2023 Vol. 14, No. 3
2023, 14(3): 241-247.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.001
Abstract:
‘One Health’ is a global strategy, which promotes the integration of human, animal and environmental health. The aim is to prevent and mitigate crises of public health, thus improving global health and well-being. As a pilot province for deepening its all-round reform in China, Hainan takes the lead in implementing ‘One Health’ demonstration project. This is based on all the following factors it has collectively: unique climatic conditions, being as a communication bridge of ‘The Belt and Road Initiative’, distinct policy of free trade port, concessionary medical dividend and constant gathering of top talents. During this period, Hainan government encourages Hainan University and Hainan Medical University to collaborate with other top universities both domestically and internationally. The purposes are to strengthen the global public health governance system and capacity building, address public health and security challenges, and train a group of top talents in ‘One Health’ research areas. ‘A human community with a shared future’ and ‘Community of life’ are needed by the people and the world. Hainan will also demonstrate a Chinese-style modernization practice on building‘a community with a shared future’ in ‘One Health’, and will provide the world with an excellent example of using ‘One Health’ approach in solving public health crises.
‘One Health’ is a global strategy, which promotes the integration of human, animal and environmental health. The aim is to prevent and mitigate crises of public health, thus improving global health and well-being. As a pilot province for deepening its all-round reform in China, Hainan takes the lead in implementing ‘One Health’ demonstration project. This is based on all the following factors it has collectively: unique climatic conditions, being as a communication bridge of ‘The Belt and Road Initiative’, distinct policy of free trade port, concessionary medical dividend and constant gathering of top talents. During this period, Hainan government encourages Hainan University and Hainan Medical University to collaborate with other top universities both domestically and internationally. The purposes are to strengthen the global public health governance system and capacity building, address public health and security challenges, and train a group of top talents in ‘One Health’ research areas. ‘A human community with a shared future’ and ‘Community of life’ are needed by the people and the world. Hainan will also demonstrate a Chinese-style modernization practice on building‘a community with a shared future’ in ‘One Health’, and will provide the world with an excellent example of using ‘One Health’ approach in solving public health crises.
2023, 14(3): 248-258.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.002
Abstract:
Metabolomics is an emerging omics technology developed after genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics, and has shown its important role in plant research in recent years, and likewise the development of plant metabolomics has advanced the in-depth study of tropical plants. A review was made mainly of the development of plant metabolomics and its integrated application in important tropical crops (Cocos nucifera L., Hevea brasiliensis, Elaeis guineensis Jacq., Manihot esculenta Crantz) and medicinal plants (Areca catechu L., Piper nigrum L., Cephalotaxus hainanensis Li, Amomum villosum Lour.), and recent advances in research of tropical plants based on multi-omics technologies were also reviewed. An outlook for further research based on omics technologies was put forward to provide a reference for further research and exploitation of metabolic biology of tropical plants.
Metabolomics is an emerging omics technology developed after genomics, transcriptomics and proteomics, and has shown its important role in plant research in recent years, and likewise the development of plant metabolomics has advanced the in-depth study of tropical plants. A review was made mainly of the development of plant metabolomics and its integrated application in important tropical crops (Cocos nucifera L., Hevea brasiliensis, Elaeis guineensis Jacq., Manihot esculenta Crantz) and medicinal plants (Areca catechu L., Piper nigrum L., Cephalotaxus hainanensis Li, Amomum villosum Lour.), and recent advances in research of tropical plants based on multi-omics technologies were also reviewed. An outlook for further research based on omics technologies was put forward to provide a reference for further research and exploitation of metabolic biology of tropical plants.
2023, 14(3): 259-267.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.003
Abstract:
It is important to understand the current situation and trend of crop production and seed industry development so as to provide reference for agricultural production and scientific research decision-making and planning. The current situation of the agriculture and crop production and trade as well as the seed industry development in China and the world in recent 10 years were analyzed. The analysis showed that the agricultural output value of China accounts for 29%-37% of the world. In the top 10 major crops with the highest output value in the world, China ranks around 35th in terms of yield on average. Soybeans, corn, wheat and sugarcane are the net imported crops, and the net import dependence of soybeans is upto 87% in the year of the highest import. As to seed import and export of five major crops in China, only rice seed is mainly exported, while the others are mainly imported. In short, the food security in China is still faced with weak productivity, self-sufficiency imbalance, and weak seed industry innovation.
It is important to understand the current situation and trend of crop production and seed industry development so as to provide reference for agricultural production and scientific research decision-making and planning. The current situation of the agriculture and crop production and trade as well as the seed industry development in China and the world in recent 10 years were analyzed. The analysis showed that the agricultural output value of China accounts for 29%-37% of the world. In the top 10 major crops with the highest output value in the world, China ranks around 35th in terms of yield on average. Soybeans, corn, wheat and sugarcane are the net imported crops, and the net import dependence of soybeans is upto 87% in the year of the highest import. As to seed import and export of five major crops in China, only rice seed is mainly exported, while the others are mainly imported. In short, the food security in China is still faced with weak productivity, self-sufficiency imbalance, and weak seed industry innovation.
2023, 14(3): 269-278.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.004
Abstract:
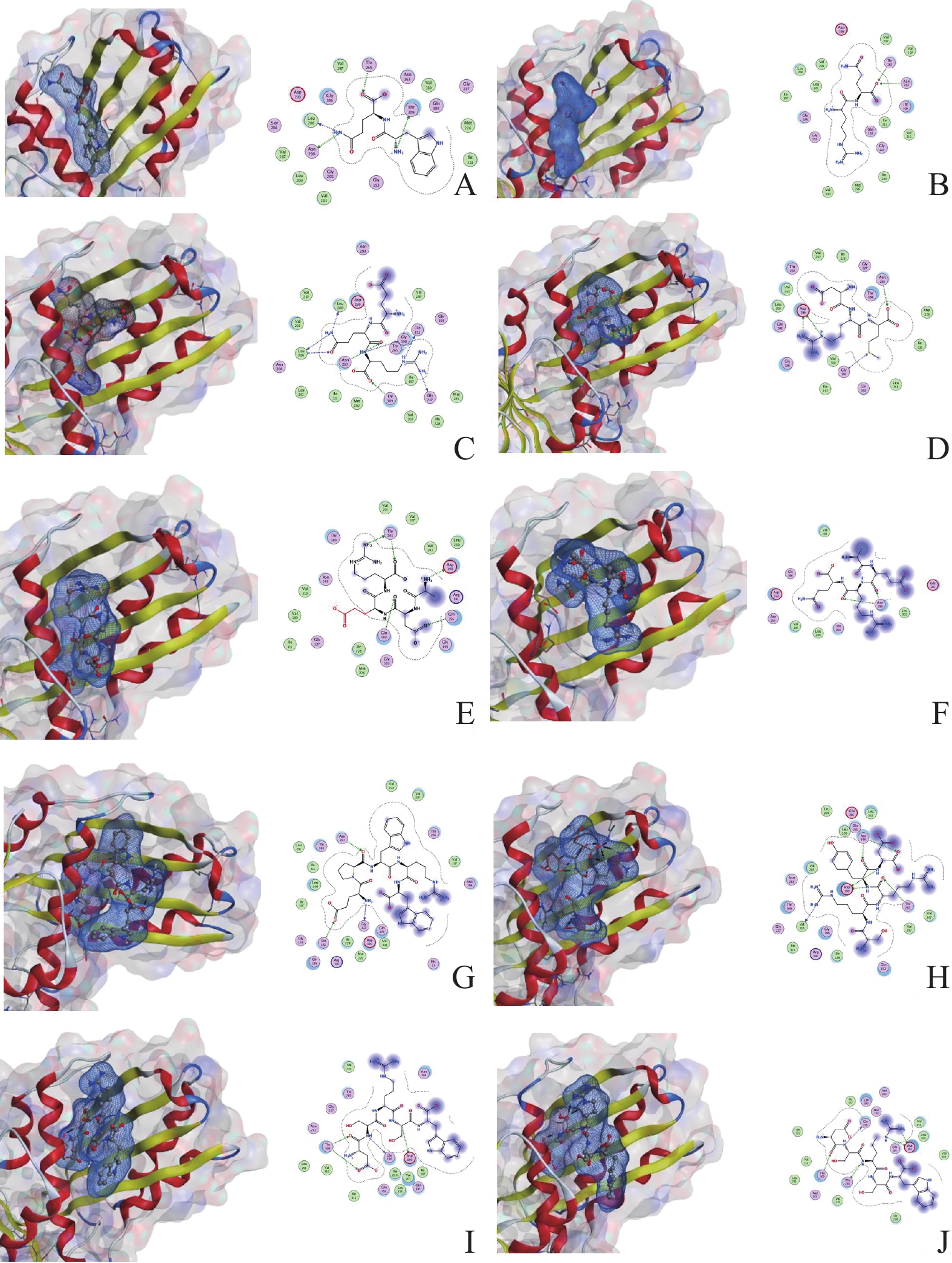
The abuse of antibiotics has led to the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria, and new targets of antibiotics need to be developed urgently. FtsZ protein is a key protein in bacterial cell division, and inhibition of its dynamic process can lead to abnormal bacterial cell division and inhibition. In order to find bacterial inhibitors with new mechanisms of action, we conducted a virtual peptide screening by targeting the FtsZ protein of Staphylococcus aureus, and calculated the root mean square deviation (RMSD) and interaction energy of the screened peptides for evaluation. We investigated their binding stability, tested the antibacterial activity of the hit peptides, and measured their effects on GTPase to explore their mechanism of action. The screened five peptides, TE101, PE101, PE102, PE103 and PE104, were tested in combination with the results of molecular docking and molecular dynamics analysis. The results showed that these five peptides inhibited the growth of S. aureus, but did not act by affecting the GTPase of FtsZ protein.
The abuse of antibiotics has led to the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria, and new targets of antibiotics need to be developed urgently. FtsZ protein is a key protein in bacterial cell division, and inhibition of its dynamic process can lead to abnormal bacterial cell division and inhibition. In order to find bacterial inhibitors with new mechanisms of action, we conducted a virtual peptide screening by targeting the FtsZ protein of Staphylococcus aureus, and calculated the root mean square deviation (RMSD) and interaction energy of the screened peptides for evaluation. We investigated their binding stability, tested the antibacterial activity of the hit peptides, and measured their effects on GTPase to explore their mechanism of action. The screened five peptides, TE101, PE101, PE102, PE103 and PE104, were tested in combination with the results of molecular docking and molecular dynamics analysis. The results showed that these five peptides inhibited the growth of S. aureus, but did not act by affecting the GTPase of FtsZ protein.
2023, 14(3): 279-287.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.005
Abstract:
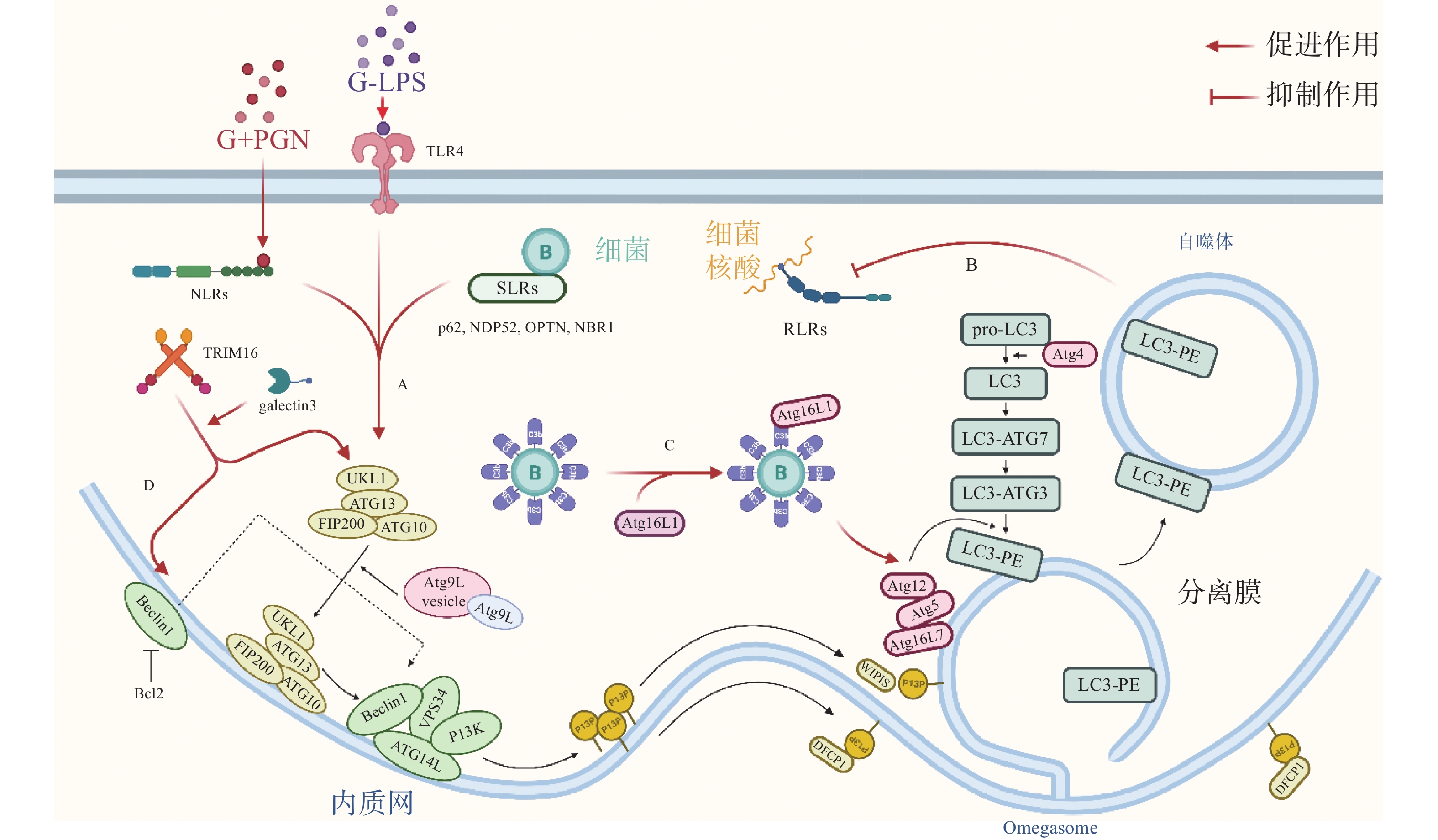
The autophagy pathway activated by bacteria has two faces in maintaining the dynamic balance between intracellular bacterial removal and proliferation. On the one hand, cells recognize and remove intracellular bacteria via autophagy; on the other hand, bacteria evolve various escape mechanisms to inhibit and utilize autophagy to promote their own proliferation. A comprehensive summary was made of the complex relationship between bacterial infection and autophagy, involving the activation of autophagic pathways by bacteria, autophagic response pathways, the interaction between bacteria and autophagy, and the regulation of autophagy in the treatment of infectious diseases to review recent advances in bacterial infection and autophagy, as well as the utilization of autophagy, so as to provide reference for subsequent autophagy exploration.
The autophagy pathway activated by bacteria has two faces in maintaining the dynamic balance between intracellular bacterial removal and proliferation. On the one hand, cells recognize and remove intracellular bacteria via autophagy; on the other hand, bacteria evolve various escape mechanisms to inhibit and utilize autophagy to promote their own proliferation. A comprehensive summary was made of the complex relationship between bacterial infection and autophagy, involving the activation of autophagic pathways by bacteria, autophagic response pathways, the interaction between bacteria and autophagy, and the regulation of autophagy in the treatment of infectious diseases to review recent advances in bacterial infection and autophagy, as well as the utilization of autophagy, so as to provide reference for subsequent autophagy exploration.
2023, 14(3): 289-297.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.006
Abstract:
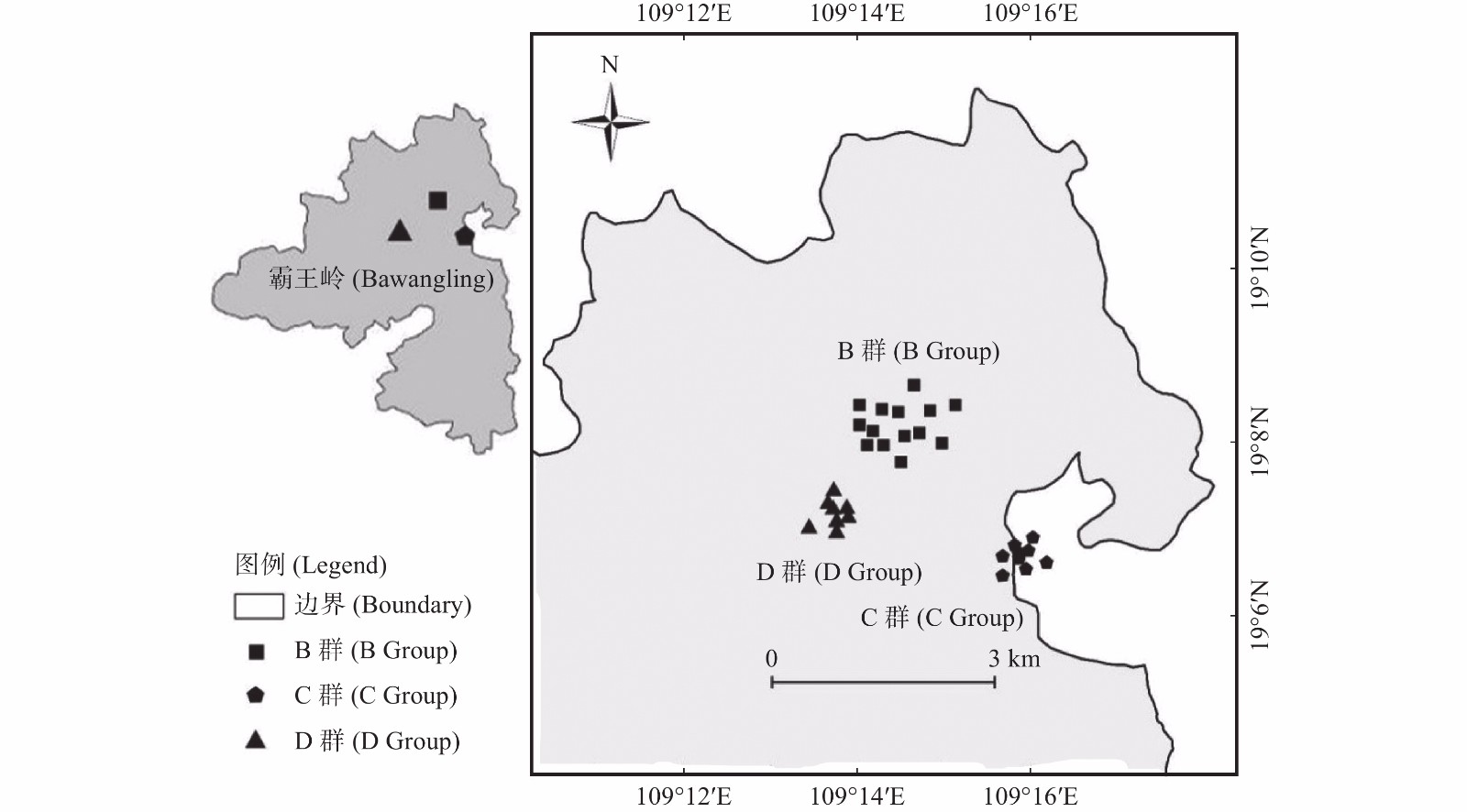
Infrared camera technology is increasingly used in wildlife diversity surveys and long-term monitoring, mainly focusing on the research of ground-dwelling birds and mammals, but less on highly arboreal endangered species, such as Hainan gibbons and associated species diversity. From January 2019 to June 2020, 66 infrared cameras were deployed in the forest canopy of the Hainan gibbon sympatric distribution area to explore the diversity of mammals and bird, the seasonality of activity intensity and changes with altitude gradients. A total of 10 species of mammals that belonged to 3 orders and 4 families were recorded, of which 2 species were under national Class II protection. The three mammals with the highest relative abundance were Hainan gibbon (Nomascus hainanus) (RAI=58.44), Petaurista hainana (RAI=17.78) and Dremomys rufigenis (RAI=14.34). There were 20 species of birds belonging to 6 orders and 11 families recorded, of which 10 species were listed under national Class II protection and three of them, Ducula badia, Treron curvirostra and Glaucidium cuculoides, were higher in relative abundance index (44.92, 20.23 and 6.74, respectively). Hainan gibbons and Petaurista hainana showed similar monthly relative abundance, with their activities being high in the dry season and low in the wet season; while other mammals and birds were not significantly correlated with seasons. The diversity of mammals showed a monotonical decrease with the increase of altitude, and had the highest level of species diversity in the range of 600 ~ 800 m asl. The diversity index of birds first increased and then decreased with the increase of altitude. This study revealed for the first time the composition of companion birds and mammals in the same area where Hainan gibbons were distributed, providing a reference for habitat restoration and ecological corridor construction of Hainan gibbons based on animal diversity in the Bawangling area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park.
Infrared camera technology is increasingly used in wildlife diversity surveys and long-term monitoring, mainly focusing on the research of ground-dwelling birds and mammals, but less on highly arboreal endangered species, such as Hainan gibbons and associated species diversity. From January 2019 to June 2020, 66 infrared cameras were deployed in the forest canopy of the Hainan gibbon sympatric distribution area to explore the diversity of mammals and bird, the seasonality of activity intensity and changes with altitude gradients. A total of 10 species of mammals that belonged to 3 orders and 4 families were recorded, of which 2 species were under national Class II protection. The three mammals with the highest relative abundance were Hainan gibbon (Nomascus hainanus) (RAI=58.44), Petaurista hainana (RAI=17.78) and Dremomys rufigenis (RAI=14.34). There were 20 species of birds belonging to 6 orders and 11 families recorded, of which 10 species were listed under national Class II protection and three of them, Ducula badia, Treron curvirostra and Glaucidium cuculoides, were higher in relative abundance index (44.92, 20.23 and 6.74, respectively). Hainan gibbons and Petaurista hainana showed similar monthly relative abundance, with their activities being high in the dry season and low in the wet season; while other mammals and birds were not significantly correlated with seasons. The diversity of mammals showed a monotonical decrease with the increase of altitude, and had the highest level of species diversity in the range of 600 ~ 800 m asl. The diversity index of birds first increased and then decreased with the increase of altitude. This study revealed for the first time the composition of companion birds and mammals in the same area where Hainan gibbons were distributed, providing a reference for habitat restoration and ecological corridor construction of Hainan gibbons based on animal diversity in the Bawangling area of Hainan Tropical Rainforest National Park.
2023, 14(3): 298-306.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.007
Abstract:
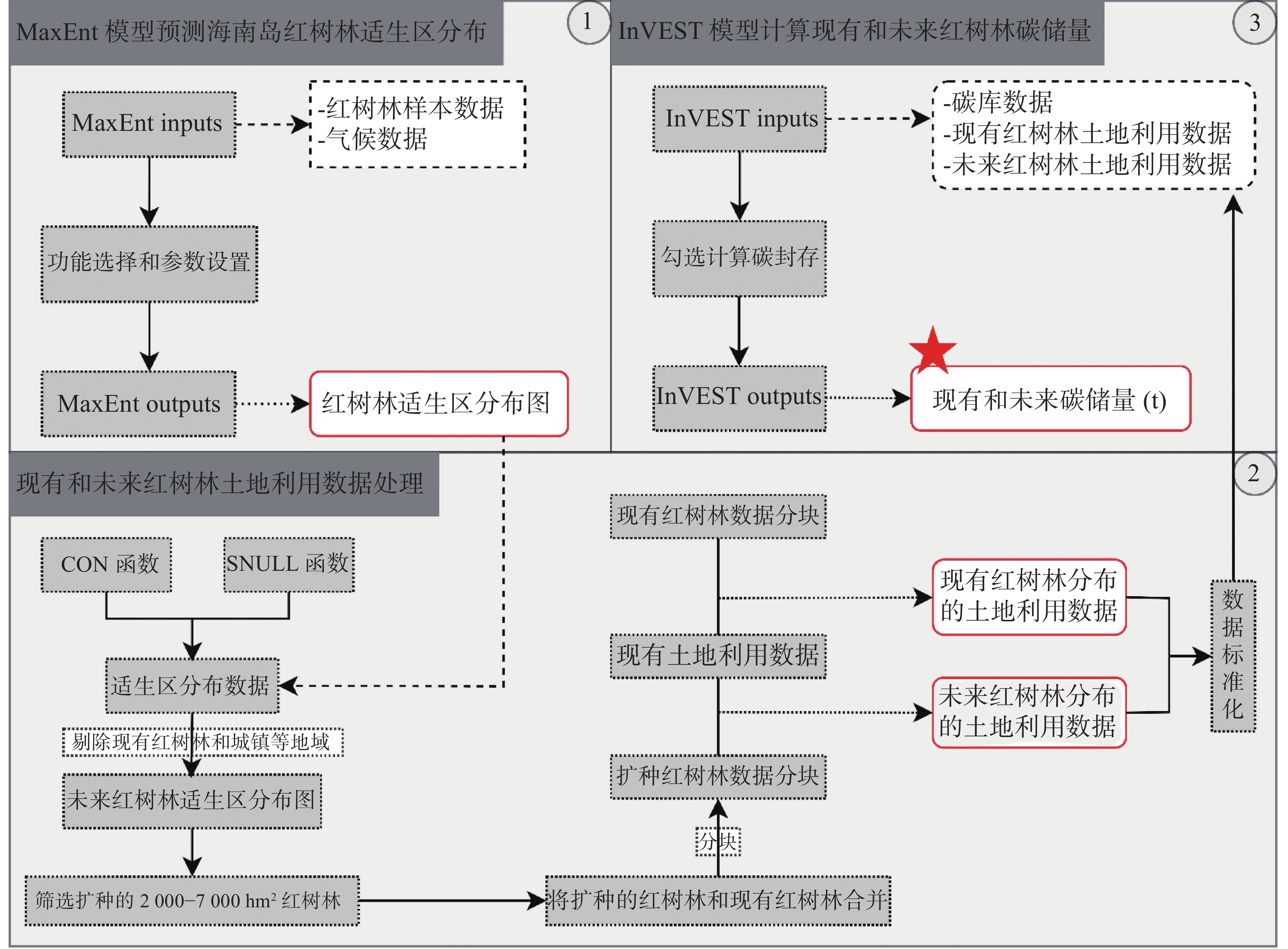
In order to solve the problem of where to plant mangroves in Hainan Island and how to plant mangroves to increase sinks, based on bioclimate, hydrology, geology and land use data, based on the maximum entropy (MaxEnt) model evaluation of the suitable growth area of mangroves in Hainan Island, the potential expansion area of mangroves in Hainan Island was predicted. Combined with the potential expansion range and the carbon density survey data of mangrove ecosystems in different regions, the InVEST model was used to estimate the increase of carbon storage of mangrove ecosystems in Hainan Island. The results show that: 1) The combination of MaxEnt model and InVEST model can well predict mangrove carbon storage, and the prediction of potential distribution areas of mangroves reaches high reliability (AUC > 0.96); 2) The current carbon storage of mangrove ecosystem in Hainan Island was about 1.24 Tg, of which soil carbon was about 0.84 Tg, the total carbon density was 217.01 t·hm−2, and the soil carbon density was 147.43 t·hm−2. Taking the largest mangrove distribution area of 12 506 hm2 in Hainan Island as the control line of potential expansion range, it is theoretically that the mangrove ecosystem in Hainan Island can contribute about 1.25 Tg to the carbon neutrality goal under the upper limit scenario, while the increase in carbon storage of about 0.38 Tg can be achieved under the scenario of the lower limit of expansion, which only guarantees the completion of the basic task of expanding 2 000 hm2 mangrove forest in the special action plan for mangrove protection and restoration (2020—2025)
In order to solve the problem of where to plant mangroves in Hainan Island and how to plant mangroves to increase sinks, based on bioclimate, hydrology, geology and land use data, based on the maximum entropy (MaxEnt) model evaluation of the suitable growth area of mangroves in Hainan Island, the potential expansion area of mangroves in Hainan Island was predicted. Combined with the potential expansion range and the carbon density survey data of mangrove ecosystems in different regions, the InVEST model was used to estimate the increase of carbon storage of mangrove ecosystems in Hainan Island. The results show that: 1) The combination of MaxEnt model and InVEST model can well predict mangrove carbon storage, and the prediction of potential distribution areas of mangroves reaches high reliability (AUC > 0.96); 2) The current carbon storage of mangrove ecosystem in Hainan Island was about 1.24 Tg, of which soil carbon was about 0.84 Tg, the total carbon density was 217.01 t·hm−2, and the soil carbon density was 147.43 t·hm−2. Taking the largest mangrove distribution area of 12 506 hm2 in Hainan Island as the control line of potential expansion range, it is theoretically that the mangrove ecosystem in Hainan Island can contribute about 1.25 Tg to the carbon neutrality goal under the upper limit scenario, while the increase in carbon storage of about 0.38 Tg can be achieved under the scenario of the lower limit of expansion, which only guarantees the completion of the basic task of expanding 2 000 hm2 mangrove forest in the special action plan for mangrove protection and restoration (2020—2025)
2023, 14(3): 307-319.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.008
Abstract:
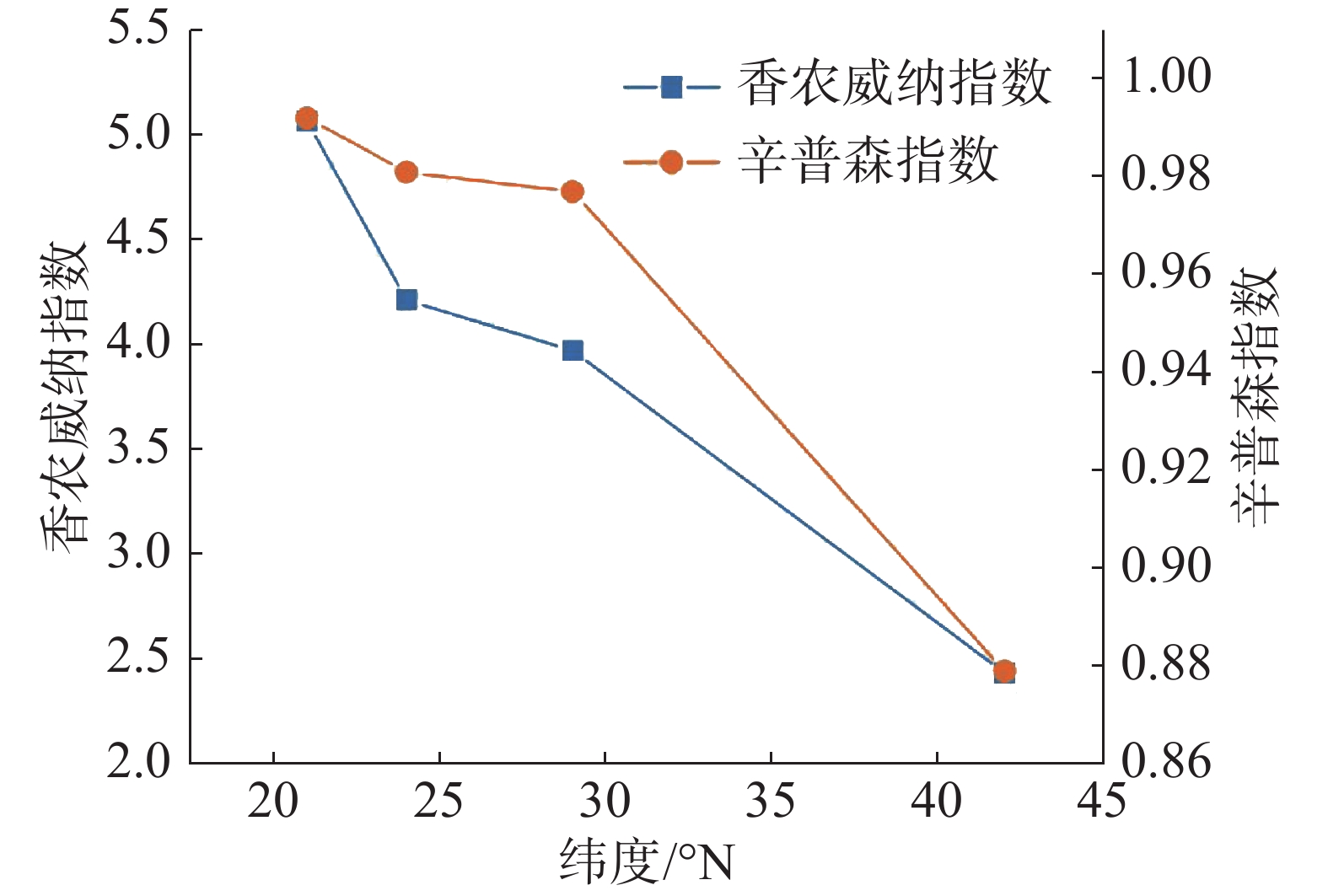
The study of species abundance in forest community can not only reveal the maintenance mechanism of community biodiversity, but also provide theoretical basis for biodiversity conservation. In order to have an in-depth understanding of the distribution characteristics of species abundance patterns in forest communities along the latitude gradient, four representative forest communities within the latitude range of 21°-42°N were selected. Species abundance distribution models based on pure statistics, neutral diversity theory and niche theory were adopted for fitting analysis, and further analysis was carried out in combination with the change characteristics of community diversity. The results showed that α diversity in each forest community decreased with the increase of latitude at this latitude gradient. In terms of species abundance model fitting, there was no difference in latitude gradient, and the fitting results showed that the metacommunity zero-sum multinomial distribution model in the neutral biodiversity theory had the best fitting effect. With the increase of latitude, the number of common and rare species in the community decreased gradually. The fitting results of rare species abundance distribution were consistent with the optimal community species abundance distribution model, while the fitting results of common species abundance distribution showed that the broken stick model in the niche theory had a better fitting effect. The proportion of rare species in tropical rainforest community is higher, which is more likely to cause species loss when disturbed, and thus has higher conservation value.
The study of species abundance in forest community can not only reveal the maintenance mechanism of community biodiversity, but also provide theoretical basis for biodiversity conservation. In order to have an in-depth understanding of the distribution characteristics of species abundance patterns in forest communities along the latitude gradient, four representative forest communities within the latitude range of 21°-42°N were selected. Species abundance distribution models based on pure statistics, neutral diversity theory and niche theory were adopted for fitting analysis, and further analysis was carried out in combination with the change characteristics of community diversity. The results showed that α diversity in each forest community decreased with the increase of latitude at this latitude gradient. In terms of species abundance model fitting, there was no difference in latitude gradient, and the fitting results showed that the metacommunity zero-sum multinomial distribution model in the neutral biodiversity theory had the best fitting effect. With the increase of latitude, the number of common and rare species in the community decreased gradually. The fitting results of rare species abundance distribution were consistent with the optimal community species abundance distribution model, while the fitting results of common species abundance distribution showed that the broken stick model in the niche theory had a better fitting effect. The proportion of rare species in tropical rainforest community is higher, which is more likely to cause species loss when disturbed, and thus has higher conservation value.
2023, 14(3): 320-328.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.009
Abstract:
In order to provide a scientific basis for the rational planning of the spatial layout of Haikou, the ecosystem service value (ESV) and its changes in the urban fringe of Haikou, Hainan was estimated in 2005, 2009, 2015 and 2020 based on the equivalent factor method. With the aid of the grey linear programming model, the land use construction was optimized with the goal of maximizing ESV, and the changes of land use and ESV before and after the optimization were discussed. The results showed that the area of construction land had increased year by year since 2005 while the arable land and wetland decreased. The total ESV increased first and then decreased, with a slight increase of 0.21%. The ESV of woodland was the highest among the lands, and the ESV of hydrological regulation was the highest among the single ecological service functions. After optimization, the total ESV value increased by 1.73%, the wetland and construction land increased, and the unused land decreased. The wetland ESV increased the most. The permanent basic farmland is protected when the demand of urban sustainable development is met.
In order to provide a scientific basis for the rational planning of the spatial layout of Haikou, the ecosystem service value (ESV) and its changes in the urban fringe of Haikou, Hainan was estimated in 2005, 2009, 2015 and 2020 based on the equivalent factor method. With the aid of the grey linear programming model, the land use construction was optimized with the goal of maximizing ESV, and the changes of land use and ESV before and after the optimization were discussed. The results showed that the area of construction land had increased year by year since 2005 while the arable land and wetland decreased. The total ESV increased first and then decreased, with a slight increase of 0.21%. The ESV of woodland was the highest among the lands, and the ESV of hydrological regulation was the highest among the single ecological service functions. After optimization, the total ESV value increased by 1.73%, the wetland and construction land increased, and the unused land decreased. The wetland ESV increased the most. The permanent basic farmland is protected when the demand of urban sustainable development is met.
2023, 14(3): 330-337.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.010
Abstract:
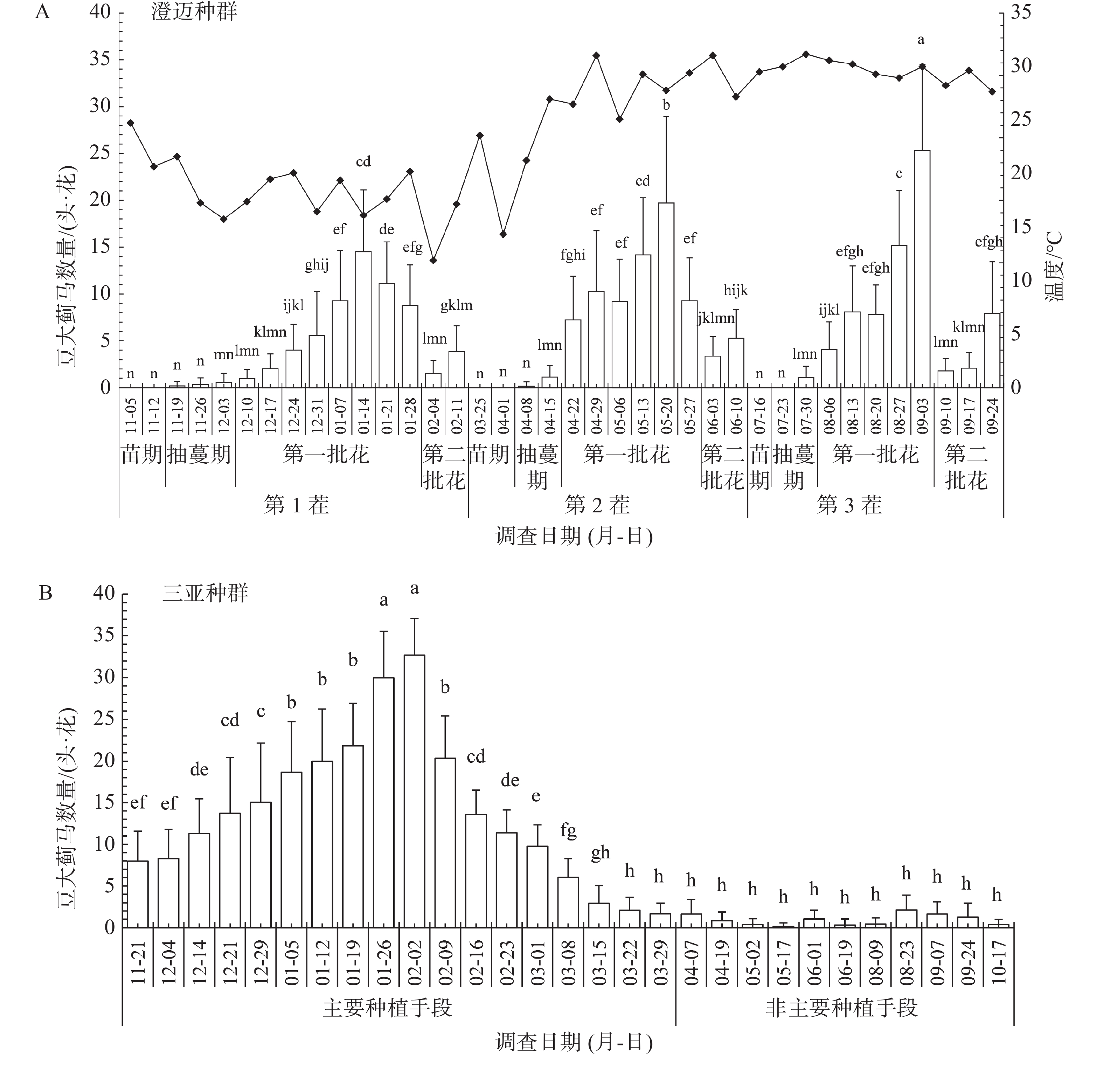
To clarify the spatiotemporal dynamics of the thrips Megalurothrips usitatus Bagnall populations and the differences of the thrips populations in adult body size in Hainan, China and screen high effective insecticides for control of thrips eggs and pupae,a systematical investigation was made into the annual occurrence of M. usitatus on cowpea in Hainan, the adult body size of the M. usitatus populations at different geographical locations were measured, and the toxicity of various insecticides against the eggs and pupae of M. usitatus was tested by using the dip method and POTTER bioassay, respectively. The investigation showed that M. usitatus occured throughout the year in Hainan. Population dynamics were significantly regulated by host phenology and temperature. The adult body size measurement showed that the adult body length and body width of M. usitatus populations were significantly higher in Danzhou than in Sanya and Chengmai. The toxicity test showed that spirotetramat had a higher ovicidal activity (LC50=18.51 mg·L−1) against M. usitatus eggs, while spinosad and chlorfenapyr had a higher activity against M. usitatus pupae, with their LC50 values being 26.18 and 27.71 mg·L−1, respectively. These insecticides could hence be recommended as candidates for controlling M. usitatus eggs and pupae in the field.
To clarify the spatiotemporal dynamics of the thrips Megalurothrips usitatus Bagnall populations and the differences of the thrips populations in adult body size in Hainan, China and screen high effective insecticides for control of thrips eggs and pupae,a systematical investigation was made into the annual occurrence of M. usitatus on cowpea in Hainan, the adult body size of the M. usitatus populations at different geographical locations were measured, and the toxicity of various insecticides against the eggs and pupae of M. usitatus was tested by using the dip method and POTTER bioassay, respectively. The investigation showed that M. usitatus occured throughout the year in Hainan. Population dynamics were significantly regulated by host phenology and temperature. The adult body size measurement showed that the adult body length and body width of M. usitatus populations were significantly higher in Danzhou than in Sanya and Chengmai. The toxicity test showed that spirotetramat had a higher ovicidal activity (LC50=18.51 mg·L−1) against M. usitatus eggs, while spinosad and chlorfenapyr had a higher activity against M. usitatus pupae, with their LC50 values being 26.18 and 27.71 mg·L−1, respectively. These insecticides could hence be recommended as candidates for controlling M. usitatus eggs and pupae in the field.
2023, 14(3): 338-346.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.03.011
Abstract:
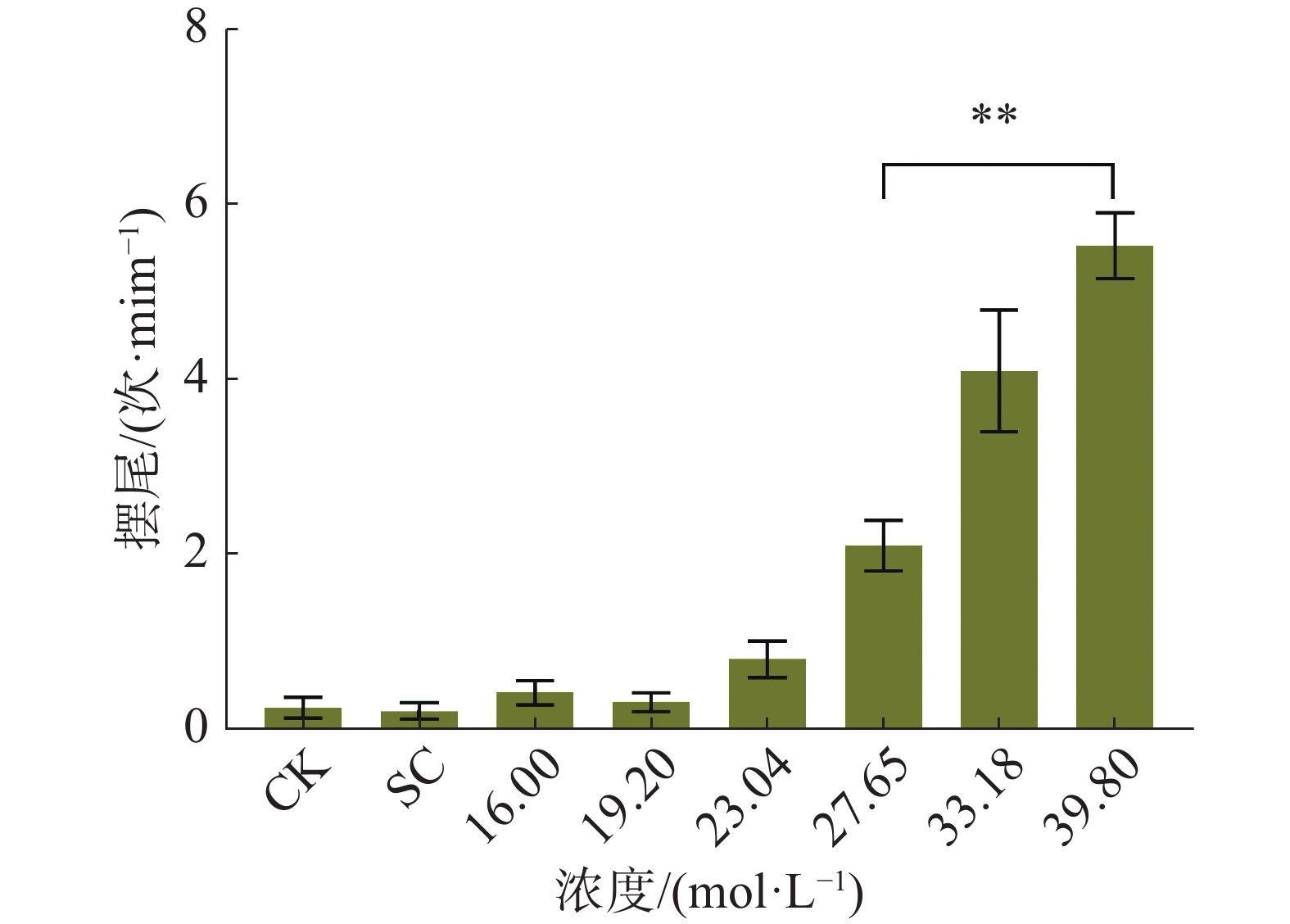
In order to provide a certain theoretical basis for the ecological risk assessment of pesticide tetrachlorantraniliprole, the concentration change of tetrachlorantraniliprole in water for 96 hours was determined by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. According to the OECD standard, embryos of Danio rerio were used as assessment of the model organisms. After static exposure to different doses of tetrachlorantraniliprole, zebrafish embryos were observed in terms of growth and development, and their voluntary movement, melanin and body length were calculated. The 96 h LC50 were evaluated by mortality rate. Genes related with the melanin biosynthesis in the embryos were determined by using the RT-qPCR. The results showed that the tetrachlorantraniliprole in water for 96 h had the highest degradation rate (7.6%), with its concentration being greater than 80%, and had a good stability in water for 96 h. The LC50 of tetrachlorantraniliprole at 96 h was 23.775 mg·L−1, indicating low toxicity. The exposure to tetrachlorantraniliprole affected the development of zebrafish embryos in voluntary movement frequency, hatching rate and body length. The frequency of voluntary movement of zebrafish embryos increased with the tetrachlorantraniliprole concentration. When the exposure concentration was 39.8 mg·L−1, the zebrafish embryos had a voluntary movement frequency of 5.5 times·min−1, which was 22 times that of the control. When the exposure concentration was 27.65 mg·L−1, the zebrafish embryos decreased their hatching rate by 75%. At an exposure concentration of 39.8 mg·L−1, zebrafish decreased its body length by 32.27% compared with the control. Moreover, during the experiment it was also found that melanin pigmentation decreased after exposure to tetrachlorantraniliprole, and that the melanin area of 96 h zebrafish embryos decreased significantly with the increase of tetrachlortraniliprole concentration, and was reduced by 65% at the highest exposure concentration of 39.8 mg·L−1 as compared with the blank control. The RT-qPCR results showed that the expression of Tyr, Sox10, Trp-1a, and Mitfa genes had certain changes. The results showed that tetrachlorantraniliprole inhibited the expression ofSox10 and Mitfa, resulting in abnormal expression of tyrosinase-related transcription factors such as Tyr and Tyr-1a, which ultimately led to the impairment of melanin synthesis and pigmentation in zebrafish embryos.
In order to provide a certain theoretical basis for the ecological risk assessment of pesticide tetrachlorantraniliprole, the concentration change of tetrachlorantraniliprole in water for 96 hours was determined by using ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. According to the OECD standard, embryos of Danio rerio were used as assessment of the model organisms. After static exposure to different doses of tetrachlorantraniliprole, zebrafish embryos were observed in terms of growth and development, and their voluntary movement, melanin and body length were calculated. The 96 h LC50 were evaluated by mortality rate. Genes related with the melanin biosynthesis in the embryos were determined by using the RT-qPCR. The results showed that the tetrachlorantraniliprole in water for 96 h had the highest degradation rate (7.6%), with its concentration being greater than 80%, and had a good stability in water for 96 h. The LC50 of tetrachlorantraniliprole at 96 h was 23.775 mg·L−1, indicating low toxicity. The exposure to tetrachlorantraniliprole affected the development of zebrafish embryos in voluntary movement frequency, hatching rate and body length. The frequency of voluntary movement of zebrafish embryos increased with the tetrachlorantraniliprole concentration. When the exposure concentration was 39.8 mg·L−1, the zebrafish embryos had a voluntary movement frequency of 5.5 times·min−1, which was 22 times that of the control. When the exposure concentration was 27.65 mg·L−1, the zebrafish embryos decreased their hatching rate by 75%. At an exposure concentration of 39.8 mg·L−1, zebrafish decreased its body length by 32.27% compared with the control. Moreover, during the experiment it was also found that melanin pigmentation decreased after exposure to tetrachlorantraniliprole, and that the melanin area of 96 h zebrafish embryos decreased significantly with the increase of tetrachlortraniliprole concentration, and was reduced by 65% at the highest exposure concentration of 39.8 mg·L−1 as compared with the blank control. The RT-qPCR results showed that the expression of Tyr, Sox10, Trp-1a, and Mitfa genes had certain changes. The results showed that tetrachlorantraniliprole inhibited the expression ofSox10 and Mitfa, resulting in abnormal expression of tyrosinase-related transcription factors such as Tyr and Tyr-1a, which ultimately led to the impairment of melanin synthesis and pigmentation in zebrafish embryos.



 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 648KB
PDF 648KB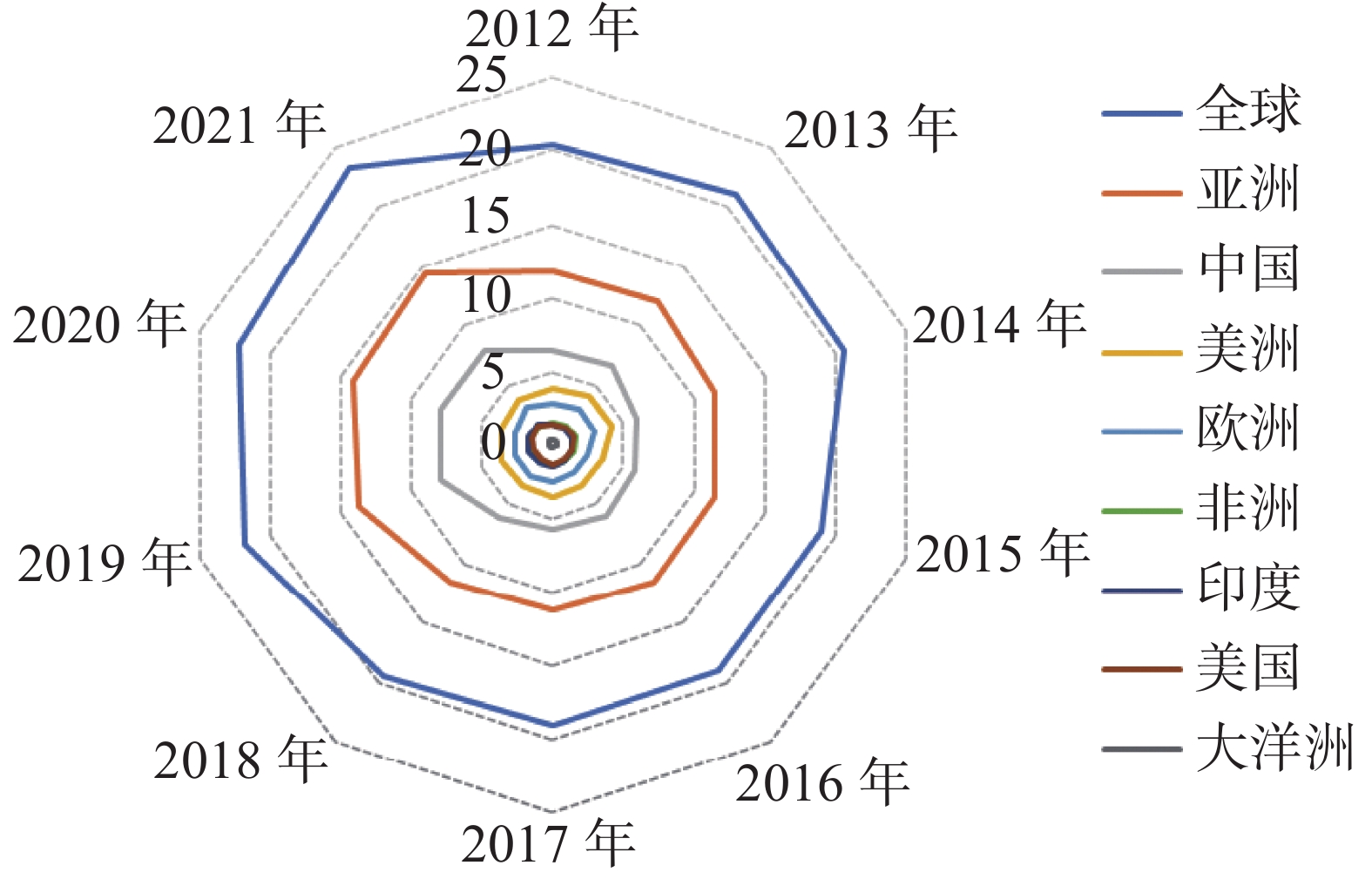





 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS