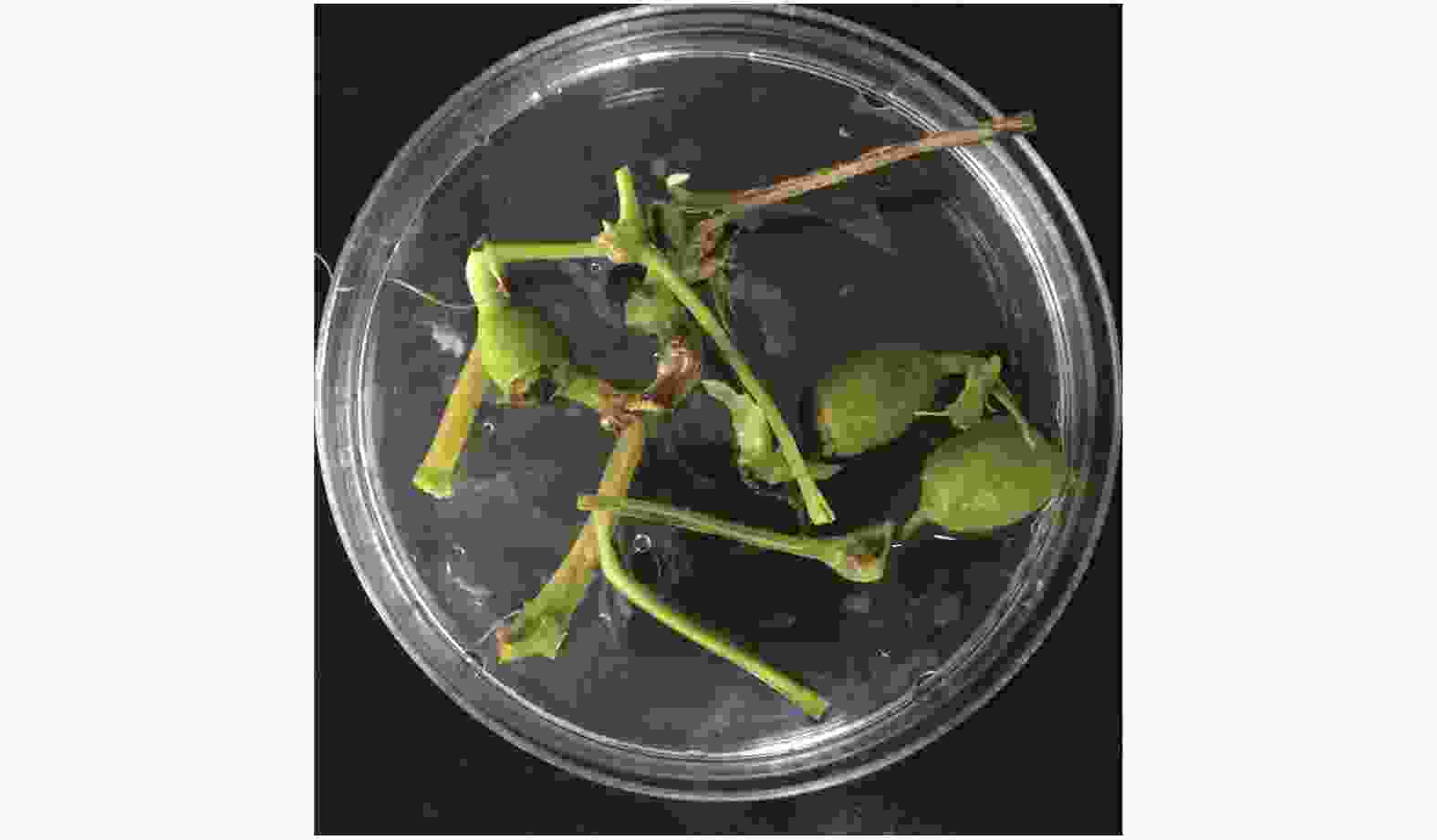
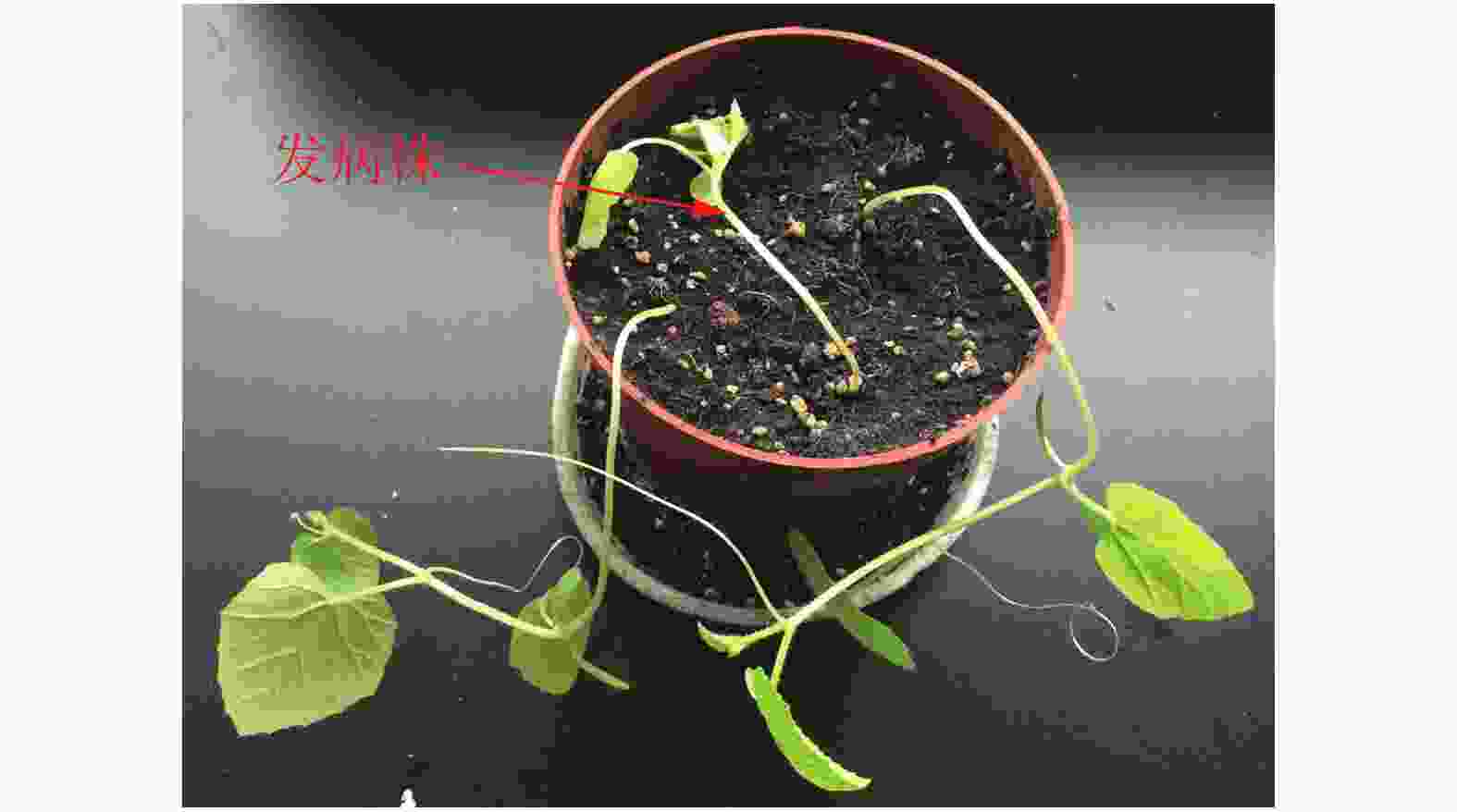
将病原菌在PDA 培养基上进行扩大培养,待菌丝长满培养皿后转入室内光照刺激产孢,用灭菌水洗下孢子镜检后接入无菌土,播种薄皮甜瓜‘美浓’种子,待发芽后持续观察发病情况。取发病症状为子叶萎蔫、真叶黄化、呈猝倒状的植株(图5),按照1.4的方法重新分离该病原菌(图6),进行柯赫氏法则验证。
-
2018−05−05定植,2018−06−25试验植株初果期,检测发病情况,结果见表2。对照‘美浓’的发病率为83.33%;新土佐类型的砧木品种中‘甬砧’、‘广砧1号’、‘砧8’的发病率都为0,‘银光’的发病率为12.5%;中国南瓜类型中‘连大’、‘夏利’的发病率为0,‘壮士’的发病率为25.0%。
砧木类型 Rootstock 品种 Varieties 定植株 Plants planted 发病株 Plants infected 发病率% Infection rate CK(美浓) 24 20 83.33 新土佐 银光 24 3 12.50 甬砧 24 0 0 广砧1号 24 0 0 大白 24 2 8.33 砧8 24 0 0 中国南瓜 连大 24 0 0 大正 24 2 8.33 壮士 24 6 25.00 厦利 24 0 0 注:2018−06−25定植的盆栽接种枯萎病菌试验结果。
Note: Experiment of potted muskmeon plants inoculated with fusarium wilt pathogen and planted on 25 June 2018.Table 2. Field infection of thin-skinned muskmelon rootstocks with fusarium wilt pathogen
2.1. 甜瓜枯萎病症状
2.2. 病原菌形态特征及分子鉴定
2.3. 病菌柯氏法则验证
2.4. 抗病砧木田间发病状况
-
甜瓜枯萎病是典型的土传真菌病害,在植株整个生育期均可发生,但以开花坐果期发病最重。枯萎病菌受到瓜类蔬菜根系分泌物的刺激,在适宜的温、湿度下萌发出牙管,从根部、根尖或伤口侵入,刺穿表皮、皮质组织,进入维管束,在导管内生长发育。病菌在导管内分泌果胶酶、纤维素酶分解破坏细胞,使有毒物质堵塞导管,阻碍水分的运输,当植物蒸发量大时,供水不足而导致萎蔫,严重的出现死秧[1]。朱利林等[2]通过鉴定发现海南省哈密瓜枯萎病是由尖孢镰刀菌甜瓜专化型引起。本研究从海南薄皮甜瓜主产区的田间薄皮甜瓜病株上分离到病原菌,经形态学及rDNA序列测定鉴定为尖孢镰刀菌(F. oxysporum)。将该病原菌孢子液加入土壤,播种薄皮甜瓜种子,幼苗生长约3周后发病,再次从茎部分离病原菌和分子检测,证明与接种病菌一致。
枯萎病具有明显的寄主专化型,利用这一特性进行嫁接栽培,可有效防止瓜类枯萎病的发生。最常用的砧木是南瓜,嫁接后可显著提高甜瓜抗枯萎病的能力,但不同品种的南瓜砧木抗病能力差异明显[3]。利用抗病南瓜种间杂交种作砧木,能更显著增强西甜瓜的生长势、抗逆性,有效防止甜瓜土传病害的发生,降低连作障碍的不良影响,最终达到抗病、优质、高产的目的。如大和农园株式会社培育出的新土佐系列,韩国神砧、甜香砧系列,台湾农友种苗的‘壮士’,宁波市农业科学研究院的甬砧系列砧木等[4]。本研究将9种不同的甜瓜砧木接种薄皮甜瓜枯萎病原菌、以‘美浓’为对照,后定植于营养钵中,在初果期(约50 d)观察田间发病情况,筛选出5种发病率为0的抗病砧木品种:‘广砧1号’、‘连大’、‘厦利’、‘甬砧’、‘砧8’,为薄皮甜瓜的嫁接砧木品种筛选提供抗病性依据。










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: