-
方斑东风螺(Babylonia areolata)隶属蛾螺科(Buccinidae)、东风螺属(Babylonia),是一种具有重要经济价值的海洋腹足类动物,广泛分布于印度洋-太平洋的热带和亚热带海域[1-2]。在我国,方斑东风螺养殖区主要分布于福建、广东和海南等[3]。由于其经济价值高、生长速度快,方斑东风螺深受水产养殖从业者的青睐,并被认为是具有巨大发展潜力的养殖品种。目前,我国的方斑东风螺年产量已超过1.25万t[4]。近年来,由于其自然资源被过度开发,人们开始不断探索方斑东风螺的育苗和养成技术,其产业规模也随之不断扩大。目前,方斑东风螺的养殖方式主要为水泥池流水养殖,这种养殖方式虽然简单高效,但是依然伴随着养殖水质不稳定和病害多发的问题[5-6],而采用工厂化循环水养殖模式进行方斑东风螺的养殖可以加强对养殖水质和养殖动物的疾病管控,还可以进行高密度养殖,提高单位面积的产量[7-8]。利用循环水养殖系统进行方斑东风螺的养殖,主要是通过物理过滤、生物过滤、曝气和泵吸等方式实现对养殖用水的循环利用。由于在循环水养殖系统中,温度、盐度、pH和溶解氧等水质指标可控性较强,可以实现高密度养殖。在循环水养殖系统与流水养殖系统中,不同规格的稚螺对生存空间的需求不相同[9]。因此,选择合理的养殖密度是关键问题。有研究表明,在流水条件下,一般东风螺稚螺的中间培育密度为1.0×104~2.0×104 只·m−2[10]。故本实验以2×104 只·m−2的密度为基准设置了1.2×104 、1.8×104 、2.4×104 和3.0×104 只·m−2 4个密度梯度,以探索较为适宜的方斑东风螺循环水中间培育密度,旨在为后续的方斑东风螺循环水中间培育技术提供参考。
-
实验在海南省海洋与渔业科学院(琼海基地)进行。方斑东风螺循环水养殖系统由养殖单元和水处理单元组成,水处理单元包括袋式过滤器(过滤精度为10 µm)和生物滤池(滤料为珊瑚骨和细菌屋)等设备。
养殖池为正方形玻璃钢养殖桶(1 m×1 m×0.9 m),底部铺设底滤板,在底滤板上方固定0.25 mm的聚乙烯塑料网箱,将网箱3等分为3个独立的养殖单元,每个养殖单元配备2个气石,并在网箱底部铺设厚度约为1~2 cm的泥沙。生物滤池为直径0.6 m,高0.65 m的聚乙烯塑料圆桶,生物滤池滤料为珊瑚骨与细菌屋,按照1∶1的比例(质量比)组成生物滤池。物理过滤设备为精度10 μm的精密过滤器,养殖单元水体为700 L,生物滤池水体为100 L。日循环量为7.2 m3。
实验所用方斑东风螺稚螺,购自海南坤田海洋生物科技有限公司,螺苗个体起始质量为(0.023±0.006) g,起始壳长为(4.58±0.75) mm,起始壳宽为(2.72±0.48) mm,大小均匀,健康无伤。
-
实验分为4组,依次编号为D1~D4,分别对应养殖密度为1.2×104、1.8×104、2.4×104和3.0×104只·m−2,每组3个重复。
在每天的上午8:00进行投喂,投喂的饵料为新鲜的牡蛎(Ostreidae)肉,每日的投喂饵料量约为螺苗体质量的30%。在养殖过程中,每4 h用海水将爬出水面的稚螺冲至水面以下,实验时长为30 d(2022−09−13—2022−10−13)。
每天观察稚螺的运动和摄食情况,每5天取1次养殖池中的水样和底质样品,并于实验结束时测量稚螺壳长、壳宽、体质量和存活率。
-
养殖实验周期结束后,将各组的稚螺经过24 h饥饿处理后称重、计数,从每个养殖单元中随机取样10只,将稚螺的壳外泥沙冲洗干净,敲碎螺壳,取出螺肉,放入冻存管中,立即将其放入液氮中进行速冻,然后放入超低温冰箱中(−80 ℃)保存,用于酶活检测。
称取新鲜底质10 g(精确至0.1 g)放于250 mL三角瓶中,加100 mL氯化钾溶液(2 mol·L−1),用橡皮塞塞紧,振荡30 min,立即过滤于100 mL三角瓶中,用于底质铵态氮(NH4+-N)检测。
称取新鲜底质10 g放入100 mL三角瓶中,加入0.1 g硫酸钙和50 mL水,塞盖后振荡10 min,静置5 min,过滤上清液,用于底质亚硝态氮(NO2−-N)和底质硝酸态氮(NO3−-N)的测定。
-
稚螺体内的α-淀粉酶(α-Amylase, AMS)、脂肪酶(Lipase, LPS)、胃蛋白酶(Pepsin, PPS)、过氧化氢酶(Catalase, CAT)、超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide Dismutase, SOD)和丙二醛(Malondialdehyde, MDA)水平使用南京建成生物技术研究所生产α-淀粉酶测试盒(Catalog No. C016-1-1)、脂肪酶测定试剂盒(Catalog No. A054-2-1)、胃蛋白酶测定试剂盒(Catalog No. A080-1-1)、过氧化氢酶测定试剂盒(Catalog No. A007-1-1)、总超氧化物歧化酶测定试剂盒(Catalog No. A001-3-2)和丙二醛测定试剂盒(Catalog No. A003-1-2),并按照试剂盒内详细说明书的检测步骤进行。
-
系统中的水质铵态氮(NH4+-N)、亚硝态氮(NO2−-N)、硝酸态氮(NO3−-N)以及底质铵态氮(NH4+-N)、亚硝态氮(NO2−-N)、硝酸态氮(NO3−-N)的测定均参照相关标准方法进行 [11]。
-
实验数据以平均值±标准差(Mean±SD)表示。使用DPS统计软件进行单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),设P<0.05为差异显著,P<0.01为差异极显著。
-
从表1可知,养殖密度对稚螺的终末壳长有显著影响(P<0.05),其中,D1组最高[(11.18±1.08) mm],D4组最低[(8.91±0.83) mm]。养殖密度对稚螺的日平均生长速度有显著影响(P<0.05),其中,D1组最高[(0.22±0.04) mm·d−1],D4组最低[(0.14±0.03) mm·d−1]。养殖密度对稚螺的壳长增长率有显著影响(P<0.05),其中,D1组最高[(144.10±24.58)%],D4组最低[(94.54±18.12)%]。养殖密度对稚螺的存活率也有显著影响(P<0.05),其中,D2组最高[(94.77±2.18)%],D4组最低[(57.84±1.90)%]。
分组 终末
壳长/mm日平均生长
速度/(mm·d−1)壳长
增长率/%存活
率/%D1 11.18±1.08a 0.22±0.04a 144.10±24.58a 93.69±2.51a D2 11.14±0.72a 0.22±0.02a 143.23±15.72a 94.77±2.18a D3 8.92±1.14b 0.14±0.04b 94.76±24.89b 73.08±0.80b D4 8.91±0.83b 0.14±0.03b 94.54±18.12b 57.84±1.90c 注:不同字母表示不同组之间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
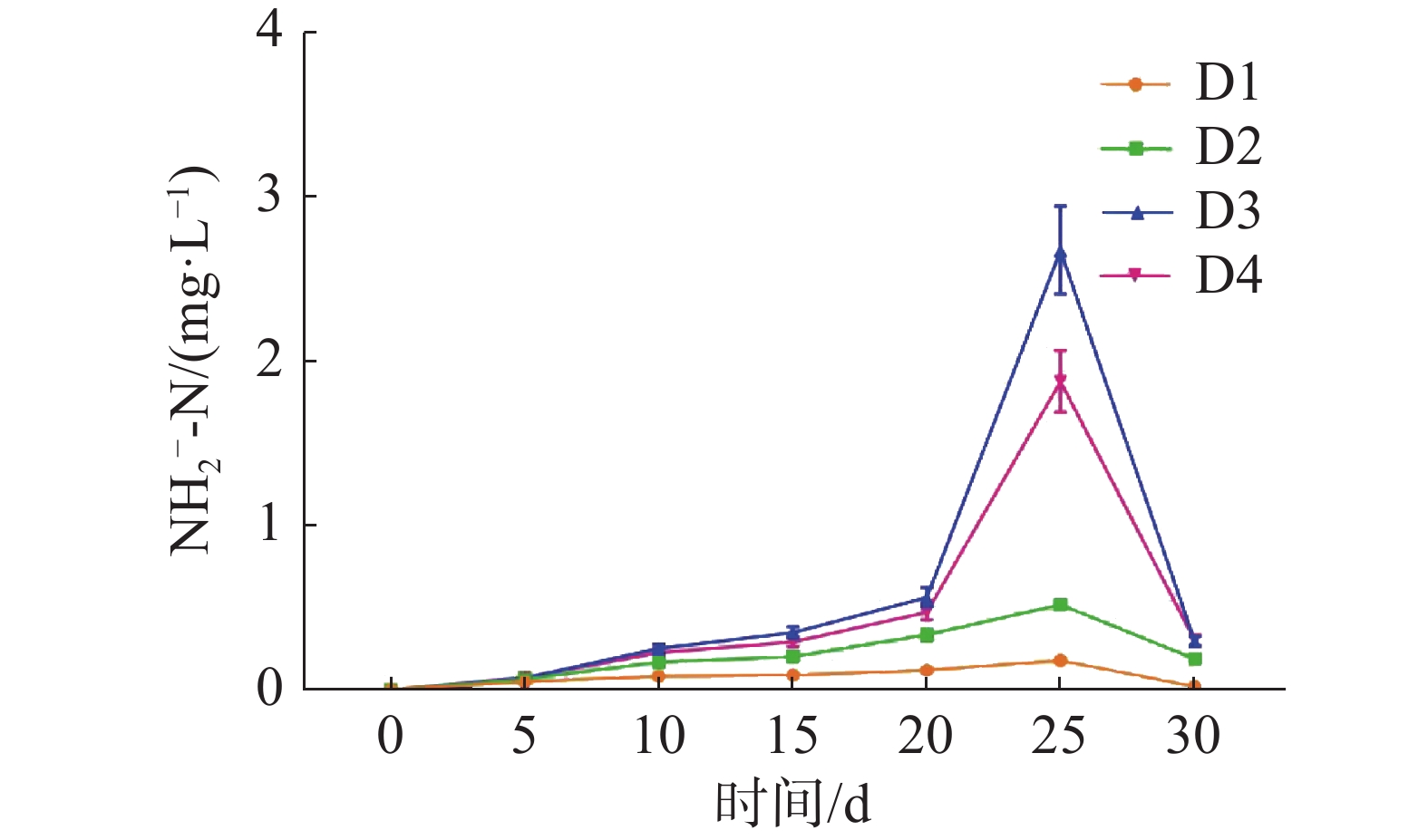
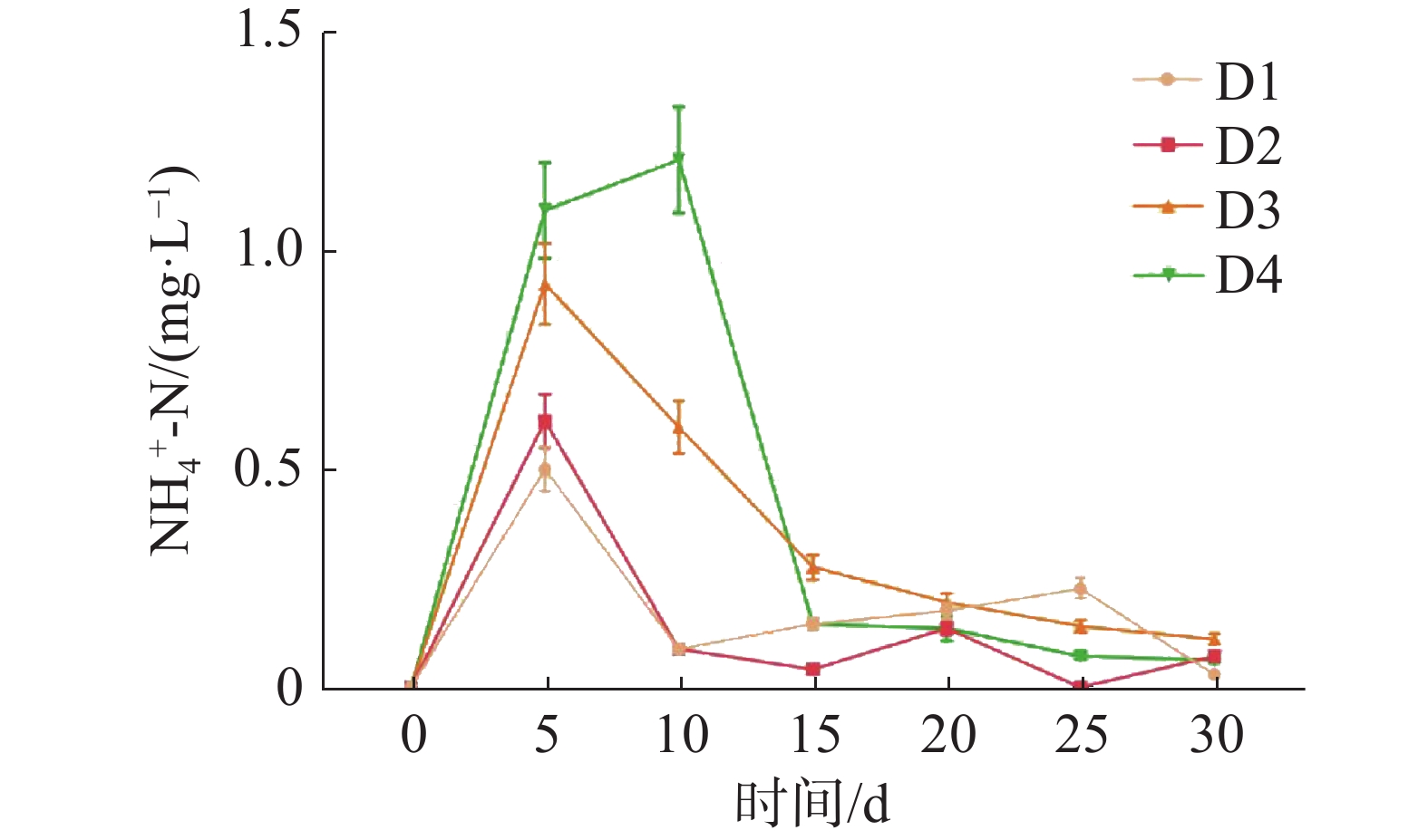
如图1所示,养殖密度对循环水养殖系统水质的NH4+-N浓度高峰有显著影响(P<0.05)。D1、D2、D3组的NH4+-N浓度在第5天时到达峰值,D4组的NH4+-N浓度在第10天时到达峰值。NH4+-N浓度峰值随养殖密度的升高而显著升高(P<0.05),其中,D4组的NH4+-N浓度峰值最高,为(1.21±0.12)mg·L−1,D1组的NH4+-N浓度峰值最低,为(0.50±0.05) mg·L−1。
如图2所示,养殖密度对循环水养殖系统水质的NO2−-N浓度高峰有极显著影响(P<0.01)。各实验组的均在实验第25天迎来了NO2−-N浓度的高峰,且NO2−-N浓度的峰值随养殖密度的升高而显著升高(P<0.01)。其中D4组最高,为(1.90±0.18) mg·L−1,D1组最低,为(0.18±0.02) mg·L−1。
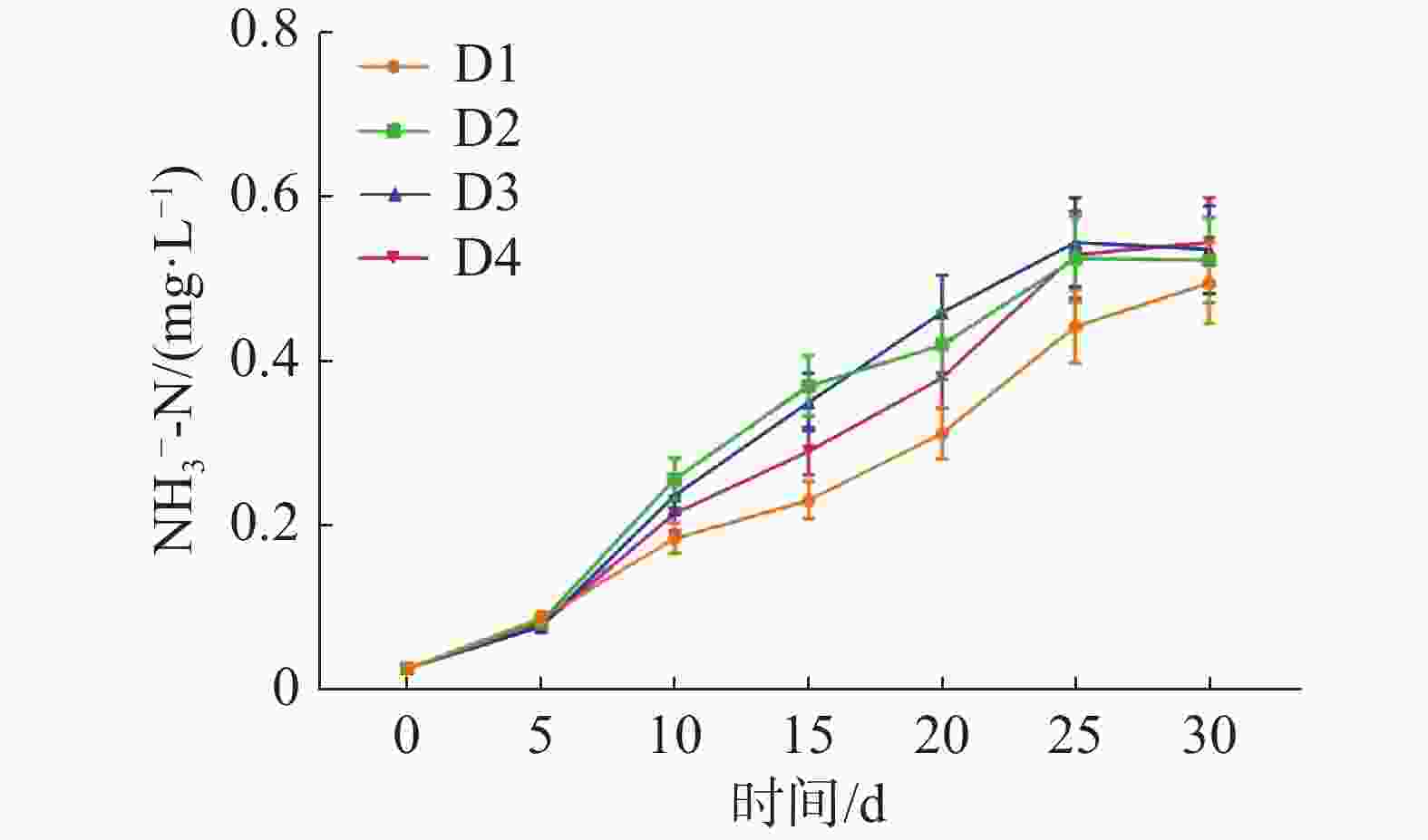
如图3所示,在整个实验过程中,NO3−-N不断积累,在实验结束时,D1、D2、D3、D4各组的NO3−-N浓度分别为(0.50±0.05)、(0.52±0.05)、(0.54±0.03)和(0.54±0.02)mg·L−1。
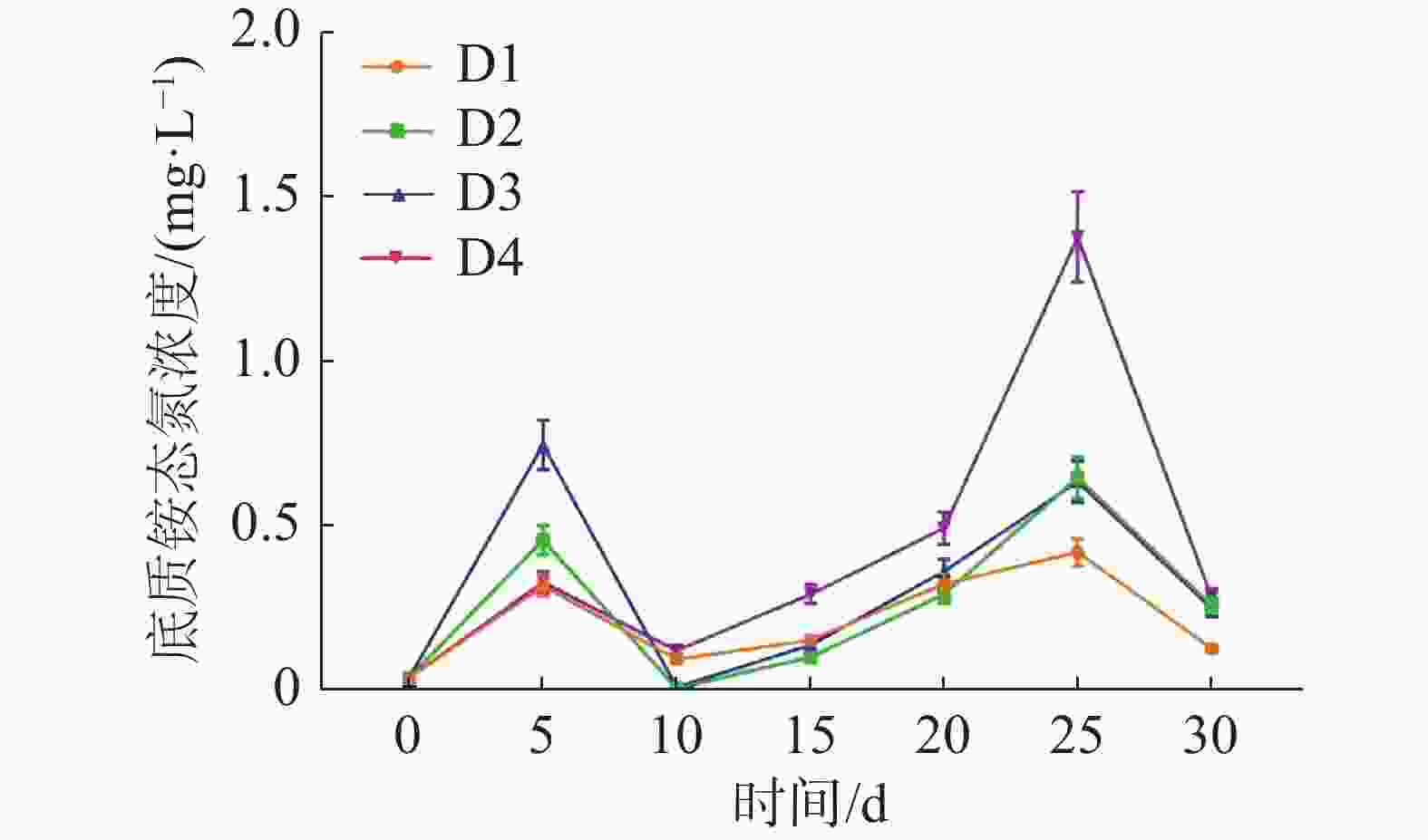
如图4所示,养殖密度对循环水养殖系统底质NH4+-N浓度高峰有极显著影响(P<0.01)。实验各组在实验第5天迎来第一次底质NH4+-N浓度高峰,其中D3组最高为(0.74±0.06) mg·L−1,D1组最低,为(0.31±0.03) mg·L−1。在实验第25天,各实验组迎来第二次底质NH4+-N浓度高峰,其中D4组最高,为(1.38±0.14) mg·L−1,D1组最低,为(0.42±0.04) mg·L−1。
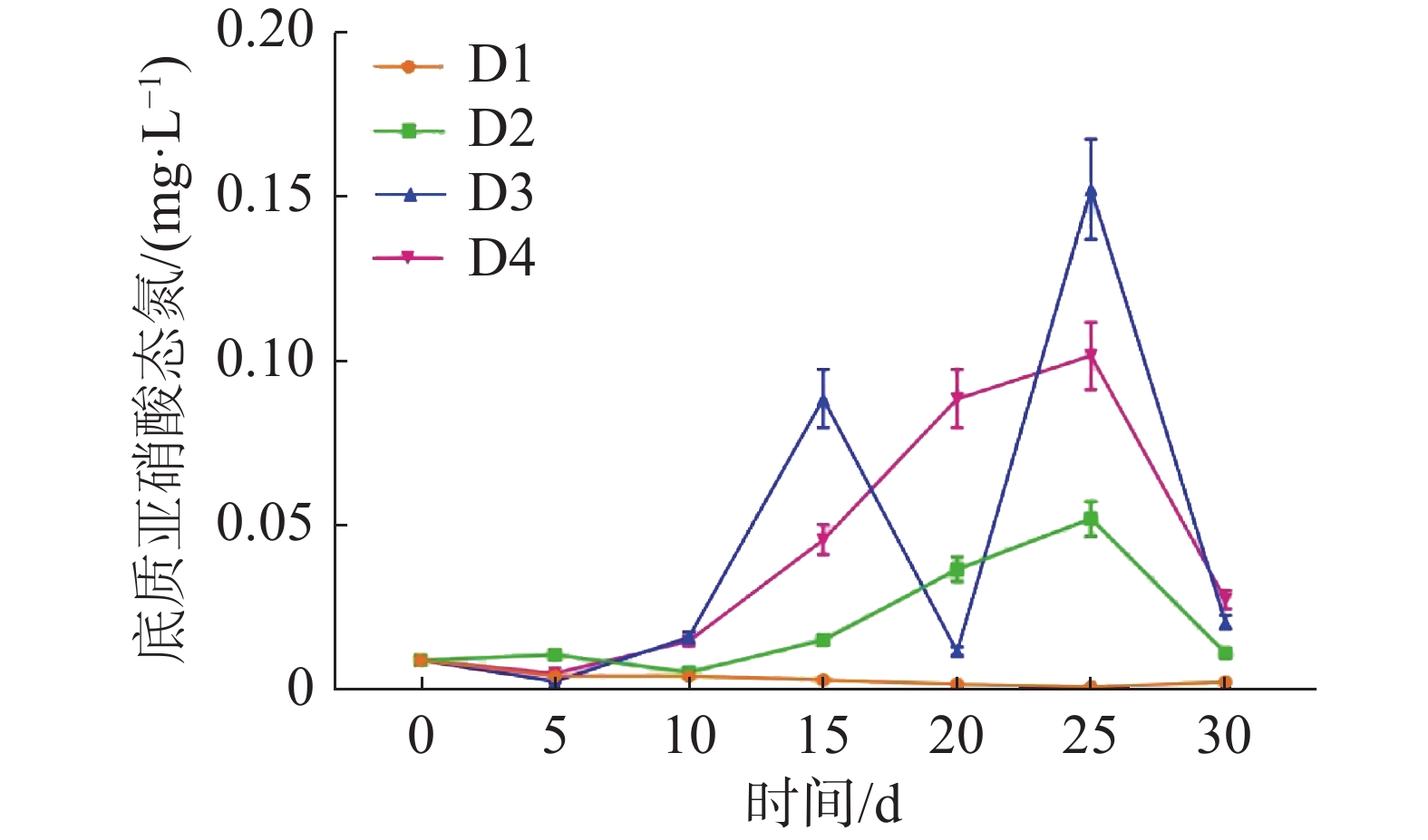
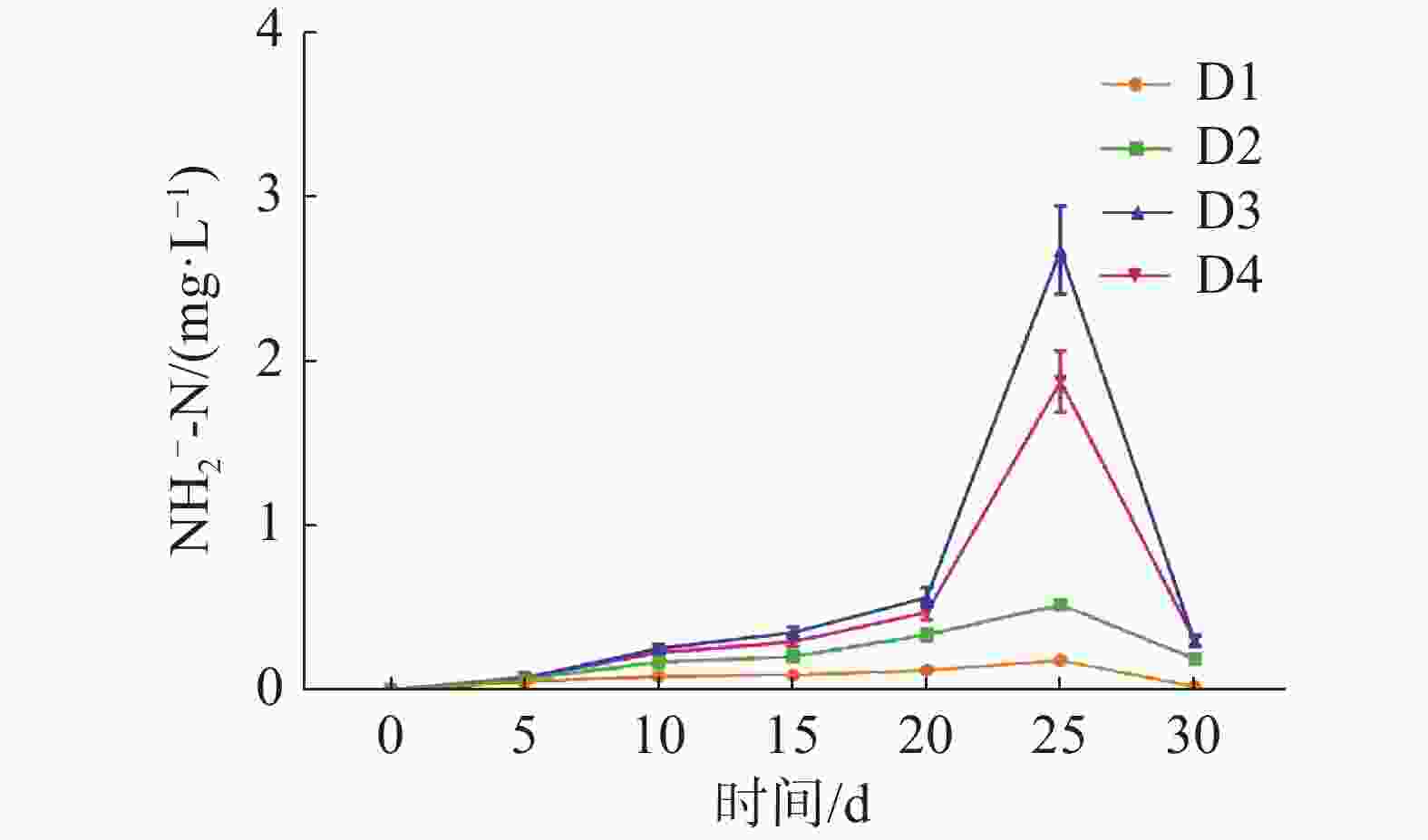
如图5所示,养殖密度对循环水养殖系统底质NO2−-N浓度高峰有极显著影响(P<0.01)。D2、D3、D4组的底质NO2−-N浓度于第25天达到峰值,而D1组的底质NO2−-N浓度并未出现底质NO2−-N浓度高峰。其中D3组峰值最高,为(0.15±0.02)mg·L−1,D2组峰值最低,为(0.052±0.005 )mg·L−1。
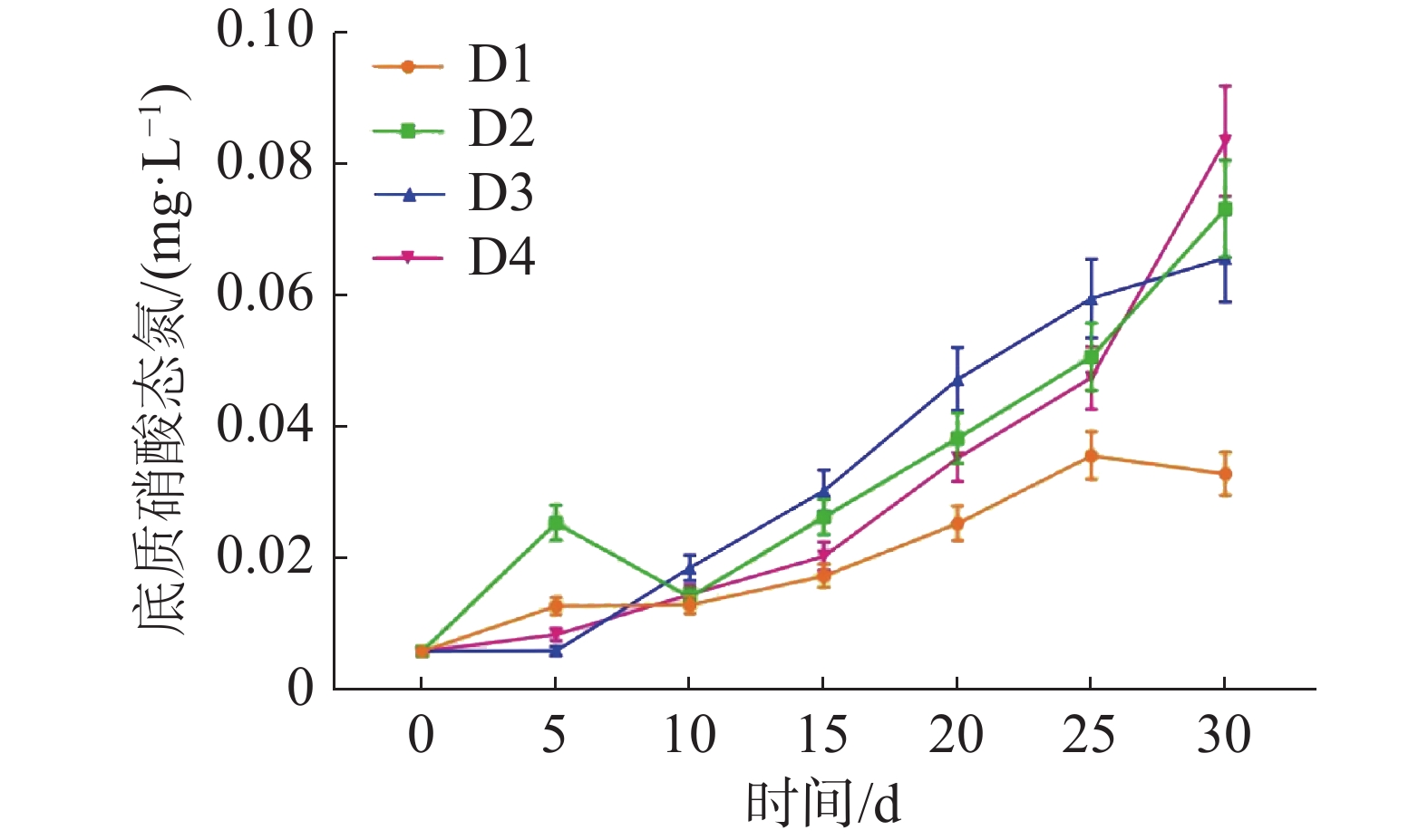
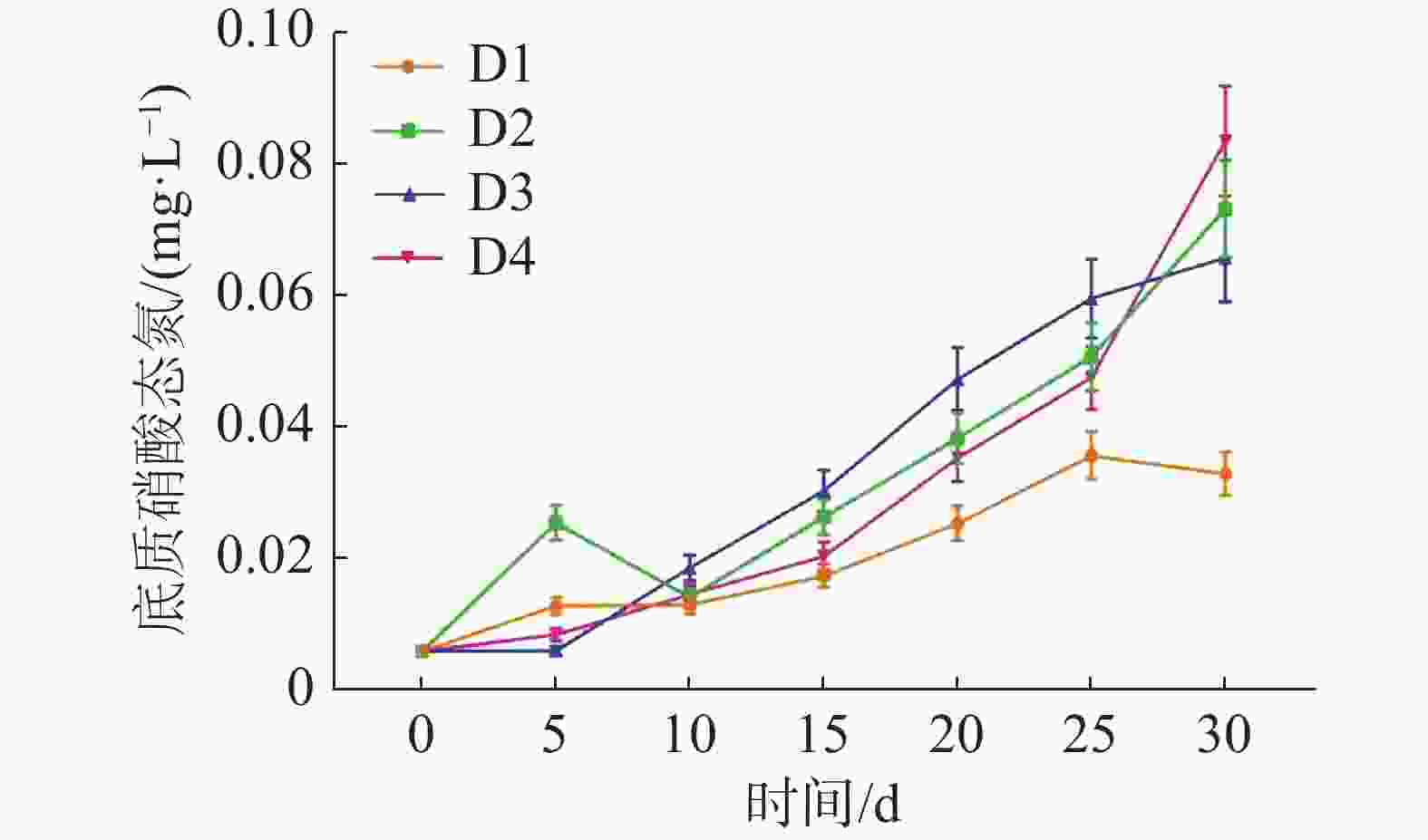
如图6所示,各实验组中的底质NO3−-N不断积累,在实验结束时,D1、D2、D3、D4各组的底质NO3−-N浓度分别为(0.034±0.003)、(0.074±0.007)、(0.066±0.007)和(0.084±0.008) mg·L−1。
-
如图7所示,养殖密度对稚螺AMS、LPS以及PPS的活力具有极显著影响(P<0.01)。稚螺体内的AMS活力随养殖密度的提高而显著降低(P<0.01),其中D1组最高,为(10.30±1.02)U,D4组最高,为(3.64±0.61)U。稚螺体内的LPS活力随养殖密度的提高而显著降低(P<0.01),其中D1组最高,(4.14±0.28)U,D4组最高,为(1.93±0.31)U。稚螺体内的LPS活力随养殖密度的提高而显著降低(P<0.01),其中D1组最高,(13.52±0.70)U,D4组最高,为(3.38±0.99)U。
-
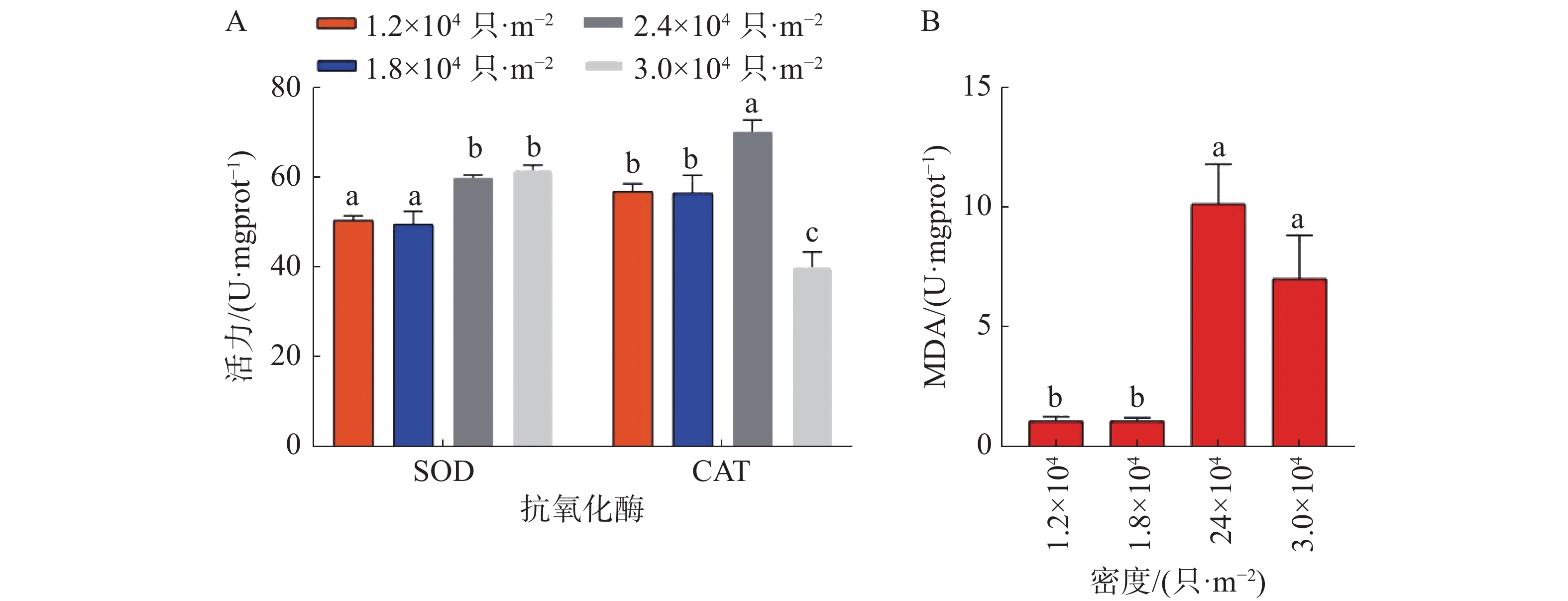
如图8所示,养殖密度对稚螺SOD、CAT以及MDA的活力具有极显著影响(P<0.01)。稚螺体内的SOD活力随养殖密度的提高而显著提高(P<0.01),其中D4组最高,为(61.67±1.11)U,D2组最低,为(49.54±2.94)U。稚螺体内的CAT活力随养殖密度的提高而显著提高(P<0.01),其中D3组最高,为(70.23±2.6)U,D2组最低,为(56.56±3.94)U。稚螺体内的MDA活力随养殖密度的提高而显著提高(P<0.01),其中D3组最高,为(10.12±1.65)nmol·mL−1,D2组最低,为(1.05±0.14)nmol·mL−1。
-
本实验对比了在相同循环水系统养殖条件下,方斑东风螺稚螺在不同密度下的养殖效果。研究发现,在循环水系统下,以D1(1.2×104 只·m−2)和D2(1.8×104 只·m−2)组的密度养殖的稚螺生长最快,而D3(2.4×104 只·m−2)和D4(3.0×104 只·m−2)组的密度养殖的稚螺生长较慢,这与在刺参(Apostichopus japonicus Selenka)、高体革鯻(Scortum barcoo)、锯缘青蟹(Scylla serrata)、大西洋鲑(Salmo salar L.)中的研究结果一致[12-15],说明在循环水养殖系统中过高的密度会抑制方斑东风螺的生长速度。
在实验第25天,D1、D2组中的稚螺生存状态正常,但D3、D4组的稚螺均出现了食欲不振,行动迟缓的现象,且有大量的稚螺“翻背”和死亡。这一现象可能是养殖环境中过高的NH4+-N和NO2−-N浓度导致的。在循环水养殖过程中,过大的养殖密度会导致过量的代谢废物进入养殖系统,这些代谢废物如果无法及时分解,就会导致养殖系统产生过高的NH4+-N和NO2−-N[16-17]。养殖环境中的NH4+-N和NO2−-N浓度过高会对养殖生物的机体组织造成损伤,甚至会导致养殖生物的死亡[18-19]。在这种养殖环境下,养殖生物会受到严重的环境胁迫[20]。在实验第25天时,D3组的NO2−-N和底质NO2−-N均达到了(2.68±0.27)和(0.15±0.02)mg·L−1的峰值,D4组的NO2−-N、底质NH4+-N和底质NO2−-N均达了(1.88±0.19)、(1.38±0.14)和(0.10±0.01)mg·L−1的峰值。
在消化酶活性方面,消化酶是生物消化系统中的关键物质,其活性的高低直接关系到生物对营养物质的消化能力,所以消化酶的活性常用来了解生物的消化能力。在本实验结束时,方斑东风螺稚螺体内的AMS、LPS和PPS的活性均呈现出随密度的升高而降低的趋势。这可能是由于养殖过程中过高的NH4+-N和NO2−-N浓度峰值破坏了稚螺的消化系统,从而导致稚螺的食欲不振和消化酶活性降低[21- 22]。这说明过高的养殖密度会增加循环水养殖系统的负荷,从而导致水质败坏,对方斑东风螺的消化系统造成破坏。
在抗氧化酶活性方面,贝类在受到环境因子胁迫时,体内会产生超氧阴离子自由基(ROS),并激活抗氧化防御系统,其中SOD首先被激活,将O2•−转化为H2O2和O2,随后被激活的CAT会将H2O2分解为HO2和O2,若生物体内的ROS不断积累,生物体内的生物膜系统会产生损伤,并产生MDA[23]。在本研究中,D3、D4组稚螺体内的SOD活性和MDA浓度均显著高于D1、D2组(P<0.01)。这说明养殖系统中过高的NH4+-N和NO2−-N浓度使D3、D4组中的稚螺处于较强的应激状态。而D4组中的CAT活性显著低于D1、D2组,可能是因为严重的应激使D4组中稚螺的氧化系统遭到了破坏[18],本实验中,D3、D4组显著升高的MDA含量证明了这一点。
综上所述,从生长速度和提高养殖产量的方面考虑,1.8×104 只·m−2的密度是比较适合本研究中循环水养殖系统下的方斑东风螺中间培育的。这对后续的循环水方斑东风螺中间培育技术的进一步探究具有一定的参考意义。
Effects of different culture densities on the intermediate cultivation of Babylonia areolate in a recirculating aquaculture system
DOI: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230058
- Received Date: 2023-04-28
- Accepted Date: 2023-05-23
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-05-15
- Available Online: 2023-11-23
- Publish Date: 2023-11-24
-
Key words:
- Babylonia areolate /
- recirculating aquaculture system /
- stocking density /
- survival rate /
- growth
Abstract: To enhance the water quality and disease control during the intermediate culture process of Babylonia areolate, a recirculating aquaculture experiment with a 30-day cycle was conducted. The effects of different stocking densities on the growth performance, physiological enzyme activity, and water quality changes in the recirculating aquaculture system were analyzed. Results showed that when the stocking density exceeded 1.8×104 individuals·m−2, the survival rate, final shell length, daily average growth rate, and shell growth rate of the juveniles B. areolate decreased significantly (P<0.05), and that the activities of α-amylase (AMS), lipase (LPS), and pepsin (PPS) decreased significantly (P<0.01), while the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) increased significantly (P<0.01). Meanwhile, the peaks of ammonium nitrogen and nitrite in the culture system significantly increased with the increase of stocking density (P<0.05). Taking into account the aquaculture production performance and unit area yield, the optimal stocking density for intermediate culture of B. areolata in the recirculating aquaculture system was 1.8×104 individuals·m−2.
| Citation: | LIU Ziling, SHI Yaohua, ZHENG Xing, GU Zhifeng. Effects of different culture densities on the intermediate cultivation of Babylonia areolate in a recirculating aquaculture system[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2023, 14(6): 675-680. doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230058 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: