2022 Vol. 13, No. 1
2022, 13(1): 1-6.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.001
Abstract:
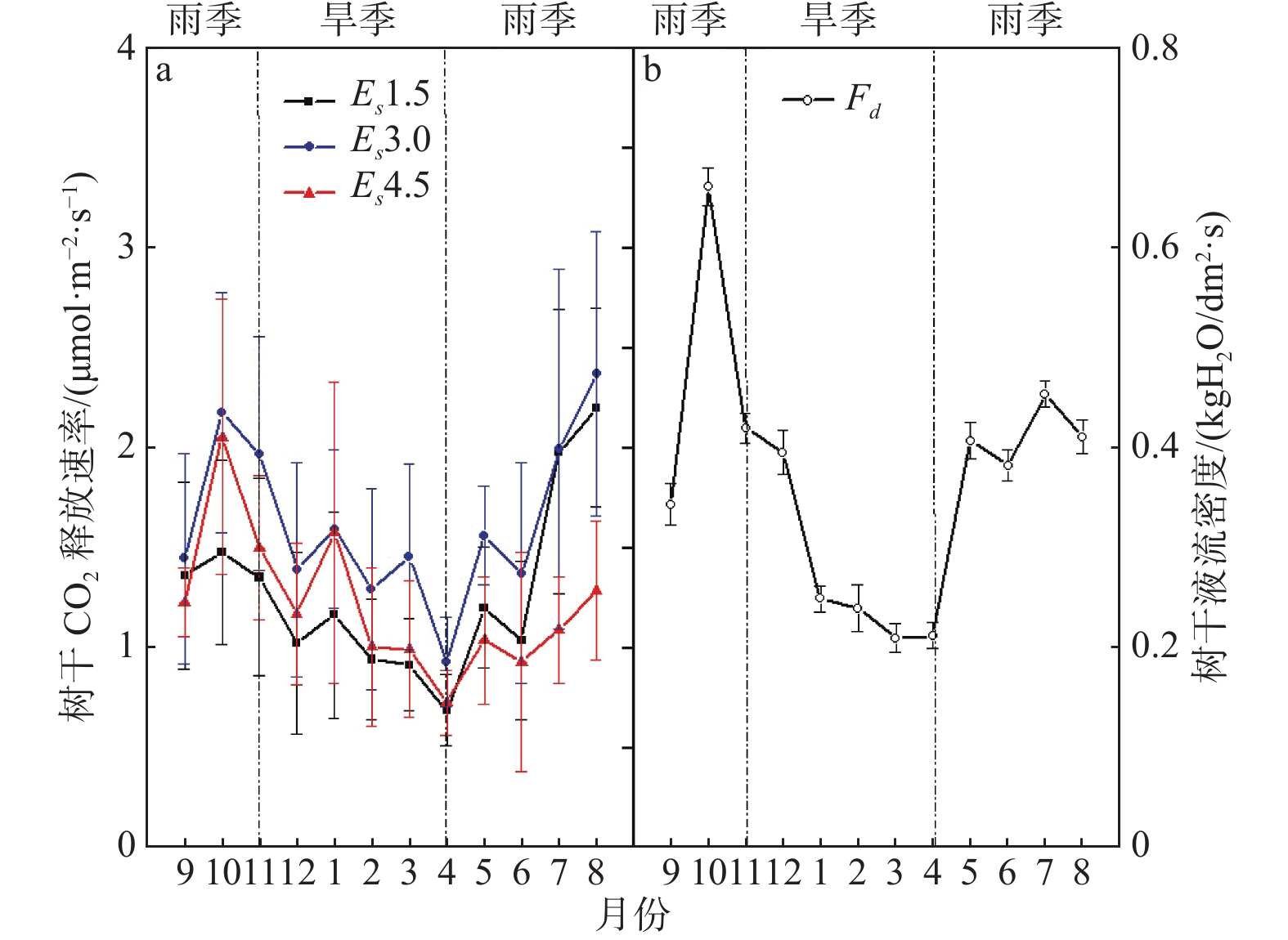
An attempt was made to study the temporal and spatial dynamic characteristics of stem CO2 efflux rate (Es) and its influencing factors for development of tree stem respiration flux models, which improve the accuracy of respiration calculations in the rubber plantation ecosystem. A portable infrared gas analyzer (IRGA) was used to monitor in situ Es of a rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) plantation for one year in Hainan Island. The Es measured include those at 1.5 m height (Es1.5), 3.0m height (Es3.0) and 4.5m height (Es4.5) of the sample rubber trees. In addition, stem sap flow density (Fd) was also monitored at the same time, and the anatomical structures of the xylem vessels at different heights of the sample rubber trees were observed and analyzed by using microsection method. The results showed that Es showed seasonal changes in dry and wet season, which were in the order of Es3.0>Es4.5>Es1.5 from October to April, and Es3.0>Es1.5>Es4.5 from May to September. The Es was significantly influenced by stem sap flow and xylem structure. Analysis of the differences between density and diameter of the xylem vessels of the sample rubber trees at different heights showed that the xylem vessel diameter was the main factor influencing Fd and Es. With the increase of xylem vessel diameter, the stem sap flow velocity tended to increase and then the Es tended to increase.
An attempt was made to study the temporal and spatial dynamic characteristics of stem CO2 efflux rate (Es) and its influencing factors for development of tree stem respiration flux models, which improve the accuracy of respiration calculations in the rubber plantation ecosystem. A portable infrared gas analyzer (IRGA) was used to monitor in situ Es of a rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) plantation for one year in Hainan Island. The Es measured include those at 1.5 m height (Es1.5), 3.0m height (Es3.0) and 4.5m height (Es4.5) of the sample rubber trees. In addition, stem sap flow density (Fd) was also monitored at the same time, and the anatomical structures of the xylem vessels at different heights of the sample rubber trees were observed and analyzed by using microsection method. The results showed that Es showed seasonal changes in dry and wet season, which were in the order of Es3.0>Es4.5>Es1.5 from October to April, and Es3.0>Es1.5>Es4.5 from May to September. The Es was significantly influenced by stem sap flow and xylem structure. Analysis of the differences between density and diameter of the xylem vessels of the sample rubber trees at different heights showed that the xylem vessel diameter was the main factor influencing Fd and Es. With the increase of xylem vessel diameter, the stem sap flow velocity tended to increase and then the Es tended to increase.
2022, 13(1): 7-12.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.002
Abstract:
Osmotic regulation plays an important role in maintaining plant turgor, protecting cell function, regulating water relationship and coping with environmental stresses. However, the osmotic regulators and their contribution to osmotic potential are different in different plant organs. Polybag tissue cultured rubber plants of clone Reyan 73397 were selected to determine the contents of osmatic regulators such as soluble sugar, free amino acid, organic acid, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+, NO3−, Cl−, P and S in the roots and leaves to analyze the contribution of the osmotic regulators to osmotic regulation. The results showed that osmotic regulators in the roots were mainly composed of inorganic substances, while osmatic regulators in the leaves were mainly composed of organic substances, the total content of which was much higher than those in the roots. The contents of soluble sugar, free amino acids, K+ and Ca2+ in the roots and leaves contributed differently to the osmatic potential, but they were the main osmotic regulators.
Osmotic regulation plays an important role in maintaining plant turgor, protecting cell function, regulating water relationship and coping with environmental stresses. However, the osmotic regulators and their contribution to osmotic potential are different in different plant organs. Polybag tissue cultured rubber plants of clone Reyan 73397 were selected to determine the contents of osmatic regulators such as soluble sugar, free amino acid, organic acid, Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+, NO3−, Cl−, P and S in the roots and leaves to analyze the contribution of the osmotic regulators to osmotic regulation. The results showed that osmotic regulators in the roots were mainly composed of inorganic substances, while osmatic regulators in the leaves were mainly composed of organic substances, the total content of which was much higher than those in the roots. The contents of soluble sugar, free amino acids, K+ and Ca2+ in the roots and leaves contributed differently to the osmatic potential, but they were the main osmotic regulators.
2022, 13(1): 13-18.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.003
Abstract:
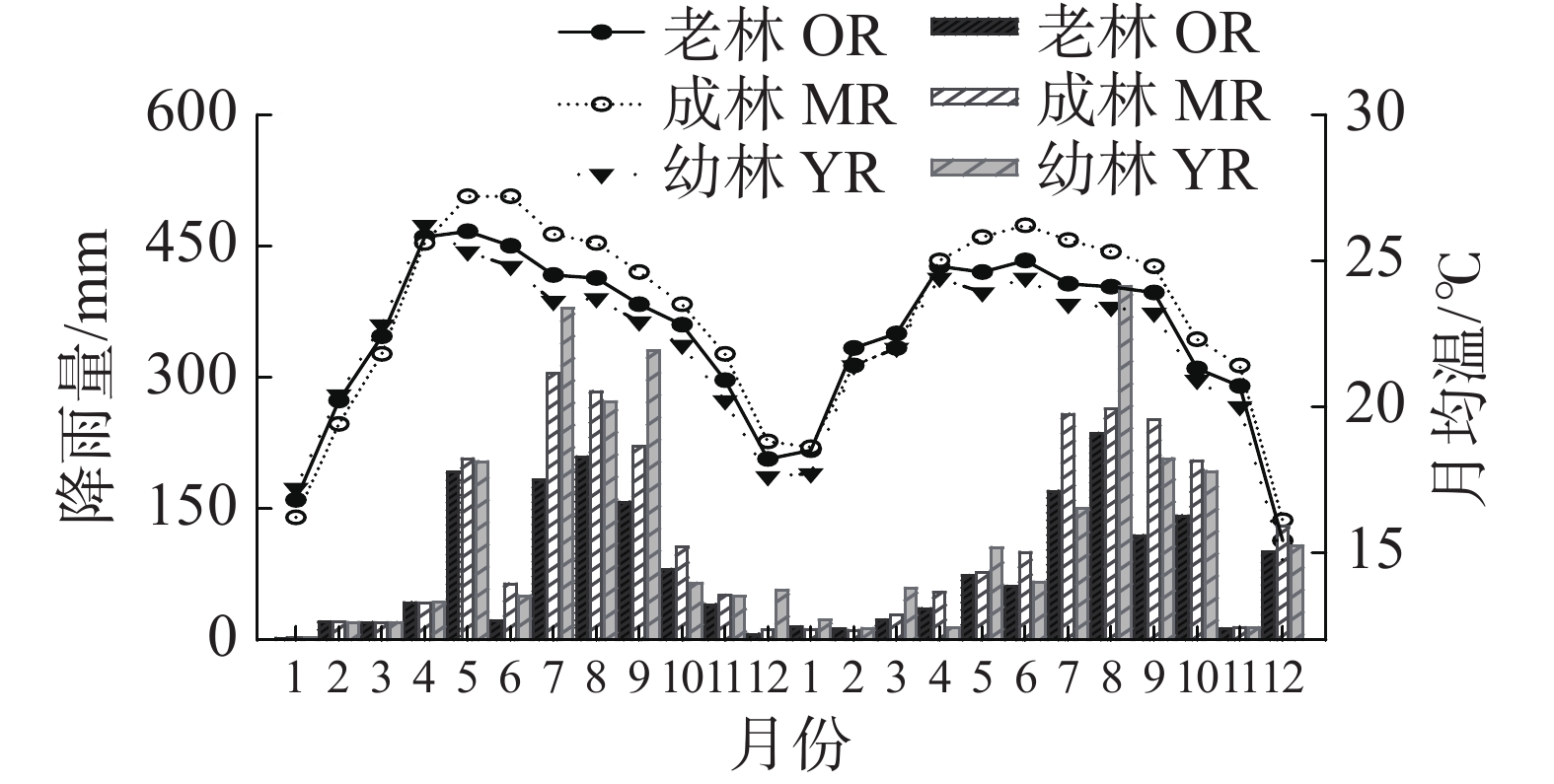
In order to explore the changes of soil respiration rate (Rs) and the relationship between Rs and hydrothermal factors in rubber plantations of different ages, rubber plantations at three different stand ages (2 a, 7 a, 30 a) were selected for analysis. The change characteristics of soil respiration rate (Rs), soil temperature (Ts) and soil moisture (Ms) in 5 cm soil surface were measured in situ every month for two years. The results showed that the Rs of rubber plantations at the three stand ages were significantly different (P < 0.05). The Rs of the 2 a rubber plantation (young rubber plantation, YR) was significantly higher than that of the 7 a rubber plantation (mature rubber plantations, MR), and the Rs of the 30 a rubber plantation (old rubber plantation, OR) was the lowest. The Rs, Ts and Ms of the rubber plantations at the three stand ages had obvious seasonal variation, showing significantly higher values in rainy season than in dry season. The peak of soil respiration rate of the rubber plantations at different ages appeared in different months, and the highest Rs values of YR, MR and OR occurred in September, July and June respectively. The Rs had a highly significant positive correlation (P < 0.01) with Ts and Ms in the rubber plantations at different stand ages, the highest with Ms and the lower with Ts. Regression analysis showed that the change characteristics of the Rs in the rubber plantations of different stand ages are the results of combined effect of multiple hydrothermal factors and that Rs is affected mostly by Ms and relatively less by Ts.
In order to explore the changes of soil respiration rate (Rs) and the relationship between Rs and hydrothermal factors in rubber plantations of different ages, rubber plantations at three different stand ages (2 a, 7 a, 30 a) were selected for analysis. The change characteristics of soil respiration rate (Rs), soil temperature (Ts) and soil moisture (Ms) in 5 cm soil surface were measured in situ every month for two years. The results showed that the Rs of rubber plantations at the three stand ages were significantly different (P < 0.05). The Rs of the 2 a rubber plantation (young rubber plantation, YR) was significantly higher than that of the 7 a rubber plantation (mature rubber plantations, MR), and the Rs of the 30 a rubber plantation (old rubber plantation, OR) was the lowest. The Rs, Ts and Ms of the rubber plantations at the three stand ages had obvious seasonal variation, showing significantly higher values in rainy season than in dry season. The peak of soil respiration rate of the rubber plantations at different ages appeared in different months, and the highest Rs values of YR, MR and OR occurred in September, July and June respectively. The Rs had a highly significant positive correlation (P < 0.01) with Ts and Ms in the rubber plantations at different stand ages, the highest with Ms and the lower with Ts. Regression analysis showed that the change characteristics of the Rs in the rubber plantations of different stand ages are the results of combined effect of multiple hydrothermal factors and that Rs is affected mostly by Ms and relatively less by Ts.
2022, 13(1): 19-26.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.004
Abstract:
In order to standardize the cultivation process of rubber tree cold injury mitigation, improve disaster prevention and reduction capability and the sustainable and stable development of rubber planting industry, the author based on the recent 70 years (1952–2020) literature data and rubber planting practice of rubber planting industry cold injury mitigation, this study clarifies the characteristics of cold injury mitigation and the relevant concepts of rubber tree cold injury mitigation. And clarify the regional division of injury mitigation, the division of rubber planting environmental ecological types, and the classification of rubber tree cold injury mitigation are summarized. Meanwhile, this study also puts forward management, cold injury mitigation, cold damage tree treatment principle. Moreover, cold damage tree treatment method, tending and management after cold damage of rubber tree, and re-tapping of cold damage rubber tree are pointed out. In addition, a systematic rubber tree cold injury mitigation system has been built.
In order to standardize the cultivation process of rubber tree cold injury mitigation, improve disaster prevention and reduction capability and the sustainable and stable development of rubber planting industry, the author based on the recent 70 years (1952–2020) literature data and rubber planting practice of rubber planting industry cold injury mitigation, this study clarifies the characteristics of cold injury mitigation and the relevant concepts of rubber tree cold injury mitigation. And clarify the regional division of injury mitigation, the division of rubber planting environmental ecological types, and the classification of rubber tree cold injury mitigation are summarized. Meanwhile, this study also puts forward management, cold injury mitigation, cold damage tree treatment principle. Moreover, cold damage tree treatment method, tending and management after cold damage of rubber tree, and re-tapping of cold damage rubber tree are pointed out. In addition, a systematic rubber tree cold injury mitigation system has been built.
2022, 13(1): 27-35.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.005
Abstract:
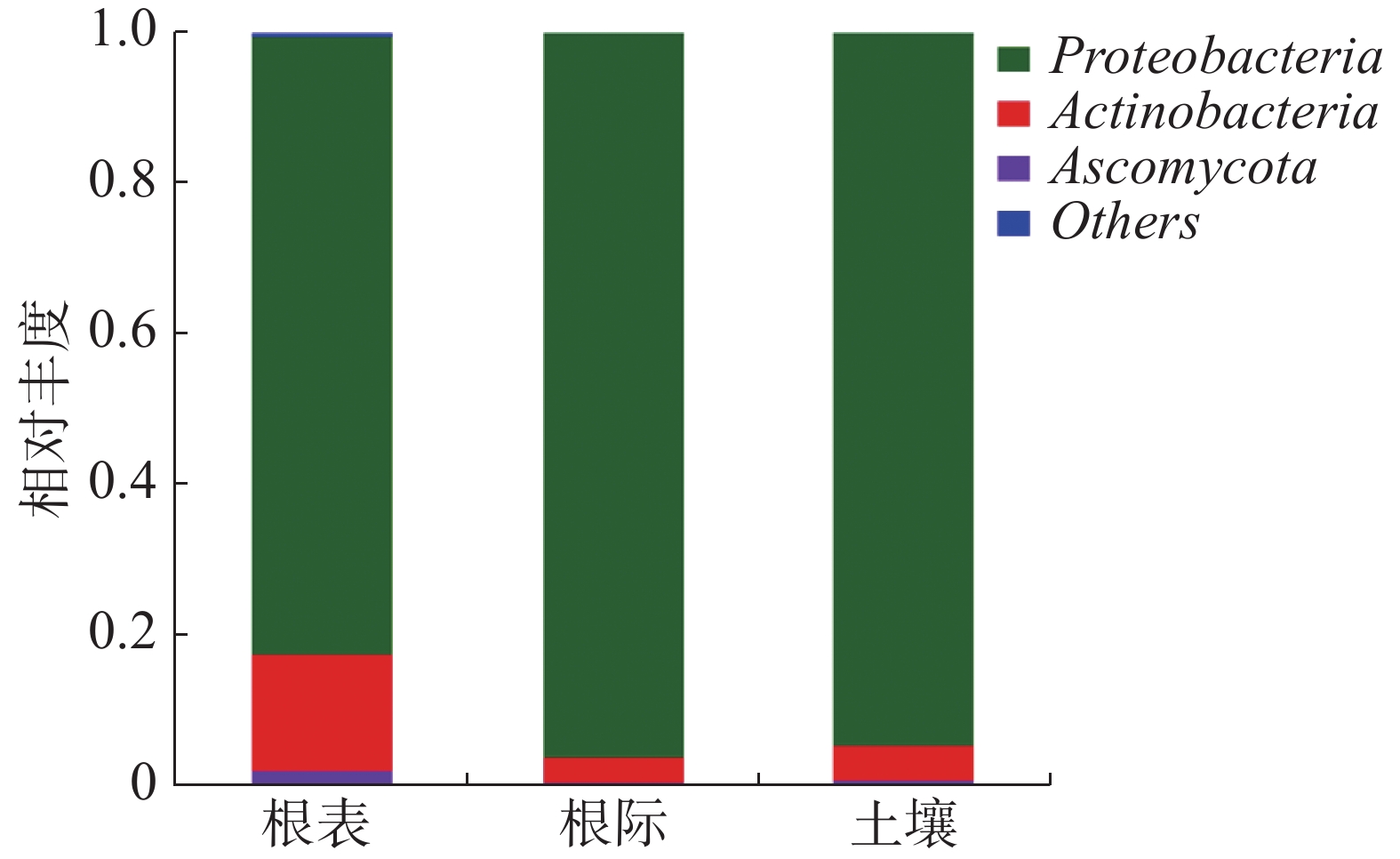
In order to understand the composition and influencing factors of broad-spectrum pathogenic microorganisms in soil and root (rhizosphere and rhizoplane) of rubber plantations, metagenome sequencing was used to analyze the composition and influencing factors of pathogenic microorganisms in soil, rhizosphere and rhizoplane of healthy rubber plantations in Hainan (Danzhou, Wanning and Ledong) and Xishuangbanna (Jinghong, Menglun and Mengman). The results showed that plant pathogenic microorganisms belonged to Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria and Ascomycota at the phylum level, and to Pseudomonas, Ralstonia, Burkholderia, Streptomyces, Agrobacterium, Xanthomonas, Pantoea, Clavibacter, Pectobacterium and Xylella at the genus level with Ascomycota as the main pathogen at the genus level. There was no significant difference in pathogenic microorganisms in the rhizospheres between the rubber plantations in Hainan and Xishuangbanna. The composition of pathogenic microorganisms was similar in the soil and rhizosphere samples, and similar in the rhizoplane samples. There was a significant positive correlation between NH4-N and pathogenic microorganisms. In conclusion there was no significant difference in pathogenic microorganisms in soil, rhizosphere and rhizoplane between the rubber plantations in Hainan and Xishuangbanna. A significant positive correlation was observed between pathogenic microorganisms and NH4-N, and that the composition of pathogenic microorganisms was related to the exudates of the rhizoplane.
In order to understand the composition and influencing factors of broad-spectrum pathogenic microorganisms in soil and root (rhizosphere and rhizoplane) of rubber plantations, metagenome sequencing was used to analyze the composition and influencing factors of pathogenic microorganisms in soil, rhizosphere and rhizoplane of healthy rubber plantations in Hainan (Danzhou, Wanning and Ledong) and Xishuangbanna (Jinghong, Menglun and Mengman). The results showed that plant pathogenic microorganisms belonged to Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria and Ascomycota at the phylum level, and to Pseudomonas, Ralstonia, Burkholderia, Streptomyces, Agrobacterium, Xanthomonas, Pantoea, Clavibacter, Pectobacterium and Xylella at the genus level with Ascomycota as the main pathogen at the genus level. There was no significant difference in pathogenic microorganisms in the rhizospheres between the rubber plantations in Hainan and Xishuangbanna. The composition of pathogenic microorganisms was similar in the soil and rhizosphere samples, and similar in the rhizoplane samples. There was a significant positive correlation between NH4-N and pathogenic microorganisms. In conclusion there was no significant difference in pathogenic microorganisms in soil, rhizosphere and rhizoplane between the rubber plantations in Hainan and Xishuangbanna. A significant positive correlation was observed between pathogenic microorganisms and NH4-N, and that the composition of pathogenic microorganisms was related to the exudates of the rhizoplane.
2022, 13(1): 36-41.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.006
Abstract:
A good understanding of soil fertility in the rubber plantations in Hainan Province is very important to well manage the rubber plantations for higher rubber yield through fertilizer application. In this study 144 soil samples were collected from rubber plantations in major rubber producing cities and counties of Hainan Province, and their soil pH, and contents of organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium were determined to evaluate and analyze the soil chemical fertility of rubber plantations by using the principal component analysis (PCA). The results showed that the values of the integrated fertility index (IFI) of the soil chemical fertility in the main rubber producing areas ranged from −9.08 to 16.79. According to the IFI values and the Ward’s method, the soil fertility of rubber plantations in Hainan Island can be divided into three levels: high (IFI: 3.29~16.79), medium (IFI: −1.8~2.74) and low (IFI: −9.08~2.0). The soil chemical fertility varied greatly in the rubber plantations in different major rubber producing cities and counties, higher in Qiongzhong and Qionghai, moderate in Tunchang and Danzhou and lower in Lingao and Chengmai, and the soil chemical fertility in the rubber plantations in Baisha was highly different. Soil organic matter and total nitrogen are the main limiting factors for soil chemical fertility in the rubber plantations in Hainan Province, followed by available potassium. It is suggested that organic fertilizer and potassium fertilizer should be applied to improve the soil chemical fertility in the rubber plantations of different cities/counties of Hainan Province.
A good understanding of soil fertility in the rubber plantations in Hainan Province is very important to well manage the rubber plantations for higher rubber yield through fertilizer application. In this study 144 soil samples were collected from rubber plantations in major rubber producing cities and counties of Hainan Province, and their soil pH, and contents of organic matter, total nitrogen, available phosphorus and available potassium were determined to evaluate and analyze the soil chemical fertility of rubber plantations by using the principal component analysis (PCA). The results showed that the values of the integrated fertility index (IFI) of the soil chemical fertility in the main rubber producing areas ranged from −9.08 to 16.79. According to the IFI values and the Ward’s method, the soil fertility of rubber plantations in Hainan Island can be divided into three levels: high (IFI: 3.29~16.79), medium (IFI: −1.8~2.74) and low (IFI: −9.08~2.0). The soil chemical fertility varied greatly in the rubber plantations in different major rubber producing cities and counties, higher in Qiongzhong and Qionghai, moderate in Tunchang and Danzhou and lower in Lingao and Chengmai, and the soil chemical fertility in the rubber plantations in Baisha was highly different. Soil organic matter and total nitrogen are the main limiting factors for soil chemical fertility in the rubber plantations in Hainan Province, followed by available potassium. It is suggested that organic fertilizer and potassium fertilizer should be applied to improve the soil chemical fertility in the rubber plantations of different cities/counties of Hainan Province.
2022, 13(1): 42-47.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.007
Abstract:
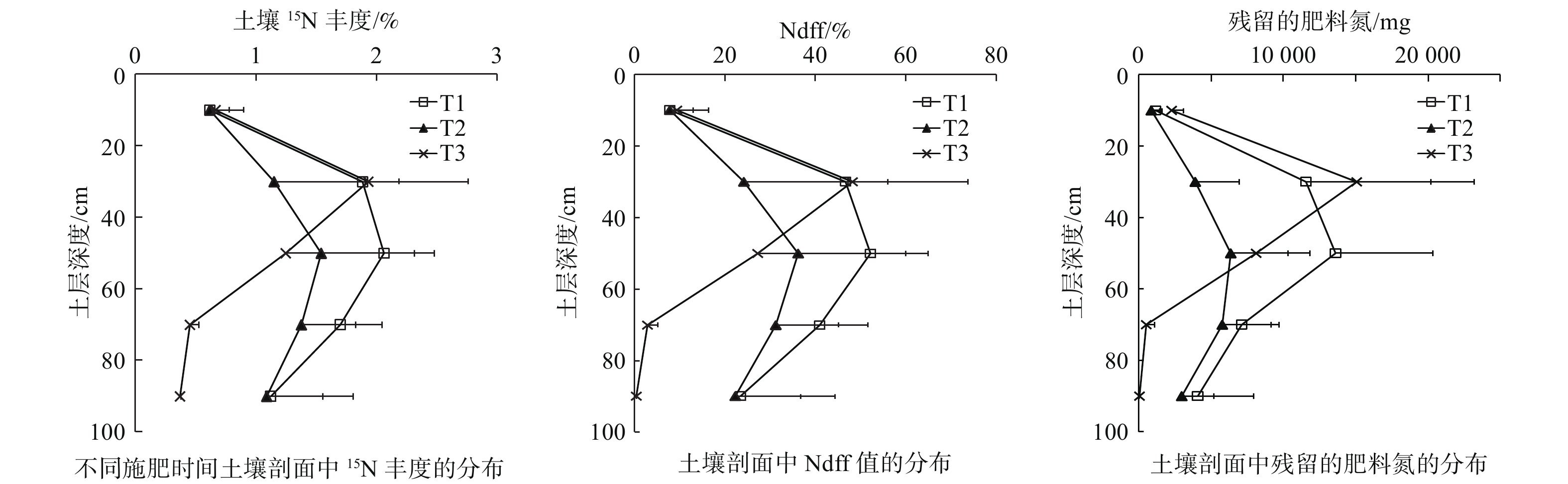
A field experiment was carried out, in which 15N labeled nitrogen fertilizer was used to study the migration and distribution characteristics of nitrogen fertilizer applied at different stages in rubber plantation. The contents of total N, alkali-hydrolyzable N and residual fertilizer N in soil layers were determined after fertilizer application. The results showed that the leaching effects of nitrogen fertilizer applied in the early and middle stages were strong, which could move to 100cm underground. Significant accumulation of nitrogen fertilizer in the shallow layer was observed after the application at later stage, which didn’t move below 60cm layer. The results indicated that the migration and distribution of nitrogen fertilizer applied at different stages are obviously different. Therefore, the practices such as slow and controlled release fertilizer application and adjusting of fertilizer ratio at different stages should be taken into consideration in nitrogen nutrient management in rubber plantation.
A field experiment was carried out, in which 15N labeled nitrogen fertilizer was used to study the migration and distribution characteristics of nitrogen fertilizer applied at different stages in rubber plantation. The contents of total N, alkali-hydrolyzable N and residual fertilizer N in soil layers were determined after fertilizer application. The results showed that the leaching effects of nitrogen fertilizer applied in the early and middle stages were strong, which could move to 100cm underground. Significant accumulation of nitrogen fertilizer in the shallow layer was observed after the application at later stage, which didn’t move below 60cm layer. The results indicated that the migration and distribution of nitrogen fertilizer applied at different stages are obviously different. Therefore, the practices such as slow and controlled release fertilizer application and adjusting of fertilizer ratio at different stages should be taken into consideration in nitrogen nutrient management in rubber plantation.
2022, 13(1): 48-56.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.008
Abstract:
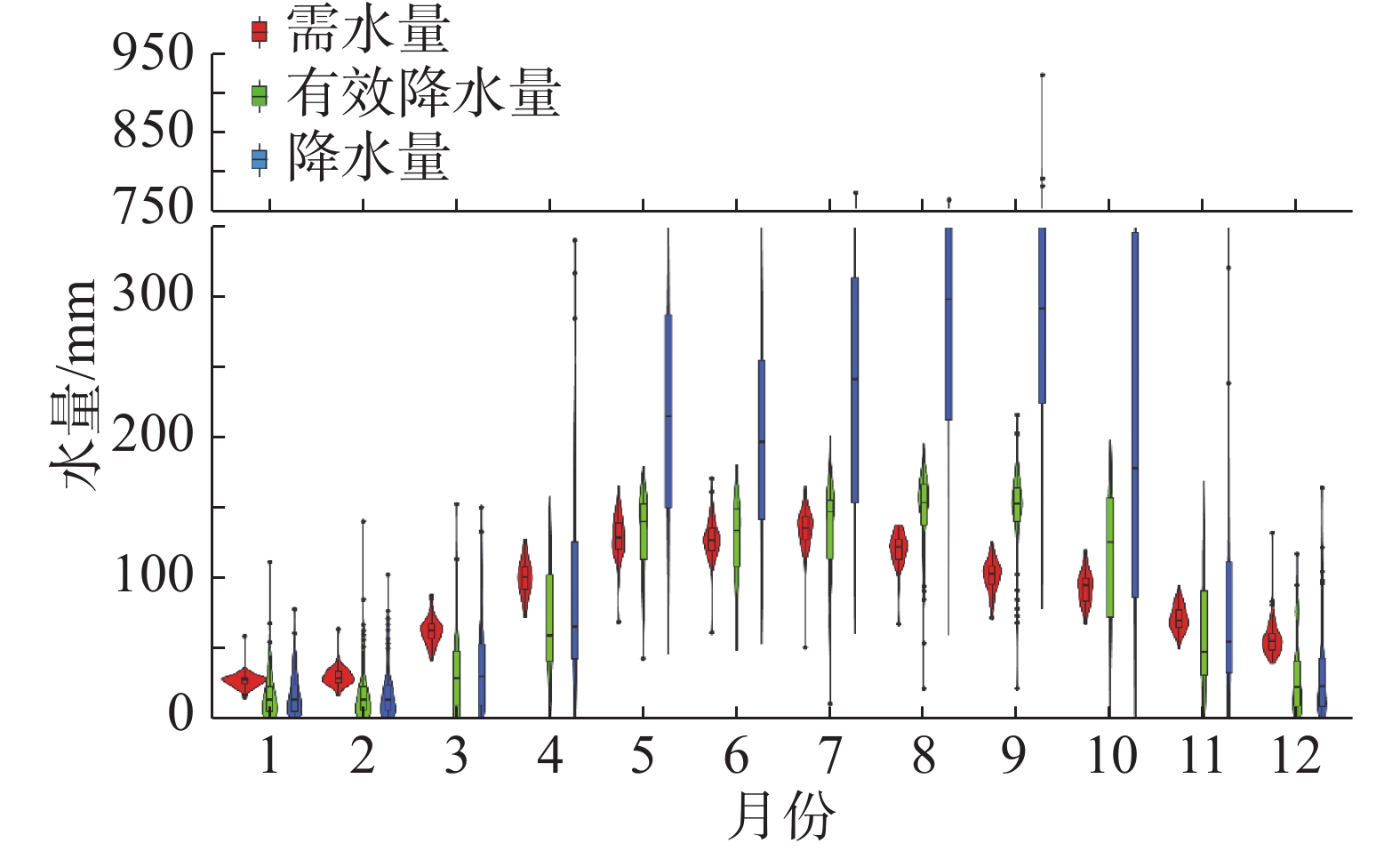
Seasonal drought is an important factor affecting the yield of rubber trees in China. Nevertheless few studies investigated the water requirement and irrigation system of rubber trees. Using the CROPWAT model, water requirement of rubber trees and the coupling of water requirements and effective precipitation in different hydrological years were investigated based on the weather data from 1954—2020 in Danzhou, Hainan, China. The results showed that the annual water requirement of rubber trees was 1069.8 mm, and that the annual effective precipitation in this area was 1048.3 mm. According to the precipitation in the dry season (November to April) the patterns of hydrological years could be precisely divided, based on which the water requirements of rubber trees in rainy years, normal years, drought years and severe drought years in Danzhou, Hainan were 1060.7 mm, 1072.0 mm, 1069.3 mm and 1156.6 mm, respectively. The effective precipitation from June to October was maximum, and the effective precipitation from January to April was low, which failed to meet the water requirement of rubber trees for evapotranspiration and hence led readily to suffering of the rubber trees from drought. This study provides a new method for estimation of water requirements of rubber trees and a theoretical support for the evaluation of drought disaster and the design of irrigation regimes for rubber trees.
Seasonal drought is an important factor affecting the yield of rubber trees in China. Nevertheless few studies investigated the water requirement and irrigation system of rubber trees. Using the CROPWAT model, water requirement of rubber trees and the coupling of water requirements and effective precipitation in different hydrological years were investigated based on the weather data from 1954—2020 in Danzhou, Hainan, China. The results showed that the annual water requirement of rubber trees was 1069.8 mm, and that the annual effective precipitation in this area was 1048.3 mm. According to the precipitation in the dry season (November to April) the patterns of hydrological years could be precisely divided, based on which the water requirements of rubber trees in rainy years, normal years, drought years and severe drought years in Danzhou, Hainan were 1060.7 mm, 1072.0 mm, 1069.3 mm and 1156.6 mm, respectively. The effective precipitation from June to October was maximum, and the effective precipitation from January to April was low, which failed to meet the water requirement of rubber trees for evapotranspiration and hence led readily to suffering of the rubber trees from drought. This study provides a new method for estimation of water requirements of rubber trees and a theoretical support for the evaluation of drought disaster and the design of irrigation regimes for rubber trees.
2022, 13(1): 57-63.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.009
Abstract:
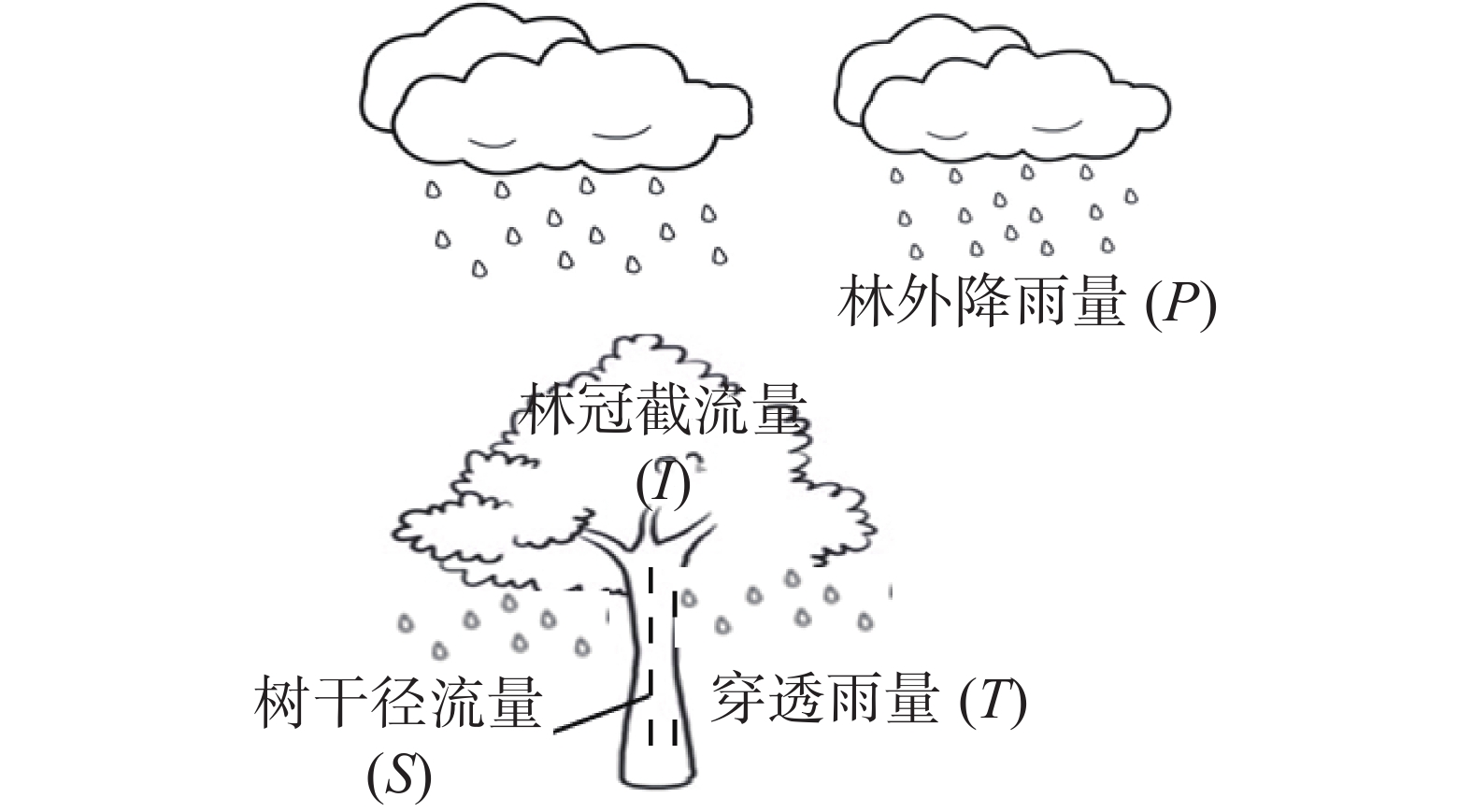
Study on the canopy interception characteristics of rubber plantation can provide the basic information for rubber plantation management and regional hydro-ecology effect assessment. The rubber plantations at three age stages (young, 7 years old; middle, 12 years old; old, 32 years old) were selected for observation. The throughfall, stem flow, canopy interception of the rubber plantations at the three age stages were measured, and the effects of tree age, leaf area index and meteorological factors on the throughfall, stem flow and canopy interception were analyzed. The results showed that the annual throughfalls of the young, middle and old rubber plantations were 1087.90 mm, 846.27 mm and 730.55 mm, respectively, accounting for 61.34%, 47.71%, 41.19% of the annual precipitation. The annual stemflows were 524 mm, 809.16 mm and 912.80 mm, respectively, accounting for 29.54%, 45.61%, 51.46% of the annual precipitation. The annual canopy interceptions were 54.37 mm, 147.57 mm and 123.04 mm, respectively, accounting for 3.06%, 8.32% and 6.94% of the annual precipitation. In general, with the increase of tree age the throughfall decreased, while the stemflow and canopy interception increased. The leaf area index was inferred as the main factor affecting the difference of canopy interception between rubber plantations at different ages. Among the meteorological factors precipitation has the greatest impact on canopy interception.
Study on the canopy interception characteristics of rubber plantation can provide the basic information for rubber plantation management and regional hydro-ecology effect assessment. The rubber plantations at three age stages (young, 7 years old; middle, 12 years old; old, 32 years old) were selected for observation. The throughfall, stem flow, canopy interception of the rubber plantations at the three age stages were measured, and the effects of tree age, leaf area index and meteorological factors on the throughfall, stem flow and canopy interception were analyzed. The results showed that the annual throughfalls of the young, middle and old rubber plantations were 1087.90 mm, 846.27 mm and 730.55 mm, respectively, accounting for 61.34%, 47.71%, 41.19% of the annual precipitation. The annual stemflows were 524 mm, 809.16 mm and 912.80 mm, respectively, accounting for 29.54%, 45.61%, 51.46% of the annual precipitation. The annual canopy interceptions were 54.37 mm, 147.57 mm and 123.04 mm, respectively, accounting for 3.06%, 8.32% and 6.94% of the annual precipitation. In general, with the increase of tree age the throughfall decreased, while the stemflow and canopy interception increased. The leaf area index was inferred as the main factor affecting the difference of canopy interception between rubber plantations at different ages. Among the meteorological factors precipitation has the greatest impact on canopy interception.
2022, 13(1): 64-72.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.010
Abstract:
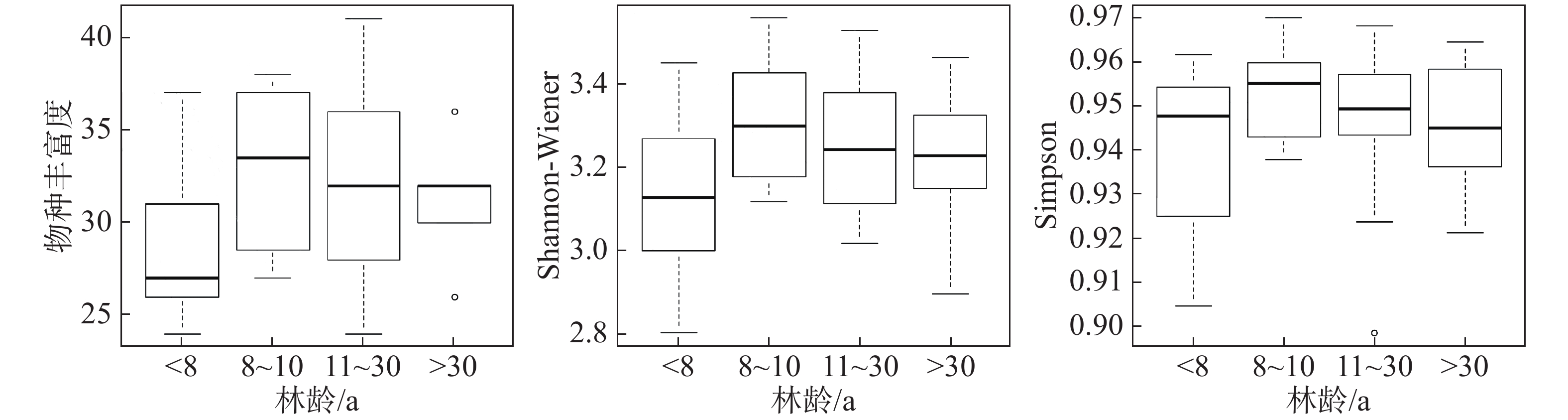
A survey on plant diversity was made in the rubber plantations in Myanmar to understand the basic characteristics of the diversity of the undergrowth plants in the rubber plantations in Myanmar. Undergrowth plants in 47 quadrats (10 m×10 m) in the rubber plantations were sampled from the quadrats for analysis. The species composition and species diversity of the undergrowth plants in the rubber plantations are analyzed based on species richness index (S), importance value (IV), Shannon-Wiener index (H), Simpson index (D) and Sorensen coefficient (Cs). The survey showed that there are 81 families, 224 genera, and 283 species of the undergrowth plants in the rubber plantations in Myanmar, of which Gramineae and Fabaceae are two dominant families. The similarity coefficient between Mon State and Delindayi Province is the highest, reaching 0.59, while the similarity coefficient of the rubber plantations in between Shan State and Delindayi Province is the lowest, being 0.21. The species richness values, Simpson index values and Shannon-Wiener index values of the undergrowth plants in the plantations at the age of between 8 and 10 years old are the highest; the richness index, Simpson index and Shannon-Wiener index are the highest in the rubber plantations located at an altitude of <200 m; Shannon-Wiener index and species richness are the highest in the rubber plantations located at a slope of <2°, and the Simpson index is the highest at the slope of 2°−15°; the plant diversity in the rubber plantations is the highest on the southern slope.
A survey on plant diversity was made in the rubber plantations in Myanmar to understand the basic characteristics of the diversity of the undergrowth plants in the rubber plantations in Myanmar. Undergrowth plants in 47 quadrats (10 m×10 m) in the rubber plantations were sampled from the quadrats for analysis. The species composition and species diversity of the undergrowth plants in the rubber plantations are analyzed based on species richness index (S), importance value (IV), Shannon-Wiener index (H), Simpson index (D) and Sorensen coefficient (Cs). The survey showed that there are 81 families, 224 genera, and 283 species of the undergrowth plants in the rubber plantations in Myanmar, of which Gramineae and Fabaceae are two dominant families. The similarity coefficient between Mon State and Delindayi Province is the highest, reaching 0.59, while the similarity coefficient of the rubber plantations in between Shan State and Delindayi Province is the lowest, being 0.21. The species richness values, Simpson index values and Shannon-Wiener index values of the undergrowth plants in the plantations at the age of between 8 and 10 years old are the highest; the richness index, Simpson index and Shannon-Wiener index are the highest in the rubber plantations located at an altitude of <200 m; Shannon-Wiener index and species richness are the highest in the rubber plantations located at a slope of <2°, and the Simpson index is the highest at the slope of 2°−15°; the plant diversity in the rubber plantations is the highest on the southern slope.
2022, 13(1): 73-80.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.011
Abstract:
In order to gain an in-depth understanding of the situation of alien invasive plants in hilly rubber plantations, a field survey of the invasive alien plants in 6 prefectures/cities of Yunnan Province was conducted, and the species composition, origin, life form, distribution types and invasiveness of the invasive alien plants were analyzed in combination of the literature consulted. The results showed that were 82 species of invasive alien plants, belonging to 26 families and 63 genera in the hilly rubber plantations in Yunnan Province. Of the 26 families the families Asteraceae (18 species), Papilionaceae (10 species), Poaceae (6 species), Amaranthaceae (5 species) and Solanaceae (5 species) were dominant, with their species accounting for 53.66% of the total species. The invasive alien plants were mainly herbaceous in life form, and there were 57 species of herbaceous plants, accounting for 69.51% to the total species of the invasive alien plants. From the origin of the invasive plants the number of the species native to America was the highest, with 62 species in the hilly rubber plantations, accounting for 75.61% of the total species. From the distribution types of families and genera the invasive alien plants were all of tropical distribution at the levels of families and genera. From the pathway of introduction 47 species were introduced intentionally, accounting for 57.32% of the total species of the invasive alien plants. From the invasion severity 17 species were noxious, and 24 species serious, both of which were accounting for half of the total invasive alien species. In addition, this survey recorded four new species. Stachytarpheta urticaefolia (Salisb.) Sims, Stachytarpheta cayennensis (Rich.) Vahl and Gomphrena celosioides Mart. are new records of Yunnan Province, and Calopogonium caeruleum (Benth.) Britton is a new record of China. All of the four newly recorded species were naturalized. In general there are many species of invasive alien plants in the hilly rubber plantations in Yunnan Province, and their invasion is relatively severe, which has a direct or indirect impact on the growth of rubber trees, and effective measures should hence be taken to prevent and control of the invasive alien plants in the hilly rubber plantations in Yunnan province.
In order to gain an in-depth understanding of the situation of alien invasive plants in hilly rubber plantations, a field survey of the invasive alien plants in 6 prefectures/cities of Yunnan Province was conducted, and the species composition, origin, life form, distribution types and invasiveness of the invasive alien plants were analyzed in combination of the literature consulted. The results showed that were 82 species of invasive alien plants, belonging to 26 families and 63 genera in the hilly rubber plantations in Yunnan Province. Of the 26 families the families Asteraceae (18 species), Papilionaceae (10 species), Poaceae (6 species), Amaranthaceae (5 species) and Solanaceae (5 species) were dominant, with their species accounting for 53.66% of the total species. The invasive alien plants were mainly herbaceous in life form, and there were 57 species of herbaceous plants, accounting for 69.51% to the total species of the invasive alien plants. From the origin of the invasive plants the number of the species native to America was the highest, with 62 species in the hilly rubber plantations, accounting for 75.61% of the total species. From the distribution types of families and genera the invasive alien plants were all of tropical distribution at the levels of families and genera. From the pathway of introduction 47 species were introduced intentionally, accounting for 57.32% of the total species of the invasive alien plants. From the invasion severity 17 species were noxious, and 24 species serious, both of which were accounting for half of the total invasive alien species. In addition, this survey recorded four new species. Stachytarpheta urticaefolia (Salisb.) Sims, Stachytarpheta cayennensis (Rich.) Vahl and Gomphrena celosioides Mart. are new records of Yunnan Province, and Calopogonium caeruleum (Benth.) Britton is a new record of China. All of the four newly recorded species were naturalized. In general there are many species of invasive alien plants in the hilly rubber plantations in Yunnan Province, and their invasion is relatively severe, which has a direct or indirect impact on the growth of rubber trees, and effective measures should hence be taken to prevent and control of the invasive alien plants in the hilly rubber plantations in Yunnan province.
2022, 13(1): 81-87.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.012
Abstract:
In order to establish an appropriate intercropping pattern and explore the suitable intercropping density of Amorphophallus bulbifer in rubber plantations, Amorphophallus bulbifer was planted as an intercrop at different densities in conventional and paired row rubber plantations to observe the effects of planting density of A. bulbifer on leaf morphological indexes, the number of bulbils of the leaves and plant lodging rate, the contents of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in corms, yield and quality of the corms in the rubber plantations. The results showed that the paired row rubber plantation was more suitable for intercropping with A. bulbifer than conventional rubber plantation, and that the suitable planting densities of A. bulbifer intercropped in the rubber plantations were 40020 and 33345 plants/ha, respectively. Planting systems of the rubber plantations had a greater effect on the growth of the intercrop A. bulbifer than the planting density of the intercrop. The planting density of the intercrop in the conventional rubber plantation had no significant effect on the leaf morphological index, and the corm yield and quality, but its effects on the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium content and absorption varied with the change of planting density of the intercrop in the conventional rubber plantation. In the paired row rubber plantation, the lower the planting density, the shorter the plant, the thicker the petiole, the larger the leaf disc, the more the number of bulbils of the leaves, and the stronger the plant lodging resistance. In the paired row rubber plantation, the plant was shorter with thicker petiole, and was higher in propagation coefficient of the bulbils of the leaves, plant lodging resistance, corm enlargement coefficient, weight of single corm, and corm yield and quality, while the contents of N, P and K in corms were decreased but with slightly higher absorption, as compared to those in the conventional rubber plantation. These results showed that intercropping of A. bulbifer is much better in the paired row rubber plantation than in the conventional rubber plantation, which is more conducive to improvement of corm yield and quality, lodging resistance, and propagation of bulbils of the leaves of A. bulbifer.
In order to establish an appropriate intercropping pattern and explore the suitable intercropping density of Amorphophallus bulbifer in rubber plantations, Amorphophallus bulbifer was planted as an intercrop at different densities in conventional and paired row rubber plantations to observe the effects of planting density of A. bulbifer on leaf morphological indexes, the number of bulbils of the leaves and plant lodging rate, the contents of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in corms, yield and quality of the corms in the rubber plantations. The results showed that the paired row rubber plantation was more suitable for intercropping with A. bulbifer than conventional rubber plantation, and that the suitable planting densities of A. bulbifer intercropped in the rubber plantations were 40020 and 33345 plants/ha, respectively. Planting systems of the rubber plantations had a greater effect on the growth of the intercrop A. bulbifer than the planting density of the intercrop. The planting density of the intercrop in the conventional rubber plantation had no significant effect on the leaf morphological index, and the corm yield and quality, but its effects on the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium content and absorption varied with the change of planting density of the intercrop in the conventional rubber plantation. In the paired row rubber plantation, the lower the planting density, the shorter the plant, the thicker the petiole, the larger the leaf disc, the more the number of bulbils of the leaves, and the stronger the plant lodging resistance. In the paired row rubber plantation, the plant was shorter with thicker petiole, and was higher in propagation coefficient of the bulbils of the leaves, plant lodging resistance, corm enlargement coefficient, weight of single corm, and corm yield and quality, while the contents of N, P and K in corms were decreased but with slightly higher absorption, as compared to those in the conventional rubber plantation. These results showed that intercropping of A. bulbifer is much better in the paired row rubber plantation than in the conventional rubber plantation, which is more conducive to improvement of corm yield and quality, lodging resistance, and propagation of bulbils of the leaves of A. bulbifer.
2022, 13(1): 88-94.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.013
Abstract:
Due to the continuous downturn of China's natural rubber industry, the economy under rubber plantations has gradually become a hot topic in recent years. A variety of rubber-based farming models integrating farming of other crops and animals under rubber plantations have been found to achieve some good results. However, at present, the rubber-based farming in China is mainly focused on cultivation of other crops under rubber plantations. The economic benefits derived from the crops cultivated under rubber plantations are not high, and these crops cultivated are far from the demand for processing, resulting in poor economic benefits from these crops in their whole industries and difficulty in promoting the crop cultivation models under the rubber plantations. Although rubber-based farming models under rubber plantations can obtain better economic benefits, there exist some problems such as high risk and high technical requirements. With the continuous improvement of people's living standards, the use of antibiotics in livestock and poultry farming has been gradually abandoned, and Chinese herbal medicine in the form of feed additive or extract has been a good choice to gradually replace the antibiotics used in the animal farming. The development of eco-circular rubber-based farming models can not only make full use of the land space under the rubber plantations, but also obtain high quality of livestock and poultry meat, which improve economic benefits and have a broad market prospect. A review is made of the development status and existing problems of rubber-based farming models in China, based on which eco-circular rubber-based farming models are proposed. Moreover the economic development prospect for rubber-based framing under rubber plantations is analyzed in order to provide reference for the economic development under rubber plantations in China.
Due to the continuous downturn of China's natural rubber industry, the economy under rubber plantations has gradually become a hot topic in recent years. A variety of rubber-based farming models integrating farming of other crops and animals under rubber plantations have been found to achieve some good results. However, at present, the rubber-based farming in China is mainly focused on cultivation of other crops under rubber plantations. The economic benefits derived from the crops cultivated under rubber plantations are not high, and these crops cultivated are far from the demand for processing, resulting in poor economic benefits from these crops in their whole industries and difficulty in promoting the crop cultivation models under the rubber plantations. Although rubber-based farming models under rubber plantations can obtain better economic benefits, there exist some problems such as high risk and high technical requirements. With the continuous improvement of people's living standards, the use of antibiotics in livestock and poultry farming has been gradually abandoned, and Chinese herbal medicine in the form of feed additive or extract has been a good choice to gradually replace the antibiotics used in the animal farming. The development of eco-circular rubber-based farming models can not only make full use of the land space under the rubber plantations, but also obtain high quality of livestock and poultry meat, which improve economic benefits and have a broad market prospect. A review is made of the development status and existing problems of rubber-based farming models in China, based on which eco-circular rubber-based farming models are proposed. Moreover the economic development prospect for rubber-based framing under rubber plantations is analyzed in order to provide reference for the economic development under rubber plantations in China.
2022, 13(1): 95-99.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2022.01.014
Abstract:
Plant allelopathy is incredibly important in nature and plays a key important role in the transmission of information between plants and their surrounding organisms. A review was made of the concept of plant allelopathy, and the types and mechanisms of plant allelopathy in recent years such as inhibiting effect and its mechanism, toxic effect and its mechanism, self-promoting effect and its mechanism, and facilitation and its mechanism, as well as the research progress of allelopathy in rubber tree. And an outlook was made on the research in allelopathy in the complex rubber ecosystem.
Plant allelopathy is incredibly important in nature and plays a key important role in the transmission of information between plants and their surrounding organisms. A review was made of the concept of plant allelopathy, and the types and mechanisms of plant allelopathy in recent years such as inhibiting effect and its mechanism, toxic effect and its mechanism, self-promoting effect and its mechanism, and facilitation and its mechanism, as well as the research progress of allelopathy in rubber tree. And an outlook was made on the research in allelopathy in the complex rubber ecosystem.


 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 1805KB
PDF 1805KB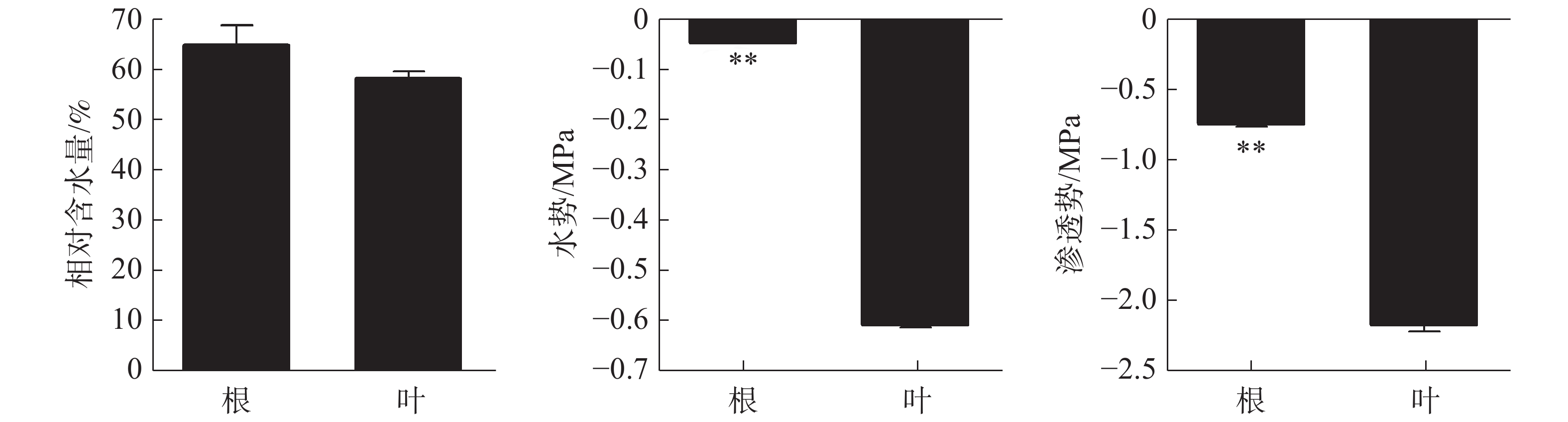






 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS