2024 Vol. 15, No. 1
2024, 15(1): 1-9.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230004
Abstract:
To explore the role of sucrose non-fermentation associated protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) in the response of Hevea brasiliensis to low temperature stress, a member of the SnRK2 subfamily, named HbSnRK2.7, was cloned from the leaves of the cold-resistant clone Reyan ‘93-114’ of Hevea brasiliensis by using RT-PCR. The gene cloned contains an open reading frame of 1 095 bp that encodes a protein of 364 amino acids. HbSnRK2.7 has a conserved serine/threonine protein kinase domain with a molecular weight of 41.39 kD and an isoelectric point of 4.70. It is predicted that it can catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to the serine/threonine residues on the protein substrate, which is also the concentrated region of phosphorylation sites. It also has domains needed for abiotic stress and ABA-dependent domains for HbSnRK2.7 activation. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) results showed that HbSnRK2.7 gene was down-regulated in response to ABA induction. When treated with ABA for 8 h, the expression was down-regulated to the lowest point. Under low temperature stress, the expression of HbSnRK2.7 decreased significantly. The expression of HbSnRK2.7 was down-regulated continuously under low temperature stress for 4 h and 8 h, and the expression of HbSnRK2.7 was down-regulated to the lowest level at 24 h under low temperature stress, which was about 1/2 of non-stress expression. Moreover, the expression of HbSnRK2.7 was significantly higher in the cold-susceptible clones than in the cold-resistant clones. These results suggest that HbSnRK2.7 may act as a negative regulatory factor to mediate the formation of low temperature stress resistance of Hevea brasiliensis dependent on ABA.
To explore the role of sucrose non-fermentation associated protein kinase 2 (SnRK2) in the response of Hevea brasiliensis to low temperature stress, a member of the SnRK2 subfamily, named HbSnRK2.7, was cloned from the leaves of the cold-resistant clone Reyan ‘93-114’ of Hevea brasiliensis by using RT-PCR. The gene cloned contains an open reading frame of 1 095 bp that encodes a protein of 364 amino acids. HbSnRK2.7 has a conserved serine/threonine protein kinase domain with a molecular weight of 41.39 kD and an isoelectric point of 4.70. It is predicted that it can catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to the serine/threonine residues on the protein substrate, which is also the concentrated region of phosphorylation sites. It also has domains needed for abiotic stress and ABA-dependent domains for HbSnRK2.7 activation. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) results showed that HbSnRK2.7 gene was down-regulated in response to ABA induction. When treated with ABA for 8 h, the expression was down-regulated to the lowest point. Under low temperature stress, the expression of HbSnRK2.7 decreased significantly. The expression of HbSnRK2.7 was down-regulated continuously under low temperature stress for 4 h and 8 h, and the expression of HbSnRK2.7 was down-regulated to the lowest level at 24 h under low temperature stress, which was about 1/2 of non-stress expression. Moreover, the expression of HbSnRK2.7 was significantly higher in the cold-susceptible clones than in the cold-resistant clones. These results suggest that HbSnRK2.7 may act as a negative regulatory factor to mediate the formation of low temperature stress resistance of Hevea brasiliensis dependent on ABA.
2024, 15(1): 10-18.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230035
Abstract:
The subcellular localization and expression analysis of Psbp protein MePPD3 (Manihot esculenta PsbP domain-containing protein 3, Phytozome database number: Manes.05G127800) were performed to explore whether MePPD3 is involved in disease resistance of cassava. MePPD3 gene was amplified by RT-PCR. Sequence analysis showed that MePPD3 gene was 807bp in length, encoding 268 amino acids, with PsbP domain located at position 106-266 aa. Bioinformatics analysis of MePPD3 protein was conducted by NetPhos 3.1 Server, SignalP 5.0 Server, TMHMM Servervr, PSIPRED and PHYRE2 online, respectively. The results indicated that MePPD3 protein contained 32 phosphorylation sites, 5 glycosylation sites, and 1 transmembrane domain. The secondary structure of the protein was composed of 21.3% Helix (Helix), 26.5% fold (strand) and 52.2% random curl (loop). The multiple sequence alignment, phylogenetic tree analysis and conserved domain analysis indicated that PPD3 protein had a high genetic relationship among different plants. Subcellular localization showed that MePPD3 protein was localized in chloroplast. QRT-PCR results revealed that the expression level of MePPD3 gene in different cassava tissues was significantly different, and was the highest in mature leaves. In addition, the expression of this gene was induced by Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. manihotis (Xpm), indicating MePPD3 is involved in the resistance of cassava to Xpm. After MePPD3 gene was silenced by VIGS technique, the leaf lesion area of silent plants was significantly smaller than that of the control plants, which implies that MePPD3 negatively regulates cassava resistance to bacterial fusarium wilt caused by Xpm.
The subcellular localization and expression analysis of Psbp protein MePPD3 (Manihot esculenta PsbP domain-containing protein 3, Phytozome database number: Manes.05G127800) were performed to explore whether MePPD3 is involved in disease resistance of cassava. MePPD3 gene was amplified by RT-PCR. Sequence analysis showed that MePPD3 gene was 807bp in length, encoding 268 amino acids, with PsbP domain located at position 106-266 aa. Bioinformatics analysis of MePPD3 protein was conducted by NetPhos 3.1 Server, SignalP 5.0 Server, TMHMM Servervr, PSIPRED and PHYRE2 online, respectively. The results indicated that MePPD3 protein contained 32 phosphorylation sites, 5 glycosylation sites, and 1 transmembrane domain. The secondary structure of the protein was composed of 21.3% Helix (Helix), 26.5% fold (strand) and 52.2% random curl (loop). The multiple sequence alignment, phylogenetic tree analysis and conserved domain analysis indicated that PPD3 protein had a high genetic relationship among different plants. Subcellular localization showed that MePPD3 protein was localized in chloroplast. QRT-PCR results revealed that the expression level of MePPD3 gene in different cassava tissues was significantly different, and was the highest in mature leaves. In addition, the expression of this gene was induced by Xanthomonas phaseoli pv. manihotis (Xpm), indicating MePPD3 is involved in the resistance of cassava to Xpm. After MePPD3 gene was silenced by VIGS technique, the leaf lesion area of silent plants was significantly smaller than that of the control plants, which implies that MePPD3 negatively regulates cassava resistance to bacterial fusarium wilt caused by Xpm.
2024, 15(1): 19-26.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230018
Abstract:
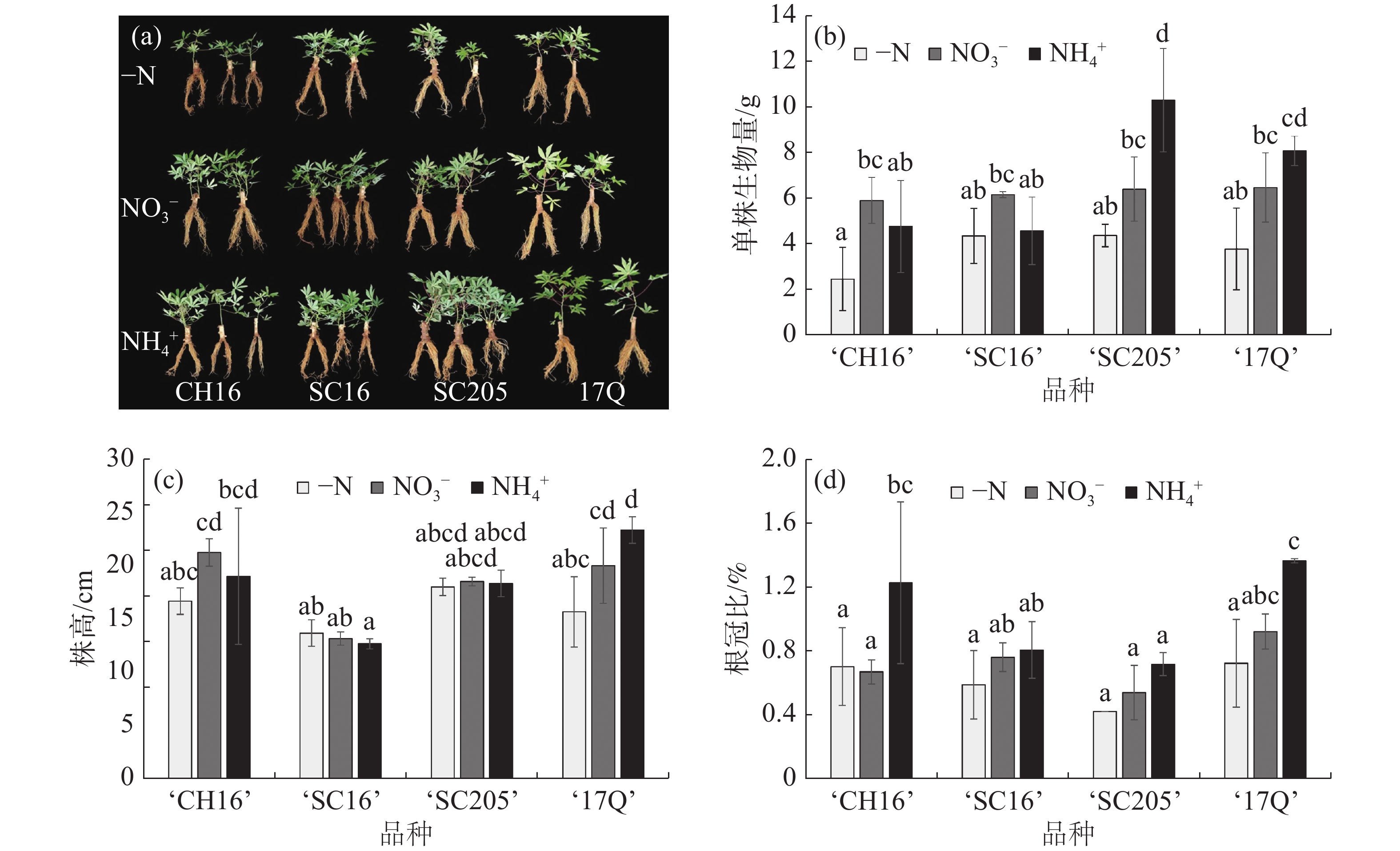
In order to explore the effects of different nitrogen sources on the growth and development of different cassava varieties and their differences, three different nitrogen sources, namely -N, NO3− and NH4+, were used to treat four cassava varieties,‘CH16’, ‘SC16’, ‘SC205’ and ‘17Q’, in the experiment. The growth status, nitrogen content, root morphology, nitrogen accumulation and nitrogen use efficiency of four cassava varieties were observed and analyzed. The results showed that under the treatment of NaNO3 (3 mmol·L−1) and NH4Cl (3 mmol·L−1), the cassava varieties ‘SC205’and ‘17Q’ had a relatively higher nitrogen utilization efficiency for ammonium nitrogen, belonging to the ammonium preferred varieties, while ‘SC16’ and ‘CH16’ had no difference in nitrogen utilization efficiency and preference for nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen. Under the condition of no nitrogen, ‘17Q’ and ‘SC16’ were nitrogen efficient cultivars with relatively high resistance to low nitrogen stress, while ‘SC205’ and ‘CH16 ’were nitrogen inefficient cultivars with relatively low resistance to low nitrogen stress, among which ‘CH16’ had the lowest tolerance to low nitrogen. The study lays the foundation for genetic improvement of nitrogen use efficiency and scientific fertilization in cassava agricultural production.
In order to explore the effects of different nitrogen sources on the growth and development of different cassava varieties and their differences, three different nitrogen sources, namely -N, NO3− and NH4+, were used to treat four cassava varieties,‘CH16’, ‘SC16’, ‘SC205’ and ‘17Q’, in the experiment. The growth status, nitrogen content, root morphology, nitrogen accumulation and nitrogen use efficiency of four cassava varieties were observed and analyzed. The results showed that under the treatment of NaNO3 (3 mmol·L−1) and NH4Cl (3 mmol·L−1), the cassava varieties ‘SC205’and ‘17Q’ had a relatively higher nitrogen utilization efficiency for ammonium nitrogen, belonging to the ammonium preferred varieties, while ‘SC16’ and ‘CH16’ had no difference in nitrogen utilization efficiency and preference for nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen. Under the condition of no nitrogen, ‘17Q’ and ‘SC16’ were nitrogen efficient cultivars with relatively high resistance to low nitrogen stress, while ‘SC205’ and ‘CH16 ’were nitrogen inefficient cultivars with relatively low resistance to low nitrogen stress, among which ‘CH16’ had the lowest tolerance to low nitrogen. The study lays the foundation for genetic improvement of nitrogen use efficiency and scientific fertilization in cassava agricultural production.
2024, 15(1): 27-35.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220094
Abstract:
A germplasm survey of Camellia oleifera was made in tropical areas of China from October to December 2021, and their geographical distribution, habitats, morphological characteristics, and correlation and variability with the economic traits were analyzed for evaluation. A total of 230 tropical Camellia oleifera germplasm resources were collected in 18 cities and counties in three provinces (Hainan, Guangxi, and Guangdong). The analysis showed that the C. oleifera germplasm resources collected in the 18 cities and counties in the three provinces had an annual average temperature of 21.2 to 24.3 ℃, an annual average precipitation of 1,304.2 to 2,684.0 mm, and an altitude of 0.56 to 1,090.00 m. A total of 33 species of companion plants for C. oleifera were found, among which 29 species were plants of angiosperms. The fruit were mainly multicolored, and mostly spheroid or citrus-like in shape, and the leaf shape index was significantly different. The variation coefficients of 11 economic traits ranged from 11.03% to 145.10%, among which the variation coefficient of the leaf shape index was relatively stable. Fruit peel thickness was the most important economic trait, and was significantly positively correlated with fruit diameter, fruit height, fresh fruit weight, fresh seed weight, fresh seed yield, number of seeds, and thousand kernel weight. There was a significant correlation between fruit peel thickness and leaf shape index.
A germplasm survey of Camellia oleifera was made in tropical areas of China from October to December 2021, and their geographical distribution, habitats, morphological characteristics, and correlation and variability with the economic traits were analyzed for evaluation. A total of 230 tropical Camellia oleifera germplasm resources were collected in 18 cities and counties in three provinces (Hainan, Guangxi, and Guangdong). The analysis showed that the C. oleifera germplasm resources collected in the 18 cities and counties in the three provinces had an annual average temperature of 21.2 to 24.3 ℃, an annual average precipitation of 1,304.2 to 2,684.0 mm, and an altitude of 0.56 to 1,090.00 m. A total of 33 species of companion plants for C. oleifera were found, among which 29 species were plants of angiosperms. The fruit were mainly multicolored, and mostly spheroid or citrus-like in shape, and the leaf shape index was significantly different. The variation coefficients of 11 economic traits ranged from 11.03% to 145.10%, among which the variation coefficient of the leaf shape index was relatively stable. Fruit peel thickness was the most important economic trait, and was significantly positively correlated with fruit diameter, fruit height, fresh fruit weight, fresh seed weight, fresh seed yield, number of seeds, and thousand kernel weight. There was a significant correlation between fruit peel thickness and leaf shape index.
2024, 15(1): 36-41.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230038
Abstract:
In order to establish a simple, rapid and less sample method for the determination of arecoline in Areca catechu callus, an ultrasonic extraction method was used to extract arecoline from A.catechu calli, and four factors including solid-liquid ratio, extraction time, extraction temperature and extraction times were selected. On the basis of single factor experiment an orthogonal L9(34) experiment was performed to optimize the extraction system for arecoline from A. catechu calli. The results showed that the optimum extraction system for arecoline included the solid-liquid ratio of 1∶9, extraction time of 30 min, extraction temperature of 75 ℃ and 4 extraction times.
In order to establish a simple, rapid and less sample method for the determination of arecoline in Areca catechu callus, an ultrasonic extraction method was used to extract arecoline from A.catechu calli, and four factors including solid-liquid ratio, extraction time, extraction temperature and extraction times were selected. On the basis of single factor experiment an orthogonal L9(34) experiment was performed to optimize the extraction system for arecoline from A. catechu calli. The results showed that the optimum extraction system for arecoline included the solid-liquid ratio of 1∶9, extraction time of 30 min, extraction temperature of 75 ℃ and 4 extraction times.
2024, 15(1): 42-51.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230006
Abstract:
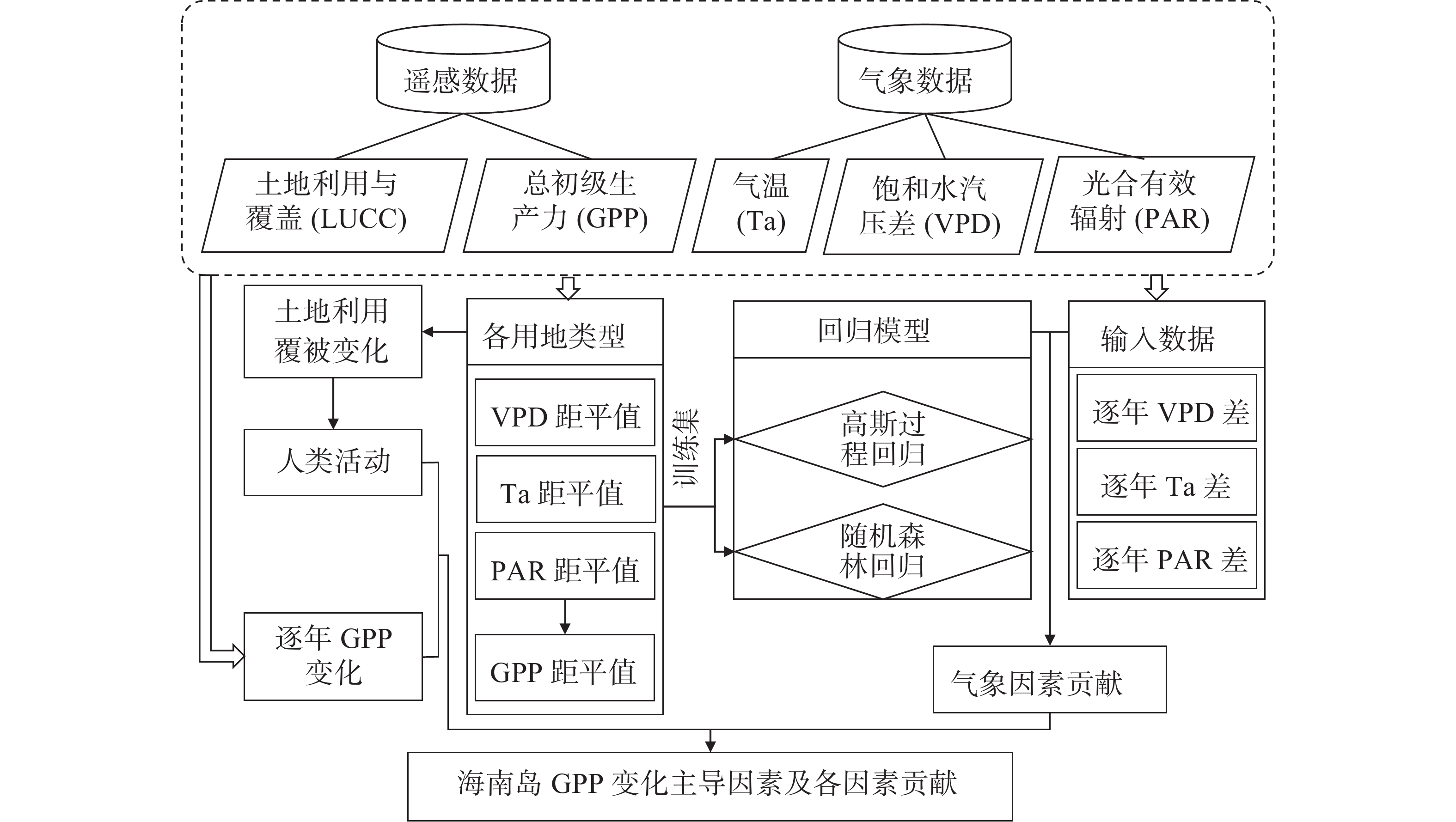
In order to explore the relative contribution of meteorological factors and human activities to the variation of gross primary production (GPP) in Hainan Island during the past 20 years, the Theil-Sen and Mann-Kendall methods were first used to obtain spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of GPP. Based on this, land Use and cover change (LUCC) was used as an indicator of human activities, air temperature (Ta), vapor pressure deficit (VPD) and photosynthetically active radiation (RAR) were used as meteorological factors. By using spatial statistics and machine learning techniques, a model attributing the variations in Hainan Island′s GPP was constructed to quantify the relative contribution of driving factors. The results showed that during the study period, GPP showed a significant increasing trend, with a rate of change of 0.44 Tg·a−1 (P=0.024) in time. Spatially, 87.8% of the island′s area showed a significant increasing trend, while a small portion region around Haikou and Sanya and other part of Hainan Island showed a decline (about 9%). Land use and cover change in Hainan Island had a total transfer of 15 528.40 km2, mainly occurring in forested areas, with a net increase of 642.88 km2 in forests, a transfer area of 4 759.28 km2 in grasslands and 4 051.23 km2 in croplands. Compared to human activities, the interannual of meteorological factors during the study period were the dominant factor influencing the variation in Hainan Island′s GPP. However, the impact of LUCC on cities and counties were more prominent in certain years.
In order to explore the relative contribution of meteorological factors and human activities to the variation of gross primary production (GPP) in Hainan Island during the past 20 years, the Theil-Sen and Mann-Kendall methods were first used to obtain spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of GPP. Based on this, land Use and cover change (LUCC) was used as an indicator of human activities, air temperature (Ta), vapor pressure deficit (VPD) and photosynthetically active radiation (RAR) were used as meteorological factors. By using spatial statistics and machine learning techniques, a model attributing the variations in Hainan Island′s GPP was constructed to quantify the relative contribution of driving factors. The results showed that during the study period, GPP showed a significant increasing trend, with a rate of change of 0.44 Tg·a−1 (P=0.024) in time. Spatially, 87.8% of the island′s area showed a significant increasing trend, while a small portion region around Haikou and Sanya and other part of Hainan Island showed a decline (about 9%). Land use and cover change in Hainan Island had a total transfer of 15 528.40 km2, mainly occurring in forested areas, with a net increase of 642.88 km2 in forests, a transfer area of 4 759.28 km2 in grasslands and 4 051.23 km2 in croplands. Compared to human activities, the interannual of meteorological factors during the study period were the dominant factor influencing the variation in Hainan Island′s GPP. However, the impact of LUCC on cities and counties were more prominent in certain years.
2024, 15(1): 52-59.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220109
Abstract:
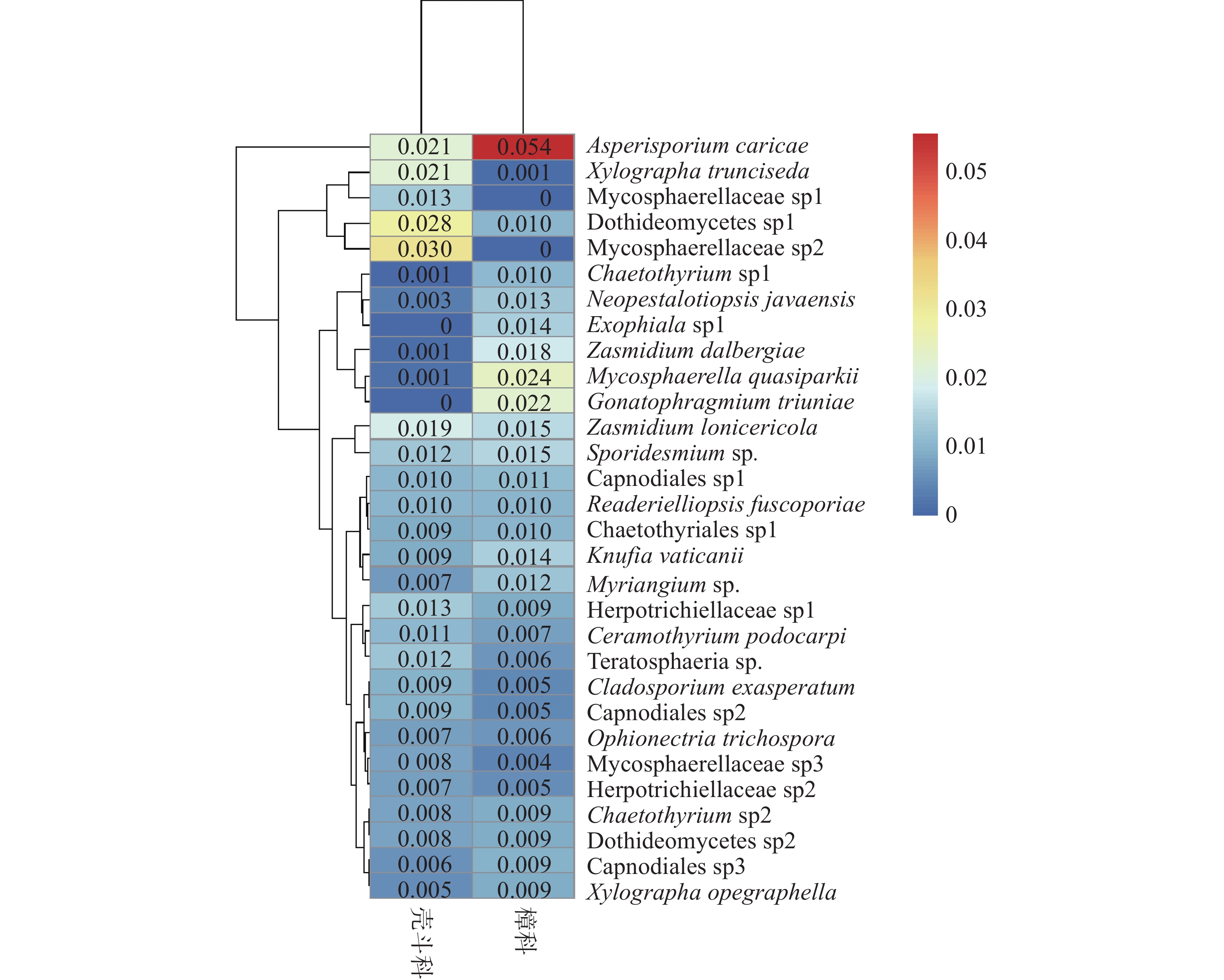
To investigate the effects of plant identity and leaf traits on foliar endophytic fungal community assembly, the species composition of foliar endophytic fungi in dominant plants in the tropical mountain rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island were determined by using the Illumina Miseq sequencing method, based on which the effects of host identity and leaf traits on the species composition of foliar endophytic fungi were explored. A total of 1,539,567 fungal ITS2 sequences were obtained from the leaves of 8 species of Lauraceae plants and 7 species of Fagaceae plants, which were classified into 5,471 Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) belonging to 8 phyla, 30 classes, 108 orders, 281 families, and 892 genera. Ascomycota was the largest group of the foliar endophytic fungi, accounting for 94.5% of all the fungal sequences. The number of endophytic fungal species in the leaves of individual Lauraceae plants (805 ± 32) OTUs was significantly higher than that of Fagaceae plants (554 ± 41) OTUs. However, there was no significant difference in Shannon-Wiener and Simpson diversity indices between the endophytic fungi in the leaves of the plants of these two families. Partial redundancy analysis showed that the host plant identities of family, genus and species significantly affected the composition of endophytic fungal communities. After removing the effect of plant traits, the host plant identities of family, genus, and species could independently explain 2.9%, 15.7%, and 33.7% of the variation in endophytic fungal species composition, respectively. After removing the effect of host plant identity, leaf traits could explain 21.3% of the variation in endophytic fungal species composition (P =0.003), of which leaf calcium content, specific leaf area, leaf nitrogen content, and leaf potassium content had significant effects on the composition of endophytic fungal communities. These findings suggest that host identity and leaf traits are important factors driving the assembly of endophytic fungal communities in the tropical mountain rainforest.
To investigate the effects of plant identity and leaf traits on foliar endophytic fungal community assembly, the species composition of foliar endophytic fungi in dominant plants in the tropical mountain rainforest in Jianfengling, Hainan Island were determined by using the Illumina Miseq sequencing method, based on which the effects of host identity and leaf traits on the species composition of foliar endophytic fungi were explored. A total of 1,539,567 fungal ITS2 sequences were obtained from the leaves of 8 species of Lauraceae plants and 7 species of Fagaceae plants, which were classified into 5,471 Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) belonging to 8 phyla, 30 classes, 108 orders, 281 families, and 892 genera. Ascomycota was the largest group of the foliar endophytic fungi, accounting for 94.5% of all the fungal sequences. The number of endophytic fungal species in the leaves of individual Lauraceae plants (805 ± 32) OTUs was significantly higher than that of Fagaceae plants (554 ± 41) OTUs. However, there was no significant difference in Shannon-Wiener and Simpson diversity indices between the endophytic fungi in the leaves of the plants of these two families. Partial redundancy analysis showed that the host plant identities of family, genus and species significantly affected the composition of endophytic fungal communities. After removing the effect of plant traits, the host plant identities of family, genus, and species could independently explain 2.9%, 15.7%, and 33.7% of the variation in endophytic fungal species composition, respectively. After removing the effect of host plant identity, leaf traits could explain 21.3% of the variation in endophytic fungal species composition (P =0.003), of which leaf calcium content, specific leaf area, leaf nitrogen content, and leaf potassium content had significant effects on the composition of endophytic fungal communities. These findings suggest that host identity and leaf traits are important factors driving the assembly of endophytic fungal communities in the tropical mountain rainforest.
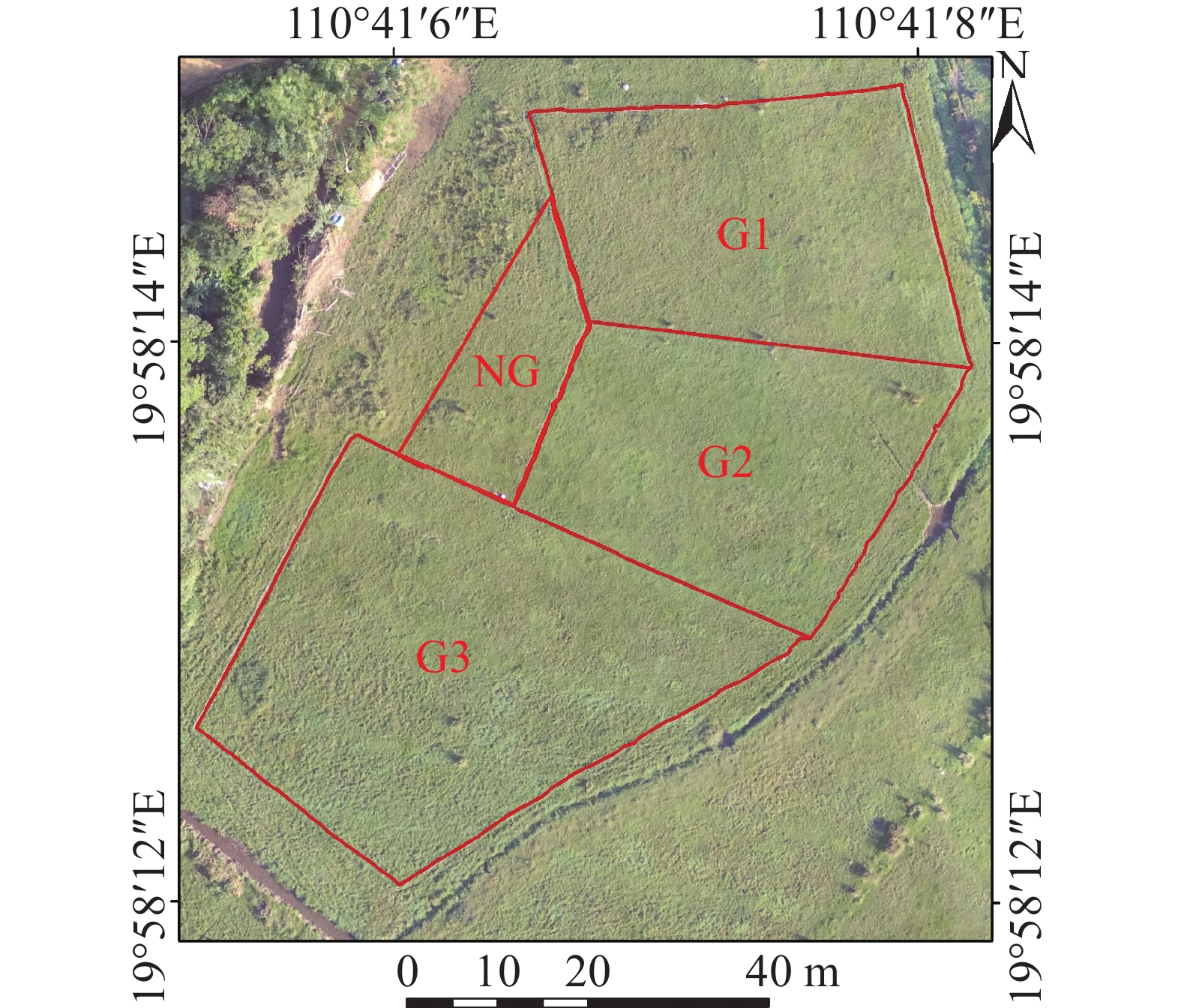
2024, 15(1): 60-72.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230047
Abstract:
Disorderly grazing in grassland on abandoned cultivated land hindered the sustainable development of the grassland in Hainan Island. Grassland grazing experiments were conducted according to different grazing methods (rotational grazing and continuous grazing) and different grazing intensities (severe, moderate, and slight). Multispectral UAVs and vegetation canopy analyzers were used to obtain daily-scale grassland leaf area index (LAI) during the grazing period, and the impact of different grazing strategies on changes in grassland leaf area index and cattle behavior were also quantitatively analyzed. Results showed that rotational grazing under moderate grazing intensity was beneficial to improving grassland LAI. Under severe grazing intensity the proportion of areas where LAI increased in rotational grazing and continuous grazing grassland accounted for 3.21% and 12.65% of the total grassland area, respectively. Under moderate grazing intensity the proportion of areas where LAI increased in rotational grazing and continuous grazing grassland accounted for 52.01% and 25.83% of the total grassland area, respectively. Under slight grazing intensity the proportion of areas where LAI increased in rotational grazing and continuous grazing grassland accounted for 61.02% and 60.37% of the total grassland area, respectively. Under severe grazing intensity the proportion of cattle's feeding time to the total behavior was always the highest. As the proportion of feeding time increased, the reduction of grassland LAI was also increased, but when the proportion of feeding time increasing to 70.88%-73.42%, the reduction of grassland LAI was gradually decreased. At this time, the leaf area index of the grassland dropped to 79.60%-79.90% of the initial leaf area index (before grazing on the first day), which meant that the number of leaves fed by the cattle was upto the limit that the LAI of the grassland could supply on the day. When this limit was exceeded, individual livestock competition would be intensified. At the same time, the proportion of time spent by cattle on gnawing behavior greatly increased. All these results will help to select the best grass and livestock management methods at the pasture scale, to provide theoretical methods and decision-making support for the sustainable development of tropical grassland livestock systems from a new perspective, and to assist the construction of the National Pilot Zone for Ecological Conservation (Hainan).
Disorderly grazing in grassland on abandoned cultivated land hindered the sustainable development of the grassland in Hainan Island. Grassland grazing experiments were conducted according to different grazing methods (rotational grazing and continuous grazing) and different grazing intensities (severe, moderate, and slight). Multispectral UAVs and vegetation canopy analyzers were used to obtain daily-scale grassland leaf area index (LAI) during the grazing period, and the impact of different grazing strategies on changes in grassland leaf area index and cattle behavior were also quantitatively analyzed. Results showed that rotational grazing under moderate grazing intensity was beneficial to improving grassland LAI. Under severe grazing intensity the proportion of areas where LAI increased in rotational grazing and continuous grazing grassland accounted for 3.21% and 12.65% of the total grassland area, respectively. Under moderate grazing intensity the proportion of areas where LAI increased in rotational grazing and continuous grazing grassland accounted for 52.01% and 25.83% of the total grassland area, respectively. Under slight grazing intensity the proportion of areas where LAI increased in rotational grazing and continuous grazing grassland accounted for 61.02% and 60.37% of the total grassland area, respectively. Under severe grazing intensity the proportion of cattle's feeding time to the total behavior was always the highest. As the proportion of feeding time increased, the reduction of grassland LAI was also increased, but when the proportion of feeding time increasing to 70.88%-73.42%, the reduction of grassland LAI was gradually decreased. At this time, the leaf area index of the grassland dropped to 79.60%-79.90% of the initial leaf area index (before grazing on the first day), which meant that the number of leaves fed by the cattle was upto the limit that the LAI of the grassland could supply on the day. When this limit was exceeded, individual livestock competition would be intensified. At the same time, the proportion of time spent by cattle on gnawing behavior greatly increased. All these results will help to select the best grass and livestock management methods at the pasture scale, to provide theoretical methods and decision-making support for the sustainable development of tropical grassland livestock systems from a new perspective, and to assist the construction of the National Pilot Zone for Ecological Conservation (Hainan).
2024, 15(1): 73-78.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230046
Abstract:
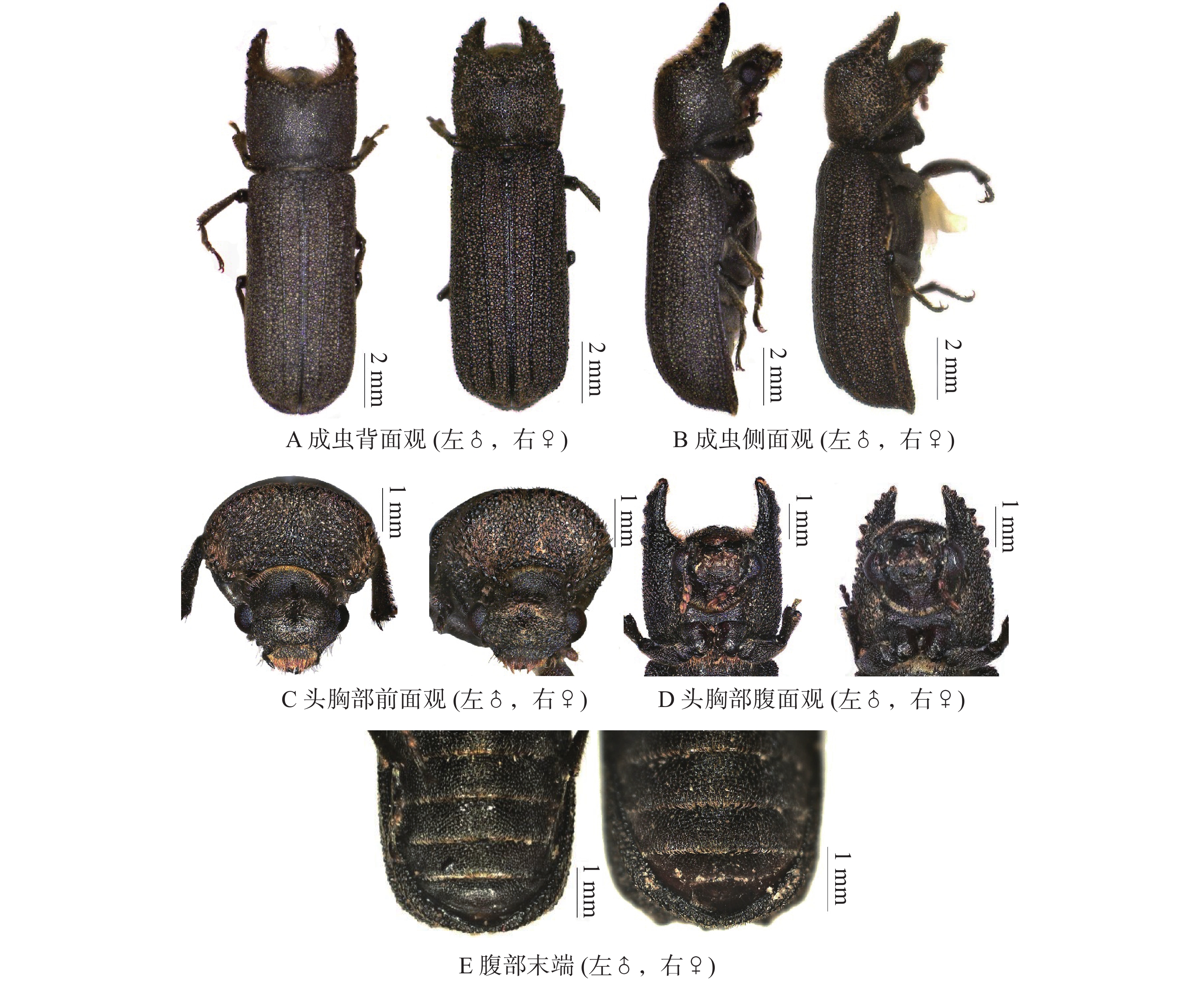
Bostrychoplites cornutus (Olivier, 1790) is distributed in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and other regions, and it mainly infests economic plants such as Triplochiton scleroxylon, Gliricidia sepium, Nesogordonia papaverifera, etc. The pest has been intercepted many times at quarantine ports in China, which is a potential threat of invasion to China. The taxonomic status, morphological characteristics, distribution, hosts, the morphological differences between Bostrychoplites species were illustrated, so as to simplify the difficulty of quarantine and identification of this pest, and provide some reference for its identification at frontier ports.
Bostrychoplites cornutus (Olivier, 1790) is distributed in Africa, Asia, Europe, North America and other regions, and it mainly infests economic plants such as Triplochiton scleroxylon, Gliricidia sepium, Nesogordonia papaverifera, etc. The pest has been intercepted many times at quarantine ports in China, which is a potential threat of invasion to China. The taxonomic status, morphological characteristics, distribution, hosts, the morphological differences between Bostrychoplites species were illustrated, so as to simplify the difficulty of quarantine and identification of this pest, and provide some reference for its identification at frontier ports.
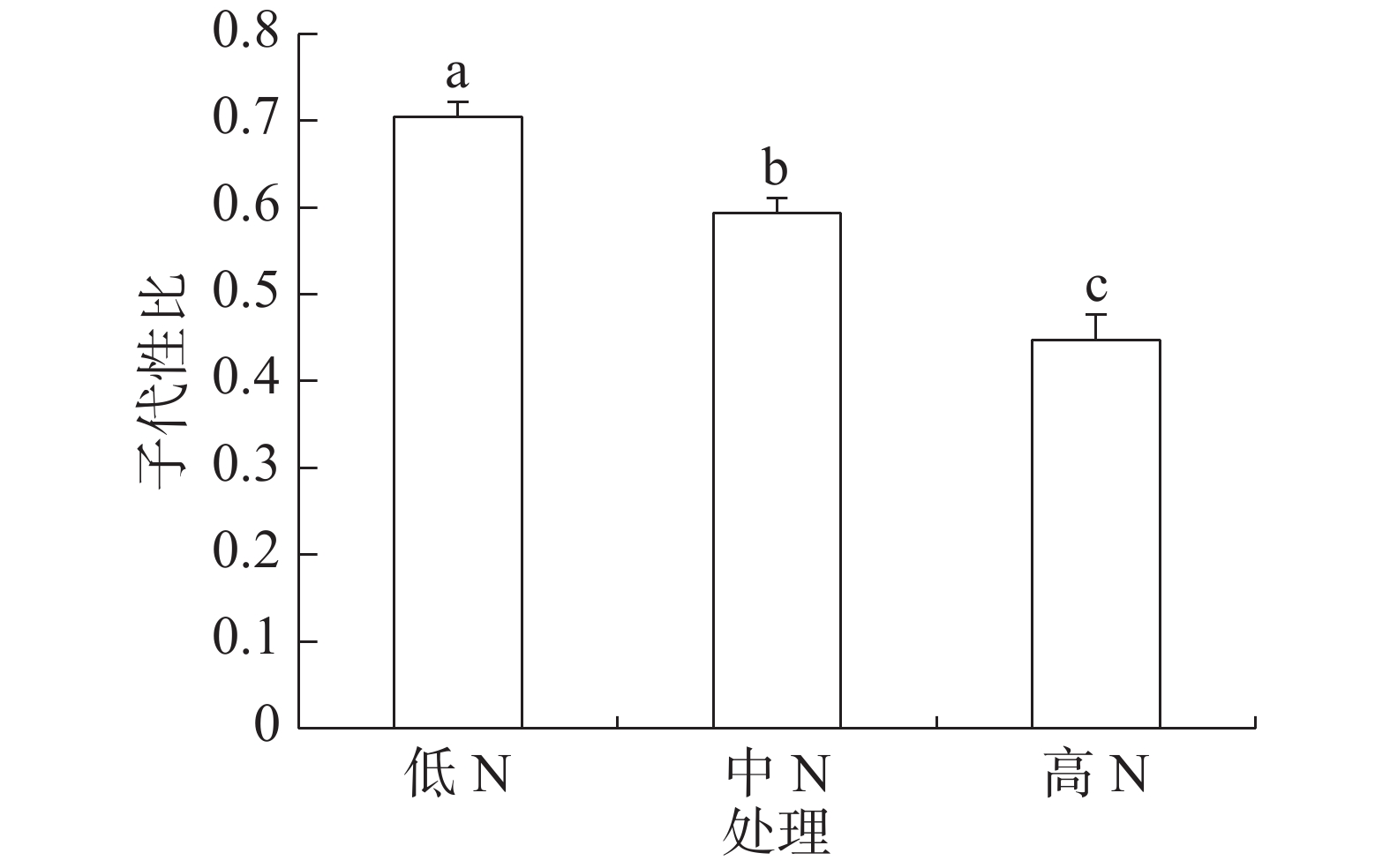
2024, 15(1): 79-84.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230061
Abstract:
In order to evaluate the influences of nitrogen fertilization on reproduction and sex ratio of Megalurothrips usitatus (Bagrall), an economically important pest of legumes, the 1-day-old mated females were provided daily with leaf disks cut from the first leaves of potted cowpea at the age of 13 to 15 days, which were fertilized as a single pre-plant application with three different levels of urea at rates of 0, 160, and 320 N kg·hm−2, respectively. After being checked the number of eggs, each leaf disk was transferred into a glass tube containing a section of young bean pod of cowpea, which was harvested from the field plants. Oviposition days of the focal females were recorded, and their offspring adult were sexed and counted. Sex ratios of offspring were calculated as proportion of males. The results showed that the females reared on leaf disks from plants fertilized with high N had significantly prolonged survival duration and oviposition duration, and shortened pre-oviposition period, and significantly greater oviposition rate and daily oviposition rate, compared to low N and medium N treatments. Offspring sex ratios for low N, medium N and high N treatments were 0.70, 0.59, and 0.45, respectively, which were significantly different among each other. The number of offspring females produced by the females increased as N application rate increased. The number of offspring adults for high N treatment was significantly higher than those for low N and medium N treatments. N application level had no effect on immature survival of the offspring. In conclusion, nitrogen fertilization impacts on development, reproduction, and sex ratio of M. usitatus. Nitrogen overfertilization increases offspring production of this thrips, with a female-biased sex ratio.
In order to evaluate the influences of nitrogen fertilization on reproduction and sex ratio of Megalurothrips usitatus (Bagrall), an economically important pest of legumes, the 1-day-old mated females were provided daily with leaf disks cut from the first leaves of potted cowpea at the age of 13 to 15 days, which were fertilized as a single pre-plant application with three different levels of urea at rates of 0, 160, and 320 N kg·hm−2, respectively. After being checked the number of eggs, each leaf disk was transferred into a glass tube containing a section of young bean pod of cowpea, which was harvested from the field plants. Oviposition days of the focal females were recorded, and their offspring adult were sexed and counted. Sex ratios of offspring were calculated as proportion of males. The results showed that the females reared on leaf disks from plants fertilized with high N had significantly prolonged survival duration and oviposition duration, and shortened pre-oviposition period, and significantly greater oviposition rate and daily oviposition rate, compared to low N and medium N treatments. Offspring sex ratios for low N, medium N and high N treatments were 0.70, 0.59, and 0.45, respectively, which were significantly different among each other. The number of offspring females produced by the females increased as N application rate increased. The number of offspring adults for high N treatment was significantly higher than those for low N and medium N treatments. N application level had no effect on immature survival of the offspring. In conclusion, nitrogen fertilization impacts on development, reproduction, and sex ratio of M. usitatus. Nitrogen overfertilization increases offspring production of this thrips, with a female-biased sex ratio.
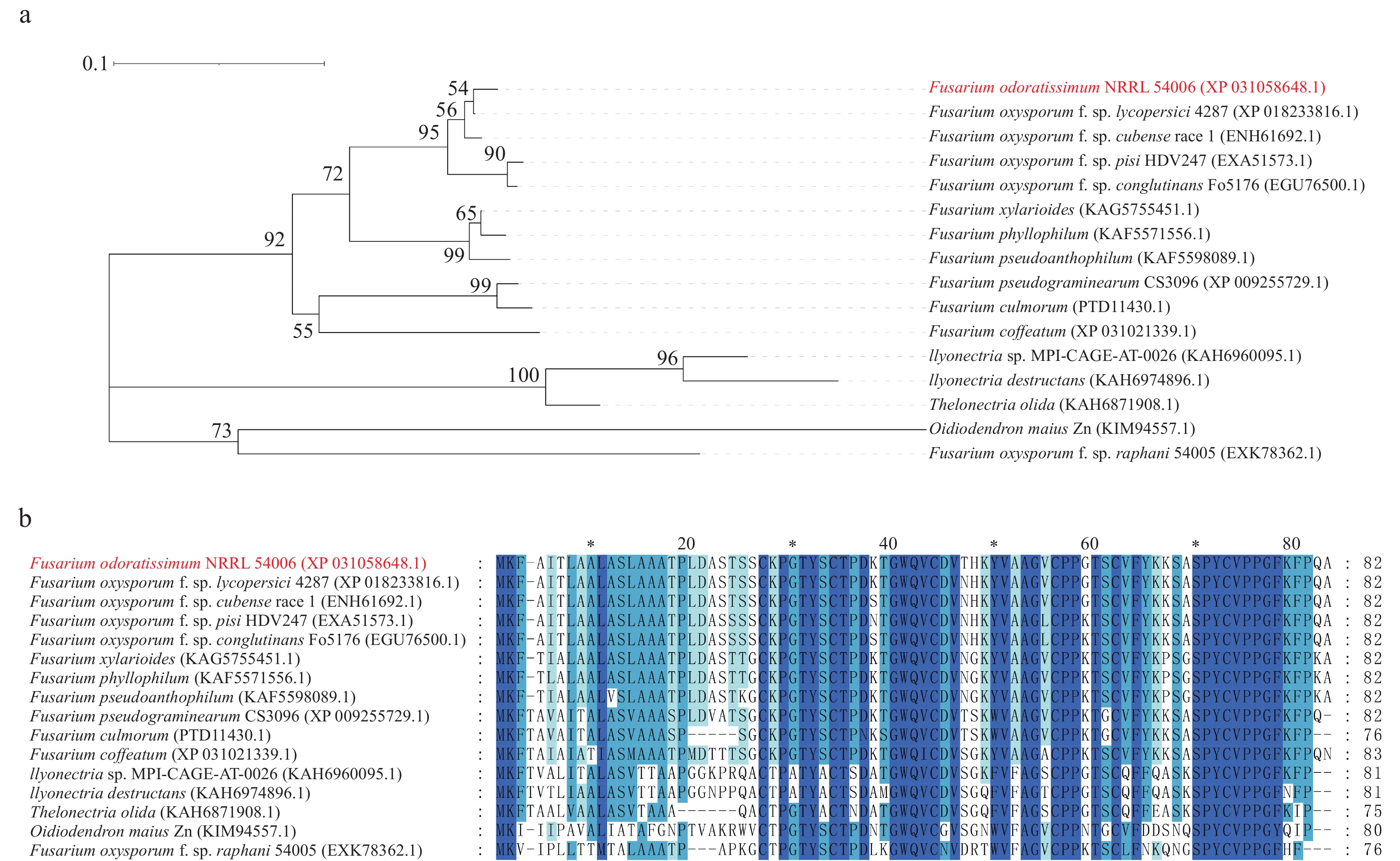
2024, 15(1): 85-93.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230045
Abstract:
Fusarium wilt of banana caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) is destructive to banana (Musa spp.) industry. Effector proteins play a key role in the interaction between Foc and banana. Previously researches screened the candidate effector FoSSP20 in Foc race 4 (Foc4) which could suppress BAX-triggered programmed cell death (PCD). In this study, yeast secretion system was used to verify the secretory function of signal peptide of FoSSP20. Subcellular localization assay showed that the FoSSP20 was localized in the nucleus and plasma membranes in Nicotiana. benthamiana cells. qRT-PCR assay showed that the expression levels of FoSSP20 was significantly up-regulated at the early infection phase. All the results showed that effector FoSSP20 is a classic secretory protein which may function well in the infection process of pathogens.
Fusarium wilt of banana caused by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense (Foc) is destructive to banana (Musa spp.) industry. Effector proteins play a key role in the interaction between Foc and banana. Previously researches screened the candidate effector FoSSP20 in Foc race 4 (Foc4) which could suppress BAX-triggered programmed cell death (PCD). In this study, yeast secretion system was used to verify the secretory function of signal peptide of FoSSP20. Subcellular localization assay showed that the FoSSP20 was localized in the nucleus and plasma membranes in Nicotiana. benthamiana cells. qRT-PCR assay showed that the expression levels of FoSSP20 was significantly up-regulated at the early infection phase. All the results showed that effector FoSSP20 is a classic secretory protein which may function well in the infection process of pathogens.
2024, 15(1): 94-99.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230012
Abstract:
Only females of Atrichopogon palmatus Tokunaga, have been recorded since 1962, while males have never been discovered. Specimens of Atrichopogon palmatus collected in Hainan Island were identified by using DNA barcoding and morphological methods. The DNA barcodes of the specimens were used to establish a phylogenetic tree for analysis, based on which the males were successfully associated with females. The males of A. palmatus collected in Hainan were newly described and illustrated, and their CO I- barcodes were also provided.
Only females of Atrichopogon palmatus Tokunaga, have been recorded since 1962, while males have never been discovered. Specimens of Atrichopogon palmatus collected in Hainan Island were identified by using DNA barcoding and morphological methods. The DNA barcodes of the specimens were used to establish a phylogenetic tree for analysis, based on which the males were successfully associated with females. The males of A. palmatus collected in Hainan were newly described and illustrated, and their CO I- barcodes were also provided.
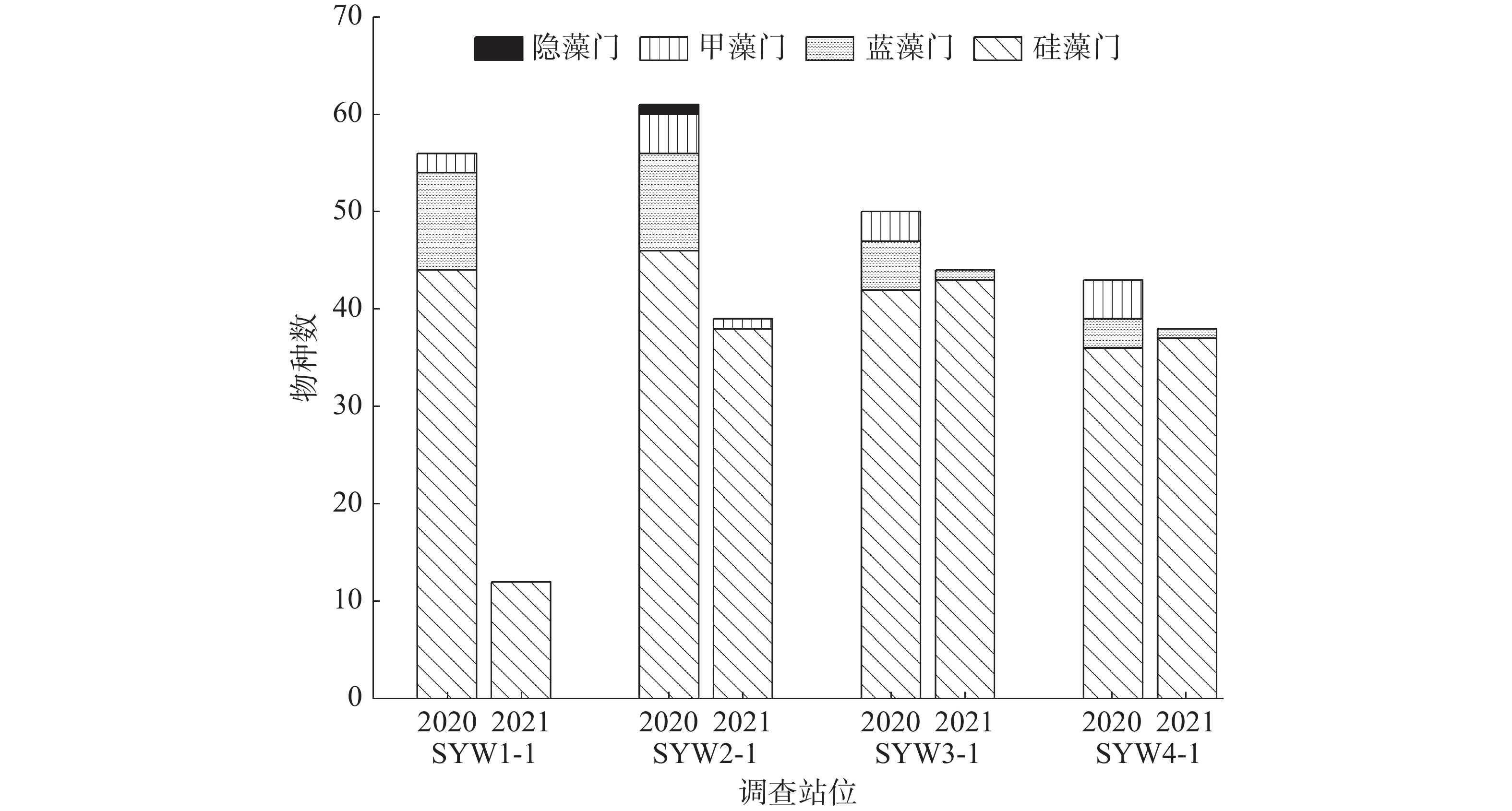
2024, 15(1): 100-108.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20220111
Abstract:
In order to study the characteristics of phytoplankton community and water quality in Sanya Bay, Hainan Province, net sampling surveys were conducted in April 2020 and 2021, respectively. Samples of phytoplankton and seawater were collected in 4 stations, and their community characteristics and water quality and environmental status were analyzed and evaluated by using Shannon-Wiener diversity index, Pielou evenness index, dominance index and richness index. Microscopic examination results showed that 98 species in 4 phyla of phytoplankton were identified in 2020 and 65 species in 3 phyla in 2021. Diatoms were the dominant group in both surveys. The number of dominant phytoplankton species was 8 in 2020 and 9 in 2021. Cluster analysis and Kruskal-Wallis test showed that the phytoplankton community structure in 2020 was significantly different from that in 2021. The diversity index and richness index in 2020 are 3.35 and 3.72, respectively, both of which are higher than those (3.27 and 2.5, respectively) in 2021, while the evenness index is 0.59, which is lower than that (0.66) in 2021. The average phytoplankton cell density in 2021 was 41.95% lower than that in 2020. The redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that ammonia nitrogen, conductivity and total phosphorus were the main environmental factors affecting the phytoplankton community structure in Sanya Bay in 2020 and 2021. All the results showed that the sea water in Sanya Bay is generally excellent ecologically in 2020 and 2021. The phytoplankton community structure is mainly composed of diatoms. The sea water has poor nutrients, indicating no possibility of occurrence of red tides or eutrophication.
In order to study the characteristics of phytoplankton community and water quality in Sanya Bay, Hainan Province, net sampling surveys were conducted in April 2020 and 2021, respectively. Samples of phytoplankton and seawater were collected in 4 stations, and their community characteristics and water quality and environmental status were analyzed and evaluated by using Shannon-Wiener diversity index, Pielou evenness index, dominance index and richness index. Microscopic examination results showed that 98 species in 4 phyla of phytoplankton were identified in 2020 and 65 species in 3 phyla in 2021. Diatoms were the dominant group in both surveys. The number of dominant phytoplankton species was 8 in 2020 and 9 in 2021. Cluster analysis and Kruskal-Wallis test showed that the phytoplankton community structure in 2020 was significantly different from that in 2021. The diversity index and richness index in 2020 are 3.35 and 3.72, respectively, both of which are higher than those (3.27 and 2.5, respectively) in 2021, while the evenness index is 0.59, which is lower than that (0.66) in 2021. The average phytoplankton cell density in 2021 was 41.95% lower than that in 2020. The redundancy analysis (RDA) showed that ammonia nitrogen, conductivity and total phosphorus were the main environmental factors affecting the phytoplankton community structure in Sanya Bay in 2020 and 2021. All the results showed that the sea water in Sanya Bay is generally excellent ecologically in 2020 and 2021. The phytoplankton community structure is mainly composed of diatoms. The sea water has poor nutrients, indicating no possibility of occurrence of red tides or eutrophication.
2024, 15(1): 109-121.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230027
Abstract:
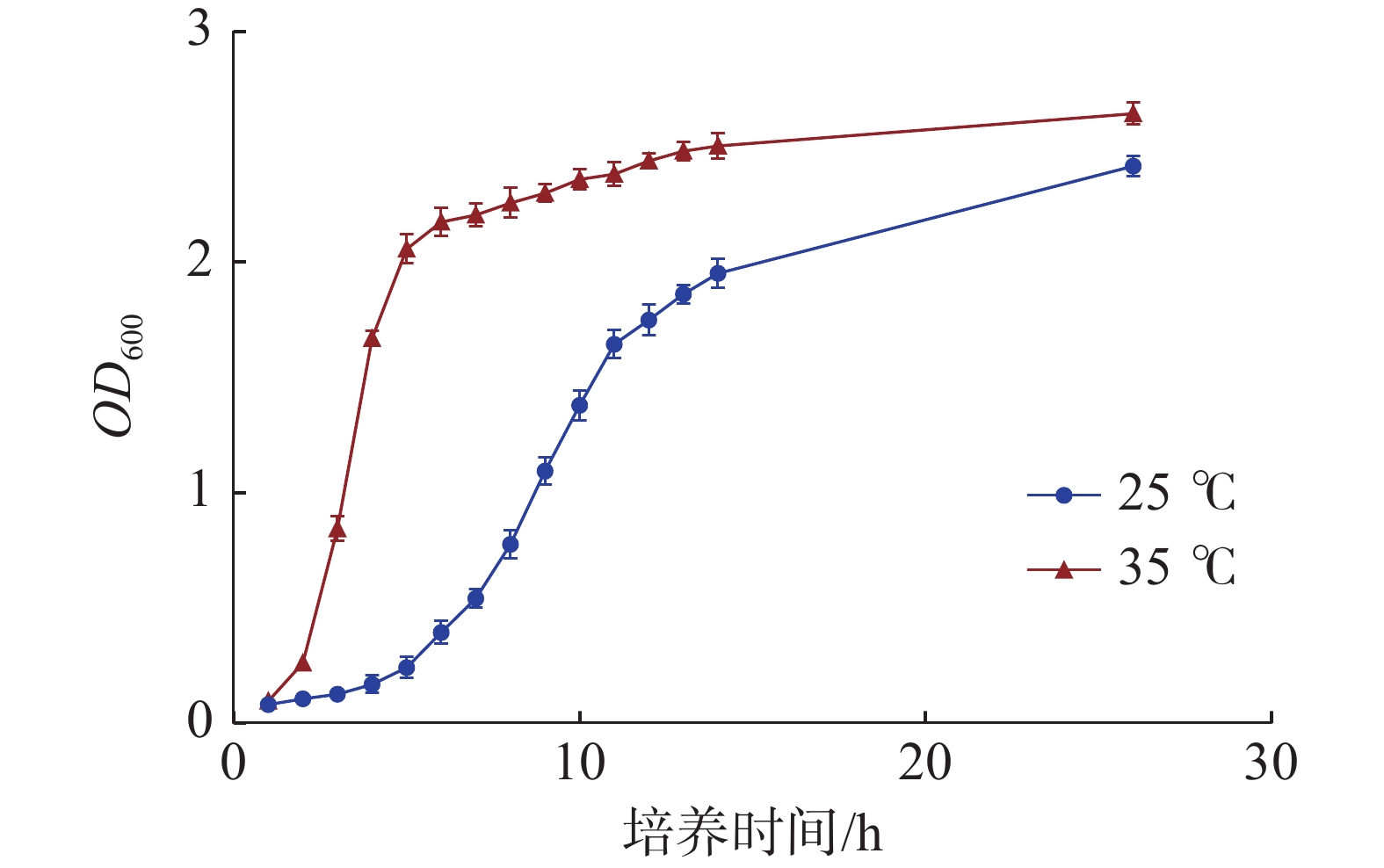
To identify the differences in transcription level of Streptococcus iniae at different temperatures, the growth and pathogenicity of S. iniae cultured at 25 ℃ and 35 ℃ were analyzed by using growth curve and artificial infection test, and strand-specific RNA-seq technology was used for sequencing analysis of S. iniae Tozj-1 strain cultured at 25 ℃ and 35 ℃. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened and their GO function and KEGG pathway enrichment were analyzed based on the GO (Gene Ontology) database and KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database. The key differentially expressed virulence genes were filtrated using virulence factor database (VFDB) and verified by real-time quantitative PCR. The results showed that S. iniae grew faster with a higher virulence at 35 ℃. A total of 927 significantly differentially expressed genes were screened (P<0.05), including 820 up-regulated genes and 107 down-regulated genes. GO functional enrichment analysis showed that the DEGs were mainly enriched in metabolic process, cellular process, binding process and catalytic activity. KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the DEGs were mainly enriched in ribosome, quorum sensing, ABC transporters and other signaling pathways. These results indicated that temperature regulated the transcription and expression of S .iniae genes and the enrichment of related pathways, which provided data support for further research in the pathogenesis of S .iniae.
To identify the differences in transcription level of Streptococcus iniae at different temperatures, the growth and pathogenicity of S. iniae cultured at 25 ℃ and 35 ℃ were analyzed by using growth curve and artificial infection test, and strand-specific RNA-seq technology was used for sequencing analysis of S. iniae Tozj-1 strain cultured at 25 ℃ and 35 ℃. The differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened and their GO function and KEGG pathway enrichment were analyzed based on the GO (Gene Ontology) database and KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database. The key differentially expressed virulence genes were filtrated using virulence factor database (VFDB) and verified by real-time quantitative PCR. The results showed that S. iniae grew faster with a higher virulence at 35 ℃. A total of 927 significantly differentially expressed genes were screened (P<0.05), including 820 up-regulated genes and 107 down-regulated genes. GO functional enrichment analysis showed that the DEGs were mainly enriched in metabolic process, cellular process, binding process and catalytic activity. KEGG enrichment analysis revealed that the DEGs were mainly enriched in ribosome, quorum sensing, ABC transporters and other signaling pathways. These results indicated that temperature regulated the transcription and expression of S .iniae genes and the enrichment of related pathways, which provided data support for further research in the pathogenesis of S .iniae.
2024, 15(1): 122-132.
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230007
Abstract:
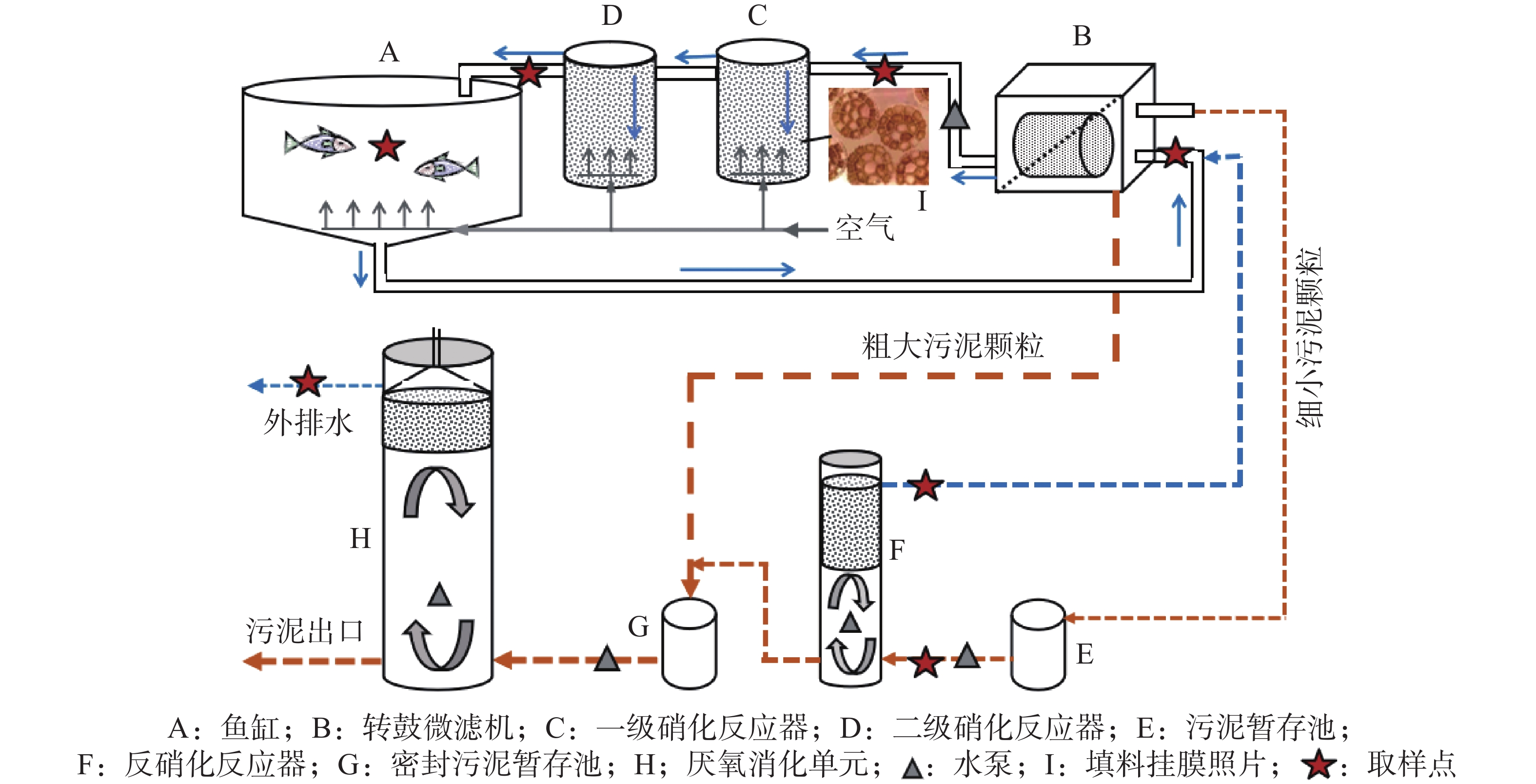
In order to meet the increasing demand for high-quality fish protein and environmental protection requirements, a pilot intensive three-loop recirculating freshwater aquaculture system (RAS) was developed in Qionghai, Hainan province, China. Backwashing water from a microfilter is used as the carbon source for the denitrification process, and an operation mode is established to ensure the treatment of water quality and fish sludge to comply with the requirements for fish growth and pollution control. Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) was cultured in the pilot three-loop freshwater RAS for 121 days in an aquaculture experiment, and the fish growth, water quality and microbial communities in the system were observed and analyzed. The results showed that the tilapia had a survival rate of 100%, with the stocking density and the feed conversion ratio (FCR) being 107.7 kg·m−3 and 1.74, respectively. The average concentrations of total ammonia (TAN), nitrite (NO2−-N) and nitrate (NO3−-N) were 0.95, 0.15 and 43.01 mg·L−1 respectively. The volume for daily water drainage was 2.66% of the total water volume in the system, and 6.67% of the water volume in the fish tank. No fish sludge was discharged throughout the experiment, and only a small amount of sludge existed in the anaerobic digestion unit by the end of the experiment. Microbial community analysis showed that a total of 21 genera of microorganism were involved in nitrogen metabolism, including Rhodobacte, Flavobacterium and Azospira. These results implicated that the recirculating aquaculture system provides a potentially sustainable and ecological aquaculture mode for freshwater fish such as tilapia.
In order to meet the increasing demand for high-quality fish protein and environmental protection requirements, a pilot intensive three-loop recirculating freshwater aquaculture system (RAS) was developed in Qionghai, Hainan province, China. Backwashing water from a microfilter is used as the carbon source for the denitrification process, and an operation mode is established to ensure the treatment of water quality and fish sludge to comply with the requirements for fish growth and pollution control. Tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) was cultured in the pilot three-loop freshwater RAS for 121 days in an aquaculture experiment, and the fish growth, water quality and microbial communities in the system were observed and analyzed. The results showed that the tilapia had a survival rate of 100%, with the stocking density and the feed conversion ratio (FCR) being 107.7 kg·m−3 and 1.74, respectively. The average concentrations of total ammonia (TAN), nitrite (NO2−-N) and nitrate (NO3−-N) were 0.95, 0.15 and 43.01 mg·L−1 respectively. The volume for daily water drainage was 2.66% of the total water volume in the system, and 6.67% of the water volume in the fish tank. No fish sludge was discharged throughout the experiment, and only a small amount of sludge existed in the anaerobic digestion unit by the end of the experiment. Microbial community analysis showed that a total of 21 genera of microorganism were involved in nitrogen metabolism, including Rhodobacte, Flavobacterium and Azospira. These results implicated that the recirculating aquaculture system provides a potentially sustainable and ecological aquaculture mode for freshwater fish such as tilapia.



 Abstract
Abstract FullText HTML
FullText HTML PDF 2501KB
PDF 2501KB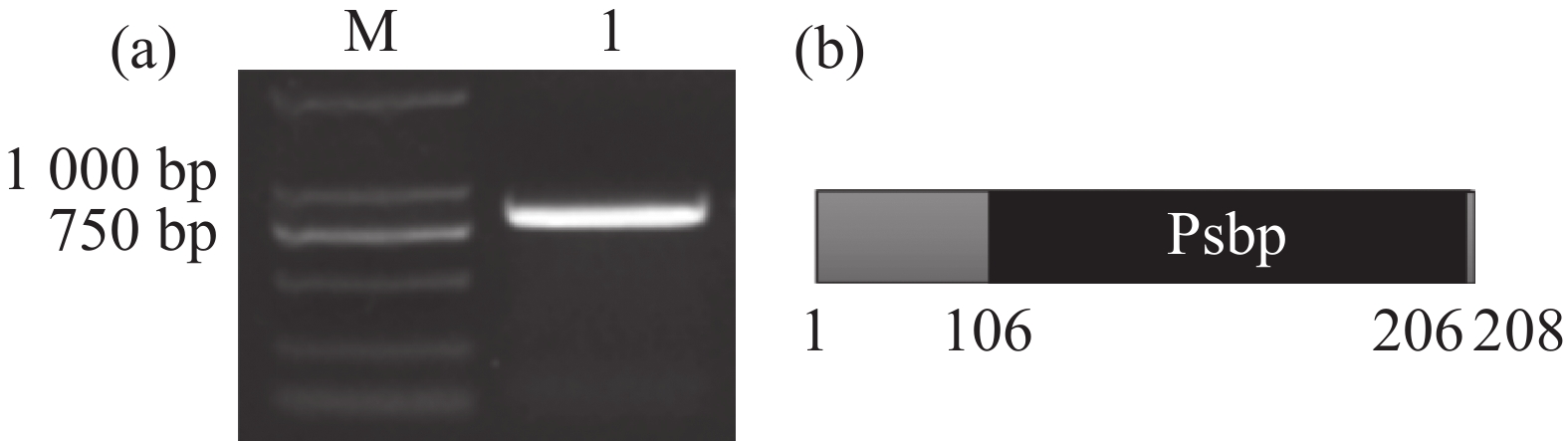









 Email alert
Email alert RSS
RSS