-
火龙果(Hylocereus undulatus)是热带地区重要经济作物,土壤肥力与线虫病害会严重影响火龙果产量和品质。土壤的基础是土壤肥力,土壤肥力反映了土壤为植物提供适宜条件的能力[1-2]。土壤肥力会影响火龙果的生长发育及营养品质 [3-4]。此外,线虫也会影响火龙果生长发育。其中,根结线虫(Meloidogyne spp.)是一类重要的植物寄生线虫,严重威胁世界各地蔬菜、果树及其他农作物的生产,每年在全球范围内造成的经济损失达到数十亿美元[5]。海南属于热带、亚热带地区,病虫害多,根结线虫危害就是其中之一,严重影响了火龙果的产量及品质[6]。目前,国内对火龙果的研究主要集中在温度、光照等栽培生物学特性方面[7-10],关于土壤养分肥力和根结线虫防治方面的研究鲜见报道。因此,笔者对海南火龙果主产区果园的土壤样品进行收集,并对收集到的204份火龙果土样肥力和线虫数量进行了调查分析,旨在为海南火龙果园土壤的改良、培肥和火龙果的高产、稳产、优质生产提供基础数据和理论支持。
-
根据火龙果的生长周期和线虫的生活习性,于2021年7—8月进行调查采样,在海南多个地区的火龙果园进行了火龙果土壤样品采集,共调查了11个地区68家火龙果园(本次调研未涉及五指山、琼中以及三沙市南海区域,因为上述区域火龙果种植面积较小,并非火龙果主产区)。分别对各个地区采集的土样进行编号,其中A: 海南省万宁市北大镇下三村柚树村3份、海南省万宁市后安镇田墩村3份;B: 海南省三亚市天涯区21份;C: 海南省陵水县12份;D: 海南省琼海市大路镇9份;E:海南省乐东县尖峰镇24份、海南省乐东县利国镇15份、海南省乐东县千家镇12份、海南省乐东县抱由镇9份、海南省乐东县抱由镇3份;F:海南省海口市美兰区6份;G:海南省儋州市9份;H:海南省临高县博厚镇6份;I:海南省澄迈县老城镇3份、海南省澄迈县中兴镇3份;J:海南省昌江县叉河镇老羊地村3份、海南省昌江县海尾镇双塘村3份;K:海南省东方市大田镇30份、海南省东方市三家镇9份、海南省东方市板桥镇15份、海南省东方市新龙镇3份、海南省东方市八所镇3份,共计204份。按照调查方案开展,每个火龙果种植园依据果园面积,选取具有代表整个果园植株生长情况的3个位点,每个位点采用5点取样法用土钻钻取0~20 cm表层混合土样1 kg(剔除石块等杂质)。土壤样品分成2份,1份风干后过2 mm筛(用过0.25 mm筛的土测有机质),用以测定土壤基础养分含量;另1份存放在4 ℃冰箱内,7 d内进行根结线虫的分离及数量统计。
-
土壤养分测定方法参照文献[11]的方法进行:pH值通过电位法测定;有机质测定采用重铬酸钾容量法;碱解氮测定采用碱解扩散法;有效磷测定采用酸性氟化铵浸提法;速效钾采用乙酸铵浸提法;交换性钙、镁采用原子吸收分光光度法测定。
-
根结线虫J2采用改良的蔗糖离心漂浮法[12]分离。吸取1mL线虫悬浮液,利用体式显微镜统计根结线虫J2数量,1个样品重复3次,取平均值。通过测定土壤含水率(105 ℃烘干至恒重),计算根结线虫J2丰度(每100 g干土的根结线虫条数)。利用文献[13]的方法测定土壤含水率。
-
采用模糊综合评判法对海南岛的火龙果园土壤肥力状况进行综合评价[14]。隶属度函数可以分成2种类型,即S型(正相关型)隶属度函数和抛物线型隶属度函数。它是按照土壤肥力质量指标对农作物产量和品质的效应曲线来划分的。S型隶属度函数是指在一定范围内评价元素指标与作物生长效果呈正相关,但是达到一定临界值后效应趋于稳定,有机质、碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾、交换性钙、交换性镁均属于公式1类型[14]。抛物线型隶属度函数是指在一定范围内作物生长效应最好,但是超出这个范围时作物生长效果变差,土壤pH值属于公式2类型。
式中,f(x)为隶属函数,x为土壤属性测定值,x1、x2依次为2个转折点。
式中,f(x)为隶属函数,x为土壤属性测定值,x1、x2、x3、x4依次为4个转折点。
结合实际情况,确定了隶属度函数曲线转折点处各指标的对应值。将各土壤肥力关键指标实际测的数值和转折点的取值带进对应的函数表达式,就得到各土壤肥力指标的隶属度值Ni。运用各指标间相关系数来确定权重系数。利用加权综合法对土壤综合肥力指数进行计算[15],计算公式为:
式中,IFI代表综合肥力指数;Wi代表第i种养分指标的权重系数; Ni代表第i种养分指标的隶属度值。土壤综合肥力指数范围为 0~1.0。其中0~0.2为极低肥力、0.2~0.4为低肥力、0.4~0.6 为中等肥力、0.6~0.8 为高肥力、0.8~1.0为极高肥力[16]。
-
土壤肥力指标采用SPSS25.0进行描述性统计分析,各指标等级所占比例采用Excel2010进行分析,各养分指标及根结线虫数量间的相关性分析采用Origin进行分析。
-
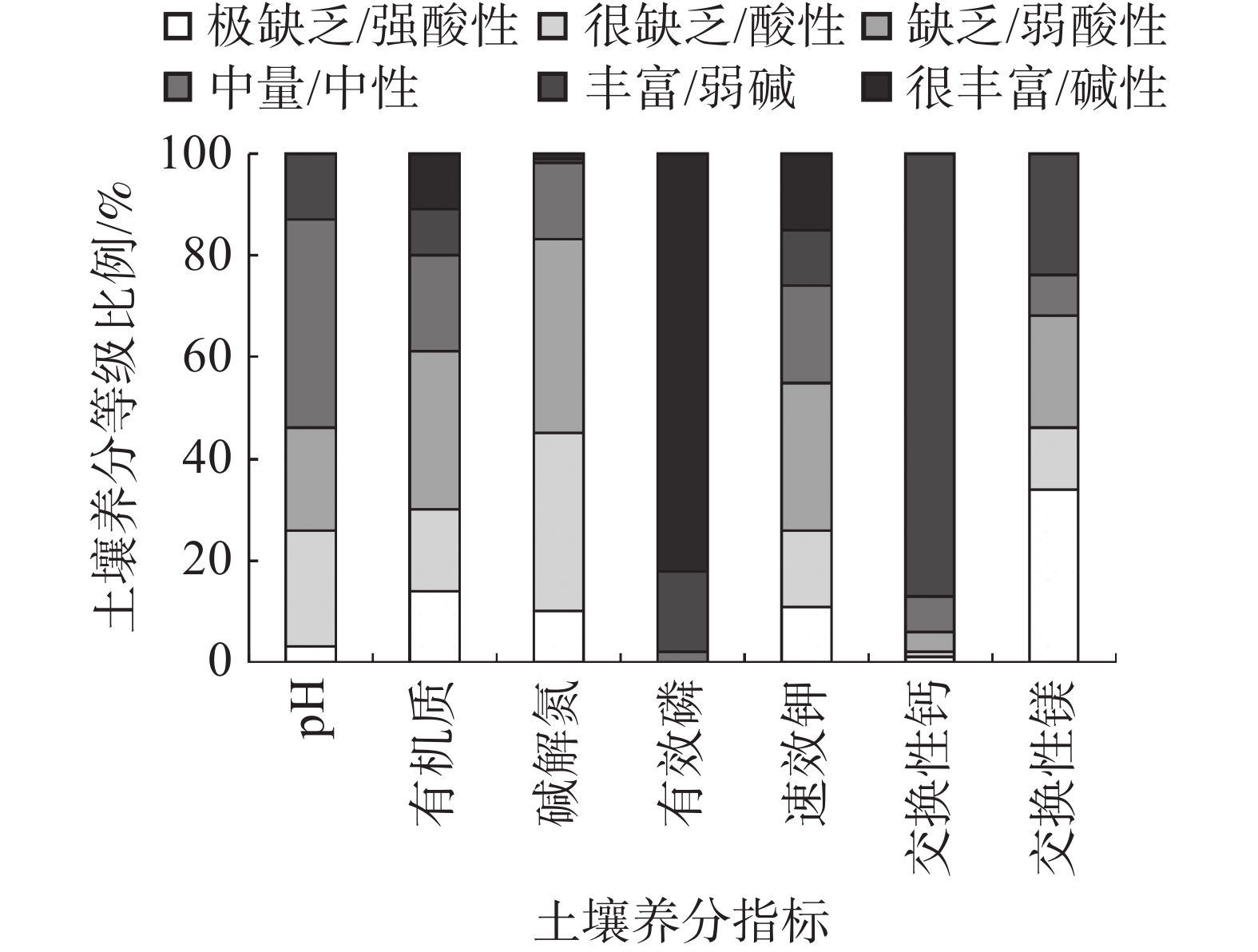
以全国第2次土壤普查标准[17]作为参考,对海南岛火龙果园土壤养分含量进行描述性统计分析及养分含量分级(表1、图1)。可以看出,海南岛火龙果园的pH变化范围是3.5~7.9,平均值为6.4,变异系数为 16.3%。大部分土壤pH处于酸性/弱酸性/中性水平,土壤pH为中性(6.5~7.5)的果园最多,占41%;其次是酸性(4.5~5.5)和弱酸性,分别占比23%和20%。海南火龙果园有机质含量的变化范围是1.9~75.5 g·kg−1,平均值为19.9 g·kg−1,变异系数为77.21%;有61%的土样有机质含量处于较为缺乏状态(小于20 g·kg−1),有19%的土样有机质含量是中量,仅20%的土样有机质含量为丰富及以上等级。因此,从整体上看,海南岛火龙果园土壤有机质含量较为缺乏。海南岛火龙果园的碱解氮含量范围是14.0~203.0 mg·kg−1,平均值是63.9 mg·kg−1,变异系数为47.14%;土壤碱解氮是缺乏/极缺/很缺等级的占样品总数83%,而中量、丰富及很丰富水平的土壤样品仅有17%,说明海南岛火龙果园土壤碱解氮含量处于缺乏状态。土壤有效磷含量为 7.3~355.3 mg·kg−1,其平均值是95.8 mg·kg−1,变异系数为75.64%;有81%的土样有效磷含量是很丰富,有16%的土样有效磷含量是丰富,说明海南岛大多数火龙果园土壤有效磷含量是丰富及以上等级。海南岛火龙果园土壤速效钾含量为 13.2~741.4 mg·kg−1,速效钾含量平均为124.9 mg·kg−1,变异系数为105.9%;土壤速效钾处于缺乏及以下水平的占总样品数目的55%,中量水平占比19%,丰富和很丰富水平占比26%,说明海南岛火龙果果园土壤速效钾含量较为缺乏。土壤交换性钙变幅为 168.0~9756.0 mg·kg−1,平均含量为 2 802.7 mg·kg−1,变异系数为 66.3%,87%的火龙果园土样交换性钙处于丰富水平。土壤交换性镁含量在4.8~2126.4 mg·kg−1之间,平均值为213.2 mg·kg−1,变异系数达到162.0%,68%的火龙果园土样交换性镁处于缺乏及以下水平。
土壤指标 最大值 最小值 极差 均值 标准差 变异系数 等级 pH 7.9 3.5 4.4 6.4 1.0 16.3 弱酸性 有机质/(g·kg−1) 75.5 1.9 73.6 19.9 15.5 77.2 缺乏 碱解氮/(mg·kg−1) 203.0 14.0 189.0 63.9 30.1 47.1 缺乏 有效磷/(mg·kg−1) 355.3 7.3 348.0 95.8 72.7 75.6 很丰富 速效钾 /(mg·kg−1) 741.4 13.2 728.2 124.9 132.3 105.9 中量 交换性钙/(mg·kg−1) 9756.0 168.0 9588.0 2802.7 1860.2 66.3 丰富 交换性镁/(mg·kg−1) 2126.4 4.8 2121.6 213.2 345.2 162.0 中量 -
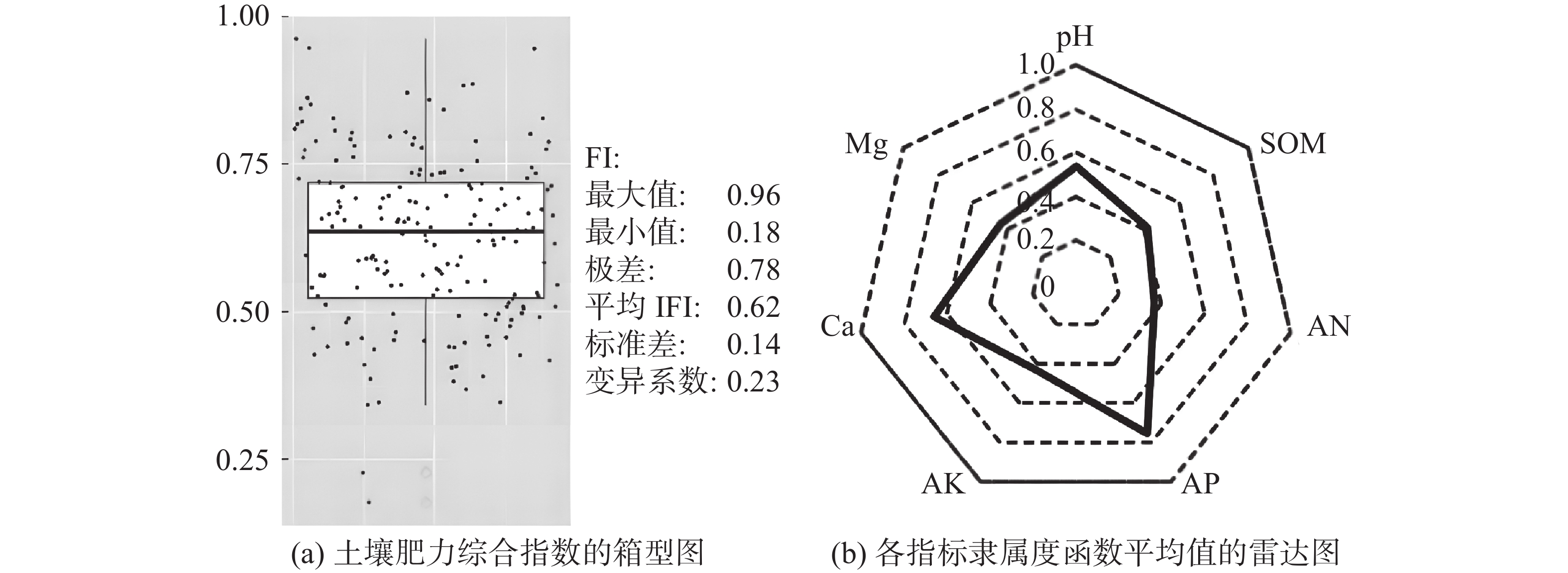
对204个样点的土壤综合肥力指数进行描述性统计分析得出,海南岛火龙果园IFI值在0.18~0.96 之间,平均值为0.62,肥力处于高水平,变异系数为0.23,属于中等变异。用各指标对应的平均隶属度制作雷达图反映各指标的状态及研究区整体肥力水平(图2)。根据雷达图的几何含义,坐标轴上的点越靠近原点,代表它所反映的指标的肥力水平越低,反之越高。从图中可以看出碱解氮隶属度函数值最小,仅约0.4;有机质、速效钾、交换性镁、pH次之;有效磷和交换性钙隶属度值最大。土壤隶属度函数值大小依次为:有效磷、交换性钙、pH、交换性镁、速效钾、有机质、碱解氮。
-
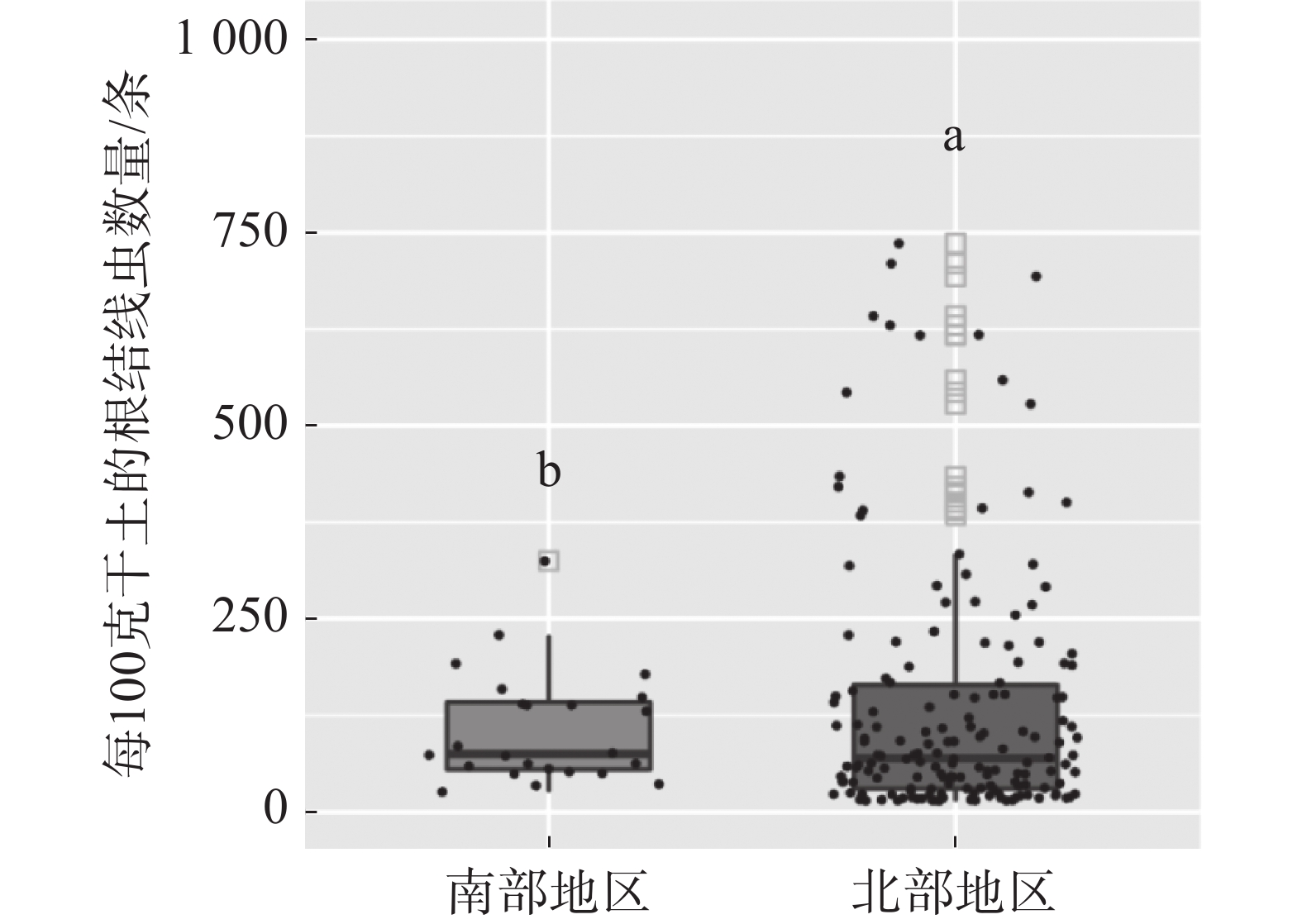
从海南岛参与调研的各地区根结线虫J2数量结果可以发现(表2),万宁和三亚的火龙果园土壤中的根结线虫比较严重,而东方和昌江火龙果园根结线虫情况比较轻,其余各市轻重情况从重到轻依序为陵水、琼海、乐东、海口、儋州、临高、澄迈。整体上海南岛北部地区(海口、临高、澄迈、琼海、儋州、昌江)火龙果果园根结线虫J2数量低于海南岛南部地区(三亚、陵水、万宁、乐东、东方)果园根结线虫数量。此外,海南岛各火龙果果园根结线虫J2数量差异较大,数量较少每100 g干土仅有14条,而较多的高达736条(图3)。
地区 采样点数量 每100 g干土的根结线虫数/条 万宁 6 290.1±100.6 a 三亚 21 275.9±46.1 ab 陵水 12 160.5±45.2 abc 琼海 9 141.4±26.2 abc 乐东 63 138.5±20.3 abc 海口 6 136.7±94.6 abc 儋州 9 119.7±29.4 abc 临高 6 98.7±19.6 abc 澄迈 6 88.1±45.2 bc 昌江 6 65.5±13.8 c 东方 60 63.9±8.4 c 注:不同小写字母表示各处理间在0.05水平差异显著。 -
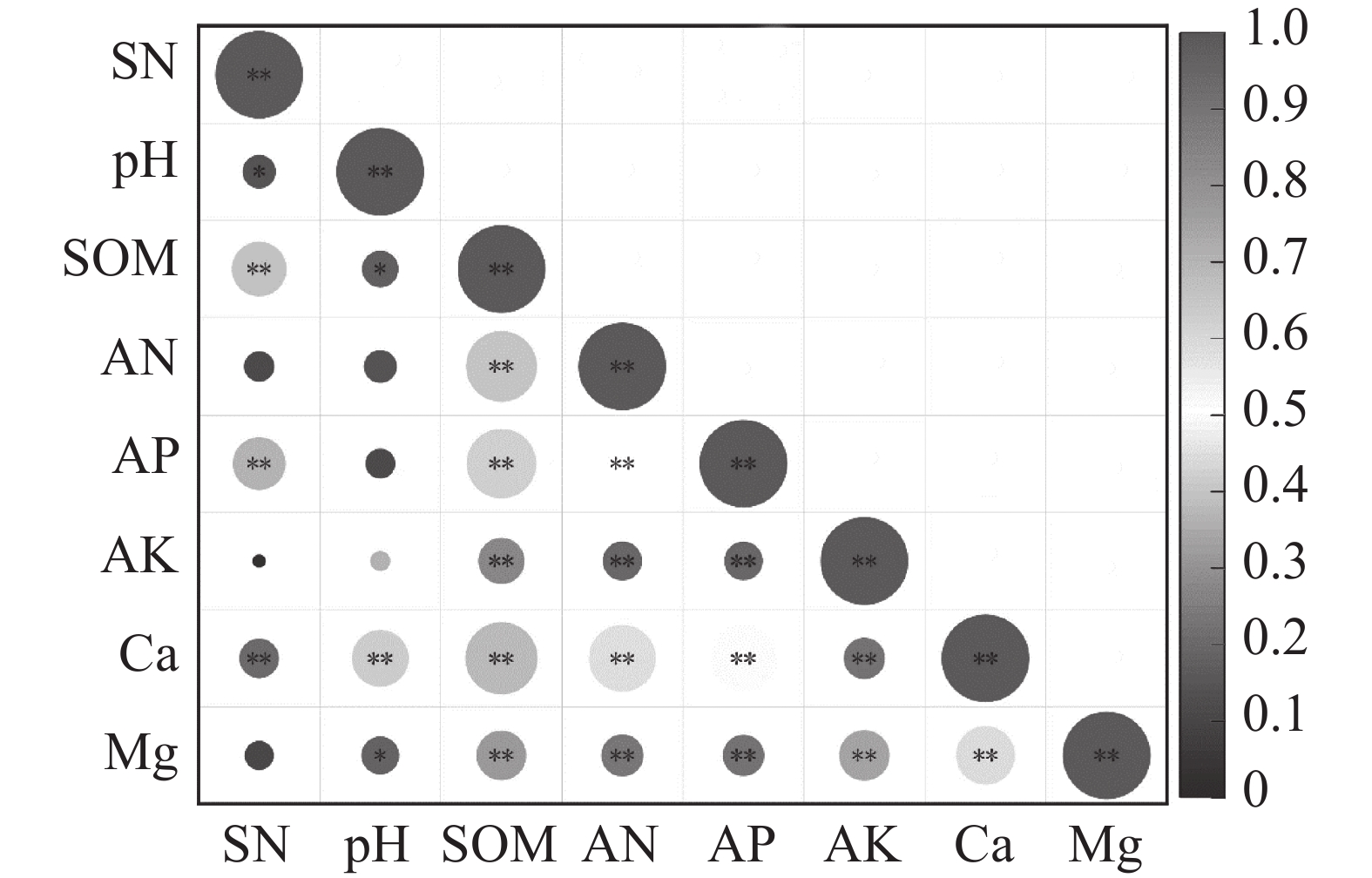
从表3和图4可以看出,土壤pH与有机质、交换性钙、镁含量呈显著正相关,土壤有机质与碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾、交换性钙、镁呈显著正相关。碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾、交换性钙、镁含量这5个指标两两之间呈显著正相关。土壤pH、有机质含量、有效磷、交换性钙与根结线虫数量呈正相关;土壤碱解氮、速效钾、交换性镁与根结线虫数量无相关性。
指标 SN pH SOM AN AP AK Ca Mg SN 1.00 pH 0.15 1.00 SOM 0.39 0.17 1.00 AN 0.12 0.14 0.66 1.00 AP 0.36 0.12 0.63 0.50 1.00 AK 0.02 0.05 0.28 0.20 0.19 1.00 Ca 0.21 0.42 0.68 0.58 0.52 0.22 1.00 Mg 0.11 0.19 0.32 0.23 0.22 0.34 0.45 1.00 -
火龙果种植最适宜的土壤pH值范围为6.0~7.5[18]。本研究中采集的土壤样品pH平均值为6.4,基本处于最宜生长的范围。然而,从具体分布结果看,海南岛火龙果园46%的土壤pH为酸性至强酸性,土壤偏酸不利于火龙果植株根系的生长[19],从而降低产量和品质,这可能与海南本地的红壤、砖红壤等土壤种类有关,而且果园管理过程中可能缺乏土壤酸碱改良剂的使用。同时,值得注意的是,有部分果园土壤pH值甚至达到7.9,表明部分火龙果果园管理过程中已经注意到土壤酸化带来的危害,做了相应的土壤改良,然而改良过程中缺乏经验,可能使用了过量的改良剂。
柴冠群等[20]的研究结果表明,贵州火龙果园土壤有机质含量为25.7 g·kg−1,远高于海南岛火龙果园土壤有机质含量(19.9 g·kg−1)。本次参调的火龙果园中,有61%的果园土壤有机质含量小于20 g·kg−1,可见海南岛大多数火龙果园有机质含量处于缺乏状态。这可能是与海南岛的气候有关,热带气候下,自然土本身在强烈的生物作用下有机质分解快,含量低,加之果农施有机肥少,所以有机质含量低[21]。火龙果是高产出经济水果之一,特别是海南火龙果一年采收多季,有机肥对火龙果品质至关重要,目前,各果园的有机质含量参差不齐,但总体水平较低,应注重施用有机肥,培肥土壤[22]。
研究表明,每收获100 kg的火龙果会从土壤中带走约225 g纯氮[23]。笔者调研中发现,海南岛火龙果果园产量5 250~6 000 kg·hm−2,可见火龙果对氮的需求量非常高。因此,在种植火龙果时,合理把控氮肥用量,保证土壤中氮含量丰富,并定时对土壤中氮元素含量进行检测是十分有必要的。碱解氮是土壤中有效氮的一个常用指标[24],碱解氮的含量反应了土壤的供氮能力。此次测定结果中,海南参与调研采样的土壤的碱解氮含量绝大部分处于缺乏、很缺甚至极缺的水平,占样品总数的83%。一方面可能由于海南岛降雨量较大,氮肥可能通过淋洗、挥发的方式损失,另一方面可能因为作物不间断生产,对氮素的需求较高所致,从而造成土壤氮含量较低。因此,未来果园在施用化肥的过程中,建议在土壤检测的基础上,及时补充氮肥。
海南岛火龙果园土壤有效磷含量为 7.3~355.3 mg·kg−1,其平均值是95.9 mg·kg−1,变异系数达到75.6%,有81%的土壤中的有效磷含量是很丰富,有16%的土壤中的有效磷含量是丰富。因此,从整体上看,海南岛火龙果园土壤有效磷含量很丰富。有研究表明,有效磷含量大于20 mg·kg−1时,作物便能从土壤中获取充足的磷[25]。本次调研的果园土壤中,有效磷大于20 mg·kg−1的样本有97%,大多数果园有效磷含量均处于较高水平。出现这种现象主要与果农的施肥观念和施肥习惯有很大的关系,果农普遍认为要提高农产品的产量和品质只能通过大量施肥来改善,于是在实际的农业生产中就大量投入化肥。化肥投入往往采用平衡肥,然而作物对氮磷钾的需求量并不一样,因此使得过量的磷素累积在土壤中,不仅造成了肥料的浪费,还会出现潜在的环境风险。
土壤中速效钾为土壤全钾中能够被当季植物直接吸收利用的部分[26]。海南岛火龙果园土壤速效钾含量为13.2~741.4 mg·kg−1,速效钾含量平均为124.8 mg·kg−1,变异系数达到105.9%。土壤速效钾处于缺乏及以下水平的占总样品数目的55%,因此,从整体上看,海南岛火龙果果园土壤速效钾含量较为缺乏。火龙果属于高钾作物,对钾素的需求远远超过对氮磷的需求,因此,应重视对火龙果园钾元素的补充,增加钾肥的施用。
钙元素在植物体内也能够起到增强抗逆能力,增加植物对盐碱、干旱、低温等逆境的抗性,同时增强植株抗病虫能力[27]。土壤如果缺钙,则植物生长发育受到限制,会使一些作物的品质下降,甚至会出现裂果等现象,严重的导致死亡。此次测定结果中,海南参与调研采样的火龙果园里有87%的果园土壤交换性钙处于丰富水平,说明大多数果园交换性钙含量丰富,土壤供钙能力较强。这可能是因为果农担心海南土壤普遍酸化以及受降雨淋洗导致的土壤钙缺乏,在生产中补充了较多的以钙为主要形态的酸碱调理剂。因此,在火龙果生产管理中要合理把握钙肥的施用量。
热带经济作物对镁的需求量较高,作物缺镁时,容易出现果实品质下降[28]。白由路等[29]对我国土壤有效镁含量的研究发现,我国54%的土壤因为有效镁含量低而需要不同程度补充镁肥,特别是我国南方酸性土壤地区,其原因是该地区湿热多雨以及不合理施用化肥导致土壤酸化,加剧了土壤中镁的淋失[30]。Tong等[31]也指出,我国南方酸性土壤中镁因土壤风化强烈,大部分已淋失,因此土壤镁含量很低。此次测定结果中,土壤交换性镁含量均值为213.0 mg·kg−1,尽管该均值处于有效镁含量的中量等级,但根据各等级所占总体样本比例来看,全部样点中处于中量等级的比例仅为8%,变异系数为162.03%,在空间上表现为较强的变异性。海南火龙果园土壤交换性镁含量最低的仅有4.8 mg·kg−1,最高达到2 126.4 mg·kg−1,最大值是最小值的443倍。68%的火龙果园土壤交换性镁处于缺乏及以下水平,这可能是因为海南岛属于热带地区,气温高、雨量充沛,成土过程中矿物风化淋溶作用强烈;在灌溉水的长期浸泡下,水分渗漏导致土壤中可溶性镁淋失,造成土壤中镁含量缺乏[32]。建议在镁含量较低的土壤上,增施镁肥,为火龙果园补充镁素营养。
土壤综合肥力指数的结果表明,海南岛火龙果园土壤综合肥力数值在0.2~1.0之间,平均值为0.7,整体肥力处于较高水平。土壤隶属度较高的为有效磷、交换性钙、pH,较低的为交换性镁、速效钾、有机质、碱解氮,因此未来应该整体控制磷肥和钙肥的投入,增加氮、钾和有机肥的投入。
土壤养分相关性结果分析表明,土壤pH与土壤有机质、交换性钙、镁含量呈显著正相关,表明维持中性的pH水平有利于土壤有机质的积累,对钙、镁有效性的提高具有重要意义。土壤有机质含量与碱解氮、有效磷、速效钾、交换性钙、镁呈显著正相关,说明土壤有机质的提高,有助于提升土壤基础矿质养分的含量。调研中也发现,果园在管理过程中,土壤有机质的提高已经得到较高的重视,尽管从全国土壤有机质分级结果看仍处于较低水平,但是考虑到海南高温高湿的环境,土壤有机质本身分解快含量低的现实,果园有机质含量接近20 g·kg−1,已经是较高的水平。
-
近年来,线虫对地上植物的影响越来越受到重视,关于线虫方面的研究也越来越多。苏兰茜等[33]的研究结果表明,菠萝蜜幼苗地上部干重与土壤食细菌线虫丰度、有机质和pH呈显著正相关,而植食性线虫丰度与土壤pH、有机质、碱解氮含量和食微线虫丰度呈显著负相关,食细菌线虫丰度与土壤有机质和pH呈显著正相关。范琳娟等[26]的研究结果表明,土壤中丰度较高的植物寄生线虫,如垫刃线虫属、根结线虫属、短体线虫属等数量与土壤有效磷、速效钾含量呈正相关,与土壤pH值、有机质和铵态氮含量呈负相关,而大部分食微线虫与土壤pH值及有机质和铵态氮含量呈正相关。本研究结果表明,土壤pH、有机质含量、有效磷、交换性钙与根结线虫数量呈正相关;土壤碱解氮、速效钾、交换性镁与根结线虫数量无显著相关。其中土壤速效钾与根结线虫数量相关性结论与范琳娟等[26]的研究一致,pH、有机质与根结线虫的相关性结论与之相反。值得注意的是很多研究表明,有机质与根结线虫数量呈负相关,而本研究的数据结果与之相反,可能与各果园防控条件有关。本研究中还得出海南岛北部地区火龙果果园根结线虫数量显著低于南部地区,表明南部地区果园更容易受到根结线虫的侵害,这可能与南部地区整体气候湿热,雨水多,适宜线虫的发育繁殖有关,因此,在日常管理中南部地区更应加强植物病原线虫的防治。
A survey of soil fertility and number of root-knot nematodes in dragon fruit orchards in Hainan
DOI: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230034
- Received Date: 2023-03-11
- Accepted Date: 2023-05-11
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-05-05
- Available Online: 2023-05-17
- Publish Date: 2024-03-20
-
Key words:
- Hainan /
- dragon fruit orchard /
- soil fertility /
- number of root knot nematodes
Abstract: To clarify soil fertility and damage of root-knot nematodes in dragon fruit orchards in Hainan Island, a total of 186 soil samples were collected from 62 dragon fruit orchards, and the soil contents of nutrient elements such as nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium and magnesium, and the number of root-knot nematodes in the orchards were analyzed. The comprehensive soil fertility in the orchards was evaluated by using the fuzzy comprehensive evaluation method, and the correlation between the number of root-knot nematodes and soil nutrients was analyzed. The results showed that the average soil pH was 6.4 in the dragon fruit orchards, with the soil being generally neutral or weakly acidic in the orchards. The average soil content was 19.9 g/kg for organic matter, 63.9 mg/kg for alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen and 95.8mg /kg for available potassium content, all of which were in the state of deficiency. The soil contents of available phosphorus and exchangeable calcium were abundant or above, and the soil exchangeable magnesium content was in the medium level. The soil pH was positively correlated with the soil contents of organic matter, exchangeable calcium and magnesium, indicating that a neutral soil pH level was conducive to the accumulation of organic matter in the soil and had important significance for the availability of calcium and magnesium. The soil content of organic matter was positively correlated with the soil contents of alkali-hydrolyzed nitrogen, available phosphorus, available potassium, exchangeable calcium and magnesium, which indicated that the increase of soil organic matter would help to increase the contents of soil basic mineral nutrients. The number of root-knot nematodes in the dragon fruit orchards varied greatly. The maximum number of second-stage juveniles (J2) of root-knot nematodes in the orchards was 736 per 100 g dry soil, while the minimum number of the J2 root-knot nematodes was only 14 per 100 g dry soil. The incidence of the root-knot nematodes was different between the orchards in the north and the south of Hainan Island. On the whole, the number of the root-knot nematodes in the dragon fruit orchards was lower in the north than that in the south of Hainan Island. The soil pH and the soil contents of organic matter, available phosphorus and exchangeable calcium were positively correlated with the number of the root-knot nematodes in the soil. The findings of this survey showed that the comprehensive soil fertility index of the dragon fruit orchards in Hainan Island is at a high level. The changes of the soil pH and the contents of organic matter, available phosphorus and exchangeable calcium might have some reference for integrated management of the root knot nematodes in the dragon fruit orchards in Hainan.
| Citation: | LI Juan, GAO Xiang, CHEN Siru, WU Jiamin, GAO Wei, ZHANG Hong, RUAN Yunze. A survey of soil fertility and number of root-knot nematodes in dragon fruit orchards in Hainan[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2024, 15(2): 182-189. doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230034 |










 DownLoad:
DownLoad: