2022 Vol. 13, No. 3
2022, 13(3): 203-211.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.001
Abstract:
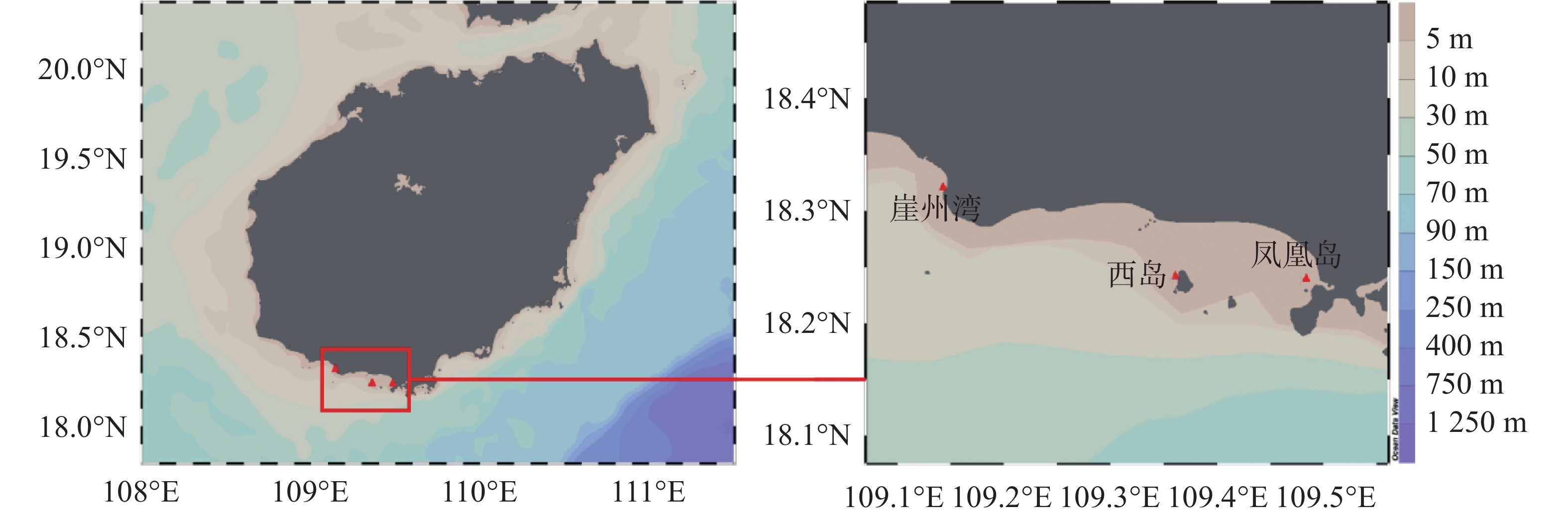
Elevated concentrations of suspended solids in seawater threaten the survival of scleractinian corals, but little is known about the mechanism of this phenomenon. During May-September 2020, a survey was made of the concentration of suspended solids in seawater in the coral reef areas of Yazhou Bay, Phoenix Island and West Island in Sanya, Hainan, China and the physiological indexes of the scleractinian coral Porites pukoensis and its Symbiodiniaceae symbionts were determined, from which sensitive biomarkers were screened to evaluate the effect of suspended solids on P. pukoensis. The results showed that the concentration of suspended solids in the seawater of Yazhou Bay reef area was 13.7 − 19.4 mg·L−1, which was significantly higher than that in Phoenix Island (1.9 − 8.8 mg·L−1) and West Island (0.7 − 5.3 mg·L−1). The correlation analysis revealed significant positive correlations between suspended solids and the symbiotic density (R = 0.27, P < 0.05) or nitric oxide synthase activities (R = 0.27, P < 0.05), while the glutathione S-transferase activities in the symbionts were significantly negatively correlated with the concentration of the suspended solids. All these results suggest that P. pukoensis is adapted to the reef environment with a high concentration of suspended solids through the induction of symbiotic density and NOS activity and the inhibition of GST activity. Moreover, the integrated biomarker response (IBR) index established herein is in the descending order of Yazhou Bay > Phoenix Island > West Island, which is consistent with the order of the contents of the suspended solids in this coral reef area, indicating that the IBR index can be used for ecological risk assessment of coral reefs.
Elevated concentrations of suspended solids in seawater threaten the survival of scleractinian corals, but little is known about the mechanism of this phenomenon. During May-September 2020, a survey was made of the concentration of suspended solids in seawater in the coral reef areas of Yazhou Bay, Phoenix Island and West Island in Sanya, Hainan, China and the physiological indexes of the scleractinian coral Porites pukoensis and its Symbiodiniaceae symbionts were determined, from which sensitive biomarkers were screened to evaluate the effect of suspended solids on P. pukoensis. The results showed that the concentration of suspended solids in the seawater of Yazhou Bay reef area was 13.7 − 19.4 mg·L−1, which was significantly higher than that in Phoenix Island (1.9 − 8.8 mg·L−1) and West Island (0.7 − 5.3 mg·L−1). The correlation analysis revealed significant positive correlations between suspended solids and the symbiotic density (R = 0.27, P < 0.05) or nitric oxide synthase activities (R = 0.27, P < 0.05), while the glutathione S-transferase activities in the symbionts were significantly negatively correlated with the concentration of the suspended solids. All these results suggest that P. pukoensis is adapted to the reef environment with a high concentration of suspended solids through the induction of symbiotic density and NOS activity and the inhibition of GST activity. Moreover, the integrated biomarker response (IBR) index established herein is in the descending order of Yazhou Bay > Phoenix Island > West Island, which is consistent with the order of the contents of the suspended solids in this coral reef area, indicating that the IBR index can be used for ecological risk assessment of coral reefs.
2022, 13(3): 212-219.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.002
Abstract:
In order to explore the response mechanism of seagrass in low light environment and clarify the reasons for the decline of seagrass ecosystem, Enhalus acoroides as the dominant species in Hainan was selected for analysis. Shades were built in situ in the sampling sites to simulate different light intensities, and E. acoroides under the shades were sampled to determine their morphological characteristics, biomass and element contents. The results showed that the leaf length, leaf width, stem length, leaf number, and plant density of E. acoroides were all lower under different shading treatments than under the control. The aboveground biomass of E. acoroides was significantly decreased under shading treatments, but the underground biomass was not significantly affected by shading treatments. Under the shading treatments, the C content of the leaves and the rhizome showed a decreasing trend, and the allocation ratio of total N and total P contents in the leaves was higher than that in the rhizome, indicating that the low light environment induces E. acoroides to distribute more energy and nutrients to the aboveground parts, thereby better enhancing its own photosynthesis. Shading treatments significantly reduced the C:P and N:P ratios in the leaves, and the C:N ratio in the rhizomes slightly decreased, while the C:P and N:P ratios in the rhizomes showed a trend of decreasing first and then increasing although their impact was not at a significant level. The experiments indicated that the light reduction would inhibit growth and development of E.acoroides.
In order to explore the response mechanism of seagrass in low light environment and clarify the reasons for the decline of seagrass ecosystem, Enhalus acoroides as the dominant species in Hainan was selected for analysis. Shades were built in situ in the sampling sites to simulate different light intensities, and E. acoroides under the shades were sampled to determine their morphological characteristics, biomass and element contents. The results showed that the leaf length, leaf width, stem length, leaf number, and plant density of E. acoroides were all lower under different shading treatments than under the control. The aboveground biomass of E. acoroides was significantly decreased under shading treatments, but the underground biomass was not significantly affected by shading treatments. Under the shading treatments, the C content of the leaves and the rhizome showed a decreasing trend, and the allocation ratio of total N and total P contents in the leaves was higher than that in the rhizome, indicating that the low light environment induces E. acoroides to distribute more energy and nutrients to the aboveground parts, thereby better enhancing its own photosynthesis. Shading treatments significantly reduced the C:P and N:P ratios in the leaves, and the C:N ratio in the rhizomes slightly decreased, while the C:P and N:P ratios in the rhizomes showed a trend of decreasing first and then increasing although their impact was not at a significant level. The experiments indicated that the light reduction would inhibit growth and development of E.acoroides.
2022, 13(3): 220-226.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.003
Abstract:
The nests of Red Junglefowl (Gallus gallus jabouillei) in Datian National Nature Reserve of Hainan were searched and their GPS points were recorded during the breeding seasons in 2020 and 2021 to reveal the main factors affecting the selection of nest sites by the red jungle fowl. After reproduction, a survey of the nest sites was made by using the quadrat method, and the nest site characteristics were recorded and analyzed. A total of 12 nests of the red junglefowl were found in this survey, among which 4 nests successfully hatched, and 8 nests were abandoned by female birds, with the reproductive success rate of 33.3 %. Large quadrats of 10 m × 10 m for the nests and small quadrats of 1 m × 1 m for the nest centers were conducted for measurement and recording, and a control quadrat was also conducted for analysis and comparison. Mann-Whitney U test was used to analyze the parameters of quadrat samples and the control sample. The results showed that there were significant differences in mean shrub coverage, shrub coverage 2 (>3−6 m), bare land ratio, deciduous layer thickness and distance from the road. Principal component analysis showed that theaverage value of shrubcoverage was the largest, followed by the proportion of bare land.All these indicated that the selection of nest sites by the red jungle fowl was specific and non-random, and that the red jungle fowl were more inclined to nest under grass or shrubs with relatively dense branches and leaves in a broad area near the road. Nest concealment is the main factor affecting the selection of nest sites by the red jungle fowl, and the human disturbance and edge effect also affect the selection of nest sites by the red jungle fowl.
The nests of Red Junglefowl (Gallus gallus jabouillei) in Datian National Nature Reserve of Hainan were searched and their GPS points were recorded during the breeding seasons in 2020 and 2021 to reveal the main factors affecting the selection of nest sites by the red jungle fowl. After reproduction, a survey of the nest sites was made by using the quadrat method, and the nest site characteristics were recorded and analyzed. A total of 12 nests of the red junglefowl were found in this survey, among which 4 nests successfully hatched, and 8 nests were abandoned by female birds, with the reproductive success rate of 33.3 %. Large quadrats of 10 m × 10 m for the nests and small quadrats of 1 m × 1 m for the nest centers were conducted for measurement and recording, and a control quadrat was also conducted for analysis and comparison. Mann-Whitney U test was used to analyze the parameters of quadrat samples and the control sample. The results showed that there were significant differences in mean shrub coverage, shrub coverage 2 (>3−6 m), bare land ratio, deciduous layer thickness and distance from the road. Principal component analysis showed that theaverage value of shrubcoverage was the largest, followed by the proportion of bare land.All these indicated that the selection of nest sites by the red jungle fowl was specific and non-random, and that the red jungle fowl were more inclined to nest under grass or shrubs with relatively dense branches and leaves in a broad area near the road. Nest concealment is the main factor affecting the selection of nest sites by the red jungle fowl, and the human disturbance and edge effect also affect the selection of nest sites by the red jungle fowl.
2022, 13(3): 227-234.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.004
Abstract:
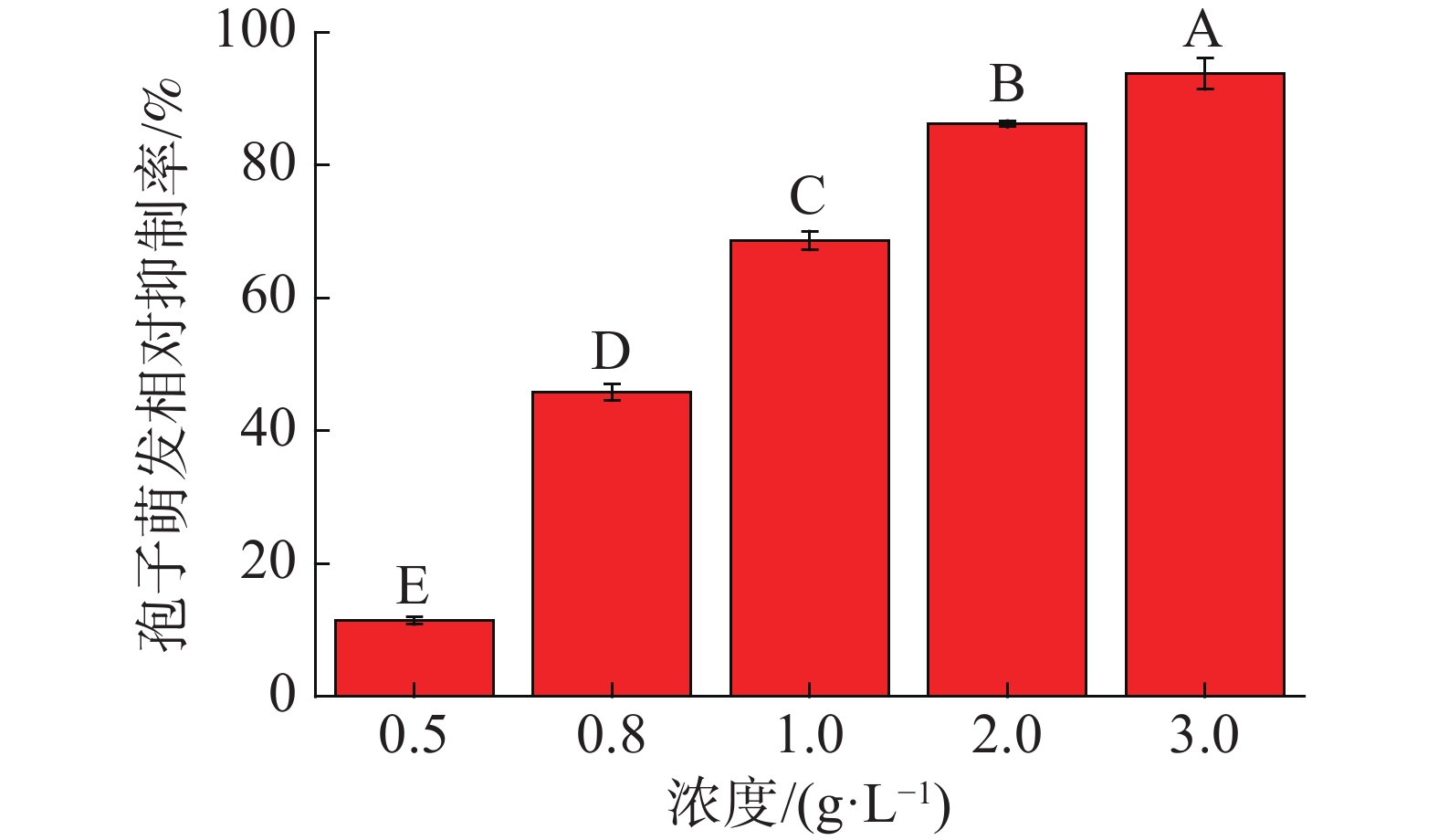
The twigs and leaves of Derris fordii were extracted with methanol and then partitioned to factions in petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water to assess the fungistatic activity of the methanol extracts and their fractions against plant pathogenic fungi. Eight plant pathogenic fungi were selected for treatment with the methanol extracts and their fractions of D. fordii to determine the mycelial growth inhibition activities by using the mycelium growth rate method, and the inhibition activities against the spore germination of Colletotrichum musae by using the spore germination method. The control effects of the methanol extracts of D. fordii against C. musae infecting banana fruit were determined by inoculation method, and the control effects of the methanol extracts of D. fordii and their solvent-partitioned fractions against Podosphaera xanthii in vivo were determined by pot culture method. The results showed that the methanol extracts and their factions of Derris fordii had different degrees of mycelial growth inhibition effects on the eight plant pathogenic fungi with the EC50 being 0.24~1.33 g·L−1, of which the methanol extract at the concentration of 2.00 g·L−1 had an inhibition rate of 82.15% against C. musae, and the ethyl acetate fraction at 1.00 g·L−1 had a relative inhibition rate of 89.92% against the spore germination of C. musae. The in vivo experiments indicated that the methanol extract of D. fordii at 3.20 g·L−1 had a control effect of 71.11% against C. musae in the inoculation experiment and that the methanol extract and the n-butanol fraction of Derris fordii when both at the concentration of 1.00 g·L−1 gave control effects of 91.67% and 94.07% against P. xanthii, respectively. Therefore, the methanol extracts and the petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol, and water fractions of D. fordii are potentially valuable in the prevention and control of plant pathogenic fungal diseases.
The twigs and leaves of Derris fordii were extracted with methanol and then partitioned to factions in petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol and water to assess the fungistatic activity of the methanol extracts and their fractions against plant pathogenic fungi. Eight plant pathogenic fungi were selected for treatment with the methanol extracts and their fractions of D. fordii to determine the mycelial growth inhibition activities by using the mycelium growth rate method, and the inhibition activities against the spore germination of Colletotrichum musae by using the spore germination method. The control effects of the methanol extracts of D. fordii against C. musae infecting banana fruit were determined by inoculation method, and the control effects of the methanol extracts of D. fordii and their solvent-partitioned fractions against Podosphaera xanthii in vivo were determined by pot culture method. The results showed that the methanol extracts and their factions of Derris fordii had different degrees of mycelial growth inhibition effects on the eight plant pathogenic fungi with the EC50 being 0.24~1.33 g·L−1, of which the methanol extract at the concentration of 2.00 g·L−1 had an inhibition rate of 82.15% against C. musae, and the ethyl acetate fraction at 1.00 g·L−1 had a relative inhibition rate of 89.92% against the spore germination of C. musae. The in vivo experiments indicated that the methanol extract of D. fordii at 3.20 g·L−1 had a control effect of 71.11% against C. musae in the inoculation experiment and that the methanol extract and the n-butanol fraction of Derris fordii when both at the concentration of 1.00 g·L−1 gave control effects of 91.67% and 94.07% against P. xanthii, respectively. Therefore, the methanol extracts and the petroleum ether, ethyl acetate, n-butanol, and water fractions of D. fordii are potentially valuable in the prevention and control of plant pathogenic fungal diseases.
2022, 13(3): 235-242.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.005
Abstract:
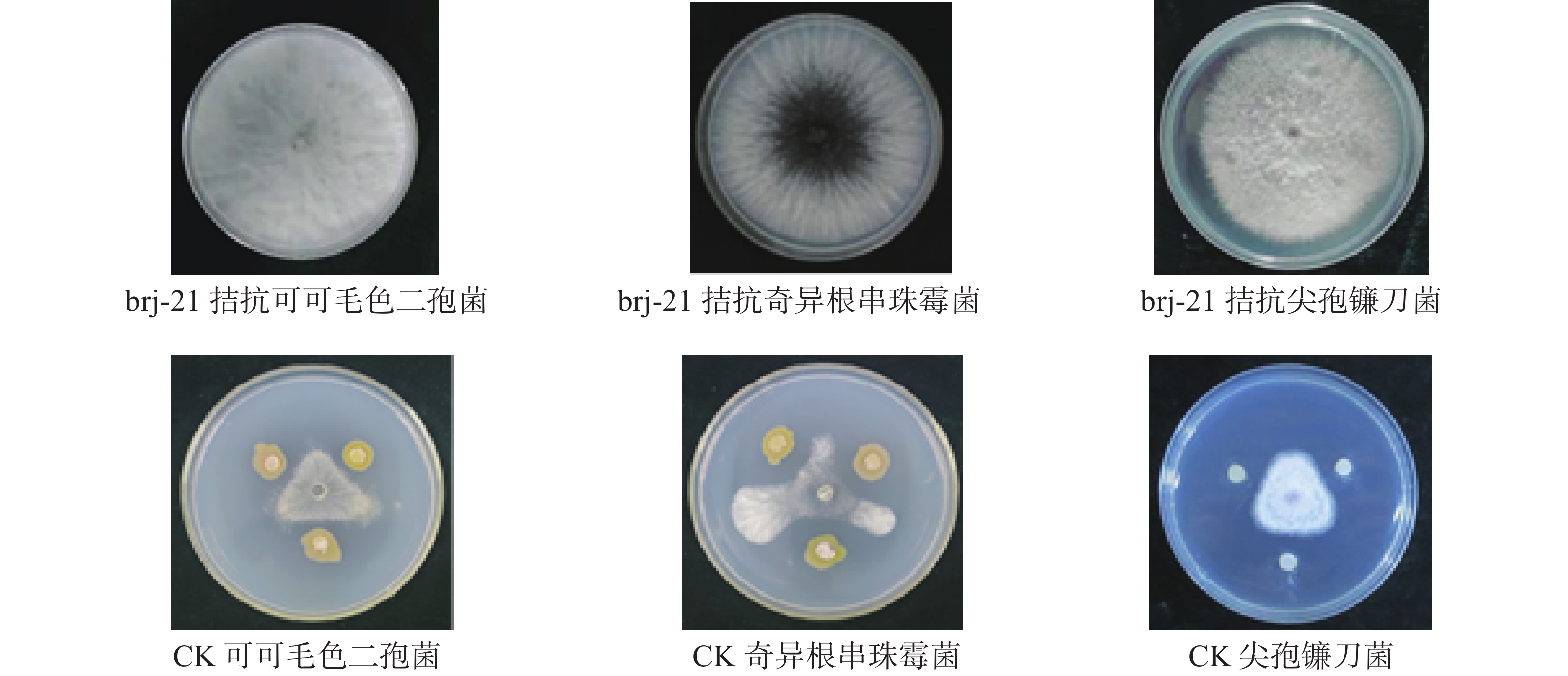
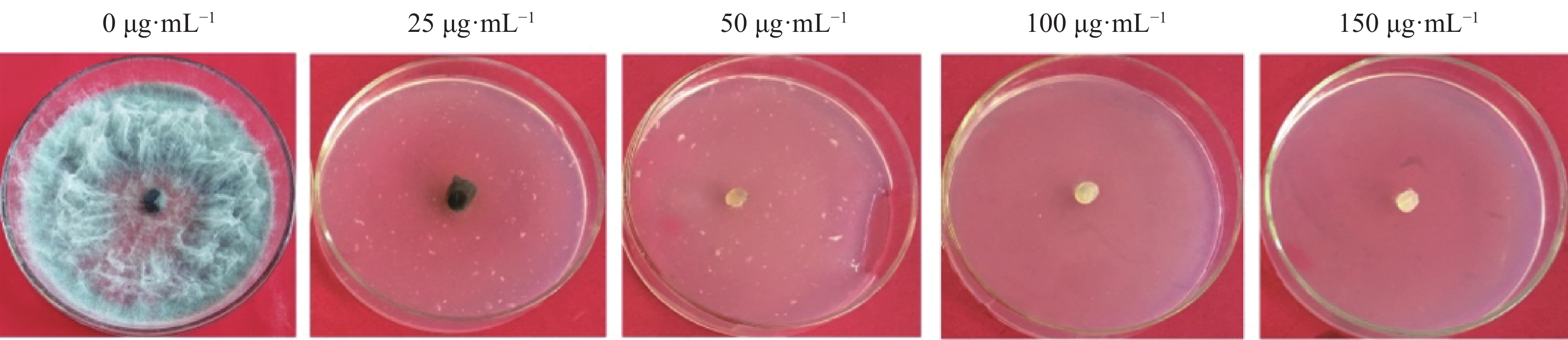
An attempt was made to select biocontrol strains against the pathogens of areca root rot, the roots and rhizosphere soil of healthy arecanut palms (Areca catechu L.) in the arecanut plantation infected with root rot disease were collected to isolate antagonistic bacterial strains against the root rot pathogens Lasiodiplodia theobromae, F.oxysporum and Thielaviopsis paradoxa by dual culture method. There were 247 bacterial strains isolated, of which a bacterial strain brj-21 was found to have good stable antagonistic effects against F. oxysporum, L. theobromae and T. paradoxa with inhibition rates of 68% ,73.66% and 74.33%, respectively. Based on morphological observation, physiological and biochemical characteristics as well as 16S rDNA sequence analysis, the strain brj-21 was identified as Alcaligenes faecalis. Furthermore, the culture medium for the strain brj-21 was optimized by single factor and orthogonal experiments, and the optimal medium was composed of 2.5 g yeast extract powder, 1 g glucose, 0.4 g MgSO4 · 7H2O and 100 mL water. The laboratory experiments showed preliminarily that the strain brj-21 had good control effect on areca root rot caused by L. theobromae, which can be developed and utilized as a potential biocontrol bacterial strain.
An attempt was made to select biocontrol strains against the pathogens of areca root rot, the roots and rhizosphere soil of healthy arecanut palms (Areca catechu L.) in the arecanut plantation infected with root rot disease were collected to isolate antagonistic bacterial strains against the root rot pathogens Lasiodiplodia theobromae, F.oxysporum and Thielaviopsis paradoxa by dual culture method. There were 247 bacterial strains isolated, of which a bacterial strain brj-21 was found to have good stable antagonistic effects against F. oxysporum, L. theobromae and T. paradoxa with inhibition rates of 68% ,73.66% and 74.33%, respectively. Based on morphological observation, physiological and biochemical characteristics as well as 16S rDNA sequence analysis, the strain brj-21 was identified as Alcaligenes faecalis. Furthermore, the culture medium for the strain brj-21 was optimized by single factor and orthogonal experiments, and the optimal medium was composed of 2.5 g yeast extract powder, 1 g glucose, 0.4 g MgSO4 · 7H2O and 100 mL water. The laboratory experiments showed preliminarily that the strain brj-21 had good control effect on areca root rot caused by L. theobromae, which can be developed and utilized as a potential biocontrol bacterial strain.
2022, 13(3): 243-248.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.006
Abstract:
Pitaya is a nutrient-rich fruit with high economic value and great development potential in tropical and subtropical region. Pitaya stem canker caused by Neoscytalidium dimidiatum is one of the most serious fungal diseases infecting pitaya, which has become a main factor restricting the development of pitaya. In order to control the disease effectively, it is necessary to study the pathogenic mechanism of the pathogen causing pitaya stem canker. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation was hence used to establish a genetic transformation system for N. dimidiatum. The effects of three main factors, concentration of A. tumefaciens, germination time of conidia, and co-culture temperature, on the transformation efficiency were analyzed, and transformants were screened. The results showed that the genetic transformation efficiency of N. dimidiatum was the highest, as high as 833 transformants / 106 conidia, when the OD600 of A. tumefaciens was 0.5, the germination time of conidia was 24 h, and the co-culture temperature was 25 ℃. Two hundred transformants were randomly selected from the genetic transformation for screening, of which 3 transformants with different colony morphology, 4 with decreased spore production, 5 with increased spore production, and 6 with decreased pathogenicity were generated.
Pitaya is a nutrient-rich fruit with high economic value and great development potential in tropical and subtropical region. Pitaya stem canker caused by Neoscytalidium dimidiatum is one of the most serious fungal diseases infecting pitaya, which has become a main factor restricting the development of pitaya. In order to control the disease effectively, it is necessary to study the pathogenic mechanism of the pathogen causing pitaya stem canker. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated genetic transformation was hence used to establish a genetic transformation system for N. dimidiatum. The effects of three main factors, concentration of A. tumefaciens, germination time of conidia, and co-culture temperature, on the transformation efficiency were analyzed, and transformants were screened. The results showed that the genetic transformation efficiency of N. dimidiatum was the highest, as high as 833 transformants / 106 conidia, when the OD600 of A. tumefaciens was 0.5, the germination time of conidia was 24 h, and the co-culture temperature was 25 ℃. Two hundred transformants were randomly selected from the genetic transformation for screening, of which 3 transformants with different colony morphology, 4 with decreased spore production, 5 with increased spore production, and 6 with decreased pathogenicity were generated.
2022, 13(3): 249-258.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.007
Abstract:
The strong concealment and difficult control of Megalurothrips usitatus lead to the extensive use of pyrethroids, which results in continuously increase in pesiticidal resistance of M. usitatus population in the field. The target of pyrethroid to pest insects is the sodium channel. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the characteristics of M. usitatus sodium channel (MuNav) and analyze its resistance molecular mechanism. MuNav (Accession number: MZ043856) was cloned by PCR with a full-length of 6 279 bp, which encodes 2093aa. MuNav is embedded with four homologous domains containing six transmembrane fragments. Homologous comparison showed that the similarity of sodium channel between M. usitatus and Thrips palmi was 94.88%, indicating their close relationship.
The strong concealment and difficult control of Megalurothrips usitatus lead to the extensive use of pyrethroids, which results in continuously increase in pesiticidal resistance of M. usitatus population in the field. The target of pyrethroid to pest insects is the sodium channel. Therefore, it is of great significance to explore the characteristics of M. usitatus sodium channel (MuNav) and analyze its resistance molecular mechanism. MuNav (Accession number: MZ043856) was cloned by PCR with a full-length of 6 279 bp, which encodes 2093aa. MuNav is embedded with four homologous domains containing six transmembrane fragments. Homologous comparison showed that the similarity of sodium channel between M. usitatus and Thrips palmi was 94.88%, indicating their close relationship.
2022, 13(3): 259-263.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.008
Abstract:
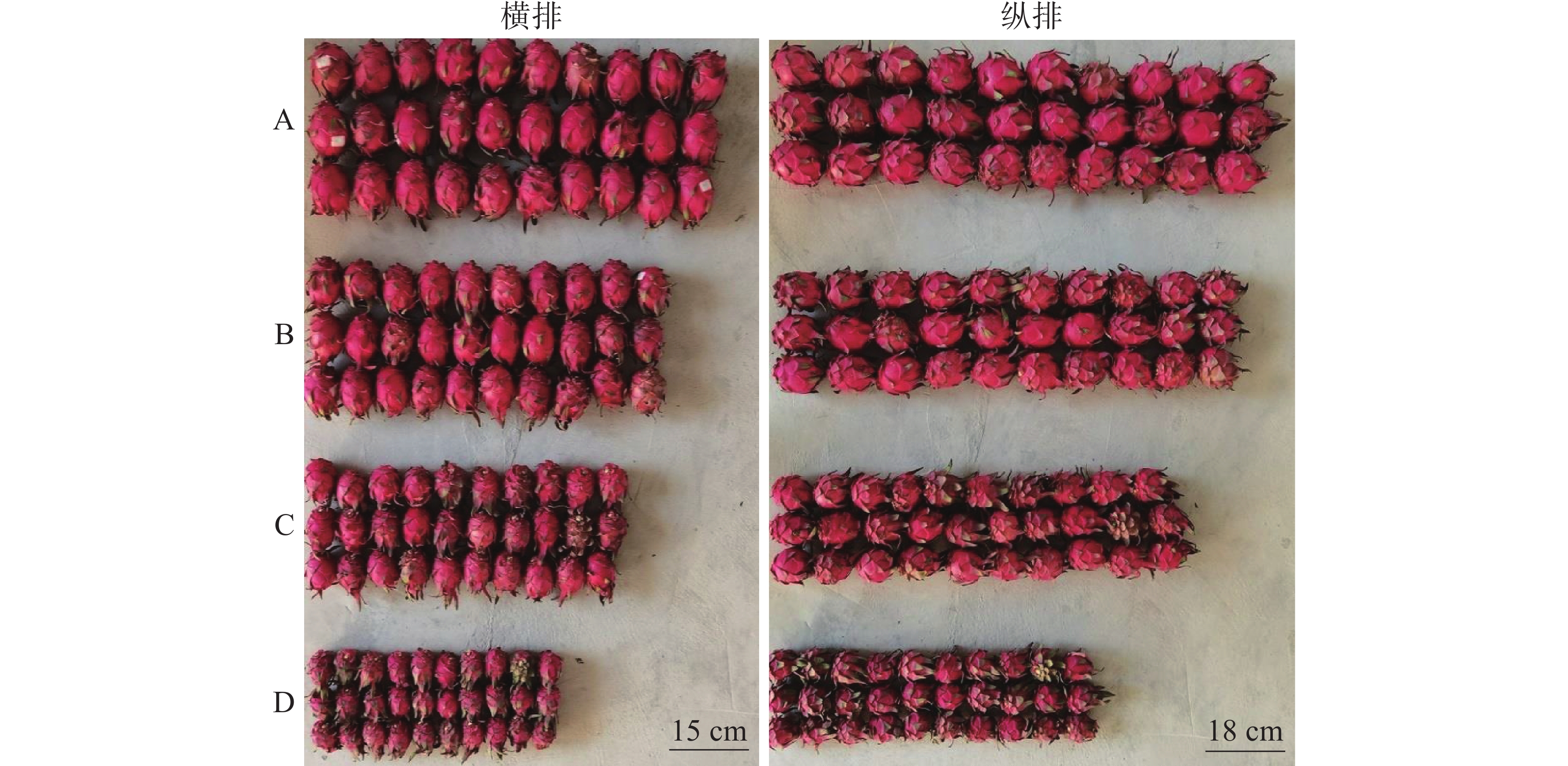
In order to explore the fruit yield formation mechanism of pitaya, taking red-flesh pitaya(Hylocereus polyrhizus) fruit as experimental material, the fruit yield traits and seed yield traits of pitaya were investigated, the correlation between fruit yield traits and seed yield traits was studied. The results showed that the seed number and seed weight of single pitaya fruits were highly correlated with the single fruit weight of pitaya; The transverse diameter and longitudinal diameter of pitaya fruit are highly correlated with single fruit weight. The 100-seed weight had no significant correlation with single fruit weight, transverse diameter and longitudinal diameter. Therefore, it is beneficial to improve the fruit yield of pitaya by adopting appropriate cultivation and management measures to increase the seed number in pitaya fruit.
In order to explore the fruit yield formation mechanism of pitaya, taking red-flesh pitaya(Hylocereus polyrhizus) fruit as experimental material, the fruit yield traits and seed yield traits of pitaya were investigated, the correlation between fruit yield traits and seed yield traits was studied. The results showed that the seed number and seed weight of single pitaya fruits were highly correlated with the single fruit weight of pitaya; The transverse diameter and longitudinal diameter of pitaya fruit are highly correlated with single fruit weight. The 100-seed weight had no significant correlation with single fruit weight, transverse diameter and longitudinal diameter. Therefore, it is beneficial to improve the fruit yield of pitaya by adopting appropriate cultivation and management measures to increase the seed number in pitaya fruit.
2022, 13(3): 264-270.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.009
Abstract:
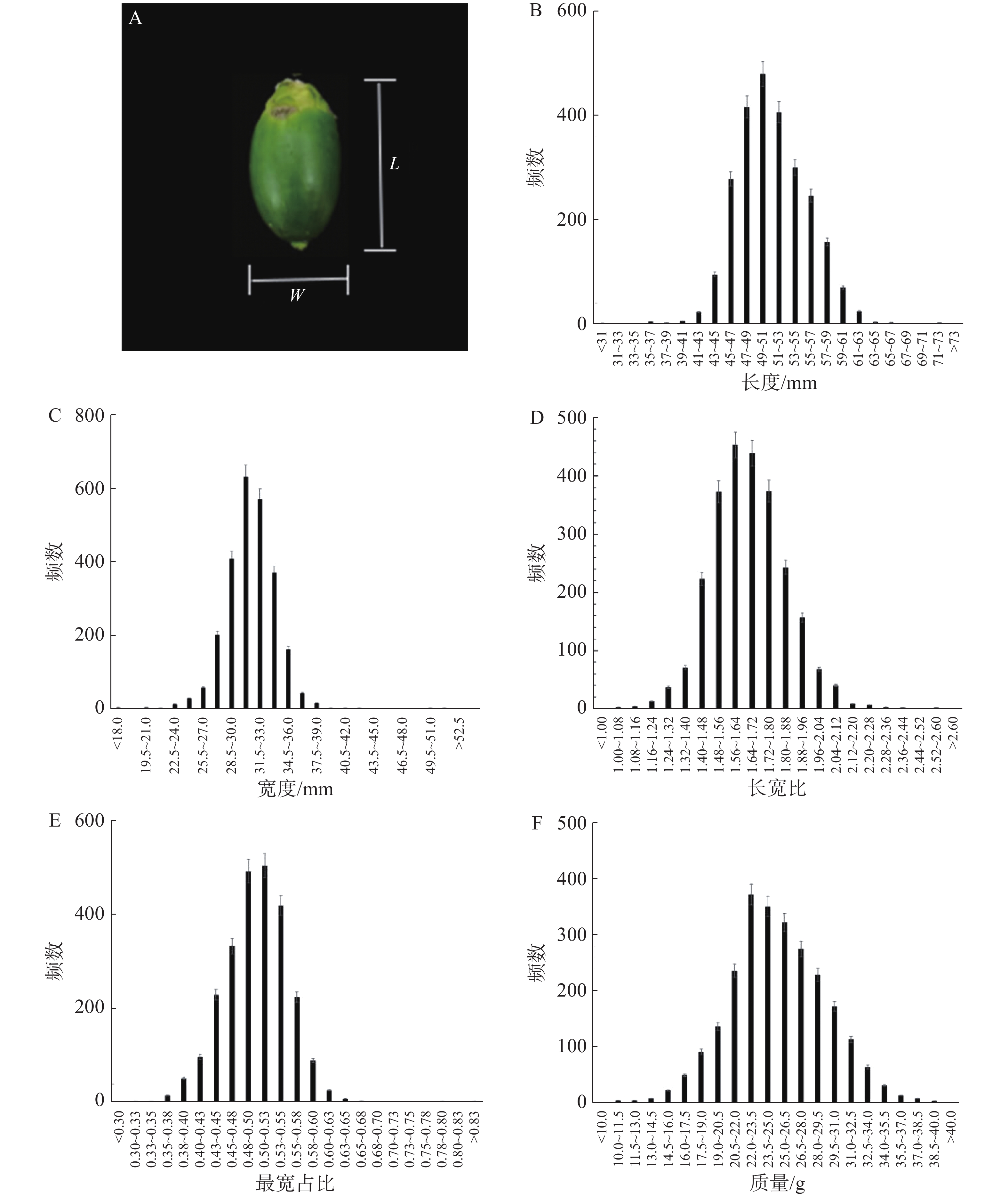
The agronomic traits of the green fruits of betel nut (Areca catechu L.) have an important effect on the quality of green fruits of betel nut after drying, which could be conducive to screening of high-quality green fruits of betel nut. In Hainan 2 518 green betel nut fruit samples were selected and their seven agronomic trait indexes were measured, including fruit length, fruit width, length-width ratio, fruit weight, the widest length-full length ratio, peel thickness and alkaloids. Of which 1 871 green betel nut fruit samples were preliminarily screened based on fruit weight, and then grouped based on length-width ratio and the widest length-full length ratio. The results showed that the good green betel nut fruit rate was the highest in the comprehensive group A1B1 (56.67%) and the lowest in the comprehensive group A2B2 (18.64%). The comprehensive group A1B1 was the best choice when green betel nut fruits were screened with the purpose of the good green fruit rate of betel nut. The green fruits of betel nut in the comprehensive groups were evaluated according to the good green betel nut fruit rate after primary processing, and a standard for three-level grading of green fruits of betel nut was developed, with which green betel nut fruits can be graded for processing according to the needs of production.
The agronomic traits of the green fruits of betel nut (Areca catechu L.) have an important effect on the quality of green fruits of betel nut after drying, which could be conducive to screening of high-quality green fruits of betel nut. In Hainan 2 518 green betel nut fruit samples were selected and their seven agronomic trait indexes were measured, including fruit length, fruit width, length-width ratio, fruit weight, the widest length-full length ratio, peel thickness and alkaloids. Of which 1 871 green betel nut fruit samples were preliminarily screened based on fruit weight, and then grouped based on length-width ratio and the widest length-full length ratio. The results showed that the good green betel nut fruit rate was the highest in the comprehensive group A1B1 (56.67%) and the lowest in the comprehensive group A2B2 (18.64%). The comprehensive group A1B1 was the best choice when green betel nut fruits were screened with the purpose of the good green fruit rate of betel nut. The green fruits of betel nut in the comprehensive groups were evaluated according to the good green betel nut fruit rate after primary processing, and a standard for three-level grading of green fruits of betel nut was developed, with which green betel nut fruits can be graded for processing according to the needs of production.
2022, 13(3): 271-280.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.010
Abstract:
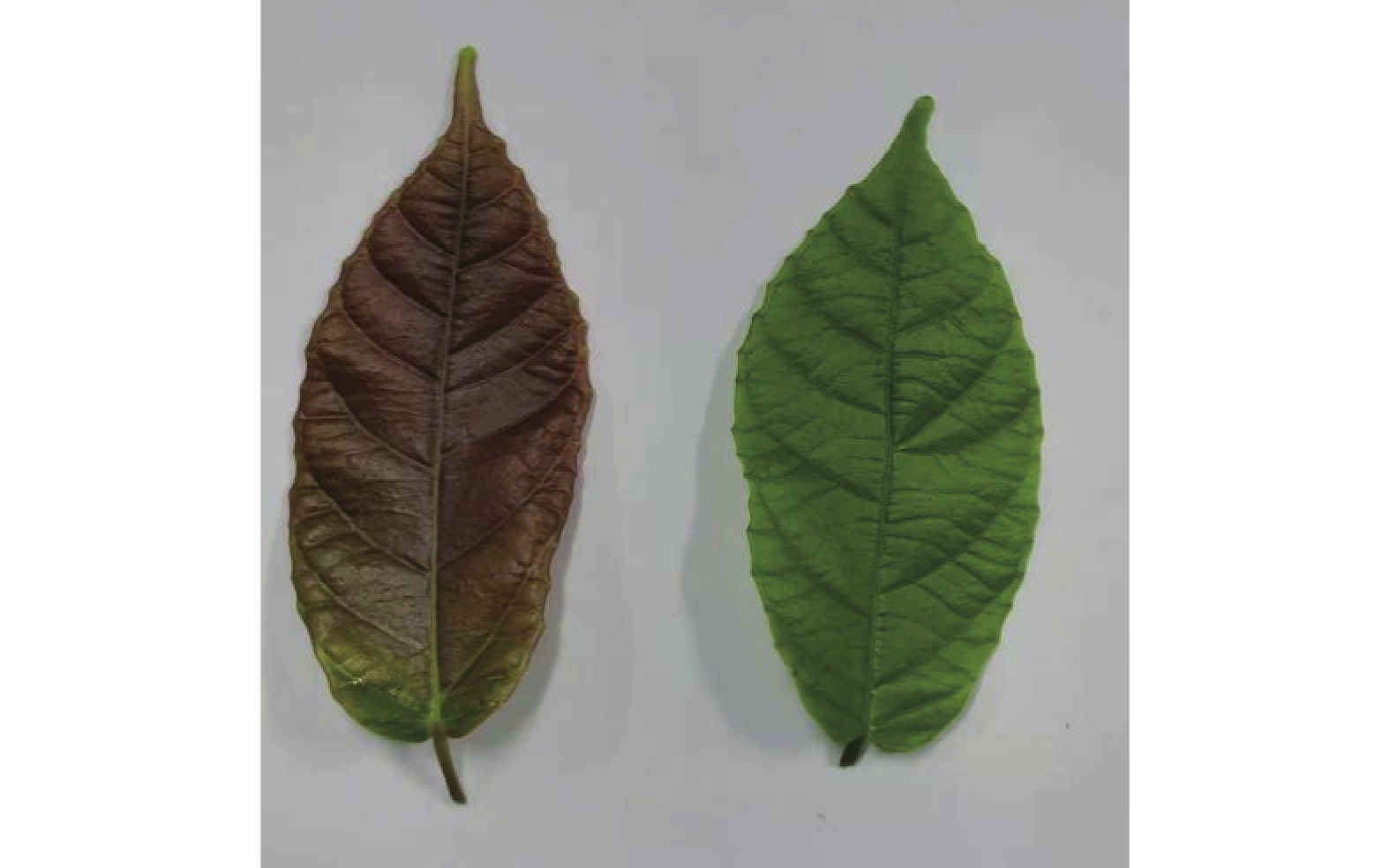
In order to clarify the difference in volatile compounds between the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of Mallotus oblongifolius and analyze the mechanism of generation of different aroma in the fresh leaves of these two varieties, the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of M. oblongifolius were collected and their low molecular weight volatile metabolites were analyzed by using the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The differential volatile metabolites in the fresh leaves of both varieties were analyzed by using multivariate analysis. GC-MS analysis showed that there were a total of 156 volatile compounds in the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of M. oblongifoliu. Principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis (OPLS-DA) found there were significant differences in 15 volatile compounds between the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of M. oblongifolius. Further analysis showed that the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of M. oblongifolius were highly significantly different in the content of nerolidol, indicating that nerolidol may be the determinant of the aroma difference between the two varieties of M. oblongifolius.
In order to clarify the difference in volatile compounds between the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of Mallotus oblongifolius and analyze the mechanism of generation of different aroma in the fresh leaves of these two varieties, the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of M. oblongifolius were collected and their low molecular weight volatile metabolites were analyzed by using the gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The differential volatile metabolites in the fresh leaves of both varieties were analyzed by using multivariate analysis. GC-MS analysis showed that there were a total of 156 volatile compounds in the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of M. oblongifoliu. Principal component analysis (PCA) and orthogonal partial least squares discrimination analysis (OPLS-DA) found there were significant differences in 15 volatile compounds between the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of M. oblongifolius. Further analysis showed that the fresh leaves of the red- and green-leaf varieties of M. oblongifolius were highly significantly different in the content of nerolidol, indicating that nerolidol may be the determinant of the aroma difference between the two varieties of M. oblongifolius.
2022, 13(3): 281-286.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.011
Abstract:
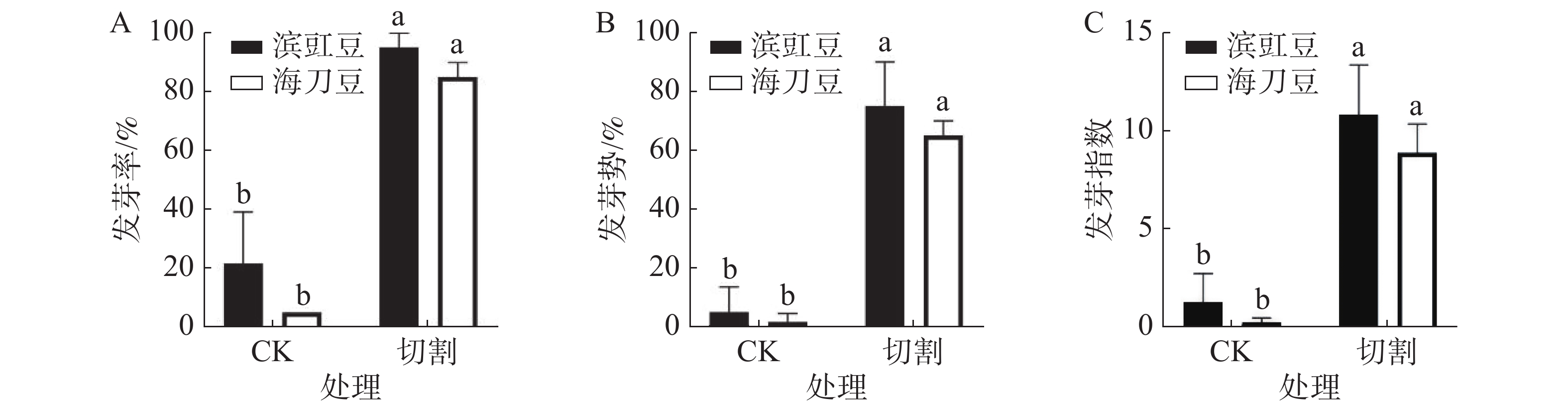
Beachpea (Vigna marina (Burm.) Merr.) and bay bean (Canavalia rosea (Sw.) DC.) are high quality forage legumes and ecological improvement plants in coastal saline-alkali land. It is of great significance to improve their propagation. Seed dormancy is a suspension in viable seeds. The morphological structure and physiological characteristics of the seeds of different plants are various, so seed scarification methods for breaking seed dormancy are also different. Seeds of beachpea and bay bean were treated by mechanical scarification (cutting), chemical scarification (with liquid nitrogen and sulfuric acid) and hot water scarification (with hot water at 80 °C), respectively to break their dormancy. The results showed that mechanical cutting, dipping in hot water (80 °C), and soaking in sulfuric acid and in liquid nitrogen had significant effects on breaking the dormancy of and promoting germination of the beachpea seeds. Compared with the other three treatments, soaking in hot water (80 °C) had the lowest cost and is easy to operate, and could be used as the main seed scarification method for pretreatment to break the dormancy of the beachpea seeds. For bay bean, seed coat is thick and hard to break the dormancy of the seeds. Soaking in sulfuric acid and mechanical cutting could effectively scarify seed coat and significantly improve germination rate of the bay bean seeds. Compared with the chemical scarification with sulfuric acid, mechanical cutting was lower in cost and easy to operate, and hence could be used as the main seed scarification method for breaking the dormancy of the bay bean seeds.
Beachpea (Vigna marina (Burm.) Merr.) and bay bean (Canavalia rosea (Sw.) DC.) are high quality forage legumes and ecological improvement plants in coastal saline-alkali land. It is of great significance to improve their propagation. Seed dormancy is a suspension in viable seeds. The morphological structure and physiological characteristics of the seeds of different plants are various, so seed scarification methods for breaking seed dormancy are also different. Seeds of beachpea and bay bean were treated by mechanical scarification (cutting), chemical scarification (with liquid nitrogen and sulfuric acid) and hot water scarification (with hot water at 80 °C), respectively to break their dormancy. The results showed that mechanical cutting, dipping in hot water (80 °C), and soaking in sulfuric acid and in liquid nitrogen had significant effects on breaking the dormancy of and promoting germination of the beachpea seeds. Compared with the other three treatments, soaking in hot water (80 °C) had the lowest cost and is easy to operate, and could be used as the main seed scarification method for pretreatment to break the dormancy of the beachpea seeds. For bay bean, seed coat is thick and hard to break the dormancy of the seeds. Soaking in sulfuric acid and mechanical cutting could effectively scarify seed coat and significantly improve germination rate of the bay bean seeds. Compared with the chemical scarification with sulfuric acid, mechanical cutting was lower in cost and easy to operate, and hence could be used as the main seed scarification method for breaking the dormancy of the bay bean seeds.
2022, 13(3): 287-296.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.012
Abstract:
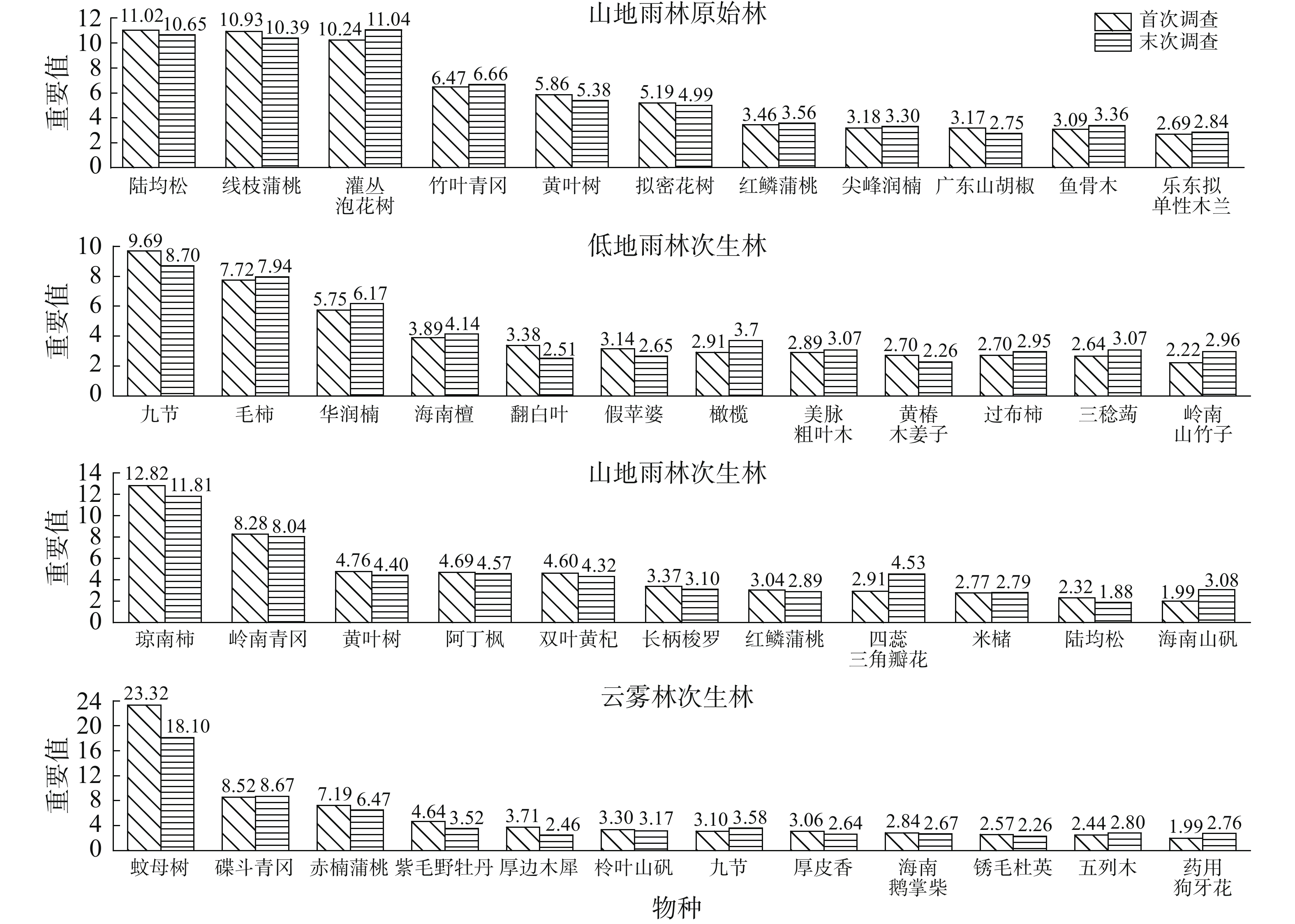
In order to study the changes of species composition and community characteristics of tropical natural forests in the central area of Hainan Island, two vegetation surveys were conducted in the primary forest of montane rain forest, secondary forest of lowland rain forest, secondary forest of mountain rain forest and secondary forest of cloud forest from 2012 to 2020. The community dynamic characteristics of the tropical natural forests in the recovery process were analyzed in terms of species composition, flora composition and leaf characteristics. The results showed that from 2012 to 2020 the Srensen index was 0.960 for the primary forest of montane rain forest, with the species composition being the most stable, 0.921 for the secondary forest of lowland rain forest, 0.889 for the secondary forest of the mountain rain forest, and 0.794 for the secondary forest of the cloud forest, with the species replacement being the most obvious during succession. With the succession the Srensen index among communities increased, and more species were the same over years. The importance value of the first dominant species decreased in each community. The important value of the dominant species of the secondary forest of the cloud forest decreased significantly, and the secondary forest of the cloud forest tended to develop into communities of multi-dominant species. With the short-term succession, the canopy density of the communities increased. Sun-loving species were gradually replaced by shade-tolerant species. Pioneer species were gradually replaced by transitional species. Hainan endemic species entered into the communities as a supplementary species. The dominant floristic elements of all the forests at the generic levels of woody plants were the tropical distribution, mainly the tropical Asia distribution (India-Malaysia). With the increase of altitude, the temperature decreases and the dominant floristic elements were low in tropical distribution and high in temperate distribution. During the period of eight years, the geographical components of flora were more complex. The leaves of the tropical natural forests showed obvious indigenous characteristics in tropical regions, and they are mainly medium leaves, single leaves, leathery leaves and entire leaves. During the period of 8 years the proportion of the forests with medium leaves increased, which indicates that the tropical natural forests under survey have been restored to some extent due to reduced human disturbance.
In order to study the changes of species composition and community characteristics of tropical natural forests in the central area of Hainan Island, two vegetation surveys were conducted in the primary forest of montane rain forest, secondary forest of lowland rain forest, secondary forest of mountain rain forest and secondary forest of cloud forest from 2012 to 2020. The community dynamic characteristics of the tropical natural forests in the recovery process were analyzed in terms of species composition, flora composition and leaf characteristics. The results showed that from 2012 to 2020 the Srensen index was 0.960 for the primary forest of montane rain forest, with the species composition being the most stable, 0.921 for the secondary forest of lowland rain forest, 0.889 for the secondary forest of the mountain rain forest, and 0.794 for the secondary forest of the cloud forest, with the species replacement being the most obvious during succession. With the succession the Srensen index among communities increased, and more species were the same over years. The importance value of the first dominant species decreased in each community. The important value of the dominant species of the secondary forest of the cloud forest decreased significantly, and the secondary forest of the cloud forest tended to develop into communities of multi-dominant species. With the short-term succession, the canopy density of the communities increased. Sun-loving species were gradually replaced by shade-tolerant species. Pioneer species were gradually replaced by transitional species. Hainan endemic species entered into the communities as a supplementary species. The dominant floristic elements of all the forests at the generic levels of woody plants were the tropical distribution, mainly the tropical Asia distribution (India-Malaysia). With the increase of altitude, the temperature decreases and the dominant floristic elements were low in tropical distribution and high in temperate distribution. During the period of eight years, the geographical components of flora were more complex. The leaves of the tropical natural forests showed obvious indigenous characteristics in tropical regions, and they are mainly medium leaves, single leaves, leathery leaves and entire leaves. During the period of 8 years the proportion of the forests with medium leaves increased, which indicates that the tropical natural forests under survey have been restored to some extent due to reduced human disturbance.
2022, 13(3): 297-299.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.013
Abstract:
Wenchang chicken is a broiler breed in Hainan, and has strong adaptability, heat resistance, and good meat quality. At present, Wenchang chickens have the problems of low feed conversion rate and high abdominal fat rate, which restrict the development of Wenchang chicken industry. An attempt was made to analyze the body fat distribution and deposition pattern of Wenchang chickens, which might provide some reference for the breeding of Wenchang chickens. Wenchang chickens at 27, 53, 79, 105 days of age and at 2, 4, 6, 8 weeks of fattening, respectively, were slaughtered, and their abdominal fat percentage, subcutaneous fat thickness, intramuscular fat content and liver crude fat content were determined. The results showed that the fat deposition in the abdomen, subcutaneous tissue and muscle were significantly increased with age (P<0.05). The fat content in the breast muscle was the highest at 6 weeks of fattening, similar to that in the leg muscle. The crude fat content in the liver had a wavy change, and was the highest at 105 days of age.
Wenchang chicken is a broiler breed in Hainan, and has strong adaptability, heat resistance, and good meat quality. At present, Wenchang chickens have the problems of low feed conversion rate and high abdominal fat rate, which restrict the development of Wenchang chicken industry. An attempt was made to analyze the body fat distribution and deposition pattern of Wenchang chickens, which might provide some reference for the breeding of Wenchang chickens. Wenchang chickens at 27, 53, 79, 105 days of age and at 2, 4, 6, 8 weeks of fattening, respectively, were slaughtered, and their abdominal fat percentage, subcutaneous fat thickness, intramuscular fat content and liver crude fat content were determined. The results showed that the fat deposition in the abdomen, subcutaneous tissue and muscle were significantly increased with age (P<0.05). The fat content in the breast muscle was the highest at 6 weeks of fattening, similar to that in the leg muscle. The crude fat content in the liver had a wavy change, and was the highest at 105 days of age.
2022, 13(3): 300-308.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.014
Abstract:
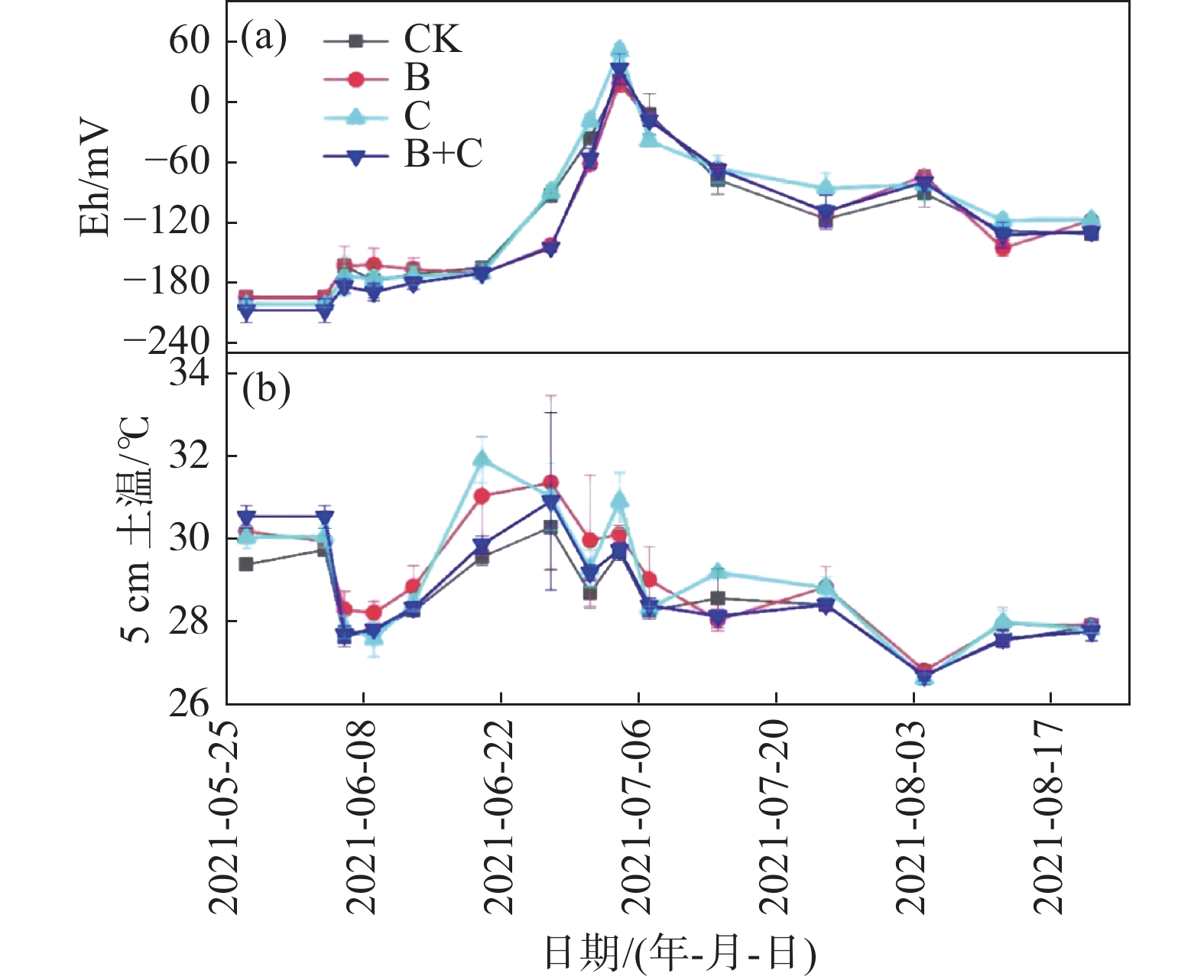
Effective measures of greenhouse gas emission mitigation in paddy field in tropical China are still unclear. In order to explore the effect of biochar, straw amendment and the mixture of biochar and straw on greenhouse gas emission in paddy fields in tropical China, a pot experiment was conducted, and four treatments were arranged, including conventional fertilizer application as control (CK), conventional fertilizer application plus 40 t·hm−2 of biochar (B), conventional fertilizer application plus 3 t·hm−2 of rice straw (C), conventional fertilizer application plus 40 t·hm−2 of biochar + 3 t·hm−2 of rice straw (B+C). Static chamber-gas chromatography was used to monitor CH4 and N2O emissions for estimation of global warming potential (GWP), and the crop yield was measured after harvest. The results showed that compared with CK Treatments B, C and B+C significantly reduced the cumulative N2O emissions by 21.43%, 21.89%, and 14.77%, respectively, but only Treatment B significantly reduced the cumulative emission of CH4 by 38.21%, while Treatments C and B+C significantly increased the cumulative emission of CH4 by 14.63% and 19.85%, respectively. Meanwhile, Treatments C and B+C significantly increased GWP, while Treatment B significantly decreased GWP (P < 0.05), which indicated that Treatment B had better greenhouse gas emission mitigation effect as compared to the other treatments. Treatments B and C significantly increased rice yield per plant by 5.22% and 8.76%, respectively, while Treatment B+C significantly decreased rice yield per plant by 18.39%. Thus, application of 40 t·hm−2 of biochar in the paddy fields in tropical China is recommended to achieve greenhouse gas emission reduction and yield increase.
Effective measures of greenhouse gas emission mitigation in paddy field in tropical China are still unclear. In order to explore the effect of biochar, straw amendment and the mixture of biochar and straw on greenhouse gas emission in paddy fields in tropical China, a pot experiment was conducted, and four treatments were arranged, including conventional fertilizer application as control (CK), conventional fertilizer application plus 40 t·hm−2 of biochar (B), conventional fertilizer application plus 3 t·hm−2 of rice straw (C), conventional fertilizer application plus 40 t·hm−2 of biochar + 3 t·hm−2 of rice straw (B+C). Static chamber-gas chromatography was used to monitor CH4 and N2O emissions for estimation of global warming potential (GWP), and the crop yield was measured after harvest. The results showed that compared with CK Treatments B, C and B+C significantly reduced the cumulative N2O emissions by 21.43%, 21.89%, and 14.77%, respectively, but only Treatment B significantly reduced the cumulative emission of CH4 by 38.21%, while Treatments C and B+C significantly increased the cumulative emission of CH4 by 14.63% and 19.85%, respectively. Meanwhile, Treatments C and B+C significantly increased GWP, while Treatment B significantly decreased GWP (P < 0.05), which indicated that Treatment B had better greenhouse gas emission mitigation effect as compared to the other treatments. Treatments B and C significantly increased rice yield per plant by 5.22% and 8.76%, respectively, while Treatment B+C significantly decreased rice yield per plant by 18.39%. Thus, application of 40 t·hm−2 of biochar in the paddy fields in tropical China is recommended to achieve greenhouse gas emission reduction and yield increase.
2022, 13(3): 309-314.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.03.015
Abstract:
With the rapid development of economy, environmental problems have attracted much attention. Long-term practice has proved that chemical control of crop pests will produce pesticidal residues and cause pollution to the environment to some degrees, whereas biological control is much safer and environment-friendly. Entomopathogenic fungi, as an important biocontrol agent, can rationally control insect pests and protect the original ecological environment. They can not only promote the sustainable development of agricultural production, but also ensure the green production and safety of food in China. In recent years biocontrol has played an excellent role in the prevention and control of crop pests. In this review representative species of entomopathogenic fungi, such as beauveria, metarhizium, paecilamyces and verticillium, were described separately in terms of colony characteristics, control, pathogenesis and virulence, and a progress in application of the entomopathogenic fungi in agriculture in China was reviewed in respect of characteristics of biocontrol products, preparation of biocontrol products and their release for application. This review might provide reference for ecological security and development and application of entomopathogenic fungi in China.
With the rapid development of economy, environmental problems have attracted much attention. Long-term practice has proved that chemical control of crop pests will produce pesticidal residues and cause pollution to the environment to some degrees, whereas biological control is much safer and environment-friendly. Entomopathogenic fungi, as an important biocontrol agent, can rationally control insect pests and protect the original ecological environment. They can not only promote the sustainable development of agricultural production, but also ensure the green production and safety of food in China. In recent years biocontrol has played an excellent role in the prevention and control of crop pests. In this review representative species of entomopathogenic fungi, such as beauveria, metarhizium, paecilamyces and verticillium, were described separately in terms of colony characteristics, control, pathogenesis and virulence, and a progress in application of the entomopathogenic fungi in agriculture in China was reviewed in respect of characteristics of biocontrol products, preparation of biocontrol products and their release for application. This review might provide reference for ecological security and development and application of entomopathogenic fungi in China.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 2115KB
PDF 2115KB









 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS