-
主持人:徐 冉
根瘤菌(rhizobia)属于革兰氏阴性细菌[1],呈杆状或球状、有鞭毛和荚膜、不生芽孢[2],可在多数豆科植物的根或茎上诱发其皮层细胞增生,形成根瘤或茎瘤固氮共生体系[3],将空气中的氮气转化成植物可利用的形式,对寄主植物氮素供应和土壤氮素富集意义重大[4]。近年来,木本豆科植物根瘤菌在生态改良和农林业可持续发展中的作用日益凸显,研究人员对木本豆科植物根瘤菌研究关注度增强,其中刺槐(Robinia pseudoacacia)[5]、花榈木(Ormosia henryi)[6-7]、厚荚相思(Acacia crassicarpa)[8]等树种在根瘤菌新种的发现、根瘤菌遗传多样性及系统发育、优良菌株筛选及生理生态效应等方面取得了阶段性研究成果。南洋楹Falcataria falcata 是豆科Leguminosae含羞草亚科Mimosaceae常绿高大乔木,是国际林业研究协会(IUFRO)大力提倡并推广的热带亚热带速生固氮树种之一[9]。我国自1940 年开始引种南洋楹,该树种在广东、广西、海南等南方省(区)表现出较强的适应性和速生性,主要以短周期速生工业用材树种定位发展,其卓越的速生能力为增加森林碳汇、缓解木材供给压力作出了重要贡献,而其根瘤菌及其应用的相关研究目前尚较为缺乏。在仅有的2篇相关报道中,王作明等[10]通过对8种豆科植物回接根瘤菌对比研究时发现,南洋楹根瘤菌的固氮效率高达92.13%,对幼苗生长促进作用最显著;潘超美等[11]利用感染南洋楹根瘤的土壤来育苗,发现其地上部分生物量比不接种的增加20%左右,但上述二者的研究均在常规育苗并结合施肥的条件下开展,无法精准考察根瘤菌对南洋楹幼苗生长的影响。因此,本研究在实验室控肥控杂菌条件下,通过开展不同基质中接种根瘤菌与施营养元素的对比育苗试验,揭示不同试验处理下南洋楹幼苗的生长动态特征及生长效应的差异性,筛选有利于根瘤菌充分发挥效应的育苗基质类型,为根瘤菌在南洋楹苗木培育生产上的应用提供科学依据。
HTML
-
以广东省林业科学研究院选育的C086南洋楹家系种子为试材培育幼苗。用于接种的根瘤菌为广东省森林培育与保护利用重点实验室分离得到的ZS530-8菌株,经NBCI数据库Blast程序、SILVA数据库进行16S rDNA基因序列比对[12],该菌株与埃氏慢生根瘤菌Bradyrhizobium elkanii NBRC 14791 相似度为98.22%。
-
在无菌操作台中,先将种子放入 5%高锰酸钾溶液浸泡 30 min,用无菌水清洗3次,再加入85 ℃无菌水浸泡约24 h直至种子肿胀,用无菌水清洗3次。在已灭菌的培养皿中,垫上湿润的无菌滤纸,将种子均匀置于其中并封盖,28 ℃培养箱中暗培养,2~4 d后种子可发育成芽苗。
-
用无菌接种环蘸取菌株ZS530-8划线接种于YMA 斜面培养基上活化,28 ℃恒温倒置活化培养后,挑取单菌落接种于500 mL YMA 液体培养基中,28 ℃180 r·min-1摇床振荡培养2~4 d,分光光度计检测菌液 OD600值大于 0.5 时可用于接种[13]。
-
待种子萌发幼根后脱去种皮,采用浆根法[3]接种30 min。育苗基质为高纯度的石英砂和蛭石。育苗基值经121 ℃灭菌1.5 h,分别分装于8.4 cm(内口径)×7.2 cm(高)塑料育苗盆中。试验采用完全随机设计,2因素(基质和施肥方式)分别设2水平(石英砂和蛭石)和3水平(接种根瘤菌、施营养液、空白对照),共计4个试验处理组合(石英砂+根瘤菌、石英砂+营养液、蛭石+根瘤菌、蛭石+营养液)和2个对照组合(石英砂CK、蛭石CK),每个处理组合种植18盆,3次重复。将育苗盆放入人工气候箱(光照强度7 000 lx、温度28 ºC 、湿度75%、光照时长12 h)中培养,每2 天喷施1次纯净水。其中,接种根瘤菌苗木全程不施加任何营养元素;施营养液苗木不接种根瘤菌,自苗木长出第一对复叶后,每10天额外施加霍格兰(Hoagland)营养液1次,每盆10 mL·次;不接种根瘤菌、不施营养液为空白对照(CK)。
-
在苗龄为30、60、90 d时,观测各试验处理苗木生长情况,剔除未正常生长发育植株后,记录苗高和地径。
-
采用SAS V8软件AVON程序对苗期生长数据进行方差分析及LSD多重比较,GraphPad Prism 9进行作图分析。
-
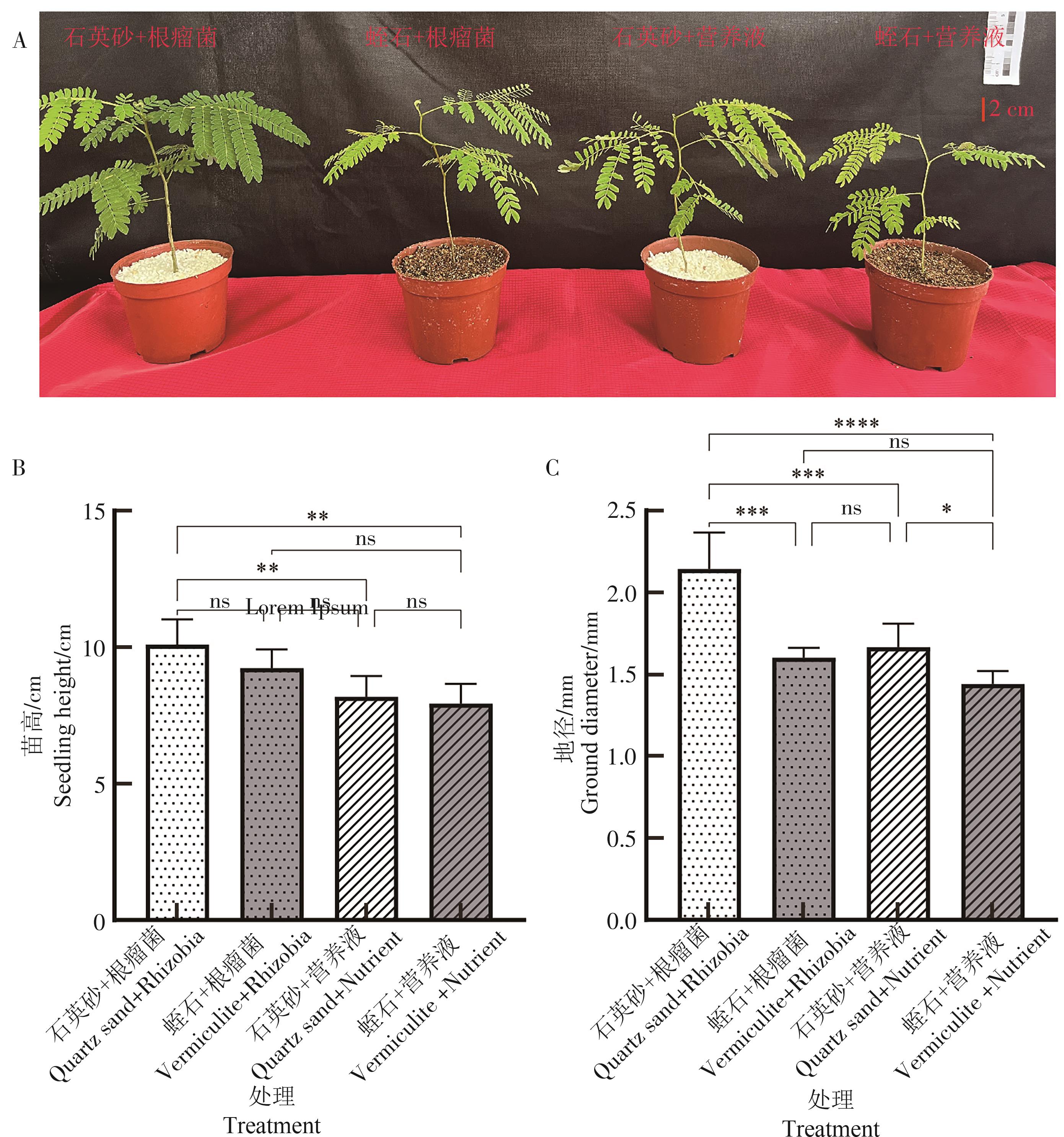
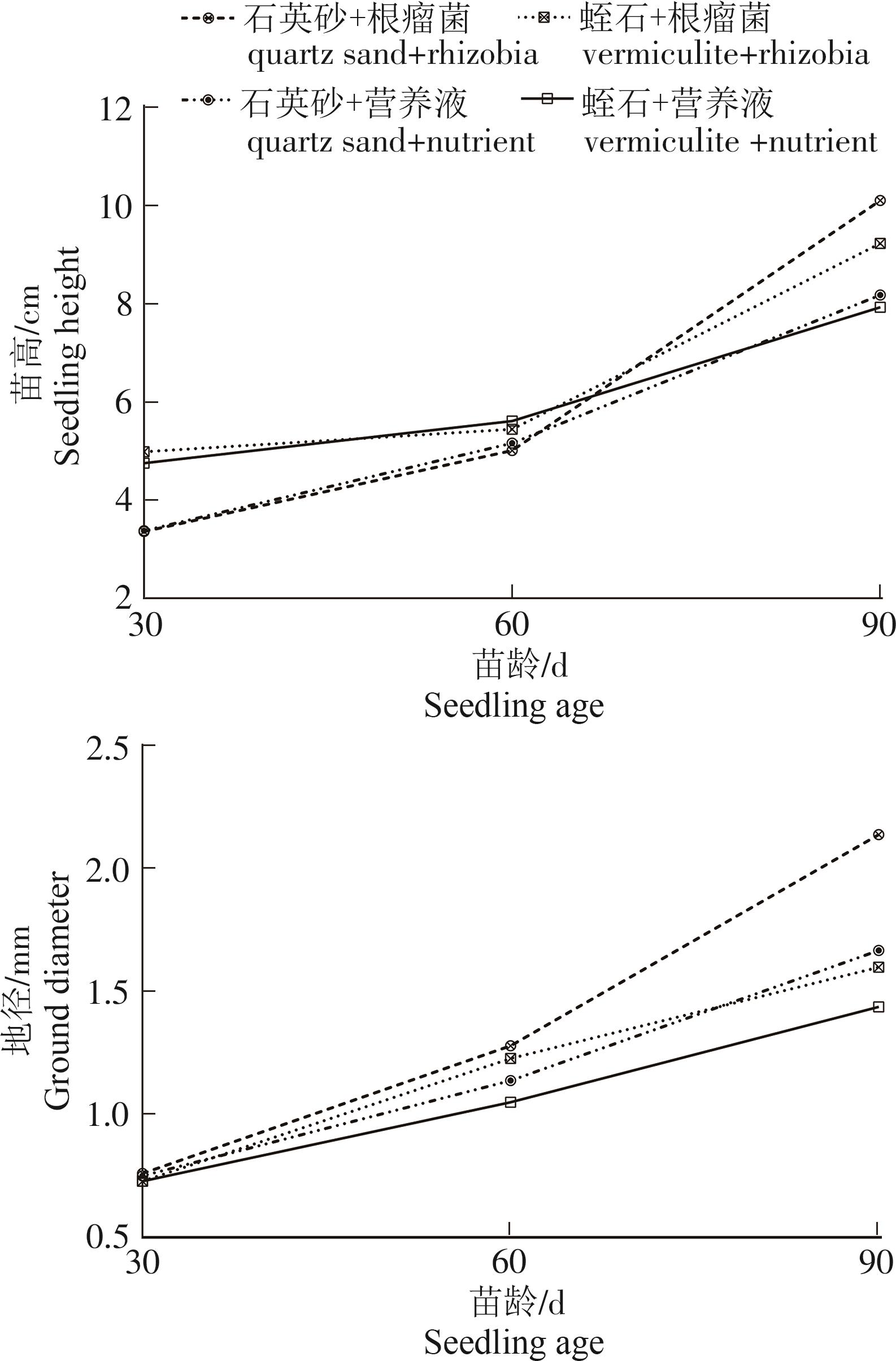
南洋楹苗龄30~90 d的生长情况、生长动态见表1和图1。苗龄30 d时,不同处理组合幼苗均能正常生长,基质为蛭石的苗高生长量优于石英砂35.0%~48.2%,但地径生长差异不大,介于0.60~0.76 mm间。苗龄60 d时,不同处理组合的苗高差异缩小,介于5.01~5.61 mm间,其中,石英砂+根瘤菌、石英砂+营养液的苗高生长表现均比较迅速,生长量分别比苗龄30 d时增长1.65 cm和1.78 cm;蛭石+根瘤菌、蛭石+营养液的苗高生长表现则相对缓慢,生长量分别比苗龄30 d时增长0.85 cm和0.47 mm,不同处理组合的地径出现显著差异(P<0.05);石英砂+根瘤菌、蛭石+根瘤菌的地径显著优于或优于石英砂+营养液、蛭石+营养液,而对照组合明显表现出缺乏养分的状态,生长迟缓,叶片黄化、掉落,蛭石CK的叶缘出现褐斑。苗龄90 d时,不同处理组合的幼苗进入生长高峰期,其中,石英砂+根瘤菌的苗高生长量和地径分别比苗龄60 d时增长了5.00 cm、0.86 mm。石英砂基质的苗木壮实、叶色较浓绿;蛭石基质的苗木细长、叶色偏黄,而对照组合则全部枯黄、生长停滞。从整体生长动态对比而言,接种处理的幼苗整体呈现出先平稳后加速的生长趋势,其地径的生长速度持续高于同种基质施营养液的幼苗,施营养液处理的幼苗始终保持一定速度的持续生长趋势,而对照组合缓慢生长至60 d后,逐渐枯黄、生长停滞。
苗龄/d Seedling age/d 处理 Treatment 苗高/cm Seedling height/cm 地径/mm Ground diameter/mm 生长状况 Growth status 30 石英砂+根瘤菌Quartz sand + Rhizobia 3.36±0.92 b 0.76±0.10 a 叶色嫩绿,生长正常 light green leaf,normal growth 蛭石+根瘤菌 Vermiculite + Rhizobia 4.98±0.77 a 0.73±0.13 a 叶色嫩绿,生长正常 light green leaf,normal growth 石英砂+营养液 Quartz sand+Nutrient 3.38±0.33 b 0.75±0.08 a 叶色嫩绿,生长正常 light green leaf,normal growth 蛭石+营养液 Vermiculite +Nutrient 4.76±0.88 a 0.73±0.11 a 叶色嫩绿,生长正常 light green leaf,normal growth 石英砂CK Quartz sand CK 3.20±0.72 b 0.69±0.15 ab 叶色嫩绿、偏黄,生长正常 light green and slightly yellow leaf, normal growth 蛭石CK Vermiculite CK 4.33±1.05 ab 0.60±0.12 b 叶色嫩绿、偏黄,生长正常 light green and slightly yellow leaf, normal growth 60 石英砂+根瘤菌Quartz sand + Rhizobia 5.01±1.13 ab 1.28±0.07 a 叶色绿,植株壮实 green and strong 蛭石+根瘤菌 Vermiculite + Rhizobia 5.45±0.70 a 1.23±0.20 ab 叶色较绿生长正常 green leaf,normal growth 石英砂+营养液 Quartz sand+Nutrient 5.16±0.78 ab 1.14±0.18 b 叶色较绿,生长正常 green leaf,normal growth 蛭石+营养液 Vermiculite +Nutrient 5.61±1.07 a 1.05±0.31 bc 叶色较绿,植株细长 green and slender 石英砂CK Quartz sand CK 4.52±0.83 ab 0.83±0.11 c 叶黄化,出现掉叶现象 yellowing and leaf shedding 蛭石CK Vermiculite CK 4.86±1.20 ab 0.71±0.14 c 叶黄化、叶缘出现褐斑,掉叶 yellowing and leaf shedding,foxiness 90 石英砂+根瘤菌Quartz sand + Rhizobia 10.1±0.65 a 2.14±0.17a 叶色浓绿,生长旺盛 dark green and grow vigorously 蛭石+根瘤菌 Vermiculite + Rhizobia 9.23±0.48 ab 1.60±0.05 bc 叶色较绿,植株细长 green and slender 石英砂+营养液 Quartz sand+Nutrient 8.18±0.58 b 1.67±0.11 b 叶色绿,生长正常 green leaf,normal growth 蛭石+营养液 Vermiculite +Nutrient 7.93±0.57 c 1.44±0.05 c 叶色黄绿,生长正常 light green and slightly yellow leaf ,normal growth 石英砂CK Quartz sand CK 全株枯黄,生长停滞 vegetative chlorosis,stop growing 蛭石CK Vermiculite CK 全株枯黄,生长停滞 vegetative chlorosis,stop growing 注: 不同字母表示差异达显著水平(P<0.05)。Note: Different letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level.Table 1. Growth of seedlings of Paraserianthes falcataria
-
对不同试验处理幼苗在苗龄90 d时的苗高和地径进行方差分析(表2)和生长量柱状图比较分析(图2)。方差分析结果(表2)表明,4种不同试验处理间的苗高和地径差异均达到极显著水平(P<0.01)。进一步进行多重比较,结果(图2-B、C)表明,石英砂+根瘤菌的苗高显著优于施营养液的2个处理(P<0.01),其他3个处理间的苗高差异不显著;石英砂+根瘤菌的地径与其他3个处理间差异达到极显著水平(P<0.001),蛭石+根瘤菌的地径与2个施营养液处理间差异均不显著,而石英砂+施营养液的地径与蛭石+施营养液的处理间达到显著水平(P<0.05)。
性状Trait 自由度Freedom 平方和Squares 均方Mean square F值F value P 苗高Seedling height 3 14.102 5 4.700 8 7.93 0.001 8 地径Ground diameter 3 1.002 1 0.334 1 19.24 <0.000 1 Table 2. Variance analysis of seedling height and ground diameter of different treatments

Figure 2. Histogram of seedling height and ground diameter at 90 d for different experimental treatments
通过90 d接种处理与施营养液处理生长效应量化对比分析(表3),石英砂基质中接种处理的苗高和地径分别达10.10 cm和2.14 mm,优于同种基质施加营养液的生长效果,其中苗高比施营养液处理提高9.4%,地径提高33.8%,说明接种对地径的促生作用大于苗高。由图2-A可见,接种处理的幼苗枝叶浓绿、健壮,表现出旺盛的生长态势;蛭石基质中接种处理的苗高和地径分别为8.18 cm和1.67 mm,比施营养液处理提高3.2%和16.0%,但该基质中的幼苗表现为地径生长较慢、叶色黄绿、植株纤细、枝叶稀疏的状态。
性状Trait 石英砂基质Quartz sand 蛭石基质Vermiculite 接种Inoculation 施营养液Nutrient application 接种/施营养液高 %Inoculation/nutrient application % 接种Inoculation 施营养液Nutrient application 接种/施营养液高 %Inoculation/nutrient application % 苗高/cmSeedling height 10.10 a 8.18 bc 9.4 9.23 ab 7.93 c 3.2 地径/mmGround diameter 2.14 a 1.67 b 33.8 1.60 bc 1.44 c 16.0 注: 表中同行不同字母表示差异达显著水平(P<0.05)。Note: Different letters indicate significant difference at 0.05 level.Table 3. Comparison of the growth effect of inoculation and nutrient application treatments
-
根瘤菌与多数豆科植物形成的结瘤共生体能显著增加土壤有机碳、速效氮和全氮含量,减少磷肥、钾肥的施用量[14],具有典型的肥力岛效应[15]。根瘤菌的接种及其在生产上的应用研究在花生(Arachis hypogaea )[16]、大豆(Glycine max)[17]、苜蓿(Medicago sativa )[18]等蝶形花亚科的农作物和牧草中最为成熟,木本豆科植物已有相关研究结果也表明[10,19-20],相思类树种、格木(Erythrophleum fordii)、银合欢(Leucaena glauca)、降香黄檀(Dalbergia odorifera)等回接高效根瘤菌菌株后,植株的株高、干质量及总氮量分别比对照植株高70%~320%、130%~1 580%、130%~1 480%,其共生体使土壤全氮量提高 21.4%~31.6%,土壤有机质提高31.0%~38.7%,土壤磷酸酶活性提高23.4%~34.7%,且固氮作用还能增加植物对磷、钾元素的吸收和积累。本研究在实验室控肥控杂菌条件下实证了南洋楹芽苗接种根瘤菌后,在2种基质中全程只浇纯净水幼苗也能正常生长,且苗龄90 d的苗高和地径达到8.18~10.10 cm和1.67~2.14 mm,分别比对应基质中施营养液处理提高3.2%~9.4%和16.0%~33.8%。可见,根瘤菌为南洋楹幼苗生长提供的以氮元素为主的必需养分元素比施加的营养液更加高效以及更加易于幼苗直接吸收利用,对南洋楹幼苗生长特别是苗期地径生长具有明显促进作用。
黄维南等[21]对南洋楹的固氮结瘤研究发现,田间条件下接种根瘤菌18 d的南洋楹幼苗开始着生根瘤,苗木初期生长缓苗,2个月后植物迅速生长;李东等[22]通过滤纸斜面半封闭管观测刺槐接种根瘤菌发现,苗龄13~15 d可见圆形瘤体,苗龄30~40 d根瘤数量最多、苗龄60 d根瘤发育稳定。本研究结果表明南洋楹芽苗从种植到苗龄30 d时,不同试验处理及对照组合均能正常生长,苗高的差异仅体现于不同育苗基质间,与是否接种和施营养液相关性不大,其生长所需的物质和能量基本由子叶贮藏和自身光合作用提供。接种处理苗木在苗龄30 d之前根瘤菌的效应表现不明显,在苗龄30~60 d苗高和地径生长速度逐渐加快,在苗龄60~90 d出现生长高峰期,可推测接种处理的苗木在苗龄30 d之后开始结瘤固氮,且随着苗龄的增长,根瘤促生效应逐渐增强。在苗龄90 d后苗木生长情况及根瘤菌的作用周期还有待进一步观测。
为精确考察根瘤菌对南洋楹幼苗生长的影响,本研究采用了易于灭菌且成分稳定的2种不同理化特性的材料石英砂和蛭石[23]作为育苗基质。结果表明,苗龄30~60 d时,蛭石+根瘤菌处理的苗高优于石英砂+根瘤菌处理的,苗龄60~90 d时石英砂+根瘤菌处理的苗高迅速生长最终苗高生长量均跃居第一位;石英砂+根瘤菌处理的地径始终优于蛭石+根瘤菌处理的,苗龄90 d时差异达到极显著水平(P<0.001)。由于蛭石基质的保水性较好,质地柔软疏松,有利于南洋楹幼苗早期的根系发育和苗高生长,但后期吸水膨胀后蛭石基质的孔隙度减小、pH值中性偏碱、铁离子游离,不利于喜中性偏酸环境的南洋楹生长,造成植株纤细、叶色黄绿,同时也不利于好氧的根瘤菌生长发育;而石英砂基质质地稳定、疏松透气、pH值中性偏酸,根瘤菌可持续稳定发挥促生效应。可见,根瘤菌对于生长基质具有较强的选择性以及和寄主的互惠共生性,在不适宜的基质中南洋楹幼苗生长较弱影响根瘤的生长发育,根瘤固氮作用减弱,幼苗生长同时也受到影响。但本试验中仅采用单一基质苗进行初步研究探索,后期将采用不同类型混合基质开展试验,为根瘤菌促生效应的发挥创造良好的基质环境。
-
本研究发现,根瘤菌能为南洋楹幼苗生长提供以氮元素为主的必需养分元素,幼苗接种根瘤菌后,在苗龄30~60 d时,苗高和地径生长速度逐渐加快;苗龄60~90 d时,出现生长高峰期;苗龄90 d时,苗高和地径达到8.18~10.10 cm和1.67~2.14 mm,分别比对应基质中施营养液处理提高3.2%~9.4%和16.0%~33.8%。可见,根瘤菌对南洋楹幼苗生长特别是苗期地径生长具有明显促进作用,其促生效应随苗龄的增长而增强,质地稳定、疏松透气、pH值中性偏酸的基质环境更有利于根瘤菌促生效应的发挥。







 DownLoad:
DownLoad: