2024 Vol. 15, No. 4
2024, 15(4): 373-381.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230137
Abstract:
In order to understand the anatomical traits of leaves among rubber clones of Hevea brasiliensis in China and provide basis for breeding and adaptability evaluation of clones with high photosynthetic efficiency, 21main Hevea clones in China, such as ‘Reyan 73397’, ‘Reyan 917’, etc., were used for anatomical analysis, and their leaf structural traits such as the ratio of palisade tissue thickness to spongy tissue thickness, leaf thickness,stomatal density, etc., were observed by using paraffin sectioning and nail polish imprinting. The results showed that there were significant differences in leaf structural traits among the main clones. The clones ‘Nanhua 1’,‘Hongxing 1’ and ‘Reyan 917’ were higher in palisade tissue thickness, leaf thickness and ratio of palisade tissue to spongy tissue, whereas the clones ‘Reyan 879’, ‘Reken 628’ and ‘Reyan 106’ were relatively lower in stomatal length, stomatal width and stomatal density, which suggested that they had a higher photosynthetic capacity and certain drought resistance ability. Hierarchical clustering showed the aforesaid clones were divided into two groups. The clones ‘Nanhua 1’, ‘Hongxing 1’, ‘Haiken 1’ and ‘Reyan 917’ were relatively higher in leaf thickness, palisade tissue and density of the tissue structure. In summary, clones ‘Nanhua 1’,‘ Hongxing 1’and ‘Reyan 917’were higher in leaf thickness, palisade tissue thickness, density of tissue structure, and were small and dense in stomata. It is hence speculated that these three clones have higher photosynthetic performance, which needs further research. At the same time, this analysis also provides a technical basis for further study of the environmental adaptability and gas exchange characteristics of the above-mentioned clones.
In order to understand the anatomical traits of leaves among rubber clones of Hevea brasiliensis in China and provide basis for breeding and adaptability evaluation of clones with high photosynthetic efficiency, 21main Hevea clones in China, such as ‘Reyan 73397’, ‘Reyan 917’, etc., were used for anatomical analysis, and their leaf structural traits such as the ratio of palisade tissue thickness to spongy tissue thickness, leaf thickness,stomatal density, etc., were observed by using paraffin sectioning and nail polish imprinting. The results showed that there were significant differences in leaf structural traits among the main clones. The clones ‘Nanhua 1’,‘Hongxing 1’ and ‘Reyan 917’ were higher in palisade tissue thickness, leaf thickness and ratio of palisade tissue to spongy tissue, whereas the clones ‘Reyan 879’, ‘Reken 628’ and ‘Reyan 106’ were relatively lower in stomatal length, stomatal width and stomatal density, which suggested that they had a higher photosynthetic capacity and certain drought resistance ability. Hierarchical clustering showed the aforesaid clones were divided into two groups. The clones ‘Nanhua 1’, ‘Hongxing 1’, ‘Haiken 1’ and ‘Reyan 917’ were relatively higher in leaf thickness, palisade tissue and density of the tissue structure. In summary, clones ‘Nanhua 1’,‘ Hongxing 1’and ‘Reyan 917’were higher in leaf thickness, palisade tissue thickness, density of tissue structure, and were small and dense in stomata. It is hence speculated that these three clones have higher photosynthetic performance, which needs further research. At the same time, this analysis also provides a technical basis for further study of the environmental adaptability and gas exchange characteristics of the above-mentioned clones.
2024, 15(4): 382-390.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240060
Abstract:
In order to determine whether soybean(Glycine max) acyl-Coenzyme A binding protein(GmACBP6)has saline-tolerant function, the expression of GmACBP6 during the germination period was analyzed by using the real-time PCR, and analysis showed that GmACBP6 responded to saline-alkali stress in the germination period of soybean. In this context the pYES2-GmACBP6 recombinant vector was constructed and transformed into the yeast strains, The growth of pYES2-GmACBP6 yeast strain and pYES2 yeast strain cultured in salt and saline stress mediums were observed. The results show that the pYES 2-GmACBP6 yeast strain grew significantly better under salt and salt stress than the pYES2 yeast vector. It is preliminarily determined that the soybean GmACBP6gene has the function of improving the salt and alkali tolerance of yeast cells. In this study the A. thaliana materials with GmACBP6 knock-in and overexpression were also produced, and their salinity-tolerant phenotype during the germination stage was identified. The results showed that the germination rate of Arabidopsis seeds with GmACBP6 overexpression was significantly higher than that of GmACBP6 knock-in, atacbp6 mutant or wild Arabidopsis thaliana under salt and salt-alkali stress, which further confirmed the salt-alkali tolerance of the GmACBP6 gene in the soybean.
In order to determine whether soybean(Glycine max) acyl-Coenzyme A binding protein(GmACBP6)has saline-tolerant function, the expression of GmACBP6 during the germination period was analyzed by using the real-time PCR, and analysis showed that GmACBP6 responded to saline-alkali stress in the germination period of soybean. In this context the pYES2-GmACBP6 recombinant vector was constructed and transformed into the yeast strains, The growth of pYES2-GmACBP6 yeast strain and pYES2 yeast strain cultured in salt and saline stress mediums were observed. The results show that the pYES 2-GmACBP6 yeast strain grew significantly better under salt and salt stress than the pYES2 yeast vector. It is preliminarily determined that the soybean GmACBP6gene has the function of improving the salt and alkali tolerance of yeast cells. In this study the A. thaliana materials with GmACBP6 knock-in and overexpression were also produced, and their salinity-tolerant phenotype during the germination stage was identified. The results showed that the germination rate of Arabidopsis seeds with GmACBP6 overexpression was significantly higher than that of GmACBP6 knock-in, atacbp6 mutant or wild Arabidopsis thaliana under salt and salt-alkali stress, which further confirmed the salt-alkali tolerance of the GmACBP6 gene in the soybean.
2024, 15(4): 391-399.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240030
Abstract:
This study aims to quantify the nitrogen (N) input and output of Hainan’s tropical vegetable and orchard cropping systems,establish N surplus indicators,and evaluate the environmental impacts.We collected 34 papers published in Hainan since 1980,including 72 samples of conventional and optimized N management of vegetables and orchards.The N inputs,outputs,and surpluses under conventional and optimized N management were analyzed based on the soil surface nitrogen balance method,and the N surplus under the optimized management was used as the N surplus benchmark.The life cycle assessment method (LCA) was used to quantify reactive N losses,greenhouse gas emissions,carbon and N footprints under conventional and optimized N management.Under conventional N management,the N surpluses were 290 kg·hm-2 in vegetables and 432 kg·hm-2 in orchards,respectively,the corresponding N surplus benchmarks under optimized N management were reduced by 39%and 49%,which were 176 and 222 kg·hm-2,respectively.The reactive N emission,N footprint,greenhouse gas emissions(CO2-eq),and carbon footprint(CO2-eq) under conventional N management of vegetables were 145 kg·hm-2,4.5 kg·t-1,9 444 kg hm-2 and 295 kg·t-1,respectively;under optimized N management,the above indicators were reduced by 26%,24%,19%and 19%,respectively.The active N emission,N footprint,greenhouse gas emission,and carbon footprint under conventional N management of orchards were 177 kg·hm-2,4.5 kg·t-1,14 758 kg·hm-2 and 388 kg·eq t-1,respectively;Optimizing N management can reduce the above indicators by 28%,33%,21%and 26%,respectively.In conclusion,the N surplus benchmarks of Hainan’s typical vegetable and orchard systems were 176 and 222 kg·hm-2,respectively,using optimized N management (such as"4R Plus"nutrient management strategy,soil acid modification and organic carbon improvement,fertigation,etc.) can achieve the above N surplus benchmarks,and the current reactive N emissions,N footprint,greenhouse gas emissions,and carbon footprints can be reduced by 19%-33%.
This study aims to quantify the nitrogen (N) input and output of Hainan’s tropical vegetable and orchard cropping systems,establish N surplus indicators,and evaluate the environmental impacts.We collected 34 papers published in Hainan since 1980,including 72 samples of conventional and optimized N management of vegetables and orchards.The N inputs,outputs,and surpluses under conventional and optimized N management were analyzed based on the soil surface nitrogen balance method,and the N surplus under the optimized management was used as the N surplus benchmark.The life cycle assessment method (LCA) was used to quantify reactive N losses,greenhouse gas emissions,carbon and N footprints under conventional and optimized N management.Under conventional N management,the N surpluses were 290 kg·hm-2 in vegetables and 432 kg·hm-2 in orchards,respectively,the corresponding N surplus benchmarks under optimized N management were reduced by 39%and 49%,which were 176 and 222 kg·hm-2,respectively.The reactive N emission,N footprint,greenhouse gas emissions(CO2-eq),and carbon footprint(CO2-eq) under conventional N management of vegetables were 145 kg·hm-2,4.5 kg·t-1,9 444 kg hm-2 and 295 kg·t-1,respectively;under optimized N management,the above indicators were reduced by 26%,24%,19%and 19%,respectively.The active N emission,N footprint,greenhouse gas emission,and carbon footprint under conventional N management of orchards were 177 kg·hm-2,4.5 kg·t-1,14 758 kg·hm-2 and 388 kg·eq t-1,respectively;Optimizing N management can reduce the above indicators by 28%,33%,21%and 26%,respectively.In conclusion,the N surplus benchmarks of Hainan’s typical vegetable and orchard systems were 176 and 222 kg·hm-2,respectively,using optimized N management (such as"4R Plus"nutrient management strategy,soil acid modification and organic carbon improvement,fertigation,etc.) can achieve the above N surplus benchmarks,and the current reactive N emissions,N footprint,greenhouse gas emissions,and carbon footprints can be reduced by 19%-33%.
2024, 15(4): 400-406.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240018
Abstract:
Tea prepared from wild tea leaves in the Wuzhishan region have become popular in the market over recent years. However, its metabolomic characteristics are seldom reported. An attempt was made to compare the metabolites found in the leaves of wild and cultivated tea in Wuzhishan, Hainan, China by employing a metabolomic method. A total of 398 metabolites were identified significantly up-regulated, and 247 were significantly down-regulated in the wild tea leaves compared to those from the leaves of tea cultivated in the tea plantations. Partial least squares discrimination analysis suggested that wild and cultivated tea could each be grouped into their respective categories. Enrichment analysis indicated that the functions of the metabolites with significant high content in the wild tea leaves were mainly concentrated in metabolic pathways such as glycolysis,pyruvate synthesis, amino sugar metabolism, and nucleotide sugar metabolism, as well as pathways for the synthesis of phenolic substances, riboflavin metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, and flavonoid synthesis. The functions of the metabolites with significantly low content were mainly enriched in primary metabolic pathways,such as amino acid metabolism and lipid metabolism.
Tea prepared from wild tea leaves in the Wuzhishan region have become popular in the market over recent years. However, its metabolomic characteristics are seldom reported. An attempt was made to compare the metabolites found in the leaves of wild and cultivated tea in Wuzhishan, Hainan, China by employing a metabolomic method. A total of 398 metabolites were identified significantly up-regulated, and 247 were significantly down-regulated in the wild tea leaves compared to those from the leaves of tea cultivated in the tea plantations. Partial least squares discrimination analysis suggested that wild and cultivated tea could each be grouped into their respective categories. Enrichment analysis indicated that the functions of the metabolites with significant high content in the wild tea leaves were mainly concentrated in metabolic pathways such as glycolysis,pyruvate synthesis, amino sugar metabolism, and nucleotide sugar metabolism, as well as pathways for the synthesis of phenolic substances, riboflavin metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, and flavonoid synthesis. The functions of the metabolites with significantly low content were mainly enriched in primary metabolic pathways,such as amino acid metabolism and lipid metabolism.
2024, 15(4): 407-413.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240004
Abstract:
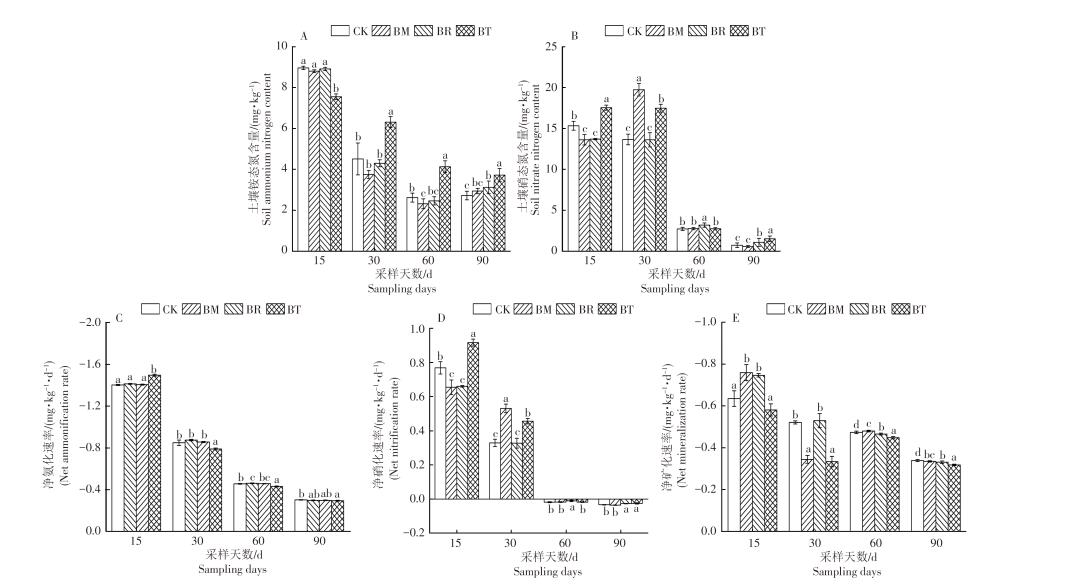
An attempt was made to explore the changes of soil nitrogen transformation and nitrogen metabolism in banana plantations intercropped with leguminous green manure crops. A pot experiment was conducted to set up five treatments: monoculture of banana(CK), intercropping with Trifolium repens L(BT), intercropping with Melilotus officinalis(BM), intercropping with Lolium perenne L(BR). The changes of soil nutrient content and key enzymes for nitrogen metabolism in different sampling periods were determined. The results showed that the soil pH and the contents of organic matter, available nitrogen, total nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium in banana and intercrops, leguminous green manure crops, were increased in different degrees, and also increased were the soil contents of NH4+-N and NO3--N, and the net mineralization rate and the net nitrification rate of nitrogen in the soil. After intercropping with leguminous green manure crops, the activities of nitrate reductase(NR), nitrite reductase(NiR) and glutamine synthetase(GS) in banana leaves were significantly higher than those in the monoculture banana. The soil NH4+-N and NO3--N were significantly positively correlated with the NiR, GS and glutamate synthetase(GOGAT) in the banana leaves.
An attempt was made to explore the changes of soil nitrogen transformation and nitrogen metabolism in banana plantations intercropped with leguminous green manure crops. A pot experiment was conducted to set up five treatments: monoculture of banana(CK), intercropping with Trifolium repens L(BT), intercropping with Melilotus officinalis(BM), intercropping with Lolium perenne L(BR). The changes of soil nutrient content and key enzymes for nitrogen metabolism in different sampling periods were determined. The results showed that the soil pH and the contents of organic matter, available nitrogen, total nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium in banana and intercrops, leguminous green manure crops, were increased in different degrees, and also increased were the soil contents of NH4+-N and NO3--N, and the net mineralization rate and the net nitrification rate of nitrogen in the soil. After intercropping with leguminous green manure crops, the activities of nitrate reductase(NR), nitrite reductase(NiR) and glutamine synthetase(GS) in banana leaves were significantly higher than those in the monoculture banana. The soil NH4+-N and NO3--N were significantly positively correlated with the NiR, GS and glutamate synthetase(GOGAT) in the banana leaves.
2024, 15(4): 414-418,436.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230084
Abstract:
In order to have a good picture of the wildlife resources in the core area of Maorui Area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, a survey was made from January 2022 to February 2023, and 95 infrared camera monitoring points were deployed to record birds and mammals in the core area of the Maorui Area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. The survey recorded 12 species of wild mammals in 9 families and 4orders, among which the top three species with relative abundance were Asiatic brush-tailed porcupine(Atherurus macrourus), wild boar(Sus scrofa), and Asian red-cheeked squirrel(Dremomys rufigenis). There are 8 species of wild birds in 6 families and 4 orders, and the top three species with relative abundance are silver pheasant(Lophura nycthemera), orange-headed thrush(Geokichla citrina), and red jungle fowl(Gallus gallus). There are two species of wild animals under the first class of the State key protection, Hainan partridge(Arborophila ardens)and small Indian civet(Viverricula indica). There are 8 species of wild animals under the second class of the State key protection, Bornean red muntjac(Muntiacus nigripes), macaque(Macaca mulatta), silver pheasant, red jungle fowl, coconut civet(Paradoxurus hermaphroditus), leopard cat(Prionailurus bengalensis), yellow-breasted magpie(Cissa hypoleuca) and Malayan night-heron(Gorsachius melanolophus). Among the monitored species, the top three species with relative abundance were analyzed and compared, and it was found that the intensity of species activity varied with season. This survey might provide reference for the protection, management, research and subsequent management policies of the protected areas in the Maorui area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park.
In order to have a good picture of the wildlife resources in the core area of Maorui Area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park, a survey was made from January 2022 to February 2023, and 95 infrared camera monitoring points were deployed to record birds and mammals in the core area of the Maorui Area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. The survey recorded 12 species of wild mammals in 9 families and 4orders, among which the top three species with relative abundance were Asiatic brush-tailed porcupine(Atherurus macrourus), wild boar(Sus scrofa), and Asian red-cheeked squirrel(Dremomys rufigenis). There are 8 species of wild birds in 6 families and 4 orders, and the top three species with relative abundance are silver pheasant(Lophura nycthemera), orange-headed thrush(Geokichla citrina), and red jungle fowl(Gallus gallus). There are two species of wild animals under the first class of the State key protection, Hainan partridge(Arborophila ardens)and small Indian civet(Viverricula indica). There are 8 species of wild animals under the second class of the State key protection, Bornean red muntjac(Muntiacus nigripes), macaque(Macaca mulatta), silver pheasant, red jungle fowl, coconut civet(Paradoxurus hermaphroditus), leopard cat(Prionailurus bengalensis), yellow-breasted magpie(Cissa hypoleuca) and Malayan night-heron(Gorsachius melanolophus). Among the monitored species, the top three species with relative abundance were analyzed and compared, and it was found that the intensity of species activity varied with season. This survey might provide reference for the protection, management, research and subsequent management policies of the protected areas in the Maorui area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park.
2024, 15(4): 419-426.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230112
Abstract:
Plesiomyzon baotingensis is endemic to Hainan province. Due to river pollution, overfishing, invasive species and habitat degradation, the wild population of P. baotingensis is quite small in Hainan Province. An attempt was made to estimate genetic diversity of P. baotingensis to provide experimental data of its germplasm resources. An analysis was made of 103 individuals including 5 geographic populations(Bacun, Yinggeling,Qiongzhong, Hongjuntan and Bengling). Partial sequences of Cytb gene(1 047 bp) were obtained from these individuals. Fifty-eight variable sites and 11 haplotypes were identified in the whole populations, respectively with relatively high haplotype diversity(h=0.815) and high nucleotide diversity(π=0.024 71). The analysis of molecular variance of the populations indicated that most of genetic variation(77.86%) came from between population. Fst value among five populations was 0.779(P < 0.01), and the genetic distance between populations ranged from 0.000 3 to 0.046 4; the farthest genetic distance(0.046 4) of P. baotingensis was identified between Bacun and Hongjuntan populations, and the closest genetic distance(0.000 3) was found between Yinggeling and Qiongzhong populations. Fu’s Fs neutral test showed that historical population expansion was observed in the Yinggeling population. Phylogenetic tree showed there were two lineages in the five P. baotingensis populations in Hainan. In order to better conserve the wild resources and genetic structure of P. baotingensis, two mitochondrial DNA lineages should be paid more attention to. The geographical population of P. baotingensis in Bengling was found to contain two lineages, and its haplotypes and endemic haplotypes were the largest in number among the five geographical populations. It is suggested to strengthen the conservation of P. baotingensis in the Bengling area.
Plesiomyzon baotingensis is endemic to Hainan province. Due to river pollution, overfishing, invasive species and habitat degradation, the wild population of P. baotingensis is quite small in Hainan Province. An attempt was made to estimate genetic diversity of P. baotingensis to provide experimental data of its germplasm resources. An analysis was made of 103 individuals including 5 geographic populations(Bacun, Yinggeling,Qiongzhong, Hongjuntan and Bengling). Partial sequences of Cytb gene(1 047 bp) were obtained from these individuals. Fifty-eight variable sites and 11 haplotypes were identified in the whole populations, respectively with relatively high haplotype diversity(h=0.815) and high nucleotide diversity(π=0.024 71). The analysis of molecular variance of the populations indicated that most of genetic variation(77.86%) came from between population. Fst value among five populations was 0.779(P < 0.01), and the genetic distance between populations ranged from 0.000 3 to 0.046 4; the farthest genetic distance(0.046 4) of P. baotingensis was identified between Bacun and Hongjuntan populations, and the closest genetic distance(0.000 3) was found between Yinggeling and Qiongzhong populations. Fu’s Fs neutral test showed that historical population expansion was observed in the Yinggeling population. Phylogenetic tree showed there were two lineages in the five P. baotingensis populations in Hainan. In order to better conserve the wild resources and genetic structure of P. baotingensis, two mitochondrial DNA lineages should be paid more attention to. The geographical population of P. baotingensis in Bengling was found to contain two lineages, and its haplotypes and endemic haplotypes were the largest in number among the five geographical populations. It is suggested to strengthen the conservation of P. baotingensis in the Bengling area.
2024, 15(4): 427-436.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230136
Abstract:
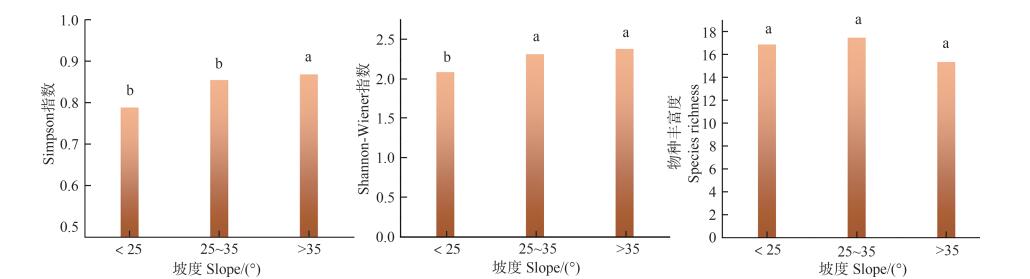
In order to explore the species composition and diversity of plants in the rubber plantations of Mengla County, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China, 94 plant quadrates(20×20 m) and 20 soil quadrates were arranged for observation in the understory of the rubber plantations in Mengla County to analyze the effects of environmental and spatial factors on the species distribution and plant diversity in the rubber plantations. The results showed that there were 87 families, 197 genera and 300 species of understory plants in the rubber plantations in Mengla County, and that the dominant species were Aporusa dioica, Indocalamus latifolius, Pueraria lobata and so on.The contents of total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in the 20 soil quadrates varied moderately, and their highest contents were 1.09%, 0.17% and 2.65%, respectively. The analysis of factors influencing the distribution of plant species and dominant species by using the RDA method showed that topography had significant effect on the distribution of dominant species, and that soil total phosphorus and slope had significant effects on plant species distribution(P < 0.01). In the analysis of plant diversity, the effect of slope on plant diversity was significantly higher than that of other factors(P < 0.05). Simpson(D) index and Shannon-Wiener(H) index were the highest at the slope > 35°, and the fit degree was higher in regression analysis. The D and H were higher at the altitudes greater than 600 m, and species richness(S) was higher at the elevations between 600 m and 700 m than at the other elevations. The plant species richness was the highest in the rubber plantations at the age of 8 ~14 years old. The plant species under the rubber plantations in Mengla County are abundant, but the plant diversity is poor due to artificial disturbance. The plant diversity under the rubber plantations can be increased through reasonable management and control, which is conducive to ecological recovery.
In order to explore the species composition and diversity of plants in the rubber plantations of Mengla County, Xishuangbanna, Yunnan, China, 94 plant quadrates(20×20 m) and 20 soil quadrates were arranged for observation in the understory of the rubber plantations in Mengla County to analyze the effects of environmental and spatial factors on the species distribution and plant diversity in the rubber plantations. The results showed that there were 87 families, 197 genera and 300 species of understory plants in the rubber plantations in Mengla County, and that the dominant species were Aporusa dioica, Indocalamus latifolius, Pueraria lobata and so on.The contents of total nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in the 20 soil quadrates varied moderately, and their highest contents were 1.09%, 0.17% and 2.65%, respectively. The analysis of factors influencing the distribution of plant species and dominant species by using the RDA method showed that topography had significant effect on the distribution of dominant species, and that soil total phosphorus and slope had significant effects on plant species distribution(P < 0.01). In the analysis of plant diversity, the effect of slope on plant diversity was significantly higher than that of other factors(P < 0.05). Simpson(D) index and Shannon-Wiener(H) index were the highest at the slope > 35°, and the fit degree was higher in regression analysis. The D and H were higher at the altitudes greater than 600 m, and species richness(S) was higher at the elevations between 600 m and 700 m than at the other elevations. The plant species richness was the highest in the rubber plantations at the age of 8 ~14 years old. The plant species under the rubber plantations in Mengla County are abundant, but the plant diversity is poor due to artificial disturbance. The plant diversity under the rubber plantations can be increased through reasonable management and control, which is conducive to ecological recovery.
2024, 15(4): 437-444.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230094
Abstract:
In order to study the nest site selection preferences and main influencing factors of Oriental MagpieRobin(Copsychus saularis), a total of 150 artificial nest boxes were set up in Hainan Tropical Wildlife and Botanical Garden. The selection behavior of Oriental Magpie-Robin population reproduced in the artificial nest boxes was investigated during the breeding season in 2021 and 2022. The results showed that a total of 59artificial nest boxes were used for reproduction by Oriental Magpie-Robin in two years. Among all the artificial nest boxes 90 were monitored in 2021, and 34 were used for reproduction; the utilization rate of the nest boxes was 37.78%, and the reuse rate was 14.71%. In 2022, 60 nest boxes were monitored and 25 were used for reproduction; the utilization rate of the nest boxes was 41.67%, and the reuse rate was 16.00%. The reproductive success rates in these 2 years were 67.65% and 68.00%, respectively. The nest box with a closer distance from the water source(14.25 ± 13.66 m) and a higher branch distance above the nest boxes(2.57 ± 1.81 m) were preferred by the Oriental Magpie-Robin. At the same time, the height from the ground(2.82 ± 0.53 m), the distance from the road(9.34 ± 7.02 m), the herb coverage(34.07 ± 28.15%), the trunk diameter at breast height of the nest tree(91.30 ± 24.30 cm) and the ground exposure(30.00 ± 22.40%) were also the important influencing factors. The main factors affecting the nest site selection of the Oriental Magpie-Robin are the degree of concealment(34.32%), the interference factor(25.76%) and the survival resource factor(17.65%). The quality of the nest sites mainly depends on the concealment and inaccessibility of nesting. In this study, the factors of concealment, interference and survival resources were considered by the Oriental Magpie-Robin in their selection of nest boxes. Subsequent studies will focus on the impact of urbanization on nest site selection and the reproductive success rate among different populations.
In order to study the nest site selection preferences and main influencing factors of Oriental MagpieRobin(Copsychus saularis), a total of 150 artificial nest boxes were set up in Hainan Tropical Wildlife and Botanical Garden. The selection behavior of Oriental Magpie-Robin population reproduced in the artificial nest boxes was investigated during the breeding season in 2021 and 2022. The results showed that a total of 59artificial nest boxes were used for reproduction by Oriental Magpie-Robin in two years. Among all the artificial nest boxes 90 were monitored in 2021, and 34 were used for reproduction; the utilization rate of the nest boxes was 37.78%, and the reuse rate was 14.71%. In 2022, 60 nest boxes were monitored and 25 were used for reproduction; the utilization rate of the nest boxes was 41.67%, and the reuse rate was 16.00%. The reproductive success rates in these 2 years were 67.65% and 68.00%, respectively. The nest box with a closer distance from the water source(14.25 ± 13.66 m) and a higher branch distance above the nest boxes(2.57 ± 1.81 m) were preferred by the Oriental Magpie-Robin. At the same time, the height from the ground(2.82 ± 0.53 m), the distance from the road(9.34 ± 7.02 m), the herb coverage(34.07 ± 28.15%), the trunk diameter at breast height of the nest tree(91.30 ± 24.30 cm) and the ground exposure(30.00 ± 22.40%) were also the important influencing factors. The main factors affecting the nest site selection of the Oriental Magpie-Robin are the degree of concealment(34.32%), the interference factor(25.76%) and the survival resource factor(17.65%). The quality of the nest sites mainly depends on the concealment and inaccessibility of nesting. In this study, the factors of concealment, interference and survival resources were considered by the Oriental Magpie-Robin in their selection of nest boxes. Subsequent studies will focus on the impact of urbanization on nest site selection and the reproductive success rate among different populations.
2024, 15(4): 445-451.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20240039
Abstract:
To investigate whether bacterial outer membrane vesicles(OMVs) secreted by the conditionally pathogenic bacterium Proteus mirabilis have the function of inducing macrophage polarization to regulate the tumor microenvironment, the mouse macrophage RAW264.7 was stimulated with the OMVs to detect macrophage polarization-related phenotype. The OMVs were isolated, extracted and then characterized using transmission electron microscopy. The OMVs were traced with PKH67 fluorescent dye, and the uptake of OMVs by RAW264.7cells was observed by using fluorescence microscopy. The total NO content secreted by RAW264.7 cells and the expression of polarization-associated factors in RAW264.7 cells were detected by using total nitric oxide(NO)detection kit and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR(RT-qPCR), respectively. The results showed that OMVs could be taken up by RAW264.7 cells, induced an increase in NO secretion in these cells, and upregulated the expression of IL-10, IL-1β, TNF1-α, and IL-6, i. e., the occurrence of M1-type and M2b-type polarizations, which activated anti-tumor activity of macrophages. The above results suggest a potential role of OMVs secreted by P. mirabilis in the bacterium’s resistance to breast tumor growth and lung metastasis.
To investigate whether bacterial outer membrane vesicles(OMVs) secreted by the conditionally pathogenic bacterium Proteus mirabilis have the function of inducing macrophage polarization to regulate the tumor microenvironment, the mouse macrophage RAW264.7 was stimulated with the OMVs to detect macrophage polarization-related phenotype. The OMVs were isolated, extracted and then characterized using transmission electron microscopy. The OMVs were traced with PKH67 fluorescent dye, and the uptake of OMVs by RAW264.7cells was observed by using fluorescence microscopy. The total NO content secreted by RAW264.7 cells and the expression of polarization-associated factors in RAW264.7 cells were detected by using total nitric oxide(NO)detection kit and real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR(RT-qPCR), respectively. The results showed that OMVs could be taken up by RAW264.7 cells, induced an increase in NO secretion in these cells, and upregulated the expression of IL-10, IL-1β, TNF1-α, and IL-6, i. e., the occurrence of M1-type and M2b-type polarizations, which activated anti-tumor activity of macrophages. The above results suggest a potential role of OMVs secreted by P. mirabilis in the bacterium’s resistance to breast tumor growth and lung metastasis.
2024, 15(4): 452-459.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230056
Abstract:
In order to construct a novel gene-knockout plasmid, a novel plasmid pSETsac B was constructed based on the plasmids pSET4s and pK18mobsac B by using PCR and cloning techniques. Then pK18mobsac B was used as control, the knockout efficiency of kdp E gene in Aeromonas dhakensis was evaluated via the newly constructed plasmid with or without tetr marker. The results showed that there was no difference in the knockout efficiency between the two plasmids with tetr marker, but the efficiency of scarless deletion by pSETsac B was significantly higher than that of the control plasmid pK18mobsac B. p SETsac B is a thermosensitive shuttle plasmid, and is hence expected to play a role in the genetic mechanism of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This study also provides important mutant material for investigating the kdp E gene of A. dhakensis.
In order to construct a novel gene-knockout plasmid, a novel plasmid pSETsac B was constructed based on the plasmids pSET4s and pK18mobsac B by using PCR and cloning techniques. Then pK18mobsac B was used as control, the knockout efficiency of kdp E gene in Aeromonas dhakensis was evaluated via the newly constructed plasmid with or without tetr marker. The results showed that there was no difference in the knockout efficiency between the two plasmids with tetr marker, but the efficiency of scarless deletion by pSETsac B was significantly higher than that of the control plasmid pK18mobsac B. p SETsac B is a thermosensitive shuttle plasmid, and is hence expected to play a role in the genetic mechanism of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. This study also provides important mutant material for investigating the kdp E gene of A. dhakensis.
2024, 15(4): 460-470.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230117
Abstract:
In recent years, coral bleaching events induced by marine heat waves have occurred frequently, and Symbiodiniaceae, as algal symbionts of coral hosts, has been proved to play an important role in controlling coral environmental tolerance. In order to explore the differences among different species of Symbiodiniaceae and their physiological characteristics, four monoclonal strains of Symbiodiniaceae were isolated and obtained from different cnidaria organisms in the South China Sea, and a series of investigations were conducted on their phylogenetic, morphological and various physiological characteristics. The results exhibited that the four strains of Symbiodiniaceae were Symbiodinium(type A3, HNUA3-1), Breviolum(type B1, HNUB1-1), Cladocopium(type C1, HNUC1-1) and Durusdinium(type D1, HNUD1-1), respectively. Observations by light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy revealed that the four strains had higher similarity in morphological characteristics but there were significant differences in specific growth rates, reflecting the species-specific growth characteristics. The specific growth rate of Breviolum sp. HNUB1-1 was the highest, and the cell density of Breviolum sp. HNUB1-1 was significantly higher than that of the other three strains on the 3rd, 5th and 7th day(P < 0.05), the specific growth rate of Symbiodinium sp. HNUA3-1 was second highest, the specific growth rate of Cladocopium sp. HNUC1-1 and Durusdinium sp. HNUD1-1 was the lowest, and there was no significant difference in cell density within 7 days of culture. Furthermore, different strains waere also specie-specific in maximum quantum efficiency of Photosystem II(Fv/Fm). Under the same conditions, the Fv/Fm of the Durusdinium sp. HNUD1-1 was significantly lower than that of the other three strains, reflecting the photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of its potential heat resistance. This study provided theoretical basis for enriching the resources of Symbiodiniaceae in the South China Sea, and clarifying the differences and characteristics of the Symbiodiniaceae, which can be used to provide basic data support for the conservation and restoration of the coral reef ecosystem in the South China Sea.
In recent years, coral bleaching events induced by marine heat waves have occurred frequently, and Symbiodiniaceae, as algal symbionts of coral hosts, has been proved to play an important role in controlling coral environmental tolerance. In order to explore the differences among different species of Symbiodiniaceae and their physiological characteristics, four monoclonal strains of Symbiodiniaceae were isolated and obtained from different cnidaria organisms in the South China Sea, and a series of investigations were conducted on their phylogenetic, morphological and various physiological characteristics. The results exhibited that the four strains of Symbiodiniaceae were Symbiodinium(type A3, HNUA3-1), Breviolum(type B1, HNUB1-1), Cladocopium(type C1, HNUC1-1) and Durusdinium(type D1, HNUD1-1), respectively. Observations by light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy revealed that the four strains had higher similarity in morphological characteristics but there were significant differences in specific growth rates, reflecting the species-specific growth characteristics. The specific growth rate of Breviolum sp. HNUB1-1 was the highest, and the cell density of Breviolum sp. HNUB1-1 was significantly higher than that of the other three strains on the 3rd, 5th and 7th day(P < 0.05), the specific growth rate of Symbiodinium sp. HNUA3-1 was second highest, the specific growth rate of Cladocopium sp. HNUC1-1 and Durusdinium sp. HNUD1-1 was the lowest, and there was no significant difference in cell density within 7 days of culture. Furthermore, different strains waere also specie-specific in maximum quantum efficiency of Photosystem II(Fv/Fm). Under the same conditions, the Fv/Fm of the Durusdinium sp. HNUD1-1 was significantly lower than that of the other three strains, reflecting the photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of its potential heat resistance. This study provided theoretical basis for enriching the resources of Symbiodiniaceae in the South China Sea, and clarifying the differences and characteristics of the Symbiodiniaceae, which can be used to provide basic data support for the conservation and restoration of the coral reef ecosystem in the South China Sea.
2024, 15(4): 471-481.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230131
Abstract:
Seagrasses that grow in the intertidal zone is adaptable to salinity fluctuations. However, considering that extreme weather and human activities may cause intensification of coastal seawater salinity fluctuation, the adaptation thresholds of seagrasses to the salinity fluctuation and the physiological mechanism are worth exploring. In this context an experiment was made with controllable salinity fluctuation amplitudes of seawater,and two seagrass species, Cymodocea rotundata and Thalassia hemprichii, were planted in the seawater with different salinity fluctuation amplitudes from 0 to 10. The changes of seagrass growth indicators related to photosynthesis were determined. The results showed that with the increase of salinity fluctuation amplitudes,average leaf area, photosynthetic products, photosynthetic pigments of the two seagrass and leaf growth rate of C.rotundata increased first and then decreased, except for the leaf growth rate and the content of Chl-a for T.hemprichii that increased continuously. Fv/Fm, Fv/Fo, qP and Y(II) of the two seagrass species increased first and then decreased, while Y(NPQ), Y(NO) and qN decreased first and then increased. Salinity fluctuation amplitudes,species and their interactions had significant influence on average leaf area, leaf growth rate, contents of starch,soluble sugar, soluble protein, Chl-a, Chl-b, carotenoids, Fv/Fm, Fv/Fo, qP, q N, Y(II), Y(NPQ), Y(NO) and maximum electron transport rate(ETRmax)(P<0.05). These results showed that the water environment with salinity fluctuations of 2 ~ 6 and 2 ~ 10 could promote the photosynthesis and growth of C. rotundata and T. hemprichii,respectively. These ranges of salinity fluctuation are optimum for both the two seagrass species, while other ranges of salinity fluctuation was not conducive to the physiological growth and photosynthesis of the two seagrass species.
Seagrasses that grow in the intertidal zone is adaptable to salinity fluctuations. However, considering that extreme weather and human activities may cause intensification of coastal seawater salinity fluctuation, the adaptation thresholds of seagrasses to the salinity fluctuation and the physiological mechanism are worth exploring. In this context an experiment was made with controllable salinity fluctuation amplitudes of seawater,and two seagrass species, Cymodocea rotundata and Thalassia hemprichii, were planted in the seawater with different salinity fluctuation amplitudes from 0 to 10. The changes of seagrass growth indicators related to photosynthesis were determined. The results showed that with the increase of salinity fluctuation amplitudes,average leaf area, photosynthetic products, photosynthetic pigments of the two seagrass and leaf growth rate of C.rotundata increased first and then decreased, except for the leaf growth rate and the content of Chl-a for T.hemprichii that increased continuously. Fv/Fm, Fv/Fo, qP and Y(II) of the two seagrass species increased first and then decreased, while Y(NPQ), Y(NO) and qN decreased first and then increased. Salinity fluctuation amplitudes,species and their interactions had significant influence on average leaf area, leaf growth rate, contents of starch,soluble sugar, soluble protein, Chl-a, Chl-b, carotenoids, Fv/Fm, Fv/Fo, qP, q N, Y(II), Y(NPQ), Y(NO) and maximum electron transport rate(ETRmax)(P<0.05). These results showed that the water environment with salinity fluctuations of 2 ~ 6 and 2 ~ 10 could promote the photosynthesis and growth of C. rotundata and T. hemprichii,respectively. These ranges of salinity fluctuation are optimum for both the two seagrass species, while other ranges of salinity fluctuation was not conducive to the physiological growth and photosynthesis of the two seagrass species.
2024, 15(4): 482-492.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230132
Abstract:
To provide a scientific basis for scientific monitoring and accurate control of Solenopsis invicta, the method of ruler-mark was used to observe and analysis the climbing height, the number of worker ants, and the restore calm time of S. invicta worker in arecanut(Areca catechu L.) plantation of Hainan Island. The results indicate that the number of worker ants and climbing height decreased gradually after reaching the peak at 45 s after being disturbed.Path analysis revealed that climbing height of the sunny side within 180 s of worker ants had the highest correlation with volume of ant nest after being disturbed. The volume of ant nest and the activity test duration positively influenced the climbing height of the sunny side at 15 s of worker ants after being disturbed, the climbing height of the shady side at 60 s of worker ants after being disturbed, the climbing height at 60 s of worker ants after being disturbed, and the climbing height within 180 s of worker ants after being disturbed. Additionally, surface height and volume of ant nest positively influenced the climbing height of sunny side at 60 s of worker ants after being disturbed.
To provide a scientific basis for scientific monitoring and accurate control of Solenopsis invicta, the method of ruler-mark was used to observe and analysis the climbing height, the number of worker ants, and the restore calm time of S. invicta worker in arecanut(Areca catechu L.) plantation of Hainan Island. The results indicate that the number of worker ants and climbing height decreased gradually after reaching the peak at 45 s after being disturbed.Path analysis revealed that climbing height of the sunny side within 180 s of worker ants had the highest correlation with volume of ant nest after being disturbed. The volume of ant nest and the activity test duration positively influenced the climbing height of the sunny side at 15 s of worker ants after being disturbed, the climbing height of the shady side at 60 s of worker ants after being disturbed, the climbing height at 60 s of worker ants after being disturbed, and the climbing height within 180 s of worker ants after being disturbed. Additionally, surface height and volume of ant nest positively influenced the climbing height of sunny side at 60 s of worker ants after being disturbed.
2024, 15(4): 493-498.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230114
Abstract:
Dendrobium nobile has great medicinal value, unique flower shape and rich color, and hence is well favored in the international market and widely planted in tropical and subtropical areas. The larvae of Contarinia maculipennis Felt are hidden in the bracts of D. nobile for infestation, which can cause the bracts to be deformed and discolored, greatly reducing the ornamental value of D. nobile, and hence affecting its economic value. At the same time, the mature larvae of the pest can also drill into the soil to pupate, and can be spread for a long distance through trade of cut flowers and potted soil due to transportation. At present, this pest has caused serious economic losses to the Dendrobium industry in Okinawa, Fukuoka, Miyazaki, Hawaii and other places in Japan.The insects of family Cecidomyidae are traditionally identified mainly through morphology, which identification method is not accurate especially for the eggs and larvae of its similar species. An accurate and rapid identification of C. maculipennis Felt is hence needed to prevent its invasion into other Dendrobium nobile plantation areas in China. DNA barcoding technology was used to successfully identify the samples collected from a China(Sanya) International Orchid Show, Hainan Island as C. maculates Felt, and the morphological characteristics of C.maculates Felt were described in detail, which provided a scientific basis for accurate and rapid identification of C.maculates Felt by relevant quarantine departments.
Dendrobium nobile has great medicinal value, unique flower shape and rich color, and hence is well favored in the international market and widely planted in tropical and subtropical areas. The larvae of Contarinia maculipennis Felt are hidden in the bracts of D. nobile for infestation, which can cause the bracts to be deformed and discolored, greatly reducing the ornamental value of D. nobile, and hence affecting its economic value. At the same time, the mature larvae of the pest can also drill into the soil to pupate, and can be spread for a long distance through trade of cut flowers and potted soil due to transportation. At present, this pest has caused serious economic losses to the Dendrobium industry in Okinawa, Fukuoka, Miyazaki, Hawaii and other places in Japan.The insects of family Cecidomyidae are traditionally identified mainly through morphology, which identification method is not accurate especially for the eggs and larvae of its similar species. An accurate and rapid identification of C. maculipennis Felt is hence needed to prevent its invasion into other Dendrobium nobile plantation areas in China. DNA barcoding technology was used to successfully identify the samples collected from a China(Sanya) International Orchid Show, Hainan Island as C. maculates Felt, and the morphological characteristics of C.maculates Felt were described in detail, which provided a scientific basis for accurate and rapid identification of C.maculates Felt by relevant quarantine departments.
2024, 15(4): 499-508.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230111
Abstract:
Photocatalysts can convert solar energy into chemical energy and show great potential for applications in pollutant degradation, hydrogen production by water photolysis, and CO2 reduction. As one of the new photocatalysts, graphitic carbon nitride(g-C3N4) has many excellent properties, low preparation cost, adjustable optical band gap, excellent chemical and physical stability, etc., which have attracted a lot of attention from researchers. However, the unmodified g-C3N4 suffers from small specific surface area, insufficient active sites for reaction, low quantum efficiency and high complexation rate of photogenerated charge carriers, which limit the application of g-C3N4 in photocatalysis. Therefore, the existing g-C3N4 photocatalysts are modified to improve their photocatalytic performance. Combined with the remarkable results achieved so far in carbon nitride modification treatment, the authors review the main methods for modification of graphite-phase carbon nitride composites,including elemental doping, defect engineering, design of various nanostructures and construction of heterojunctions, and make an outlook on the development trend of g-C3N4 in photocatalysis for reference.
Photocatalysts can convert solar energy into chemical energy and show great potential for applications in pollutant degradation, hydrogen production by water photolysis, and CO2 reduction. As one of the new photocatalysts, graphitic carbon nitride(g-C3N4) has many excellent properties, low preparation cost, adjustable optical band gap, excellent chemical and physical stability, etc., which have attracted a lot of attention from researchers. However, the unmodified g-C3N4 suffers from small specific surface area, insufficient active sites for reaction, low quantum efficiency and high complexation rate of photogenerated charge carriers, which limit the application of g-C3N4 in photocatalysis. Therefore, the existing g-C3N4 photocatalysts are modified to improve their photocatalytic performance. Combined with the remarkable results achieved so far in carbon nitride modification treatment, the authors review the main methods for modification of graphite-phase carbon nitride composites,including elemental doping, defect engineering, design of various nanostructures and construction of heterojunctions, and make an outlook on the development trend of g-C3N4 in photocatalysis for reference.



 Abstract
Abstract PDF 33200KB
PDF 33200KB
















 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS