2021 Vol. 12, No. 4
2021, 12(4): 0000-4.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.006
Abstract:
Proteins containing GGDEF and EAL domains are involved in the synthesis and degradation of the cell´s second messenger c-di-GMP. They are important regulators for bacteria to respond to the external environment, and may be involved in the interaction between pathogen and host. We analyzed the effect of CrxV containing a GGDEF and an EAL domain on the virulence and some related virulent factors of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), a causal agent of bacterial leaf blight of rice. We used the homology recombination method to construct crxV mutant (ΔcrxV), and then the leaf clipping method to analyze the infection ability of the wild-type strain, ΔcrxV, and its complementary strain (C-ΔcrxV) on rice leaves. We also compared the motility, the contents of biofilm, extracellular polysaccharides and extracellular enzymes of these strains. The results showed that the ΔcrxV mutant had lower virulence than the wild-type and complementary strains. Compared with the wild-type and complementary strains, the ΔcrxV mutant was significantly higher in biofilm content, but no significant difference was observed in its motility, extracellular polysaccharides and extracellular enzymes. These results demonstrate that the CrxV may positively regulate the virulence of Xoo through negative regulation of biofilm formation.
Proteins containing GGDEF and EAL domains are involved in the synthesis and degradation of the cell´s second messenger c-di-GMP. They are important regulators for bacteria to respond to the external environment, and may be involved in the interaction between pathogen and host. We analyzed the effect of CrxV containing a GGDEF and an EAL domain on the virulence and some related virulent factors of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), a causal agent of bacterial leaf blight of rice. We used the homology recombination method to construct crxV mutant (ΔcrxV), and then the leaf clipping method to analyze the infection ability of the wild-type strain, ΔcrxV, and its complementary strain (C-ΔcrxV) on rice leaves. We also compared the motility, the contents of biofilm, extracellular polysaccharides and extracellular enzymes of these strains. The results showed that the ΔcrxV mutant had lower virulence than the wild-type and complementary strains. Compared with the wild-type and complementary strains, the ΔcrxV mutant was significantly higher in biofilm content, but no significant difference was observed in its motility, extracellular polysaccharides and extracellular enzymes. These results demonstrate that the CrxV may positively regulate the virulence of Xoo through negative regulation of biofilm formation.
2021, 12(4): 403-411.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.001
Abstract:
The receptor containing α6 subunit is one of the special nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Recent studies have found that the α6/α3β4 subtypes have a certain regulatory effect on the nervous system. And it is related to the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as neuropathic pain, addiction, etc., which have been regarded as potential therapeutic targets. The sequences of rat and human α6 and β4 subunits were compared, and three mutant α6/α3β4 receptor genes with adjacent site mutations were produced on the basis of wild-type genes by site-directed mutagenesis. The α6/α3β4 receptors and their mutants were expressed on Xenopus oocytes by transcription in vitro, microinjection and other methods. And the functions of the receptors were detected by using the two-electrode voltage voltage-clamp system. The results indicated that the mutant receptor α6/α3β4 [S52N, I53V] was more sensitive to ACh, with its EC50 being 59.58 μmol·L−1, which is half of the wild-type receptor. Meanwhile, the other two mutant receptors had similar sensitivities to the wild type.
The receptor containing α6 subunit is one of the special nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Recent studies have found that the α6/α3β4 subtypes have a certain regulatory effect on the nervous system. And it is related to the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as neuropathic pain, addiction, etc., which have been regarded as potential therapeutic targets. The sequences of rat and human α6 and β4 subunits were compared, and three mutant α6/α3β4 receptor genes with adjacent site mutations were produced on the basis of wild-type genes by site-directed mutagenesis. The α6/α3β4 receptors and their mutants were expressed on Xenopus oocytes by transcription in vitro, microinjection and other methods. And the functions of the receptors were detected by using the two-electrode voltage voltage-clamp system. The results indicated that the mutant receptor α6/α3β4 [S52N, I53V] was more sensitive to ACh, with its EC50 being 59.58 μmol·L−1, which is half of the wild-type receptor. Meanwhile, the other two mutant receptors had similar sensitivities to the wild type.
2021, 12(4): 412-418.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.002
Abstract:
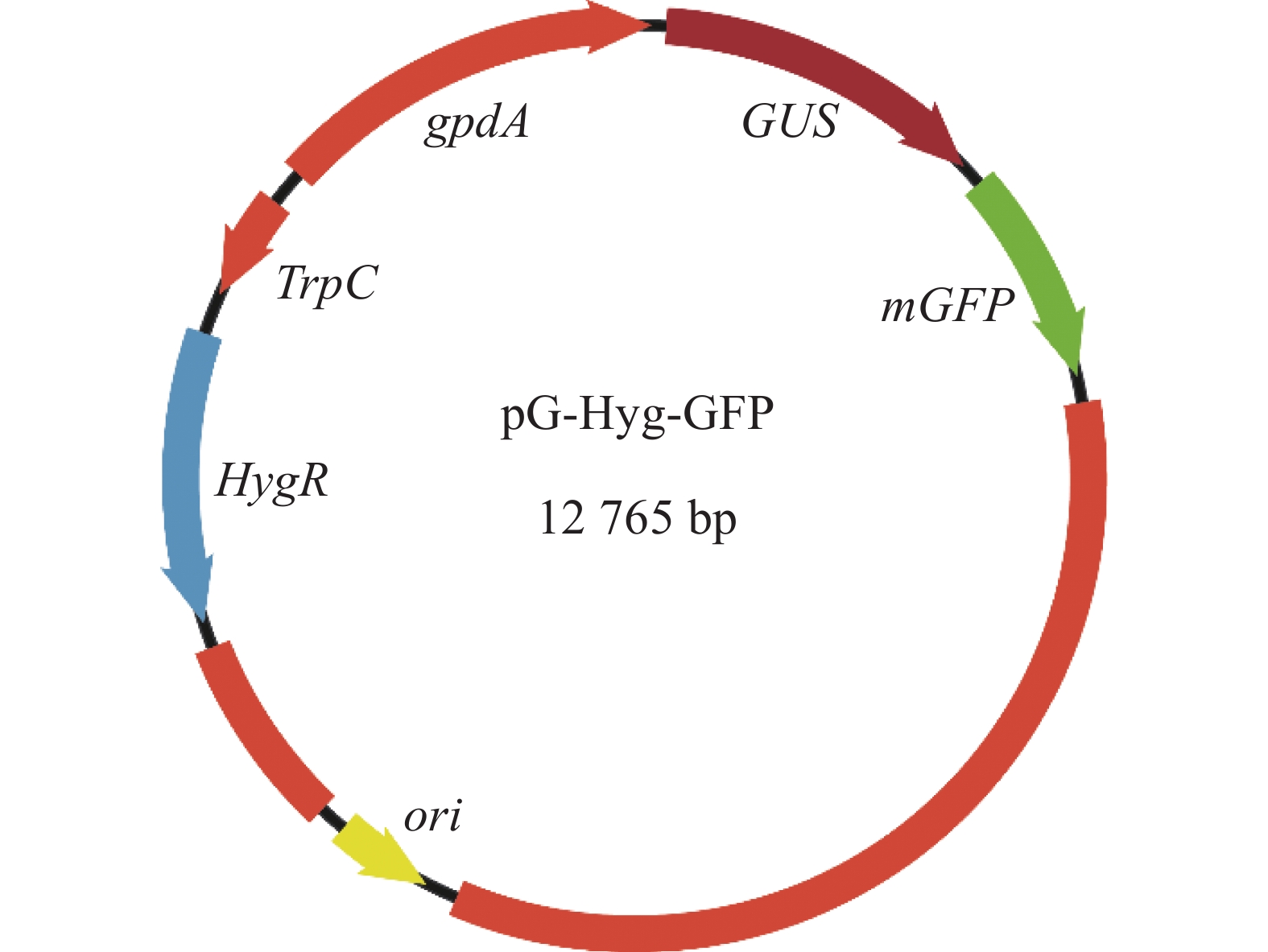
In recent years, pitaya (Hylocereus spp.) has gradually become a newly-emerging tropical fruit. With the continuous increase of planting area, diseases infecting pitaya have become more serious. Among them stem canker is the most important disease, which is caused by Neoscytalidium dimidiatum. To explore the genetic variation and gene function of N. dimidiatum, an effective genetic transformation system must be established. However, there have been no reports documented at home or abroad in this aspect. A binary expression vector containing gpdA promoter, green fluorescent protein (mGFP) and hygromycin resistance gene as screening markers was constructed to establish a genetic transformation system for N. dimidiatum through Agrobacterium tumefacien-mediation, and positive transformants from the spores of N. dimidiatumwere successfully generated. Fluorescence microscope observations showed that the positive transformant hyphae could produce green fluorescence, while the wild-type hyphae could not produce green fluorescence. The PCR test confirmed the integration of hygromycin resistance gene in the transformant genome. Therefore, this Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation system produced stable genetic expression of mGFP gene in N. dimidiatum , which lays a technical foundation for the further study of the pathogenicity mechanism of dragon fruit canker disease.
In recent years, pitaya (Hylocereus spp.) has gradually become a newly-emerging tropical fruit. With the continuous increase of planting area, diseases infecting pitaya have become more serious. Among them stem canker is the most important disease, which is caused by Neoscytalidium dimidiatum. To explore the genetic variation and gene function of N. dimidiatum, an effective genetic transformation system must be established. However, there have been no reports documented at home or abroad in this aspect. A binary expression vector containing gpdA promoter, green fluorescent protein (mGFP) and hygromycin resistance gene as screening markers was constructed to establish a genetic transformation system for N. dimidiatum through Agrobacterium tumefacien-mediation, and positive transformants from the spores of N. dimidiatumwere successfully generated. Fluorescence microscope observations showed that the positive transformant hyphae could produce green fluorescence, while the wild-type hyphae could not produce green fluorescence. The PCR test confirmed the integration of hygromycin resistance gene in the transformant genome. Therefore, this Agrobacterium tumefaciens mediated transformation system produced stable genetic expression of mGFP gene in N. dimidiatum , which lays a technical foundation for the further study of the pathogenicity mechanism of dragon fruit canker disease.
2021, 12(4): 419-427.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.003
Abstract:
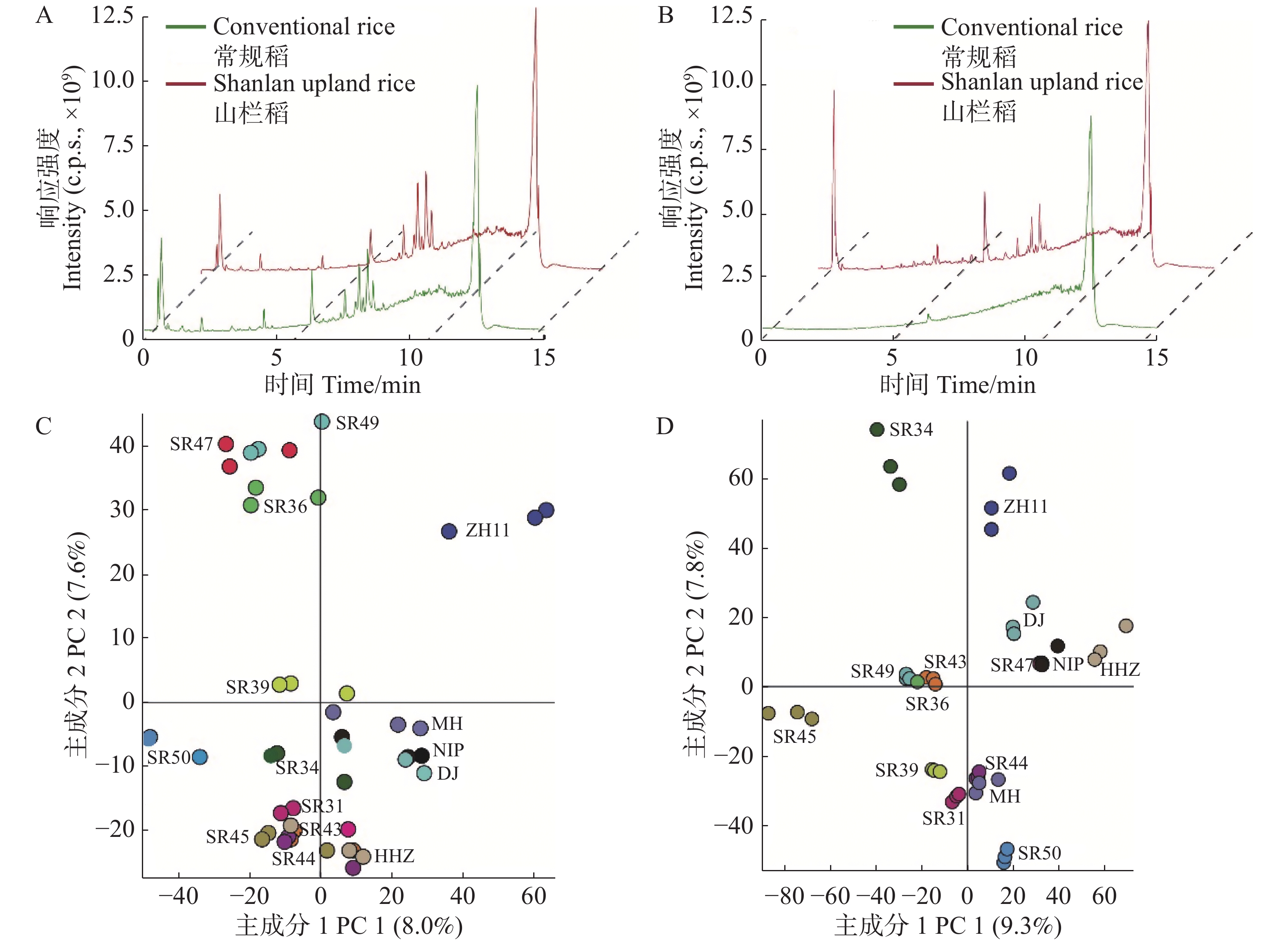
Seeds of 10 accessions of Shanlan upland rice were determined by using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry to establish a Shanlan upland rice seed metabolism database, based on which the metabolites of the seeds of different types of Shanlan upland rice before germination and at different germination stages were analyzed by performing quantitative analysis. A database for Shanlan upland rice seed metabolism containing 1 058 metabolic signals was constructed, including 645 known substances such as amino acids, lipids, vitaminsvitamins, and flavonoids. Comparison and analysis of the metabolic profile of the seeds of Shanlan upland rice and conventional rice found that the relative contents of unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and other substances were higher in Shanlan upland rice seeds than in the conventional rice seeds.T while the contents of glycerophospholipids and flavonoids were lower in the Shanland upland rice seeds than in the conventional rice. During seed germination, there were differences in the accumulation patterns of metabolites in the seeds of the Shanlan upland rice and the conventional rice, especially in the accumulation of proline, ethyl linolenate, pantothenic acid and pyridoxine.
Seeds of 10 accessions of Shanlan upland rice were determined by using ultra-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometry to establish a Shanlan upland rice seed metabolism database, based on which the metabolites of the seeds of different types of Shanlan upland rice before germination and at different germination stages were analyzed by performing quantitative analysis. A database for Shanlan upland rice seed metabolism containing 1 058 metabolic signals was constructed, including 645 known substances such as amino acids, lipids, vitaminsvitamins, and flavonoids. Comparison and analysis of the metabolic profile of the seeds of Shanlan upland rice and conventional rice found that the relative contents of unsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and other substances were higher in Shanlan upland rice seeds than in the conventional rice seeds.T while the contents of glycerophospholipids and flavonoids were lower in the Shanland upland rice seeds than in the conventional rice. During seed germination, there were differences in the accumulation patterns of metabolites in the seeds of the Shanlan upland rice and the conventional rice, especially in the accumulation of proline, ethyl linolenate, pantothenic acid and pyridoxine.
2021, 12(4): 428-434.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.004
Abstract:
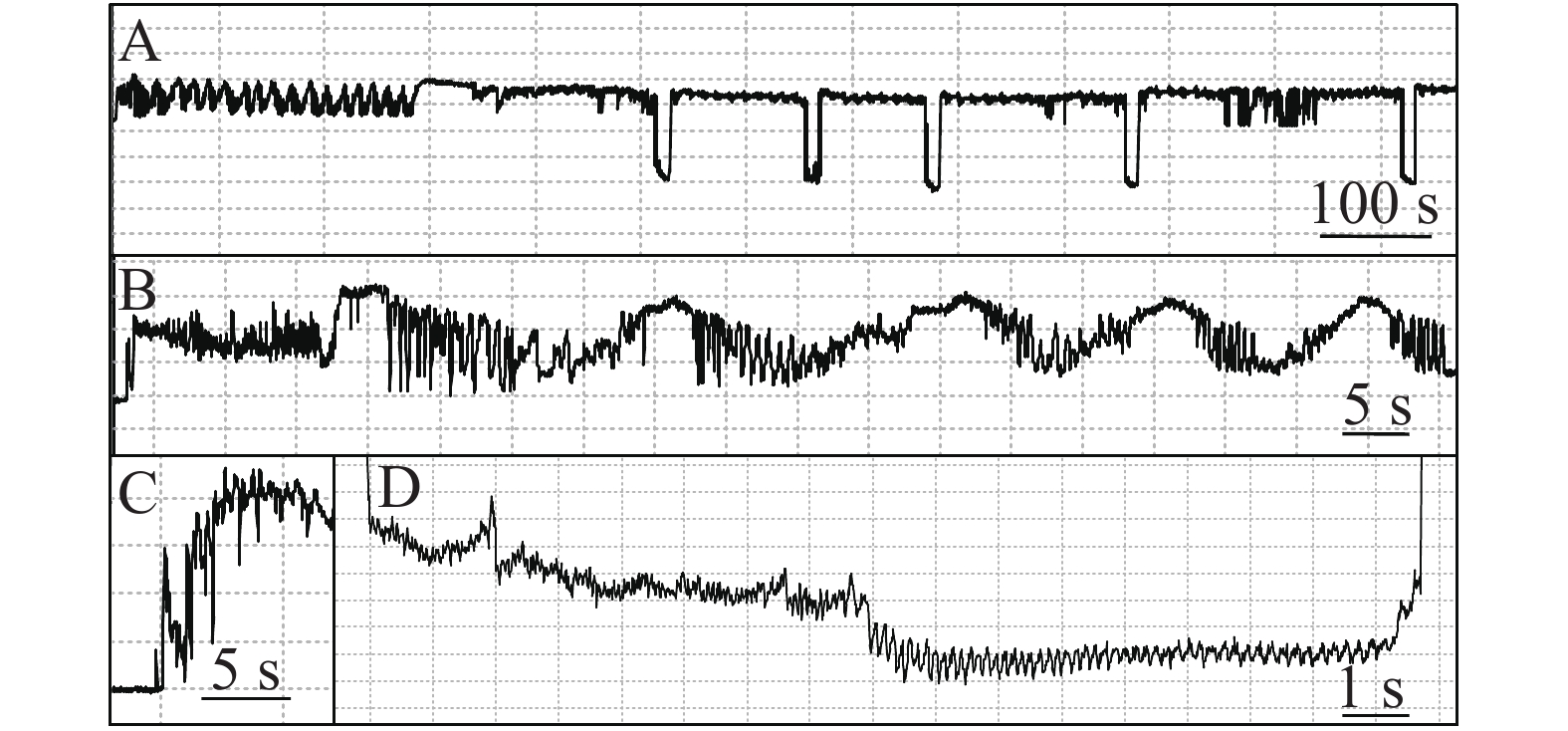
Feeding behaviors of Phenacoccus solani on Graptopetalum paraguayense and Lycopersicon esculentum were characterized by using electropenetrationgraphy (EPG), respectively. The results showed that the basic waveforms including waveforms A, B, C, pd, E, E1e and F were generated when P. solani was feeding on the two plants. Waveform E1e was the main persistent feeding waveform, while waveform E occurred occasionally without typical passive feeding waveform (waveform E2) when P. solani was feeding on L. esculentum. Feeding behaviors of P. solani on these two plants were significantly different. Compared to the performance on L. esculentum, P. solani feeding on G. paraguayense showed lower site transition frequency, faster penetration of the leaf surface, more access to foliar nutrients, and longer duration of persistent feeding, and generated no waveform E but waveform E1e with prolonged occurrence. There were typical subwaveforms of the waveforms E1 and E2 (but with the zero level of electric potential) within the waveform Ele. These results indicated that the EPG waveforms of feeding behaviors of P. solani on these two plants were similar to those of the phloem-feeding insects, but the waveform Ele was the main feeding waveform, which confirms that P. solani have greater adaptability and infestation risk on the succulent plant G. paraguayense.
Feeding behaviors of Phenacoccus solani on Graptopetalum paraguayense and Lycopersicon esculentum were characterized by using electropenetrationgraphy (EPG), respectively. The results showed that the basic waveforms including waveforms A, B, C, pd, E, E1e and F were generated when P. solani was feeding on the two plants. Waveform E1e was the main persistent feeding waveform, while waveform E occurred occasionally without typical passive feeding waveform (waveform E2) when P. solani was feeding on L. esculentum. Feeding behaviors of P. solani on these two plants were significantly different. Compared to the performance on L. esculentum, P. solani feeding on G. paraguayense showed lower site transition frequency, faster penetration of the leaf surface, more access to foliar nutrients, and longer duration of persistent feeding, and generated no waveform E but waveform E1e with prolonged occurrence. There were typical subwaveforms of the waveforms E1 and E2 (but with the zero level of electric potential) within the waveform Ele. These results indicated that the EPG waveforms of feeding behaviors of P. solani on these two plants were similar to those of the phloem-feeding insects, but the waveform Ele was the main feeding waveform, which confirms that P. solani have greater adaptability and infestation risk on the succulent plant G. paraguayense.
2021, 12(4): 435-440.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.005
Abstract:
In order to identify the pathogenic bacteria of dead cattle in a cattle farm in Dongfang City, Hainan Province, and to explore the specific causes of cattle deaths in the cattle farm, the lung tissues of the diseased cattle were collected, and the pathogenic strains were isolated. purified and determined by 16S rDNA and biochemical identification methods to identify the genetic background of the pathogenic bacteria, and the 50% lethal dose of the pathogenic bacteria to mice and its drug sensitivity were determined at the same time. The experimental results showed that the homology between the pathogenic strain and Acinetobacter baumannii was as high as 99.8%. The pathogenic strain was highly pathogenic to experimental mice, and its half lethal dose in mice was 8.89 × 107 CFU·mL−1. Drug sensitivity tests showed that the pathogenic strain is sensitive to carbenicillin, ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin.
In order to identify the pathogenic bacteria of dead cattle in a cattle farm in Dongfang City, Hainan Province, and to explore the specific causes of cattle deaths in the cattle farm, the lung tissues of the diseased cattle were collected, and the pathogenic strains were isolated. purified and determined by 16S rDNA and biochemical identification methods to identify the genetic background of the pathogenic bacteria, and the 50% lethal dose of the pathogenic bacteria to mice and its drug sensitivity were determined at the same time. The experimental results showed that the homology between the pathogenic strain and Acinetobacter baumannii was as high as 99.8%. The pathogenic strain was highly pathogenic to experimental mice, and its half lethal dose in mice was 8.89 × 107 CFU·mL−1. Drug sensitivity tests showed that the pathogenic strain is sensitive to carbenicillin, ofloxacin and ciprofloxacin.
2021, 12(4): 448-455.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.007
Abstract:
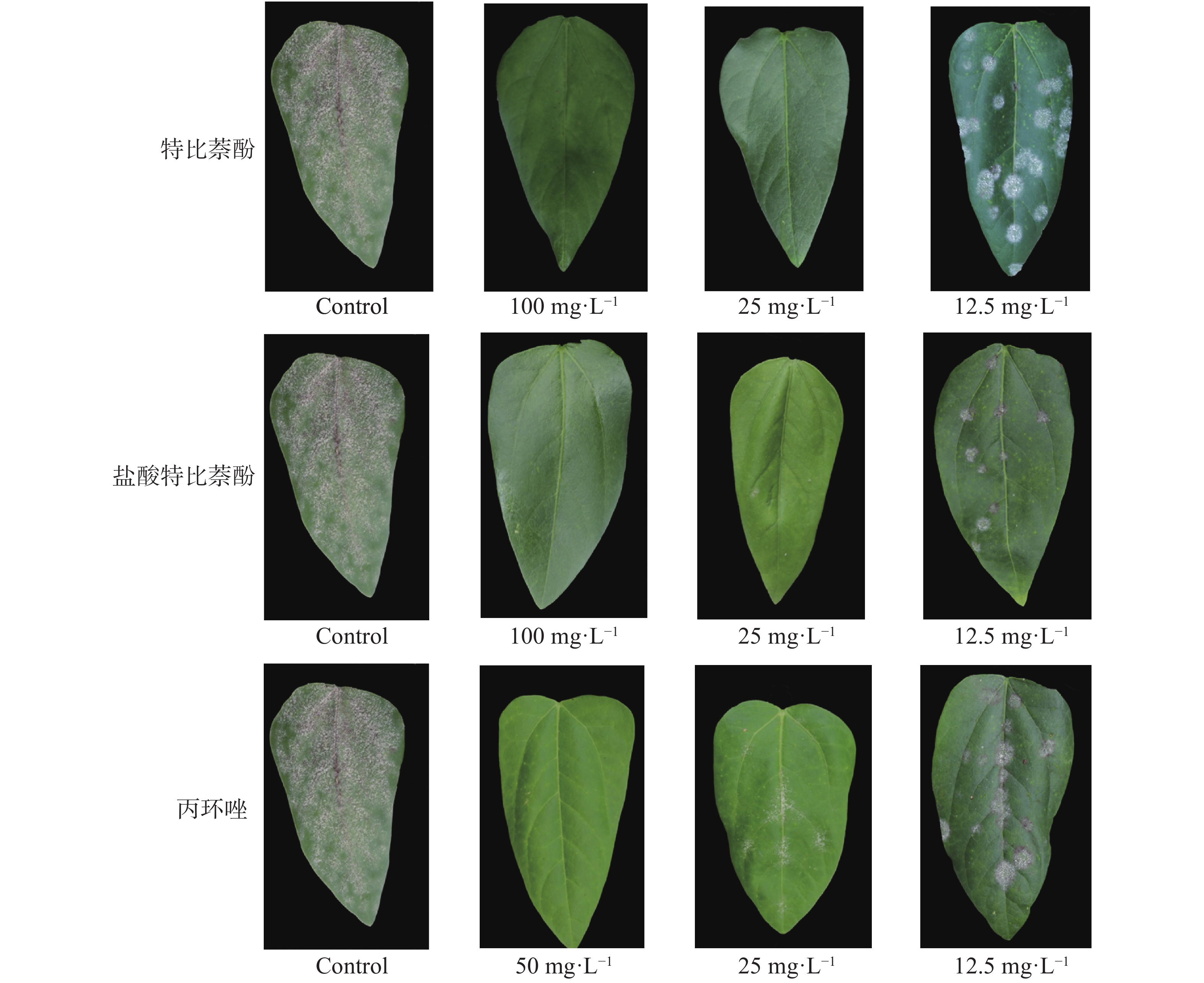
Sixteen species of plant pathogenic fungi and 9 plant fungal diseases were treated with fungicides terbinafine and terbinafine hydrochloride to observe their mycelium growth in vitro and in vivo control effect by pot-spraying, respectively. Results showed terbinafine and terbinafine hydrochloride had a good antifungal activity against many of the plant pathogenic fungi. Terbinafine showed a higher inhibitory effect against 8 species of the plant pathogenic fungi, i.e., Pestalotipsis guepinii, Fusarium graminearum, Gibberella zeae, Alternaria solan, Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, Fusarium oxysporum, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Colletotrichum orbiculare, and its EC50 values for these 8 fungal species were 0.03~0.24 mg·L−1. The terbinafine hydrochloride had a higher inhibitory effect against 5 fungal species, Pestalotipsis guepinii, Fusarium graminearum, Gibberella zeae, Alternaria solan and Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, and its EC50 values for these 5 fungal species were 0.03~0.22 mg·L−1. In vivo potted experiments showed that terbinafine and terbinafine hydrochloride effectively controlled many crop diseases. These two fungicides had a 100% control effect against cowpea powdery mildew (Podosphaera xanthii) when sprayed at a concentration of 100 mg·L−1, and a 90.00%~100.00% control of rice sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani), wheat powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis), cucumber target leaf spot (Corynespora cassiicola), cucumber powdery mildew (Erysiphe cichoracearum), and northern corn leaf blight (Setosphaeria turcica) by when sprayed at 400 mg·L−1.
Sixteen species of plant pathogenic fungi and 9 plant fungal diseases were treated with fungicides terbinafine and terbinafine hydrochloride to observe their mycelium growth in vitro and in vivo control effect by pot-spraying, respectively. Results showed terbinafine and terbinafine hydrochloride had a good antifungal activity against many of the plant pathogenic fungi. Terbinafine showed a higher inhibitory effect against 8 species of the plant pathogenic fungi, i.e., Pestalotipsis guepinii, Fusarium graminearum, Gibberella zeae, Alternaria solan, Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, Fusarium oxysporum, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and Colletotrichum orbiculare, and its EC50 values for these 8 fungal species were 0.03~0.24 mg·L−1. The terbinafine hydrochloride had a higher inhibitory effect against 5 fungal species, Pestalotipsis guepinii, Fusarium graminearum, Gibberella zeae, Alternaria solan and Neoscytalidium dimidiatum, and its EC50 values for these 5 fungal species were 0.03~0.22 mg·L−1. In vivo potted experiments showed that terbinafine and terbinafine hydrochloride effectively controlled many crop diseases. These two fungicides had a 100% control effect against cowpea powdery mildew (Podosphaera xanthii) when sprayed at a concentration of 100 mg·L−1, and a 90.00%~100.00% control of rice sheath blight (Rhizoctonia solani), wheat powdery mildew (Blumeria graminis), cucumber target leaf spot (Corynespora cassiicola), cucumber powdery mildew (Erysiphe cichoracearum), and northern corn leaf blight (Setosphaeria turcica) by when sprayed at 400 mg·L−1.
2021, 12(4): 456-465.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.008
Abstract:
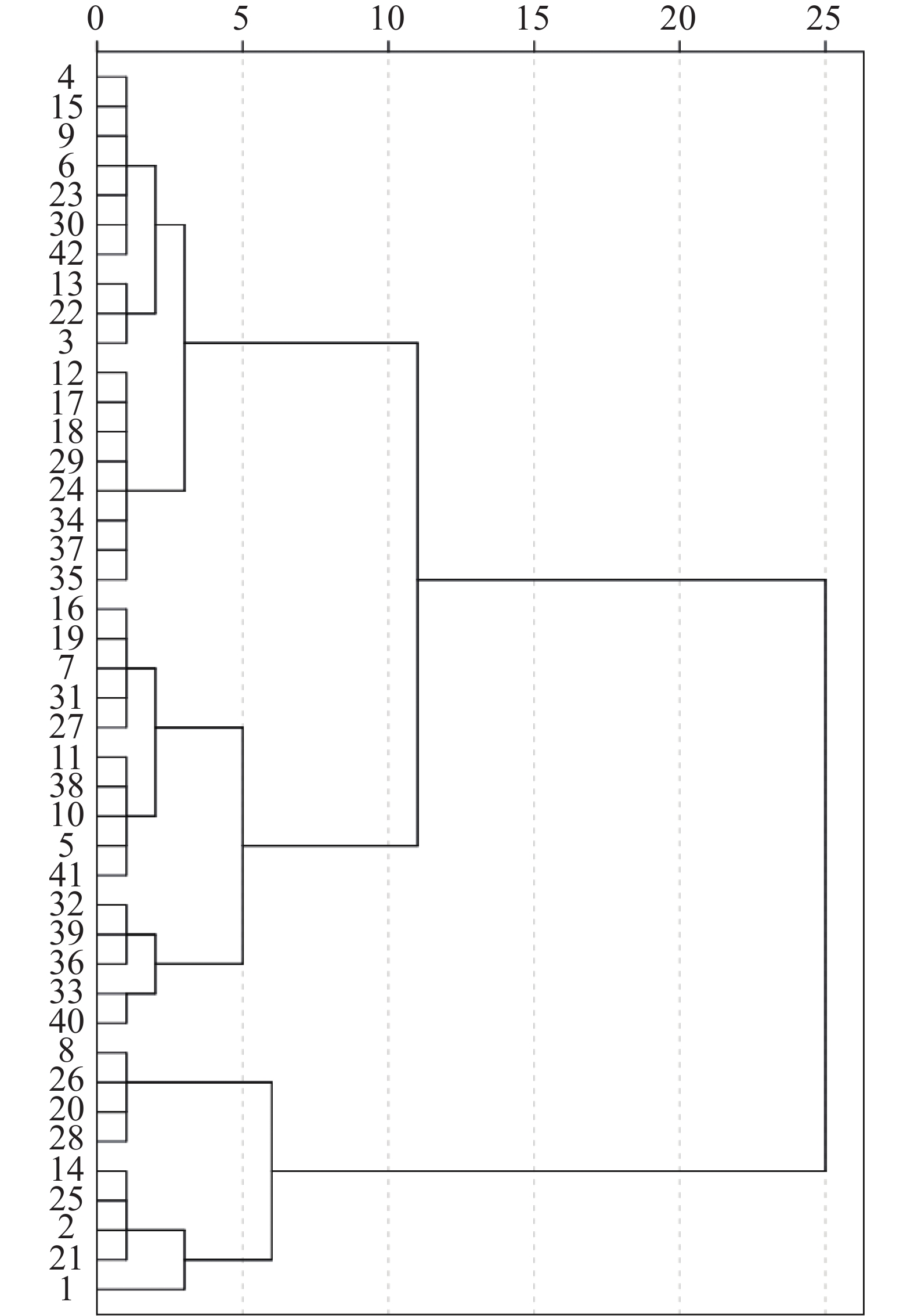
The correlation of agronomic traits and yield of 42 indica hybrid rice varieties under regional rice variety trial in Dehong Prefecture, Yunnan in 2020 was analyzed, and these rice varieties were comprehensively evaluated by using simple correlation, partial correlation, regression and path analysis. The results indicated that yields of the rice varieties were positively correlated with effective panicle number, filled grain per panicle and thousand-grain weight. Principal components analysis extracted four principal components, tiller, grain, grain weight and panicle length as factor, and the cumulative contribution rate these four factors was 85.29%. According to comprehensive sorting results of the principal component score of each rice variety, the rice varieties Jinliangyou 906, Luyou 164 and Huayou 33 were ranked in the top. The 42 rice varieties were divided into five groups by cluster analysis, among which the fifth group could be used as good cultivars for high-yield cultivation in production, and the fourth group could be used as excellent resource for breeding of rice varieties with early maturity and high yield. The high yield breeding objectives and main cultivation suggestions were proposed appropriately according to the characteristics of the rice varieties in various groups.
The correlation of agronomic traits and yield of 42 indica hybrid rice varieties under regional rice variety trial in Dehong Prefecture, Yunnan in 2020 was analyzed, and these rice varieties were comprehensively evaluated by using simple correlation, partial correlation, regression and path analysis. The results indicated that yields of the rice varieties were positively correlated with effective panicle number, filled grain per panicle and thousand-grain weight. Principal components analysis extracted four principal components, tiller, grain, grain weight and panicle length as factor, and the cumulative contribution rate these four factors was 85.29%. According to comprehensive sorting results of the principal component score of each rice variety, the rice varieties Jinliangyou 906, Luyou 164 and Huayou 33 were ranked in the top. The 42 rice varieties were divided into five groups by cluster analysis, among which the fifth group could be used as good cultivars for high-yield cultivation in production, and the fourth group could be used as excellent resource for breeding of rice varieties with early maturity and high yield. The high yield breeding objectives and main cultivation suggestions were proposed appropriately according to the characteristics of the rice varieties in various groups.
2021, 12(4): 466-472.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.009
Abstract:
In order to select sweetpotato varieties with healthy leaves as vegetables in Hainan Province, 10 sweetpotato varieties were comprehensively evaluated in terms of leaf antioxidant activities. The leaf contents of three pigments (chlorophylls, carotenoids, and anthocyanins), total phenolics and total flavonoids were determined, and the ABTS (2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)) and DPPH (2,2′-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging abilities, which directly represent antioxidant activities, were also detected in the leaves. The results showed that the leaf antioxidant activities in all the sweetpotato varieties were positively correlated with the leaf contents of total flavonoids (P < 0.01), anthocyanins (P < 0.01), chlorophylls (P < 0.05), and total phenolics (P > 0.05).The vegetable sweetpotato variety ‘Fushu 7-6’ was higher in the contents of chlorophylls and carotenoids, but lower in the contents of total flavonoids, total phenolics and anthocyanins, and hence was the lowest in the antioxidant activity among the 10 sweetpotato varieties. Sweetpotato varieties ‘Yu 15’ and ‘Xuzicai 8’ had significantly higher leaf contents of total phenols, total flavonoids and anthocyanins than the other 8 sweetpotato varieties, and were the highest in antioxidant activity. The red color of the leaves of sweetpotato varieties indicated higher antioxidant activity in the leaves, based on which sweetpotato varieties with healthy leaves as vegetables can be selected to reduce the breeding cost.
In order to select sweetpotato varieties with healthy leaves as vegetables in Hainan Province, 10 sweetpotato varieties were comprehensively evaluated in terms of leaf antioxidant activities. The leaf contents of three pigments (chlorophylls, carotenoids, and anthocyanins), total phenolics and total flavonoids were determined, and the ABTS (2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)) and DPPH (2,2′-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging abilities, which directly represent antioxidant activities, were also detected in the leaves. The results showed that the leaf antioxidant activities in all the sweetpotato varieties were positively correlated with the leaf contents of total flavonoids (P < 0.01), anthocyanins (P < 0.01), chlorophylls (P < 0.05), and total phenolics (P > 0.05).The vegetable sweetpotato variety ‘Fushu 7-6’ was higher in the contents of chlorophylls and carotenoids, but lower in the contents of total flavonoids, total phenolics and anthocyanins, and hence was the lowest in the antioxidant activity among the 10 sweetpotato varieties. Sweetpotato varieties ‘Yu 15’ and ‘Xuzicai 8’ had significantly higher leaf contents of total phenols, total flavonoids and anthocyanins than the other 8 sweetpotato varieties, and were the highest in antioxidant activity. The red color of the leaves of sweetpotato varieties indicated higher antioxidant activity in the leaves, based on which sweetpotato varieties with healthy leaves as vegetables can be selected to reduce the breeding cost.
2021, 12(4): 473-480.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.010
Abstract:
Monostroma nitidum samples collected in the Naozhou sea area, Zhanjiang, Guangdong province were treated differently and their main nutrient composition, amino acids content and mineral composition were determined to evaluate their nutritional values. The results showed that the contents of carbohydrate (41.88%-46.10%) and minerals (28.68%-40.69%) in all the samples were higher. The contents of protein varied from 5.10% to 9.29% and the contents of crude fiber (0.94%-4.94%) and fats (0.60%-1.82%) were lower. The contents of protein, fat, crude fiber and minerals were significantly different between the samples (P < 0.05), while the total sugar content was not significantly different. Significant difference in carbohydrate content was only detected in the samples collected at different time. Although all the samples of M. nitidum contained low protein, the amino acid analysis showed they all had a complete set of amino acids, with the contents of seven essential amino acids accounting for 40.51%-41.48% of the total content of amino acids. The contents of flavor amino acids were higher in the samples of M. Nitidum, accounting for 46.16%-48.14% of the total content of amino acids. The essential amino acid composition of the sample collected in late April was basically agreeable with the FAO model standard, and its amino acid score was 72.63, the highest in all the samples. After the release of gametes, the contents of protein, carbohydrate and fats in M. Nitidum decreased by 45.10%, 2.04% and 4.95%, respectively, whereas the contents of total sugar, crude fiber and minerals increased by 11.47%, 72.34% and 15.96%, respectively. The contents of mineral elements such as sodium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, potassium and iron in M. nitidum were quite high. M. nitidum was rich in dietary fiber, with ideal protein pattern and abundant mineral elements. The nutrient contents in M. nitidum varied with the collection time and whether the gametes were released or not.
Monostroma nitidum samples collected in the Naozhou sea area, Zhanjiang, Guangdong province were treated differently and their main nutrient composition, amino acids content and mineral composition were determined to evaluate their nutritional values. The results showed that the contents of carbohydrate (41.88%-46.10%) and minerals (28.68%-40.69%) in all the samples were higher. The contents of protein varied from 5.10% to 9.29% and the contents of crude fiber (0.94%-4.94%) and fats (0.60%-1.82%) were lower. The contents of protein, fat, crude fiber and minerals were significantly different between the samples (P < 0.05), while the total sugar content was not significantly different. Significant difference in carbohydrate content was only detected in the samples collected at different time. Although all the samples of M. nitidum contained low protein, the amino acid analysis showed they all had a complete set of amino acids, with the contents of seven essential amino acids accounting for 40.51%-41.48% of the total content of amino acids. The contents of flavor amino acids were higher in the samples of M. Nitidum, accounting for 46.16%-48.14% of the total content of amino acids. The essential amino acid composition of the sample collected in late April was basically agreeable with the FAO model standard, and its amino acid score was 72.63, the highest in all the samples. After the release of gametes, the contents of protein, carbohydrate and fats in M. Nitidum decreased by 45.10%, 2.04% and 4.95%, respectively, whereas the contents of total sugar, crude fiber and minerals increased by 11.47%, 72.34% and 15.96%, respectively. The contents of mineral elements such as sodium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium, potassium and iron in M. nitidum were quite high. M. nitidum was rich in dietary fiber, with ideal protein pattern and abundant mineral elements. The nutrient contents in M. nitidum varied with the collection time and whether the gametes were released or not.
2021, 12(4): 481-490.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.011
Abstract:
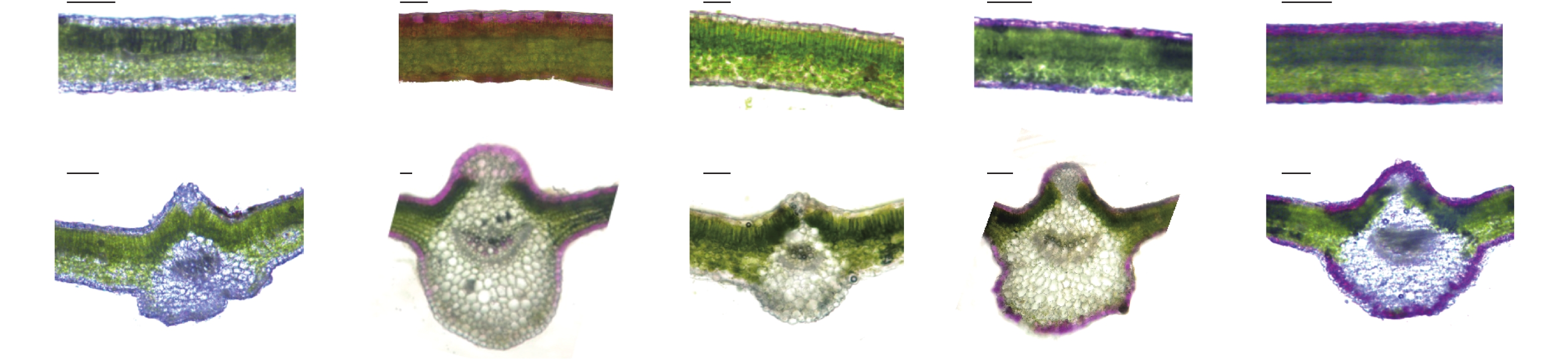
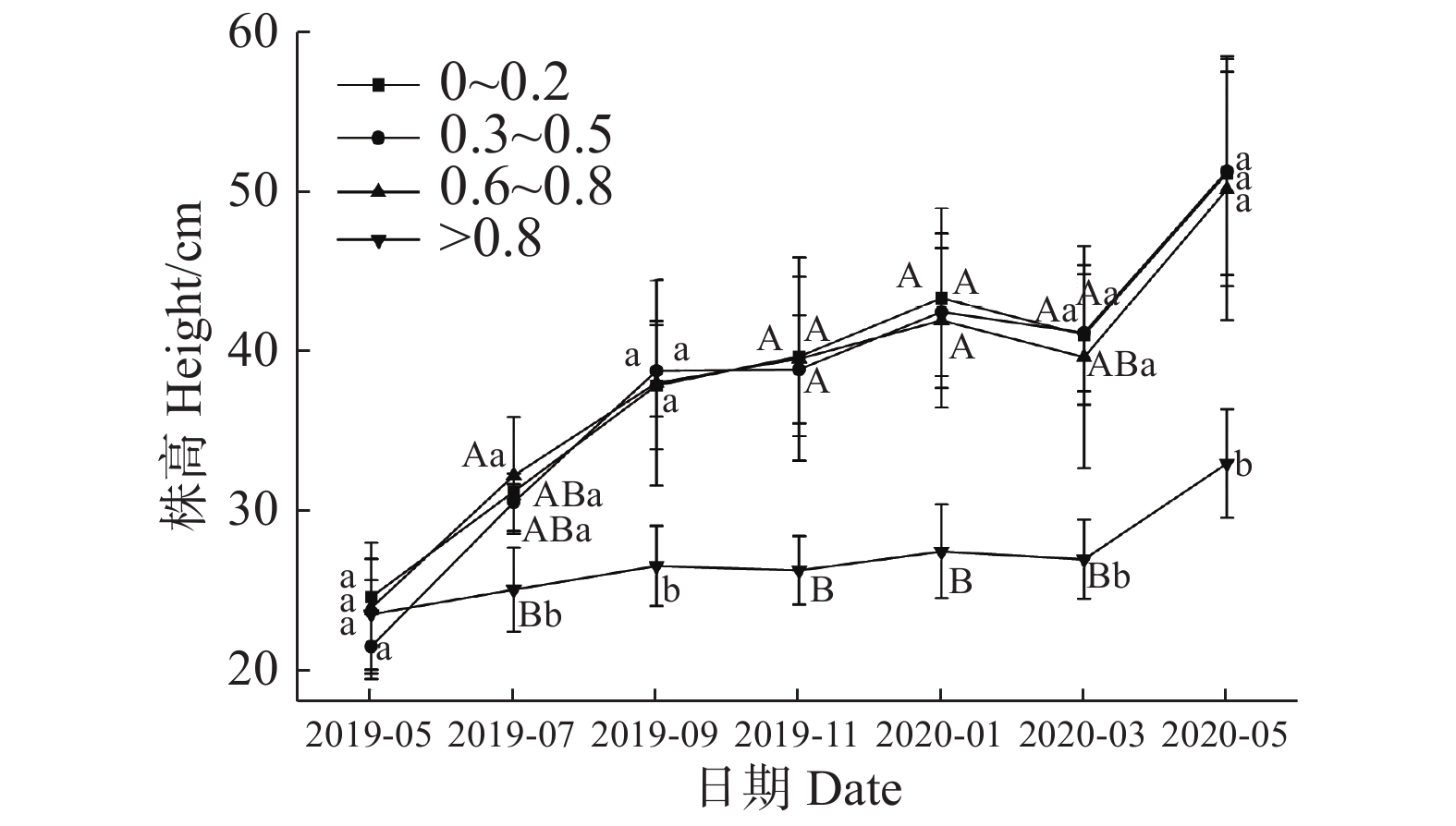
In order toTo explore the impact of different reintroduction methods on the growth of Horsfieldia. hainanensis Merr., three-year-old trees of H. hainanensis Merr. were reintroduced intoo the areas for planting at different altitudes (300, 600, 900 m) under different canopy closures (0~0.2, 0.3~0.5, 0.6~0.8, >0.8) to observe the changes in their growth indicators, leaf traits and leaf shape. The results showed that higher canopy closure (>0.8) significantly reduced the plant height, ground diameter, leaf length (LL) and leaf width (LB) of H. hainanensis Merr reintroduced, but had no significant effect on photosynthetic pigments and other indicators. The altitude of 600 m significantly increased the plant height, leaf water content (CLWC), specific leaf area (SLAM), chlorophyll b (Chl b) of H. hainanensis Merr. reintroduced, and there was no significant difference in leaf shape. It is concluded that the altitude of 600 m and the low canopy closure (0.3~0.8) is beneficial to the growth of the 3-year-old trees of H. hainanensis Merr. reintroduced, which provides a reference for the effective conservation and restoration of H. hainanensis Merr.
In order toTo explore the impact of different reintroduction methods on the growth of Horsfieldia. hainanensis Merr., three-year-old trees of H. hainanensis Merr. were reintroduced intoo the areas for planting at different altitudes (300, 600, 900 m) under different canopy closures (0~0.2, 0.3~0.5, 0.6~0.8, >0.8) to observe the changes in their growth indicators, leaf traits and leaf shape. The results showed that higher canopy closure (>0.8) significantly reduced the plant height, ground diameter, leaf length (LL) and leaf width (LB) of H. hainanensis Merr reintroduced, but had no significant effect on photosynthetic pigments and other indicators. The altitude of 600 m significantly increased the plant height, leaf water content (CLWC), specific leaf area (SLAM), chlorophyll b (Chl b) of H. hainanensis Merr. reintroduced, and there was no significant difference in leaf shape. It is concluded that the altitude of 600 m and the low canopy closure (0.3~0.8) is beneficial to the growth of the 3-year-old trees of H. hainanensis Merr. reintroduced, which provides a reference for the effective conservation and restoration of H. hainanensis Merr.
2021, 12(4): 491-499.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.012
Abstract:
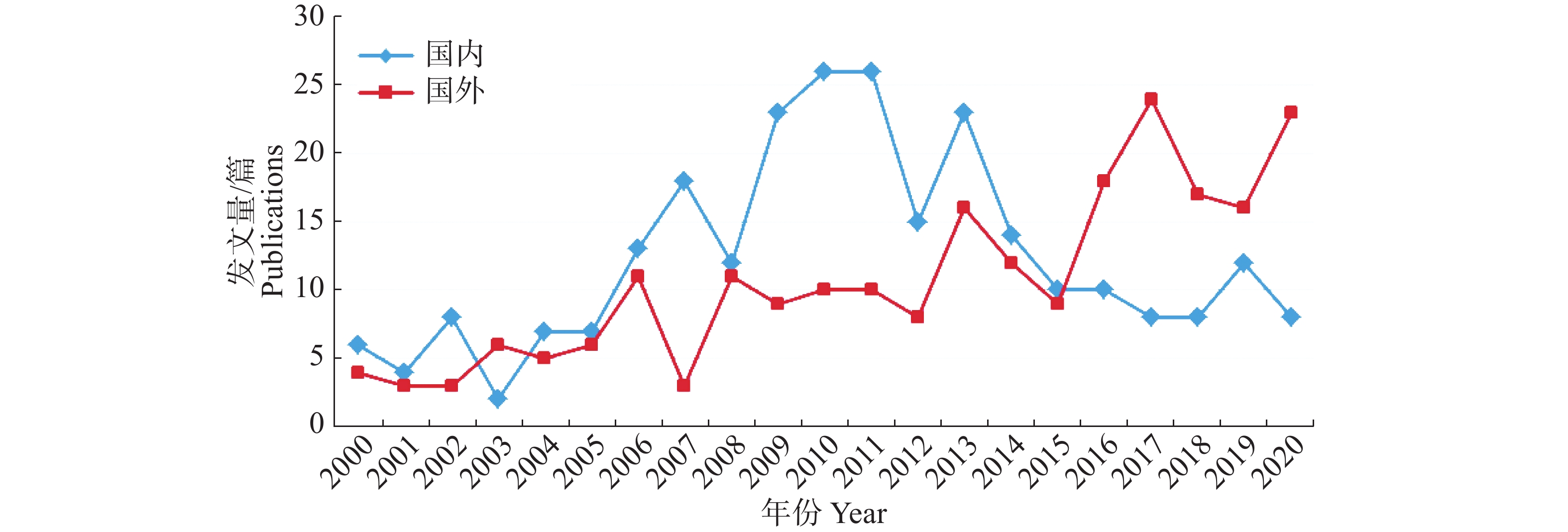
In order to fully grasp the progress of road greening research at domestic and overseas, core journal data from CNKI and WOS were used as the source. A visual analysis of Chinese and English literature on road, street or highway greening research from 2000 to 2020 were made by using CiteSpace software, based on which the hotspots, interests and frontiers of research in China and other countries were concluded. The analysis showed that research on road, street or highway greening in China had a declining trend with its peak period in between 2010 and 2011, while the research in other countries was at a good stage of development. In terms of research interests researchers in China mainly focused on planning and design and landscape evaluation, plant arrangement patterns and maintenance management, and plant diversity and ecological benefits, while researchers in other countries were mainly aimed at the diversity of plants, the physical and chemical properties of soil, health risk assessment and research of road environments, mechanism of plant and animal invasion and dispersal. In terms of research frontiers the researchers in China and other countries all tended to focus on the ecological service function of the road, street or highway greening.
In order to fully grasp the progress of road greening research at domestic and overseas, core journal data from CNKI and WOS were used as the source. A visual analysis of Chinese and English literature on road, street or highway greening research from 2000 to 2020 were made by using CiteSpace software, based on which the hotspots, interests and frontiers of research in China and other countries were concluded. The analysis showed that research on road, street or highway greening in China had a declining trend with its peak period in between 2010 and 2011, while the research in other countries was at a good stage of development. In terms of research interests researchers in China mainly focused on planning and design and landscape evaluation, plant arrangement patterns and maintenance management, and plant diversity and ecological benefits, while researchers in other countries were mainly aimed at the diversity of plants, the physical and chemical properties of soil, health risk assessment and research of road environments, mechanism of plant and animal invasion and dispersal. In terms of research frontiers the researchers in China and other countries all tended to focus on the ecological service function of the road, street or highway greening.
2021, 12(4): 500-507.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.013
Abstract:
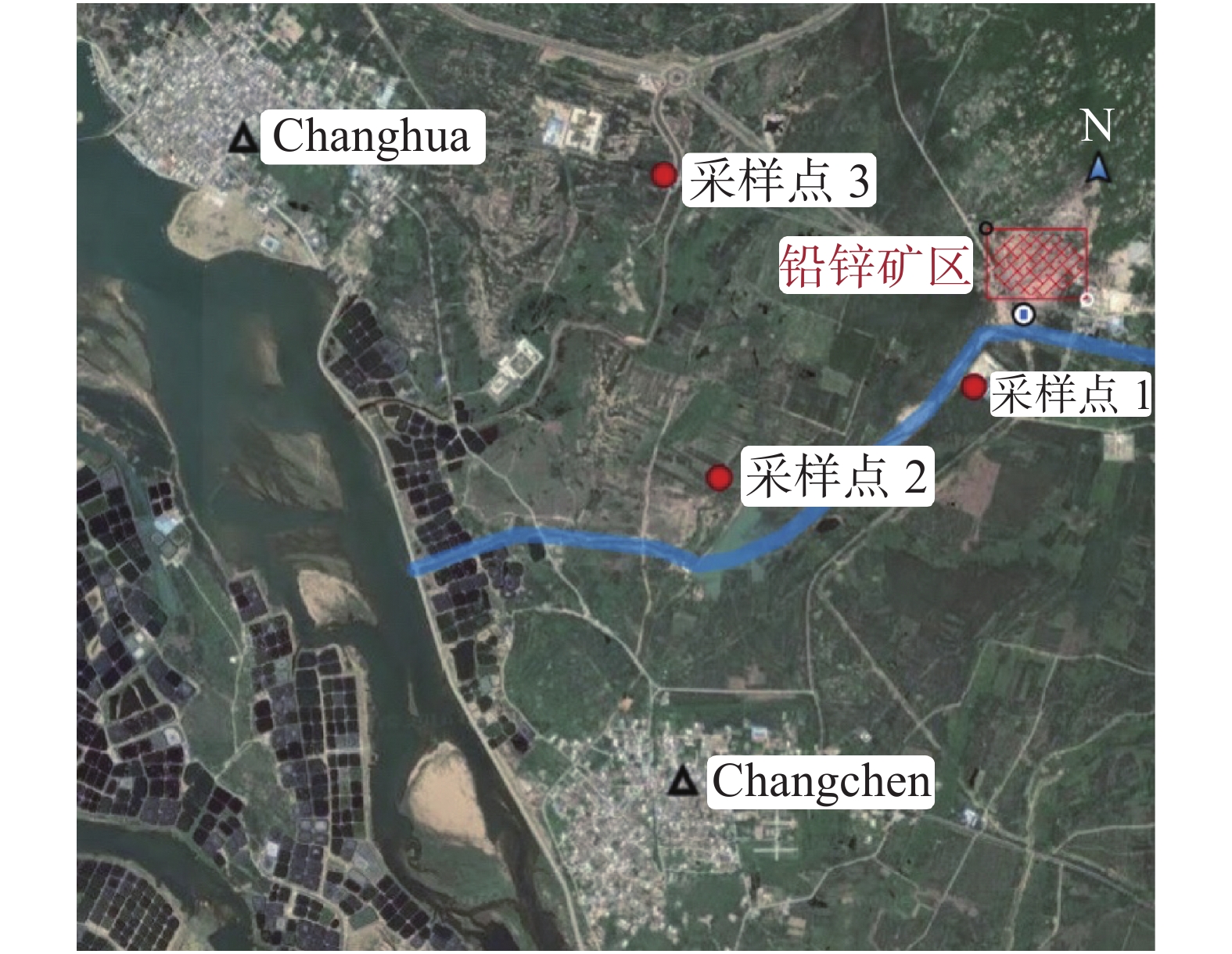
A survey was made of the soil and plants around the abandoned lead-zinc mine in Changhua Town, Changjiang County, Hainan Province, and three sampling sites were arranged. The soil and 13 species of plants in the sampling sites were collected to determine and analyze their contents of heavy metals. The results showed that the soil around the lead-zinc mine is generally contaminated by Pb, Cd, Zn and Cu, with a comprehensive heavy metal contamination index of 19.86, indicating the soil contamination level around the lead-zinc mine is high according to the grading standard for the comprehensive soil heavy metal contamination evaluation. Of the 13 species of plants sampled around the lead-zinc mine, Artemisia chinensis showed an enrichment potential for the heavy metal Cd, and Atalantia buxifolia showed an enrichment potential for the heavy metal Zn.
A survey was made of the soil and plants around the abandoned lead-zinc mine in Changhua Town, Changjiang County, Hainan Province, and three sampling sites were arranged. The soil and 13 species of plants in the sampling sites were collected to determine and analyze their contents of heavy metals. The results showed that the soil around the lead-zinc mine is generally contaminated by Pb, Cd, Zn and Cu, with a comprehensive heavy metal contamination index of 19.86, indicating the soil contamination level around the lead-zinc mine is high according to the grading standard for the comprehensive soil heavy metal contamination evaluation. Of the 13 species of plants sampled around the lead-zinc mine, Artemisia chinensis showed an enrichment potential for the heavy metal Cd, and Atalantia buxifolia showed an enrichment potential for the heavy metal Zn.
2021, 12(4): 508-513.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.04.014
Abstract:
Megalurothrips usitatus is one of the main pests of cowpea in Hainan Province. It infests cowpea mainly by laying eggs in cowpea and feeding on flowers and pods, which seriously affects the quality and yield of cowpea. Hainan Province is located in the tropics, and its unique environmental conditions are very suitable for the growth and reproduction of thrips. Thrips are small in size, fast in transmission, high in concealment and strong in reproductive ability, and its outbreak easily occurs, causing huge economic losses. In recent years the abuse and irrational use of chemical insecticides resulted in high resistance of M. usitatus populations to conventional insecticides in different areas of Hainan province, which further aggravated the infestation of this insect pest and brought up many risks including insecticide residues and environmental pollution. In order to achieve green sustainable management of this insect pest, the ecological mechanism for the outbreak of M. usitatus was reviewed and discussed in terms of occurrence and damages, biological characteristics and insecticide resistances. The current domestic and overseas research progress of the integrated control of this pest was reviewed. This review might provide reference for control and prevention of M. usitatus in the field.
Megalurothrips usitatus is one of the main pests of cowpea in Hainan Province. It infests cowpea mainly by laying eggs in cowpea and feeding on flowers and pods, which seriously affects the quality and yield of cowpea. Hainan Province is located in the tropics, and its unique environmental conditions are very suitable for the growth and reproduction of thrips. Thrips are small in size, fast in transmission, high in concealment and strong in reproductive ability, and its outbreak easily occurs, causing huge economic losses. In recent years the abuse and irrational use of chemical insecticides resulted in high resistance of M. usitatus populations to conventional insecticides in different areas of Hainan province, which further aggravated the infestation of this insect pest and brought up many risks including insecticide residues and environmental pollution. In order to achieve green sustainable management of this insect pest, the ecological mechanism for the outbreak of M. usitatus was reviewed and discussed in terms of occurrence and damages, biological characteristics and insecticide resistances. The current domestic and overseas research progress of the integrated control of this pest was reviewed. This review might provide reference for control and prevention of M. usitatus in the field.



 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 1905KB
PDF 1905KB







 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS