-
大叶桃花心木(Swietenia macrophylla)是楝科(Meliaceae)桃花心木亚科桃花心木属(Swietenia)多年生落叶乔木,原产于中美洲和南美洲,广泛分布于印度西部、马来西亚和中国南部[1]。由于大叶桃花心木具有抗菌、抗炎、抗氧化、抗诱变、抗癌、抗肿瘤和抗糖尿病的药用活性,其果实和种子在很多亚洲国家被用于民间治疗各种疾病[2]。大叶桃花心木在农用活性方面的研究,如花、叶提取物对菜青虫(Pieris rapae)、斜纹夜蛾(Spodoptera litura)、桃花心木斑螟(Hypsipyla grandella)等农林害虫具有较好的拒食和毒杀活性;其种子提取物对大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)和蜡样芽孢杆菌(Bacillus cereus)具有一定的抑制活性[3-7],但关于其精油的农用研究鲜见报道。植物精油直接来源于植物生物系统,可作为宿主植物防御微生物入侵机制的一部分,为此,植物精油被视为天然的抗菌剂[8]。植物精油可用于食品储存以防止病原菌入侵引起食品腐烂变质;植物精油还可用于防治田间有害生物,实现绿色农业经济效益。由于精油具有可生物降解性、高挥发性和低残留等特点,对生态环境不会造成负面影响,被视为绿色农药开发的重要来源之一。本研究以大叶桃花心木的花粉为原材料,通过超临界CO2萃取花粉精油,测试花粉精油的杀虫活性和抑菌活性,旨在为大叶桃花心木花粉精油农用价值开发提供理论依据。
-
莴苣指管蚜(Uroleucon formosanum)和棉蚜(Aphis gossypii)取自海南大学实验基地蔬菜叶片。斜纹夜蛾(Spodoptera litura)和玉米象(Sitophilus zeamais)由海南大学植物保护学院实验室提供。
-
水稻稻瘟病菌(Pyricularia oryzae)、芒果蒂腐病菌(Phomosis mangiferae)、香蕉枯萎病菌(Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense)、香蕉炭疽病菌(Colletotrichum musae)、西瓜枯萎病菌(F. oxysporum f. sp. niveum)、芒果炭疽病菌(C. gloeosporioides Penz.)、匍枝根霉病菌(Rhizopus nigricans)和黑曲霉病菌(Aspergillus niger)均由海南大学植物保护学院实验室提供。
-
大叶桃花心木花粉采自海南大学儋州校园内。将采集的花粉风干后,用粉碎机充分粉碎,制成植物干粉,采用SFT-100XW型超临界萃取仪,在CO2流量为14.4 mL·min−1,温度为30 ℃,压力为3750 Pa的条件下静态萃取60 min[9]。萃取率为0.94%,精油4 ℃保存,备用。
-
称取0.2 g适量大叶桃花心木花粉精油,溶于V丙酮∶V水=1∶4混合液中,配成2 g·L−1处理药液。以2 g·L−1 1%印楝素乳油为药剂对照,以V丙酮∶V水=1∶4混合液为溶液对照。
-
将莴苣指管蚜和棉蚜连同采样叶片放入各处理药液中浸渍10 s后取出,用吸水纸吸去多余药液,放入培养皿中(20头·皿),25 ℃培养。分别培养12、24 h用毛笔尖轻触蚜虫腹部,蚜虫不动则视为死亡。每个处理重复3次,统计各处理组试虫死亡数量,计算校正死亡率。
校正死亡率=(处理死亡率−对照死亡率)/(1−对照死亡率)×100%
-
参照俞瑞鲜等[10]的方法,在非选择性条件和选择性条件下测定拒食活性。将新鲜蓖麻叶片用圆形打孔器打成直径为2 cm的叶碟,放入各处理药液中浸泡5 s,取出晾干,备用。选择性拒食作用测定:将2张处理叶碟和2张对照叶碟交错放入直径9 cm的培养皿中。在培养皿中央放入1头饥饿4 h,个体大小一致的3龄斜纹夜蛾幼虫,每处理10个培养皿。非选择性拒食作用测定:将2片处理叶碟和2片对照叶碟分别放入2个直径9 cm培养皿内,在培养皿中央分别放入1头饥饿4 h个体大小一致的3龄斜纹夜蛾幼虫,每处理10个培养皿。在培养皿中放入棉球保湿。分别于处理12 、24 h,用方格坐标纸统计试虫取食叶片面积,并计算拒食率。
非选择拒食率=(Sck−S)/ Sck×100%;
选择性拒食率=(Sck−S)/(Sck+S)×100%,
其中,Sck为对照组的平均取食面积;S为处理组的平均取食面积。
-
将直径9 cm的圆形滤纸裁成两半,一半浸入2 g·L−1大叶桃花心木花粉精油或2 g·L−1 1%印楝素乳油,室温晾干;另一半浸入溶剂对照液,晾干作为对照。将两半滤纸重新拼接,用粘胶纸固定后置于直径9 cm培养皿内,每个处理重复3次。每皿内接入玉米象成虫20头。室温25 ℃培养,培养12 、24 h 后分别检查成虫分布情况,并计算各处理组的驱避率。进一步用0.5、1.0、2.0、4.0和8.0 g·L−1大叶桃花心木花粉精油测定对玉米象(培养12、24、48 h)的驱避率,采用SPSS软件绘制毒力曲线,计算LC50值。
驱避率=(对照区试虫数−处理区试虫数)/ 对照试区试虫数×100%
-
称取2 g大叶桃花心木花粉精油,溶于V丙酮∶V水=1∶4混合液中,配成400 g·L−1处理药剂,用无菌滤膜过滤,备用。以V丙酮∶V水=1∶4混合液作为对照。采用生长速率法测定大叶桃花心木花粉精油的抑菌活性。无菌条件下,取0.5 mL过滤药剂和混合溶剂,分别加入到99.5 mL已融化的PDA培养基内,迅速摇匀后分装于培养皿中制成供试浓度为2 g·L−1的含药平板。每处理3次重复。培养基冷却凝固后,将活化培养好的病原菌,用直径为5 mm灭菌打孔器自菌落边缘均匀切取菌饼,并用接种针将菌饼接于含药平板中央,将培养皿置于28 ℃培养箱中培养。当空白对照组的菌落大小长到2/3培养皿时,采用十字交叉法测量菌落直径(mm),取平均值,并计算抑制率。按照同样方法测定0.5、1.0、5.0、10.0和20.0 g·L−1大叶桃花心木花粉精油对匍枝根霉和黑曲霉的生长抑制率,计算EC50值和用SPSS软件计算毒力方程。
抑制率=[(对照菌落直径−5)−(处理组生长直径−5)]/(对照组生长直径−5)×100%
-
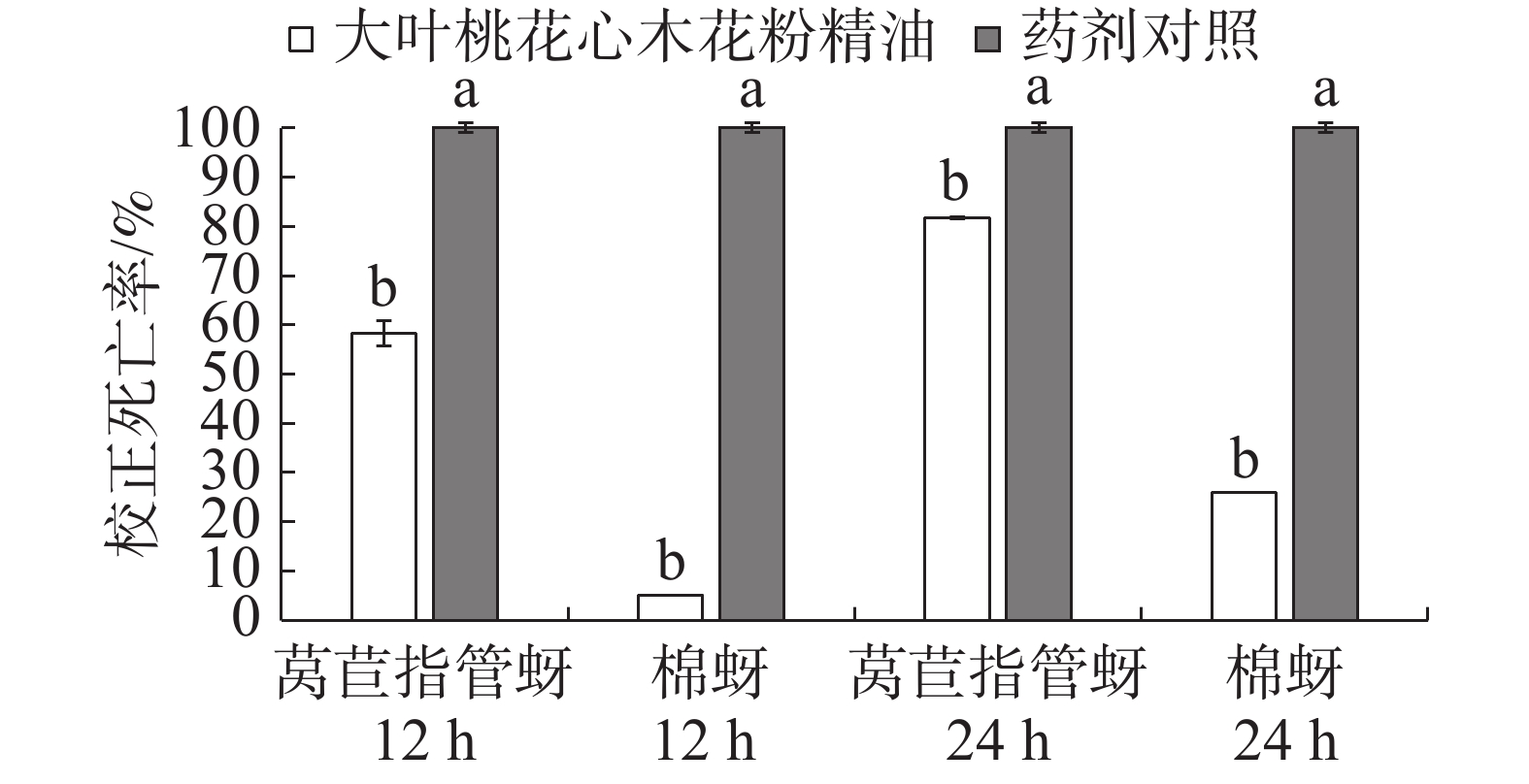
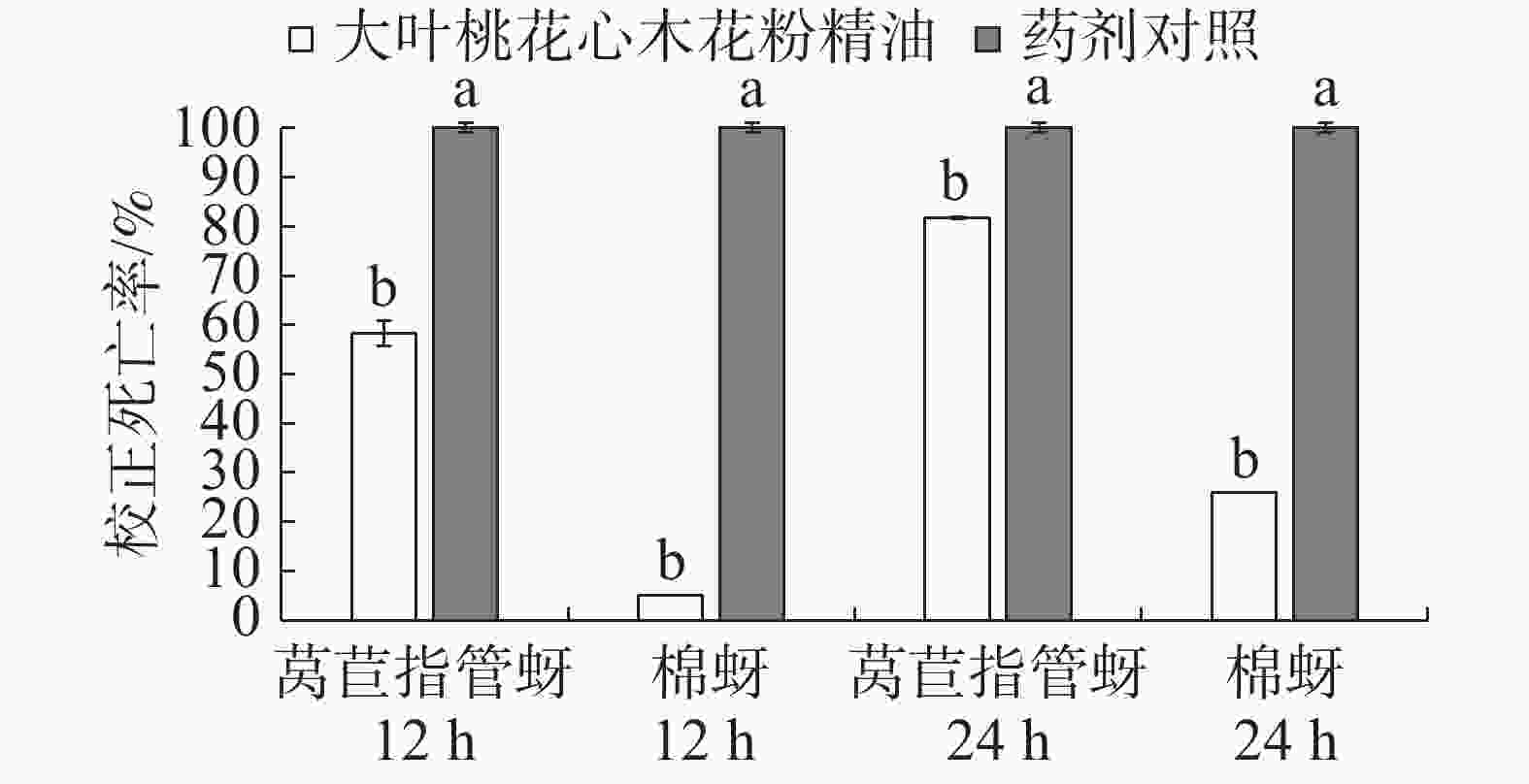
处理12 h的结果为大叶桃花心木花粉精油2 g·L−1浓度的莴苣指管蚜致死率为58.3%,棉蚜致死率为5%;2 g·L−1 1%乳油印楝素处理的莴苣指管蚜、棉蚜的致死率均为100%,均显著高于2 g·L−1大叶桃花心木花粉精油处理。处理24 h的结果为大叶桃花心木花粉精油对2种蚜虫的致死率均有所升高,莴苣指管蚜致死率可达81.7%,棉蚜致死率为26%(图1)。总体来看,大叶桃花心木花粉精油对莴苣指管蚜具有较好的触杀活性,对棉蚜的触杀毒力不理想,但随着处理时间的增加,对2种蚜虫的毒力都有所增加,说明精油的持效期较好,但大叶桃花心木花粉精油与标准药剂对照相比,活性不如对照药剂。
-
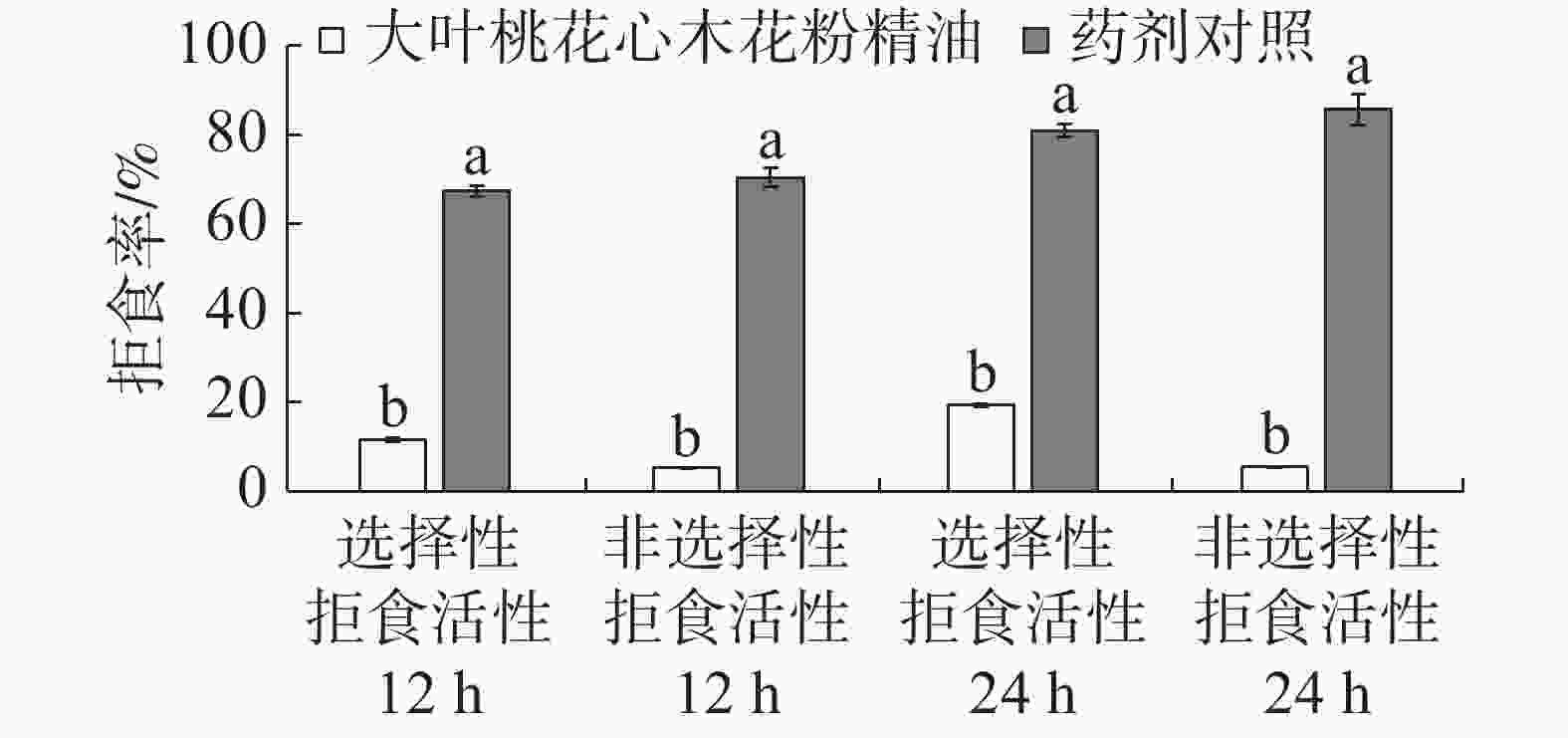
处理12、24 h的结果为2 g·L−1大叶桃花心木花粉精油对3龄斜纹夜蛾拒食活性均不理想,选择性拒食作用和非选择性拒食作用的拒食率均显著低于2 g·L−1 1%印楝素乳油(药剂对照)的拒食活性(图2)。
-
采用滤纸药膜法测定2 g·L−1浓度下,大叶桃花心木花粉精油和印楝素乳油对玉米象的驱避活性结果见图3。处理12 h,印楝素乳油的驱避率为46%,大叶桃花心木花粉精油的驱避率为76.1%,显著高于印楝素乳油;24 h时印楝素乳油的驱避率为82%,大叶桃花心木花粉精油驱避率87.9%,与印楝素乳油效果相当。
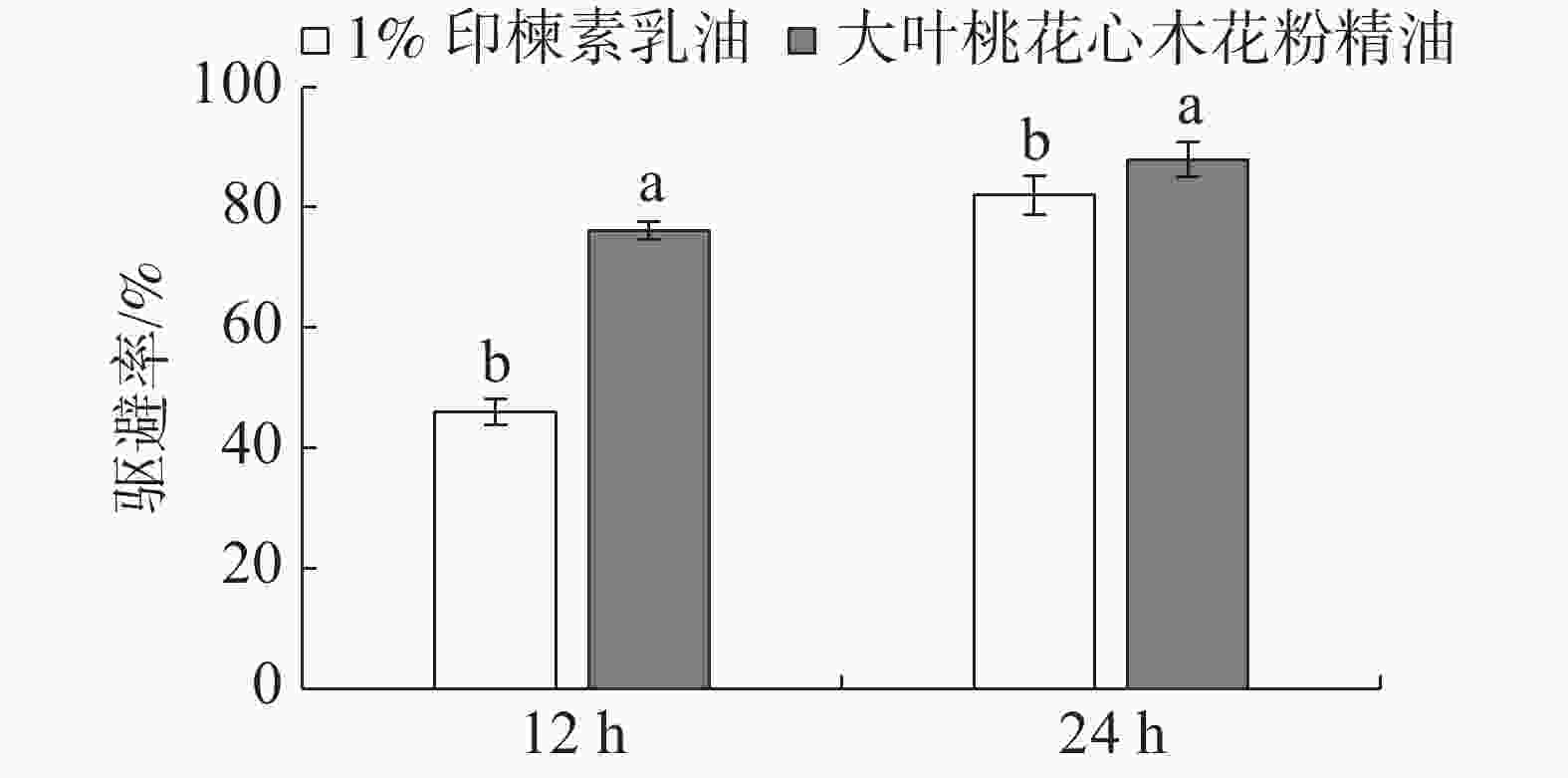
图 3 大叶桃花心木花粉精油对玉米象的驱避活性
Figure 3. Repellent activity of the essential oil extracted from the pollen of Swietenia macrophylla against Sitophilus zeamais
为进一步研究大叶桃花心木花粉精油对玉米象的驱避效果,试验选取了5个浓度(0.5、1.0、2.0、4.0和8.0 g·L−1)的精油测定对玉米象12、24 和48 h的驱避效果,并计算对玉米象的毒力回归方程。由结果可知(表1),不同处理时间的方程相关系数R值均大于0.9,可见方程相关性好,可信度高;12、24、48 h的驱避中浓度(LC50)依次为0.11、2.54、5.86 g·L−1,可见随着处理时间的延长,大叶桃花心木花粉精油驱避效果有所下降。
表 1 大叶桃花心木花粉精油对玉米象的驱避毒力测定
Table 1. Determination of repellent toxicity of the essential oil extracted from the pollen of Swietenia macrophylla to Sitophilus zeamais
测定时间/h Time 回归方程 Regression equation R值 LC50/(g·L−1) 置信区间 Confidence interval 12 y = 0.7879x +5.7709 0.9954 0.11 0.05~0.24 24 y = 1.15131x + 4.5344 0.9776 2.54 1.73~3.73 48 y = 1.0520x + 4.1923 0.9515 5.86 3.06~11.22 -
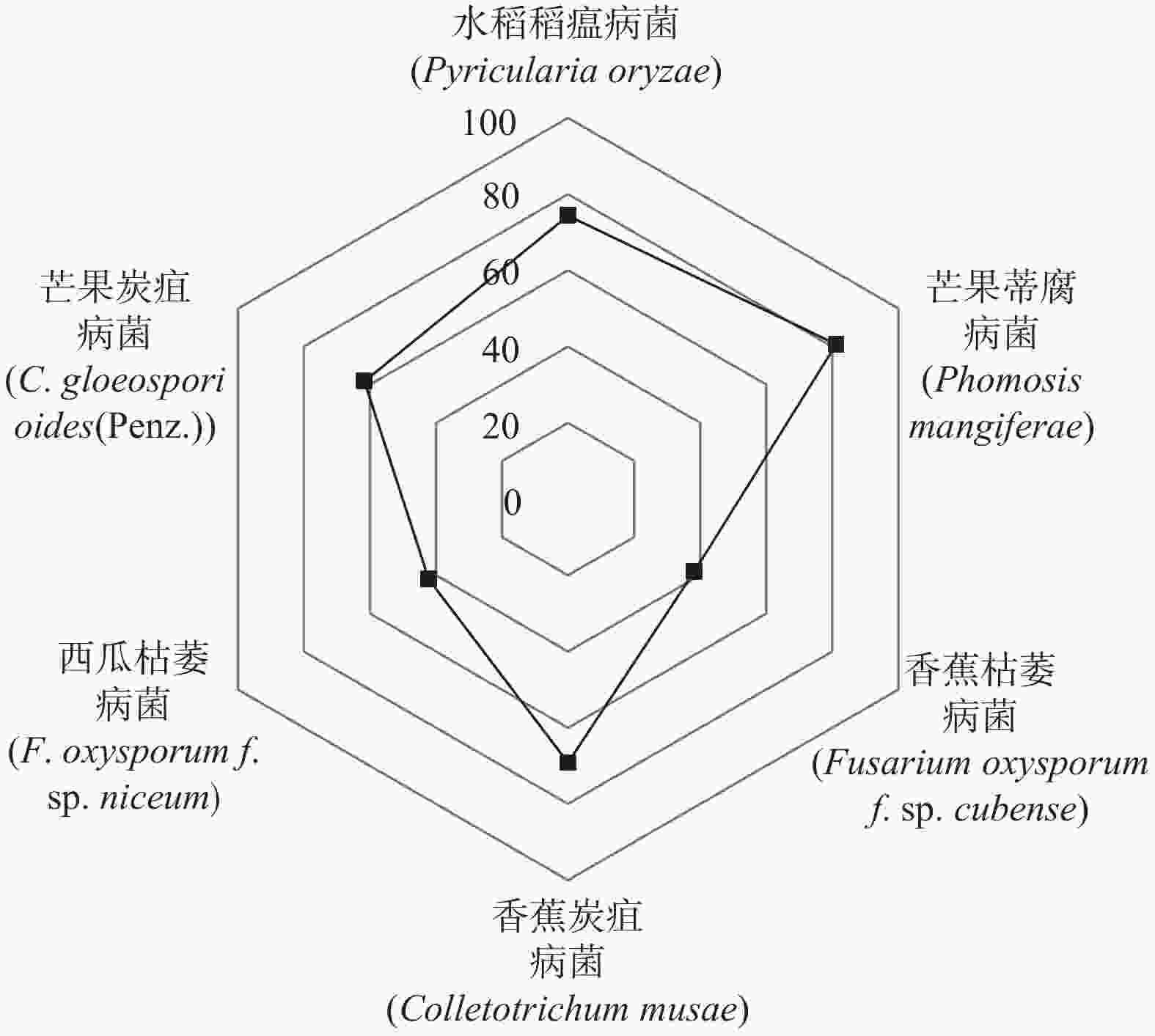
由图4可知,大叶桃花心木花粉精油对不同的植物病原真菌的抑制效果不同,对芒果蒂腐、水稻稻瘟、香蕉炭疽和芒果炭疽病菌均表现出良好的抑制效果,抑制率分别达81.21%、74.32%、69.17%和61.76%;对香蕉枯萎病菌和西瓜枯萎病菌的抑制效果较差。
-
由表2可知,测定的毒力方程R值均大于0.9,说明方程相关性好,可信度高;大叶桃花心木花粉精油对食品微生物(匍枝根霉和黑曲霉)的抑制中浓度(EC50)分别为18.79 g·L−1和7.94 g·L−1,表明,黑曲霉对该精油更为敏感。
表 2 大叶桃花心木花粉精油对匍枝根霉和黑曲霉抑菌活性统计分析
Table 2. Statistical analysis of baceriostatic activity of the essential oil extracted from the pollen of Swietenia macrophylla against Rhizopus nigricans and Aspergillus niger
靶标菌 Bacterium 回归方程 Regression equation R EC50/(g·L−1) 置信区间 Confidence interval 匍枝根霉 y = 0.7576x + 4.0349 0.9979 18.79 18.42~19.25 黑曲霉 y = 1.0332x + 4.0700 0.9849 7.94 5.19~8.82 -
活性植物资源的筛选一直是植物源农药研发中最基础的工作[11],而大叶桃花心木的花粉包含着植物体生命的遗传信息以及孕育生命体的全部营养成分,是筛选活性资源的良好材料。该树种为我国行道树,非常常见。大叶桃花心木的花小且具有自然大量落花特性,海南每年3~4月份,该树种大量落花,会造成环境不整洁,也给环卫工人清扫造成负担。采用吸尘器或清扫的方法能快速有效地收集大叶桃花心木的落花,并开展其农用活性的研究,不仅可以提升环境清洁度,还能够开发利用植物的天然资源。本研究大量收集大叶桃花心木的落花,并对其进行超临界萃取,对获得的花粉精油进行农用活性测定。研究发现,大叶桃花心木的花粉精油对莴苣指管蚜具有很好的触杀活性,对玉米象有较好的驱避活性,对芒果蒂腐、水稻稻瘟、香蕉炭疽和芒果炭疽病菌具有良好的抑制效果。由此可见,大叶桃花心木的花粉精油具有潜在的防治农业病虫害的研究价值。此外,大叶桃花心木的花粉精油对引起食品腐烂变质的病原微生物黑曲霉也有一定的抑菌活性。
精油通常是含有多种不同化合物的混合物[12],精油成分的不同使得精油具有不同的农用活性,BURT等[13]报道含酚类等较多的精油往往具有很好的抑菌活性,AMARAL等[14]发现树胡椒精油中的橙花叔醇、β-石竹烯和α-蛇麻烯对棉叶螨具有很好的杀螨和趋避活性,β-石竹烯还具有熏蒸作用。有研究报道,大叶桃花心木的叶、果实提取物中的化学成分复杂多样,有柠檬苦素,甾体,黄烷醇,挥发油等[15-17]。本研究测定了大叶桃花心木的花粉精油部分农用活性,但未对该精油的活性物质进行追踪,其所含的物质与前人报道的提取物中是否一致也有待进一步确定。因此,在后续的进一步研究中有必要对其活性物质进行分析鉴定,为该精油的应用奠定基础。
大叶桃花心木花粉精油的杀虫及抑菌活性
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.03.016 cstr: 32425.14.j.cnki.rdswxb.2021.03.016
Insecticidal and Bacteriostatic Activities of the Essential oil Extracted from the Pollen of Swietenia macrophylla
-
摘要: 采用超临界CO2萃取大叶桃花心木( Swietenia macrophylla )花粉精油,并研究其对4种田间害虫的杀虫活性以及8种植物病原真菌的抑菌效果。结果表明,在2 g·L−1浓度下,大叶桃花心木花粉精油对莴苣指管蚜( Uroleucon formosanum )具有很好的触杀活性,对玉米象(Sitophilus zeamais)有较好的驱避活性,但对棉蚜( Aphis gossypii )的触杀活性和3龄斜纹夜蛾( Spodoptera litura )的拒食活性均较低;对芒果蒂腐病菌( Phomosis mangiferae )、水稻稻瘟病菌( Pyricularia oryzae )、香蕉炭疽病菌( Colletotrichum musae )、芒果炭疽病菌[ C. gloeosporioides ( Penz. )]的菌丝生长具有明显的抑制效果,但对香蕉枯萎病菌( Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense )和西瓜枯萎病菌( F. oxysporum f. sp. niveum )抑制效果稍差;匍枝根霉病菌( Rhizopus nigricans )和黑曲霉病菌( Aspergillus niger )对该精油较敏感,抑制中浓度(EC50
)分别为18.79、7.94 g·L−1。 Abstract: Essential oil was extracted from the pollen of Swietenia macrophylla by supercritical carbon dioxide, and its insecticidal activity against four species of field insect pests and its bacteriostatic effect against eight species of pathogenic fungi were determined. The results showed that the essential oil extracted from the pollen of Swietenia macrophylla had significant contact activity against Uroleucon formosanum and excellent repellent activity against Sitophilus zeamais, but low contact toxicity to Aphis gossypii and antifeedant activity to the third instar larvae of Spodoptera litura.; and tThe pollen essential oil could effectively inhibit the growth of Phomopsis mangiferae, Pyricutaria oryzae, Calletotrichum musae, and Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, but had a less inhibitory effect on Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense and Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Niveum at the concentration of 2 g·L−1. Rhizopus nigricans and Aspergillus niger were sensitive to the pollen essential oil with the EC50 values of the essential oil being 18.79 g·L−1 and 7.94 g·L−1, respectively.-
Key words:
- Swietenia macrophylla /
- pollen essential oil /
- insecticidal /
- bacteriostatic /
- activity
-
表 1 大叶桃花心木花粉精油对玉米象的驱避毒力测定
Table 1 Determination of repellent toxicity of the essential oil extracted from the pollen of Swietenia macrophylla to Sitophilus zeamais
测定时间/h Time 回归方程 Regression equation R值 LC50/(g·L−1) 置信区间 Confidence interval 12 y = 0.7879x +5.7709 0.9954 0.11 0.05~0.24 24 y = 1.15131x + 4.5344 0.9776 2.54 1.73~3.73 48 y = 1.0520x + 4.1923 0.9515 5.86 3.06~11.22 表 2 大叶桃花心木花粉精油对匍枝根霉和黑曲霉抑菌活性统计分析
Table 2 Statistical analysis of baceriostatic activity of the essential oil extracted from the pollen of Swietenia macrophylla against Rhizopus nigricans and Aspergillus niger
靶标菌 Bacterium 回归方程 Regression equation R EC50/(g·L−1) 置信区间 Confidence interval 匍枝根霉 y = 0.7576x + 4.0349 0.9979 18.79 18.42~19.25 黑曲霉 y = 1.0332x + 4.0700 0.9849 7.94 5.19~8.82 -
[1] Mi C N, WANG H, CHEN H Q, et al. Polyacetylenes from the Roots of Swietenia macrophylla King [J]. Molecules, 2019, 24(7): 2 − 9. [2] MOGHADAMTOUSI S, GOH B, CHAN C, et al. Biological Activities and Phytochemicals of Swietenia macrophylla King [J]. Molecules, 2013, 18(9): 10465 − 10483. doi: 10.3390/molecules180910465 [3] PAMPLONA SÔNIA, ARRUDA M, CASTRO K, et al. Phragmalin Limonoids from Swietenia macrophylla and Their Antifeedant Assay against Mahogany Predator [J]. Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society, 2018, 29(8): 1621 − 1629. [4] MURSITI S, SUPARTONOL. Isolation and antimicrobial activity of flavonoid compounds from mahagony seeds (Swietenia macrophylla, King) [J]. IOP Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 172: 012055. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/172/1/012055 [5] 刘奎, 符悦冠, 彭正强, 等. 大叶桃花心木的花、叶抽提物对斜纹夜蛾的拒食活性[J]. 热带作物学报, 2004(2): 28 − 32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2561.2004.02.007 [6] 刘奎, 符悦冠, 彭正强, 等. 大叶桃花心木的花、叶抽提物对斜纹夜蛾的拒食作用研究[J]. 植物保护, 2004(2): 72 − 74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2004.02.017 [7] 李晓东, 赵善欢. 大叶桃花心木抽提物对菜青虫的杀虫活性研究[J]. 仲恺农业技术学院学报, 1997(2): 71 − 74. [8] CALO J R, CRANDALL P G, O'BRYAN C A, et al. Essential oils as antimicrobials in food systems–A review [J]. Food control, 2015, 54: 111 − 119. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.12.040 [9] HILMI M L B, SALLEH L M, JAMALUDIN R, et al. Solubility of Swietenia Macrophylla Seeds In Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction [J]. IOP Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, 2020, 884: 012021. doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/884/1/012021 [10] 俞瑞鲜, 胡秀卿, 吴声敢, 等. 几种植物精油对小菜蛾的趋避活性及其增效作用[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2018, 59(5): 767 − 771. [11] 田向荣, 李彦涛, 王智辉, 等. 5种植物源农药对假眼小绿叶蝉的田间药效[J]. 热带生物学报, 2019, 10(3): 264 − 267. [12] 邱海燕, 刘奎, 付步礼, 等. 香蕉假茎精油成分的GC-MS分析[J]. 热带生物学报, 2016, 7(2): 274 − 278. [13] BURT S A. Essential oils: their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods--a review [J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2004, 94(3): 223 − 253. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2004.03.022 [14] AMARAL A C F, RAMOS A D S, PENA, MÁRCIA REIS, et al. Acaricidal activity of Derris floribunda essential oil and its main constituent [J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 2017, 7(9): 791 − 796. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtb.2017.08.006 [15] 张荣, 曹明明, 何红平, 等. 大叶桃花心木中的柠檬苦素成分(英文)[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 2013, 25(5): 581 − 584+633. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6880.2013.05.002 [16] FALAH S, SUZUKI T, KATAYAMA T. Chemical Constituents from Swietenia macrophylla Bark and Their Antioxidant Activity [J]. Pakistan Journal of Biological Sciences, 2008, 11(16): 2007 − 2012. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2008.2007.2012 [17] 米承能, 梅文莉, 李薇, 等. 大叶桃花心木根的化学成分研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2017, 25(6): 610 − 616. -




 下载:
下载: