2023 Vol. 14, No. 1
2023, 14(1): 1-7.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.004
Abstract:
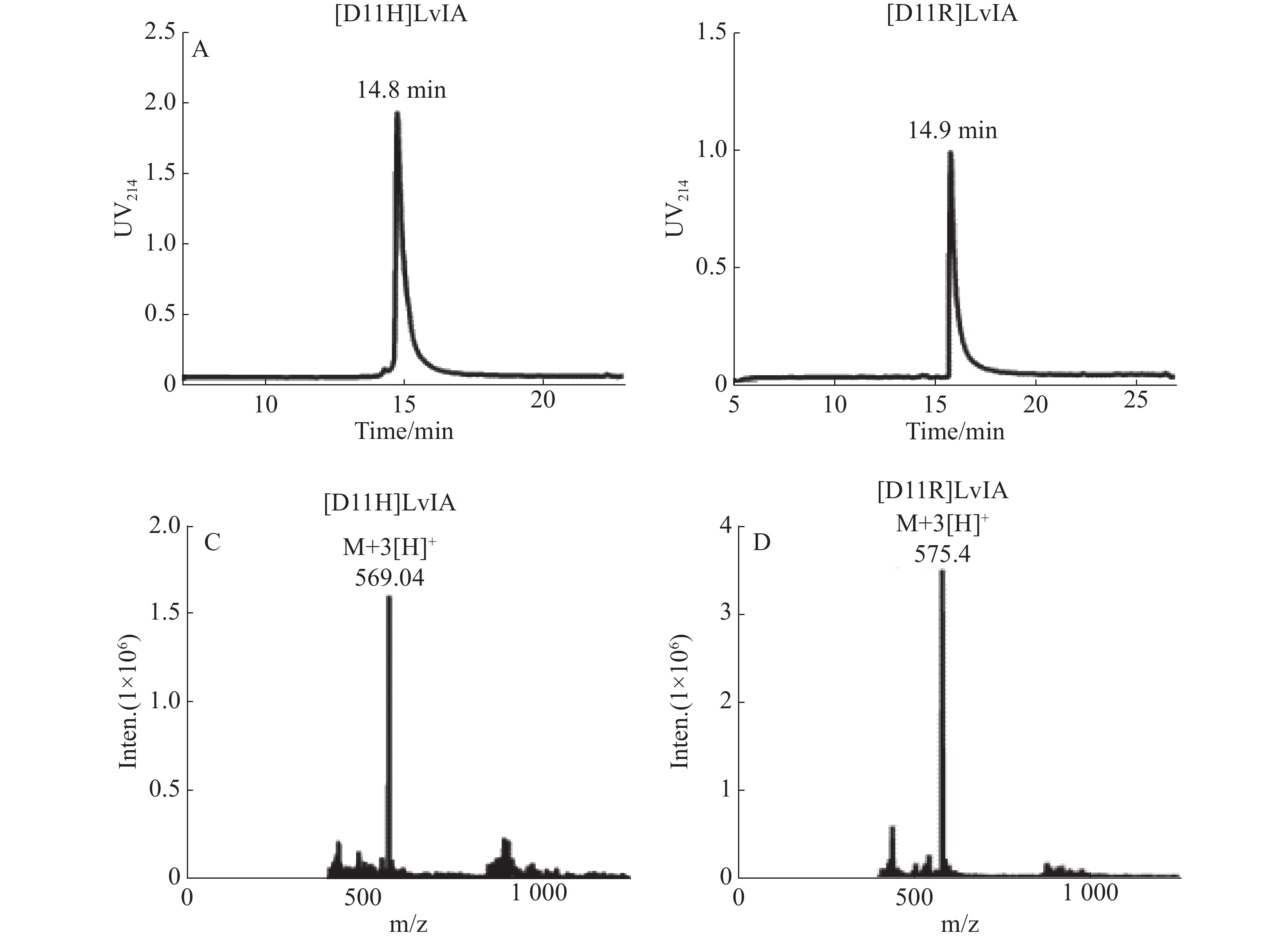
α-snail toxin LvIA is a small peptide targeting α3β2 acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), which was found in the South China Sea snail. The structure and function of LvIA were previously analyzed in our laboratory. After alanine scanning mutation it was found that the mutant [D11A] LvIA, which was replaced by alanine (A) with aspartic acid at the site 11 of LvIA, maintained its activity against α3β2 nAChR. In order to further explore the effect of the properties of amino acid at the position 11 on the binding activity of LvIA target, two new mutants of LvIA [D11R] LvIA and [D11H] LvIA were designed, namely, two basic amino acids - arginine (R) and histidine (H) were used to replace the original acid amino acid D, respectively. The linear peptides of the two new mutants were synthesized and then folded by a two-step oxidation method to obtain a disulfide bond between the first and third cysteines (Cys 1-3) and the second and fourth cysteines (Cys 2-4). The peptides containing Cys (1-3, 2-4) disulfide bond were successfully synthesized by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry. The synthesized peptides were correct in molecular weight and their purity was above 95%. The binding activity of these two mutants to α3β2 nAChR was detected by two-electrode voltage clamp electrophysiology. The results showed that when the amino acid properties of the site were changed from acidic to alkaline, LvIA activity was greatly affected, resulting in direct loss of α3β2 nAChR blocking activity. The activity of [D11R] LvIA and [D11H] LvIA was 574.38% and 408.62% lower than that of wild-type LvIA, respectively. This suggests that the acidity and basicity of the 11th amino acid is crucial to the activity of LvIA. These results provide some reference for the optimization design and modification of LvIA in the future, based on which it is expected to obtain more specific peptide tools targeting α3β2 nAChR, which can provide a better pharmacological molecular probe for the study of the structure, function and distribution of an α3β2 nAChR receptor.
α-snail toxin LvIA is a small peptide targeting α3β2 acetylcholine receptor (nAChR), which was found in the South China Sea snail. The structure and function of LvIA were previously analyzed in our laboratory. After alanine scanning mutation it was found that the mutant [D11A] LvIA, which was replaced by alanine (A) with aspartic acid at the site 11 of LvIA, maintained its activity against α3β2 nAChR. In order to further explore the effect of the properties of amino acid at the position 11 on the binding activity of LvIA target, two new mutants of LvIA [D11R] LvIA and [D11H] LvIA were designed, namely, two basic amino acids - arginine (R) and histidine (H) were used to replace the original acid amino acid D, respectively. The linear peptides of the two new mutants were synthesized and then folded by a two-step oxidation method to obtain a disulfide bond between the first and third cysteines (Cys 1-3) and the second and fourth cysteines (Cys 2-4). The peptides containing Cys (1-3, 2-4) disulfide bond were successfully synthesized by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry. The synthesized peptides were correct in molecular weight and their purity was above 95%. The binding activity of these two mutants to α3β2 nAChR was detected by two-electrode voltage clamp electrophysiology. The results showed that when the amino acid properties of the site were changed from acidic to alkaline, LvIA activity was greatly affected, resulting in direct loss of α3β2 nAChR blocking activity. The activity of [D11R] LvIA and [D11H] LvIA was 574.38% and 408.62% lower than that of wild-type LvIA, respectively. This suggests that the acidity and basicity of the 11th amino acid is crucial to the activity of LvIA. These results provide some reference for the optimization design and modification of LvIA in the future, based on which it is expected to obtain more specific peptide tools targeting α3β2 nAChR, which can provide a better pharmacological molecular probe for the study of the structure, function and distribution of an α3β2 nAChR receptor.
2023, 14(1): 8-16.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.003
Abstract:
A survey was made of macrobenthos from 2016 to 2019 to understand the composition and distribution characteristics of macrobenthos community in the coral reef areas of Xisha islands. Four quadrats were arranged in each coral reef area of Xisha islands and the quadrat size was 0.25 m × 0.25 m. A systematic analysis was made of the species composition, richness, biomass distribution and biodiversity of the macrobenthos collected. The analysis showed that 252 species of macrobenthos were found in 5 biological groups, of which crustaceans were the most common species and had 120 species, followed by mollusc (72 species), echinoderms (37 species), annelids (17 species) and other phyla (6 species). Density of macrobenthos was (334.45±396.40) ind·m−2, biomass (110.79±126.56) g·m−2, Shannon Wiener diversity index (H') 3.85±0.84, Richness index (d) 5.51 ±2.64 and Evenness index (J') 0.89±0.05. According to the diversity index, Yongxing island in 2016 and Xishazhou in 2018 were slightly disturbed. The cluster analysis of the community showed that the macrobenthos communities in these areas changed significantly over time. An abundance/biomass comparison curve (ABC method) was used to assess the status of the macrobenthos communities, and the results showed that macrobenthos communities in some islands of Xisha Islands in 2017 and 2018 were disturbed to some extent. It is concluded that the macrobenthos communities in the coral reef areas of Xisha Islands are generally mainly composed of crustaceans and mollusks, and that the change in time of survey has a greater effect on the structure of macrobenthos community than the change in geological location.
A survey was made of macrobenthos from 2016 to 2019 to understand the composition and distribution characteristics of macrobenthos community in the coral reef areas of Xisha islands. Four quadrats were arranged in each coral reef area of Xisha islands and the quadrat size was 0.25 m × 0.25 m. A systematic analysis was made of the species composition, richness, biomass distribution and biodiversity of the macrobenthos collected. The analysis showed that 252 species of macrobenthos were found in 5 biological groups, of which crustaceans were the most common species and had 120 species, followed by mollusc (72 species), echinoderms (37 species), annelids (17 species) and other phyla (6 species). Density of macrobenthos was (334.45±396.40) ind·m−2, biomass (110.79±126.56) g·m−2, Shannon Wiener diversity index (H') 3.85±0.84, Richness index (d) 5.51 ±2.64 and Evenness index (J') 0.89±0.05. According to the diversity index, Yongxing island in 2016 and Xishazhou in 2018 were slightly disturbed. The cluster analysis of the community showed that the macrobenthos communities in these areas changed significantly over time. An abundance/biomass comparison curve (ABC method) was used to assess the status of the macrobenthos communities, and the results showed that macrobenthos communities in some islands of Xisha Islands in 2017 and 2018 were disturbed to some extent. It is concluded that the macrobenthos communities in the coral reef areas of Xisha Islands are generally mainly composed of crustaceans and mollusks, and that the change in time of survey has a greater effect on the structure of macrobenthos community than the change in geological location.
2023, 14(1): 17-24.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.015
Abstract:
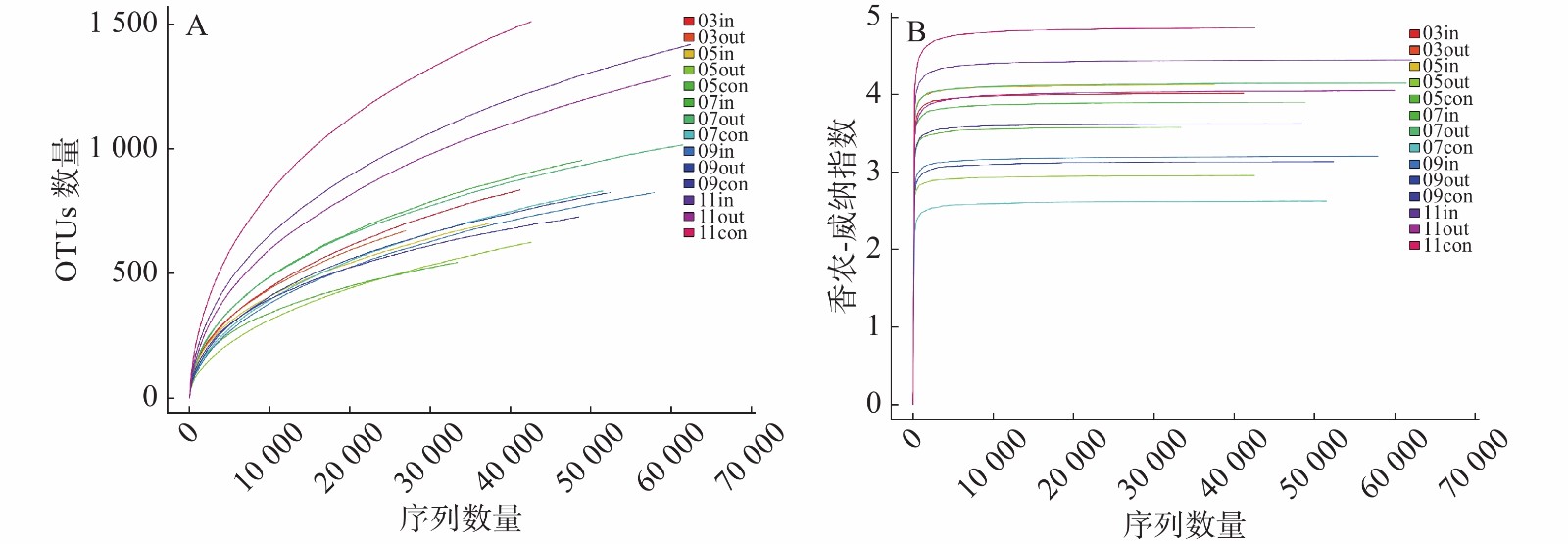
To explore the structure of bacterioplankton community and its relationship with bacterial diseases of marine fish aquacultured in cage, bacterial communities from sea water sampled in a deep-water cage mariculture area at Houshuiwan Bay, Lingao, Hainan were analyzed through Illumina Miseq sequencing based on 16S RNA gene. The results showed that bacterioplankton species detected in the sea water samples belonged to 36 phyla, 56 classes, 98 orders, 235 families and 807 genera, with their Shannon-Wiener index ranging from 2.47 to 4.5, which indicated a high diversity of bacterioplankton in the deep-sea cage mariculture area at Houshuiwan Bay. Proteobacteria were the main dominant phylum at all the sampling sites, followed by phyla Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Firmicutes and Cyanobacteria. Dominant genera were Cobetia, Roseovarius and Psychrobacter in the non-mariculture period (March), Cobetia, Pseudoalteromonas, Kushneria and Vibrio in the early period of mariculture (May), Cobetia, Halomonas, Alteromonas, Vibrio and Pseudoalteromonas in the mid-period of mariculture (July and September), GpIIa and Cobetia in the late period of mariculture. Vibrio, potential pathogens, varied greatly during the mariculture and its abundance was found higher in the early period and mid-period of mariculture, and the lower in the non- and late mariculture periods, which was consistent with the incidence of bacterial diseases of fish in the deep-water cage mariculture area, indicating that vibriosis was the main bacterial disease of fish in the mariculture area.
To explore the structure of bacterioplankton community and its relationship with bacterial diseases of marine fish aquacultured in cage, bacterial communities from sea water sampled in a deep-water cage mariculture area at Houshuiwan Bay, Lingao, Hainan were analyzed through Illumina Miseq sequencing based on 16S RNA gene. The results showed that bacterioplankton species detected in the sea water samples belonged to 36 phyla, 56 classes, 98 orders, 235 families and 807 genera, with their Shannon-Wiener index ranging from 2.47 to 4.5, which indicated a high diversity of bacterioplankton in the deep-sea cage mariculture area at Houshuiwan Bay. Proteobacteria were the main dominant phylum at all the sampling sites, followed by phyla Bacteroidetes, Actinobacteria, Firmicutes and Cyanobacteria. Dominant genera were Cobetia, Roseovarius and Psychrobacter in the non-mariculture period (March), Cobetia, Pseudoalteromonas, Kushneria and Vibrio in the early period of mariculture (May), Cobetia, Halomonas, Alteromonas, Vibrio and Pseudoalteromonas in the mid-period of mariculture (July and September), GpIIa and Cobetia in the late period of mariculture. Vibrio, potential pathogens, varied greatly during the mariculture and its abundance was found higher in the early period and mid-period of mariculture, and the lower in the non- and late mariculture periods, which was consistent with the incidence of bacterial diseases of fish in the deep-water cage mariculture area, indicating that vibriosis was the main bacterial disease of fish in the mariculture area.
2023, 14(1): 25-31.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.002
Abstract:
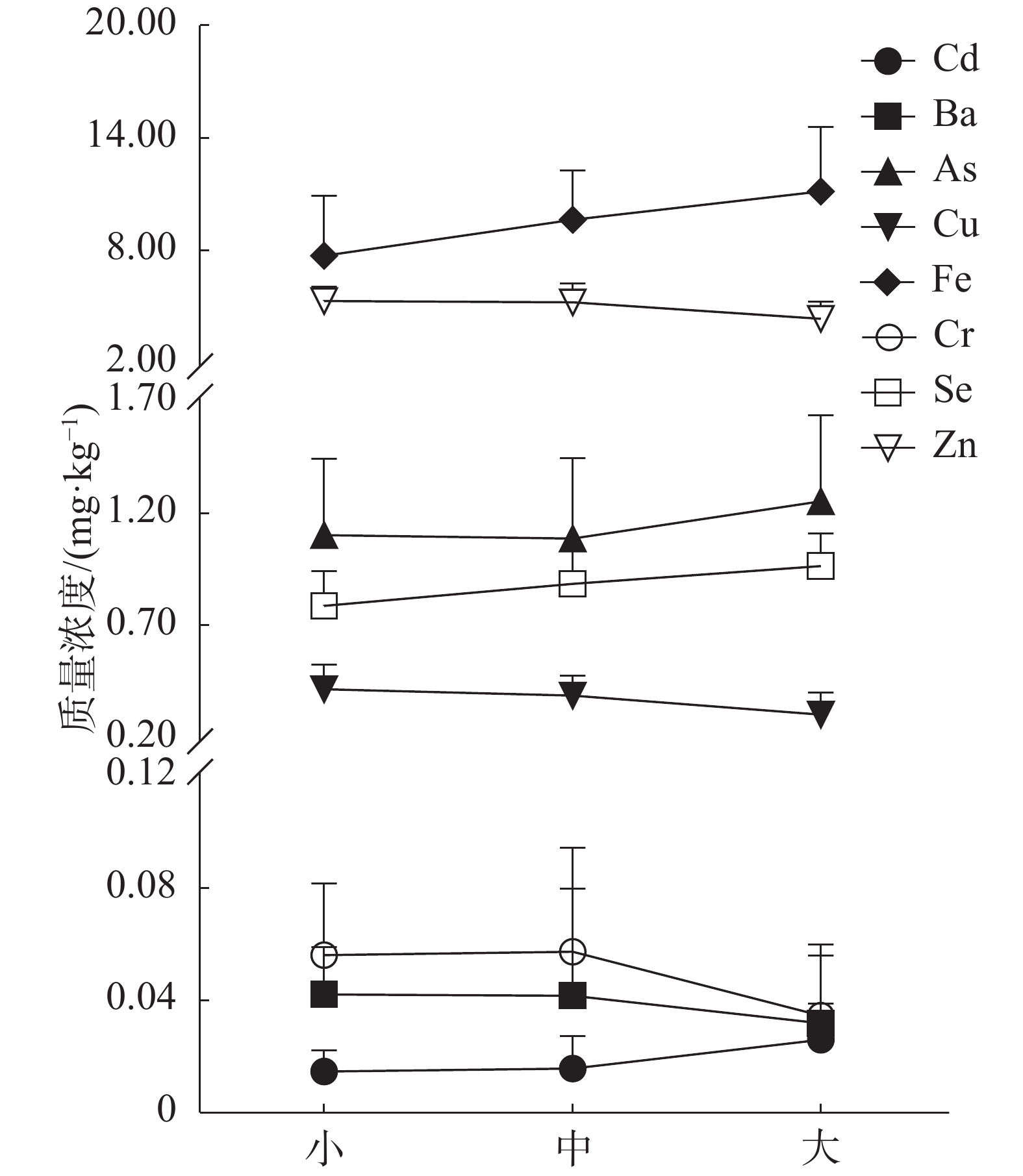
Yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) is one of the most popular fish consumed worldwide. It is crucial to determine the risk of yellowfin tuna that heavy metals pose to consumer health. In order to understand the heavy metal bioaccumulation characteristics and food safety in yellowfin tuna from the South China Sea, eight heavy metals (Cd, Ba, As, Cu, Fe, Cr, Se, and Zn) in muscle and liver tissues of the yellowfin tuna were determined. The yellowfin tuna were divided to three groups with different body sizes (large, medium, and small). The findings showed that the bioaccumulation of heavy metal elements in the yellowfin tuna varied significantly with body size. Specifically, the levels of Fe, Se, and Cd in muscle increased with body size (P<0.05), while the levels of Zn and Cu decreased with body size, and the levels of As, Ba, and Cr did not vary significantly with body size (P>0.05). The levels of Fe, Se, Cu, and Cd in liver increased steadily with body size (P<0.05), the Cr level decreased with body size (P<0.05), and the contents of Zn, As and Ba in the tuna with all the body sizes had no significant changes (P>0.05). The levels of Cd, As, Cu, Fe, Se, and Zn were substantially higher in liver than in muscle in the groups of all the three body sizes (P<0.05). In terms of food safety, the concentration of each heavy metal element in muscle was lower than that in the National Food Safety Standards of China (GB 2762-2017). The single-factor contamination index of Cd and iAs suggested the yellowfin tuna from the South China sea have a slight risk of heavy metals to human health, and it is hence recommended that the daily intake of the yellowfin tuna caught in the South China Sea be less than 120.00 g for adults and 37.71 g for children.
Yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) is one of the most popular fish consumed worldwide. It is crucial to determine the risk of yellowfin tuna that heavy metals pose to consumer health. In order to understand the heavy metal bioaccumulation characteristics and food safety in yellowfin tuna from the South China Sea, eight heavy metals (Cd, Ba, As, Cu, Fe, Cr, Se, and Zn) in muscle and liver tissues of the yellowfin tuna were determined. The yellowfin tuna were divided to three groups with different body sizes (large, medium, and small). The findings showed that the bioaccumulation of heavy metal elements in the yellowfin tuna varied significantly with body size. Specifically, the levels of Fe, Se, and Cd in muscle increased with body size (P<0.05), while the levels of Zn and Cu decreased with body size, and the levels of As, Ba, and Cr did not vary significantly with body size (P>0.05). The levels of Fe, Se, Cu, and Cd in liver increased steadily with body size (P<0.05), the Cr level decreased with body size (P<0.05), and the contents of Zn, As and Ba in the tuna with all the body sizes had no significant changes (P>0.05). The levels of Cd, As, Cu, Fe, Se, and Zn were substantially higher in liver than in muscle in the groups of all the three body sizes (P<0.05). In terms of food safety, the concentration of each heavy metal element in muscle was lower than that in the National Food Safety Standards of China (GB 2762-2017). The single-factor contamination index of Cd and iAs suggested the yellowfin tuna from the South China sea have a slight risk of heavy metals to human health, and it is hence recommended that the daily intake of the yellowfin tuna caught in the South China Sea be less than 120.00 g for adults and 37.71 g for children.
2023, 14(1): 32-41.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.005
Abstract:
A whale fall occurs when great whales such as baleen whales (Balaenoptera) and sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus) die and their carcasses fall to the ocean floor. Compared with other organisms dropped from the euphotic zone to the sea floor, great-whale carcasses highlight with giant body sizes and high bone-lipid content which allow them to support a sequence of heterotrophic and chemosynthetic microbial assemblages in the energy-poor deepsea for decades. The succession of whale fall can be divided into mobile-scavenger, enrichment opportunist, sulphophilic and reef stages. Successional mechanisms of these stages are driven by facilitation, tolerance and inhibition, while species composition and community structure are affected mainly by water depth, temperature and geographical location. No whale-fall specialist has been found in the mobile-scavenger stage to date, but 129 species that are specialized to live on whale remains have been identified in the opportunistic and chemoautotrophic stages. Based on the population size and mortality of great whales around the world, the estimation of average distance among adjacent whale falls with the same successional stage is 5-16 km. These whale falls share the similar chemoautotrophic communities and species with those of vents and seeps, and thus are considered ecological and evolutionary stepping-stones in deep-sea floor. Unfortunately, the serious decline of great whales populations caused by commercial whaling have led to a 65%-90% reduction of whale falls in the world ocean, which may have reduced species diversity and caused species extinctions in deep-sea ecosystems. The detection of natural whale falls and experimentally implanted whale remains are considered to be the two main methods for whale falls research which requires the high-performance submersible and skilled deep diving operation ability. Finally, based on cetacean resources and the development of deep-sea exploration technology in China, we highlight future research interests of whale fall.
A whale fall occurs when great whales such as baleen whales (Balaenoptera) and sperm whale (Physeter macrocephalus) die and their carcasses fall to the ocean floor. Compared with other organisms dropped from the euphotic zone to the sea floor, great-whale carcasses highlight with giant body sizes and high bone-lipid content which allow them to support a sequence of heterotrophic and chemosynthetic microbial assemblages in the energy-poor deepsea for decades. The succession of whale fall can be divided into mobile-scavenger, enrichment opportunist, sulphophilic and reef stages. Successional mechanisms of these stages are driven by facilitation, tolerance and inhibition, while species composition and community structure are affected mainly by water depth, temperature and geographical location. No whale-fall specialist has been found in the mobile-scavenger stage to date, but 129 species that are specialized to live on whale remains have been identified in the opportunistic and chemoautotrophic stages. Based on the population size and mortality of great whales around the world, the estimation of average distance among adjacent whale falls with the same successional stage is 5-16 km. These whale falls share the similar chemoautotrophic communities and species with those of vents and seeps, and thus are considered ecological and evolutionary stepping-stones in deep-sea floor. Unfortunately, the serious decline of great whales populations caused by commercial whaling have led to a 65%-90% reduction of whale falls in the world ocean, which may have reduced species diversity and caused species extinctions in deep-sea ecosystems. The detection of natural whale falls and experimentally implanted whale remains are considered to be the two main methods for whale falls research which requires the high-performance submersible and skilled deep diving operation ability. Finally, based on cetacean resources and the development of deep-sea exploration technology in China, we highlight future research interests of whale fall.
2023, 14(1): 42-49.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.016
Abstract:
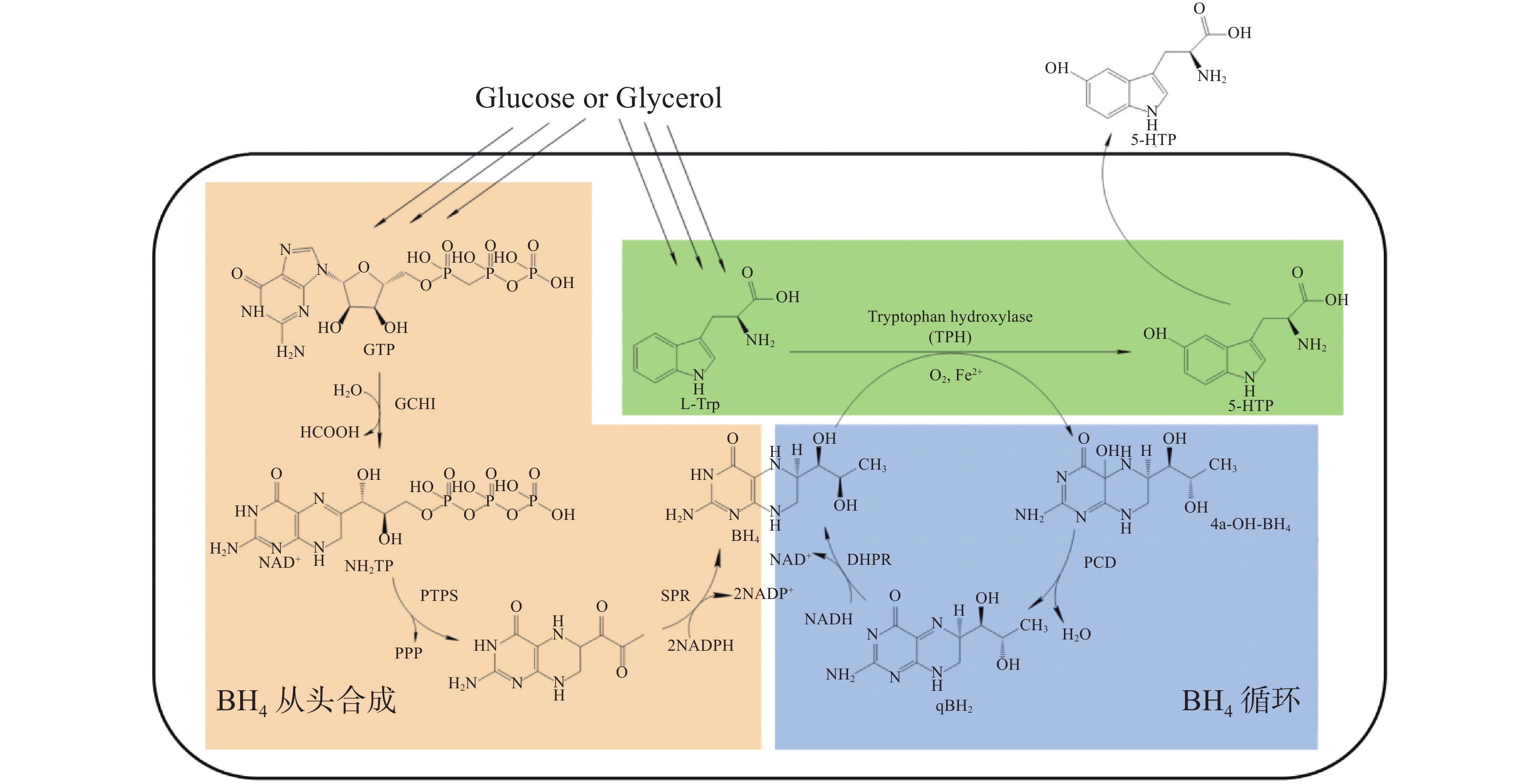
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) is an intermediate metabolite in the biosynthetic pathway of serotonin and melatonin, which can effectively treat a variety of diseases, such as depression, headache, obesity and insomnia. Traditional methods to produce 5-HTP are natural extraction or chemical synthesis. However, these methods do not meet the growing needs of market due to inefficiency and inability to mass production. With the development of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology, it is an inevitable trend to use microorganisms to synthesize 5-HTP. A comprehensive review is made of the advances in microbial synthesis of 5-HTP. Microbial synthesis of 5-HTP is achieved through directed evolution of hydroxylase, the construction of coenzyme factor biosynthesis and regeneration pathways, and further metabolic engineering efforts are made to balance metabolic flow in the host cell to increase the production of 5-HTP. This review might provide a technical support for industrial biosynthesis of 5-HTP which is of guiding significance for large-scale industrial production of 5-HTP.
5-Hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) is an intermediate metabolite in the biosynthetic pathway of serotonin and melatonin, which can effectively treat a variety of diseases, such as depression, headache, obesity and insomnia. Traditional methods to produce 5-HTP are natural extraction or chemical synthesis. However, these methods do not meet the growing needs of market due to inefficiency and inability to mass production. With the development of metabolic engineering and synthetic biology, it is an inevitable trend to use microorganisms to synthesize 5-HTP. A comprehensive review is made of the advances in microbial synthesis of 5-HTP. Microbial synthesis of 5-HTP is achieved through directed evolution of hydroxylase, the construction of coenzyme factor biosynthesis and regeneration pathways, and further metabolic engineering efforts are made to balance metabolic flow in the host cell to increase the production of 5-HTP. This review might provide a technical support for industrial biosynthesis of 5-HTP which is of guiding significance for large-scale industrial production of 5-HTP.
2023, 14(1): 50-59.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.006
Abstract:
In addition to gene overexpression and RNA interference, it is also an effective strategy to use gene editing technology to explore the function of insect genes. CRISPR/Cas9 technology is a third-generation gene editing tool that has developed rapidly in recent years. It is widely used in diverse areas of life science research due to its simple operation, low material cost, and high editing efficiency. A review was made of the application of CRISPR/Cas9 in the pigmentation, insecticide resistance, olfactory transduction, mating, and sex determination of Coleoptera, Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera, Hemiptera, Orthoptera, and Diptera insects, including gene knockout and gene knockin. And recent optimization strategies for the CRISPR/Cas9 system were summarized, based on which a prospect for application of the optimized CRISPR/Cas9 system in insect functional genomics study and agricultural pest management was made.
In addition to gene overexpression and RNA interference, it is also an effective strategy to use gene editing technology to explore the function of insect genes. CRISPR/Cas9 technology is a third-generation gene editing tool that has developed rapidly in recent years. It is widely used in diverse areas of life science research due to its simple operation, low material cost, and high editing efficiency. A review was made of the application of CRISPR/Cas9 in the pigmentation, insecticide resistance, olfactory transduction, mating, and sex determination of Coleoptera, Lepidoptera, Hymenoptera, Hemiptera, Orthoptera, and Diptera insects, including gene knockout and gene knockin. And recent optimization strategies for the CRISPR/Cas9 system were summarized, based on which a prospect for application of the optimized CRISPR/Cas9 system in insect functional genomics study and agricultural pest management was made.
2023, 14(1): 60-70.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.001
Abstract:
Angiostrongylus cantonensis is a zoonotic food-borne parasite, which has caused considerable public health problems in many countries in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Humans, as unsuitable hosts, are infected by ingesting food contaminated by infective larvae of A. cantonensis, which cause eosinophilic meningitis. Angiostrongyliasis caused by A. cantonensis is expanding, and its cases have occurred in areas previously thought to be free of A. cantonensis. The prevalence of angiostrongyliasis showed that it is relatively rare in China, but the latest epidemiological data in 2022 showed that the infection rate of the intermediate hosts is relatively high. A presumptive diagnosis is usually made based on mollusk consumption history, clinical features, and laboratory examination. A variety of serological detection methods of angiostrongyliasis have been developed, but the sensitivity and specificity of many diagnostic methods remain to be improved. Increasing awareness of angiostrongyliasis will contribute to rapid diagnosis and improved clinical outcomes. A review was made of the researches in parasite biology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, immune mechanism, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of A. cantonensis.
Angiostrongylus cantonensis is a zoonotic food-borne parasite, which has caused considerable public health problems in many countries in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. Humans, as unsuitable hosts, are infected by ingesting food contaminated by infective larvae of A. cantonensis, which cause eosinophilic meningitis. Angiostrongyliasis caused by A. cantonensis is expanding, and its cases have occurred in areas previously thought to be free of A. cantonensis. The prevalence of angiostrongyliasis showed that it is relatively rare in China, but the latest epidemiological data in 2022 showed that the infection rate of the intermediate hosts is relatively high. A presumptive diagnosis is usually made based on mollusk consumption history, clinical features, and laboratory examination. A variety of serological detection methods of angiostrongyliasis have been developed, but the sensitivity and specificity of many diagnostic methods remain to be improved. Increasing awareness of angiostrongyliasis will contribute to rapid diagnosis and improved clinical outcomes. A review was made of the researches in parasite biology, epidemiology, pathogenesis, immune mechanism, diagnosis, treatment and prevention of A. cantonensis.
2023, 14(1): 71-76.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.009
Abstract:
Nanfan (Propagation and breeding in winter in south China) is a special form of modern seed industry in China. Nanfan industry is a characteristic industry separated from seed industry in China. Nanfan breeding is one of the three emerging high-tech industries in Hainan Province. Nanfan industry is an inherent demand of local social and economic development, and will become a leading local industry or even a pillar industry, which can promote not only the sustainable development of the Nanfan industry but also the restructuring of the local agriculture. Models for leading industry selection were built based on the diamond theory, and an index system was established according to the influence factors of industrial structure evolution and the criteria of leading industry selection, and used to match the calculation models. Nanfan industry and other major agriculture-related industries in Hainan such as winter melons and vegetables, mango industry, rubber industry, etc. were assigned values for analysis to screen the indicators, and the weight of each indicator was calculated, based on which a competitiveness index for each industry was obtained. The results showed that Nanfan industry is far more competitive than other industries in the agriculture-related industries, and is taken as a future leading industry in Hainan, which is in line with the actual needs of Hainan.
Nanfan (Propagation and breeding in winter in south China) is a special form of modern seed industry in China. Nanfan industry is a characteristic industry separated from seed industry in China. Nanfan breeding is one of the three emerging high-tech industries in Hainan Province. Nanfan industry is an inherent demand of local social and economic development, and will become a leading local industry or even a pillar industry, which can promote not only the sustainable development of the Nanfan industry but also the restructuring of the local agriculture. Models for leading industry selection were built based on the diamond theory, and an index system was established according to the influence factors of industrial structure evolution and the criteria of leading industry selection, and used to match the calculation models. Nanfan industry and other major agriculture-related industries in Hainan such as winter melons and vegetables, mango industry, rubber industry, etc. were assigned values for analysis to screen the indicators, and the weight of each indicator was calculated, based on which a competitiveness index for each industry was obtained. The results showed that Nanfan industry is far more competitive than other industries in the agriculture-related industries, and is taken as a future leading industry in Hainan, which is in line with the actual needs of Hainan.
2023, 14(1): 77-81.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.010
Abstract:
In order to clarify the climate risk of two-line hybrid rice seed production in Hainan, climate risk zoning of two-line hybrid rice seed production in the key growth stages was conducted in Hainan based on the data of regional automatic meteorological observation stations with high resolution in order to provide a more scientific and reasonable reference for the promotion of two-line hybrid rice seed production in Hainan. The data of 144 regional meteorological stations in 8 cities and counties in the south of Hainan Island collected from 2006 to 2020 were used with data quality control to draw a climate risk zoning map of two-line hybrid rice seed production in the key growth stages in Hainan based on the climate risk level index of two-line hybrid rice seed production by using the spatial analysis method of geographic information system. The zoning showed that the low-risk areas of comprehensive climate for seed production of two-line hybrid rice were distributed in Changjiang, Dongfang, Ledong, Sanya, Baoting, Lingshui and Wanning when the critical sterility temperature was 22 ℃, in most areas of Dongfang, Ledong, Sanya, Baoting and Lingshui at 23 ℃, in Ledong, Sanya and most areas of Lingshui at 23.5 ℃, and in Ledong, Sanya and Lingshui coastal areas at 24 ℃. This climatic risk zoning method can provide an effective reference for the planting planning of two-line hybrid rice in Hainan, and the zoning results have important guiding significance in expansion of propagation and breeding in the south of China in winter.
In order to clarify the climate risk of two-line hybrid rice seed production in Hainan, climate risk zoning of two-line hybrid rice seed production in the key growth stages was conducted in Hainan based on the data of regional automatic meteorological observation stations with high resolution in order to provide a more scientific and reasonable reference for the promotion of two-line hybrid rice seed production in Hainan. The data of 144 regional meteorological stations in 8 cities and counties in the south of Hainan Island collected from 2006 to 2020 were used with data quality control to draw a climate risk zoning map of two-line hybrid rice seed production in the key growth stages in Hainan based on the climate risk level index of two-line hybrid rice seed production by using the spatial analysis method of geographic information system. The zoning showed that the low-risk areas of comprehensive climate for seed production of two-line hybrid rice were distributed in Changjiang, Dongfang, Ledong, Sanya, Baoting, Lingshui and Wanning when the critical sterility temperature was 22 ℃, in most areas of Dongfang, Ledong, Sanya, Baoting and Lingshui at 23 ℃, in Ledong, Sanya and most areas of Lingshui at 23.5 ℃, and in Ledong, Sanya and Lingshui coastal areas at 24 ℃. This climatic risk zoning method can provide an effective reference for the planting planning of two-line hybrid rice in Hainan, and the zoning results have important guiding significance in expansion of propagation and breeding in the south of China in winter.
2023, 14(1): 82-87.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.007
Abstract:
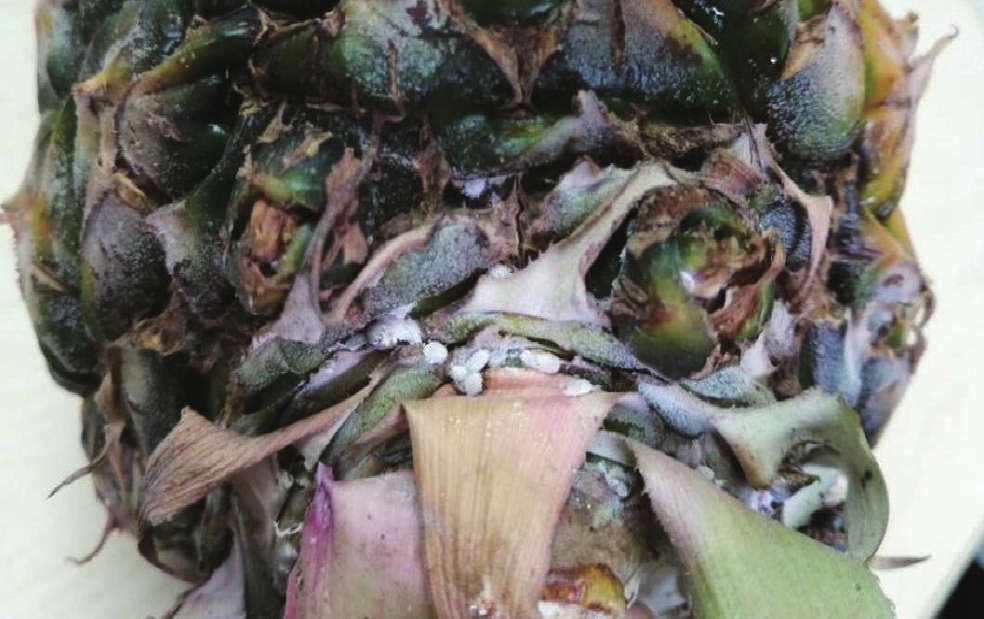
In order to clarify the species and infestation status of major mealybugs in Hainan, a field survey was made of mealybugs infesting various tropical fruits, cash crops, green plants and ornamental plants and flowers in various counties and cities of Hainan, and the genera and species of the mealybugs were identified. Ten genera and 21 species of major mealybugs under survey in Hainan were identified. Of the 21 mealybug species, 13 indigenous species, 8 invasive species and 2 new records were found in Hainan.
In order to clarify the species and infestation status of major mealybugs in Hainan, a field survey was made of mealybugs infesting various tropical fruits, cash crops, green plants and ornamental plants and flowers in various counties and cities of Hainan, and the genera and species of the mealybugs were identified. Ten genera and 21 species of major mealybugs under survey in Hainan were identified. Of the 21 mealybug species, 13 indigenous species, 8 invasive species and 2 new records were found in Hainan.
2023, 14(1): 88-104.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.008
Abstract:
Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) is a quarantine pest in the world, which has been widely spread in major tomato producing areas in the world and has become an important factor affecting the development of tomato industry. At present, this pest has spread to Xinjiang, Yunnan, Gansu and other regions in China, causing great losses to local tomato production, and posing a great threat to other tomato producing areas and related industries. Biological control methods based on natural enemy insects, entomopathogenic microorganism, botanical extracts, etc. have shown good effects in control of T. absoluta in the world and have good application prospects. A review was hence made of the research and application of biological control of T. absoluta to provide reference for efficient and sustainable control of this pest in China. The natural enemies of T. absoluta are rich in insect resources, among which the parasitic wasps of Trichogrammatidae, Eulophidae and Braconidae, and the predatory bugs of Miridae have a strong ability to control this pest. In recent years relevant studies have reported technologies for large-scale rearing and release of some natural enemies, which provide good conditions for their field application. For example, Trichogramma achaeae, Nesidiocoris tenuis, etc. have been widely used in the field control of T. absoluta in the world, and have achieved good results. In addition, entomopathogenic microorganism, such as Metarhizium anisopliae, Bacillus thuringiensis, etc., and plant extracts, such as Azadirachta indica and Jatropha curcus seed extracts, have strong insecticidal activity against this pest, and are safer than chemical pesticides in the world. Moreover, RNAi and other emerging biotechnologies also have been gradually carried out in the control of T. absoluta.
Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) is a quarantine pest in the world, which has been widely spread in major tomato producing areas in the world and has become an important factor affecting the development of tomato industry. At present, this pest has spread to Xinjiang, Yunnan, Gansu and other regions in China, causing great losses to local tomato production, and posing a great threat to other tomato producing areas and related industries. Biological control methods based on natural enemy insects, entomopathogenic microorganism, botanical extracts, etc. have shown good effects in control of T. absoluta in the world and have good application prospects. A review was hence made of the research and application of biological control of T. absoluta to provide reference for efficient and sustainable control of this pest in China. The natural enemies of T. absoluta are rich in insect resources, among which the parasitic wasps of Trichogrammatidae, Eulophidae and Braconidae, and the predatory bugs of Miridae have a strong ability to control this pest. In recent years relevant studies have reported technologies for large-scale rearing and release of some natural enemies, which provide good conditions for their field application. For example, Trichogramma achaeae, Nesidiocoris tenuis, etc. have been widely used in the field control of T. absoluta in the world, and have achieved good results. In addition, entomopathogenic microorganism, such as Metarhizium anisopliae, Bacillus thuringiensis, etc., and plant extracts, such as Azadirachta indica and Jatropha curcus seed extracts, have strong insecticidal activity against this pest, and are safer than chemical pesticides in the world. Moreover, RNAi and other emerging biotechnologies also have been gradually carried out in the control of T. absoluta.
2023, 14(1): 105-110.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.014
Abstract:
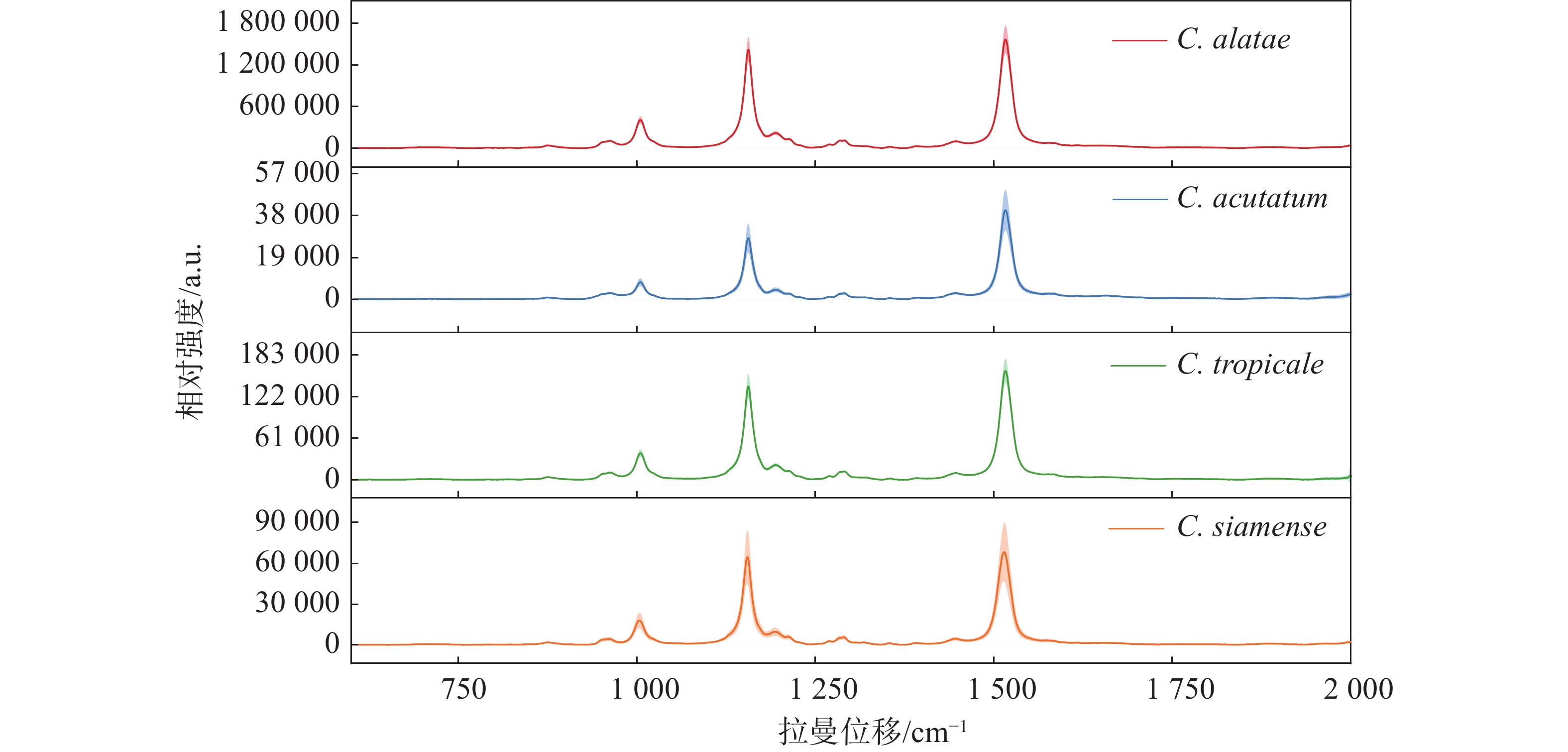
In order to solve the shortcomings of traditional identification of Colletotrichum spp. by morphology and molecular biology, a clustering method based on confocal Raman microscopy was proposed for identification of spores of three Colletotrichum species causing anthracnose of rubber trees. Raman spectra of the spores were scanned to show their spectral trends and peak characteristics, and three main Raman peaks at 1005 cm−1, 1155 cm−1, and 1515 cm−1 in common and other secondary peaks were found to preliminary confirm the contributing source of the peaks. Then, combined with Raman spectroscopy and principal component (PCA) analysis, the spores of three Colletotrichum species were quickly and efficiently distinguished by the three key Raman peaks and other secondary peaks in the 3D score plot of PC1, PC2, and PC3 components. This method provides a new way for discrimination and identification of Colletotrichum spores of the anthracnose of rubber trees, and satisfies the sensitivity and trace requirements without pre-enrichment and pre-treatment of the samples.
In order to solve the shortcomings of traditional identification of Colletotrichum spp. by morphology and molecular biology, a clustering method based on confocal Raman microscopy was proposed for identification of spores of three Colletotrichum species causing anthracnose of rubber trees. Raman spectra of the spores were scanned to show their spectral trends and peak characteristics, and three main Raman peaks at 1005 cm−1, 1155 cm−1, and 1515 cm−1 in common and other secondary peaks were found to preliminary confirm the contributing source of the peaks. Then, combined with Raman spectroscopy and principal component (PCA) analysis, the spores of three Colletotrichum species were quickly and efficiently distinguished by the three key Raman peaks and other secondary peaks in the 3D score plot of PC1, PC2, and PC3 components. This method provides a new way for discrimination and identification of Colletotrichum spores of the anthracnose of rubber trees, and satisfies the sensitivity and trace requirements without pre-enrichment and pre-treatment of the samples.
2023, 14(1): 111-119.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.013
Abstract:
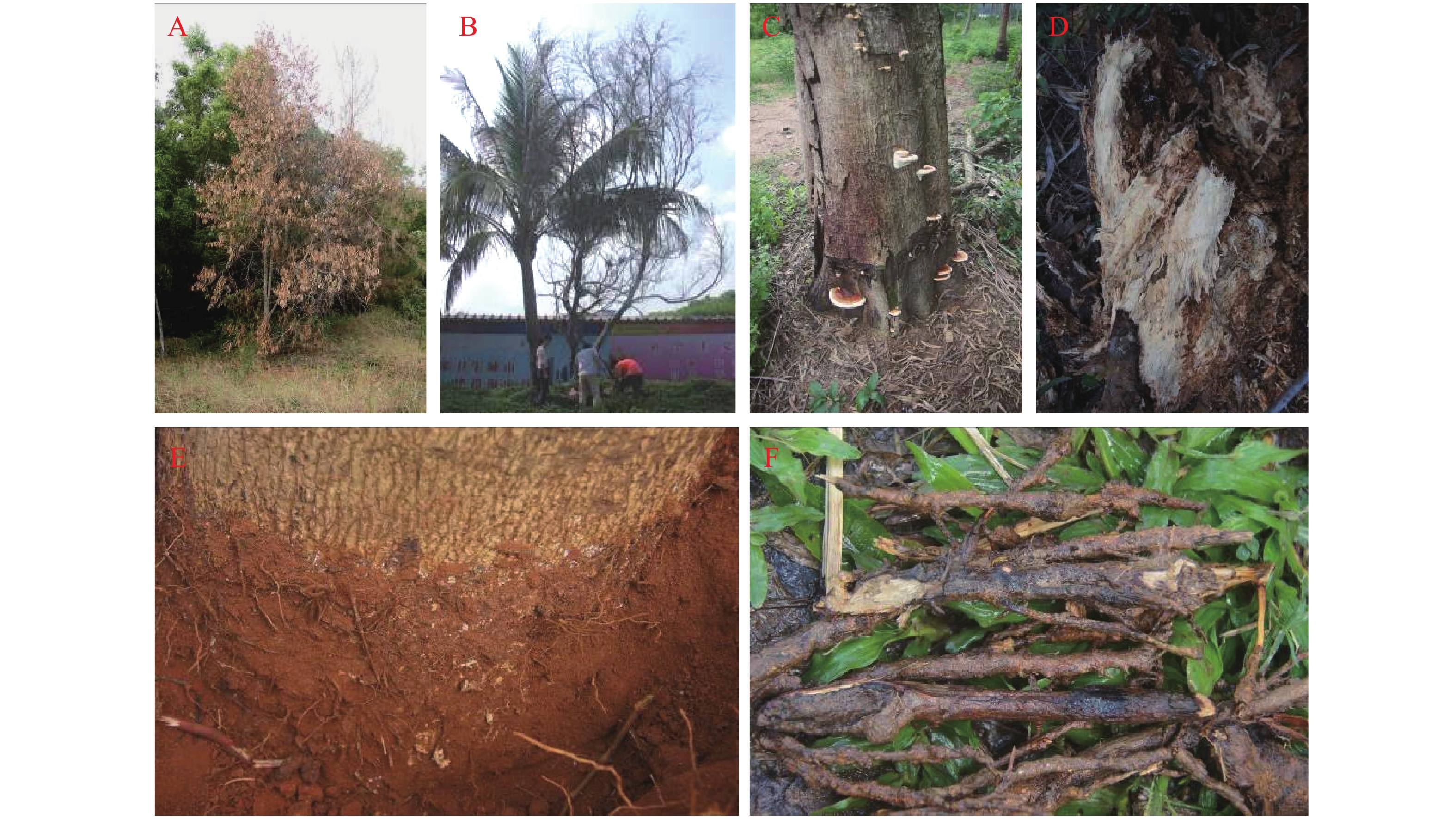
An attempt was made to identify the pathogenic Ganoderma causing red root rot on Acacia confusa, A. mangium and A. auriculiformis in several areas in Hainan in terms of morphology and molecular biology in order to provide a reference for the control of red root rot on Acacia spp. The basidiocarps of three pathogens causing red root rot of Acacia spp. were collected from Haikou, Danzhou, Changjiang and other cities or counties in Hainan, and their morphological characteristics were observed. The strains were isolated from the three pathogens by tissue isolation method, and their pathogenicity was determined. A polygenic phylogenetic tree was constructed based on genes ITS, SSU and LSU of the strains. The results from the morphological observation and molecular biological identification showed the pathogens causing red root rot on three Acacia species were all identified as Ganoderma tropicum.
An attempt was made to identify the pathogenic Ganoderma causing red root rot on Acacia confusa, A. mangium and A. auriculiformis in several areas in Hainan in terms of morphology and molecular biology in order to provide a reference for the control of red root rot on Acacia spp. The basidiocarps of three pathogens causing red root rot of Acacia spp. were collected from Haikou, Danzhou, Changjiang and other cities or counties in Hainan, and their morphological characteristics were observed. The strains were isolated from the three pathogens by tissue isolation method, and their pathogenicity was determined. A polygenic phylogenetic tree was constructed based on genes ITS, SSU and LSU of the strains. The results from the morphological observation and molecular biological identification showed the pathogens causing red root rot on three Acacia species were all identified as Ganoderma tropicum.
2023, 14(1): 120-128.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.011
Abstract:
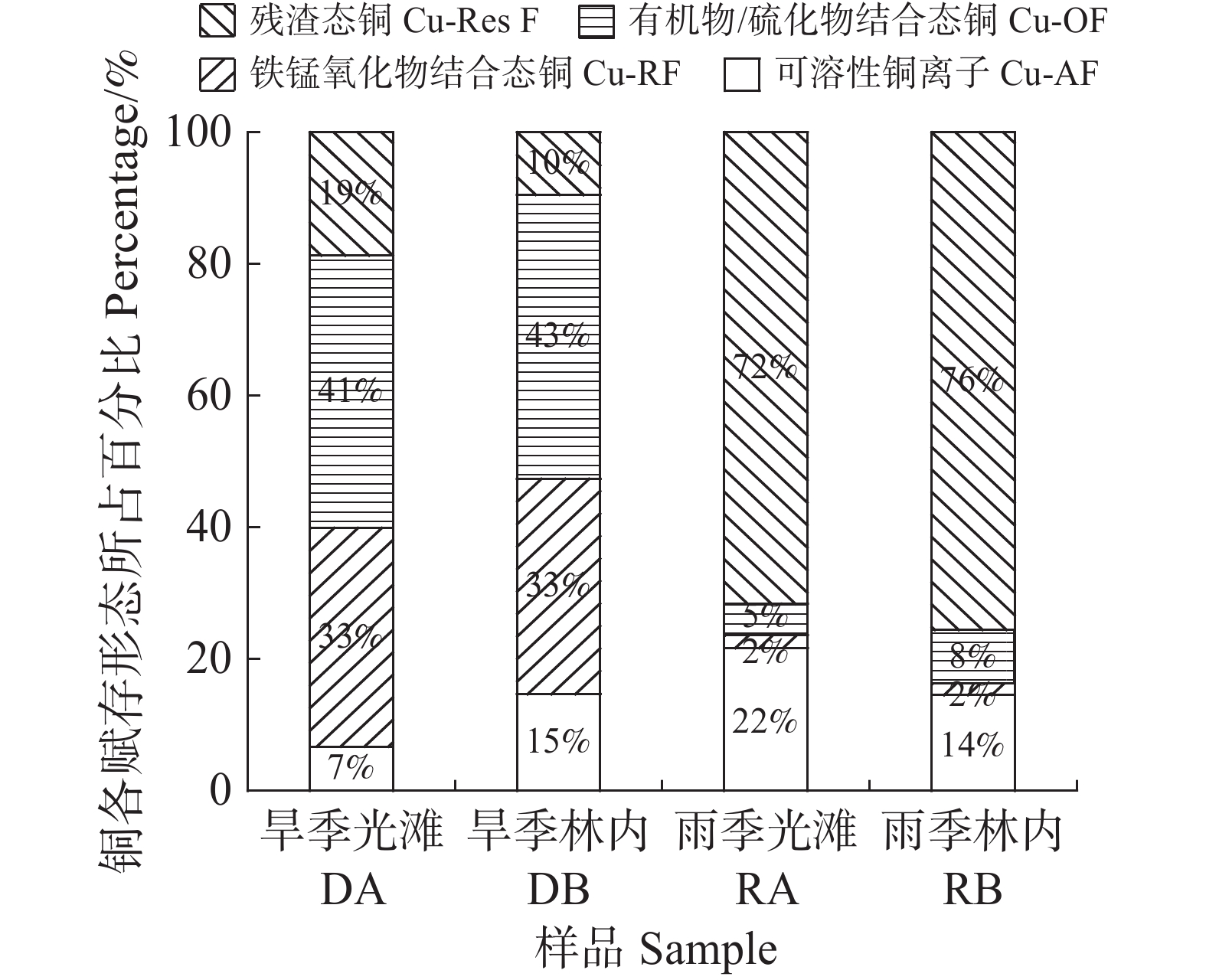
Sediments in the mangrove stands and the adjacent low-tide mudflat in the northern Hainan Island were collected, and the physio-chemical properties were determined. The seasonal variation characteristics of the community structures of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) of the in-situ sediments were analyzed by using high-throughput sequencing. The speciation of heavy metal copper and zinc in the sediments were examined and the effects of relevant eco-environmental factors on the SRB communities were analyzed. The results showed that the diversity of SRB in the mangrove sediments was significantly higher in dry season than in rainy season, and the highest in the low-tide adjacent mudflat sediments in dry season. In the family level the SRB community structure in the mangrove sediments was significantly different between dry and rainy seasons, though the relative abundance of Solibacteraceae was consistently the greatest family in both dry and rainy seasons. In the low-tide adjacent mudflat sediments Solibacteraceae was the highest in relative abundance in dry season, while Desulfobulbaceae the highest in rainy season. Correlation analysis showed that the seasonal changes of SRB community structure were significantly correlated with the total nitrogen, total phosphorus, pH and the speciation of copper and zinc in the sediments. The results preliminarily illustrated the seasonal variation of SRB community structure and the related eco-environmental factors in mangrove sediments, and might provide theoretical reference for the ecological restoration of heavy metals by mangroves.
Sediments in the mangrove stands and the adjacent low-tide mudflat in the northern Hainan Island were collected, and the physio-chemical properties were determined. The seasonal variation characteristics of the community structures of sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) of the in-situ sediments were analyzed by using high-throughput sequencing. The speciation of heavy metal copper and zinc in the sediments were examined and the effects of relevant eco-environmental factors on the SRB communities were analyzed. The results showed that the diversity of SRB in the mangrove sediments was significantly higher in dry season than in rainy season, and the highest in the low-tide adjacent mudflat sediments in dry season. In the family level the SRB community structure in the mangrove sediments was significantly different between dry and rainy seasons, though the relative abundance of Solibacteraceae was consistently the greatest family in both dry and rainy seasons. In the low-tide adjacent mudflat sediments Solibacteraceae was the highest in relative abundance in dry season, while Desulfobulbaceae the highest in rainy season. Correlation analysis showed that the seasonal changes of SRB community structure were significantly correlated with the total nitrogen, total phosphorus, pH and the speciation of copper and zinc in the sediments. The results preliminarily illustrated the seasonal variation of SRB community structure and the related eco-environmental factors in mangrove sediments, and might provide theoretical reference for the ecological restoration of heavy metals by mangroves.
2023, 14(1): 129-135.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.01.012
Abstract:
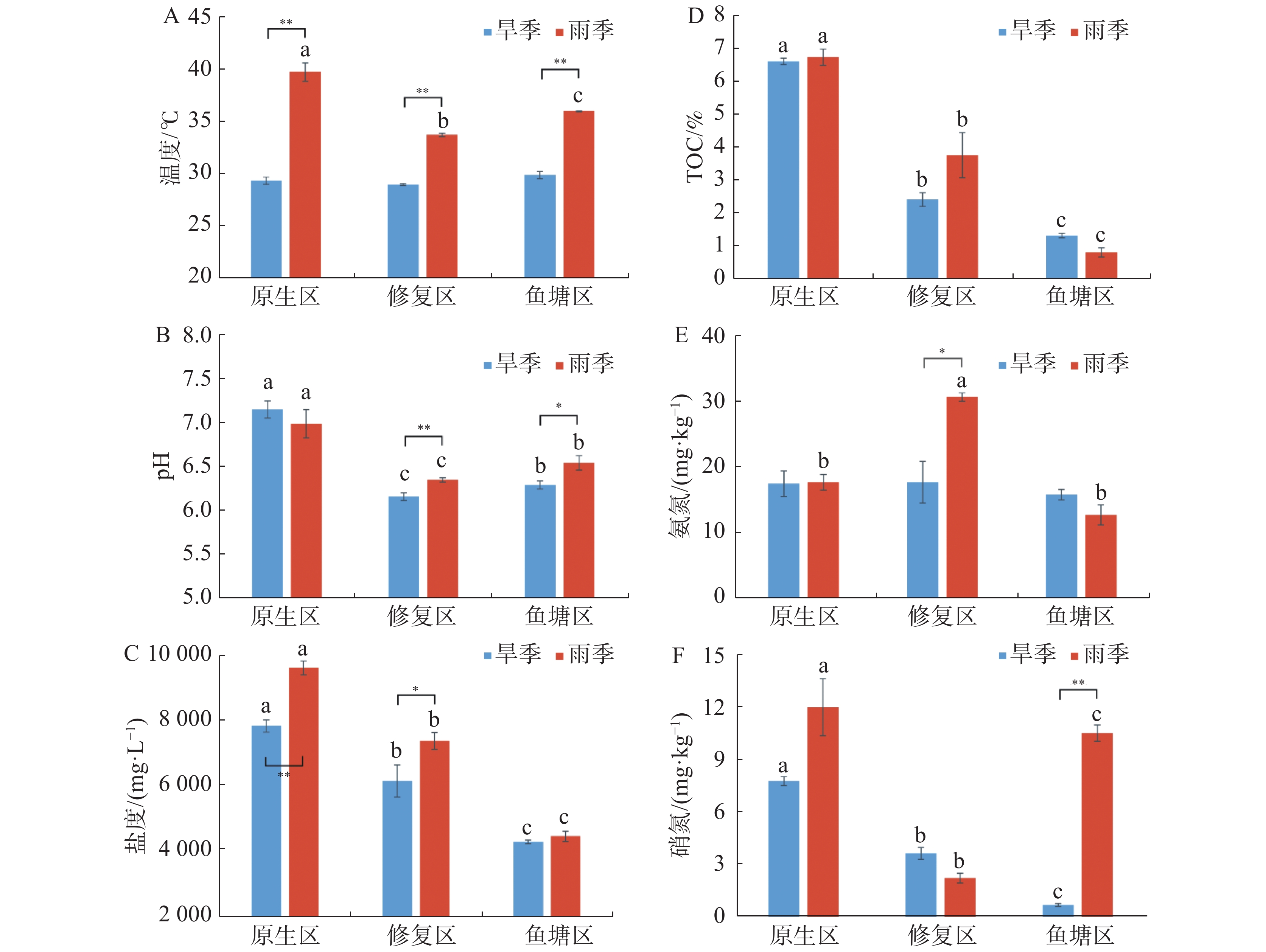
The temporal and spatial distribution of denitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) rates in mangrove sediments in different mangrove habitats (native mangrove area, restored mangrove area, and abandoned fish pond area) was analyzed by using isotope tracer technique (15N) to determine environmental factors affecting denitrification and anammox rates of the mangrove sediments. The results indicated that there were seasonal differences in physical and chemical factors of the mangrove sediments in different habitats, and that the denitrification rates of the mangrove sediments had spatial variation. The denitrification rate of the mangrove sediment was significantly higher in the restored mangrove area (14.39 nmol·g−1·h−1) than in the native mangrove area (8.08 nmol·g−1·h−1) in dry season (P < 0.05), but not significantly different from that in the abandoned fish pond area (11.48 nmol·g−1·h−1). There was no significant difference in denitrification rate among the habitats in rainy season since the denitrification rate of the mangrove sediment was 11.67 nmol·g−1·h−1 in the restored mangrove area, 11.29 nmol·g−1·h−1 in the native mangrove area and 9.62 nmol·g−1·h−1 in the abandoned fish pond area. There was no significant seasonal variation in denitrification rate among the habitats. The anammox rates of the mangrove sediments showed a temporal and spatial variation in the habitats. The anammox rates in dry season tended to showed a similar change to the denitrification rates in the sediments of different habitats in dry season, and the anammox rate in the restored mangrove area was the highest in dry season (0.52 nmol·g−1·h−1), which was significantly higher than that in the native mangrove area (0.10 nmol·g−1·h−1) (P < 0.05). No significant difference was observed in the anammox rate in all the habitats in rainy season. The anammox rate of the mangrove sediment in the native mangrove area had obvious seasonal variation, and it is higher in rainy season than in dry season (P < 0.01). Correlation analysis of various environmental factors with the denitrification rate and the anammox rate in the mangrove sediments showed difference in the correlations of sediment temperature, salinity, ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen with denitrification and anammox rates in different seasons. The sediment temperature, ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen in different habitats were significantly correlated with denitrification rate and anammox rate. Obvious synergy between denitrification rate and anammox rate was found in the mangrove areas.
The temporal and spatial distribution of denitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) rates in mangrove sediments in different mangrove habitats (native mangrove area, restored mangrove area, and abandoned fish pond area) was analyzed by using isotope tracer technique (15N) to determine environmental factors affecting denitrification and anammox rates of the mangrove sediments. The results indicated that there were seasonal differences in physical and chemical factors of the mangrove sediments in different habitats, and that the denitrification rates of the mangrove sediments had spatial variation. The denitrification rate of the mangrove sediment was significantly higher in the restored mangrove area (14.39 nmol·g−1·h−1) than in the native mangrove area (8.08 nmol·g−1·h−1) in dry season (P < 0.05), but not significantly different from that in the abandoned fish pond area (11.48 nmol·g−1·h−1). There was no significant difference in denitrification rate among the habitats in rainy season since the denitrification rate of the mangrove sediment was 11.67 nmol·g−1·h−1 in the restored mangrove area, 11.29 nmol·g−1·h−1 in the native mangrove area and 9.62 nmol·g−1·h−1 in the abandoned fish pond area. There was no significant seasonal variation in denitrification rate among the habitats. The anammox rates of the mangrove sediments showed a temporal and spatial variation in the habitats. The anammox rates in dry season tended to showed a similar change to the denitrification rates in the sediments of different habitats in dry season, and the anammox rate in the restored mangrove area was the highest in dry season (0.52 nmol·g−1·h−1), which was significantly higher than that in the native mangrove area (0.10 nmol·g−1·h−1) (P < 0.05). No significant difference was observed in the anammox rate in all the habitats in rainy season. The anammox rate of the mangrove sediment in the native mangrove area had obvious seasonal variation, and it is higher in rainy season than in dry season (P < 0.01). Correlation analysis of various environmental factors with the denitrification rate and the anammox rate in the mangrove sediments showed difference in the correlations of sediment temperature, salinity, ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen with denitrification and anammox rates in different seasons. The sediment temperature, ammonia nitrogen and nitrate nitrogen in different habitats were significantly correlated with denitrification rate and anammox rate. Obvious synergy between denitrification rate and anammox rate was found in the mangrove areas.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 801KB
PDF 801KB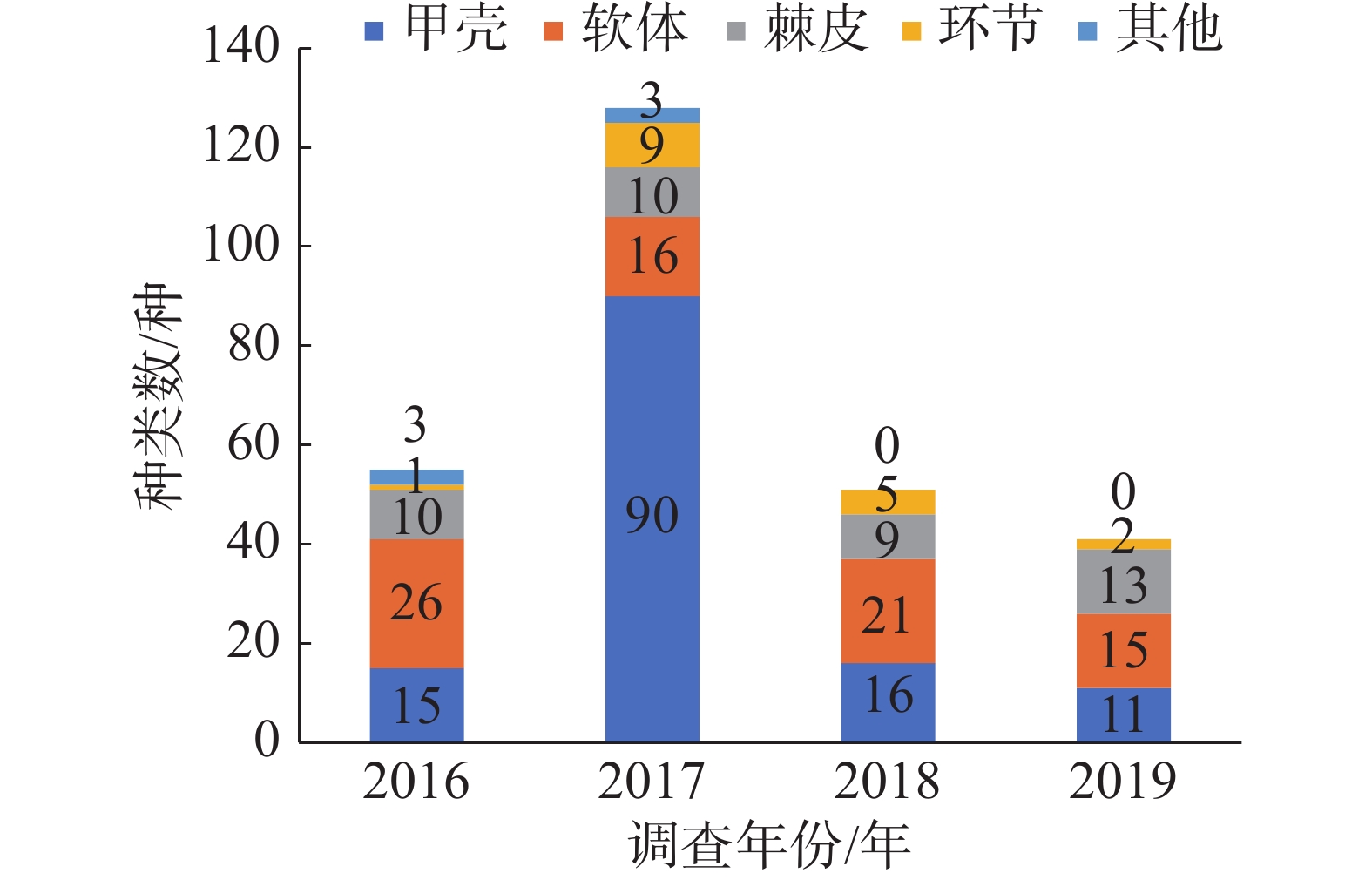









 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS