2020 Vol. 11, No. 2
2020, 11(2): 125-131.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.001
Abstract:
Conotoxin Lv68 is a new M superfamily conotoxin cloned from the cDNA of Conus lividus from Hainan. It consists of 15 amino acid residues, and contains 6 cysteine, and the cysteine framework is -CC-C-C-CC- (type III). Linear peptide of conotoxin Lv68 was synthesized by using Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. The one-step oxidative conditions of disulfide bond folding for the major folded products of Lv68 were studied and optimized. Bioactivities of the major folded products were assayed on a series of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChRs) subtypes (α3β4, α6β4, α4β2, α9α10, α1β1γδ and α1β1δε) by using the voltage patch clamp technology. The Lv68 produced maximum folding yield (18.14%) under the optimized folding conditions including reaction system composition (0.1 mol·L−1 Tris-HCl, 1 mmol·L−1 EDTA, GSH / GSSG 1 mmol·L−1 / 1 mmol·L−1), linear peptide concentration (50 μmol·L−1), and reaction time (2 h). A medium blocking effect (80% inhibition) on α9α10 nAChR subtype was detected for the Lv68 at the concentration of 1 μmol·L−1. These results confirmed the optimized folding conditions of conotoxin Lv68 and its activity to block α9α10 nAChR, which broadened the target range of the M superfamily conotoxins containing cysteine framework Ⅲ. The results not only lay the foundation for the further development of Lv68 as an analgesic drug lead targeting α9α10 nAChR, but also provide a reference and guidance for the oxidative folding, biological activity research and further development and utilization of other M-conotoxins containing cysteine framework Ⅲ.
Conotoxin Lv68 is a new M superfamily conotoxin cloned from the cDNA of Conus lividus from Hainan. It consists of 15 amino acid residues, and contains 6 cysteine, and the cysteine framework is -CC-C-C-CC- (type III). Linear peptide of conotoxin Lv68 was synthesized by using Solid Phase Peptide Synthesis. The one-step oxidative conditions of disulfide bond folding for the major folded products of Lv68 were studied and optimized. Bioactivities of the major folded products were assayed on a series of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChRs) subtypes (α3β4, α6β4, α4β2, α9α10, α1β1γδ and α1β1δε) by using the voltage patch clamp technology. The Lv68 produced maximum folding yield (18.14%) under the optimized folding conditions including reaction system composition (0.1 mol·L−1 Tris-HCl, 1 mmol·L−1 EDTA, GSH / GSSG 1 mmol·L−1 / 1 mmol·L−1), linear peptide concentration (50 μmol·L−1), and reaction time (2 h). A medium blocking effect (80% inhibition) on α9α10 nAChR subtype was detected for the Lv68 at the concentration of 1 μmol·L−1. These results confirmed the optimized folding conditions of conotoxin Lv68 and its activity to block α9α10 nAChR, which broadened the target range of the M superfamily conotoxins containing cysteine framework Ⅲ. The results not only lay the foundation for the further development of Lv68 as an analgesic drug lead targeting α9α10 nAChR, but also provide a reference and guidance for the oxidative folding, biological activity research and further development and utilization of other M-conotoxins containing cysteine framework Ⅲ.
2020, 11(2): 132-137, 155.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.002
Abstract:
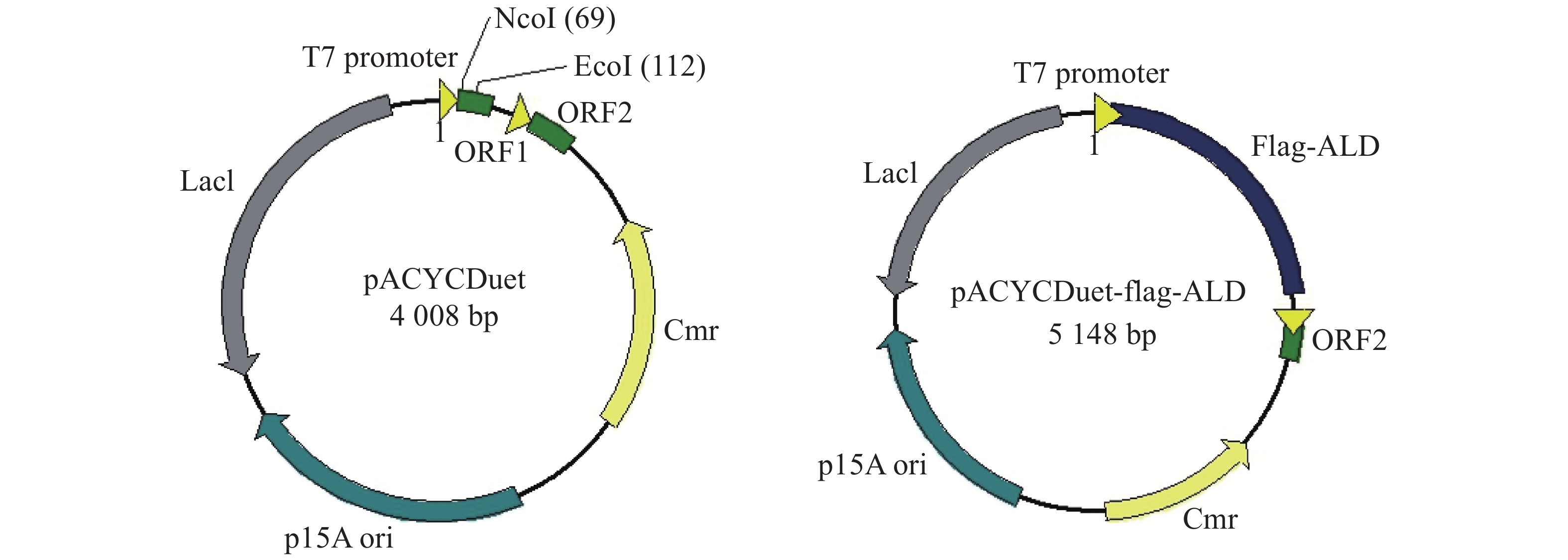
Alanine dehydrogenase (ALD, EC 1.4.1.1) is a microbial enzyme, which plays an important role in the transformation of alanine to pyruvate, carbon metabolism, nitrogen metabolism, and energy metabolism in microorganism. In order to study the function of ALD protein in Aeromonas veronii that causes important aquatic diseases, C4 genomic DNA of A. veronii was used as a template to amplify ALD gene with Flag tag on the N-terminal by PCR. The target gene was incorporated into the expression vector pACYCDuet, and the recombinant plasmid pACYCDuet-Flag-ALD was transformed into E. coli BL21. The recombinant protein was induced by Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). SDS-PAGE and Western blot showed that the recombinant protein of Flag-ALD was successfully expressed in a soluble form in E. coli. The results laid a foundation for the expression of exogenous ALD protein. The flag labeled target protein may provide a technical support for the further study on the function of alanine dehydrogenase in A. veronii and the development of bacteriostatic agents.
Alanine dehydrogenase (ALD, EC 1.4.1.1) is a microbial enzyme, which plays an important role in the transformation of alanine to pyruvate, carbon metabolism, nitrogen metabolism, and energy metabolism in microorganism. In order to study the function of ALD protein in Aeromonas veronii that causes important aquatic diseases, C4 genomic DNA of A. veronii was used as a template to amplify ALD gene with Flag tag on the N-terminal by PCR. The target gene was incorporated into the expression vector pACYCDuet, and the recombinant plasmid pACYCDuet-Flag-ALD was transformed into E. coli BL21. The recombinant protein was induced by Isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). SDS-PAGE and Western blot showed that the recombinant protein of Flag-ALD was successfully expressed in a soluble form in E. coli. The results laid a foundation for the expression of exogenous ALD protein. The flag labeled target protein may provide a technical support for the further study on the function of alanine dehydrogenase in A. veronii and the development of bacteriostatic agents.
2020, 11(2): 138-144.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.003
Abstract:
To investigate the role of secretory carrier membrane protein (SCAMP), five SCAMP genes were cloned from Arabidopsis thaliana by PCR method for bioinformatics analysis, and their expression under salt stress was analyzed by using the real time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). Bioinformatics analysis showed that the AtSCAMP proteins have a molecular weight of 30.1-33.2 kDa with an isoelectric point (pI) of 6.60-9.18, and hence belong to unstable hydrophobic proteins. The secondary structure of the AtSCAMP proteins contains four conformations: α-helix (Hh), random coil (Cc), extended strand (Ee) and β-turn (Tt), of which α-helix is the main part. There are four transmembrane domains in the AtSCAMP proteins, and the N-terminus and C-terminus are located in the cell membrane. The qRT-PCR results showed that the expression of the AtSCAMP genes was all up-regulated in response to salt stress. The expression of AtSCAMP1, AtSCAMP3, AtSCAMP4 and AtSCAMP5 was higher in the leaves of A. thaliana than in the roots, and the most significant changes were found in the expression of AtSCAMP4 and AtSCAMP5 in leaves under salt stress.
To investigate the role of secretory carrier membrane protein (SCAMP), five SCAMP genes were cloned from Arabidopsis thaliana by PCR method for bioinformatics analysis, and their expression under salt stress was analyzed by using the real time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR). Bioinformatics analysis showed that the AtSCAMP proteins have a molecular weight of 30.1-33.2 kDa with an isoelectric point (pI) of 6.60-9.18, and hence belong to unstable hydrophobic proteins. The secondary structure of the AtSCAMP proteins contains four conformations: α-helix (Hh), random coil (Cc), extended strand (Ee) and β-turn (Tt), of which α-helix is the main part. There are four transmembrane domains in the AtSCAMP proteins, and the N-terminus and C-terminus are located in the cell membrane. The qRT-PCR results showed that the expression of the AtSCAMP genes was all up-regulated in response to salt stress. The expression of AtSCAMP1, AtSCAMP3, AtSCAMP4 and AtSCAMP5 was higher in the leaves of A. thaliana than in the roots, and the most significant changes were found in the expression of AtSCAMP4 and AtSCAMP5 in leaves under salt stress.
2020, 11(2): 145-155.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.004
Abstract:
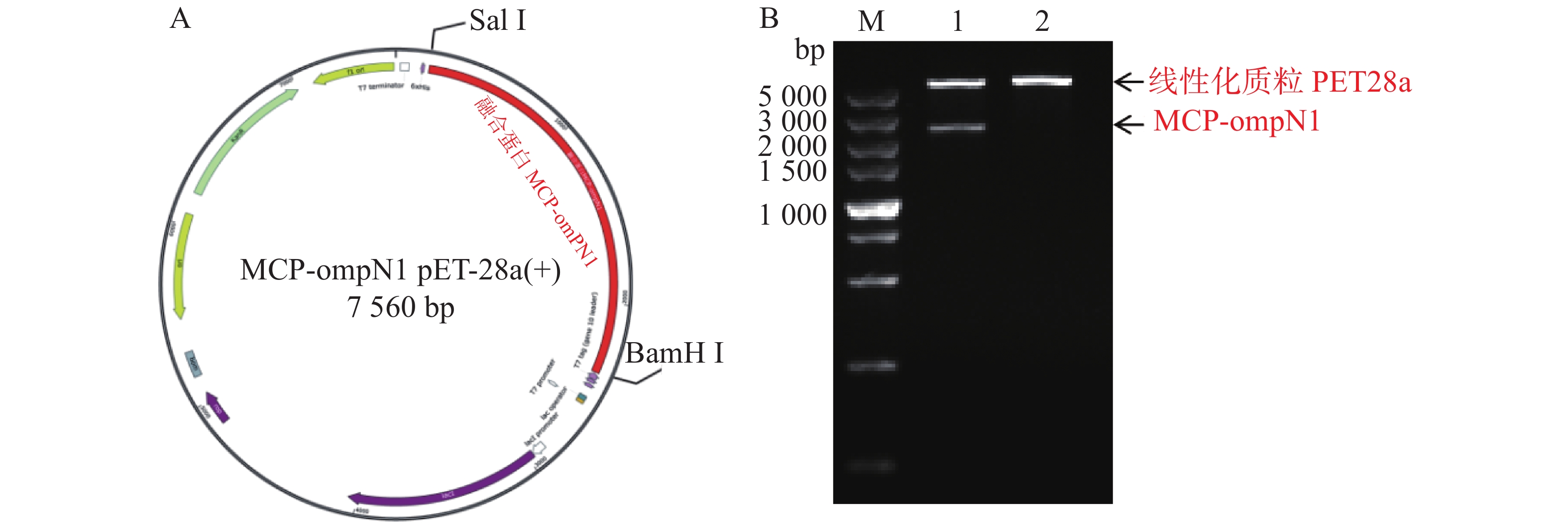
At present, certain proteins of the nervous necrosis virus are injected into fish as vaccines, but traditional injection immunization cannot effectively stimulate mucosal immunity. In this experiment, the capsid protein (MCP) of the fish nervous necrosis virus was fused with the transmucosal protein ompN1 of Edwardsiella ictaluri to prepare a mucosal vaccine against the nervous necrosis virus. The gene sequences of the coat protein MCP of the fish nervous necrosis virus and the outer membrane protein ompN1 of E. ictaluri were obtained from the NCBI GenBank, and then optimized and synthesized, and the synthesized genes were used to construct prokaryotic expression vectors respectively: MCP-ompN1 pET28a, MCP pET28a, ompN1 pET28a. The fusion proteins MCP-ompN1, MCP and ompN1 were induced and expressed in Escherichia coli, respectively, and they were purified through inclusion body purification and refolded through dialysis. SDS-PAGE results showed that the purified MCP-ompN1 fusion protein was obtained by prokaryotic expression and purification. Further Western blotting showed that the purified MCP-ompN1 fusion protein had both MCP antigenicity and ompN1 antigenicity. It is indicated that the MCP-ompN1 protein into which the fish nervous necrosis virus capsid protein MCP was fused with E. ictaluri outer membrane protein ompN1 was obtained by prokaryotic expression and purification. Further study is needed to observe whether the fusion protein MCP-ompN1 can be used as a mucosal vaccine against nervous necrosis virus.
At present, certain proteins of the nervous necrosis virus are injected into fish as vaccines, but traditional injection immunization cannot effectively stimulate mucosal immunity. In this experiment, the capsid protein (MCP) of the fish nervous necrosis virus was fused with the transmucosal protein ompN1 of Edwardsiella ictaluri to prepare a mucosal vaccine against the nervous necrosis virus. The gene sequences of the coat protein MCP of the fish nervous necrosis virus and the outer membrane protein ompN1 of E. ictaluri were obtained from the NCBI GenBank, and then optimized and synthesized, and the synthesized genes were used to construct prokaryotic expression vectors respectively: MCP-ompN1 pET28a, MCP pET28a, ompN1 pET28a. The fusion proteins MCP-ompN1, MCP and ompN1 were induced and expressed in Escherichia coli, respectively, and they were purified through inclusion body purification and refolded through dialysis. SDS-PAGE results showed that the purified MCP-ompN1 fusion protein was obtained by prokaryotic expression and purification. Further Western blotting showed that the purified MCP-ompN1 fusion protein had both MCP antigenicity and ompN1 antigenicity. It is indicated that the MCP-ompN1 protein into which the fish nervous necrosis virus capsid protein MCP was fused with E. ictaluri outer membrane protein ompN1 was obtained by prokaryotic expression and purification. Further study is needed to observe whether the fusion protein MCP-ompN1 can be used as a mucosal vaccine against nervous necrosis virus.
2020, 11(2): 156-162.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.005
Abstract:
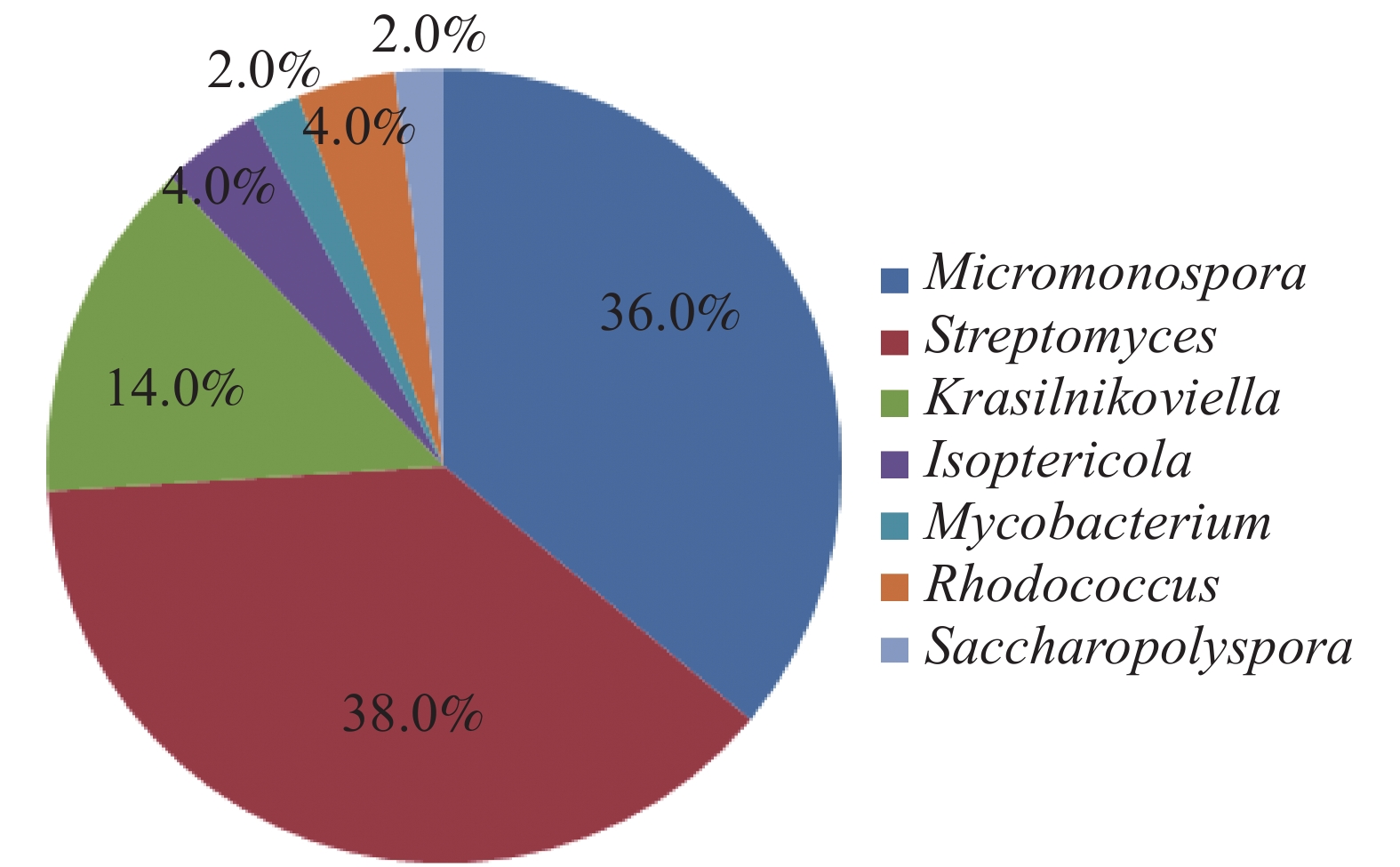
To investigate microbial diversity and potential pharmaceutical value of actinomycetes associated with marine sponges from Hainan actinomycetes associated with marine sponges from Wenchang sea area in Hainan were collected, isolated and identified, and their anti-microbial activities were analyzed. Four media were used to isolate and purify the actinomycetes from the marine sponges, and the isolates were identified according to their 16S rRNA sequences. the antibacterial activities of their fermentated products were tested using standard disk diffusion. Results showed that a total of 50 strains of actinomycetes were isolated from 4 types marine sponges. The isolates belonged to 7 genera within 6 families, 5 suborders of Actinobacteria, and contained Streptomyces, micromonospora, Rhodococcus, Saccharopolyspora, Isoptericola, Mycobacterium and Krasilnikoviella, among which Krasilnikoviella was first recorded isolated from marine sponges. Four isolates were potential novel species. The antimicrobial test showed that 48% of the total isolates displayed antibacterial activity while 24% inhibited plant filamentous pathogenic fungi. The diversity and antimicrobial activity of the fermentated products of the actinomycetes associated with marine sponges collected from Wenchang sea area in Hainan were preliminarily revealed.
To investigate microbial diversity and potential pharmaceutical value of actinomycetes associated with marine sponges from Hainan actinomycetes associated with marine sponges from Wenchang sea area in Hainan were collected, isolated and identified, and their anti-microbial activities were analyzed. Four media were used to isolate and purify the actinomycetes from the marine sponges, and the isolates were identified according to their 16S rRNA sequences. the antibacterial activities of their fermentated products were tested using standard disk diffusion. Results showed that a total of 50 strains of actinomycetes were isolated from 4 types marine sponges. The isolates belonged to 7 genera within 6 families, 5 suborders of Actinobacteria, and contained Streptomyces, micromonospora, Rhodococcus, Saccharopolyspora, Isoptericola, Mycobacterium and Krasilnikoviella, among which Krasilnikoviella was first recorded isolated from marine sponges. Four isolates were potential novel species. The antimicrobial test showed that 48% of the total isolates displayed antibacterial activity while 24% inhibited plant filamentous pathogenic fungi. The diversity and antimicrobial activity of the fermentated products of the actinomycetes associated with marine sponges collected from Wenchang sea area in Hainan were preliminarily revealed.
2020, 11(2): 163-169, 176.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.006
Abstract:
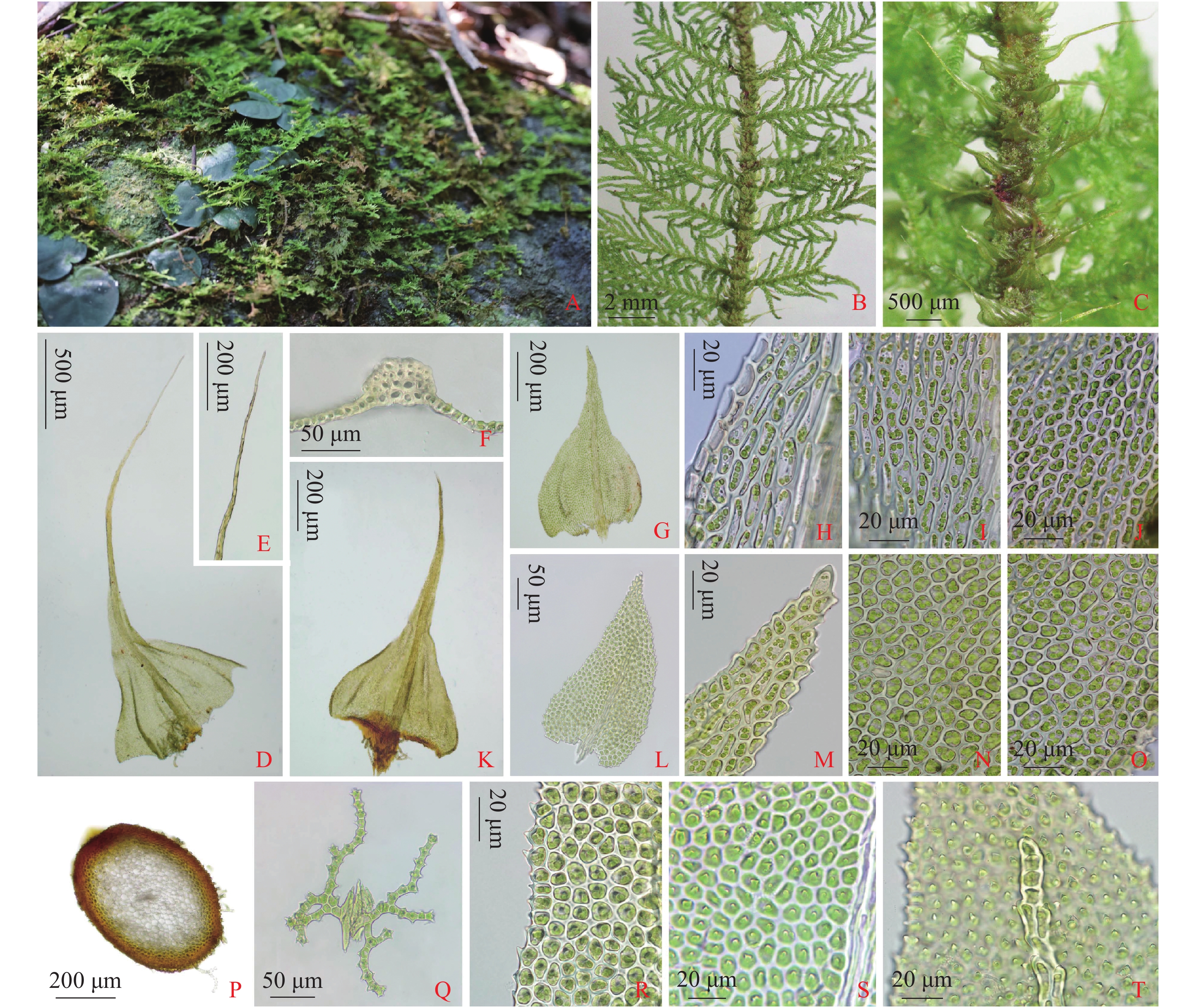
Thuidium cymbifolium, a traditional medicine, was collected from Limu Mountain in Hainan to observe its morphology and analyze its volatile composition. Its morphology was compared with that of its 4 relatives and varieties to find out their morphological difference, and its volatile compounds was extracted by using accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) with petroleum ether as solvent and then analyzed by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The analysis showed that the volatile compounds of T. cymbifolium were identified to contain 31 constituents, accounting for 91.1% of the total chemical composition. The main constituents were esters (25.48%), terpenes (22.64%), ketones (20.64%) and sterols (10.61%), including butyl butyrate (18.96%), 4-heptanone (10.90%), squalene (10.75%) and 4-heptanone,3-methyl (9.74%).
Thuidium cymbifolium, a traditional medicine, was collected from Limu Mountain in Hainan to observe its morphology and analyze its volatile composition. Its morphology was compared with that of its 4 relatives and varieties to find out their morphological difference, and its volatile compounds was extracted by using accelerated solvent extraction (ASE) with petroleum ether as solvent and then analyzed by using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The analysis showed that the volatile compounds of T. cymbifolium were identified to contain 31 constituents, accounting for 91.1% of the total chemical composition. The main constituents were esters (25.48%), terpenes (22.64%), ketones (20.64%) and sterols (10.61%), including butyl butyrate (18.96%), 4-heptanone (10.90%), squalene (10.75%) and 4-heptanone,3-methyl (9.74%).
2020, 11(2): 170-176.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.007
Abstract:
MeNOSIP (Nitric oxide synthase interaction protein) gene coding region sequence in cassava was obtained by RT-PCR cloning based on the MeRbohD candidate interaction protein MeNOSIP to study the function of cassava MeRbohD in the disease resistance pathway. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that the CDs sequence of MeNOSIP was 918 bp, encoding a polypeptide containing 305 amino acids, and MeNOSIP belongs to an unstable hydrophilic protein. The subcellular localization predicted the expression of MeNOSIP on the cell membrane. Yeast hybridization was used to verify the true interaction between MeRbohD and MeNOSIP. MeRbohD and MeNOSIP genes were up-regulated under the induction of JA, SA, and ABA treatment, and MeRbohD and MeNOSIP gene expression under the ABA treatment tended to be consistent, which indicated that that they might be involved in the ABA-mediated stress resistance pathway.
MeNOSIP (Nitric oxide synthase interaction protein) gene coding region sequence in cassava was obtained by RT-PCR cloning based on the MeRbohD candidate interaction protein MeNOSIP to study the function of cassava MeRbohD in the disease resistance pathway. Bioinformatics analysis revealed that the CDs sequence of MeNOSIP was 918 bp, encoding a polypeptide containing 305 amino acids, and MeNOSIP belongs to an unstable hydrophilic protein. The subcellular localization predicted the expression of MeNOSIP on the cell membrane. Yeast hybridization was used to verify the true interaction between MeRbohD and MeNOSIP. MeRbohD and MeNOSIP genes were up-regulated under the induction of JA, SA, and ABA treatment, and MeRbohD and MeNOSIP gene expression under the ABA treatment tended to be consistent, which indicated that that they might be involved in the ABA-mediated stress resistance pathway.
2020, 11(2): 177-189.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.008
Abstract:
The defense response of plants to stress is largely regulated by the level of gene transcription, and the recognition and combination of the transcription factor and cis-acting elements on the target gene promoter plays a key regulatory role. ERF is a type of transcription factor that plays an important role in the growth and development of plants. There is a conserved GCC-box in the promoter region of downstream target genes regulated by it. In order to analyze the regulatory pathway of ERF in the growth and development of cassava, 204 genes containing GCC-box cis-acting elements in the promoter region were screened. Chromosomal position distribution, analysis of expression patterns under pathogen infection, and promoter structure prediction of these genes were analyzed using bioinformatics methods. The qRT-PCR results showed that Manes.02G189600, Manes.03G039700, Manes.06G002000, Manes.09G063700, Manes.14G141600, Manes.15G181900 might be involved in regulating plant disease resistance pathways, and play an important way in ethylene-mediated signal transduction pathways.
The defense response of plants to stress is largely regulated by the level of gene transcription, and the recognition and combination of the transcription factor and cis-acting elements on the target gene promoter plays a key regulatory role. ERF is a type of transcription factor that plays an important role in the growth and development of plants. There is a conserved GCC-box in the promoter region of downstream target genes regulated by it. In order to analyze the regulatory pathway of ERF in the growth and development of cassava, 204 genes containing GCC-box cis-acting elements in the promoter region were screened. Chromosomal position distribution, analysis of expression patterns under pathogen infection, and promoter structure prediction of these genes were analyzed using bioinformatics methods. The qRT-PCR results showed that Manes.02G189600, Manes.03G039700, Manes.06G002000, Manes.09G063700, Manes.14G141600, Manes.15G181900 might be involved in regulating plant disease resistance pathways, and play an important way in ethylene-mediated signal transduction pathways.
2020, 11(2): 190-199.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.009
Abstract:
An AP2 homologous gene LcANT was cloned from Litchi ‘Feizixiao’ (Litchi chinensis Sonn. Feizixiao) based on the litchi whole genome database available from the Environment and Plant Protection Institute. The gene LcANT was 2 087 bp in full-length cDNA, encoded 695 amino acids and contained two AP2/EREBP conserved domains. Bioinformatics analysis showed that the LcANT contained 7 introns, and that the subcellular localization was predicted in the nuclear. The LcANT protein was hydrophobic and its secondary structure wass mostly random coils. BLAST sequence alignment analysis showed that the LcANT had a high homology in amino acid sequences with the ANT transcription factors from other plants, and had a maximum identity of up to 82% with the ANT from pistachio (Pistacia vera). The q-PCR was used to characterize the expression pattern of the LcANT in the tissues of Litchi 'Feizixiao', and the results showed that the LcANT had higher expression levels in spring shoots, ovary, inflorescence, and flower buds, implying that this gene may regulate the growth and development of floral organs and other plant vegetative organs. The acquisition of the LcANT gene provides a molecular basis for further research focused on its function on the growth and development of vegetative organs of Litchi.
An AP2 homologous gene LcANT was cloned from Litchi ‘Feizixiao’ (Litchi chinensis Sonn. Feizixiao) based on the litchi whole genome database available from the Environment and Plant Protection Institute. The gene LcANT was 2 087 bp in full-length cDNA, encoded 695 amino acids and contained two AP2/EREBP conserved domains. Bioinformatics analysis showed that the LcANT contained 7 introns, and that the subcellular localization was predicted in the nuclear. The LcANT protein was hydrophobic and its secondary structure wass mostly random coils. BLAST sequence alignment analysis showed that the LcANT had a high homology in amino acid sequences with the ANT transcription factors from other plants, and had a maximum identity of up to 82% with the ANT from pistachio (Pistacia vera). The q-PCR was used to characterize the expression pattern of the LcANT in the tissues of Litchi 'Feizixiao', and the results showed that the LcANT had higher expression levels in spring shoots, ovary, inflorescence, and flower buds, implying that this gene may regulate the growth and development of floral organs and other plant vegetative organs. The acquisition of the LcANT gene provides a molecular basis for further research focused on its function on the growth and development of vegetative organs of Litchi.
2020, 11(2): 200-209, 216.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.010
Abstract:
In order to study the role of neutral trehalase in the pathogenicity and intolerance environment of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp.cubense race 4 (Foc4-37), a neutral trehalase-encoding gene knockout mutant Δnth1 was constructed, and its pathogenicity, biological characteristics and resistance to phenamacril were determined. The results showed the neutral trehalase-encoding gene knockout mutant Δnth1 was lower in colony growth rate and conidia germination rate, and significantly lower in pathogenicity to banana (Cavendish, AAA) than the wild-type strain. However, there was no significant difference in conidia yield and sensitivity to phenamacril (EC50 = 6.07 mg·L−1) between the mutant and the wild type strain. It was inferred that NTH1 gene was involved in regulating the growth and conidia germination of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp., and responding to the cell wall synthesis and oxidative stress, but not to the osmotic pressure, high sugar stress and temperature stress.
In order to study the role of neutral trehalase in the pathogenicity and intolerance environment of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp.cubense race 4 (Foc4-37), a neutral trehalase-encoding gene knockout mutant Δnth1 was constructed, and its pathogenicity, biological characteristics and resistance to phenamacril were determined. The results showed the neutral trehalase-encoding gene knockout mutant Δnth1 was lower in colony growth rate and conidia germination rate, and significantly lower in pathogenicity to banana (Cavendish, AAA) than the wild-type strain. However, there was no significant difference in conidia yield and sensitivity to phenamacril (EC50 = 6.07 mg·L−1) between the mutant and the wild type strain. It was inferred that NTH1 gene was involved in regulating the growth and conidia germination of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp., and responding to the cell wall synthesis and oxidative stress, but not to the osmotic pressure, high sugar stress and temperature stress.
2020, 11(2): 210-216.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.011
Abstract:
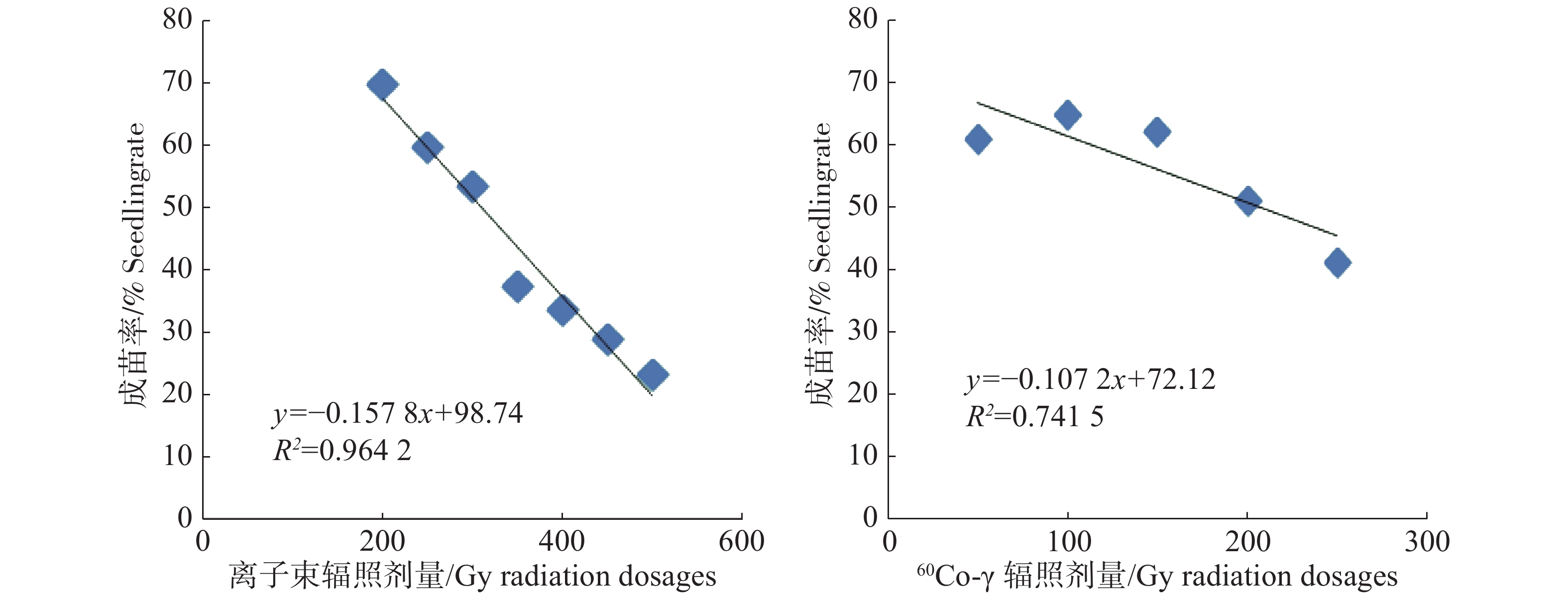
Radiation mutagenesis is an important method for plant breeding, which can improve the mutation rate and shorten the breeding time. Plants are differently sensitive to irradiation, and adequate irradiation dose could increase mutation frequency and breeding efficiency. Seeds of Lagerstroemia indica were treated with 60Co-γ and electron beam at different doses to observe their germination and seedling growth to find the best irradiation source and dose.. The results showed that the germination rates of the seeds treated with both 60Co-γ and the electron beam were first promoted and then inhibited, and that the seedling survival rate decreased significantly with the irradiation dose. The 60Co-γ irradiation was found to inhibit and then promote the plant height, while the electron beam irradiation inhibited the plant height. Both 60Co-γ and the electron beam had significant inhibition effects on the branch length and branch number of the seedlings. The 60Co-γ irradiation had little inhibition effect on the ground diameter of the seedlings, while the electron beam irradiation had highly different effect on the ground diameter. Comprehensive analysis of the seedling growth under the two sources of irradiation showed that the seedlings of L. indica treated with the electron beam at the same dose of irradiation to the 60Co-γ irradiation had longer branches and higher ground diameter and varied greatly in branch length and ground diameter. When calculated at the seedling survival rate of L.indica treated, the optimum irradiation dosage was 113.06 Gy to 299.63 Gy for 60Co-γ, and 245.5 Gy to 372.24 Gy for electron beam. L. indica was more sensitive to 60Co-γ irradiation. These results would provide a theoretical basis for mutation breeding and acceleration of the breeding process of L. indica.
Radiation mutagenesis is an important method for plant breeding, which can improve the mutation rate and shorten the breeding time. Plants are differently sensitive to irradiation, and adequate irradiation dose could increase mutation frequency and breeding efficiency. Seeds of Lagerstroemia indica were treated with 60Co-γ and electron beam at different doses to observe their germination and seedling growth to find the best irradiation source and dose.. The results showed that the germination rates of the seeds treated with both 60Co-γ and the electron beam were first promoted and then inhibited, and that the seedling survival rate decreased significantly with the irradiation dose. The 60Co-γ irradiation was found to inhibit and then promote the plant height, while the electron beam irradiation inhibited the plant height. Both 60Co-γ and the electron beam had significant inhibition effects on the branch length and branch number of the seedlings. The 60Co-γ irradiation had little inhibition effect on the ground diameter of the seedlings, while the electron beam irradiation had highly different effect on the ground diameter. Comprehensive analysis of the seedling growth under the two sources of irradiation showed that the seedlings of L. indica treated with the electron beam at the same dose of irradiation to the 60Co-γ irradiation had longer branches and higher ground diameter and varied greatly in branch length and ground diameter. When calculated at the seedling survival rate of L.indica treated, the optimum irradiation dosage was 113.06 Gy to 299.63 Gy for 60Co-γ, and 245.5 Gy to 372.24 Gy for electron beam. L. indica was more sensitive to 60Co-γ irradiation. These results would provide a theoretical basis for mutation breeding and acceleration of the breeding process of L. indica.
2020, 11(2): 217-222, 237.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.012
Abstract:
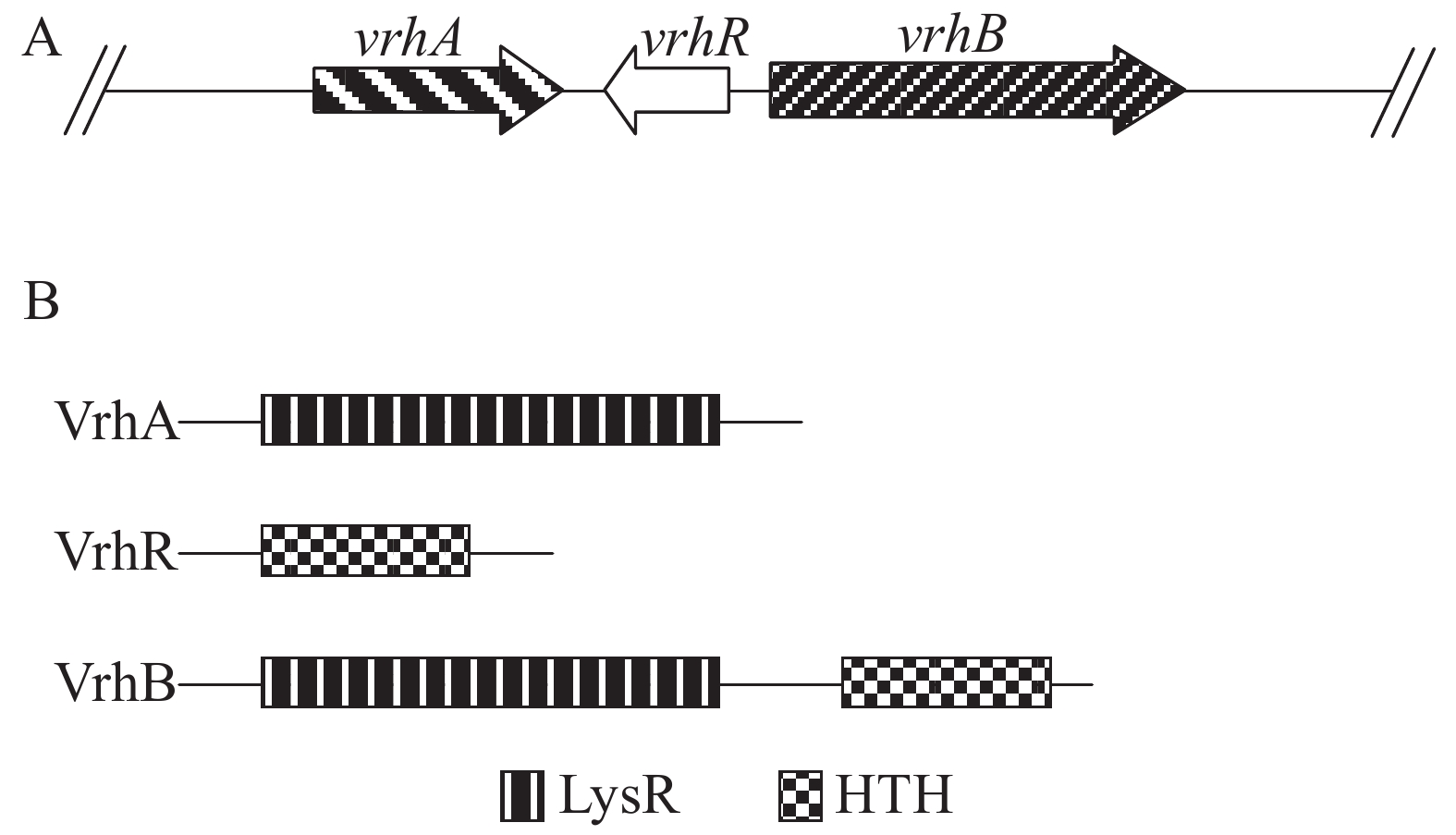
The roles of transcriptional regulators, VrhR, VrhA and VrhB, in the interaction between Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris and plants were analyzed via gene mutation and virulence analysis. The results showed that VrhR contains only one HTH (helix-turn-helix) motif and is located between the other two LysR transcriptional regulators (vrhA and vrhB) in Xcc 8004 genome, but transcribed in an opposite direction. Mutation of vrhR increased the pathogenicity of Xcc, while mutation of vrhA and vrhB did not affect Xcc virulence. However, mutation of vrhR, vrhA and vrhB did not affect bacterial motility and extracellular enzyme (protease, cellulase and amylase) activities, suggesting that vrhR may regulate bacterial virulence by regulating other pathogenic factors.
The roles of transcriptional regulators, VrhR, VrhA and VrhB, in the interaction between Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris and plants were analyzed via gene mutation and virulence analysis. The results showed that VrhR contains only one HTH (helix-turn-helix) motif and is located between the other two LysR transcriptional regulators (vrhA and vrhB) in Xcc 8004 genome, but transcribed in an opposite direction. Mutation of vrhR increased the pathogenicity of Xcc, while mutation of vrhA and vrhB did not affect Xcc virulence. However, mutation of vrhR, vrhA and vrhB did not affect bacterial motility and extracellular enzyme (protease, cellulase and amylase) activities, suggesting that vrhR may regulate bacterial virulence by regulating other pathogenic factors.
2020, 11(2): 223-230.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.013
Abstract:
Leaves and branches of a healthy rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.) and a rubber tree infected with witches’ broom disease were sampled for anatomical observation of their tissue structures and for transcriptome sequencing by using a new generation high-throughput sequencing technology Illμmina HiSeq 2000. Paraffin section observation showed that the branches of the rubber tree infected with witches’ broom disease was obviously thinner in cambium, significantly lower in the proportion of the periderm to the bark, thinner in the vessels of the secondary xylem, and absent in stone cells in the outside of the primary phloem fiber as against those of the healthy rubber tree, and that the leaves of the rubber tree infected with the witches’ broom disease was thinner in the palisade tissue and thicker in the spongy tissue as compared to those of the healthy rubber tree. The transcriptome sequencing showed that the two metabolic pathways of the biosynthesis of flavonoids and brassinosteroid in the rubber tree infected with the witches’ broom disease were obviously in disorder as compared to those in the healthy rubber tree. Metabolic disorders caused by phytoplasma –in the rubber tree may be responsible for differences in the anatomical structure of the rubber trees.
Leaves and branches of a healthy rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Muell. Arg.) and a rubber tree infected with witches’ broom disease were sampled for anatomical observation of their tissue structures and for transcriptome sequencing by using a new generation high-throughput sequencing technology Illμmina HiSeq 2000. Paraffin section observation showed that the branches of the rubber tree infected with witches’ broom disease was obviously thinner in cambium, significantly lower in the proportion of the periderm to the bark, thinner in the vessels of the secondary xylem, and absent in stone cells in the outside of the primary phloem fiber as against those of the healthy rubber tree, and that the leaves of the rubber tree infected with the witches’ broom disease was thinner in the palisade tissue and thicker in the spongy tissue as compared to those of the healthy rubber tree. The transcriptome sequencing showed that the two metabolic pathways of the biosynthesis of flavonoids and brassinosteroid in the rubber tree infected with the witches’ broom disease were obviously in disorder as compared to those in the healthy rubber tree. Metabolic disorders caused by phytoplasma –in the rubber tree may be responsible for differences in the anatomical structure of the rubber trees.
2020, 11(2): 231-237.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.014
Abstract:
Soil respiration is a frontier topic in the carbon cycle of terrestrial ecosystems. The seasonal variations and differences of soil respiration in different terrains were analyzed by measuring the soil respiration rate and soil temperature and moisture in a tropical lowland forest in Diaoluoshan, Hainan, China, and the relationship between the soil respiration and the hydrothermal factors was also analyzed. The results showed that the soil respiration rate in the flat terrain and sloping terrain had a dynamic change of "higher in rainy season and lower in dry season", with peak emissions from June to August. On the contrary, the soil respiration rate in the low-lying terrain had a dynamic change of "lower in rainy season and higher in dry season", with the peak emissions from March to May. The annual accumulation of soil respiration in different terrains varied significantly, which was in the order of the low-lying terrain (986.37 ± 46.91) g C· m−2·a−1 > the sloping terrain (901.46 ± 47.00) g C·m−2·a−1 > the flat terrain (796.85 ± 36.86) g C·m−2·a−1. The soil respiration in different terrains was not consistently correlated with the soil temperature and moisture, but the soil respiration in the sloping terrain was most significantly correlated with the soil temperature and moisture (P< 0.01), with a Q10 value of 3.19. These results indicated that there were significant differences in soil respiration in different terrains in a tropical lowland forest in Diaoluoshan, Hainan. When the soil CO2 flux is extrapolated to a larger scale, the complexity of the terrain should be taken into account.
Soil respiration is a frontier topic in the carbon cycle of terrestrial ecosystems. The seasonal variations and differences of soil respiration in different terrains were analyzed by measuring the soil respiration rate and soil temperature and moisture in a tropical lowland forest in Diaoluoshan, Hainan, China, and the relationship between the soil respiration and the hydrothermal factors was also analyzed. The results showed that the soil respiration rate in the flat terrain and sloping terrain had a dynamic change of "higher in rainy season and lower in dry season", with peak emissions from June to August. On the contrary, the soil respiration rate in the low-lying terrain had a dynamic change of "lower in rainy season and higher in dry season", with the peak emissions from March to May. The annual accumulation of soil respiration in different terrains varied significantly, which was in the order of the low-lying terrain (986.37 ± 46.91) g C· m−2·a−1 > the sloping terrain (901.46 ± 47.00) g C·m−2·a−1 > the flat terrain (796.85 ± 36.86) g C·m−2·a−1. The soil respiration in different terrains was not consistently correlated with the soil temperature and moisture, but the soil respiration in the sloping terrain was most significantly correlated with the soil temperature and moisture (P< 0.01), with a Q10 value of 3.19. These results indicated that there were significant differences in soil respiration in different terrains in a tropical lowland forest in Diaoluoshan, Hainan. When the soil CO2 flux is extrapolated to a larger scale, the complexity of the terrain should be taken into account.
2020, 11(2): 238-244, 250.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.00.015
Abstract:
The acquisition of high-quality genomic DNA is key to cloning of conotoxin genes and gene library construction. Four kits, Magnetic Bead Method Kit, Improved DNA Rapid Extraction Kit, FastPure DNA Isolation Kit, and TIANamp DNA Isolation Kit, were adopted to extract DNA from different tissues and organs of Conus litteratus, and the concentration, purity, size and integrity of the genomic DNA extracted from different tissues and organs by each kit were comprehensively compared. The results showed that the purity and concentration of the genomic DNA extracted with the Improved DNA Rapid Extraction Kit was better. Of the four different organs of C. litterantus, muscular foot had a higher purity in the genomic DNA extracted from its tissues and was the best organ used for extraction of the genomic DNA. The hepatopancreas and venom duct of C. litterantus gave the highest yield of the genomic DNA, but with poor fragment integrity and high contamination. Moreover, specific amplification products with the expected size were obtained through PCR. It is concluded that the best method to acquire the genomic DNA from C. litteratus is to extract the genomic DNA from the muscular foot with the Improved DNA Rapid Extraction Kit, with which high-quality genomic DNA can be produced and meet the requirements of subsequent research.
The acquisition of high-quality genomic DNA is key to cloning of conotoxin genes and gene library construction. Four kits, Magnetic Bead Method Kit, Improved DNA Rapid Extraction Kit, FastPure DNA Isolation Kit, and TIANamp DNA Isolation Kit, were adopted to extract DNA from different tissues and organs of Conus litteratus, and the concentration, purity, size and integrity of the genomic DNA extracted from different tissues and organs by each kit were comprehensively compared. The results showed that the purity and concentration of the genomic DNA extracted with the Improved DNA Rapid Extraction Kit was better. Of the four different organs of C. litterantus, muscular foot had a higher purity in the genomic DNA extracted from its tissues and was the best organ used for extraction of the genomic DNA. The hepatopancreas and venom duct of C. litterantus gave the highest yield of the genomic DNA, but with poor fragment integrity and high contamination. Moreover, specific amplification products with the expected size were obtained through PCR. It is concluded that the best method to acquire the genomic DNA from C. litteratus is to extract the genomic DNA from the muscular foot with the Improved DNA Rapid Extraction Kit, with which high-quality genomic DNA can be produced and meet the requirements of subsequent research.
2020, 11(2): 245-250.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.016
Abstract:
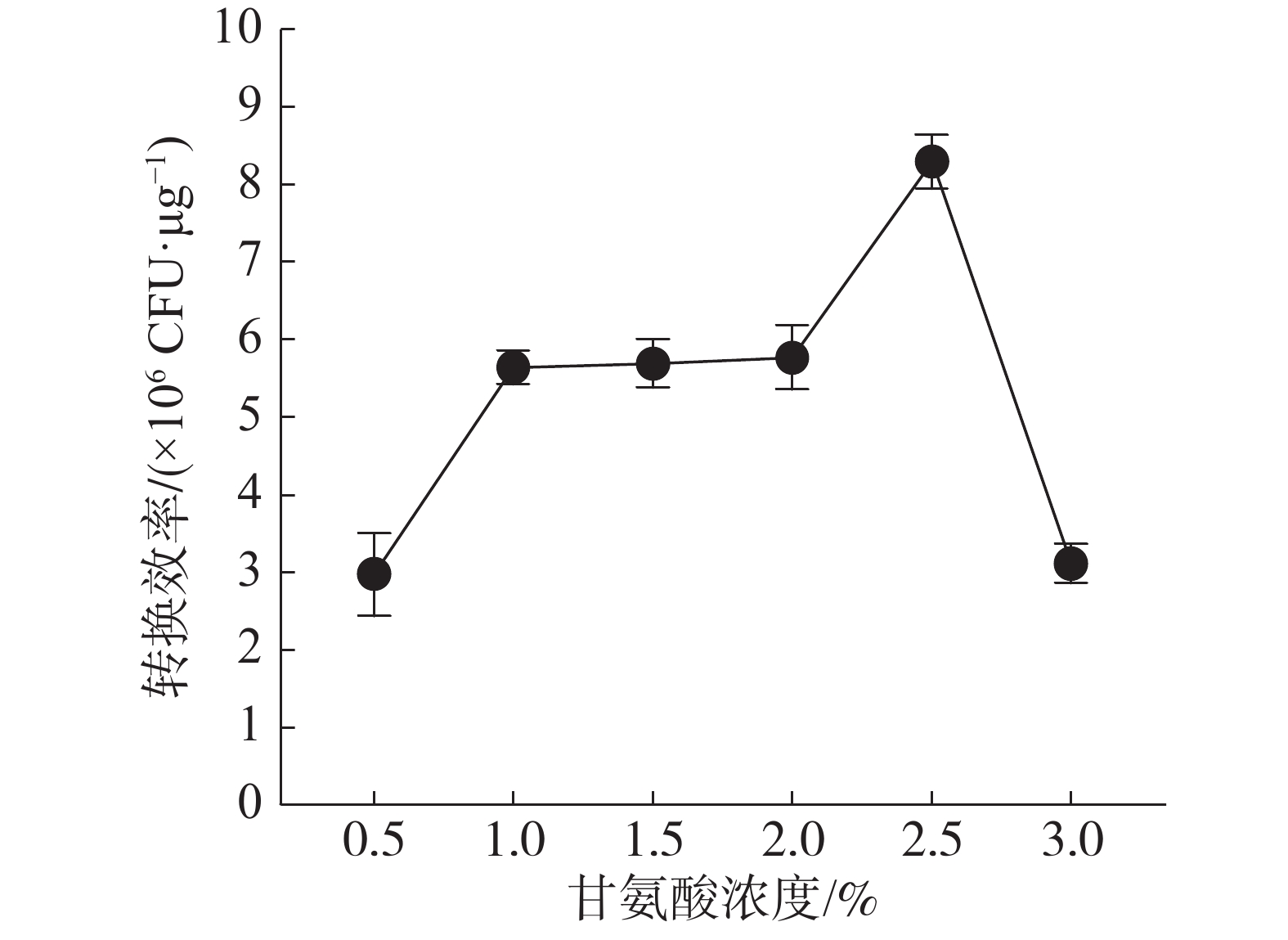
The nisin-controlled gene expression system (NICE) is a food-grade system used for gene expression in Lactococcus lactis. Electrotransformation was optimized via the NICE, consisting of an expression vector pNZ8148 and a host strain Lactococcus lactis NZ9000. The results showed that the electrotransformation of L. lactis NZ9000 with the expression vector pHZ8148 gave the highest efficiency (1.6 × 108 CFU μg−1) when L. lactis NZ9000 was cultured on the medium added with 2.5% of glycine, and its competent cells grown to 0.3 OD600 were prepared by washing with the liquid detergent formulation I (Sucrose 0.5 mol·L−1+glycerol 10%), transferred into with 0.2 μg plasmid of pNA8148, electrotranformed at 2.5 kV on a 0.2 cm gap cuvette, and mixed gently for 1.5 h before plating. This study provides optimum conditions for electrotransformation of L. lactis NZ9000 which are favorable for further study of L. lactis based on the NICE.
The nisin-controlled gene expression system (NICE) is a food-grade system used for gene expression in Lactococcus lactis. Electrotransformation was optimized via the NICE, consisting of an expression vector pNZ8148 and a host strain Lactococcus lactis NZ9000. The results showed that the electrotransformation of L. lactis NZ9000 with the expression vector pHZ8148 gave the highest efficiency (1.6 × 108 CFU μg−1) when L. lactis NZ9000 was cultured on the medium added with 2.5% of glycine, and its competent cells grown to 0.3 OD600 were prepared by washing with the liquid detergent formulation I (Sucrose 0.5 mol·L−1+glycerol 10%), transferred into with 0.2 μg plasmid of pNA8148, electrotranformed at 2.5 kV on a 0.2 cm gap cuvette, and mixed gently for 1.5 h before plating. This study provides optimum conditions for electrotransformation of L. lactis NZ9000 which are favorable for further study of L. lactis based on the NICE.
2020, 11(2): 251-256.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.02.017
Abstract:
Duckweed is a new environmental and energy plant and gradually receives public attention. Duckweed plants grow fast, and is abundant in biological protein and starch with a high capacity of adsorption and transfer of nitrogen and phosphorus, organic matter and heavy metals. Duckweed is well reported to be used not only as a phytoremediation agent with good effect and low cost, but also as raw materials for feed and bio-energy, while a little research is documented on duckweed in agricultural production like paddy rice in their symbiosis and synergism. Some researches showed that duckweed had different influences on paddy rice in different growing seasons, had an inhibitory effect on rice rejuvenation at the transplanting stage and at the tillering and joint stage, and could inhibit the volatilization of ammonium nitrogen (NH4+) in the paddy field, which was beneficial to rice growth and yield. The research and development of duckweed as phytoremediation agent, feed, energy and medicine were reviewed, and prospects of comprehensive utilization of duckweed and research of duckweed in paddy field were proposed.
Duckweed is a new environmental and energy plant and gradually receives public attention. Duckweed plants grow fast, and is abundant in biological protein and starch with a high capacity of adsorption and transfer of nitrogen and phosphorus, organic matter and heavy metals. Duckweed is well reported to be used not only as a phytoremediation agent with good effect and low cost, but also as raw materials for feed and bio-energy, while a little research is documented on duckweed in agricultural production like paddy rice in their symbiosis and synergism. Some researches showed that duckweed had different influences on paddy rice in different growing seasons, had an inhibitory effect on rice rejuvenation at the transplanting stage and at the tillering and joint stage, and could inhibit the volatilization of ammonium nitrogen (NH4+) in the paddy field, which was beneficial to rice growth and yield. The research and development of duckweed as phytoremediation agent, feed, energy and medicine were reviewed, and prospects of comprehensive utilization of duckweed and research of duckweed in paddy field were proposed.



 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 302KB
PDF 302KB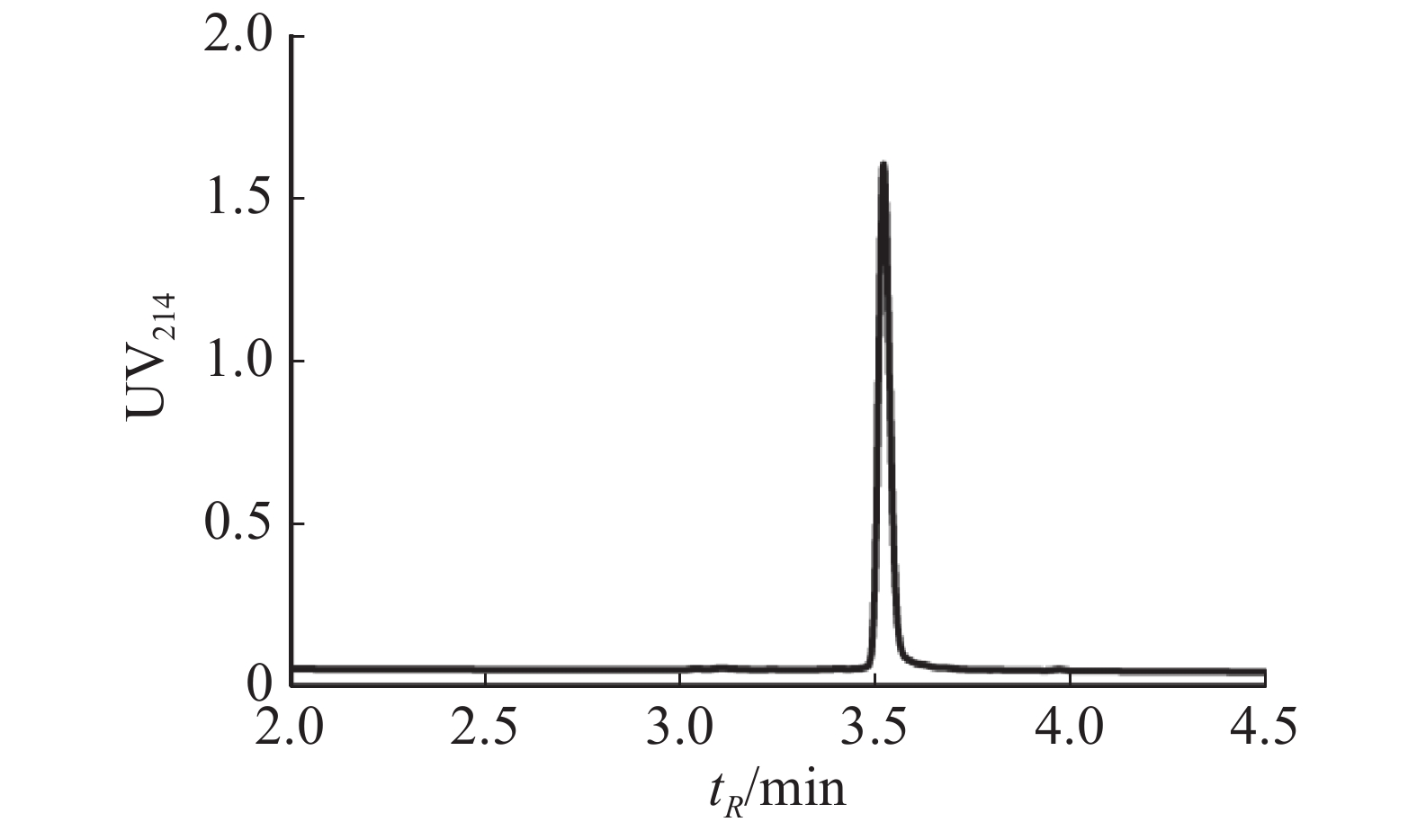








 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS