-
自然界中,植物利用自身的2道免疫防线来抵御病原微生物的侵染。第1道免疫防线是病原菌相关分子模式或微生物相关因子(pathogen or microbe associated molecular patterns, PAMPs/MAMPs)激发的免疫反应 (PAMPs triggered immunity, PTI)[1-2]。第2道免疫防线是植物抗病基因(resistance gene,R gene)识别病原微生物的效应蛋白后激发免疫反应(effectors triggered immunity, ETI),该免疫反应在侵染部位产生大量的细胞死亡,又称为超敏反应(Hypersensitive Response, HR)[3]。EDS1(enhanced disease susceptibility 1)在植物的2道免疫防线中均发挥着非常重要的作用[4-5],尤其在第2道免疫防线中,植物大多数TIR-NB-LRR(Toll-Interleukin1 Receptor-nucleotide binding-leucine-rich repeat)类抗病基因功能的正常发挥都需要EDS1的参与[6]。EDS1不仅可以与病原菌效应蛋白发生相互作用,还可以与植物体内TIR-NB-LRR类蛋白形成复合体,从而实现抗病信号通路的正常传递[7]。同时,植物体内存在与EDS1结构同源的另外2个蛋白PAD4(Phytoalexin Deficient 4)和SAG101(Senescence Associated Gene 101),EDS1,PAD4,SAG101三者都含有1个酰基酯酶结构域和1个EP(EDS1-PAD4)结构域[5,8]。EDS1可以分别与另外2个蛋白发生相互作用,介导不同的抗病信号通路[9]。近期的研究[10]发现,EDS1,PAD4,SAG101三者还可以形成复合体来发挥功能。综上所述,虽然研究者对EDS1在植物抗病中的功能有一定了解,但具体的EDS1信号通路上、下游作用元件是什么,目前还不清楚。橡胶树白粉菌 (Oidium heveae)是一种专性活体寄生真菌,侵染橡胶树引发橡胶树白粉病,对天然橡胶的产量造成了巨大的损失。近期的研究发现,橡胶树白粉菌还可以侵染拟南芥,在拟南芥野生型Col-0激发抗病反应,并且该抗病反应完全依赖于EDS1和PAD4,部分依赖于SAG101以及SA信号通路[11]。为了进一步研究橡胶树白粉菌在拟南芥上激发的抗病信号通路,本实验室对接种橡胶树白粉菌Oidium heveae HN1106的拟南芥野生型Col-0进行了RNA-seq数据分析,笔者旨在为进一步探讨EDS1参与的植物抗病信号通路奠定良好的基础。
-
拟南芥野生型Col-0、拟南芥突变体ataf2-1(SALK_136355)[12]、拟南芥ataf2-2(SALK_015750)[12]、拟南芥突变体eds1[13] (eds1-2,快中子轰击基因缺失突变体)等植物材料。橡胶树白粉菌菌株Oidium heveae HN1106[11]。
-
将生长了5周的拟南芥放入40 cm×40 cm 50 μm尼龙膜接种箱中,利用毛笔刷把橡胶树白粉菌刷到尼龙膜上,进行接种。10 d后,对拟南芥叶片发病症状进行观察并拍照。剪取叶片,进行脱色过夜(脱色液为V乙醇∶V苯酚∶V水∶V乳酸=2∶1∶1∶1)。将脱色后的叶片在考马斯亮蓝染色液(G250 6 g·L−1乙醇溶液)中染色30 s,显微镜观察,计数单个孢子产生的分生孢子数。
-
液氮预冷研钵,放入拟南芥叶片,反复加入液氮,研磨3次。加入1 mL Invitrogen Trizol (Lot No. 66223)溶液,提取拟南芥叶片总RNA。加入DNA酶,37 ℃消化1 h后,利用Invitrogen公司的RNA反转录试剂盒III (Lot No. 696045)进行反转录。采用SYBR®Premix Ex TaqⅡ(Lot No. AK2702)试剂盒进行荧光定量PCR,PCR采用20 μL反应体系,PCR程序:95 ℃ 40 s,95 ℃ 6 s,62 ℃ 40 s,40个循环。PCR引物 ACTIN:5′-TGGTGGAAGCACAGAAGTTG-3′;5′-GATCCATGTTTGGCTCCTTC-3′,ATAF2F:5′-ACGGACGAGGAGCTTGTGAA-3′;ATAF2 R:5′-CTCCGGTAGCTTTCCAATAAC-3′。
-
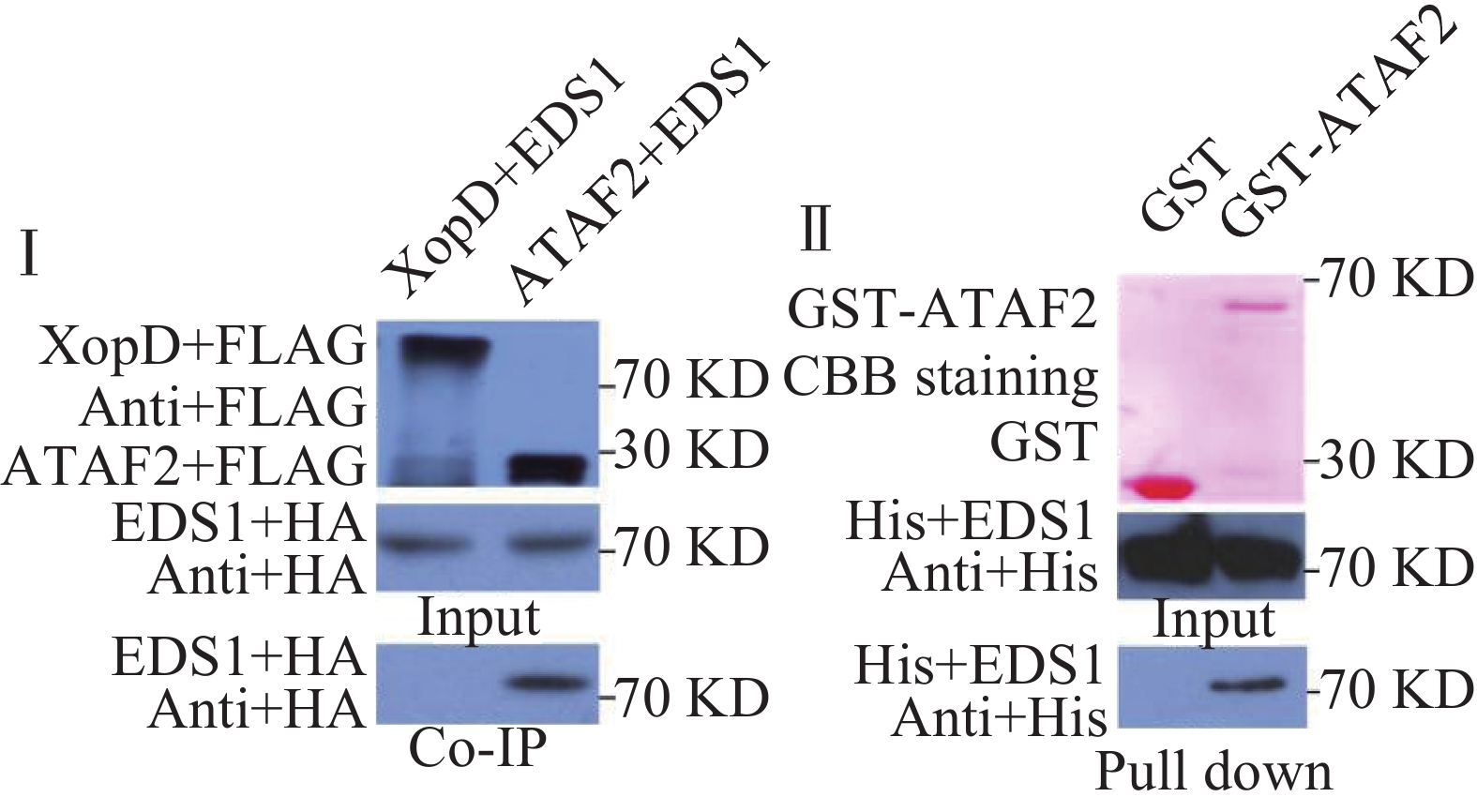
利用氯化铯密度梯度离心的方法提取XopD-FLAG,ATAF2-FLAG和EDS1-HA质粒。制备拟南芥Col-0的原生质体,于原生质中分别转化ATAF2-FLAG和EDS1-HA的混合质粒各60 μg以及XopD-FLAG和EDS1-HA的混合质粒各60 μg作为对照,弱光下过夜培养。100 g离心2 min,弃去上清,与原生质体沉淀中加入1 mL蛋白提取缓冲液(0.15 mol∙L−1 KCl,50 m mol∙L−1 HEPES-KOH pH7.5,1 mmol∙L−1 EDTA,1 mmol∙L−1 DTT,0.2% Triton-X 100,cocktail蛋白酶抑制剂)提取原生质体总蛋白。然后分别加入anti-Flag M2 agarose (sigma) 20 μL。4 ℃孵育4 h。500 g离心1 min,弃去上清,沉淀用1 mL漂洗缓冲液(0.15 mol∙L−1 KCl,50 mmol∙L−1 HEPES-KOH pH7.5,1 mmol∙L−1 EDTA,1 mmol∙L−1 DTT,0.5% Triton-X 100,cocktail蛋白酶抑制剂)漂洗6次后,加入洗脱缓冲液(0.5 mmol∙L−1 3XFLAG多肽)50 μL,4 ℃孵育1 h。离心,取上清进行SDA-PAGE电泳,分别用FLAG抗体和HA抗体检测蛋白相互作用。
-
分别将GST-ATAF2和GST与HIS-EDS1各50 μg混合于2个1.5 mL离心管中,用缓冲液[0.025 mol∙L−1 Tris-HCl (pH7.5), 0.1 mol∙L−1 NaCl,0.001 mol∙L−1 DTT]定容至1 mL,4 ℃孵育0.5 h。然后再分别加入50 μL Glutathione SepharoseTM4B, 4 ℃孵育1 h。500 g离心1 min,弃去上清,沉淀用1 mL漂洗缓冲液[0.025 mol∙L−1 Tris-HCl (pH7.5);0.1 mol∙L−1 NaCl;0.001 mol∙L−1 DTT;0.2% Triton-X 100]反复清洗离心,洗涤5次。最后加入100 μL洗脱缓冲液(10 mmol∙L−1还原型谷胱甘肽、50 mmol∙L−1 pH8.0 Tris-HCl),4 ℃孵育10 min。离心,取上清进行SDS-PAGE电泳,分别用立春红染色和HIS抗体检测相互作用。
-
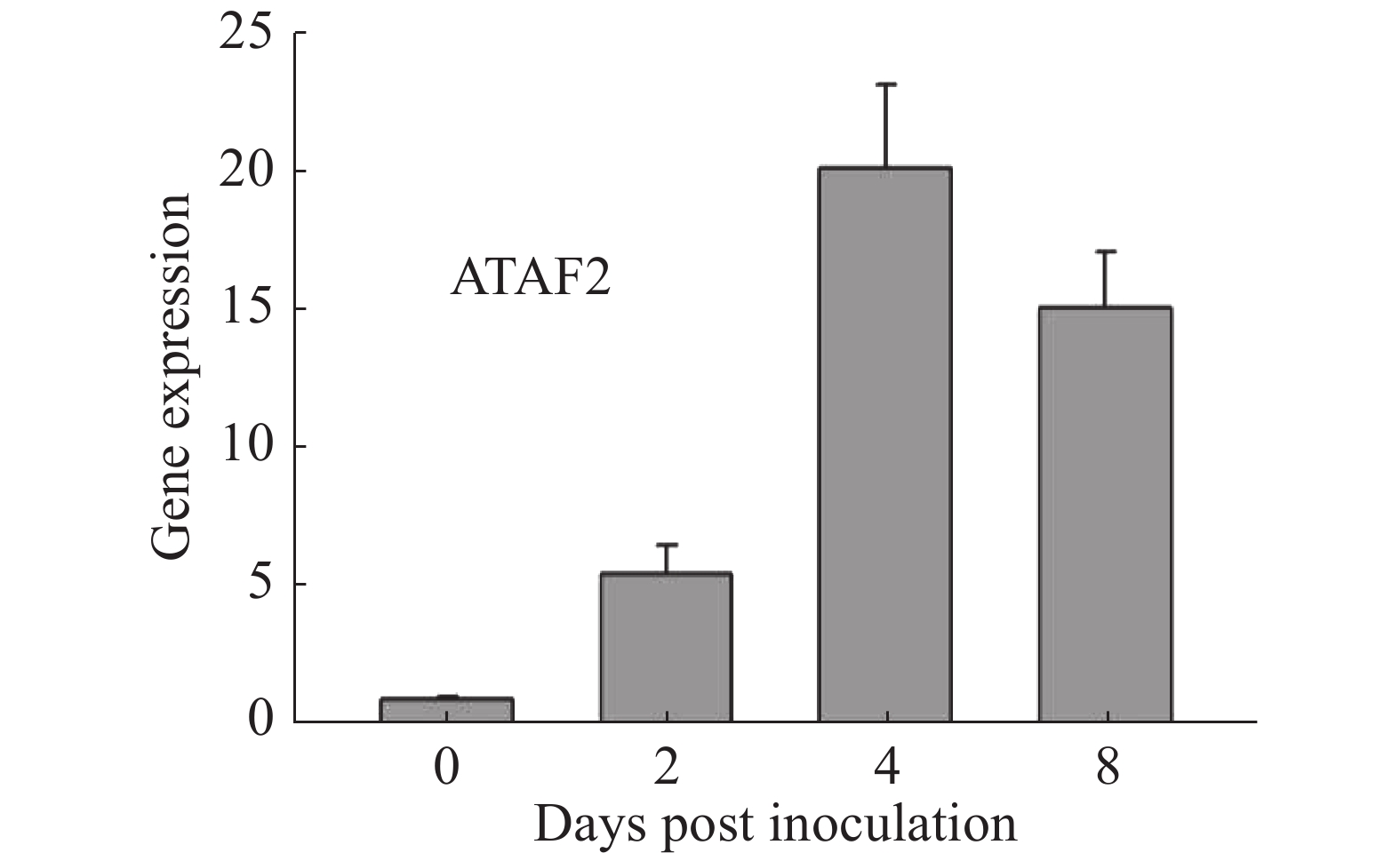
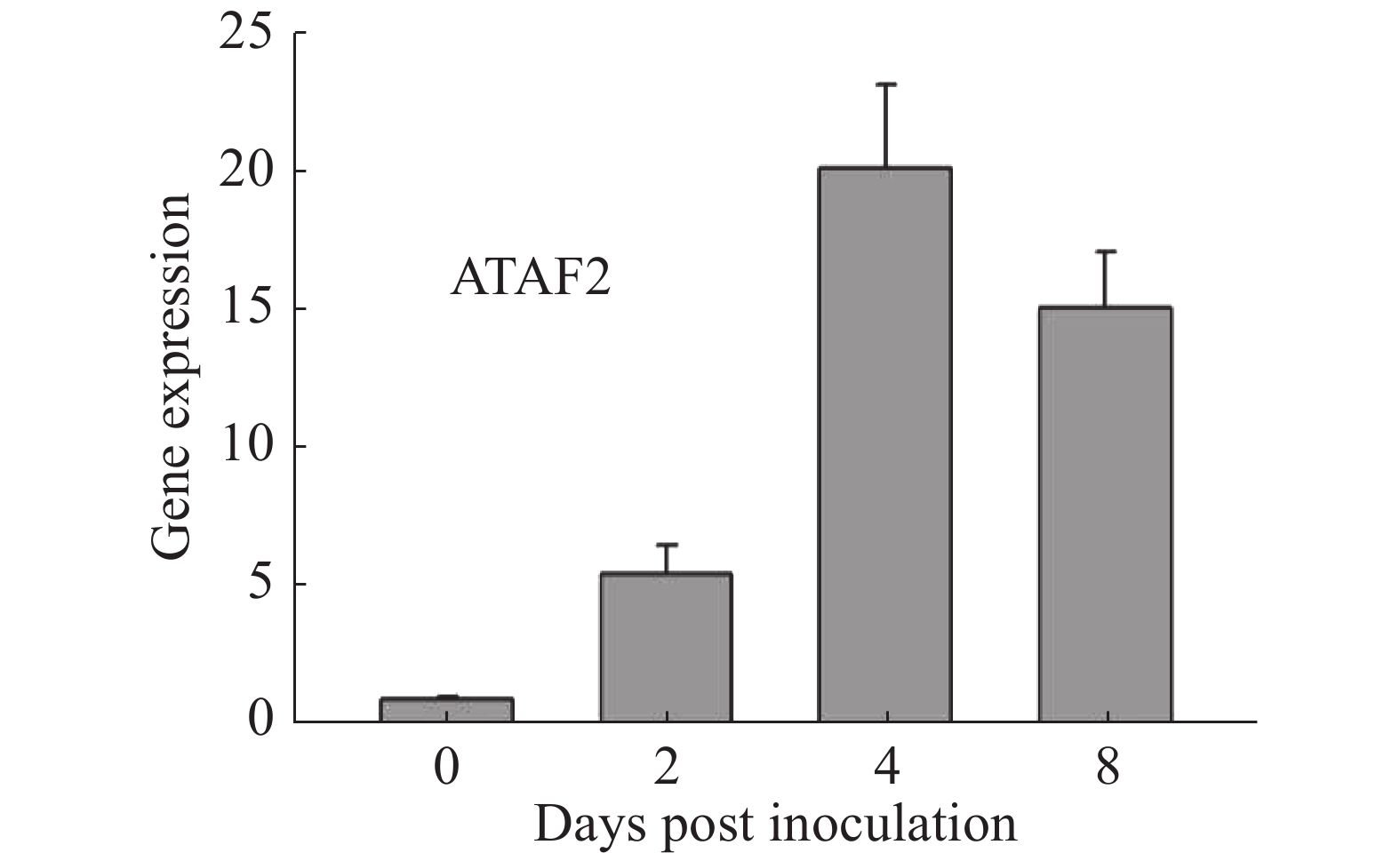
通过在拟南芥野生型Col-0上接种Oidium heveae HN1106,进行RNA-seq数据分析。接种后4 d,发现拟南芥NAC家族转录因子ATAF2上调表达6倍。为了验证该结果的准确性,对培养约5周的拟南芥野生型Col-0接种Oidium heveae HN1106,分别剪取接种后0,2,4,8 d的拟南芥野生型Col-0的叶片,提取总RNA,进行反转录和荧光定量PCR试验。结果表明,在接种后2 d,ATAF2基因大约上调表达5倍(图1),在接种后4 d上调20倍(图1),接种后8 d上调表达15倍(图1),表达趋势与RNA-seq数据一致,表明ATAF2基因受橡胶树白粉菌诱导上调表达。
-
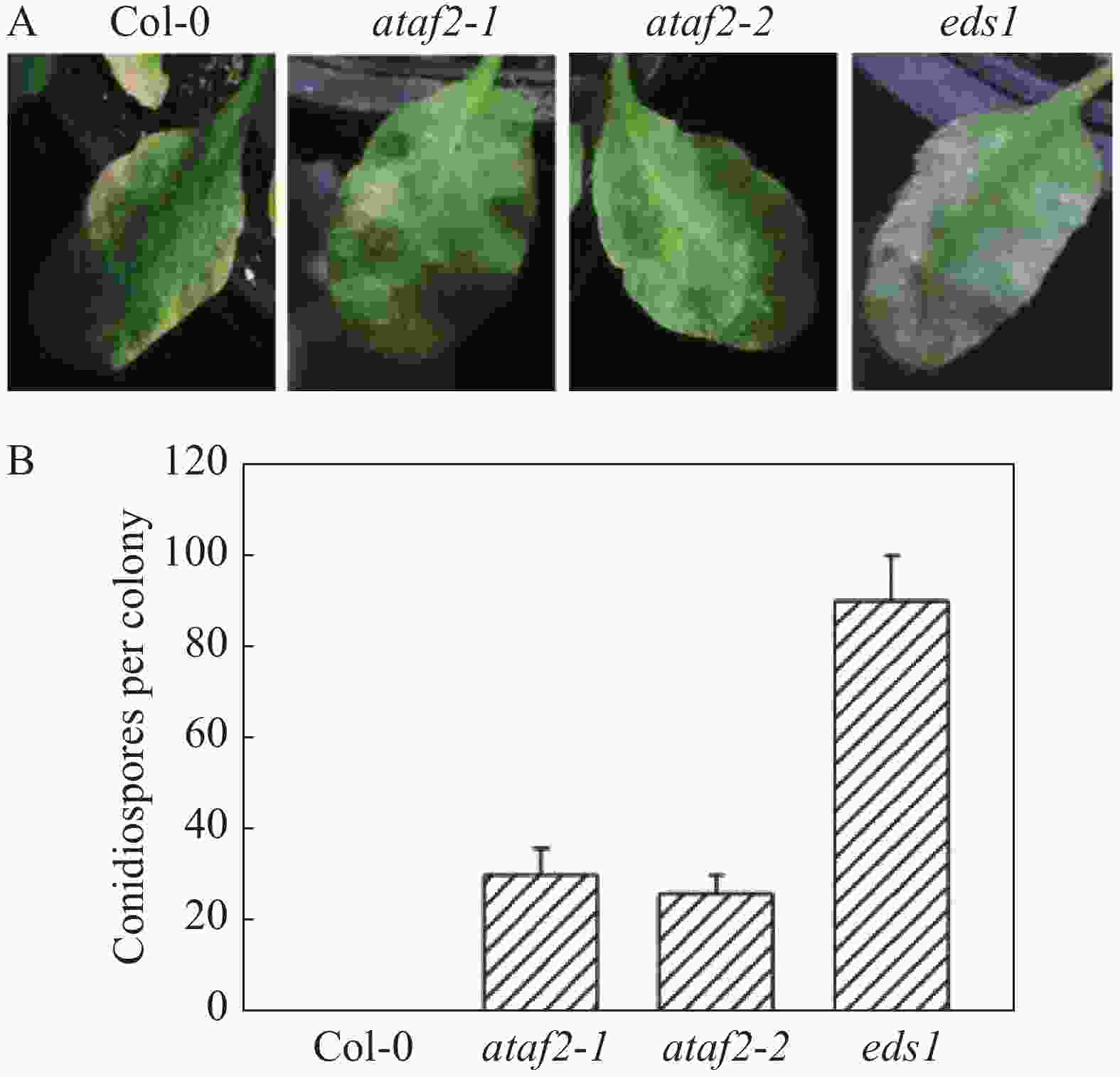
文献[12]报道了ATAF2参与调控拟南芥对腐生真菌的抗病性。且ATAF2基因在接种橡胶树白粉菌后发生明显上调表达(图1),为此,笔者推测ATAF2可能参与了拟南芥对橡胶树白粉菌的抗病性的调控。为了验证该可能性,笔者获得了ataf2 T-DNA插入纯和系拟南芥突变体ataf2-1和ataf2-2,并且在拟南芥野生型Col-0,拟南芥突变体ataf2和拟南芥突变体eds1上接种橡胶树白粉菌。接种10 d后发现,野生型拟南芥出现明显的抗病发黄的表型(图2A),而拟南芥突变体eds1表现出明显的白粉病病斑(图2A),拟南芥突变体ataf2-1和ataf2-2出现了微弱的白粉病病斑(图2A)。进一步通过分生孢子计数分析,橡胶树白粉菌不能在野生型上产生分生孢子,在突变体ataf2上产生了少量的分生孢子(图2B),eds1上形成了大量的分生孢子(图2B)。综上结果表明,ataf2突变体表现出对橡胶树白粉菌感病的表型。
-
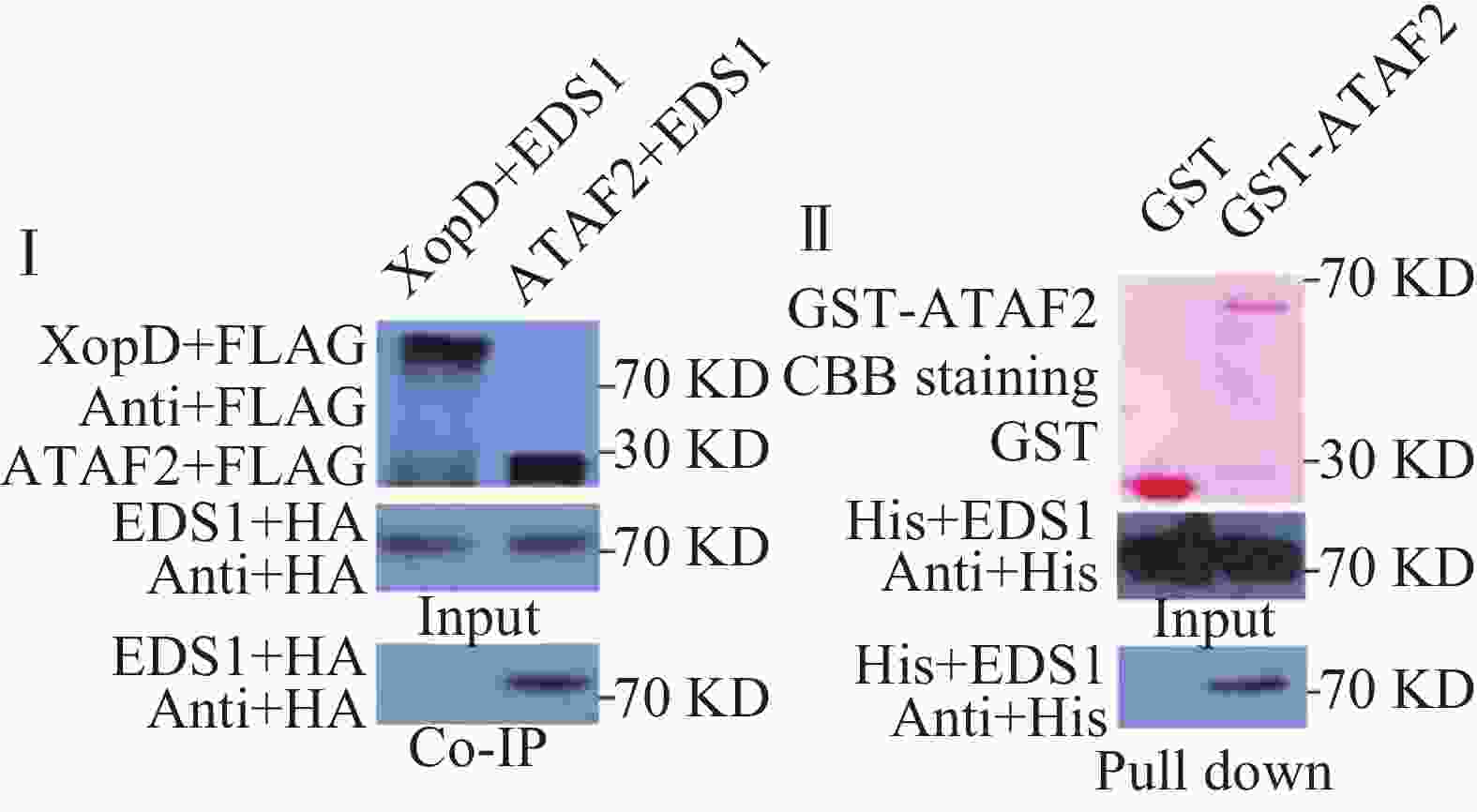
橡胶树白粉菌在拟南芥上激发抗病性依赖于EDS1,因此,笔者推测ATAF2可能参与了EDS1的抗病信号通路,二者在植物体内可能发生相互作用。为了验证二者是否在植物体内相互作用,笔者构建了带有FLAG标签的ATAF2和带有HA标签的EDS1原生质体表达载体。通过氯化铯密度梯度离心提取质粒后,共同转化拟南芥原生质体,黄单胞菌XOPD蛋白作为对照,进行免疫共沉淀实验。实验结果表明,ATAF2可以与EDS1发生相互作用,而对照蛋白XOPD则不能发生相互作用(图3Ⅰ)。为了进一步验证二者是否直接相互作用,笔者构建了GST-ATAF2蛋白和HIS-EDS1蛋白原核表达载体。转化大肠杆菌BL21,IPTG诱导蛋白表达,分别纯化GST,GST-ATAF2和HIS-EDS1蛋白,进行pull down实验。免疫印迹结果表明,GST-ATAF2可以与HIS-EDS1发生相互作用,而对照GST则不能相互作用,暗示着ATAF2与EDS1是直接相互作用(图3Ⅱ)。
-
笔者通过筛选橡胶树白粉菌接种拟南芥后的上下调基因,发现NAC家族转录因子ATAF2基因受橡胶树白粉菌的诱导上调表达,并且参与了拟南芥对白粉菌的抗病性的调控。笔者进一步通过蛋白质相互作用证实ATAF2与EDS1发生相互作用。文献[14-15]报道,ATAF2作为转录激活或抑制因子,在植物抗逆,光合作用以及激素合成等方面发挥非常重要的作用,但EDS1与ATAF2的互作机制,以及二者在抗病信号通路中的上、下游关系还需要进一步从遗传上证明。在拟南芥植物体内,存在着超过90个NAC家族的转录因子[12]。通过接种橡胶树白粉菌的实验,笔者发现与拟南芥eds1突变体相比,拟南芥ataf2突变体表现出部分抗性缺失的表型,表明其他的同类型转录因子可能也参与了拟南芥对橡胶树白粉菌的抗病性的调控,但具体是哪些蛋白参与,还需要进一步筛选。文献[12]报道ATAF2受病原菌的诱导表达,负调控拟南芥对尖孢镰刀菌的抗病性。然而,在笔者的实验中,发现ATAF2受橡胶树白粉菌的诱导表达,正调控拟南芥对橡胶树白粉菌的抗病性。因此,ATAF2对2个不同病原菌的抗性作用机制可能是不一样的,但具体的作用机制,还需进一步探索。
ATAF2 positively contributes to the disease resistance against Oidium heveae in Arabidopsis
doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.01.009
- Received Date: 2019-10-11
- Rev Recd Date: 2019-11-27
- Available Online: 2020-07-03
- Publish Date: 2019-11-01
-
Key words:
- ATAF2 /
- EDS1 /
- Arabidopsis /
- Oidium heveae /
- Resistance
Abstract: It has been reported that Oidium heveae triggers the disease resistance in model plant Arabidopsis thaliana in an Enhanced Disease Susceptibility 1 (EDS1) dependent manner, and EDS1 plays an important role in the signal pathway mediated by Toll-Interliukin 1 Receptor-nucleaotide binding-leucine-rich repeat (TIR-NB-LRR) type resistance genes. However, the upstream and downstream signaling of EDS1 is still unknown. In this study, A. thaliana Col-0 was inoculated with O. heveae HN1106, and we found the expression of ATAF2 gene, a member of plant NAC transcription factor family, was up-regulated 20 times after 4 days of inoculation as against 0 day of inoculation. Moreover, ATAF2 positively contributed to the disease resistance to O. heveae in A.thaliana. Furthermore, we found ATAF2 directly interacted with EDS1 in vitro and in vivo by GST pull-down and Co-immunoprecipitation assays, which lays a basis for the future study of EDS1 mediated resistance pathway.
| Citation: | YE Hongying, MEI Shuangshuang, RONG Wei. ATAF2 positively contributes to the disease resistance against Oidium heveae in Arabidopsis[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2020, 11(1): 58-62. doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.2020.01.009 |






 DownLoad:
DownLoad: