2022 Vol. 13, No. 2
2022, 13(2): 101-111.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.001
Abstract:
Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park is one of the first national parks officially established in China, and it is also the only national park with expressway in China. In order to reveal the possible impact of the expressway and other roads on landscape patterns and integrity of ecosystem of the national park, the landscape change trend of different level of roads, the influence on the integrity of the ecosystem and the landscape pattern caused by expressway, national road and provincial road were analyzed by using buffer zone analysis method based on the road distribution and land use data in 2000, 2010, and 2019 (the expressway completed). The analysis show that the road length and density in national parks increased by 2, 134.6 km and 0.500 km/km2 in the national park from 2000 to 2019, respectively. The length of rural and other smaller roads increased by 2030 km from 2000 to 2010. The expressway was completed and the Provincial Road 310 was upgraded to the National Road 361 in 2019. A descent of the patch density index (PD) and landscape shape index (LSI) and an ascent of the aggregation index (AI) on both sides of the expressway, national road and provincial road were observed in the range of 0 ~ 500 m, 0 ~ 300 m and 0 ~ 250 m, respectively, followed by a gentle movement. The maximum influence ranges for the expressway, national road and provincial road were 500 m, 300 m and 250 m, respectively. The area of cultivated land, woodland, grassland and open forest land decreased within the area affected by roads; the area of woodland and grassland near expressway and provincial road, and the area of cultivated land near national road showed the greatest descent; the area of water, shrub land, construction land and other woodland (including the orchards) increased; the area of other woodland (including the orchards) around expressway, national road, and provincial road showed the greatest ascent from 2000 to 2019. Within the influence range of roads, LSI index, PD index and splitting index (SPLIT) increased slightly, while contagion index (CONTAG) and AI decreased slightly. At present, roads have a slight effect on the landscape of the national park. However, it is still necessary to pay attention to the possible impact of roads on the authenticity and integrity of the national park ecosystem, which may be affected by the obvious cumulative effect and spreading effect of roads. It is recommended that further research is needed on the confluence and purification of the runoff from large roads such as expressway, building of ecological corridors on both sides of the roads, long-term environmental monitoring, etc.
Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park is one of the first national parks officially established in China, and it is also the only national park with expressway in China. In order to reveal the possible impact of the expressway and other roads on landscape patterns and integrity of ecosystem of the national park, the landscape change trend of different level of roads, the influence on the integrity of the ecosystem and the landscape pattern caused by expressway, national road and provincial road were analyzed by using buffer zone analysis method based on the road distribution and land use data in 2000, 2010, and 2019 (the expressway completed). The analysis show that the road length and density in national parks increased by 2, 134.6 km and 0.500 km/km2 in the national park from 2000 to 2019, respectively. The length of rural and other smaller roads increased by 2030 km from 2000 to 2010. The expressway was completed and the Provincial Road 310 was upgraded to the National Road 361 in 2019. A descent of the patch density index (PD) and landscape shape index (LSI) and an ascent of the aggregation index (AI) on both sides of the expressway, national road and provincial road were observed in the range of 0 ~ 500 m, 0 ~ 300 m and 0 ~ 250 m, respectively, followed by a gentle movement. The maximum influence ranges for the expressway, national road and provincial road were 500 m, 300 m and 250 m, respectively. The area of cultivated land, woodland, grassland and open forest land decreased within the area affected by roads; the area of woodland and grassland near expressway and provincial road, and the area of cultivated land near national road showed the greatest descent; the area of water, shrub land, construction land and other woodland (including the orchards) increased; the area of other woodland (including the orchards) around expressway, national road, and provincial road showed the greatest ascent from 2000 to 2019. Within the influence range of roads, LSI index, PD index and splitting index (SPLIT) increased slightly, while contagion index (CONTAG) and AI decreased slightly. At present, roads have a slight effect on the landscape of the national park. However, it is still necessary to pay attention to the possible impact of roads on the authenticity and integrity of the national park ecosystem, which may be affected by the obvious cumulative effect and spreading effect of roads. It is recommended that further research is needed on the confluence and purification of the runoff from large roads such as expressway, building of ecological corridors on both sides of the roads, long-term environmental monitoring, etc.
2022, 13(2): 112-119.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.002
Abstract:
Biodiversity monitoring is the core basis for the protection of ecosystem integrity and authenticity in national parks. In order to improve the ability of biodiversity monitoring and explore the feasibility of application of remote sensing in biodiversity monitoring, the relationship between biodiversity at landscape and species scale in Giant Panda National Park (Sichuan area) was analyzed by using spatial mapping, redundancy analysis (RDA) and other technical methods. The results showed that the species diversity of the Giant Panda National Park (Sichuan area) was generally higher, especially in Baoxing, Tianquan and Wenchuan counties. The park boasts of 5675 species of plants belonging to 1302 genera and 231 families, and 1049 species of animals belonging to 141 families and 39 orders. The landscape diversity of the Giant Panda National Park (Sichuan area) is higher in the north than in the south, and higher in the mountain valley near the northwest of Sichuan than in the Chengdu plain. The model interpretation rate of landscape diversity on species diversity was 41.64%. Species diversity had a high positive correlation with landscape indices the patch richness (PR) and the standard deviation of Euclidean nearest neighbor distance (ENN_SD), and a high negative correlation with the patch richness density (PRD). It is suggested to give full play to the advantages of remote sensing technology to strengthen the dynamic monitoring of the biodiversity in the Giant Panda National Park at the landscape scale. It is also suggested to further strengthen the baseline inventory of biodiversity species and integrate the existing databases of various species and genetic resources so as to find out the resources as soon as possible and provide objective policy suggestions for the construction of the Giant Panda National Park.
Biodiversity monitoring is the core basis for the protection of ecosystem integrity and authenticity in national parks. In order to improve the ability of biodiversity monitoring and explore the feasibility of application of remote sensing in biodiversity monitoring, the relationship between biodiversity at landscape and species scale in Giant Panda National Park (Sichuan area) was analyzed by using spatial mapping, redundancy analysis (RDA) and other technical methods. The results showed that the species diversity of the Giant Panda National Park (Sichuan area) was generally higher, especially in Baoxing, Tianquan and Wenchuan counties. The park boasts of 5675 species of plants belonging to 1302 genera and 231 families, and 1049 species of animals belonging to 141 families and 39 orders. The landscape diversity of the Giant Panda National Park (Sichuan area) is higher in the north than in the south, and higher in the mountain valley near the northwest of Sichuan than in the Chengdu plain. The model interpretation rate of landscape diversity on species diversity was 41.64%. Species diversity had a high positive correlation with landscape indices the patch richness (PR) and the standard deviation of Euclidean nearest neighbor distance (ENN_SD), and a high negative correlation with the patch richness density (PRD). It is suggested to give full play to the advantages of remote sensing technology to strengthen the dynamic monitoring of the biodiversity in the Giant Panda National Park at the landscape scale. It is also suggested to further strengthen the baseline inventory of biodiversity species and integrate the existing databases of various species and genetic resources so as to find out the resources as soon as possible and provide objective policy suggestions for the construction of the Giant Panda National Park.
2022, 13(2): 120-126.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.003
Abstract:
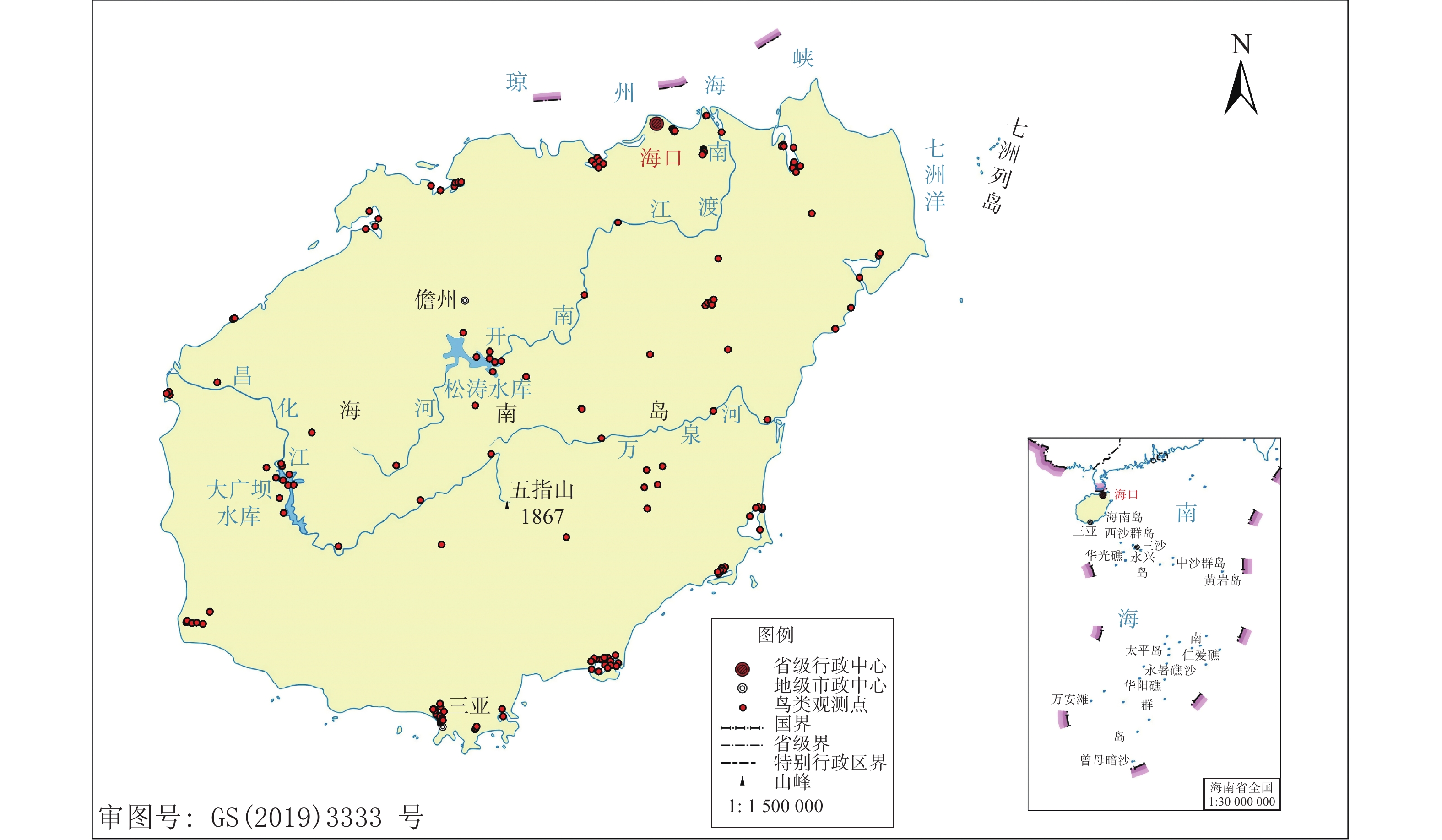
A bird survey was carried out in 32 wetlands of Hainan Island in December 2020 and May 2021, and a total of 215 transect lines and 157 survey points were established for bird inventory. The survey recorded 34673 birds of 206 species, belonging to 17 orders and 61 families. There are 4 species of birds found in the list of the national first-class conservation, and 34 species of birds in the list of the national second-class conservation. The number of waders and songbirds accounted for the majority of the birds recorded, which are 59.9% and 32.2%, respectively. The survey recorded 28 dominant and common birds recorded, such as Egretta garzetta, Spodiopsar sericeus, Charadrius mongolus, Bubulcus coromandus, etc., which accounted for 78% of the total bird records in the wetlands of Hainan Island. The Shannon Wiener index is the highest in the riverine wetlands (5.225), and the lowest in the lacustrine wetlands (2.843); the Pielo index is the highest in the marshy wetlands (0.776) and the lowest in the man-made wetland (0.618); the bird similarity is the highest in the riverine wetlands and the man-made wetlands (0.67), and the lowest (0.22) in the coastal wetland and the lacustrine wetlands.
A bird survey was carried out in 32 wetlands of Hainan Island in December 2020 and May 2021, and a total of 215 transect lines and 157 survey points were established for bird inventory. The survey recorded 34673 birds of 206 species, belonging to 17 orders and 61 families. There are 4 species of birds found in the list of the national first-class conservation, and 34 species of birds in the list of the national second-class conservation. The number of waders and songbirds accounted for the majority of the birds recorded, which are 59.9% and 32.2%, respectively. The survey recorded 28 dominant and common birds recorded, such as Egretta garzetta, Spodiopsar sericeus, Charadrius mongolus, Bubulcus coromandus, etc., which accounted for 78% of the total bird records in the wetlands of Hainan Island. The Shannon Wiener index is the highest in the riverine wetlands (5.225), and the lowest in the lacustrine wetlands (2.843); the Pielo index is the highest in the marshy wetlands (0.776) and the lowest in the man-made wetland (0.618); the bird similarity is the highest in the riverine wetlands and the man-made wetlands (0.67), and the lowest (0.22) in the coastal wetland and the lacustrine wetlands.
2022, 13(2): 127-135.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.004
Abstract:
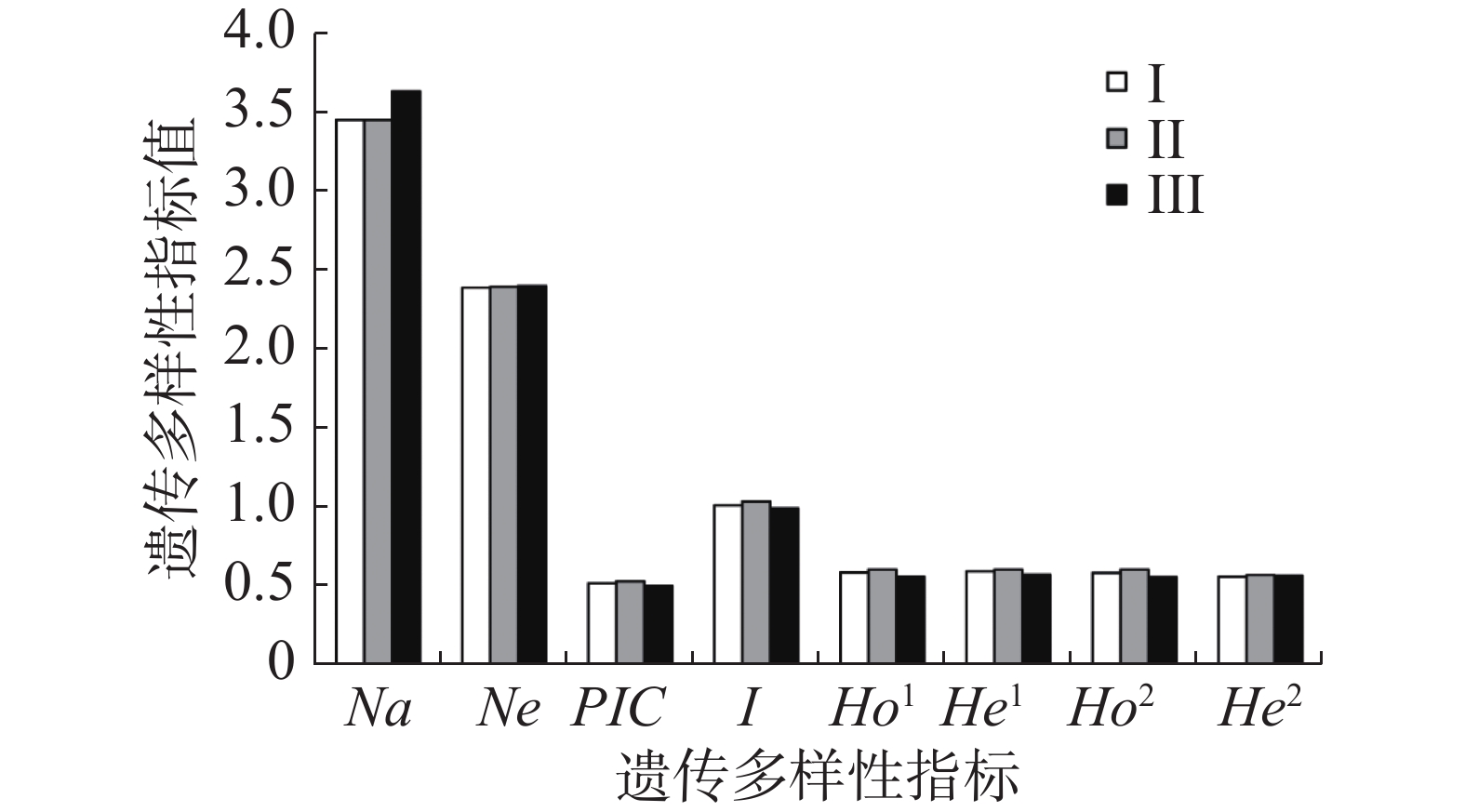
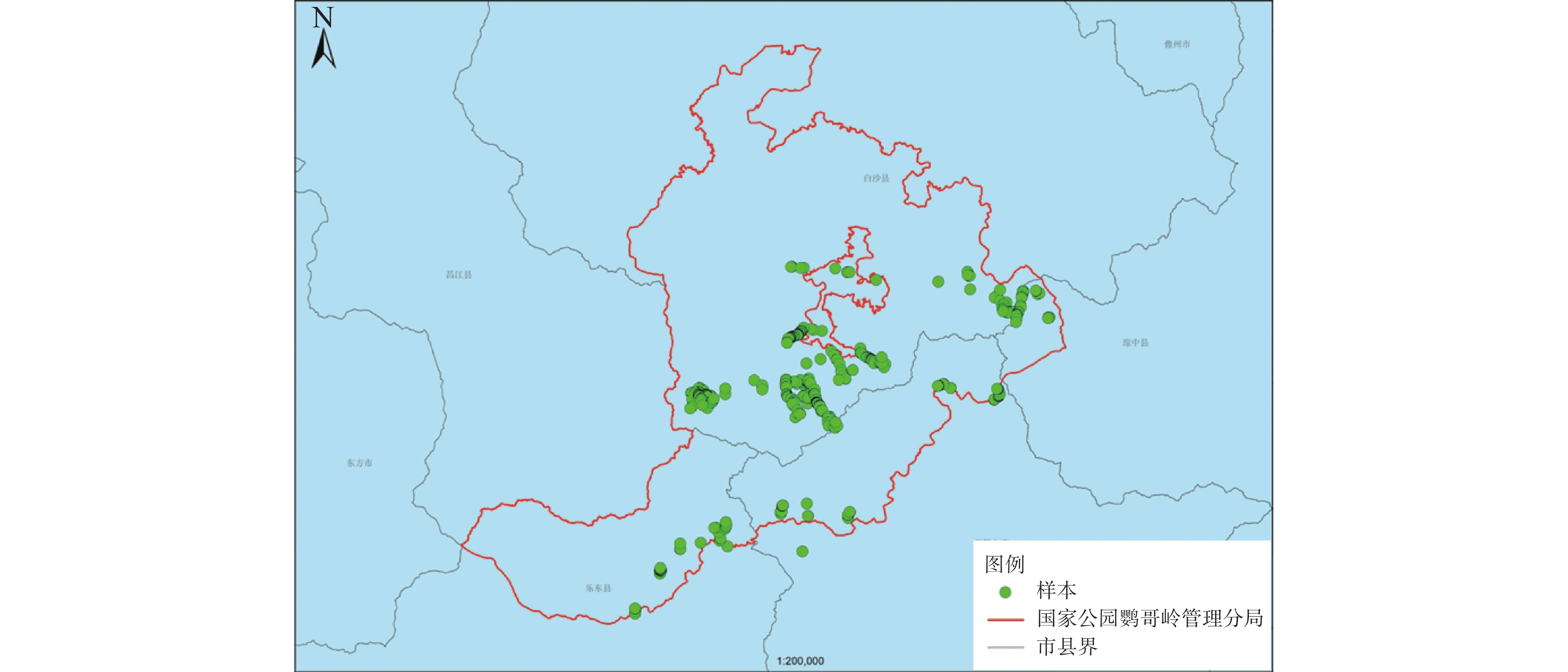
In order to understand the genetic diversity of Hopea reticulata Tardieu and its genetic structure among different age groups, the genetic diversity of H. reticulate was assessed by using 11 pairs of microsatellite (simple sequence repeat, SSR) markers, and then divided into three age groups, namely juvenile, intermediate and mature groups, according to DBH to determine the genetic differences among different age groups. The mechanism of endangerment of H. reticulate was explored, based on which a strategy for conservation of H. reticulate was proposed from a genetic perspective. The results show that the number of alleles and expected heterozygosis of H. reticulate (Na=3.636, He=0.599) were lower than those of H. dryobalanoides (Na=5.600, He=0.678), but obviously higher than those of H. hainanensis (Na=2.417, He=0.432). There was no apparent difference in genetic diversity and composition among the three age groups. The number of low-frequency alleles in H. reticulata decreased significantly compared with that of non-endangered species of Dipterocarpaceae. It is likely that many low-frequency alleles in H. reticulata were lost due to the reduction of population size caused by a bottleneck event. However, considering a relatively large population size, H. reticulata gave a higher genetic diversity than H. hainanensis. Based on the results of the genetic diversity analysis by using the SSR markers, it is suggested to promote the population renewal through artificial propagation to restore the genetic diversity and evolutionary potential for the stable survival of H. reticulate while maintain the existing variation of H. reticulate.
In order to understand the genetic diversity of Hopea reticulata Tardieu and its genetic structure among different age groups, the genetic diversity of H. reticulate was assessed by using 11 pairs of microsatellite (simple sequence repeat, SSR) markers, and then divided into three age groups, namely juvenile, intermediate and mature groups, according to DBH to determine the genetic differences among different age groups. The mechanism of endangerment of H. reticulate was explored, based on which a strategy for conservation of H. reticulate was proposed from a genetic perspective. The results show that the number of alleles and expected heterozygosis of H. reticulate (Na=3.636, He=0.599) were lower than those of H. dryobalanoides (Na=5.600, He=0.678), but obviously higher than those of H. hainanensis (Na=2.417, He=0.432). There was no apparent difference in genetic diversity and composition among the three age groups. The number of low-frequency alleles in H. reticulata decreased significantly compared with that of non-endangered species of Dipterocarpaceae. It is likely that many low-frequency alleles in H. reticulata were lost due to the reduction of population size caused by a bottleneck event. However, considering a relatively large population size, H. reticulata gave a higher genetic diversity than H. hainanensis. Based on the results of the genetic diversity analysis by using the SSR markers, it is suggested to promote the population renewal through artificial propagation to restore the genetic diversity and evolutionary potential for the stable survival of H. reticulate while maintain the existing variation of H. reticulate.
2022, 13(2): 136-148.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.005
Abstract:
In order to find out the general situation of orchid germplasm resources in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park and formulate reasonable conservation strategies, a comprehensive evaluation system for urgency of orchid conservation was established based on an overall survey of wild orchid plants in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park to analyze the causes of endangerment, and screen out key orchid species for conservation. The results showed that among the 81 genera and 230 species of orchids under survey a total of 98 species needed to be monitored and conserved first, with 12 of the top ten species being selected (3 species were tied for the 10th species). There were 14 narrowly distributed orchid species, accounting for 6.09 % of the species under survey, and there were 7 critically endangered species, 26 endangered species, and 48 vulnerable species, all of which accounted for 35.22 % of the species under survey. There were 148 threatened orchid species, accounting for 64.35% of the species under survey. A total of 17 orchid hotspots were screened out. The diversity of orchid species in the study area increased compared with the earlier studies, and habitat destruction was found to have the greatest impact on orchids. A priority conservation and monitoring area for wild orchids in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park was hence established, and more orchid species have been conserved in this area, which might provide baseline data and theoretical support for formulating strategies for reasonable, scientific and effective conservation of orchids.
In order to find out the general situation of orchid germplasm resources in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park and formulate reasonable conservation strategies, a comprehensive evaluation system for urgency of orchid conservation was established based on an overall survey of wild orchid plants in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park to analyze the causes of endangerment, and screen out key orchid species for conservation. The results showed that among the 81 genera and 230 species of orchids under survey a total of 98 species needed to be monitored and conserved first, with 12 of the top ten species being selected (3 species were tied for the 10th species). There were 14 narrowly distributed orchid species, accounting for 6.09 % of the species under survey, and there were 7 critically endangered species, 26 endangered species, and 48 vulnerable species, all of which accounted for 35.22 % of the species under survey. There were 148 threatened orchid species, accounting for 64.35% of the species under survey. A total of 17 orchid hotspots were screened out. The diversity of orchid species in the study area increased compared with the earlier studies, and habitat destruction was found to have the greatest impact on orchids. A priority conservation and monitoring area for wild orchids in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park was hence established, and more orchid species have been conserved in this area, which might provide baseline data and theoretical support for formulating strategies for reasonable, scientific and effective conservation of orchids.
2022, 13(2): 149-159.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.006
Abstract:
The relationship between species composition and distribution of epiphytic orchids and ecological factors is of great significance for epiphytic orchids conservation and habitat protection. A survey was made of the epiphytic orchid species in the Yinggeling Mountain section of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. The influence of ecological factors on the composition of epiphytic orchids was analyzed by using Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) and the total effect and the net effect of the factors on the epiphytic orchid species were calculated by using partial CCA. The epiphytic orchid species richness and abundance in environmental changes at different gradients were analyzed. Results showed that the selected 9 ecological factors explained 7.8% of the variation of the species, with their net effect being in the order of vegetation type > bark type > annual average air temperature > average of monthly difference between the highest and lowest temperatures > precipitation in the driest month > altitude > canopy density > slope aspect > slope gradient. The factors except the slope gradient had significant net effect. The species richness of the epiphytic orchids increased and then decreased with the increase of altitude, and the species richness was the highest at the altitude of between 700 m and 900 m, but the abundance of the epiphytic orchids showed an increasing trend. The species richness and abundance of the epiphytic orchids were higher on the gentle slopes, and lower on the sunny and semi-sunny slopes than on the shady and semi-shady slopes. The rough bark was more likely to give rise to epiphytic orchids, and the covering on the barks provided comfortable growth environment for epiphytic orchids. Most epiphytic orchids tended to grow in a low-light environment. The epiphytic orchid species were the most abundant in tropical lowland rainforest, and the epiphytic orchids had higher dominance in tropical coniferous forests. The epiphytic orchids tended to be distributed in the habitats at low temperature, and the difference between monthly maximum temperature and monthly minimum temperature was (7.8 − 7.85) ℃. The species richness and abundance of the epiphytic orchids were higher in the environment with higher rainfall in the Yinggeling mountain.
The relationship between species composition and distribution of epiphytic orchids and ecological factors is of great significance for epiphytic orchids conservation and habitat protection. A survey was made of the epiphytic orchid species in the Yinggeling Mountain section of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. The influence of ecological factors on the composition of epiphytic orchids was analyzed by using Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) and the total effect and the net effect of the factors on the epiphytic orchid species were calculated by using partial CCA. The epiphytic orchid species richness and abundance in environmental changes at different gradients were analyzed. Results showed that the selected 9 ecological factors explained 7.8% of the variation of the species, with their net effect being in the order of vegetation type > bark type > annual average air temperature > average of monthly difference between the highest and lowest temperatures > precipitation in the driest month > altitude > canopy density > slope aspect > slope gradient. The factors except the slope gradient had significant net effect. The species richness of the epiphytic orchids increased and then decreased with the increase of altitude, and the species richness was the highest at the altitude of between 700 m and 900 m, but the abundance of the epiphytic orchids showed an increasing trend. The species richness and abundance of the epiphytic orchids were higher on the gentle slopes, and lower on the sunny and semi-sunny slopes than on the shady and semi-shady slopes. The rough bark was more likely to give rise to epiphytic orchids, and the covering on the barks provided comfortable growth environment for epiphytic orchids. Most epiphytic orchids tended to grow in a low-light environment. The epiphytic orchid species were the most abundant in tropical lowland rainforest, and the epiphytic orchids had higher dominance in tropical coniferous forests. The epiphytic orchids tended to be distributed in the habitats at low temperature, and the difference between monthly maximum temperature and monthly minimum temperature was (7.8 − 7.85) ℃. The species richness and abundance of the epiphytic orchids were higher in the environment with higher rainfall in the Yinggeling mountain.
2022, 13(2): 160-165.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.007
Abstract:
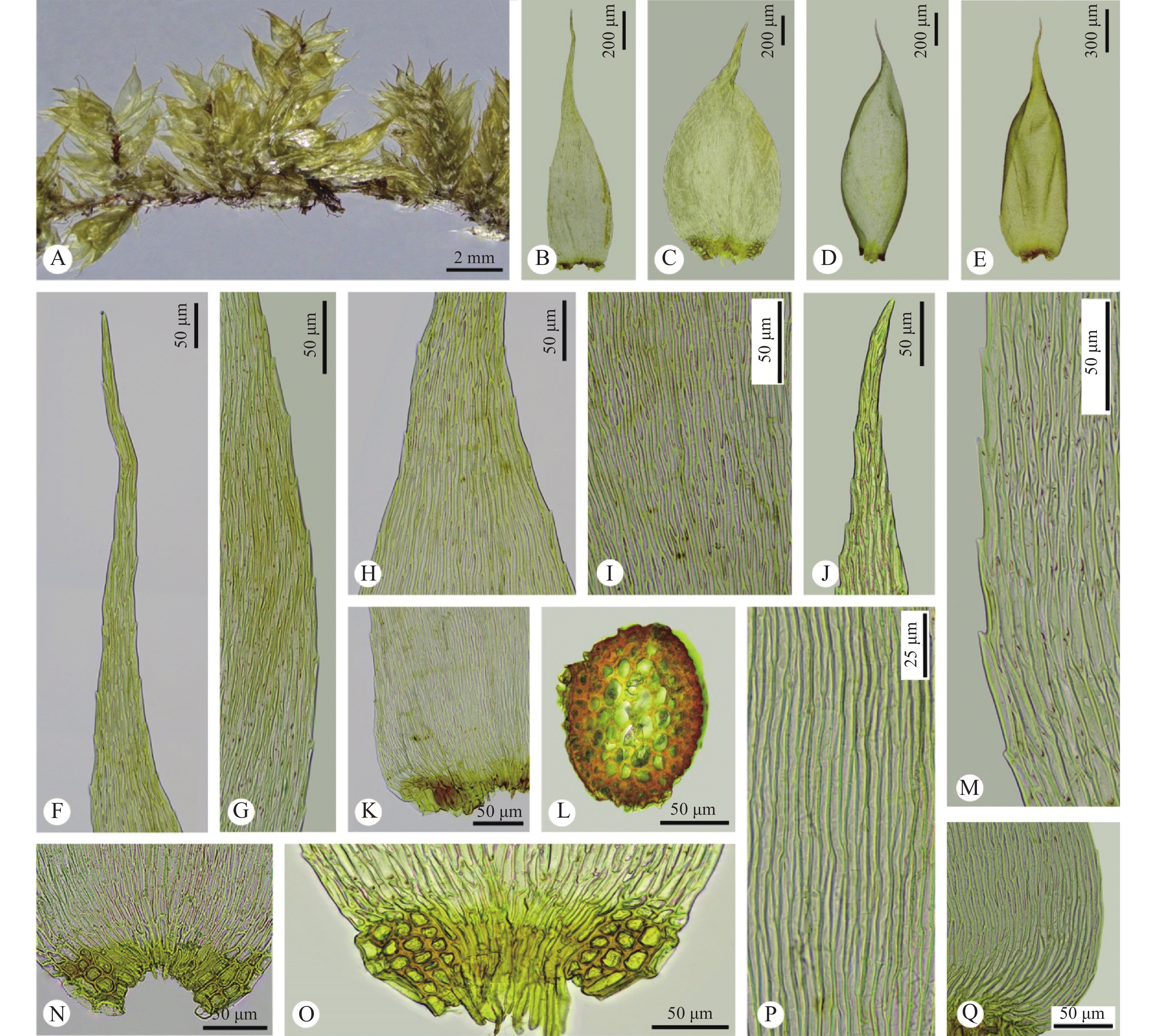
Field investigations were conducted in tropical montane cloud forests of Bawangling National Nature Reserve from 2019 to 2020 to explore the distribution and species diversity of epiphytic mosses in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. Here, we firstly found and reported the genus Yakushimabryum H.Akiyama, Ying Chang, T.Yamag. & B.C.Tan and two species, namely Yakushimabryum tonkinense (Broth. & Paris) H.Akiyama and Trachycladiella sparsa (Mitt.) M.Menzel based on species taxonomic identification and pertinent literature, which were new additions to the bryoflora of Hainan Province, China. Their detailed information, including the description and pictures of morphological characteristics, habitats and geographical distribution were provided. The new records enriched the diversity of epiphytic bryophytes in Hainan and China.
Field investigations were conducted in tropical montane cloud forests of Bawangling National Nature Reserve from 2019 to 2020 to explore the distribution and species diversity of epiphytic mosses in Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park. Here, we firstly found and reported the genus Yakushimabryum H.Akiyama, Ying Chang, T.Yamag. & B.C.Tan and two species, namely Yakushimabryum tonkinense (Broth. & Paris) H.Akiyama and Trachycladiella sparsa (Mitt.) M.Menzel based on species taxonomic identification and pertinent literature, which were new additions to the bryoflora of Hainan Province, China. Their detailed information, including the description and pictures of morphological characteristics, habitats and geographical distribution were provided. The new records enriched the diversity of epiphytic bryophytes in Hainan and China.
2022, 13(2): 166-176.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.008
Abstract:
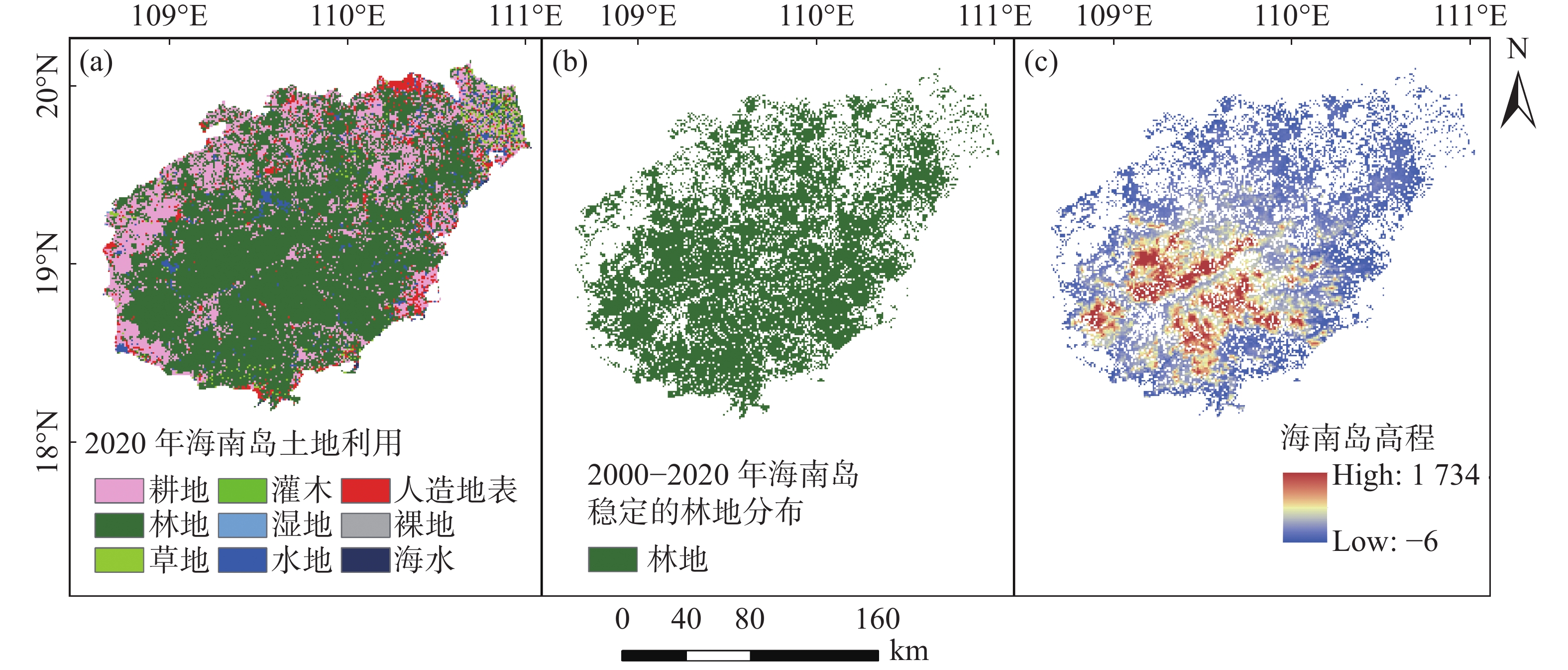
An attempt was made to analyze the spatial and temporal variation of the net ecosystem productivity (NEP) of forests in Hainan Island and its association with climate and topography. The spatial and temporal variation patterns of NEP in different seasons over the past 20 years was analyzed by using time series analysis and one-dimensional linear regression methods, and the contribution of climate and topography factors was assessed based on Boosted Regression Trees (BRT). The results showed that the NEP of the forests in Hainan Island showed significant seasonal changes, and that the overall NEP showed a non-significant decreasing trend in the last 20 years, with a rate of change of −0.57 g·m−2 ·a (P > 0.05). The forests in Hainan Island were carbon sinks at three time scales: interannual, dry season and wet season, and the intensity of carbon sinks in the wet season was higher than that in the dry season. Spatially, interannual NEP and wet-season NEP showed a significant increasing trend in the northeastern part of Hainan Island, and a significant decreasing trend in the central and western part of Hainan Island. The BRT analysis showed that the contribution of elevation to NEP was 45.46% (interannual), 40.58% (dry season), and 21.88% (wet season), respectively. The trend correlation and multiple linear regression analysis showed that NEP had significant trend correlation with precipitation. The NEP of low-elevation forests in Hainan Island was influenced by temperature and precipitation. In the dry season, precipitation had a significant negative contribution (−53%, P < 0.05) to the NEP of low elevation forests in Hainan Island, while in the wet season, temperature had a significant positive contribution (90%,P< 0.05) to the NEP of low elevation forests in Hainan Island.
An attempt was made to analyze the spatial and temporal variation of the net ecosystem productivity (NEP) of forests in Hainan Island and its association with climate and topography. The spatial and temporal variation patterns of NEP in different seasons over the past 20 years was analyzed by using time series analysis and one-dimensional linear regression methods, and the contribution of climate and topography factors was assessed based on Boosted Regression Trees (BRT). The results showed that the NEP of the forests in Hainan Island showed significant seasonal changes, and that the overall NEP showed a non-significant decreasing trend in the last 20 years, with a rate of change of −0.57 g·m−2 ·a (P > 0.05). The forests in Hainan Island were carbon sinks at three time scales: interannual, dry season and wet season, and the intensity of carbon sinks in the wet season was higher than that in the dry season. Spatially, interannual NEP and wet-season NEP showed a significant increasing trend in the northeastern part of Hainan Island, and a significant decreasing trend in the central and western part of Hainan Island. The BRT analysis showed that the contribution of elevation to NEP was 45.46% (interannual), 40.58% (dry season), and 21.88% (wet season), respectively. The trend correlation and multiple linear regression analysis showed that NEP had significant trend correlation with precipitation. The NEP of low-elevation forests in Hainan Island was influenced by temperature and precipitation. In the dry season, precipitation had a significant negative contribution (−53%, P < 0.05) to the NEP of low elevation forests in Hainan Island, while in the wet season, temperature had a significant positive contribution (90%,P< 0.05) to the NEP of low elevation forests in Hainan Island.
2022, 13(2): 177-184.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.009
Abstract:
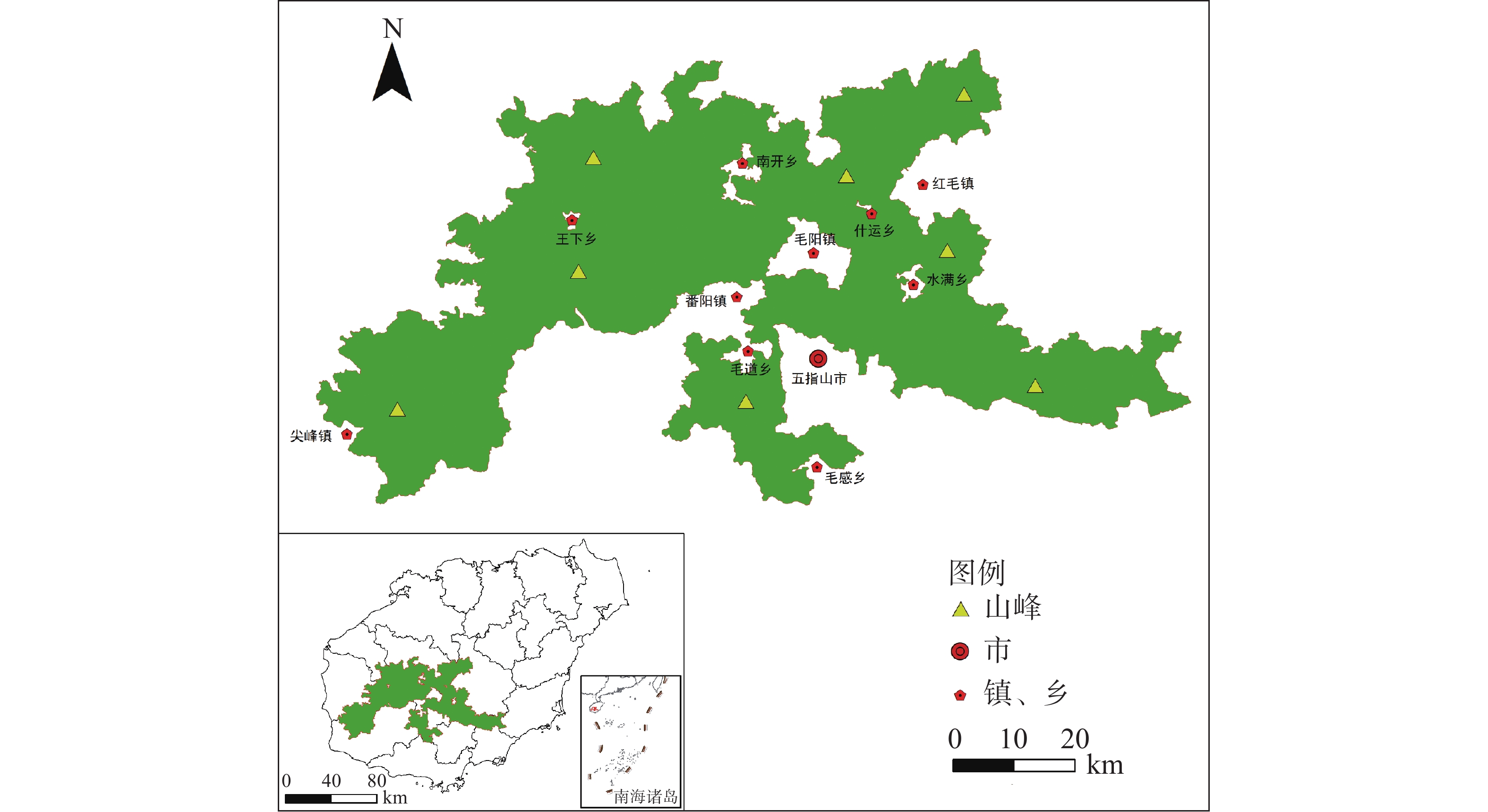
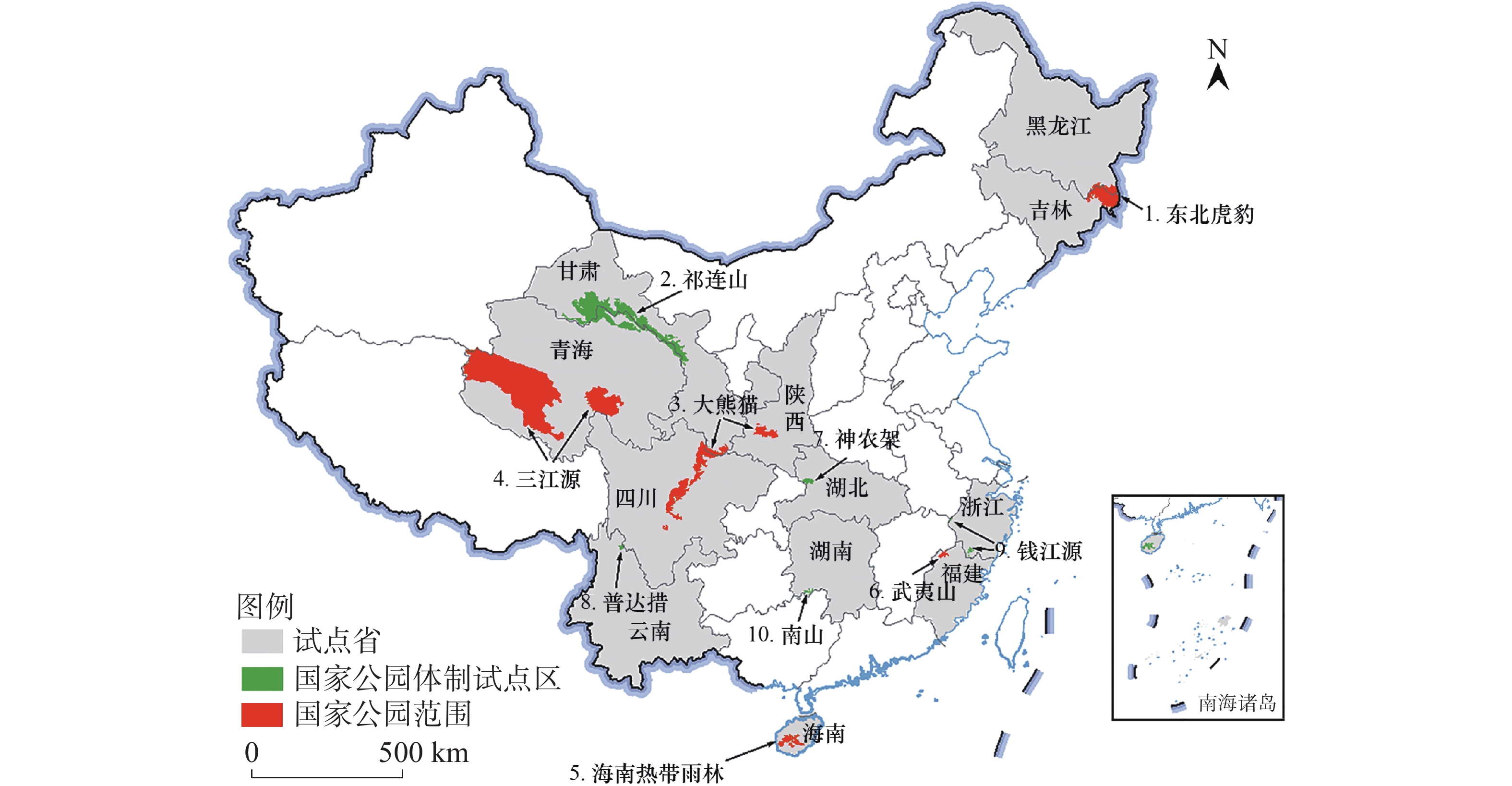
The establishment of national park system is an important part of China's ecological civilization construction. It is of great significance to promote the scientific protection and rational utilization of natural resources, build a beautiful China and promote the harmonious coexistence between man and nature. National Park is already a special land type. The contradiction between National Park and surrounding communities caused by the area of National Park has become increasingly prominent. The determination of the appropriate area of National Parks has become an urgent issue to be solved in the construction of National Parks. In this context a review was made of the area of national parks in the United States, Canada, Japan and other countries, as well as the area of various natural reserves in China. It is suggested from the aspects of land area, social economy and ecosystem that the index for appropriate area of National Parks in China should be selected based on the integrity and typicalness of the ecosystem and the socio-economic sustainability. The area of each National Park should be decided on not only to protect the integrity of the ecosystem, but also to realize the sustainable development of communities in line with its local conditions.
The establishment of national park system is an important part of China's ecological civilization construction. It is of great significance to promote the scientific protection and rational utilization of natural resources, build a beautiful China and promote the harmonious coexistence between man and nature. National Park is already a special land type. The contradiction between National Park and surrounding communities caused by the area of National Park has become increasingly prominent. The determination of the appropriate area of National Parks has become an urgent issue to be solved in the construction of National Parks. In this context a review was made of the area of national parks in the United States, Canada, Japan and other countries, as well as the area of various natural reserves in China. It is suggested from the aspects of land area, social economy and ecosystem that the index for appropriate area of National Parks in China should be selected based on the integrity and typicalness of the ecosystem and the socio-economic sustainability. The area of each National Park should be decided on not only to protect the integrity of the ecosystem, but also to realize the sustainable development of communities in line with its local conditions.
2022, 13(2): 185-194.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.010
Abstract:
Community participation is a key to realize the coordinated development of ecological protection and community in national parks. Herdsman’s cognition of and participatory willingness for protection of national parks are important influencing factors of community participation behavior. A survey was made of the cognition of and the participatory willingness of the herdsmen in the communities to the ecological protection in Sanjiangyuan National Park, based on which the current situation and problems of community participation in Sanjiangyuan National Park were analyzed. The analysis showed that the herdsmen in the communities have a high awareness of ecological protection, which is the result of the joint influence of environmental protection publicity and Tibetan ecological culture. The herdsman’s participation behavior is not only in line with the hypothesis of ‘rational economic man’, but also due to a sense of belonging and local attachment under the influence of traditional ecological culture, and it also shows the characteristics of altruism and mutual aid. Herdsman’s participation behavior is not completely consistent with the willingness of the herdsmen to protect the natural park, that is a reflection of the incompatibility between community ecological protection and community development. Herdsman’s participation is not so high in the communities, with symbolic or fake participation. It is therefore recommended to improve the community co-management mechanism and build a diversified participation path to include the government, the market and the whole society so as to realize the sustainable protection and development of Sanjiangyuan National Park.
Community participation is a key to realize the coordinated development of ecological protection and community in national parks. Herdsman’s cognition of and participatory willingness for protection of national parks are important influencing factors of community participation behavior. A survey was made of the cognition of and the participatory willingness of the herdsmen in the communities to the ecological protection in Sanjiangyuan National Park, based on which the current situation and problems of community participation in Sanjiangyuan National Park were analyzed. The analysis showed that the herdsmen in the communities have a high awareness of ecological protection, which is the result of the joint influence of environmental protection publicity and Tibetan ecological culture. The herdsman’s participation behavior is not only in line with the hypothesis of ‘rational economic man’, but also due to a sense of belonging and local attachment under the influence of traditional ecological culture, and it also shows the characteristics of altruism and mutual aid. Herdsman’s participation behavior is not completely consistent with the willingness of the herdsmen to protect the natural park, that is a reflection of the incompatibility between community ecological protection and community development. Herdsman’s participation is not so high in the communities, with symbolic or fake participation. It is therefore recommended to improve the community co-management mechanism and build a diversified participation path to include the government, the market and the whole society so as to realize the sustainable protection and development of Sanjiangyuan National Park.
2022, 13(2): 195-202.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.02.011
Abstract:
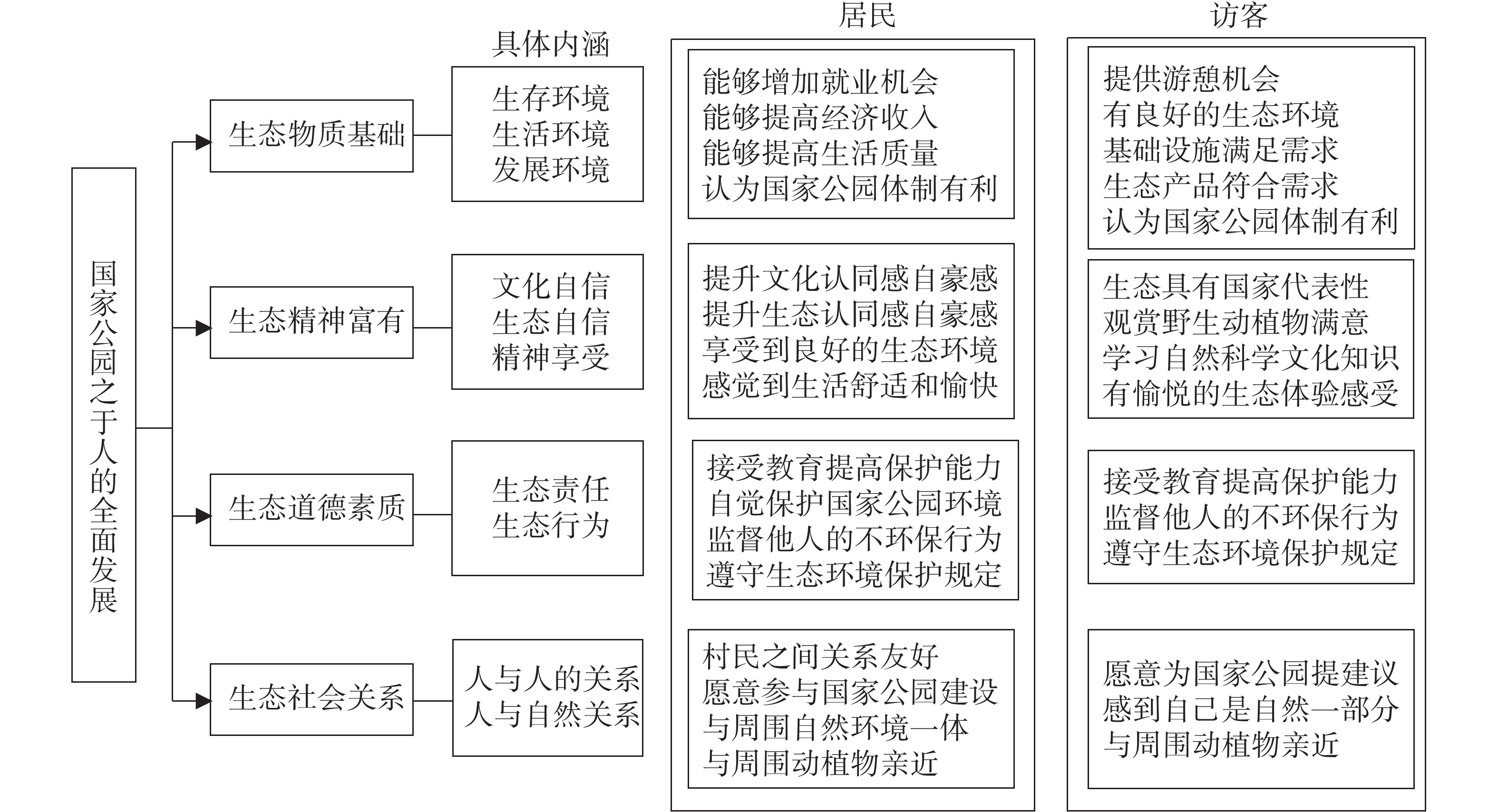
With the concept of ecological civilization as a bridge, the internal logic relation between the national parks and the all-round development of people was reviewed, with Wuyishan National Park as a case for empirical analysis to explore the inherent mechanism of national parks in promoting ‘all-round development of people’. The empirical analysis showed that national parks can promote ‘all-round development of people’ from four aspects: providing “ecological material basis”, building “ecological social relations”, improving “ecological moral quality” and promoting “rich ecological spirit”, which include the living environment, living condition, development environment, cultural self-confidence, ecological self-confidence, spiritual enjoyment, ecological responsibility, ecological behavior, relationship between people, relationship between people and nature, among others.
With the concept of ecological civilization as a bridge, the internal logic relation between the national parks and the all-round development of people was reviewed, with Wuyishan National Park as a case for empirical analysis to explore the inherent mechanism of national parks in promoting ‘all-round development of people’. The empirical analysis showed that national parks can promote ‘all-round development of people’ from four aspects: providing “ecological material basis”, building “ecological social relations”, improving “ecological moral quality” and promoting “rich ecological spirit”, which include the living environment, living condition, development environment, cultural self-confidence, ecological self-confidence, spiritual enjoyment, ecological responsibility, ecological behavior, relationship between people, relationship between people and nature, among others.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 2602KB
PDF 2602KB








 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS