2023 Vol. 14, No. 2
2023, 14(2): 138-144.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.001
Abstract:
To reveal the pathogenesis of Enterococcus faecalis and provide scientific basis for clinical treatment, several strains of E. faecalis were isolated from female vagina and their virulence genes, resistance genes, and drug resistance were detected by using PCR and Kirby Bauer (K-B) disk diffusion. The results showed that 22 strains of E. faecalis were isolated from 157 samples. Of the 22 strains isolated, efaA was the most commonly found virulence gene (100%), followed by asa1 (90.9%), cylA (90.9%), fsr (90.9%), cpd (90.9%), acm (86.4%), gelE (81.8%), esp (68.2%), ace (54.5%), and hyl (0), and the drug resistance genes detected were vanA (0), vanB (0), vanC (18.2%), aac(6')/aph(2') (40.9%), ant(6)-1 (59.1% ), ermB (68.2%), mefA (54.5%), tetM (72.2%), and tem (81.8%). Antibiotic susceptibility testing by the K-B disk diffusion method showed that the isolates were sensitive to vancomycin, nitrofurantoin, linezolid and koalaranin, but resistant to other antibiotics in different degrees. To sum up, vaginas are susceptible to E. faecalis infection, and experiment in vitro indicated that glycopeptide antibiotics were promising in the clinical treatment choice for E. faecalis infection.
To reveal the pathogenesis of Enterococcus faecalis and provide scientific basis for clinical treatment, several strains of E. faecalis were isolated from female vagina and their virulence genes, resistance genes, and drug resistance were detected by using PCR and Kirby Bauer (K-B) disk diffusion. The results showed that 22 strains of E. faecalis were isolated from 157 samples. Of the 22 strains isolated, efaA was the most commonly found virulence gene (100%), followed by asa1 (90.9%), cylA (90.9%), fsr (90.9%), cpd (90.9%), acm (86.4%), gelE (81.8%), esp (68.2%), ace (54.5%), and hyl (0), and the drug resistance genes detected were vanA (0), vanB (0), vanC (18.2%), aac(6')/aph(2') (40.9%), ant(6)-1 (59.1% ), ermB (68.2%), mefA (54.5%), tetM (72.2%), and tem (81.8%). Antibiotic susceptibility testing by the K-B disk diffusion method showed that the isolates were sensitive to vancomycin, nitrofurantoin, linezolid and koalaranin, but resistant to other antibiotics in different degrees. To sum up, vaginas are susceptible to E. faecalis infection, and experiment in vitro indicated that glycopeptide antibiotics were promising in the clinical treatment choice for E. faecalis infection.
2023, 14(2): 145-152.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.002
Abstract:
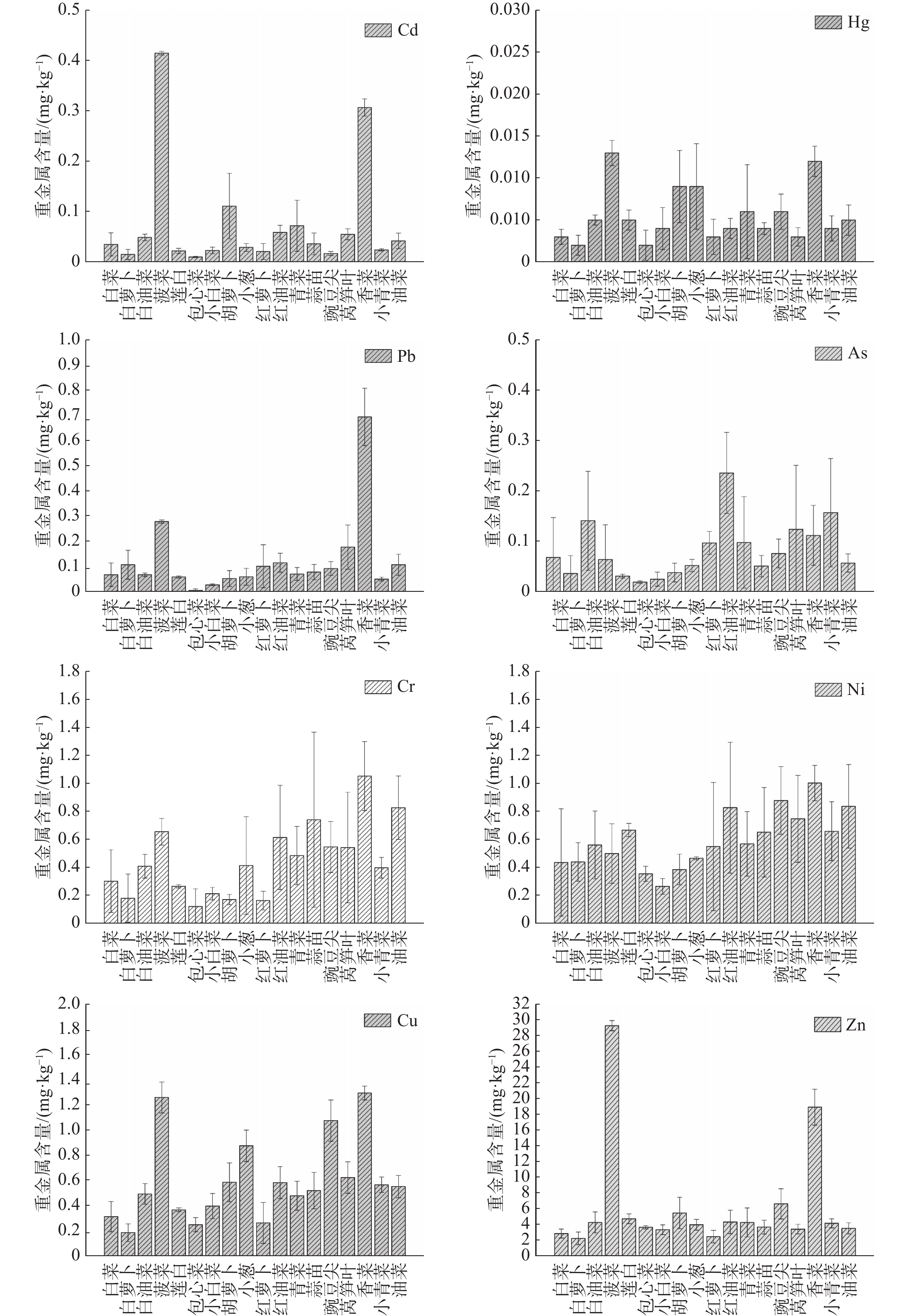
In order to reduce the risk of heavy metal pollution and ensure the safety of vegetable production, the heavy metal contents in the soil and the edible parts of 18 varieties under 5 types of vegetables were determined, and the status of heavy metal pollution in the vegetables were evaluated. Meanwhile an enrichment coefficient was used to analyze and compare the capacity of the vegetables to accumulate the heavy metals Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, Hg and As. The results showed that the soil Cd content in the area under experiment was 31.91%, which was the main pollutant, while the contents of other heavy metals fell within the national standards. The edible parts of all vegetables were mainly contaminated, and garlic and rape, spinach and coriander were slightly contaminated by heavy metals Cr, Hg, and Cd. The enrichment coefficients of the 8 heavy metals in the vegetables showed that the average enrichment coefficient of the heavy metals in 18 varieties of vegetables was in the descending order of Cd > Zn > Hg > Cu > Ni > As > Cr > Pb. The average enrichment coefficient of Cd was 0.201 1 and Pb was 0.003 1, a difference of 64.66 times between Cd and PB. The enrichment coefficient of the same element in different vegetables showed significant difference which was up to 120 folds. Generally, leaf vegetables such as coriander had a relatively higher enrichment capacity for Cd, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu, and spinach for As and Pb, which indicates that coriander and spinach in the experimental area should not be cultivated on the soil contaminated with Cd, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Zn and Cu. Red rape should not be cultivated on the As and Pb contaminated soil, However, cabbage and root vegetables, such as cabbage, white radish and carrot, had a weak capacity to accumulate Cd, Hg, Cr, Pb, As, Ni and Cu; Cd, Cr, C n, Cu, Ni and Hg; and Zn, Cr, and Cu, respectively, and can hence be used as the priority varieties of vegetables cultivated in the soils contaminated with Cd, Hg, Cr, Pb, As, Ni, Cu, and Zn in the experimental area.
In order to reduce the risk of heavy metal pollution and ensure the safety of vegetable production, the heavy metal contents in the soil and the edible parts of 18 varieties under 5 types of vegetables were determined, and the status of heavy metal pollution in the vegetables were evaluated. Meanwhile an enrichment coefficient was used to analyze and compare the capacity of the vegetables to accumulate the heavy metals Cd, Cr, Pb, Zn, Cu, Ni, Hg and As. The results showed that the soil Cd content in the area under experiment was 31.91%, which was the main pollutant, while the contents of other heavy metals fell within the national standards. The edible parts of all vegetables were mainly contaminated, and garlic and rape, spinach and coriander were slightly contaminated by heavy metals Cr, Hg, and Cd. The enrichment coefficients of the 8 heavy metals in the vegetables showed that the average enrichment coefficient of the heavy metals in 18 varieties of vegetables was in the descending order of Cd > Zn > Hg > Cu > Ni > As > Cr > Pb. The average enrichment coefficient of Cd was 0.201 1 and Pb was 0.003 1, a difference of 64.66 times between Cd and PB. The enrichment coefficient of the same element in different vegetables showed significant difference which was up to 120 folds. Generally, leaf vegetables such as coriander had a relatively higher enrichment capacity for Cd, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Zn, Cu, and spinach for As and Pb, which indicates that coriander and spinach in the experimental area should not be cultivated on the soil contaminated with Cd, Hg, Pb, Cr, Ni, Zn and Cu. Red rape should not be cultivated on the As and Pb contaminated soil, However, cabbage and root vegetables, such as cabbage, white radish and carrot, had a weak capacity to accumulate Cd, Hg, Cr, Pb, As, Ni and Cu; Cd, Cr, C n, Cu, Ni and Hg; and Zn, Cr, and Cu, respectively, and can hence be used as the priority varieties of vegetables cultivated in the soils contaminated with Cd, Hg, Cr, Pb, As, Ni, Cu, and Zn in the experimental area.
2023, 14(2): 153-158.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.003
Abstract:
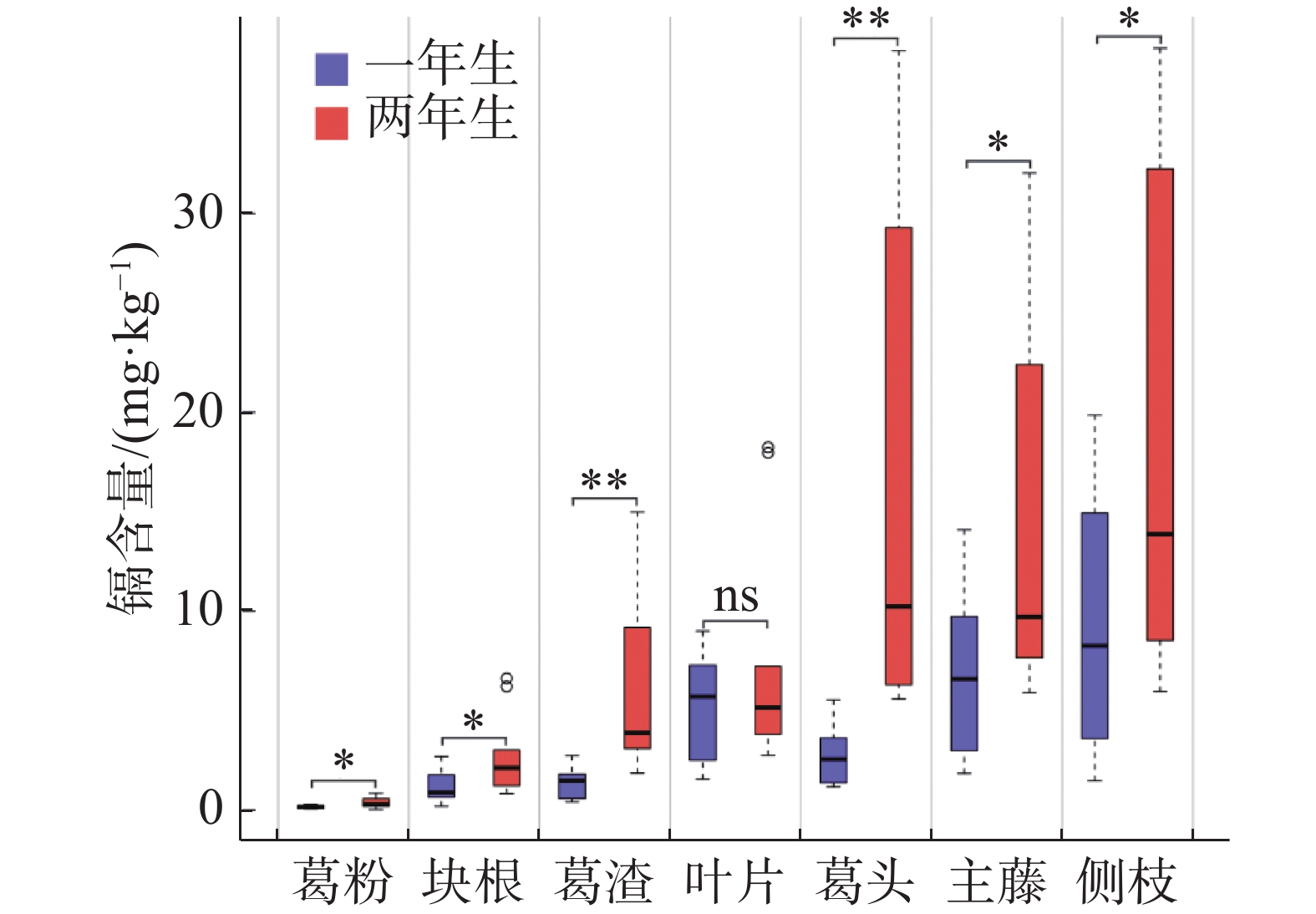
An attempt was made to reveal the cadmium enrichment characteristics of Pueraria thomsonii planted for different years. The plants of P. thomsonii grown for one year and two years on moderately cadmium-contaminated farmland in Xinyu, Jiangxi province were collected to determine the content and enrichment of the heavy metal cadmium in the tuber (meal and residues), basal stem, main stem, lateral branches, and leaves. Except for the leaves, the cadmium content was significantly higher in each part of the two years old plants than in the one year old plants. The contents of cadmium in different plant parts were in the order of lateral branch > main stem > basal stem > leaves > residues > tuber > meal. P. thomsonii has a high capacity to absorb cadmium from soil, as evidenced by the enrichment coefficient of cadmium from soil to P. thomsonii being larger than 1. Except for the meal of the tuber from the one year old plants of P. thomsonii, the cadmium contents in the tuber of 1-years old plants, and the tuber and meal of 2-years old plants were all higher than the limit of the standard. Correlation analysis showed that the content of cadmium in each part of P. thomsonii had a significantly positive correlation with the total and available cadmium in the soil and had an accumulative effect on the age of the plants. Therefore, in a moderately cadmium-contaminated farmland it is recommended to plant P. thomsonii for one year and use its tuber to produce meal as food to attain both ecological and economic benefits.
An attempt was made to reveal the cadmium enrichment characteristics of Pueraria thomsonii planted for different years. The plants of P. thomsonii grown for one year and two years on moderately cadmium-contaminated farmland in Xinyu, Jiangxi province were collected to determine the content and enrichment of the heavy metal cadmium in the tuber (meal and residues), basal stem, main stem, lateral branches, and leaves. Except for the leaves, the cadmium content was significantly higher in each part of the two years old plants than in the one year old plants. The contents of cadmium in different plant parts were in the order of lateral branch > main stem > basal stem > leaves > residues > tuber > meal. P. thomsonii has a high capacity to absorb cadmium from soil, as evidenced by the enrichment coefficient of cadmium from soil to P. thomsonii being larger than 1. Except for the meal of the tuber from the one year old plants of P. thomsonii, the cadmium contents in the tuber of 1-years old plants, and the tuber and meal of 2-years old plants were all higher than the limit of the standard. Correlation analysis showed that the content of cadmium in each part of P. thomsonii had a significantly positive correlation with the total and available cadmium in the soil and had an accumulative effect on the age of the plants. Therefore, in a moderately cadmium-contaminated farmland it is recommended to plant P. thomsonii for one year and use its tuber to produce meal as food to attain both ecological and economic benefits.
2023, 14(2): 159-165.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.004
Abstract:
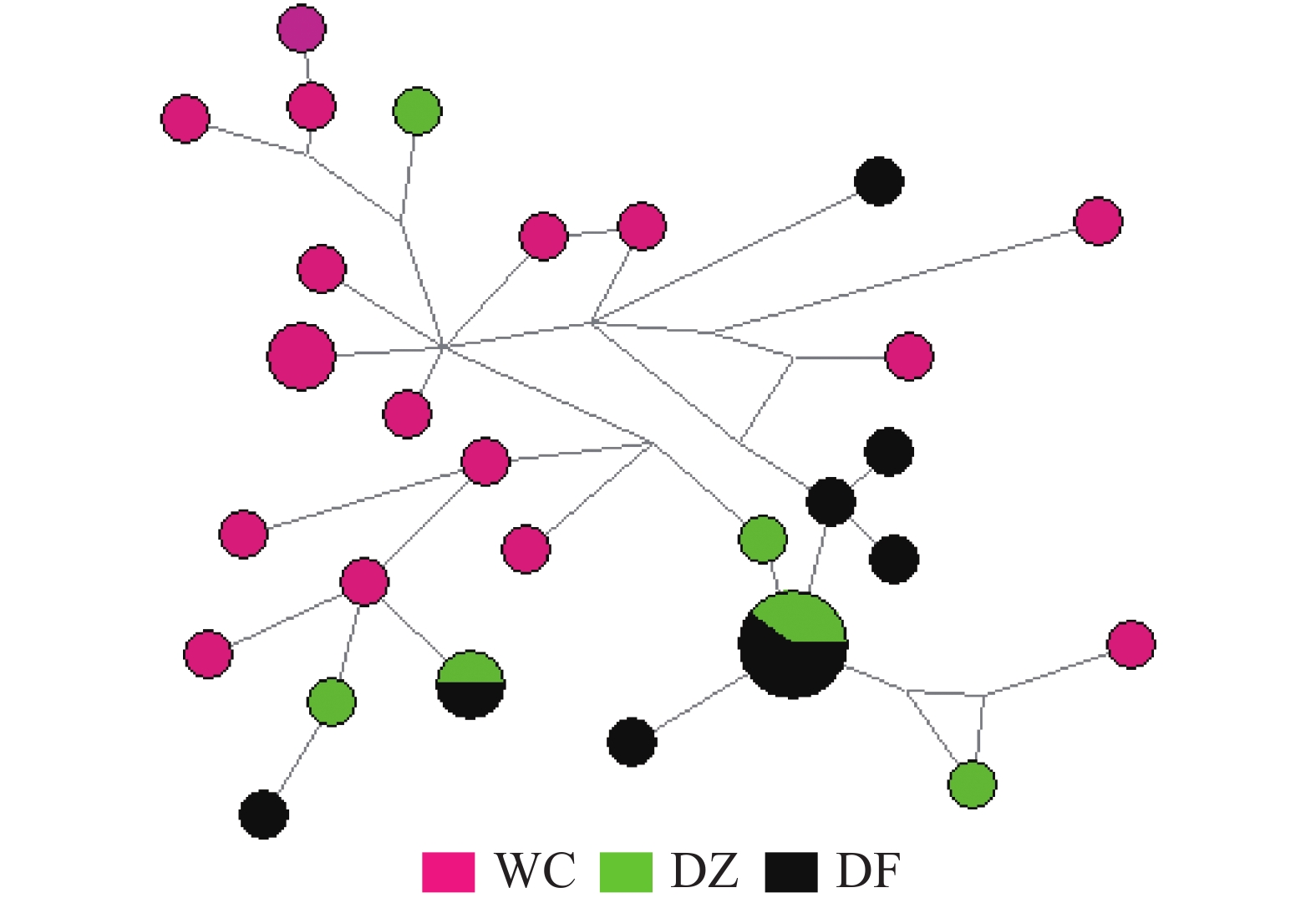
Ticks are arthropods that transmit more types of pathogens globally than any other vector, and they can transmit a variety of diseases by sucking blood from mammals, birds and reptiles, including humans. Anaplasma spp are an important tick-borne pathogens, which have a significant impact on human and animal health and the development of animal husbandry. In order to investigate the species of ticks on canine body surface and the situation of ticks carrying Anaplasma spp. in some areas of Hainan province, morphological observation, molecular biological identification and evolutionary analysis were performed on canine ticks from four regions of Hainan province, and 16S rRNA and gltA genes were used to detect Anaplasma spp in canine ticks. Morphological observation and molecular biological identification showed that all the ticks were Rhipicephalus sanguineus. The phylogenetic tree established based on tick mitochondrial 16S rDNA gene indicated that the HN-01 and HN-02 gene sequences obtained were in different genetic evolutionary clade, and that HN-01 was in the same clade as the known tick from the United States (MH018842). HN-02 was in the same branch as R. sanguineus from Thailand (KC170744), and was far related to R. sanguineus from Gansu Province (JF979377) and Beijing (KC203362). PCR results based on the gltA gene showed that A. platys was carried by canine ticks with a positive rate of 1.1% (6/546). PCR detection based on 16S rRNA gene indicated that the canine body surface ticks obtained did not carry Anaplasma pagocytophilum and Anaplasma bovis.
Ticks are arthropods that transmit more types of pathogens globally than any other vector, and they can transmit a variety of diseases by sucking blood from mammals, birds and reptiles, including humans. Anaplasma spp are an important tick-borne pathogens, which have a significant impact on human and animal health and the development of animal husbandry. In order to investigate the species of ticks on canine body surface and the situation of ticks carrying Anaplasma spp. in some areas of Hainan province, morphological observation, molecular biological identification and evolutionary analysis were performed on canine ticks from four regions of Hainan province, and 16S rRNA and gltA genes were used to detect Anaplasma spp in canine ticks. Morphological observation and molecular biological identification showed that all the ticks were Rhipicephalus sanguineus. The phylogenetic tree established based on tick mitochondrial 16S rDNA gene indicated that the HN-01 and HN-02 gene sequences obtained were in different genetic evolutionary clade, and that HN-01 was in the same clade as the known tick from the United States (MH018842). HN-02 was in the same branch as R. sanguineus from Thailand (KC170744), and was far related to R. sanguineus from Gansu Province (JF979377) and Beijing (KC203362). PCR results based on the gltA gene showed that A. platys was carried by canine ticks with a positive rate of 1.1% (6/546). PCR detection based on 16S rRNA gene indicated that the canine body surface ticks obtained did not carry Anaplasma pagocytophilum and Anaplasma bovis.
2023, 14(2): 167-172.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.005
Abstract:
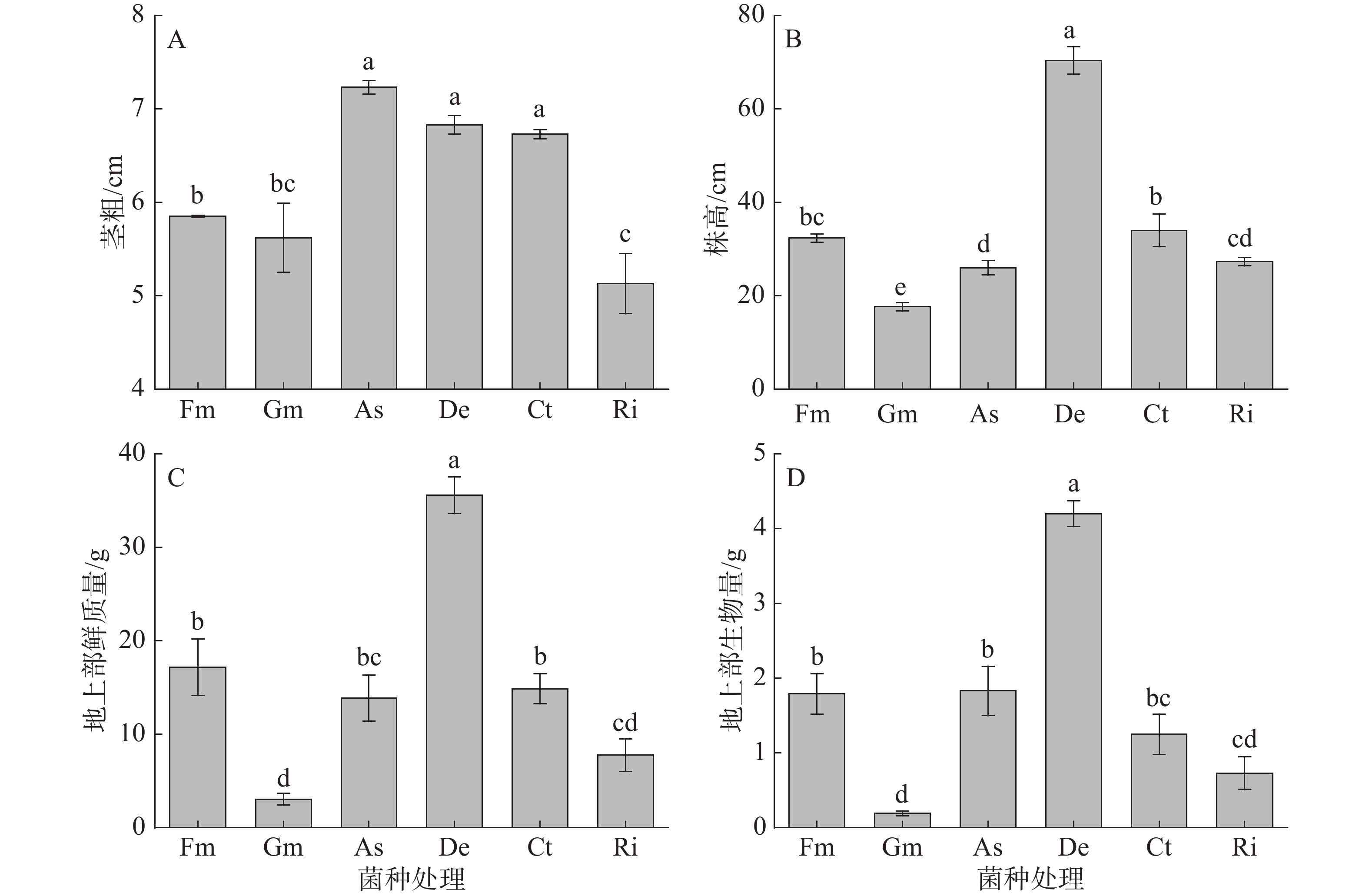
A microcosm experiment was conducted to study the effects of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on the growth and the nitrogen and phosphorus absorption of sweet corn seedlings to provide reference for the development of AMF. Sweet corn seedlings (Zea mays var. rugose Bonaf) were inoculated with 6 AMF species, Funneliformis mosseae (Fm), Gigaspora margarita (Gm), Acaulospora scrobiculata (As), Corymbiglomus tortuosum (Ct), Diversispora epigaea (De) and Rhizophagus intraradices (Ri), and their growth and uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus were observed. The results showed that the plant height, root length, aboveground fresh quality, aboveground biomass and phosphorus accumulation of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De were the highest and significantly higher than those of other treatments, and that the stem diameter and aboveground nitrogen accumulation of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De also reached a higher level. The principal component analysis showed that the comprehensive performance of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De was the best. Therefore, when sweet corn is planted in the field, it is recommended to inoculate sweet corn with De, which is more conducive to the growth of sweet corn and the accumulation of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in sweet corn.
A microcosm experiment was conducted to study the effects of different arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) on the growth and the nitrogen and phosphorus absorption of sweet corn seedlings to provide reference for the development of AMF. Sweet corn seedlings (Zea mays var. rugose Bonaf) were inoculated with 6 AMF species, Funneliformis mosseae (Fm), Gigaspora margarita (Gm), Acaulospora scrobiculata (As), Corymbiglomus tortuosum (Ct), Diversispora epigaea (De) and Rhizophagus intraradices (Ri), and their growth and uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus were observed. The results showed that the plant height, root length, aboveground fresh quality, aboveground biomass and phosphorus accumulation of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De were the highest and significantly higher than those of other treatments, and that the stem diameter and aboveground nitrogen accumulation of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De also reached a higher level. The principal component analysis showed that the comprehensive performance of sweet corn seedlings inoculated with De was the best. Therefore, when sweet corn is planted in the field, it is recommended to inoculate sweet corn with De, which is more conducive to the growth of sweet corn and the accumulation of nitrogen and phosphorus nutrients in sweet corn.
2023, 14(2): 173-177.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.006
Abstract:
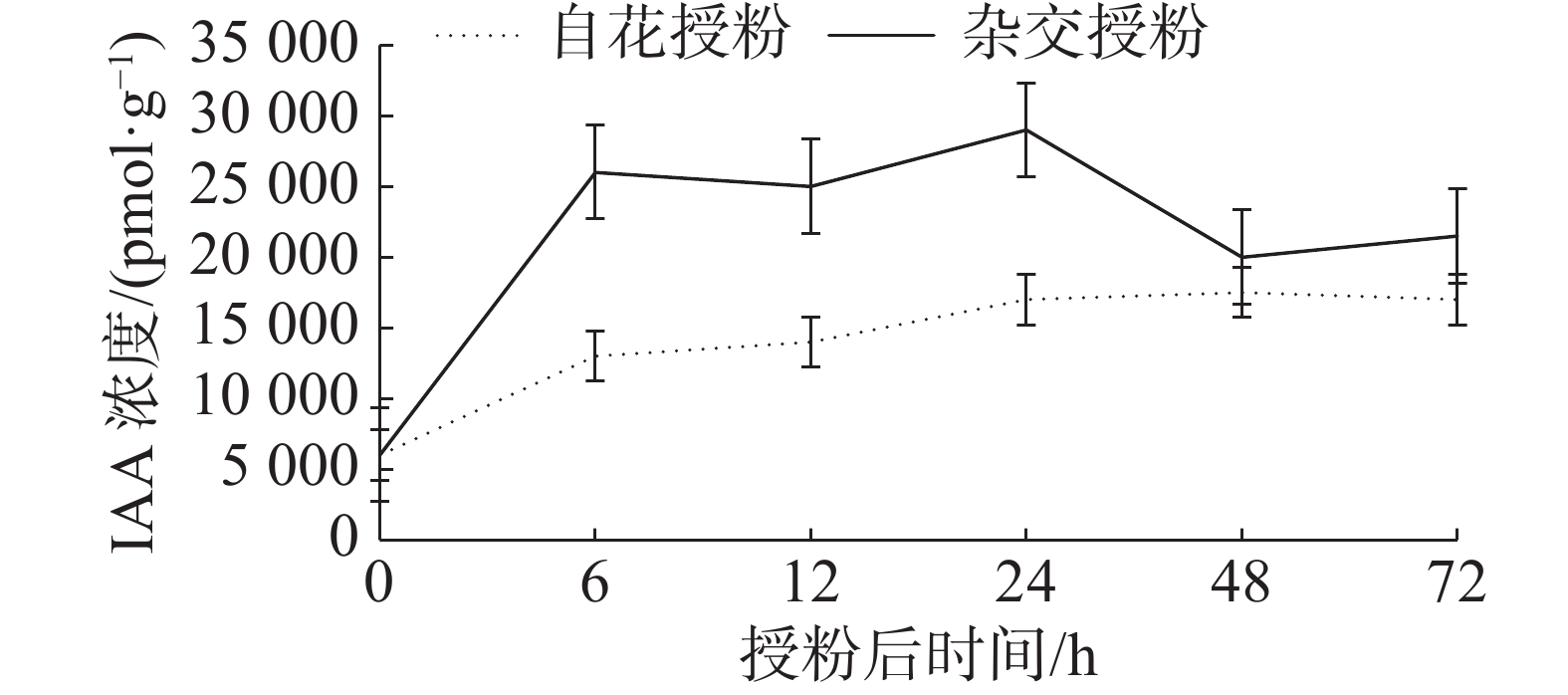
In order to understand self-pollination and cross-pollination of two camellia species, Camellia vietnamensis and Camellia furfuracea in Hainan, C. furfuracea and C. vietnamensis were self pollinated, or C. furfuracea was pollinated with the pollen of C. vietnamensis for crossing, and the pistils were sampled after different days of pollination to determine their dynamic changes in endogenous hormones, gibberellin (GA3), indole acetic acid (IAA), abscisic acid (ABA) and zeatin nucleoside (ZR), by using an enzyme-linked immunoassay. The results show that after the pollen tube enters the embryo sac, the level of IAA is reduced, which inhibits the growth of the pollen tube in the late stage, while the lower level of GA3 inhibits the growth of the pollen tube. When the pollen tube enters the embryo sac, high levels of GA3 may inhibit the growth of pollen tubes and the release of gametophytes, but high levels of ZR greatly promote the normal growth of pollen tubes in the stigma, and high levels of ABA greatly promote the growth and fertilization of pollen tubes. The imbalance of endogenous hormones plays a decisive role in the incompatibility of self-pollination of both C. furfuracea and C. vietnamensis in Hainan.
In order to understand self-pollination and cross-pollination of two camellia species, Camellia vietnamensis and Camellia furfuracea in Hainan, C. furfuracea and C. vietnamensis were self pollinated, or C. furfuracea was pollinated with the pollen of C. vietnamensis for crossing, and the pistils were sampled after different days of pollination to determine their dynamic changes in endogenous hormones, gibberellin (GA3), indole acetic acid (IAA), abscisic acid (ABA) and zeatin nucleoside (ZR), by using an enzyme-linked immunoassay. The results show that after the pollen tube enters the embryo sac, the level of IAA is reduced, which inhibits the growth of the pollen tube in the late stage, while the lower level of GA3 inhibits the growth of the pollen tube. When the pollen tube enters the embryo sac, high levels of GA3 may inhibit the growth of pollen tubes and the release of gametophytes, but high levels of ZR greatly promote the normal growth of pollen tubes in the stigma, and high levels of ABA greatly promote the growth and fertilization of pollen tubes. The imbalance of endogenous hormones plays a decisive role in the incompatibility of self-pollination of both C. furfuracea and C. vietnamensis in Hainan.
2023, 14(2): 179-188.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.007
Abstract:
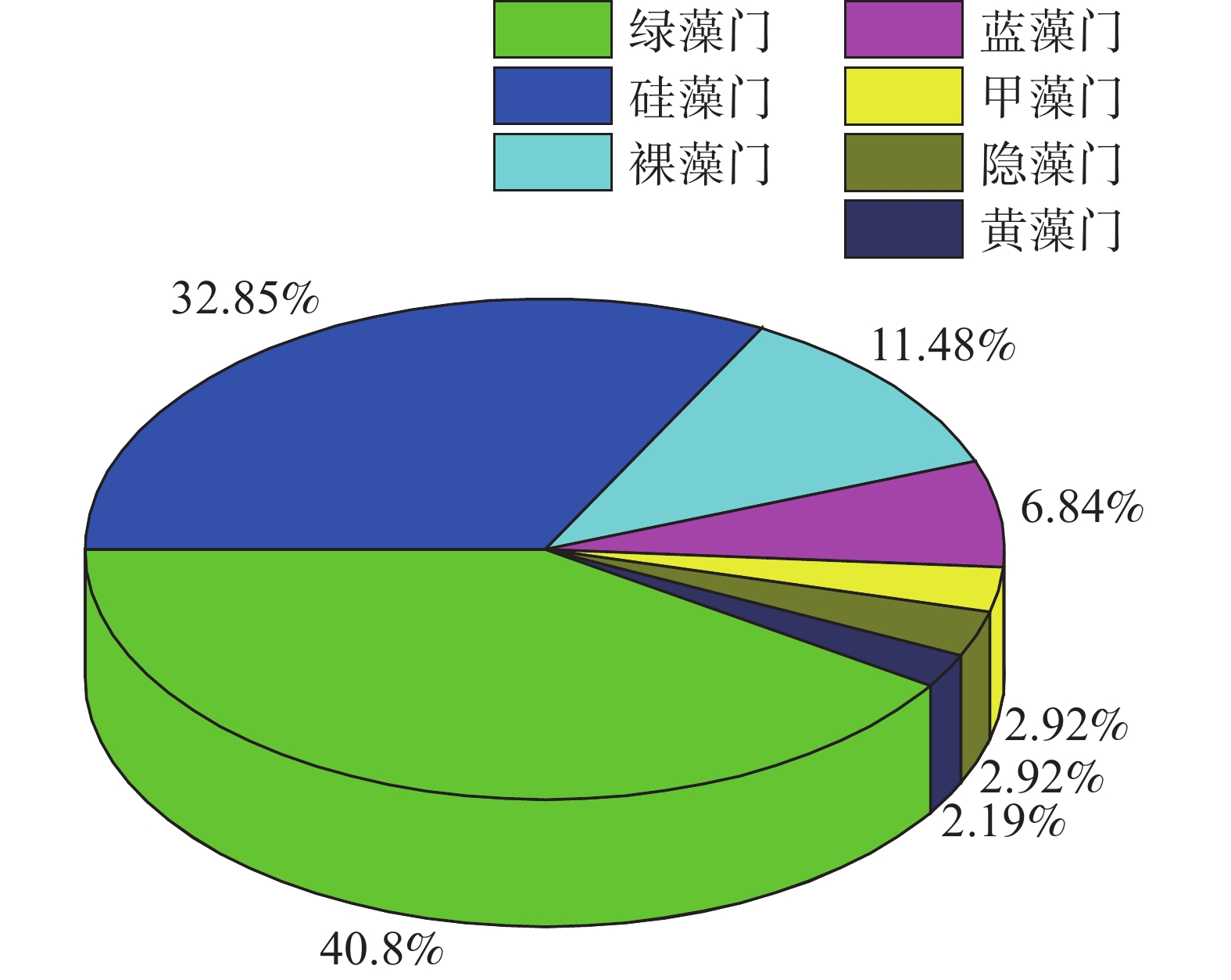
Wanquan River Basin constitutes the most important ecological barrier of Hainan province, and its ecological environment in the national economy of Hainan province and social development plays a pivotal role. However, the aquatic biological research in the basin has been less made in recent years, which greatly affected the ecological environment protection and species conservation in the basin. Therefore, a survey was made of the aquatic species and their related ecology in Yazhai section of Wanquan River Basin by using the methods of field monitoring, market survey and interview. The survey showed that the water at the Yazhai section of Wanquan River is high in quality, meeting the Class 3 of the national surface water standards, and is abundant in aquatic species with high biomass. Among the six sampling sites set up in the Yazhai section of Wanquan River Basin a total of 137 phyla of phytoplankton were collected, of which green algae species are the most abundant (60 species), accounting for 40.80% of the total phytoplankton species, and 6 types and 30 species of zooplankton were collected, of which rotifer species were most abundant (13 species), accounting for 43.33% of the total zooplankton species. There were 4 types and 14 species of zoobenthos collected, of which arthropod species were most abundant (6 species), accounting for 42.86% of the total zoobenthos species. There were 12 orders, 41 families, 68 genera and 82 species of fish collected, of which the orders of perch and cyprinid were most abundant, accounting for 45% and 27% of the total fish orders, respectively. There were 18 families and 48 species of aquatic vascular plants, of which gramineous plant species were most abundant (12 species), accounting for 25% of the total species of aquatic vascular plants. Comprehensive analysis of the diversity indexes of zooplankton, phytoplankton, zoobenthos and fish showed that the aquatic biodiversity in Yazhai section of Wanquan River is rich.
Wanquan River Basin constitutes the most important ecological barrier of Hainan province, and its ecological environment in the national economy of Hainan province and social development plays a pivotal role. However, the aquatic biological research in the basin has been less made in recent years, which greatly affected the ecological environment protection and species conservation in the basin. Therefore, a survey was made of the aquatic species and their related ecology in Yazhai section of Wanquan River Basin by using the methods of field monitoring, market survey and interview. The survey showed that the water at the Yazhai section of Wanquan River is high in quality, meeting the Class 3 of the national surface water standards, and is abundant in aquatic species with high biomass. Among the six sampling sites set up in the Yazhai section of Wanquan River Basin a total of 137 phyla of phytoplankton were collected, of which green algae species are the most abundant (60 species), accounting for 40.80% of the total phytoplankton species, and 6 types and 30 species of zooplankton were collected, of which rotifer species were most abundant (13 species), accounting for 43.33% of the total zooplankton species. There were 4 types and 14 species of zoobenthos collected, of which arthropod species were most abundant (6 species), accounting for 42.86% of the total zoobenthos species. There were 12 orders, 41 families, 68 genera and 82 species of fish collected, of which the orders of perch and cyprinid were most abundant, accounting for 45% and 27% of the total fish orders, respectively. There were 18 families and 48 species of aquatic vascular plants, of which gramineous plant species were most abundant (12 species), accounting for 25% of the total species of aquatic vascular plants. Comprehensive analysis of the diversity indexes of zooplankton, phytoplankton, zoobenthos and fish showed that the aquatic biodiversity in Yazhai section of Wanquan River is rich.
2023, 14(2): 189-195.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.008
Abstract:
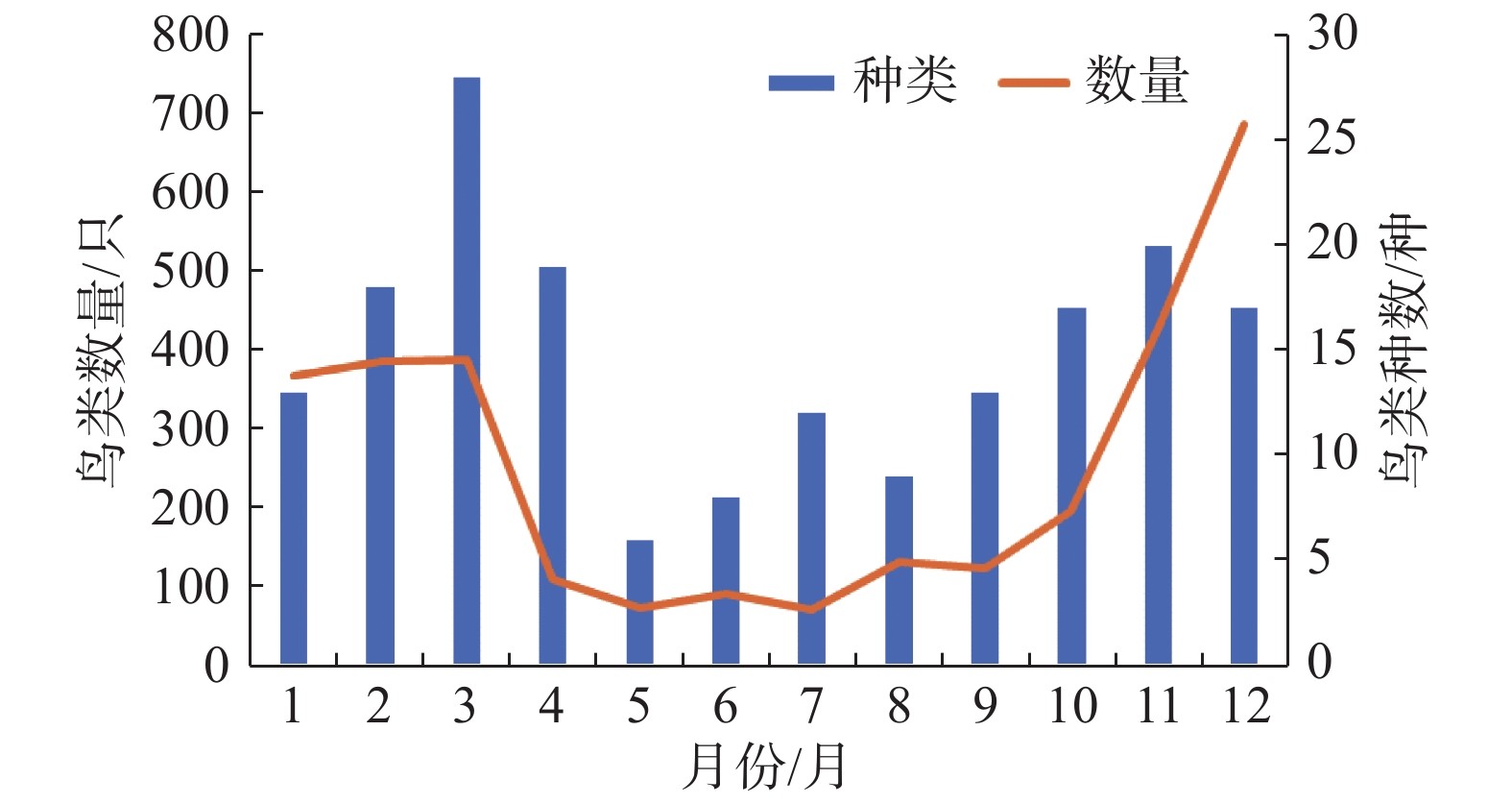
In order to have a basic picture of the birds at Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park in Danzhou, Hainan, a combination of point counts and line transects was used to estimate the bird diversity at Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park from January to December 2016, and a total of 57 species of birds in 7 orders and 19 families were recorded. Among them three species were recorded as Near Threatened (NT) on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, namely black-tailed sandpiper (Limosa limosa), red-necked sandpiper (Calidris ruficollis) and the bent-billed sandpiper (Calidris ferruginea); one species was recorded as Vulnerable (VU), blue jade (Halcyon pileata); one species of Critically Endangered (CR) and one species of Endangered (EN) birds, namely spoonbill sandpiper (Calidris pygmaea) and black-faced spoonbill (Platalea minor), respectively, which are also listed as wild animals in Class I under state protection. There are six species of wildlife at Class II under state protection, namely white-breasted emerald (Halcyon smyrnensis), Eurasian curlew (Numeniu sarquata), Osprey (Pandion haliaetus), semipalmated sandpiper (Limnodromus semipalmatus), Eurasian spoonbill (Platalea leucorodia), and white-bellied harrier (Circus spilonotus). The number of birds tended to be in the order of winter > autumn > spring > summer, and the number of bird species was in the order of spring > autumn > winter > summer. Birds were highest in number in January-March, November and December with over 300 birds, and lowest in May-July with less than 100 birds. The number of bird species (35), diversity index (2.7) and evenness index (0.76) were higher in spring than in the other three seasons, while the highest dominance index was in summer (0.17) and autumn (0.17). The survey found three species of birds for the first time at the park: the bent-billed shorebird (C. ferruginea), the grey-faced buzzard (Butastur indicus) and the black-cushioned oriole (Oriolus chinensis), which are new records of birds at the Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park, but in general, the proportion of birds under state protection at the park is lower than the national average, and the species and number of raptors are also lower than the average of raptors distributed in China, indicating that the protected area is not rich enough in species diversity and that the top taxa of the food chain are still lacking. This survey provides some data for the next long-term monitoring and evaluation of birds at the park, and the reasons for changes in the global migration of birds throughout the year were analyzed, based on which targeted conservation recommendations are proposed.
In order to have a basic picture of the birds at Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park in Danzhou, Hainan, a combination of point counts and line transects was used to estimate the bird diversity at Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park from January to December 2016, and a total of 57 species of birds in 7 orders and 19 families were recorded. Among them three species were recorded as Near Threatened (NT) on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, namely black-tailed sandpiper (Limosa limosa), red-necked sandpiper (Calidris ruficollis) and the bent-billed sandpiper (Calidris ferruginea); one species was recorded as Vulnerable (VU), blue jade (Halcyon pileata); one species of Critically Endangered (CR) and one species of Endangered (EN) birds, namely spoonbill sandpiper (Calidris pygmaea) and black-faced spoonbill (Platalea minor), respectively, which are also listed as wild animals in Class I under state protection. There are six species of wildlife at Class II under state protection, namely white-breasted emerald (Halcyon smyrnensis), Eurasian curlew (Numeniu sarquata), Osprey (Pandion haliaetus), semipalmated sandpiper (Limnodromus semipalmatus), Eurasian spoonbill (Platalea leucorodia), and white-bellied harrier (Circus spilonotus). The number of birds tended to be in the order of winter > autumn > spring > summer, and the number of bird species was in the order of spring > autumn > winter > summer. Birds were highest in number in January-March, November and December with over 300 birds, and lowest in May-July with less than 100 birds. The number of bird species (35), diversity index (2.7) and evenness index (0.76) were higher in spring than in the other three seasons, while the highest dominance index was in summer (0.17) and autumn (0.17). The survey found three species of birds for the first time at the park: the bent-billed shorebird (C. ferruginea), the grey-faced buzzard (Butastur indicus) and the black-cushioned oriole (Oriolus chinensis), which are new records of birds at the Hainan Xinying Mangrove National Wetland Park, but in general, the proportion of birds under state protection at the park is lower than the national average, and the species and number of raptors are also lower than the average of raptors distributed in China, indicating that the protected area is not rich enough in species diversity and that the top taxa of the food chain are still lacking. This survey provides some data for the next long-term monitoring and evaluation of birds at the park, and the reasons for changes in the global migration of birds throughout the year were analyzed, based on which targeted conservation recommendations are proposed.
2023, 14(2): 197-202.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.009
Abstract:
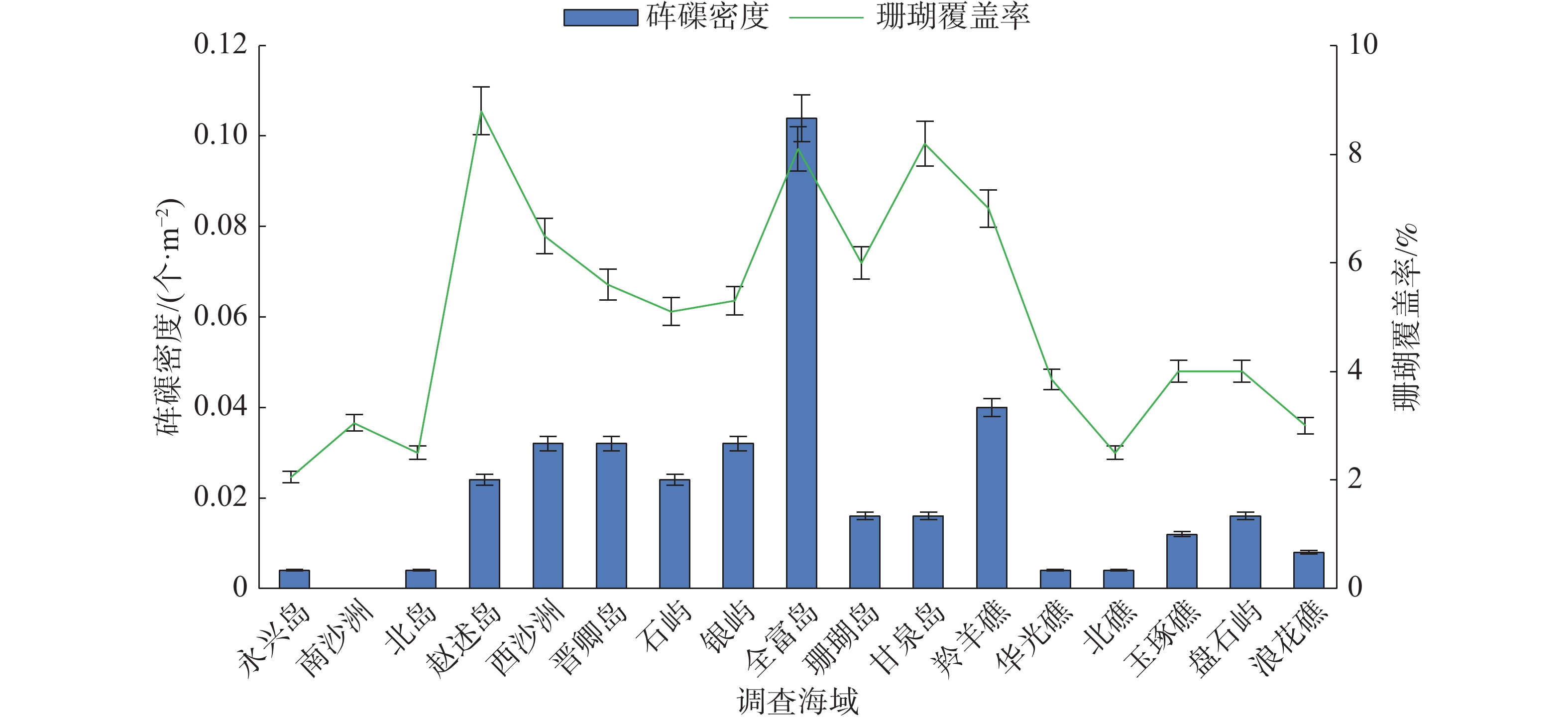
Giant clams are the largest living marine bivalves inhabiting coral reefs, and perform a significant ecological role in maintaining the balance of coral reef ecosystem. In recent years, giant clams in the waters at Xisha Islands, China are seriously threatened due to overfishing and the deterioration of the marine environment in the coastal areas. In order to master the present status of giant clam resources at Xisha Islands, a survey of giant clams in the waters at the main islands of Xisha Islands were made by using the method of line intercept transect to determine the species and distribution of the giant clams at Xisha Islands in the South China Sea from June to July 2017, and then analyze the correlation of the giant clams with the environment in the waters at the main islands of Xisha Islands. The results showed that there were four species of the giant clams in the survey area, including Tridacna squamosa, Tridacna crocea, Tridacna maxima and Hippopus hippopus, accounting for 71.9%, 15.6%, 9.4% and 3.1% of the total giant clams, respectively. The giant clams in the waters of different main islands of Xisha Islands are significantly different in habitat density and species diversity index. The average density of the giant clams is 0.026 ind/m2. Correlation analysis showed that there was a significant positive correlation between habitat density and coral reef coverage (P<0.05, R2 = 0.7065). This shows that coral reef coverage is an important factor affecting the distribution of giant clams. This result can provide scientific basis for the conservation of giant clam resources in Xisha Islands in China.
Giant clams are the largest living marine bivalves inhabiting coral reefs, and perform a significant ecological role in maintaining the balance of coral reef ecosystem. In recent years, giant clams in the waters at Xisha Islands, China are seriously threatened due to overfishing and the deterioration of the marine environment in the coastal areas. In order to master the present status of giant clam resources at Xisha Islands, a survey of giant clams in the waters at the main islands of Xisha Islands were made by using the method of line intercept transect to determine the species and distribution of the giant clams at Xisha Islands in the South China Sea from June to July 2017, and then analyze the correlation of the giant clams with the environment in the waters at the main islands of Xisha Islands. The results showed that there were four species of the giant clams in the survey area, including Tridacna squamosa, Tridacna crocea, Tridacna maxima and Hippopus hippopus, accounting for 71.9%, 15.6%, 9.4% and 3.1% of the total giant clams, respectively. The giant clams in the waters of different main islands of Xisha Islands are significantly different in habitat density and species diversity index. The average density of the giant clams is 0.026 ind/m2. Correlation analysis showed that there was a significant positive correlation between habitat density and coral reef coverage (P<0.05, R2 = 0.7065). This shows that coral reef coverage is an important factor affecting the distribution of giant clams. This result can provide scientific basis for the conservation of giant clam resources in Xisha Islands in China.
2023, 14(2): 203-213.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.010
Abstract:
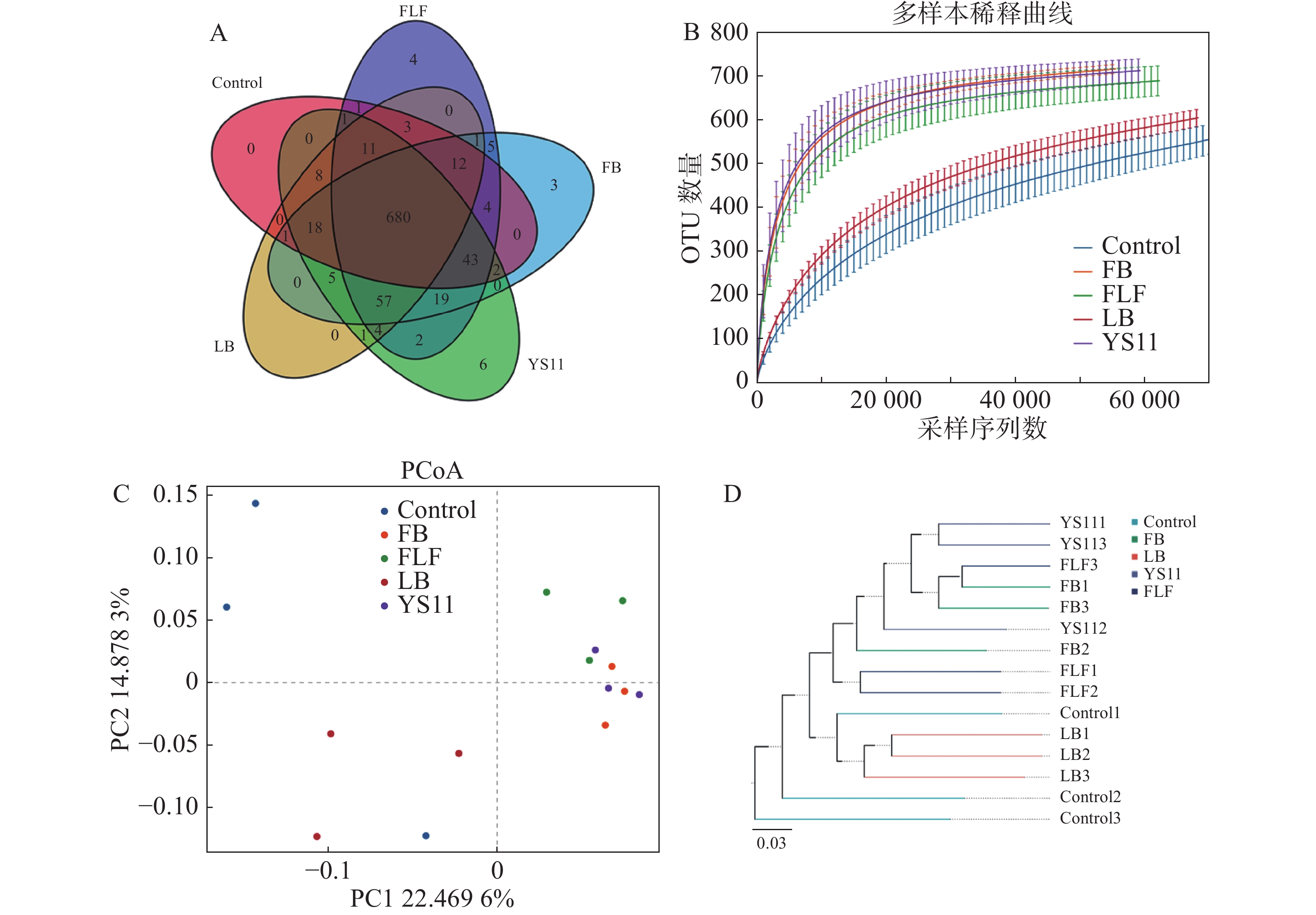
Mudskipper is a fish of goby family with high economic and ecological value. Markers of mitochondrial control region were used to analyze genetic diversity, genetic structure, and demographic history among nine populations of three mudskipper species, such as Periophthalmus modestus, Boleophthalmus pectinirostris and Periophthalmus magnuspinnatus, for better conservation of Mudskipper resources. All samples were separately collected from nine localities (Haikou, Wenchang, Chengmai, Lingao, Danzhou, Changjiang, Dongfang, Ledong and Sanya) in Hainan Island. As a result, we have obtained 195 D-Loop gene sequences of with a length of 836 bp from all the Mudskipper samples. The analysis showed that P. modestus is highest in genetic diversity with B. pectinirostris being the lowest among the three mudskipper species. The genetic differentiation indexes (Fst) of P. modestus indicated that there are moderate genetic differentiations between Sanya and each of Lingao, Dongfang and Ledong populations. The analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) of P. modestus suggested the absence of genetic variation within populations. The Fst of B. pectinirostris showed that there is a high genetic differentiation between Wenchang and Dongfang populations, and the AMOVA of B. pectinirostris suggested the existence of moderate difference within populations. The genetic distance analysis of the three mudskipper species showed that P. modestus and P. magnuspinnatus populations had the closest relationship and could be distinguished by D-Loop gene sequences. The neutrality test and mismatch distribution analysis showed that the Wenchang population of B. pectinirostris was obviously expanded in its evolution. All the results showed that genetic resources of B. pectinirostris among three mudskippers populations should be conserved as a priority.
Mudskipper is a fish of goby family with high economic and ecological value. Markers of mitochondrial control region were used to analyze genetic diversity, genetic structure, and demographic history among nine populations of three mudskipper species, such as Periophthalmus modestus, Boleophthalmus pectinirostris and Periophthalmus magnuspinnatus, for better conservation of Mudskipper resources. All samples were separately collected from nine localities (Haikou, Wenchang, Chengmai, Lingao, Danzhou, Changjiang, Dongfang, Ledong and Sanya) in Hainan Island. As a result, we have obtained 195 D-Loop gene sequences of with a length of 836 bp from all the Mudskipper samples. The analysis showed that P. modestus is highest in genetic diversity with B. pectinirostris being the lowest among the three mudskipper species. The genetic differentiation indexes (Fst) of P. modestus indicated that there are moderate genetic differentiations between Sanya and each of Lingao, Dongfang and Ledong populations. The analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) of P. modestus suggested the absence of genetic variation within populations. The Fst of B. pectinirostris showed that there is a high genetic differentiation between Wenchang and Dongfang populations, and the AMOVA of B. pectinirostris suggested the existence of moderate difference within populations. The genetic distance analysis of the three mudskipper species showed that P. modestus and P. magnuspinnatus populations had the closest relationship and could be distinguished by D-Loop gene sequences. The neutrality test and mismatch distribution analysis showed that the Wenchang population of B. pectinirostris was obviously expanded in its evolution. All the results showed that genetic resources of B. pectinirostris among three mudskippers populations should be conserved as a priority.
2023, 14(2): 214-220.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.011
Abstract:
In order to explore the preservation conditions of Lysinibacillus boronitolerans YS11 and its effect on the diversity and abundance of intestinal microorganisms in tilapia for the research and development of microbial feed additives. Four protectants, i.e. trehalose, lactose, sucrose and skim milk powder, were selected and optimized by concentration gradient. The results confirmed that YS11 maintained a high survival rate after drying in 10% trehalose. Tilapia fingerlings were fed with feeds containing bacterial fermentation broth, and after 70 days of feeding, high-throughput sequencing was performed to observe the effect of the feeds on tilapia intestinal microbial community. The results showed that the feed containing YS11 changed the tilapia gut microbiota and its diversity, increased the abundance of beneficial bacteria in the tilapia gut, and decreased the abundance of some potential pathogenic bacteria. These results confirmed that 10% trehalose was the best freeze-drying protectant. L. boronitolerans can regulate the intestinal microbiota, promote the growth of probiotics, and inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
In order to explore the preservation conditions of Lysinibacillus boronitolerans YS11 and its effect on the diversity and abundance of intestinal microorganisms in tilapia for the research and development of microbial feed additives. Four protectants, i.e. trehalose, lactose, sucrose and skim milk powder, were selected and optimized by concentration gradient. The results confirmed that YS11 maintained a high survival rate after drying in 10% trehalose. Tilapia fingerlings were fed with feeds containing bacterial fermentation broth, and after 70 days of feeding, high-throughput sequencing was performed to observe the effect of the feeds on tilapia intestinal microbial community. The results showed that the feed containing YS11 changed the tilapia gut microbiota and its diversity, increased the abundance of beneficial bacteria in the tilapia gut, and decreased the abundance of some potential pathogenic bacteria. These results confirmed that 10% trehalose was the best freeze-drying protectant. L. boronitolerans can regulate the intestinal microbiota, promote the growth of probiotics, and inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria.
2023, 14(2): 221-228.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.012
Abstract:
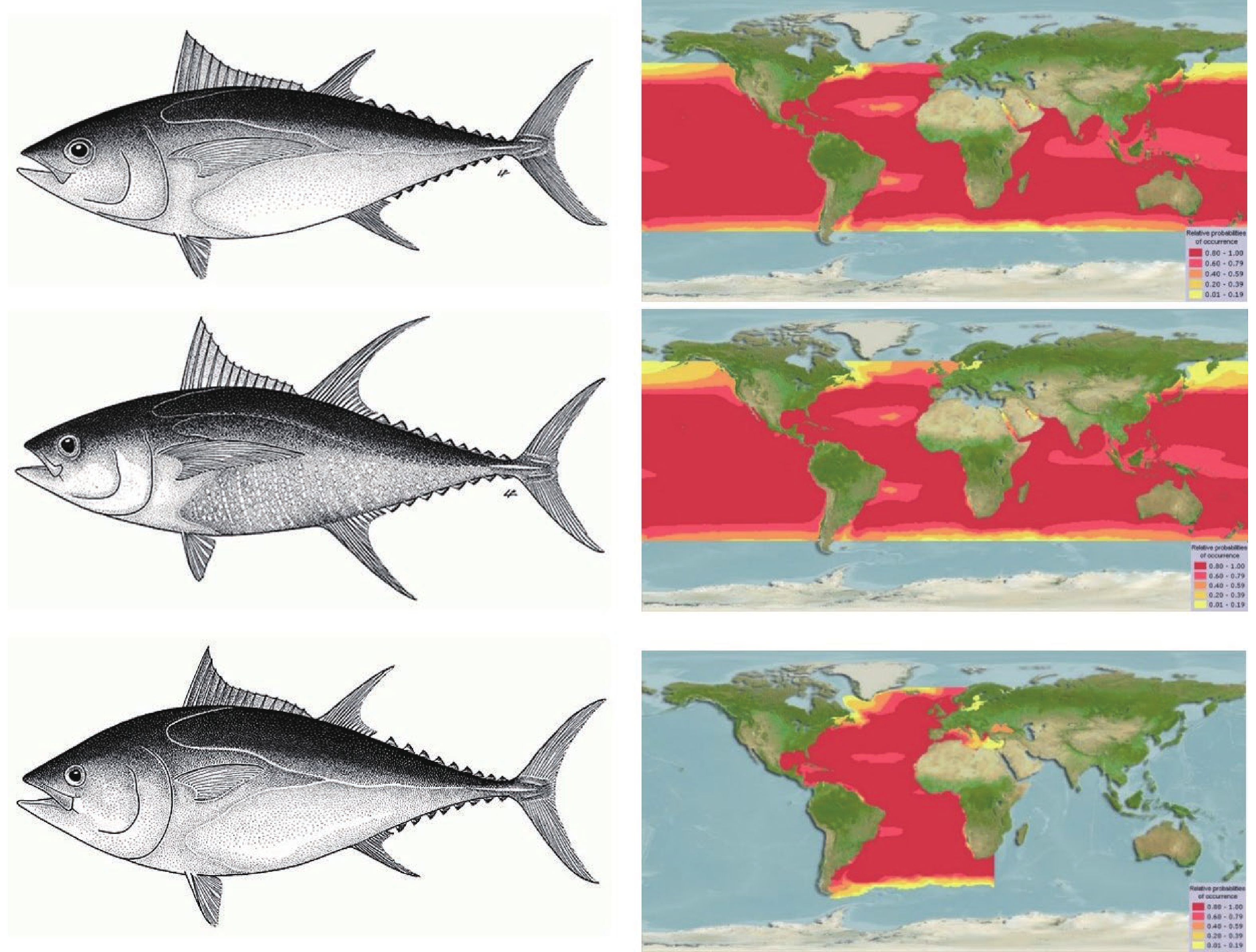
Tunas are species of bony fish belonging to the family Scombridae, order Perciformes, and class Osteichthyes. They are high trophic predators with marine migratory behavior. Tunas have acquired various distinct biological traits in response to the pressures of human overfishing and the variable marine environments. Focused on Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus), bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus), and yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacores), the most popular research methodologies and important research results in tuna biology, including age and growth, feeding, and reproduction are reviewed. The unique biological properties of tunas to boost the population's fitness (e.g., multiple growth inflection points, opportunistic predators, and multiple reproductive strategies, etc.) are illustrated. At the same time, the existing shortcomings in the field of tuna biology research are analyzed, based on which suggestions for future research, regarding research methods, equipment and technologies are hence proposed.
Tunas are species of bony fish belonging to the family Scombridae, order Perciformes, and class Osteichthyes. They are high trophic predators with marine migratory behavior. Tunas have acquired various distinct biological traits in response to the pressures of human overfishing and the variable marine environments. Focused on Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus), bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus), and yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacores), the most popular research methodologies and important research results in tuna biology, including age and growth, feeding, and reproduction are reviewed. The unique biological properties of tunas to boost the population's fitness (e.g., multiple growth inflection points, opportunistic predators, and multiple reproductive strategies, etc.) are illustrated. At the same time, the existing shortcomings in the field of tuna biology research are analyzed, based on which suggestions for future research, regarding research methods, equipment and technologies are hence proposed.
2023, 14(2): 229-233.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.013
Abstract:
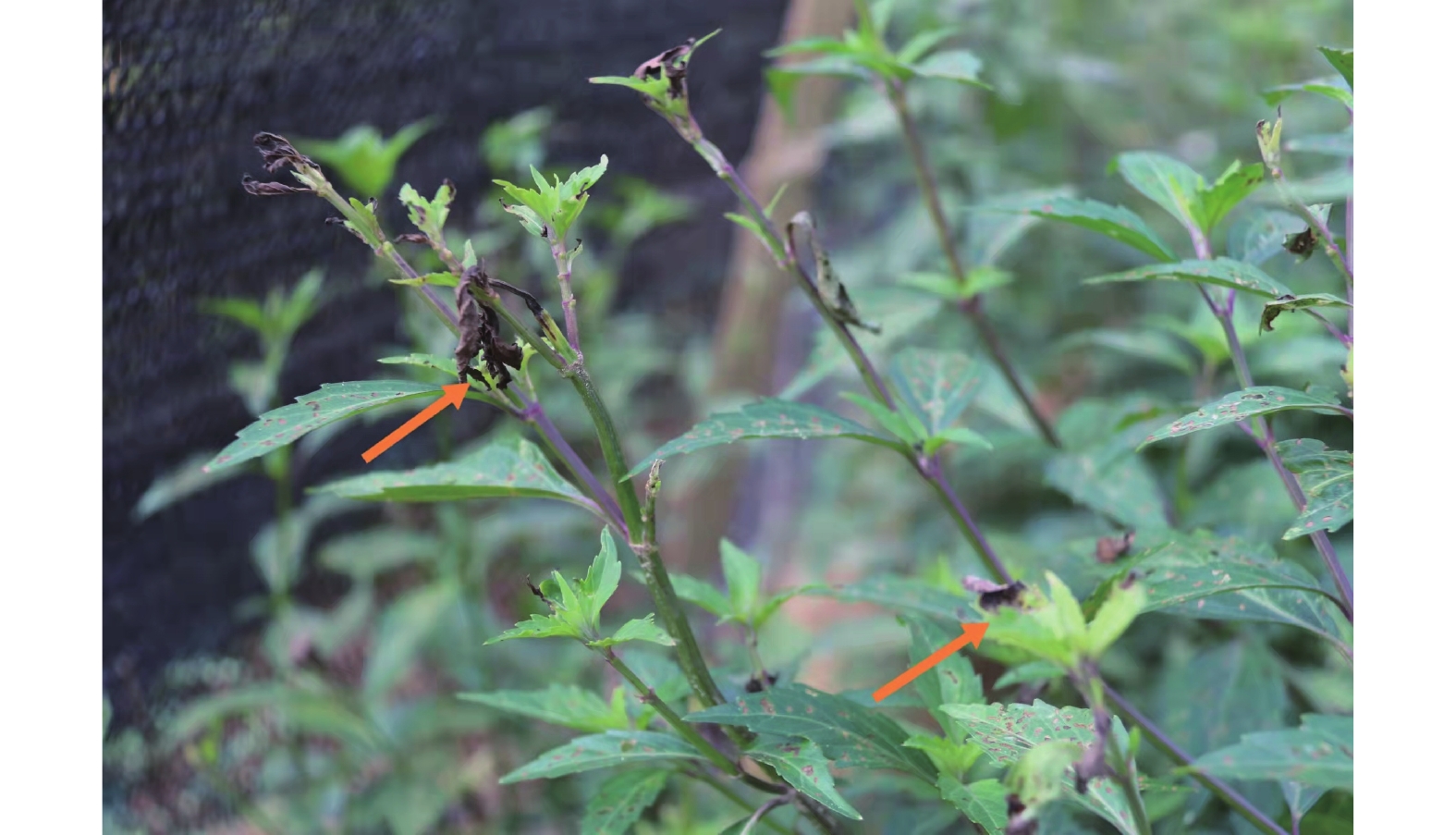
In order to determine the pathogen of leaf blight of kidney plant (Clerodendranthus spicatus (Thunb.) C.Y.Wu), the kidney plant leaves infected with leaf blight were sampled from a kidney plant producing area in Yunnan, and one strain of the pathogen was isolated from the samples and then identified morphologically and molecularly. The results showed that the pathogen cultured on the PDA medium was white in colony, and well developed in aerial mycelia. The colony in the lower part was pale pink initially and then turned yellow-brown. The apical cells of the conidia were uncinate, and the mature macroconidia have 3~5 septa. The pathogen isolated was inoculated onto the healthy plant leaves of C. spicatus. After several days of moist culture, dark-brown lesions appeared at the inoculated sites of the leaves, which were consistent with the field symptoms. Genomic DNA of the pathogen was amplified by using fungal rDNA-ITS universal primers ITS1/ITS4 and analyzed by homology analysis. The results showed that the pathogen isolated was clustered into the same branch with Fusarium nematophilum, F. equiseti, F. chlamydosporum and F. longip, and had a nucleic acid sequence homology of 99.40%−99.60%. The morphological observation, ITS sequence analysis and establishment of Koch’s postulates showed that the pathogen was preliminarily identified as F. oxysporum.
In order to determine the pathogen of leaf blight of kidney plant (Clerodendranthus spicatus (Thunb.) C.Y.Wu), the kidney plant leaves infected with leaf blight were sampled from a kidney plant producing area in Yunnan, and one strain of the pathogen was isolated from the samples and then identified morphologically and molecularly. The results showed that the pathogen cultured on the PDA medium was white in colony, and well developed in aerial mycelia. The colony in the lower part was pale pink initially and then turned yellow-brown. The apical cells of the conidia were uncinate, and the mature macroconidia have 3~5 septa. The pathogen isolated was inoculated onto the healthy plant leaves of C. spicatus. After several days of moist culture, dark-brown lesions appeared at the inoculated sites of the leaves, which were consistent with the field symptoms. Genomic DNA of the pathogen was amplified by using fungal rDNA-ITS universal primers ITS1/ITS4 and analyzed by homology analysis. The results showed that the pathogen isolated was clustered into the same branch with Fusarium nematophilum, F. equiseti, F. chlamydosporum and F. longip, and had a nucleic acid sequence homology of 99.40%−99.60%. The morphological observation, ITS sequence analysis and establishment of Koch’s postulates showed that the pathogen was preliminarily identified as F. oxysporum.
2023, 14(2): 234-239.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.02.014
Abstract:
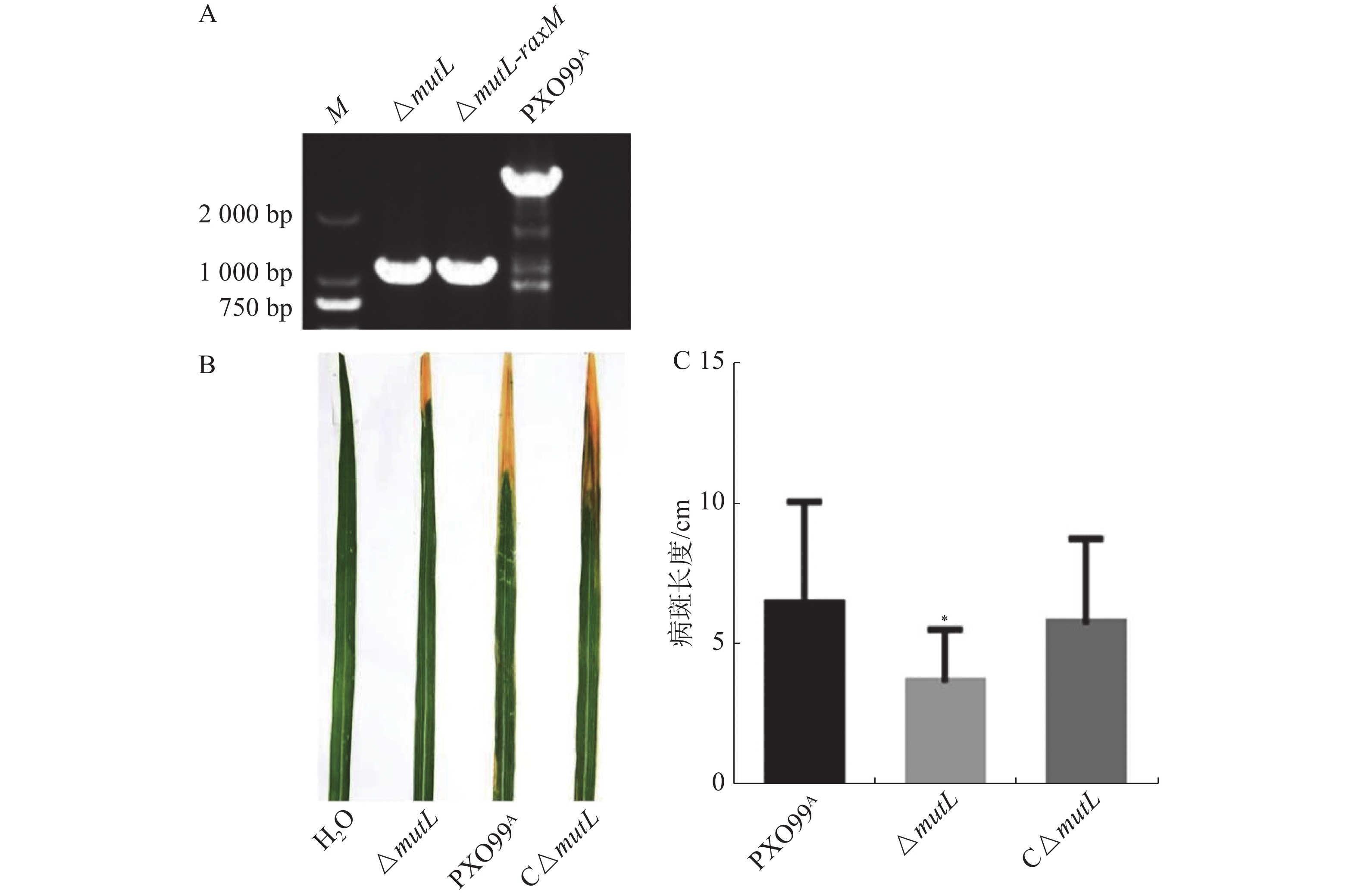
Environmental stimulus and DNA replication may cause DNA mismatch and thus genomic instability, which must be repaired by organisms. All organisms evolve DNA repair systems to cope with these damages. MutL/MutS is the key DNA repair system of bacteria, but its function remains unknown in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). Whether MutL/MutS is involved in DNA repair and virulence in Xoo needs further studies. MutL mutant and its complementary strain were constructed, and their virulence and mutation rates were analyzed. Results showed that MutL mutation increased Xoo mutation rates under H2O2 stress, indicating that MutL is important for DNA repair during the stress. It was also found that MutL mutation reduced Xoo infection ability in rice leaves, suggesting that MutL is required for Xoo-rice interaction. In summary, MutL is involved in DNA repair in Xoo, and is also vital for Xoo virulence.
Environmental stimulus and DNA replication may cause DNA mismatch and thus genomic instability, which must be repaired by organisms. All organisms evolve DNA repair systems to cope with these damages. MutL/MutS is the key DNA repair system of bacteria, but its function remains unknown in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo). Whether MutL/MutS is involved in DNA repair and virulence in Xoo needs further studies. MutL mutant and its complementary strain were constructed, and their virulence and mutation rates were analyzed. Results showed that MutL mutation increased Xoo mutation rates under H2O2 stress, indicating that MutL is important for DNA repair during the stress. It was also found that MutL mutation reduced Xoo infection ability in rice leaves, suggesting that MutL is required for Xoo-rice interaction. In summary, MutL is involved in DNA repair in Xoo, and is also vital for Xoo virulence.



 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 285KB
PDF 285KB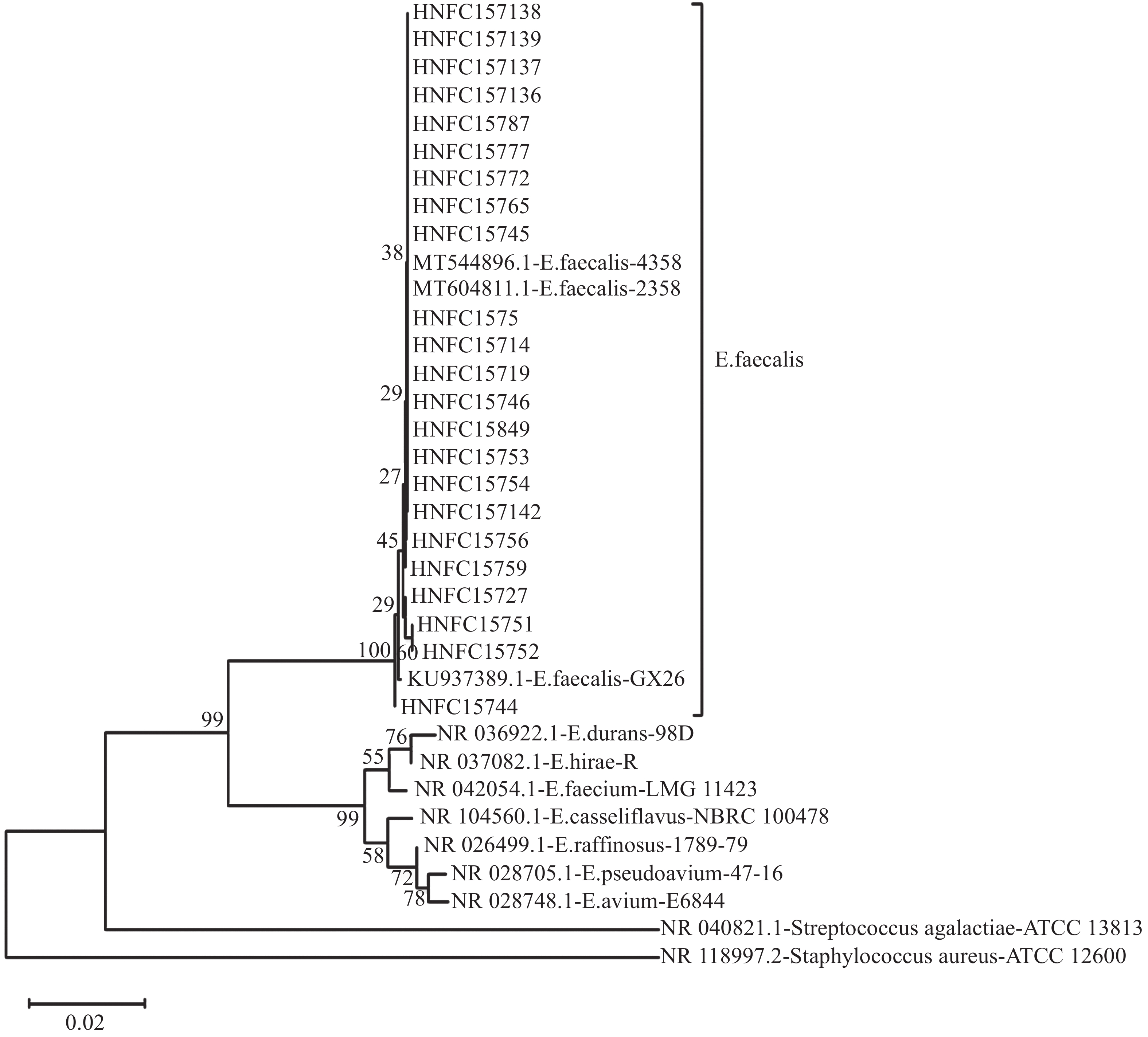







 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS