-
水稻(Oryza sativa L.)白叶枯病是一种由黄单胞菌(Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, Xoo)引起的细菌性病害,在各水稻种植区均有发生,并且危害严重,是我国水稻重要病害之一[1]。发病后叶片产生黄绿色病斑,最终变黄枯死,每年造成水稻产量减少20%~30%,严重时减产50%,甚至绝收[2]。虽然目前有一些抗病品种,但是抗病性易随着时间而逐渐减弱。防治白叶枯病的化学药剂有铜制剂、有机磷、有机氮、噻唑类等[3-8],这些药剂大部分在田间使用时易使病菌产生抗药性,对环境有影响。如噻枯唑在田间已有明显抗性[9];5-氧吩嗪类药剂持效期短,病害易复发,水稻白叶枯病的防治形势依旧严峻。
生物防治是一种高效且对环境友好的策略,可以用于植物病害的治理[10]。生防芽孢杆菌是目前应用最广泛的生防细菌之一,对各种真菌、细菌和病毒的侵染造成的植物病害,都能够有效地抑制[11],并且还具有良好的促进植物增产、诱导植物抗病的能力。目前,越来越多生防芽孢杆菌被开发成农药,得到商品化产品[12]。芽孢杆菌能够产生次级代谢物质来抑制和杀灭有害微生物,这些活性代谢物质主要包括酶类、细菌素类,以及受到关注最多的脂肽类等[13-14],如地衣形芽孢杆菌(Bacillus licheni formus)可以发酵产生一种具有良好的抑制细菌活性的脂肽类物质——杆菌肽。杆菌肽目前作为一种多肽类抗生素已经被广泛地应用于医学[15]。有研究[16]表明芽胞杆菌属(Bacillus spp.)能够产生具有较强拮抗Xoo的脂肽类活性物质。Bacillus strain D13可以产生一种挥发性物质,该挥发性物质具有较好的抑制Xoo的活性[17]。解淀粉芽孢杆菌Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42分泌的抗生素类物质bacilysin和difficidin对水稻黄单胞菌Xoo具有显著的抑菌作用[18]。笔者所在实验室的研究[19]发现,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌HN-2产生的C15surfactin A对Xoo具有较强抗菌活性,能抑制Xoo的生长,并通过介导抗氧化剂相关酶的活性而引发过敏性反应,有效地诱导水稻对Xoo的抗性。虽然目前已经有一些关于芽孢杆菌抑制Xoo的研究,然而贝莱斯芽孢杆菌抑制Xoo的作用机制尚不明确。因此,本研究以HN-2菌株发酵液正丁醇提取物处理12 h后的Xoo为研究对象,进行转录组测序和分析,拟求得Xoo应对HN-2抑菌活性成分的代谢途径基因表达差异图谱,为后续进一步揭示贝莱斯芽孢杆菌HN-2的抑植物病原细菌Xoo机理提供前期数据和理论参考。
-
贝莱斯芽孢杆菌HN-2为本实验室从土壤中分离保存,稻黄单胞菌Xoo(PXO99A)由笔者所在的实验室提供保存。杆菌肽(98%,分析纯)购自日本和光纯药株式会社有限公司。(1)HN-2发酵活性物质的提取:接种HN-2菌株于LB培养基37 ℃,180 r·min−1振荡培养48 h后,离心10 min弃去菌体,得到HN-2发酵液上清液。等比例并充分混合正丁醇和HN-2发酵上清液后,室温下静置过夜,用分液漏斗分离有机相得到上层正丁醇萃取液。在67 ℃下将得到的上层正丁醇萃取液进行旋转蒸发浓缩,蒸发浓缩后的沉淀用少量甲醇充分溶解并进行冷冻干燥12 h,得到HN-2抑菌活性成分粉末粗提物,−80 ℃保存备用,使用前称取0.01 g粗提物加入1 mL的超纯水充分溶解,并用一次性细菌过滤器过滤。(2)样品处理:从平板上挑取黄单胞菌的单菌落接种至PSA液体培养基中,共接种9瓶,在28 ℃,180 r·min−1振荡培养至生长对数期(OD600=0.300)。此时向第一组菌液中加入HN-2正丁醇提取物至终浓度为MIC50值(2.36 mg·mL−1),第二组菌液加入杆菌肽至终浓度为MIC50值(11.96 mg·mL−1),第三组菌液不做任何处理,继续振荡培养12 h,3次重复,将HN-2正丁醇提取物处理12 h的样品命名为“Xoo-HN-2”,杆菌肽处理12 h的样品命名为“Xoo-G”,对照组命名为“Xoo-CK”。
-
样品Xoo总RNA的提取使用天根RNA提取试剂盒,并将提取的RNA送到广州基地奥生物科技公司进行质检,以保证所有样品最终都获得高质量的总RNA。利用Illumina HiSeq X Ten 测序平台(Illumina Inc, CA, USA)进行转录组建库测序及分析。步骤:(1)去除核糖体RNA;(2)RNA随机打断为200 nt片段;(3)加入六碱基随机引物、缓冲液、dNTPs、RNase H和DNA聚合酶Ⅰ合成cDNA第一条链;(4)使用dUTP代替dTTP,合成cDNA第二条链;(5)末端修复3′、5′端,加A尾,连接接头;(6)使用UNG酶降解cDNA第二条链,以保留RNA方向信息;(7)PCR扩增产生DNA的聚集片段,完成文库制备;(8)利用Illumina测序平台对构建好的文库进行双末端测序,将所得数据过滤后用于后续的转录组分析[20]。
-
对样品中的Mapped reads数目和转录本长度进行归一化处理,使用RAEM软件,采用FPKM(Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million fragments mapped)作为衡量转录本的指标[21],采用皮尔森相关系数(Pearson Correlation Coefficient,PCC)法检测重复样品之间的相关性,并利用DESeq R包分析不同处理后Xoo的差异表达基因。为进一步控制该过程中的错误发现率(false discovery rate,FDR),使用edgeR[22]软件对不同样品间差异表达基因定量分析。采用FDR(false discovery rate)与log2(FoldChange)(log2FC)来作为差异表达基因筛选的关键指标,筛选条件为FDR<0.05且∣log2FC∣>1。
-
将筛选得到的差异基因进行GO富集分析,用特定的GO terms给差异表达基因的表达模式注释;利用KEGG数据库找出在差异表达基因中,富集最显著的前20条代谢通路画图展示。
-
转录组原始数据质控过滤前后的黄单胞菌Xoo(PXO99A)转录组测序数据统计情况见表1。由表1可见,CK组、HN-2组、杆菌肽组的样本通过测序获得的原始碱基数(Raw Data)分别为3 669 218 400、3 356 470 200和5 089 554 000。3组原始序列经过质控后获得的Clean data分别为3 490 096 417、3 232 110 301和502 049 243。过滤后的总碱基数占原始序列的比例分别为98.55%、98.53%和97.32%,Q20分别为98.03%、98.03%和97.32%,Q30分别为94.89%、94.89%和92.0%,GC含量分别为61.61%、61.06%和60.93%,这些结果表明过滤后所获得的序列质量较好,可靠性高,Clean reads可以用于后续的生物信息学分析。
样品碱基信息 样本名 Xoo-CK Xoo-HN-2 Xoo-G 过滤前 Raw data/bp 3669218400 3356470200 5089554000 Q20/% 3596827023 (98.03%) 3293722095 (98.03%) 4948281317 (97.22%) Q30/% 3481614115 (94.89%) 3188133592 (94.98%) 4674417659 (91.84%) N/% 5182 (0.0%) 4797 (0.0%) 41169 (0.0%) GC/% 2260575649 (61.61%) 2049438853 (61.06%) 3095193280 (60.82%) Clean data/bp 3490096417 3232110301 5020492431
过滤后Q20/% 3439489923 (98.55%) 3184723700 (98.53%) 4886066551 (97.32%) Q30/% 3336281653 (95.59%) 3087417164 (95.52%) 4618772865 (92.0%) N/% 4928 (0.0%) 4619 (0.0%) 40606 (0.0%) GC/% 2158506542 (61.85%) 1978705819 (61.22%) 3059001170 (60.93%) 注:Raw data:原始下机数据碱基总数(bp);Clean data:过滤低质量reads后获得的有效数据碱基总数及占raw data的百分比;Q20(%):测序碱基正确率达99%以上的碱基数及占过滤前/后碱基总数的比例;Q30(%):测序碱基正确率99.9%以上的碱基数占过滤前/后碱基总数的比例;N (%):N碱基的数目及百分比;GC(%):GC碱基数目及百分比。 -
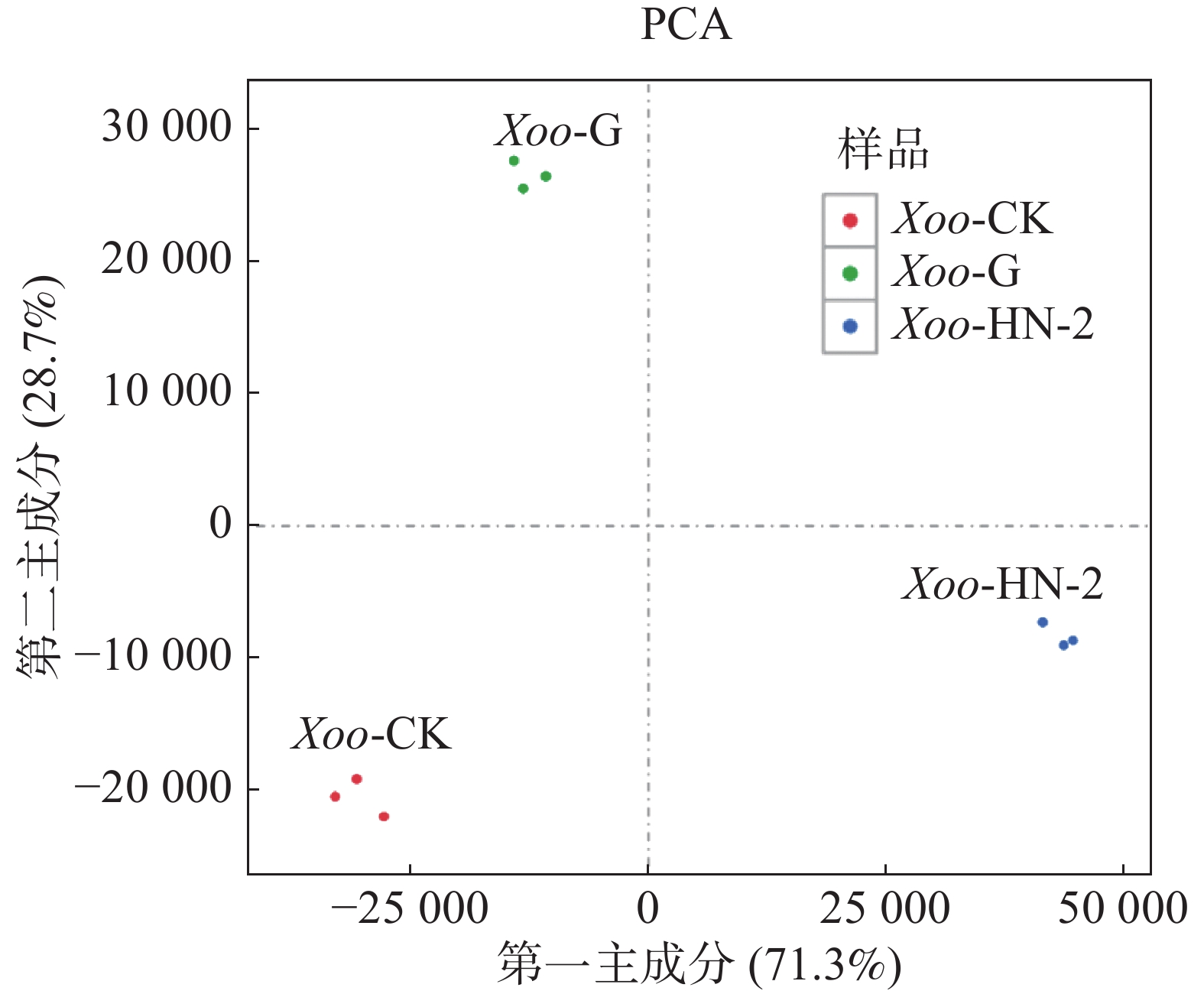
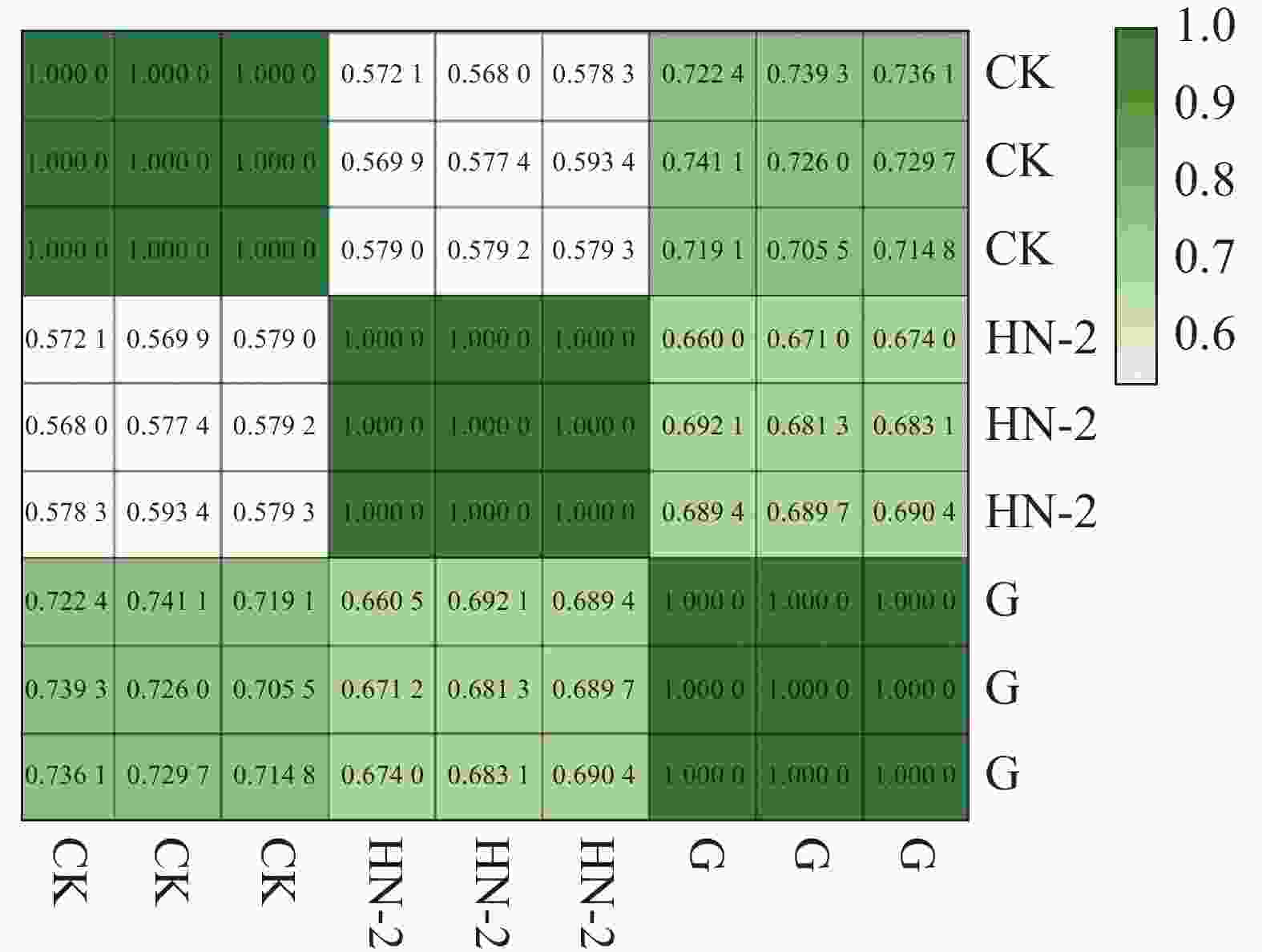
本实验共有3个样本(CK组,HN-2组,G组),通过主成分分析(PCA)可以评价样品重复性、找出离群样品、评估组间差异等。使用R语言获得各个样本在第一主成分(PC1)和第二主成分(PC2)2个综合变量中的数值大小,作二维坐标图。如图1所示,PC1可以解释原所有基因的表达量总体方差的71.3%,PC2可以解释原所有基因的表达量总体方差的28.7%,PC1与PC2共可以解释总体方差的100%,表明样品重复性高,组间差异小。通过R计算3个样本及每个样本的3个生物学重复间的皮尔森相关系数(Pearson Correlation Coefficient,PCC)。如图2所示,可以看到每个样本的3个生物学重复之间的相关系数呈对角线分布,表明测序数据具有较强的重复性和较高的可信度,可以用于后续的差异表达分析。
-
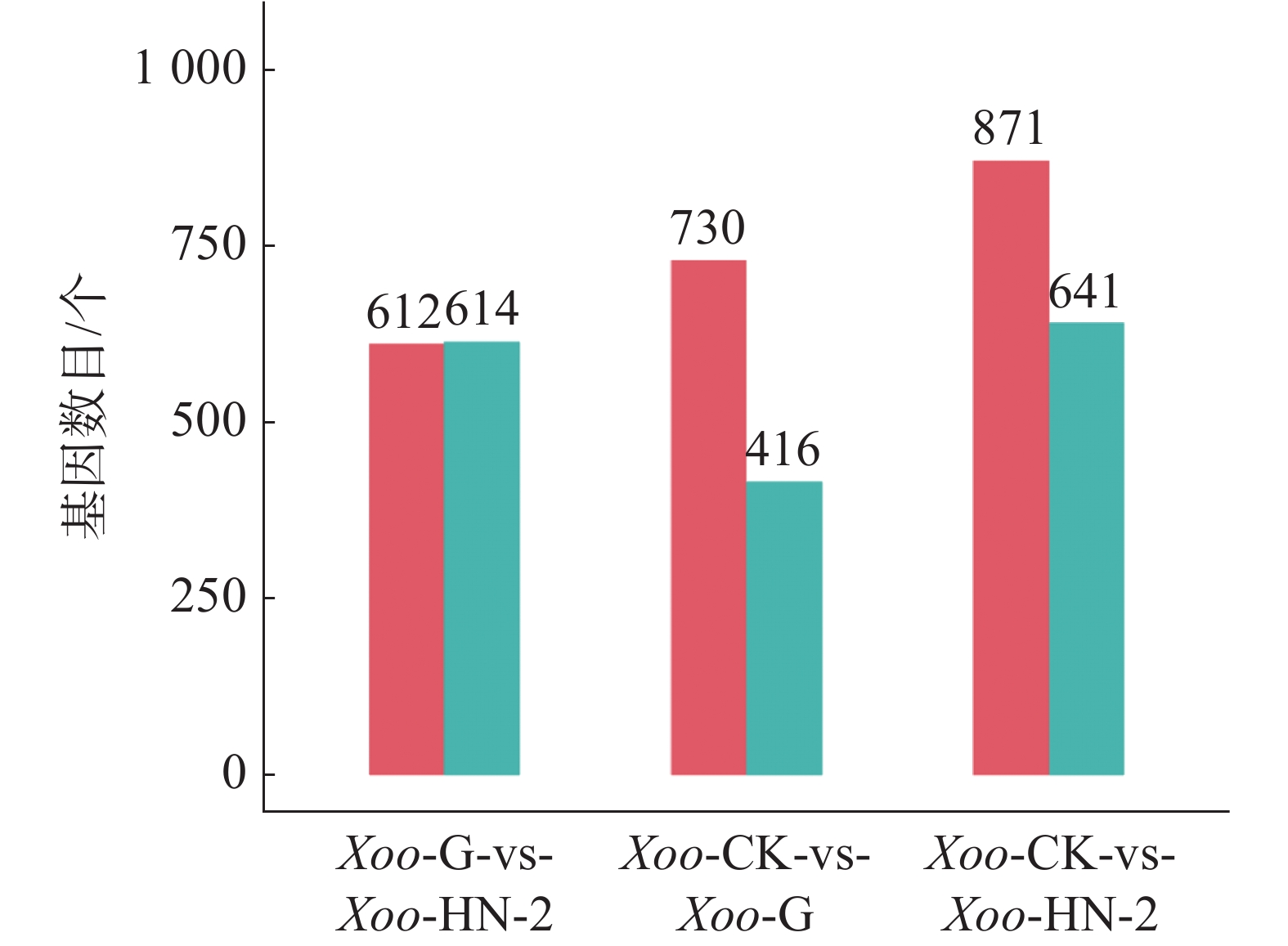
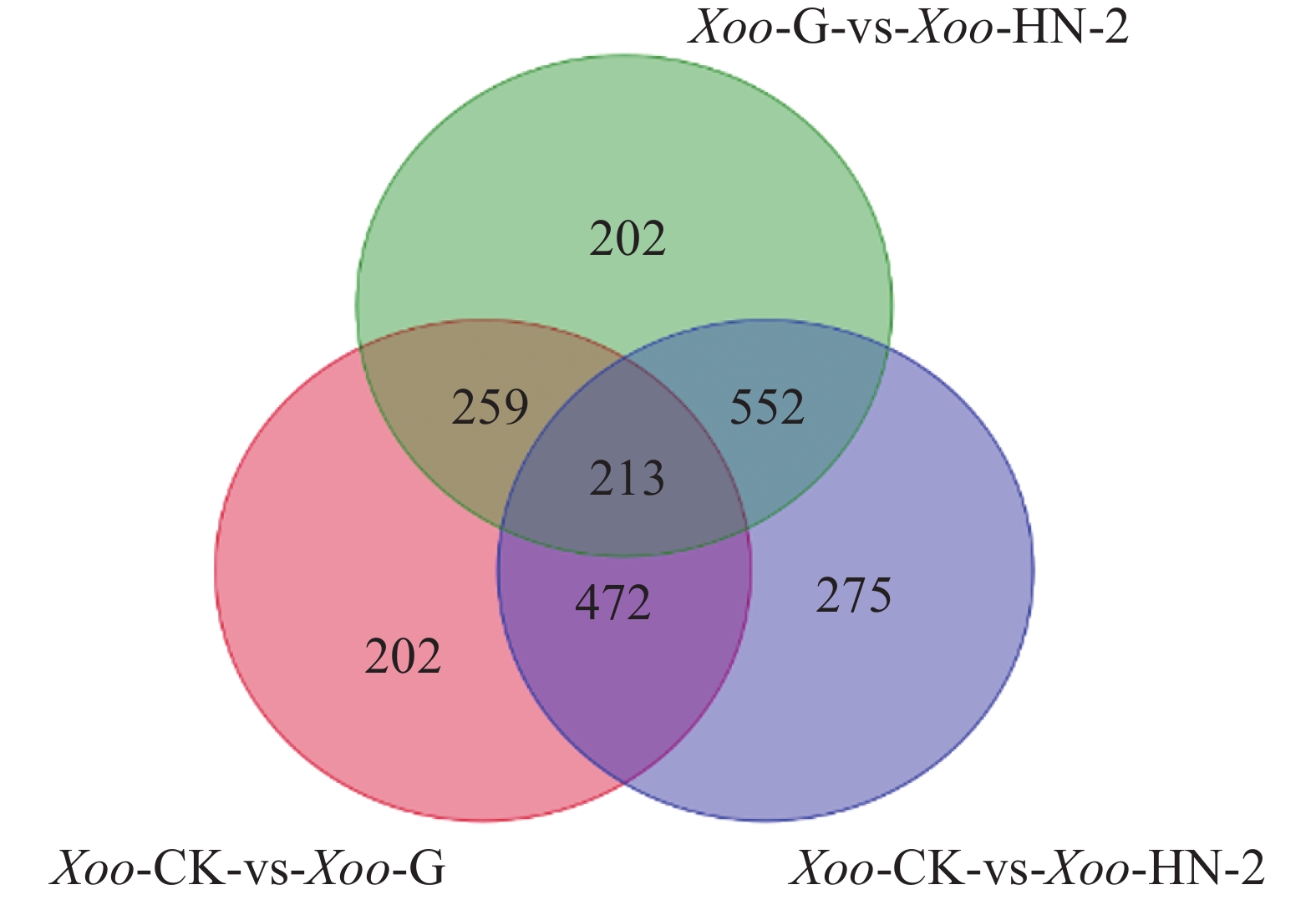
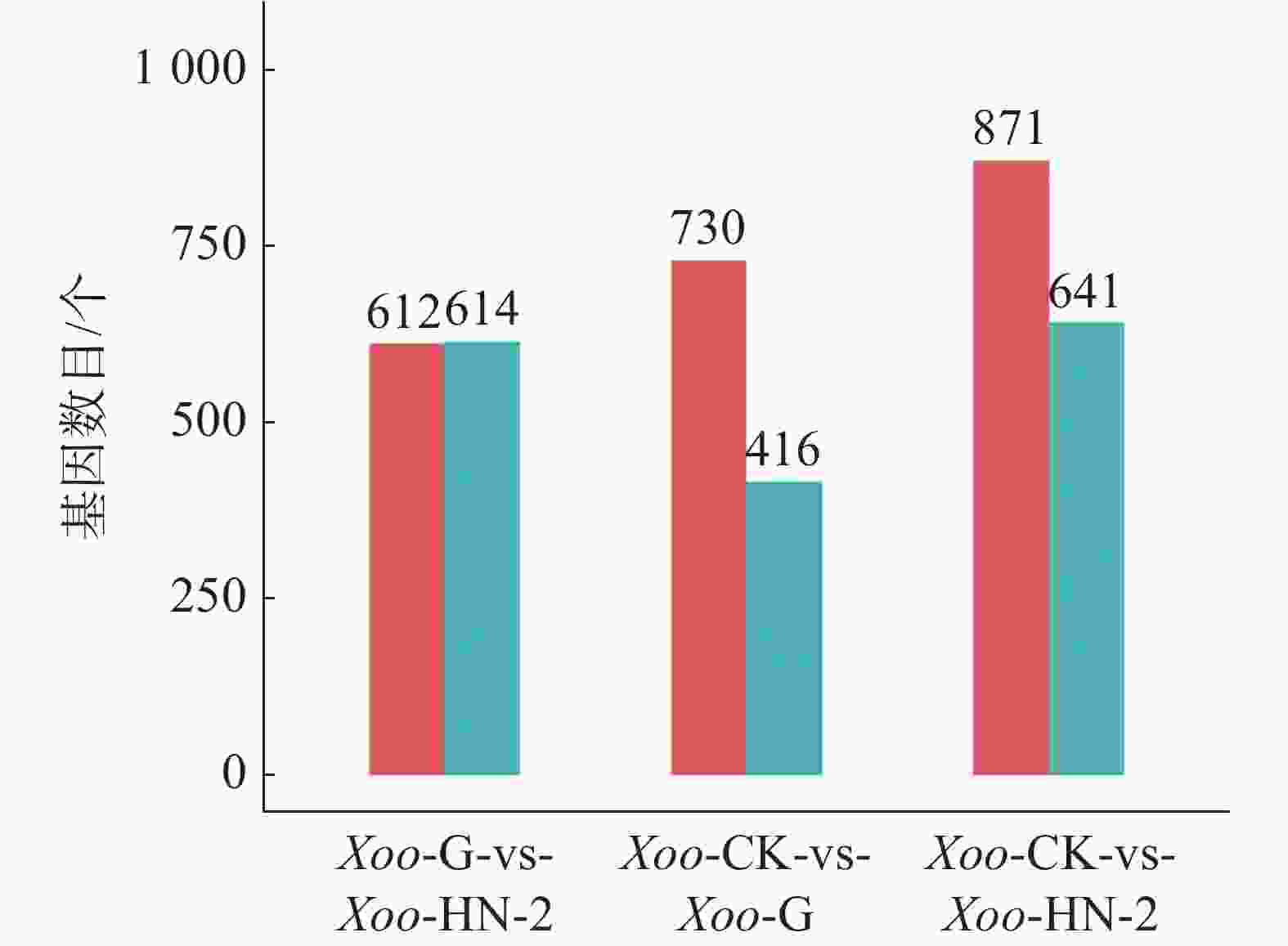
如图3所示,HN-2组和杆菌肽组相比,共筛选到1 226个差异基因,其中有612个基因在HN-2组中上调,614个基因在HN-2组中下调。杆菌肽组和CK组相比,共筛选到1 146个差异基因,其中,有730个基因在杆菌肽组中上调,416个基因在杆菌肽组中下调。HN-2组和CK组相比,共筛选到1 512个差异基因,其中有871个基因在HN-2组中上调,641个基因在HN-2组中下调。此外无论是加入HN-2还是杆菌肽,上调表达基因都多于下调表达基因,并且HN-2组表达差异的表达基因总数多于杆菌肽组,说明经HN-2处理后,Xoo有更多的基因被调控来参与到对HN-2处理后的适应过程中。本研究重点关注的是不同处理之间的差异,因此对两两比较的差异基因绘制了韦恩图(图4)。图4可见,与杆菌肽组相比,HN-2组有275个差异表达基因为其特有,是HN-2提取物与杆菌肽抑菌机制不同导致,这些HN-2组特有的差异基因有助于进一步研究HN-2对Xoo的作用机理。因此,在后续对于HN-2组的差异表达基因定性分析时,这275个差异基因将作为重点研究分析对象。
-
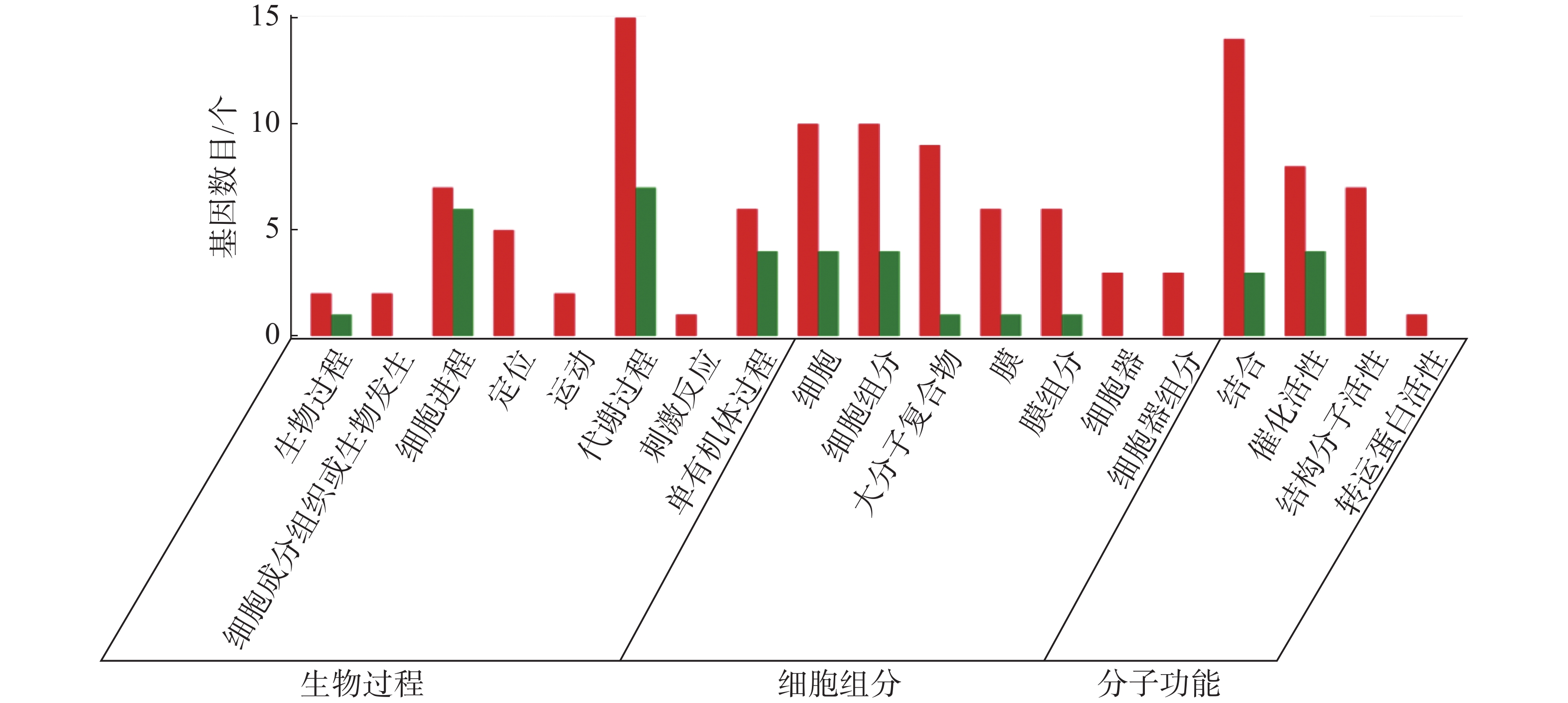
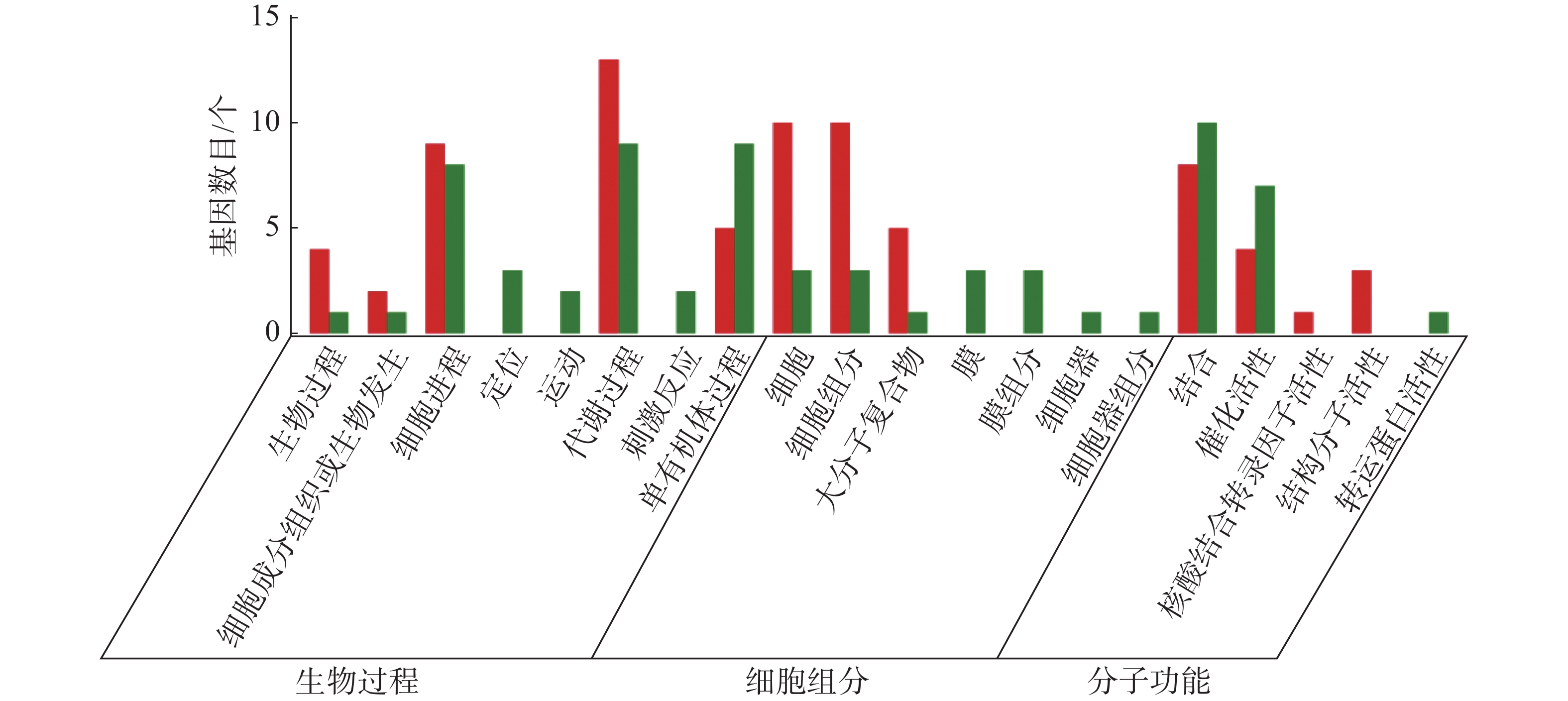
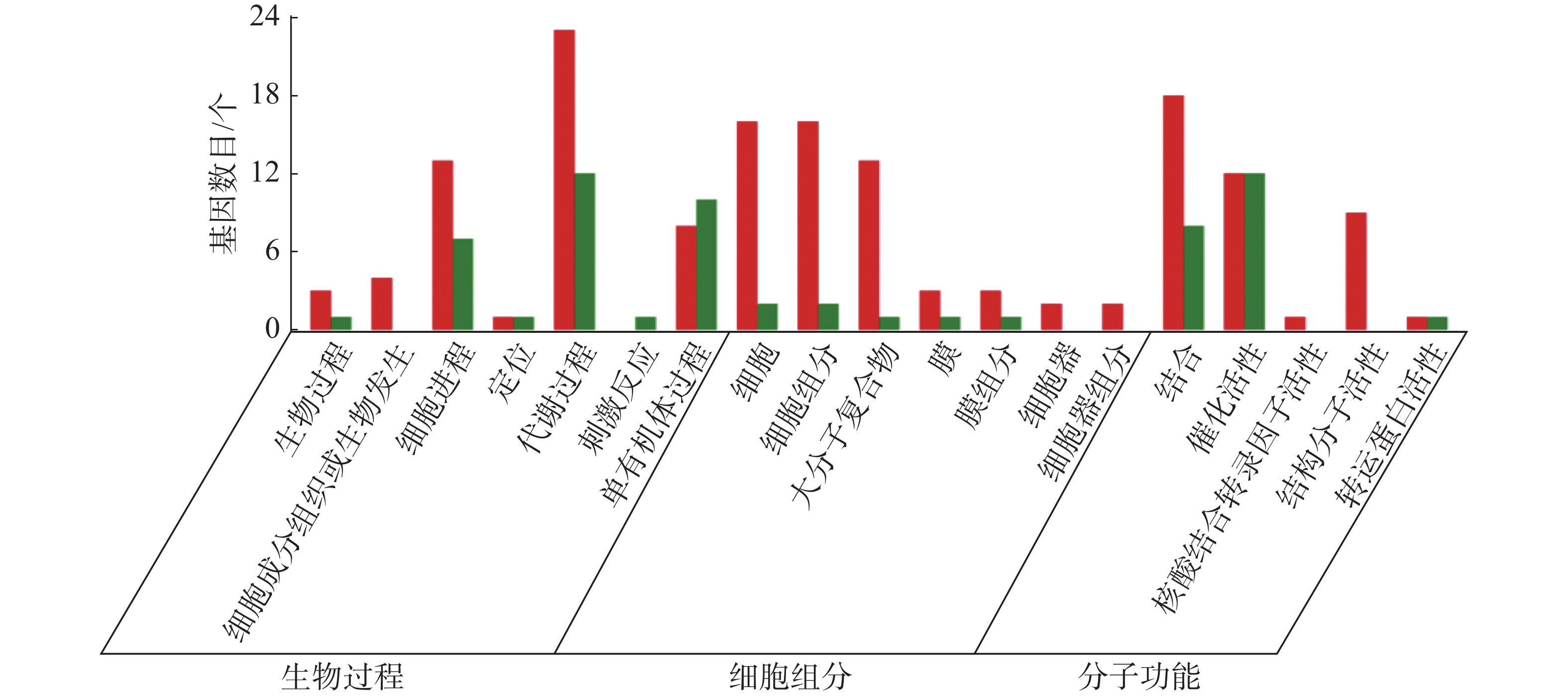
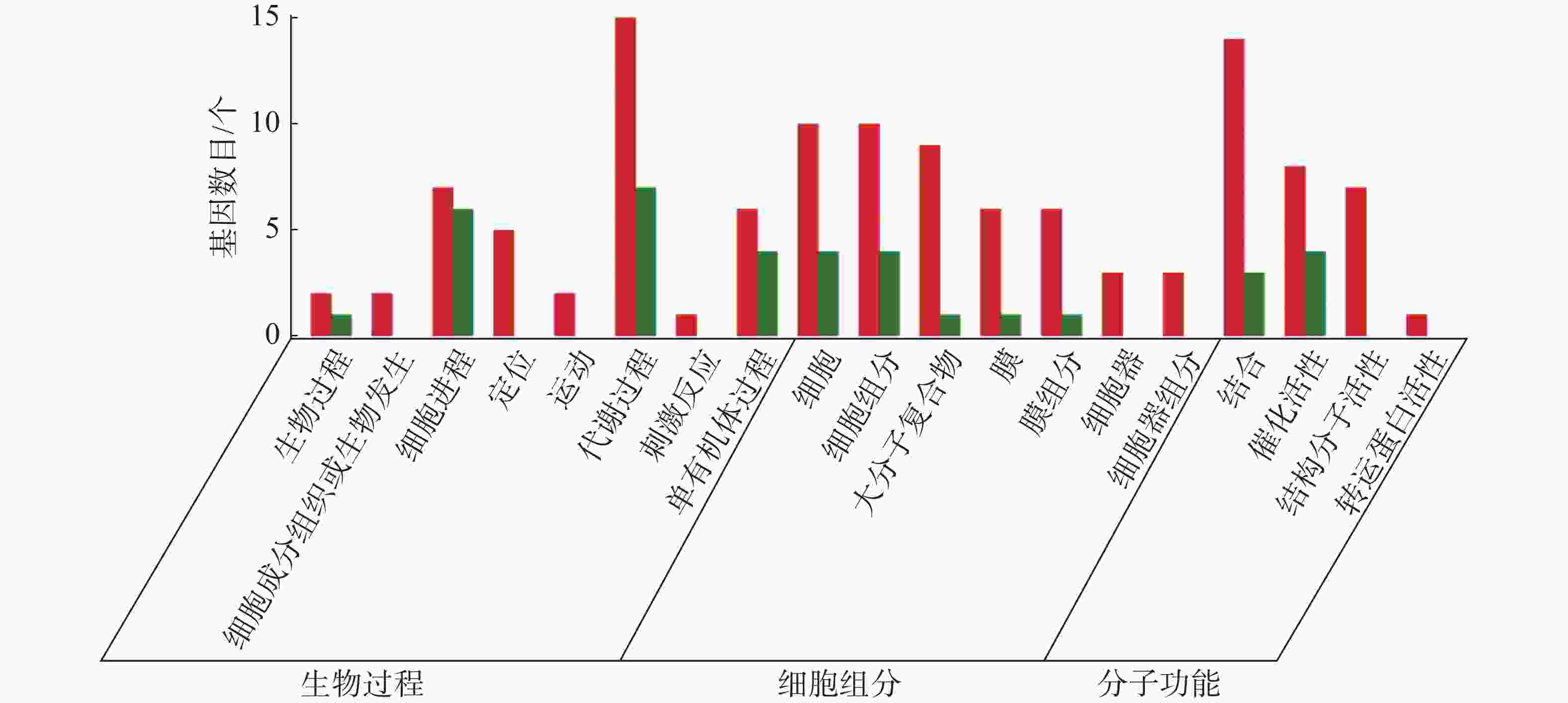
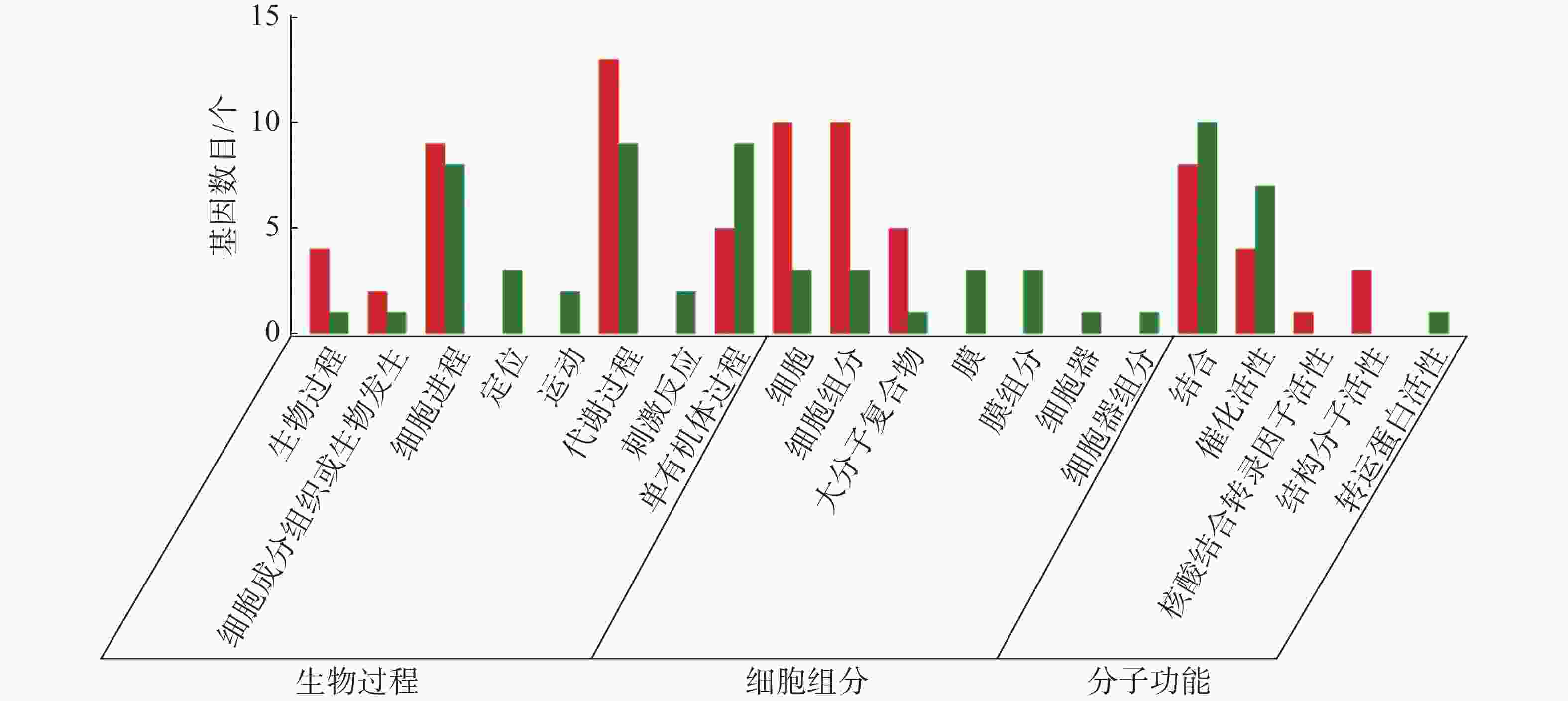
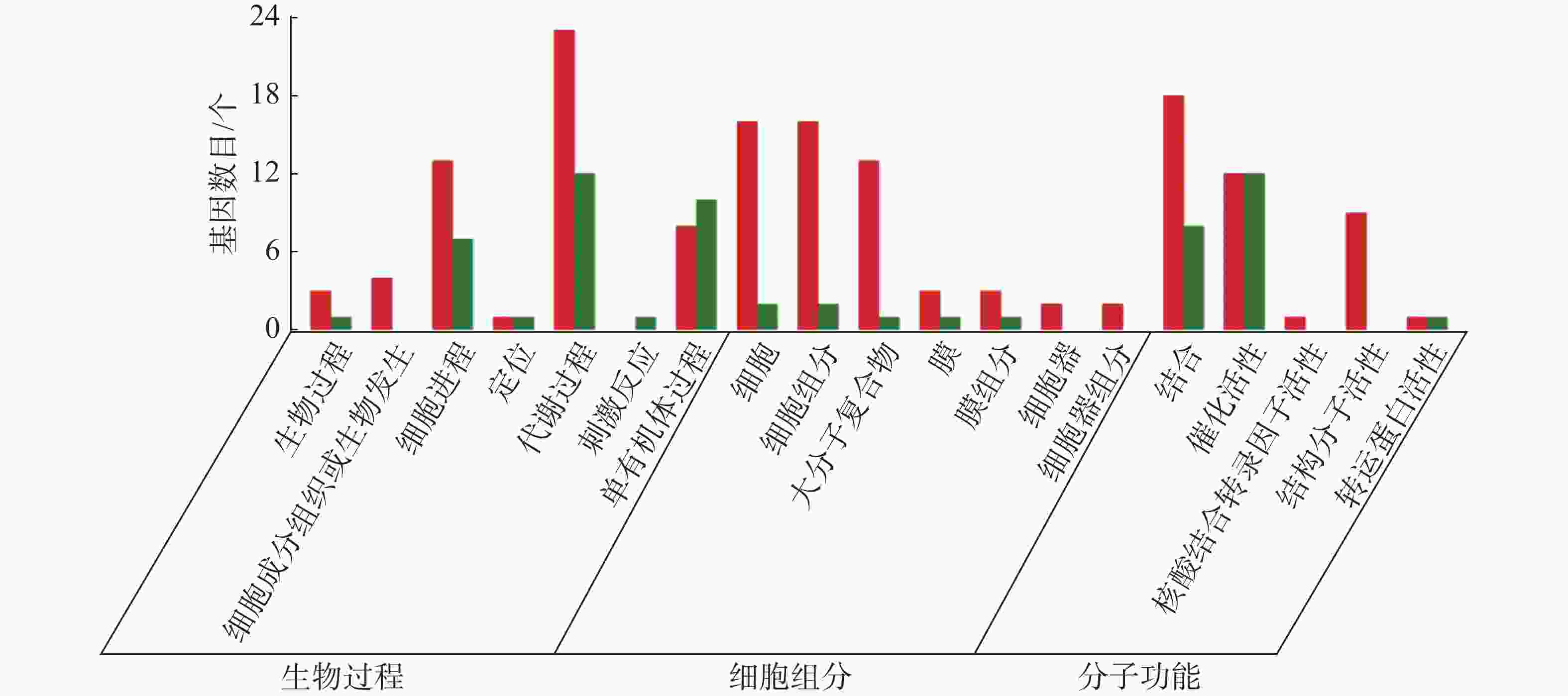
从图5~7中可以看出,在生物过程中,HN-2组的差异基因主要集中在单体有机体过程、代谢过程和细胞进程等功能条目中,其中,单体有机体过程包含33个差异基因,代谢过程包含35个差异基因;细胞进程中包含20个差异基因,在细胞组分中,HN-2组的差异基因主要富集在细胞、细胞成分和大分子复合物等功能条目中,其中,细胞核细胞成分均包含17个差异基因;在分子功能中,HN-2组的差异基因主要富集在结合、催化活性和结构分子活性等功能条目中,其中,结合过程包含26个差异基因,催化活性包含24个差异基因,结构分子活性包含9个差异基因。此外,可以看到虽然HN-2组和杆菌肽组的富集结果大致相似,但是HN-2组的差异基因数目(共148个差异基因)显著多于杆菌肽组的差异基因数目(共117个差异基因)。
-
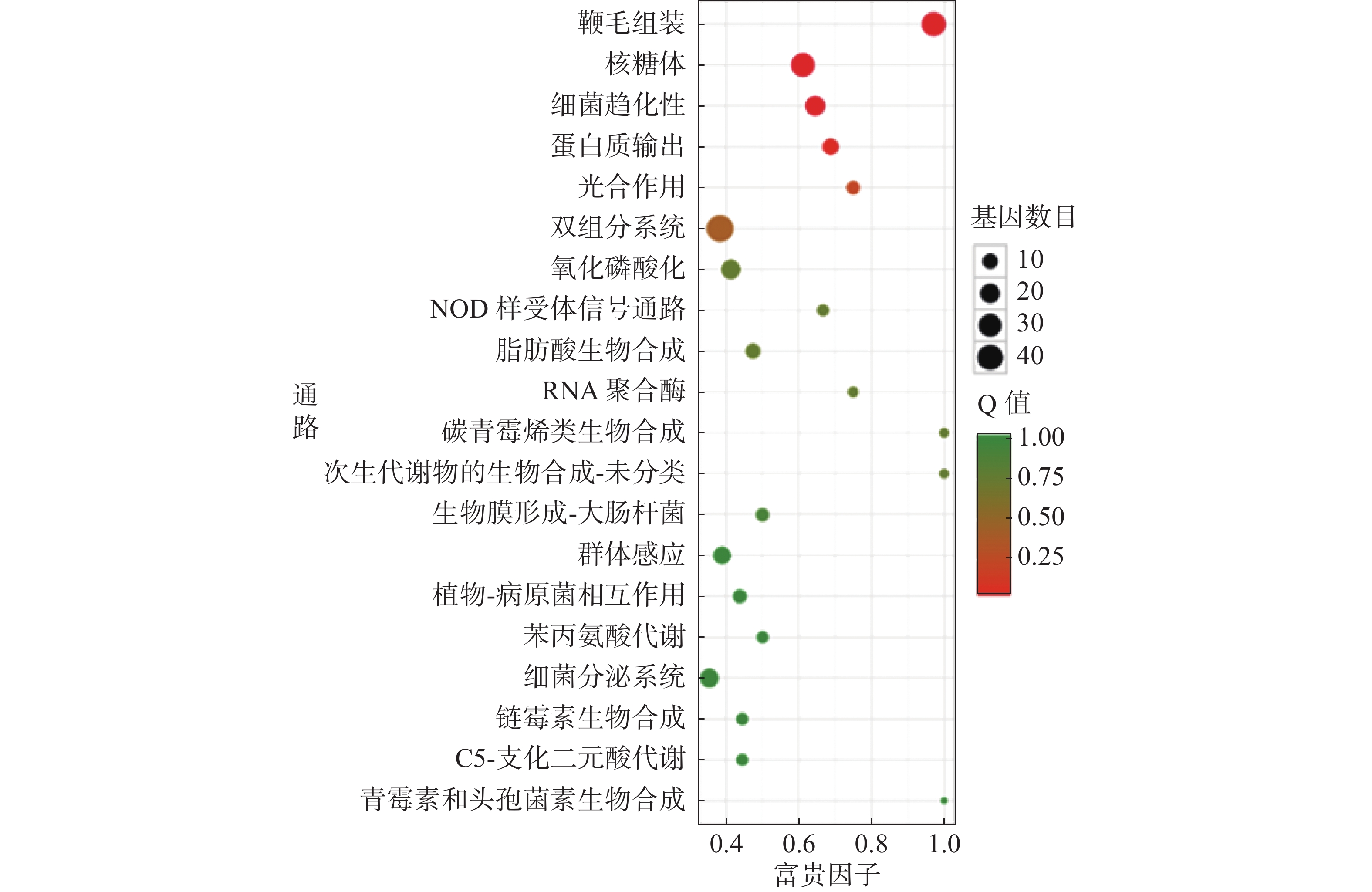
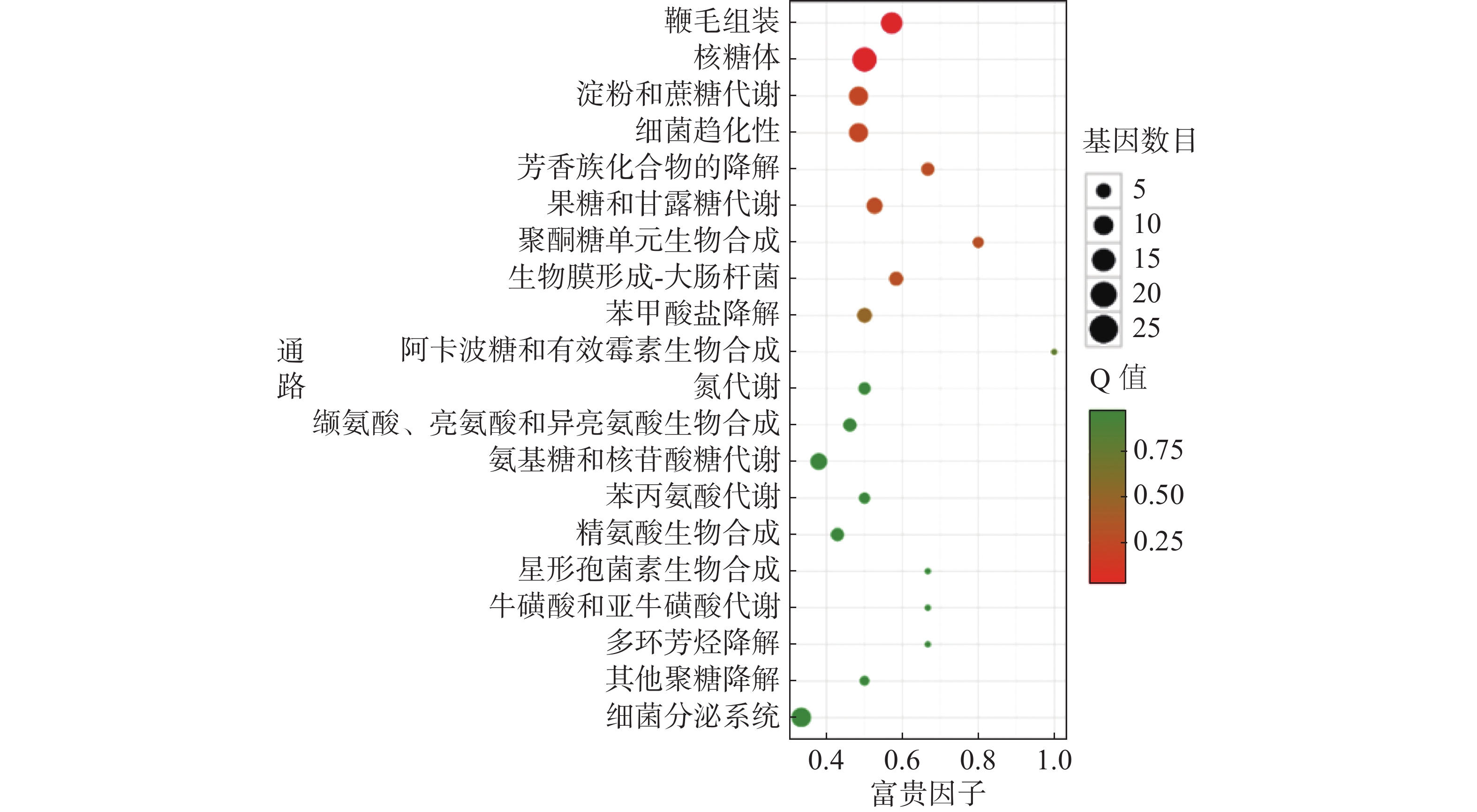
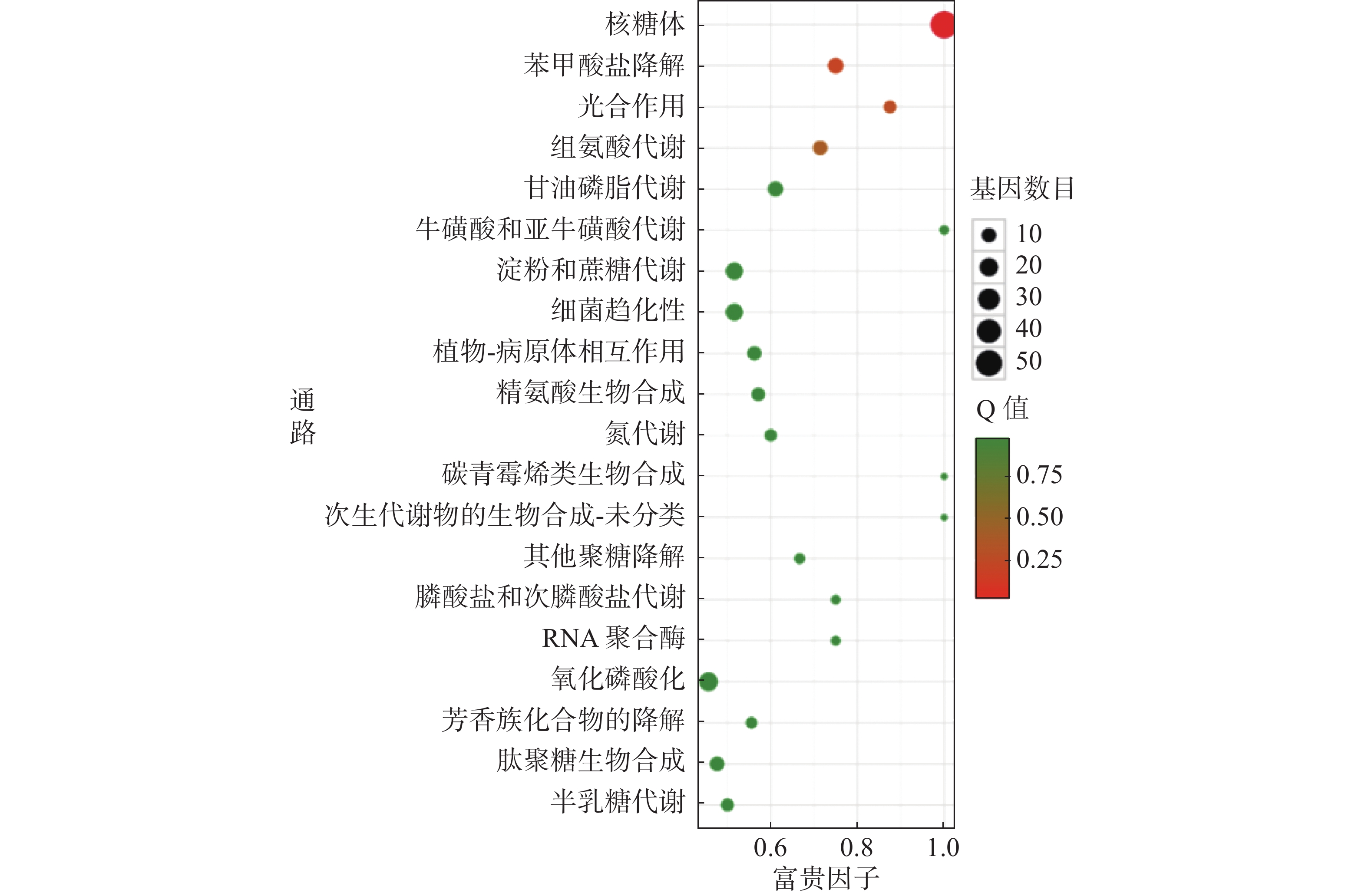
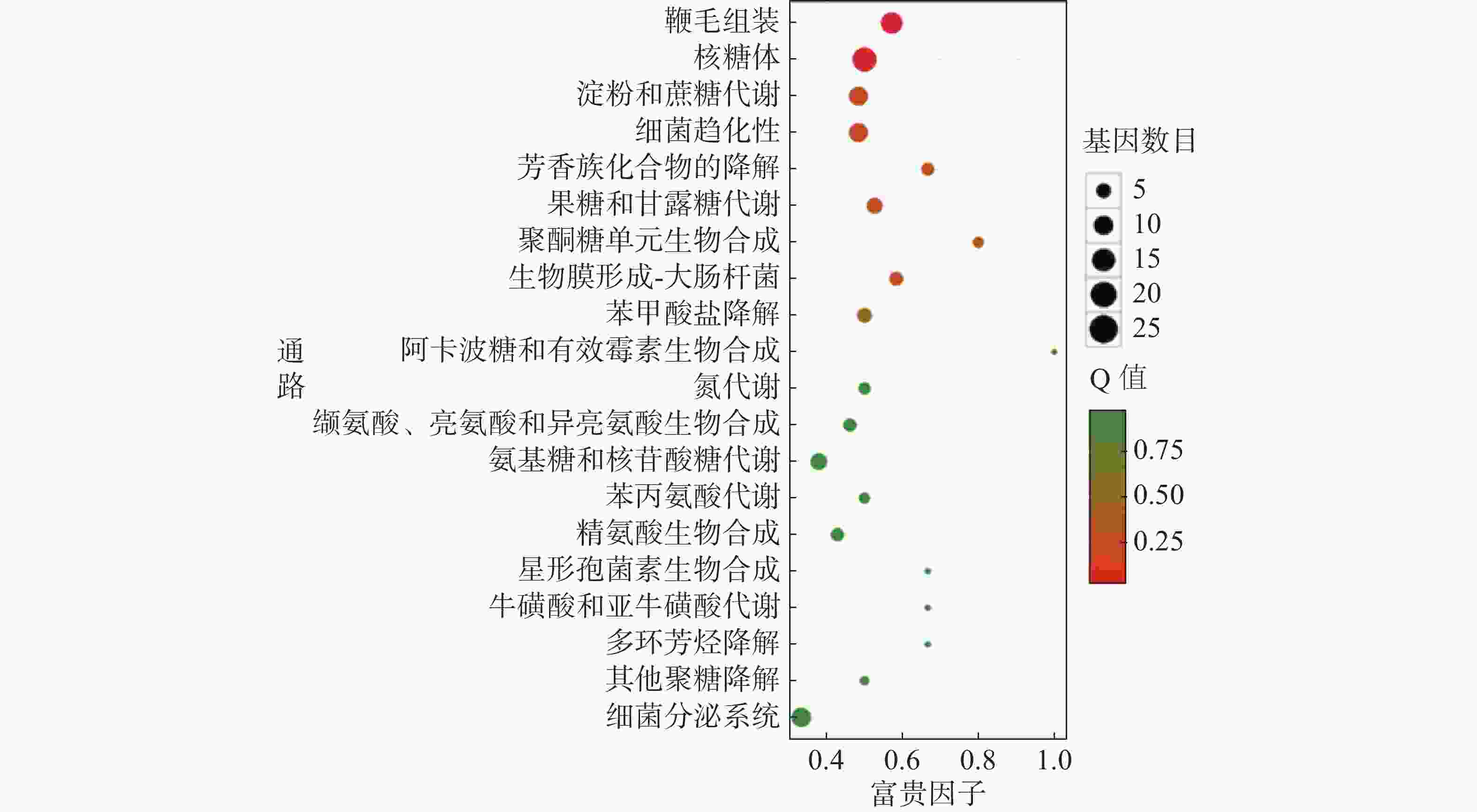
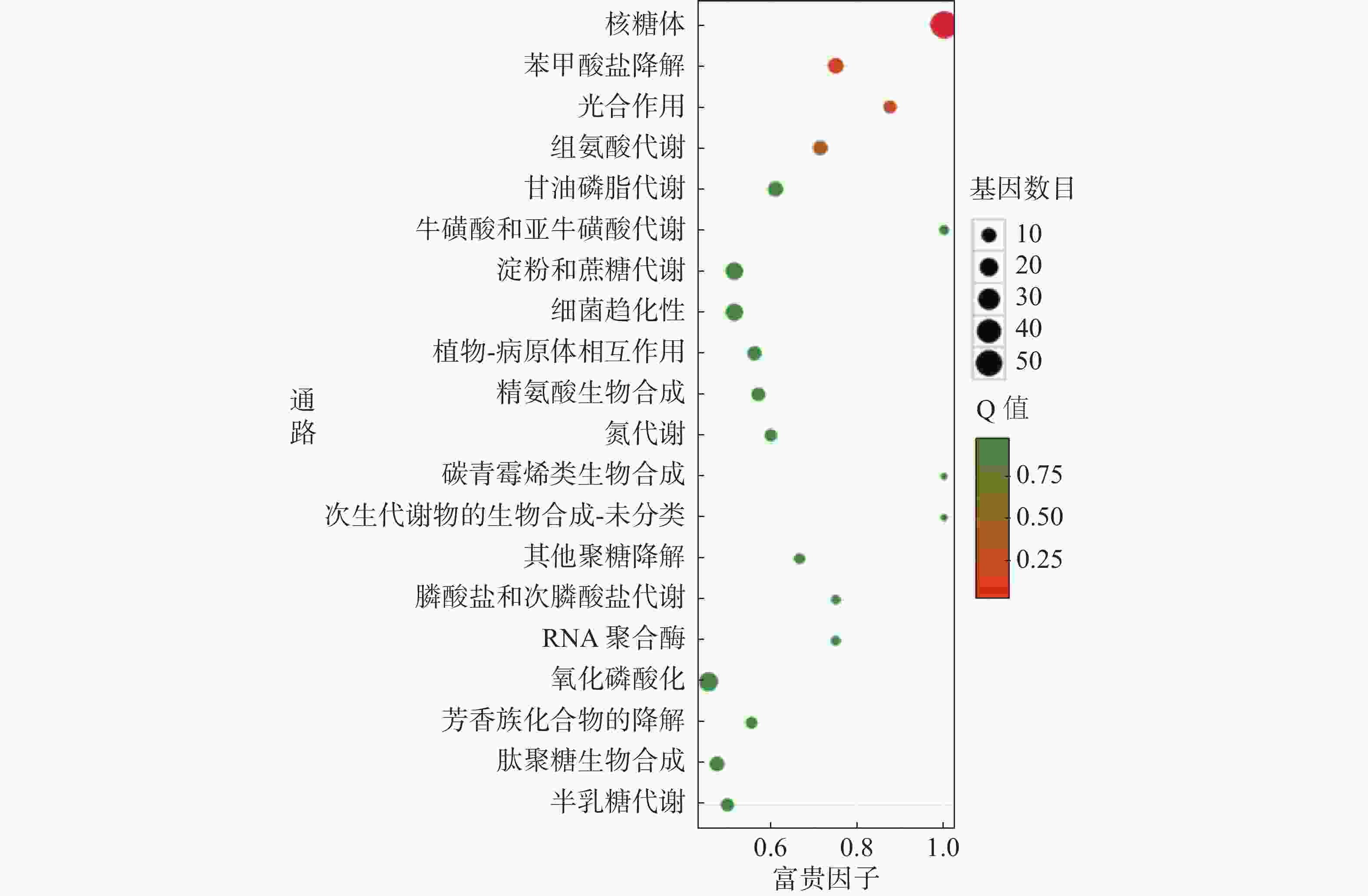
对杆菌肽与HN-2正丁醇提取物处理后,菌株Xoo的代谢通路显著性富集分析,选取了富集最为显著的20条代谢通路画图(图8~10)展示。图8表明,与对照组相比,杆菌肽处理后,富集程度较高、富集较为显著且包含差异基因数目较多的途径有鞭毛组装、核糖体途径、细菌趋化性和双组分系统氧化磷酸化等;图9表明,与对照组相比,HN-2正丁醇提取物处理后,核糖体途径所包含的差异表达基因富集的程度最高、富集最显著且差异表达基因的数目最多,其余主要参与的代谢途径有淀粉和蔗糖代谢、苯甲酸降解、甘油磷脂降解、细菌趋化性等。因此,在后续对相关代谢途径的生物学验证中,可以重点关注和研究核糖体途径的淀粉蔗糖代谢中的差异表达基因。
-
黄单胞菌能够引起的水稻白叶枯病,是水稻生产上的一类重要细菌病害[1]。生防细菌贝莱斯芽胞杆菌Bacillus velezensis由Ruiz-Garcia等[23]发现并命名,因其具有对人畜和环境友好,菌株不易产生抗药性、在自然环境中易降解等特点而受到广泛的研究和关注[24]。贝莱斯芽孢杆菌具有优越的抑制细菌能力,它能够产生许多抑菌活性物质,其中关注度最高的是脂肽类物质[15]。本实验室的前期研究结果发现,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌HN-2菌株发酵液的正丁醇提取物对Xoo具有很强的抑菌活性,通过分离纯化,得到了正丁醇提取物中的主要活性成分,并利用高效液相色谱-质谱/质谱联用(HPLC-MS/MS)技术对其结构进行了鉴定,结果表明贝莱斯芽孢杆菌(Bacillus velezensis)HN-2正丁醇提取物中的C15 surfactin A对Xoo具有较强抗菌活性,能抑制Xoo的生长[19],但其具体的抑菌机制尚不明确。
已有研究通过对药剂处理前后转录组测序来探究抑菌物质对Xoo的作用机理,如Fan等[25]对邻香豆酸处理30 min、1 h、3 h、6 h的Xoo菌与DMSO对照处理的Xoo菌进行转录组测序,KEGG聚类分析结果表明:在处理30 min后,差异表达基因没有明显聚类,主要都集中在代谢途径方面;处理1 h后,氧化磷酸化途径富集最显著;处理3 h后,差异表达基因聚类在氧化磷酸化和蛋白质合成途径中;处理6 h后,差异表达基因集中在糖代谢途径、组氨酸代谢途径和细菌趋化性等方面。并且还发现,MarR家族蛋白基因簇在4个时间段内都显著上调表达。据报道[25]MarR家族蛋白与病原细菌转运抗生素有关。Liang等[26]对经过噻枯唑处理4.5 h和9 h后的Xoo转录组进行分析,发现Xoo的组氨酸代谢途径显著被噻枯唑所抑制。Chen等[27]为了研究褪黑激素作为抗生素如何抑制黄单胞菌的生长,分析了200 µg·mL−1浓度褪黑素处理21 h的Xoo的转录组数据,结果表明,138个基因的mRNA转录水平发生了变化,以应对褪黑激素的攻击。上调基因主要集中在鞭毛成分、转运蛋白活性等途径,而催化活性、金属结合活性、碳水化合物代谢和氨基酸代谢等途径显著下调表达。在本实验中,为进一步明确HN-2的抑菌机制,将杆菌肽和HN-2正丁醇提取物处理12 h后的Xoo菌进行转录组测序。杆菌肽(Bacitracin)是一类由地衣芽孢杆菌(Bacillus licheni formus)发酵生产的一类脂肽类物质,具有良好的抑制细菌活性[28]。杆菌肽的作用机制明确,它通过抑制细胞壁的合成,对细胞膜造成损伤,使细胞质中离子和氨基酸外泄来发挥抑菌作用[29]。与地衣芽孢杆菌一样,贝莱斯芽孢杆菌也能够通过非核糖体途径合成一些具有抑菌活性的脂肽类物质,因此本实验选择杆菌肽作为对比来检验贝莱斯芽孢杆菌HN-2的主要抑菌机制与杆菌肽是否具有相似性。
转录组测序分析后发现Xoo的核糖体途径、淀粉和蔗糖代谢途径、细菌趋化性途径等在受到HN-2正丁醇提取物的影响后显著上调表达,说明HN-2正丁醇提取物很可能通过影响这些代谢途径而发挥抑菌能力。由图4可以看到,HN-2组与杆菌肽组中相同的差异基因仅占HN-2组所有差异基因的45.3%,HN-2组还有54.7%差异基因为其特有,因此,可以得出结论,HN-2正丁醇提取物的抑菌活性与杆菌肽可能有部分相似性,但是其主要抑菌机理仍需要进一步探究与分析。通过KEGG富集分析结果发现,HN-2正丁醇提取物处理后,核糖体途径富集的程度最高、富集最显著、且包含的差异表达基因数目最多。在核糖体途径中发现显著上调表达的rpoB,rpoB基因是结核分枝杆菌(M.tuberculosis)中编码RNA聚合酶β亚基的基因。万智敏等[30]的研究结果表明,rpoB基因耐药决定区(rifampin resistance-determining region,RRDR)的突变可以引起96%以上的结核分枝杆菌临床分离株对利福平耐药,并且rpoB基因不同的突变模式对利福平产生的耐药程度有显著的差异。由此可以推测菌株HN-2正丁醇提取物与利福平的抑菌机理可能存在一定相似性。此外,还发现核糖体途径中secY、secE和secG基因显著上调表达,secY、secE和secG基因所编码的蛋白是分泌途径中主要的3种膜蛋白[31],大多数细菌蛋白的运送都由secYEG复合体完成,可以推测HN-2正丁醇提取物可能影响了Xoo中蛋白的分泌与运输,从而影响Xoo菌与外界的物质交换。同时还发现HN-2正丁醇提取物处理后Xoo内淀粉和蔗糖代谢途径中的差异基因数目较多,差异较显著,可以推测HN-2正丁醇提取物可能使Xoo对淀粉和蔗糖等物质的代谢利用能力发生了改变。
本研究中,对Xoo经过HN-2正丁醇提取物和杆菌肽处理12 h转录组的分析结果表明,HN-2正丁醇提取物主要影响Xoo的核糖体途径、淀粉和蔗糖代谢途径、细菌趋化性途径。为进一步明确HN-2对Xoo的抑菌机理提供了理论基础。
Transcriptome analysis of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae under the treatment of Bacillus velezensis HN-2 secondary metabolites
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.006
- Received Date: 2022-04-28
- Accepted Date: 2022-07-21
- Rev Recd Date: 2022-06-18
- Available Online: 2022-09-06
- Publish Date: 2023-07-25
-
Key words:
- Bacillus velezensis /
- Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae /
- inhibitory activity /
- differentially expressed gene
Abstract: Bacterial blight of rice is a bacterial disease caused by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae (Xoo), and it occurs in a large area, causing serious damage, and is difficult to control. In our laboratory a Bacillus velezensis strain HN-2 with a strong biocontrol activity isolated from the paddy soil was found that its n-butanol extract has a strong inhibitory activity against Xoo. In order to study the inhibition mechanism of the n-butanol extract of the strain HN-2 on Xoo, Xoo was treated with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 and bacitracin, respectively and analyzed by using transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq)., and the transcriptome data was then analyzed by using GO database and KEGG database. Transcriptome data analysis results showed that a large number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Xoo after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 and bacitracin. A total of 1512 DEGs were obtained after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2, 871 DEGs were up-regulated and 641 down-regulated. GO enrichment analysis found that after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2, the DEGs in Xoo are mainly clustered in the cell process, metabolic process, macromolecular complex, catalytic activities, etc. KEGG cluster analysis found that after treatment with the n-butanol extract of HN-2 the ribosomal pathway in Xoo contained the largest number of DEGs while the other major metabolic pathways involved are starch and sucrose metabolism, benzoate degradation, glycerophospholipid metabolism, bacterial chemotaxis, etc. This suggests the n-butanol extract of HN-2 should have a main impact on the ribosomal pathway, and pathways of starch and sucrose metabolism and bacterial chemotaxis.
| Citation: | GAO Xue, LAO Guangshu, TAN Zheng, FANG Yukai, LIU Wenbo, JIN Pengfei, MIAO Weiguo. Transcriptome analysis of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae under the treatment of Bacillus velezensis HN-2 secondary metabolites[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2023, 14(4): 389-398. doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2023.04.006 |








 DownLoad:
DownLoad: