-
荔枝(Litchi chinensis)是无患子科荔枝属热带、亚热带常绿果树,起源于中国云南[1],是“南国四大果品”之一。我国荔枝年产量占世界总产量的70%以上[2],‘妃子笑’荔枝属于中早熟品种,是海南省的主栽品种之一,具有较高的商业价值,然而‘妃子笑’荔枝果实在成熟期内外品质发育不一致,果皮完全转红时果实糖含量下降,即“退糖”[3],这严重影响了果实品质,降低了‘妃子笑’荔枝的商品价值。
糖是影响果实内在品质的关键因素之一,‘妃子笑’荔枝主要积累果糖、葡萄糖和蔗糖,其中以己糖(果糖、葡萄糖)居多[4]。高等植物叶片光合作用产生的光合产物主要以蔗糖的形式[5]运输到果实中。蔗糖代谢酶在果实糖代谢中起关键作用[6],蔗糖代谢酶包括酸性转化酶(AI)和中性转化酶(NI)、蔗糖合成酶(SS)、蔗糖磷酸合成酶(SPS)。蔗糖合成酶催化果糖、UDPG与蔗糖之间的可逆反应[7],蔗糖磷酸合成酶催化蔗糖的合成,转化酶催化蔗糖水解生成果糖和葡萄糖[8]。另外,磷酸果糖激酶(PFK1)是糖酵解途径中的第二个关键酶,催化6磷酸果糖转化为1,6二磷酸果糖,之前的研究表明,叶面钙处理可能通过下调磷酸果糖激酶基因的表达从而降低其酶活性,导致糖代谢受到抑制,最终使得荔枝果实糖含量得以积累[9]。
果实衰老时细胞壁开始降解,果实硬度随之降低,呼吸增强。钙镁在果实的生长发育过程中十分重要,有研究表明钙能延缓成熟和抑制果实衰老[10],主要是通过减少果实呼吸[11]。甜樱桃果实中钙含量的提高伴随着果实呼吸速率的下降和果皮硬度的提升[12]。钙还能够维持细胞壁结构[13],减少果实的变质[14-15]。 镁是植物的必需元素,它在光合同化物从韧皮部到库组织的装载和运输中起重要作用[16],并参与叶片光合作用、碳水化合物、脂肪、蛋白质和核酸的合成[17-19]。
前期笔者所在课题组已发现,钙镁混合叶面肥可以解决荔枝“退糖”问题[20],但其机理还不清楚。本研究通过以叶面喷施0.3%CaCl2+0.3%MgCl2混合水溶液为处理,以喷清水为对照,测定果实糖含量、蔗糖代谢酶活性,旨在初步探讨钙镁叶面肥解决“退糖”问题的生理机制。
-
在海南省临高县金牌农场五队荔枝园选取10棵生长势相对一致、结果正常的‘妃子笑’荔枝树作为试验材料,该园‘妃子笑’荔枝4月初进入生理落果期,4月下旬进入果实膨大期,5月中旬进入果实成熟期[21]。
-
结合CaCl2、MgCl2用于果树叶面喷肥时的常用浓度及笔者所在课题组前期钙镁肥叶面对‘妃子笑’荔枝果实的喷施效果,本研究以叶面喷施0.3%CaCl2+0.3%MgCl2混合水溶液为处理,喷施清水为对照,单株小区,重复5次[21]。稳果时(花后35 d)开始处理,处理时间为2020年花后35、42、50 d的上午9 — 10点。
-
第1次取样时在每棵树的树冠外围中部选择5个大小相对一致、有代表性的果实作为取样参照果,每次取样时均以这5个果的大小和着色状况为参照,选取与这些高度相似的果实作为试验材料,取完样后及时放入液氮中速冻带回实验室于超低温冰箱(−80 ℃)中保存备用,取样时间为2020年花后35、42、50、56、63、69 d,取样在处理前进行。
-
快速称取0.5 g果肉放入微波炉中杀青30 s,加入5 mL 90%的乙醇充分研磨,10 000 g离心15 min,吸取上清液再加入5 mL 90%的乙醇提取一次,合并两次上清液放入90 ℃水浴锅中蒸干,蒸干后用去离子水定容至10 mL,用注射器吸取少量,经0.45 μm一次性水系针式过滤器过滤后待测。使用Waters2695高效液相色谱仪测定糖分含量,配有蒸发光散射检测器,色谱柱为Boston Green Amino Column(4.6×250 mm, 5 μm, 120 A),流动相为乙腈∶水 = 8∶2,流速为1 mL·min−1,柱温为35 ℃,进样量为10 μL[22]。标准品用色谱级葡萄糖、果糖和蔗糖(北京坛墨质检科技有限公司),流动相用色谱级乙腈(国药集团化学试剂有限公司)。蔗糖、果糖和葡萄糖已被确定为荔枝中的主要糖类[23],所以将果糖、葡萄糖和蔗糖含量之和作为可溶性糖含量。
-
果肉蔗糖合成酶分解(SS-C)和合成(SS-S)、酸性转化酶(AI)、中性转化酶(NI)、蔗糖磷酸合成酶(SPS)、磷酸果糖激酶(PFK1)活性采用酶联免疫试剂盒(江苏科特生物技术有限公司))进行测定,步骤按照试剂盒说明书进行。
-
用SAS软件对数据进行分析,用ANOVA程式进行方差分析,用t 检验对同一时期处理与对照的糖含量、蔗糖代谢酶活性进行差异显著性分析。
-
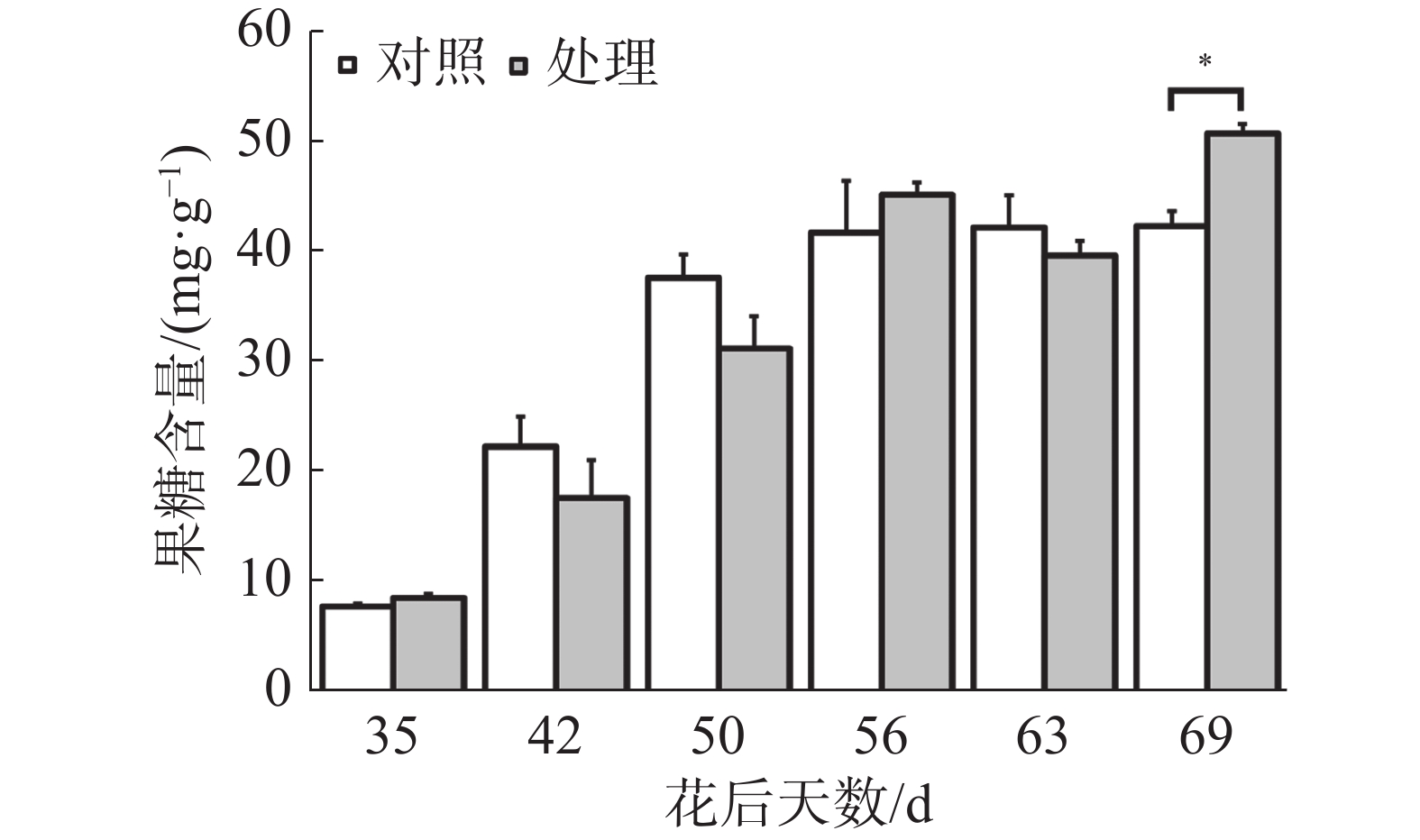
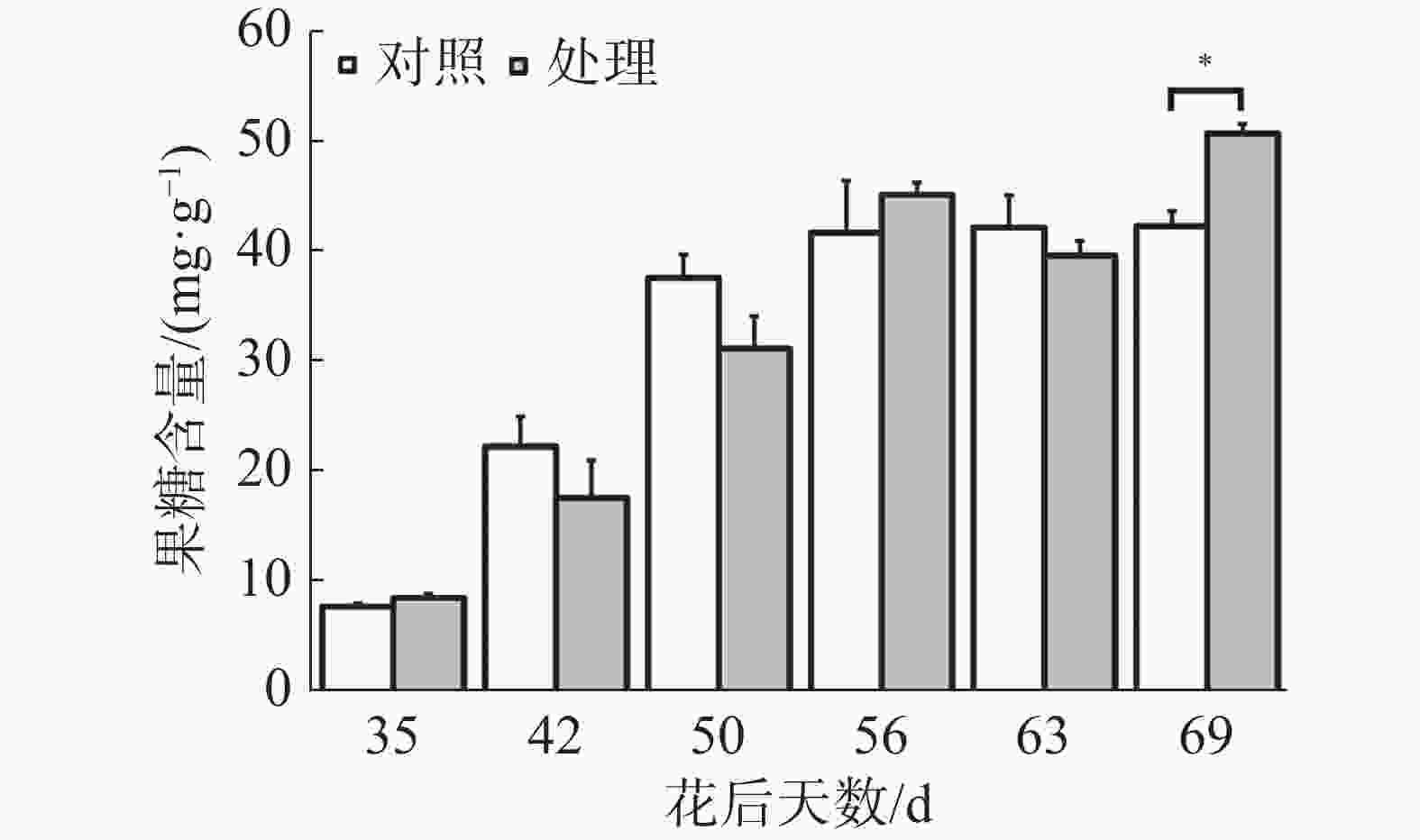
如图1所示,处理与对照果实果糖含量整体上呈现上升的趋势,在花后63 d至花后69 d对照果实果糖含量保持稳定,处理果实果糖含量显著上升,在花后69 d处理果实果糖含量显著高于对照,其余时期处理与对照均无显著差异。可见在果实生长发育过程中果糖不断积累,在成熟期处理促进了果实果糖的积累。
-
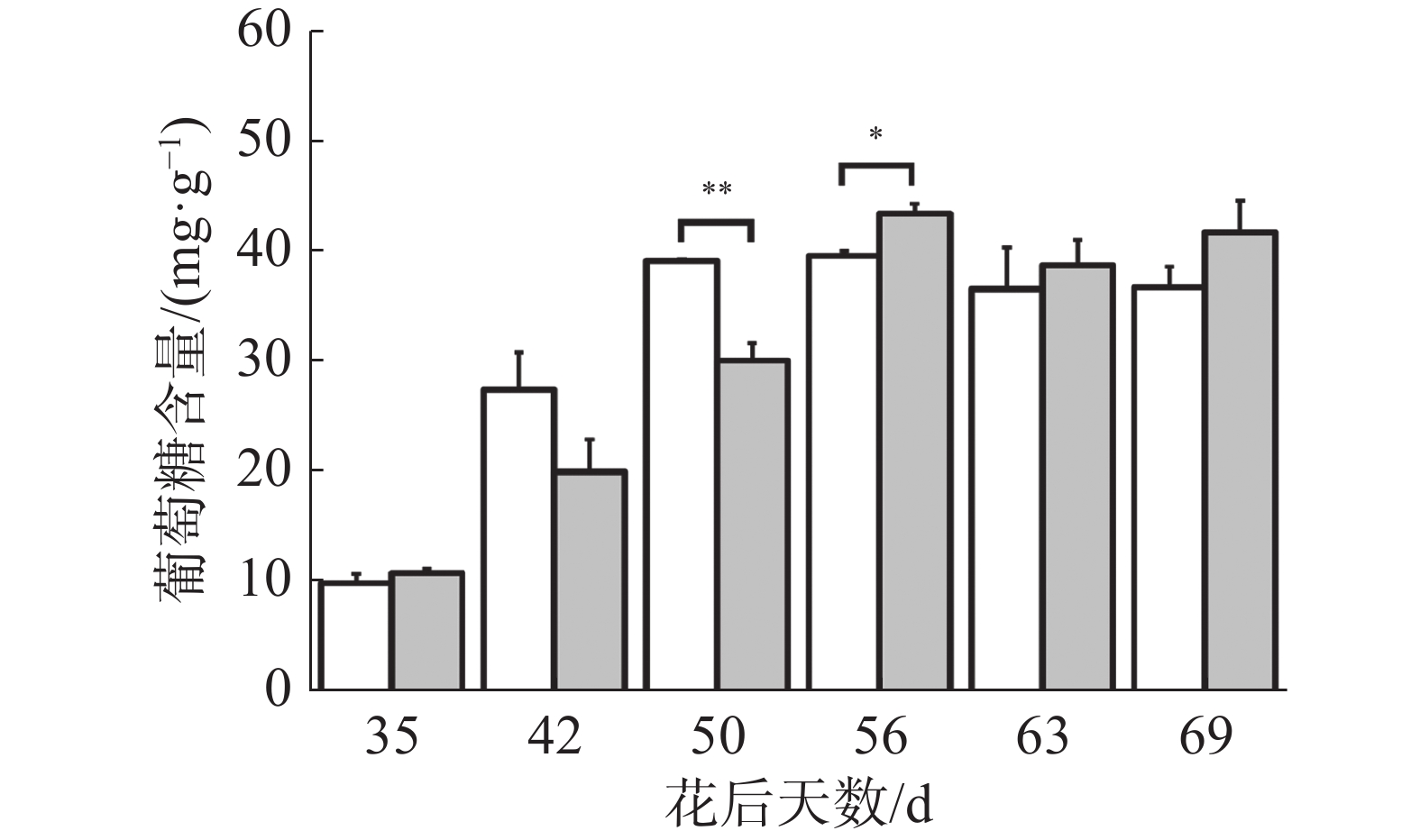
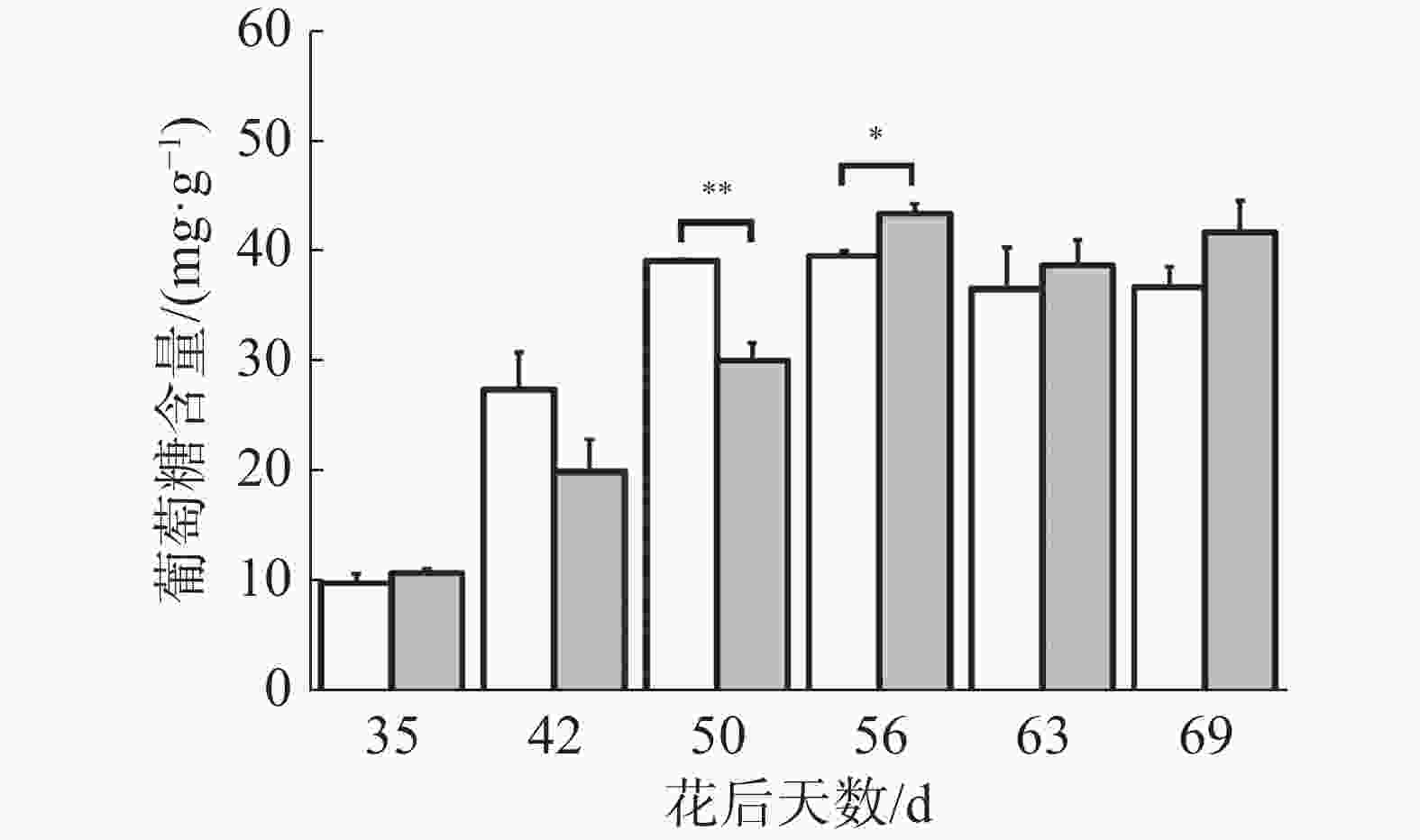
如图2所示,在花后35 d至50 d对照果实葡萄糖含量迅速上升,随后保持稳定;在花后35 d至56 d处理果实葡萄糖含量迅速上升,随后保持稳定。在花后50、56 d处理果实葡萄糖含量分别显著低于、高于对照,其余时期处理与对照均无显著差异。可见在果实生长发育前中期葡萄糖不断积累,成熟期对照果实葡萄糖含量保持稳定,处理有促进果实葡萄糖积累的趋势。
-
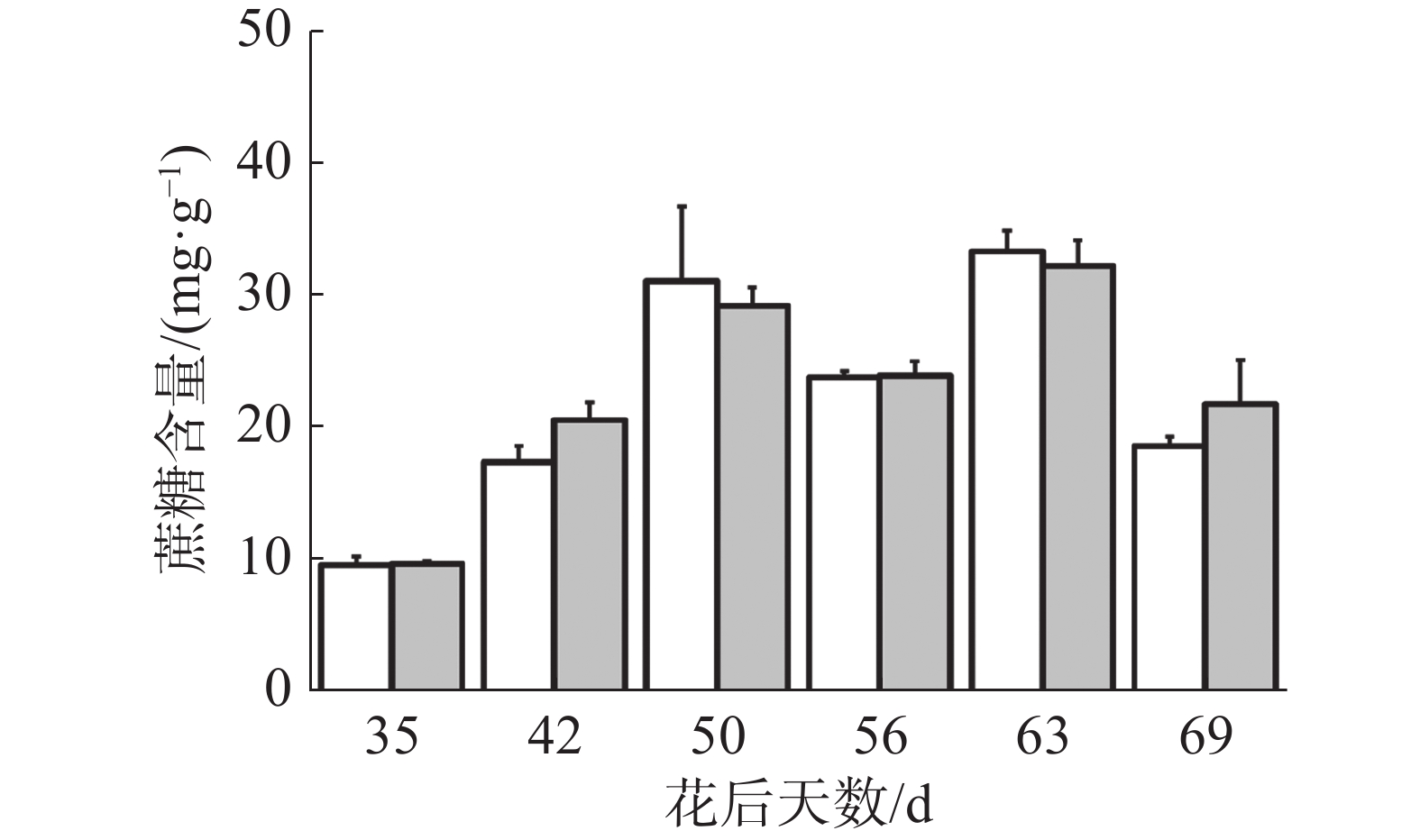
如图3所示,处理与对照果实蔗糖含量变化趋势一致,呈现在花后50 d前迅速上升、花后56 d下降、花后63 d上升及花后69 d再次下降的“M”型变化,各个时期均无显著差异,说明处理对蔗糖含量无影响。
-
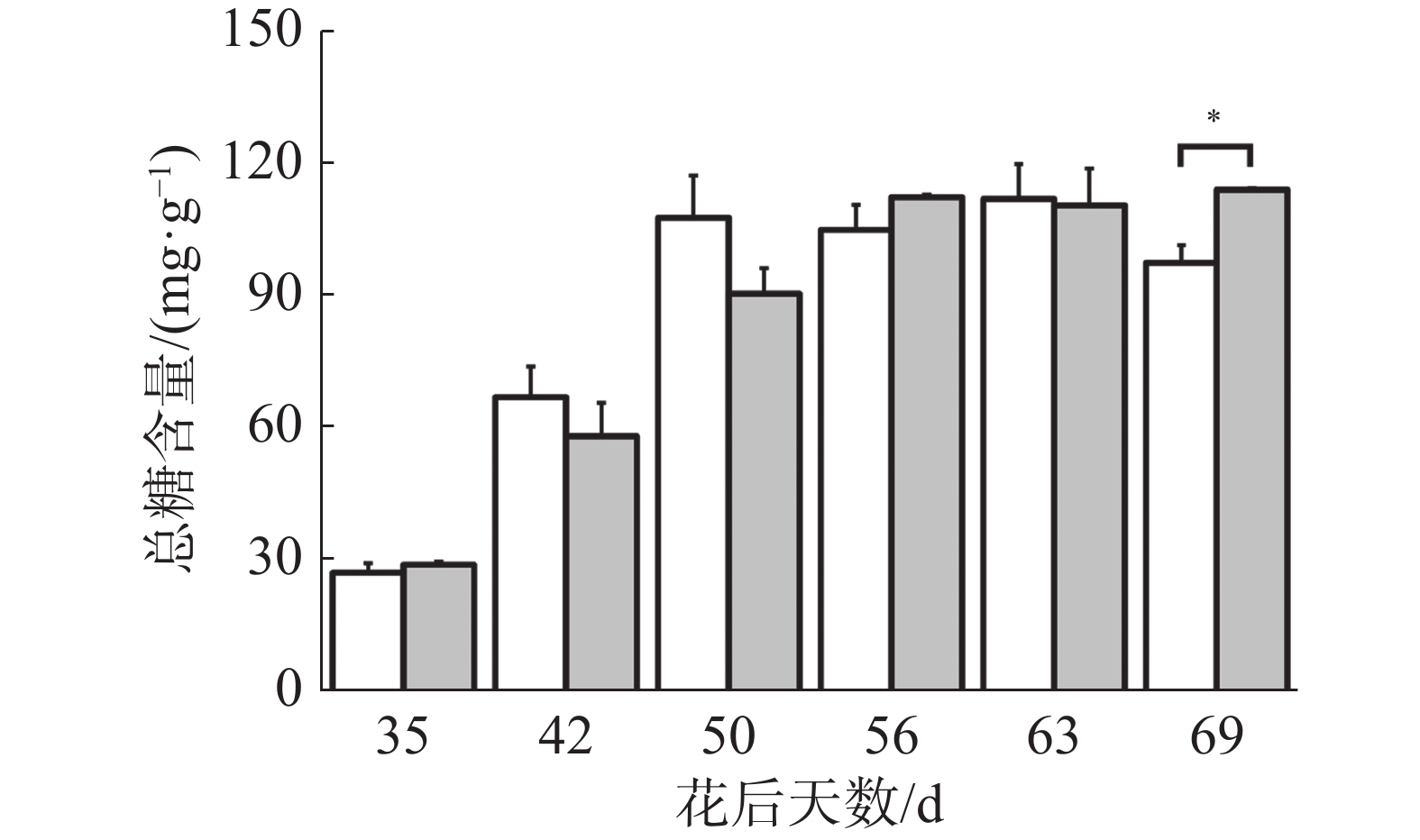
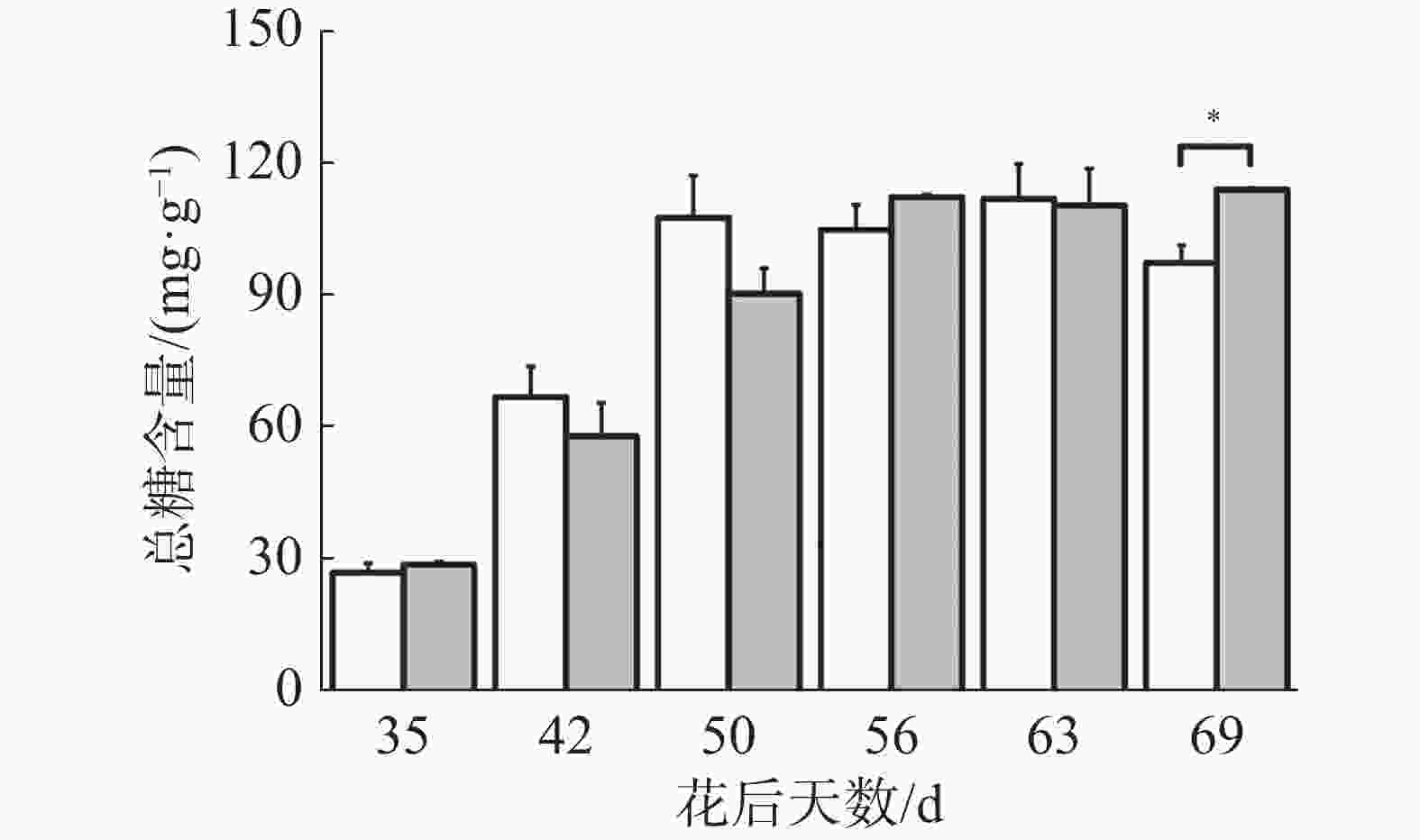
如图4所示,在花后50 d对照果实可溶性糖含量迅速上升,花后50 d至花后63 d保持稳定,花后69 d可溶性糖含量下降,出现“退糖”现象;在花后35 d至56 d处理果实可溶性糖含量迅速上升,花后56 d至69d保持稳定,其中在花后69 d处理显著高于对照,说明处理解决了“退糖”问题,其余时期均无显著差异,而花后69 d处理显著提高了果实果糖含量,可见处理主要通过提高果实果糖含量来提高可溶性糖含量。
-
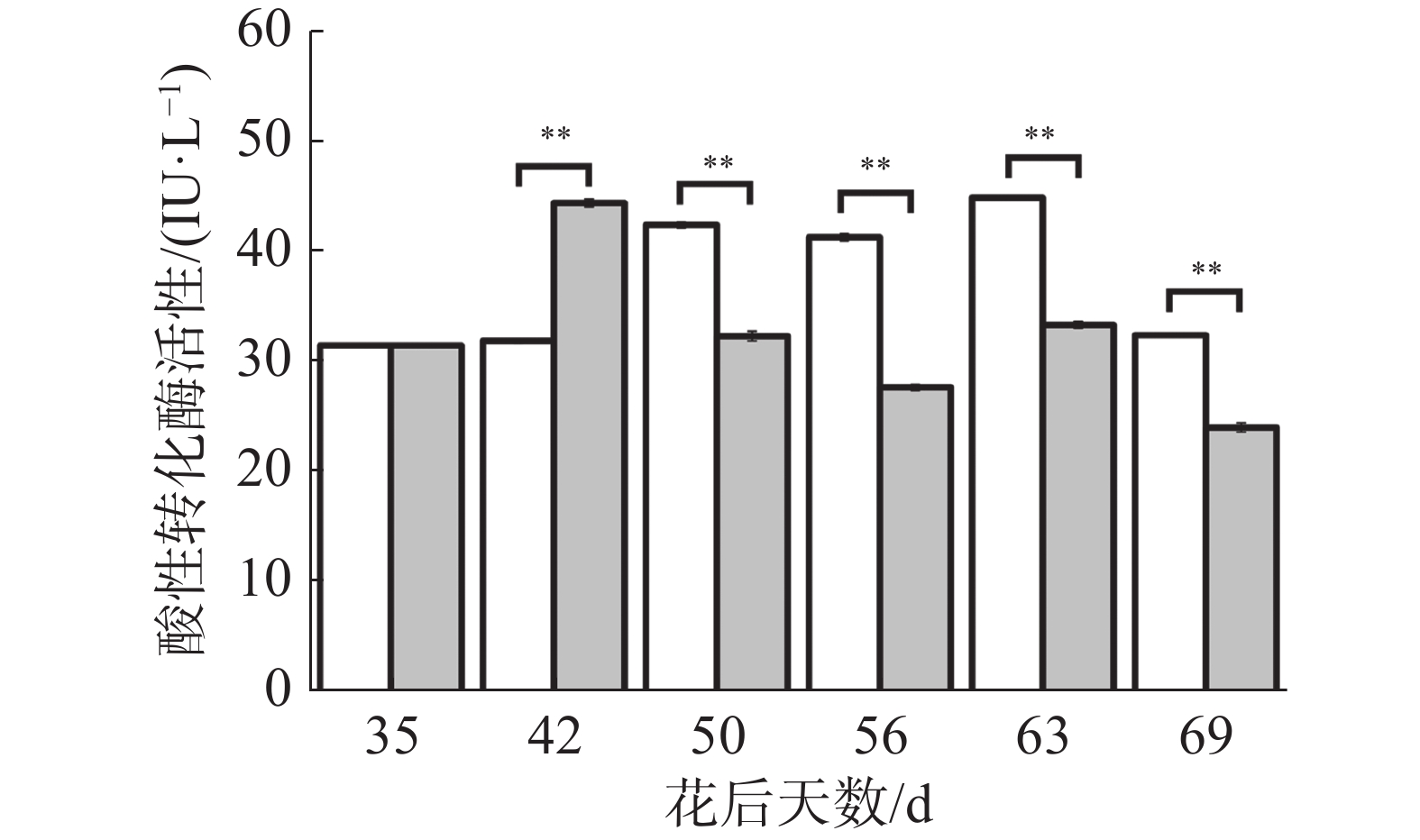
如图5所示,在花后35 d至63 d对照果实酸性转化酶活性呈上升趋势,于花后69 d下降,与其糖分含量变化较为一致;花后35 d至42 d处理果实酸性转化酶活性上升,随后大致呈现下降的趋势;在花后42 d处理极显著高于对照,花后42 d之后处理均极显著低于对照。可见处理在果实生长发育前期有提高酸性转化酶活性的趋势,中后期有降低其活性的趋势,说明花后69 d处理果实果糖、可溶性糖含量的上升可能与酸性转化酶无关。
-
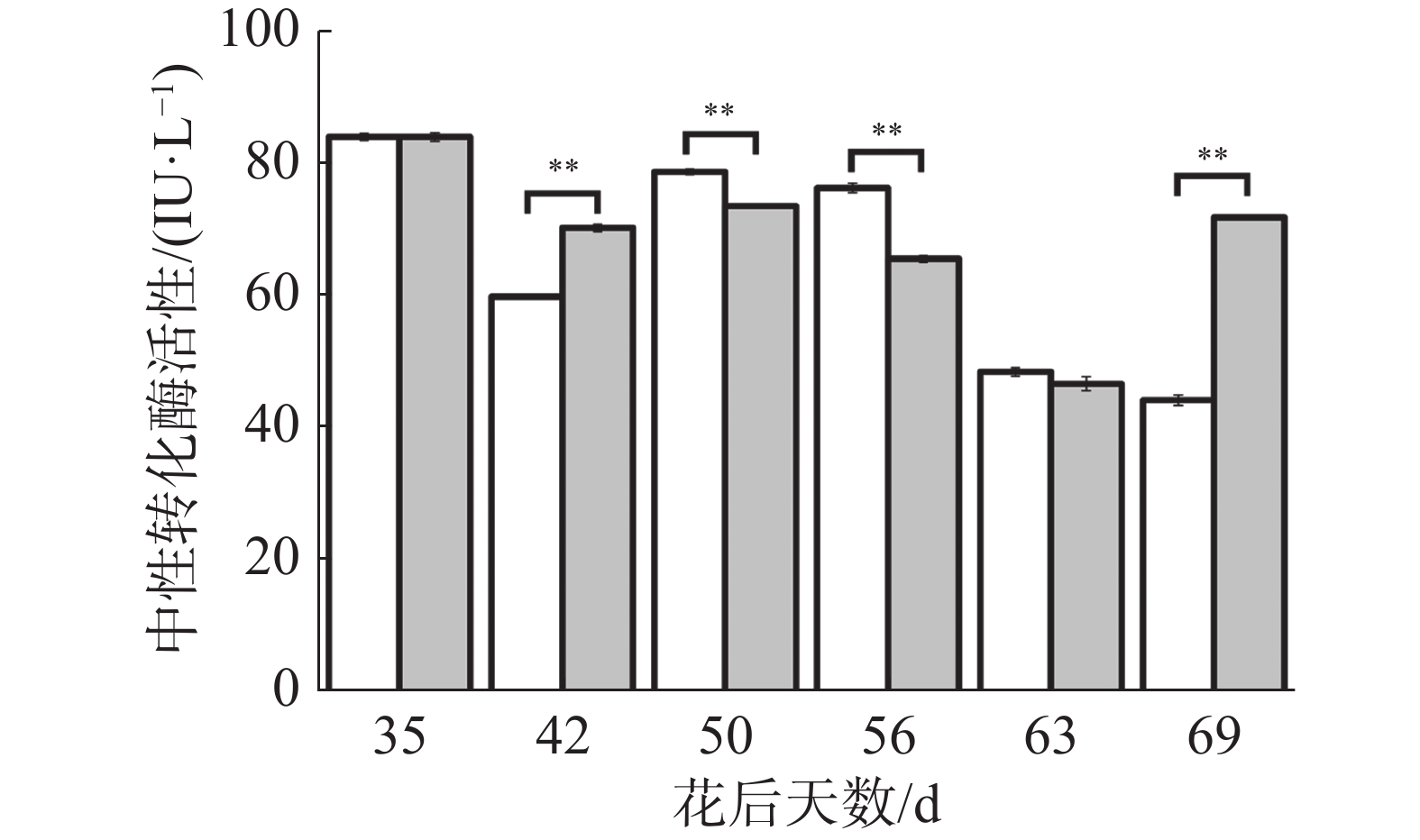
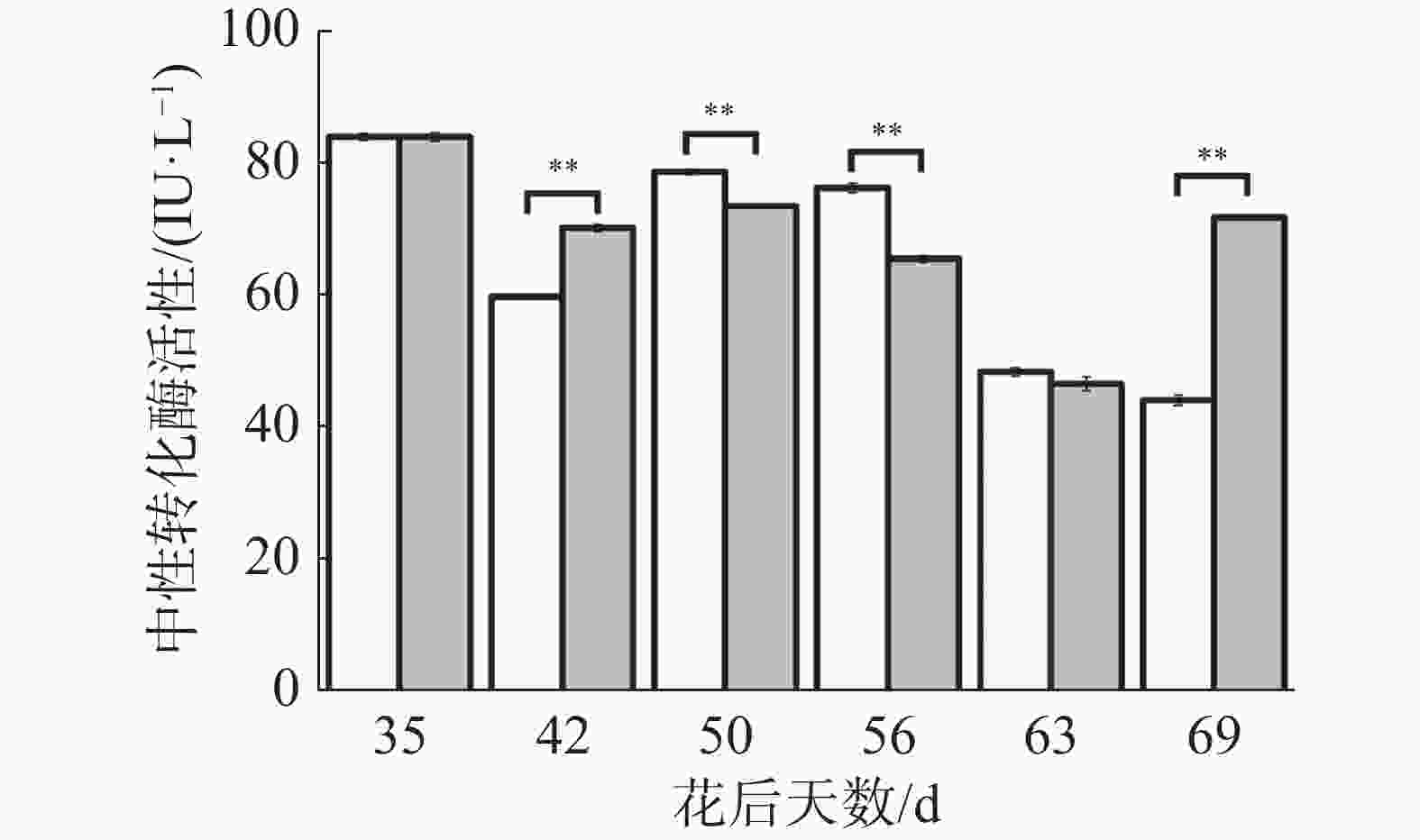
如图6所示,处理与对照果实中性转化酶活性动态变化趋势较为一致,在花后35 d至42 d下降,但处理下降幅度较小,导致处理极显著高于对照;花后42 d至50 d上升,但处理上升幅度较小,导致处理极显著低于对照;花后50 d至63 d再次下降,但处理下降幅度较大,导致花后50、56 d处理极显著低于对照;在花后69 d对照继续下降而处理上升,导致处理极显著高于对照。可见处理在果实生长发育前期有提高中性转化酶活性的趋势,中期有降低中性转化酶活性的趋势,成熟期有提高中性转化酶活性的趋势,说明花后69 d处理果实果糖、可溶性糖含量的上升可能与中性转化酶活性降低有关。
-
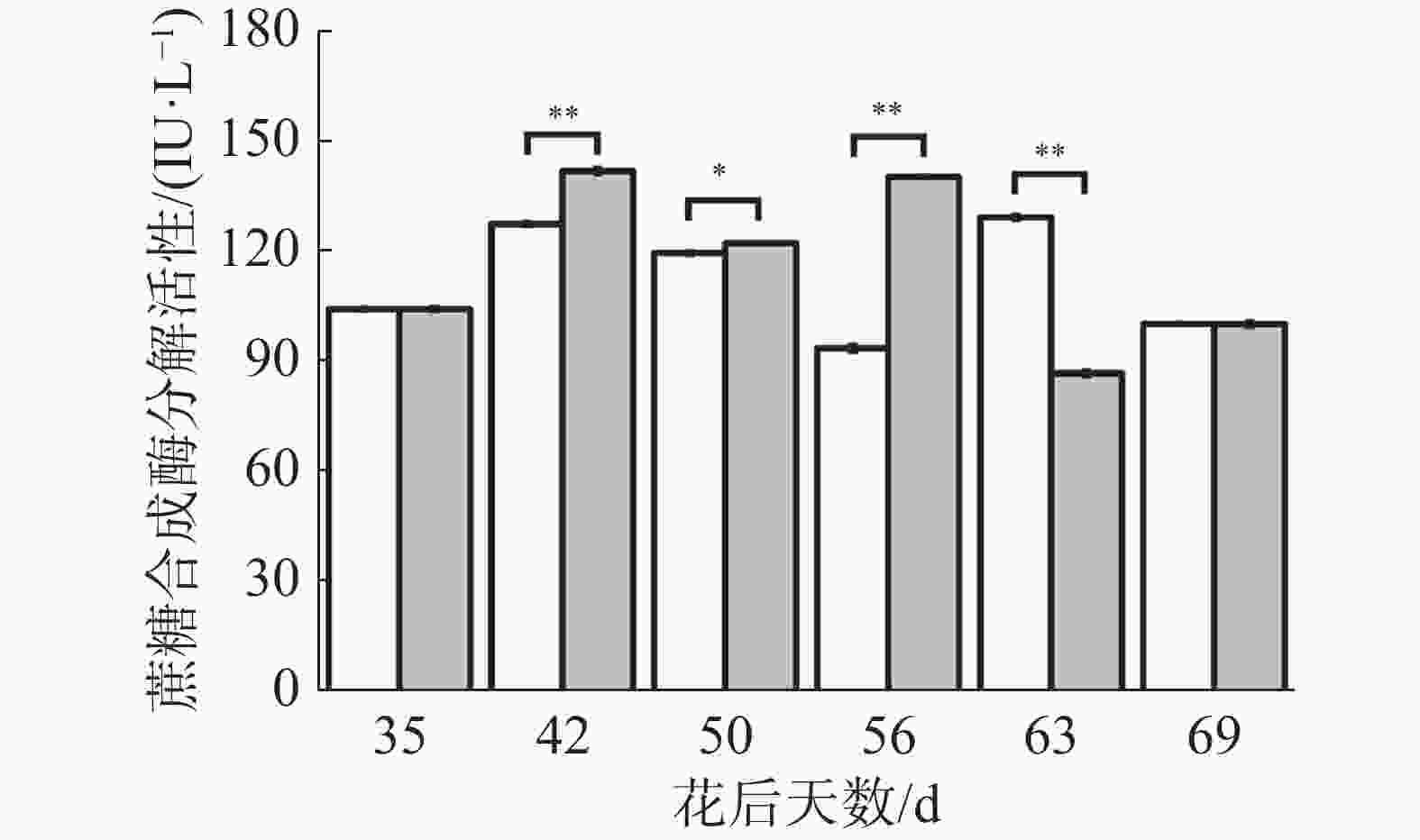
如图7所示,在花后35 d至50 d处理与对照果实蔗糖合成酶分解方向活性先上升后下降,且处理均极显著或显著高于对照;在花后56 d对照继续下降而处理上升,导致处理显著高于对照;在花后63 d对照上升而处理下降,导致处理极显著低于对照,花后69 d
处理与对照无显著差异。可见处理在果实生长发育前中期有提高蔗糖合成酶分解方向活性的趋势,在成熟期有降低其活性的趋势,花后69 d处理与对照无差异说明处理果实果糖、可溶性糖含量可能与蔗糖合成酶分解方向活性无关。
-
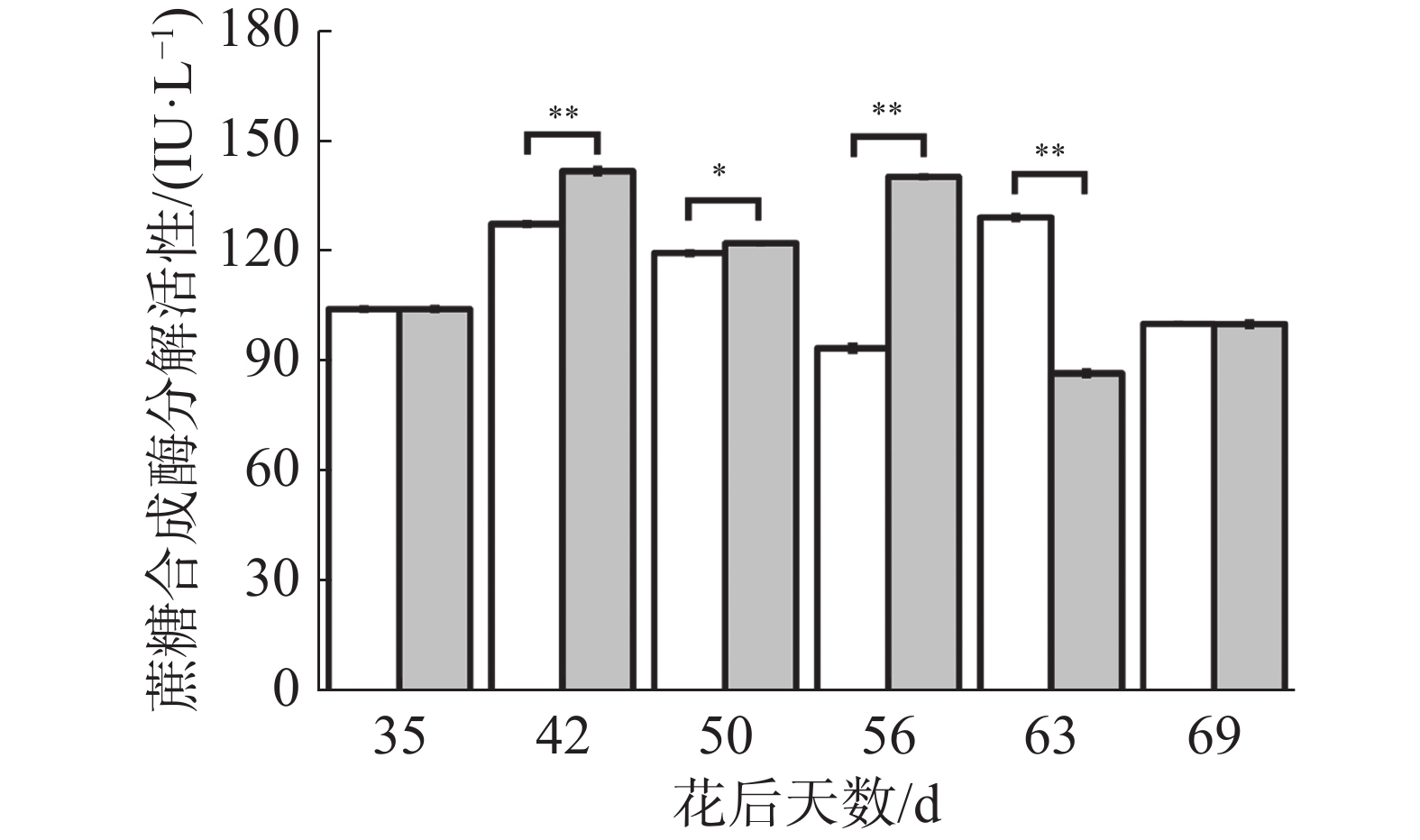
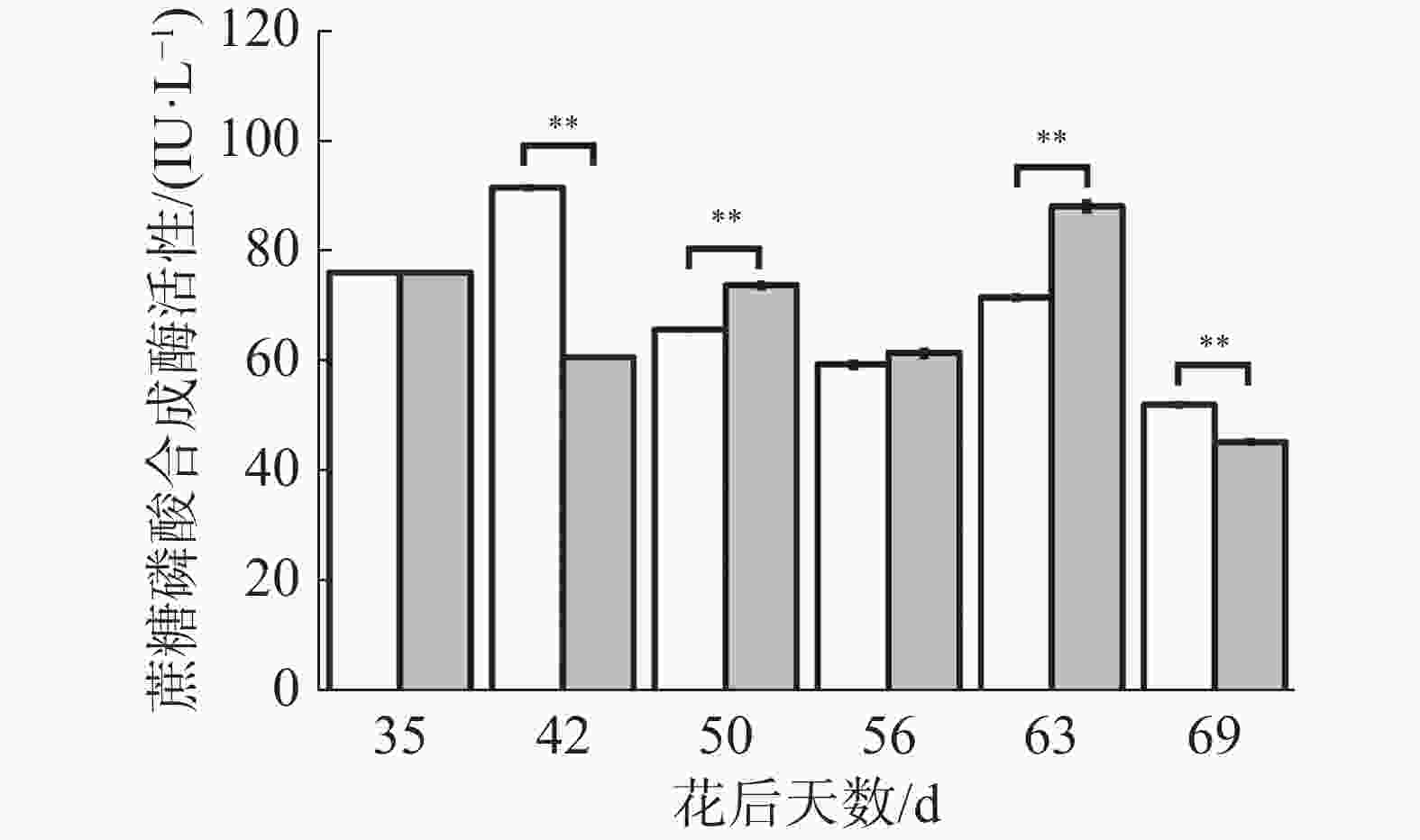
如图8所示,处理与对照蔗糖合成酶合成方向活性变化趋势基本一致,花后35 d至50 d先下降后上升,其中花后42 d处理极显著低于对照,花后50 d处理极显著高于对照;在花后42 d至56 d处理与对照先上升后保持稳定,其中花后50、56 d处理均极显著高于对照;在花后63 d处理略微上升而对照下降,导致处理显著低于对照;在花后69 d处理与对照下降,但处理下降幅度更大,导致处理极显著低于对照。可见处理在果实生长发育前期有降低蔗糖合成酶分解方向活性的趋势,在中期有提高其活性的趋势,在成熟期有降低其活性的趋势,说明花后69 d处理果实果糖、可溶性糖含量的上升可能与蔗糖合成酶合成方向活性降低有关。
-
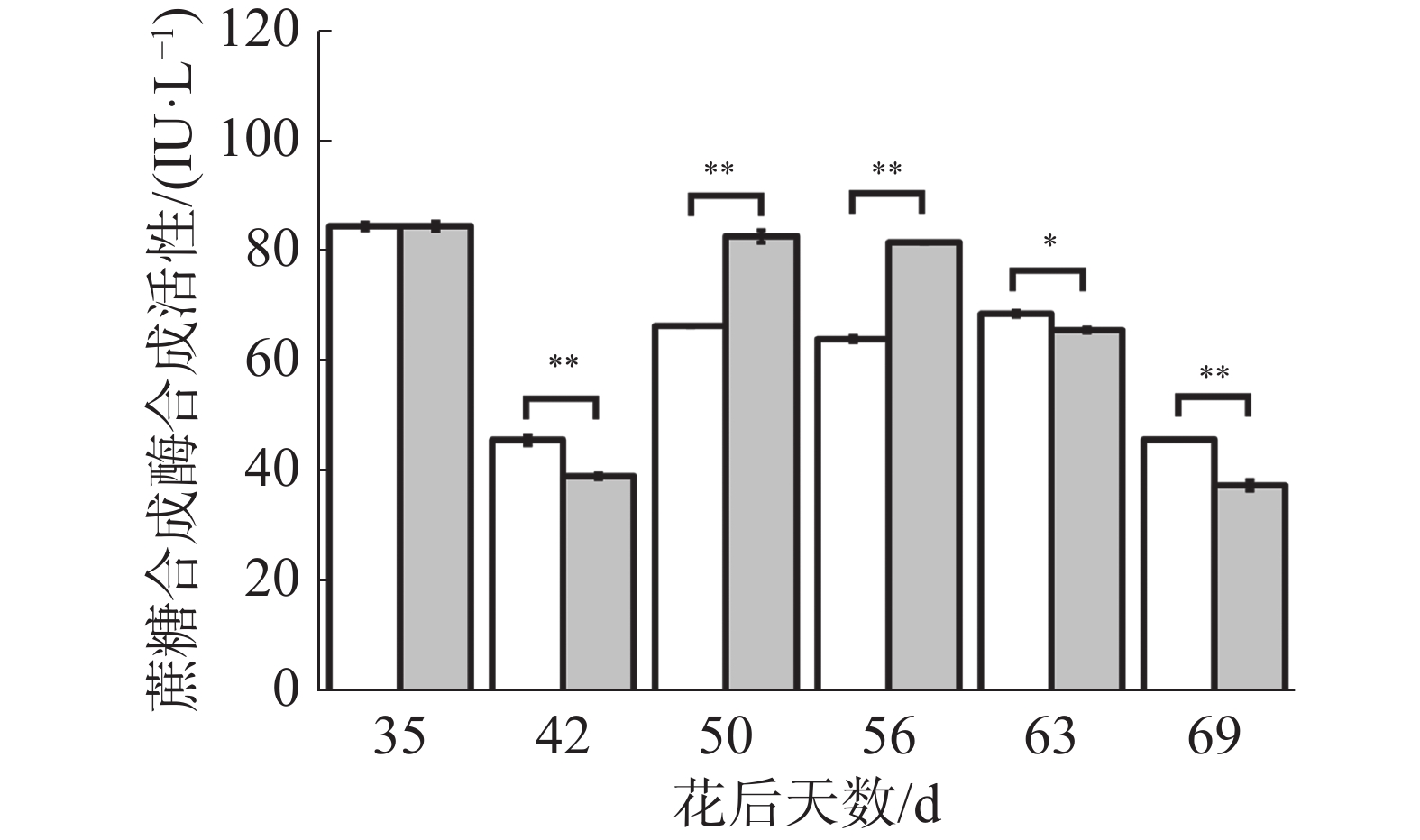
如图9所示,在花后35 d至50 d对照果实蔗糖磷酸合成酶活性先上升后下降,而处理则是先下降后上升,导致处理在花后42 d极显著低于对照,在花后50 d极显著高于对照;在花后50 d至69 d处理与对照变化趋势一致,呈现下降-上升-下降-上升的变化,其中在花后63 d处理极显著高于对照,在花后69 d处理极显著低于对照。可见处理在果实生长发育前期有降低蔗糖磷酸合成酶活性的趋势,在中后期有提高其活性的趋势,在“退糖”时有降低其活性的趋势,说明花后69 d处理果实果糖、可溶性糖含量的上升可能与蔗糖磷酸合成酶活性降低有关。
-
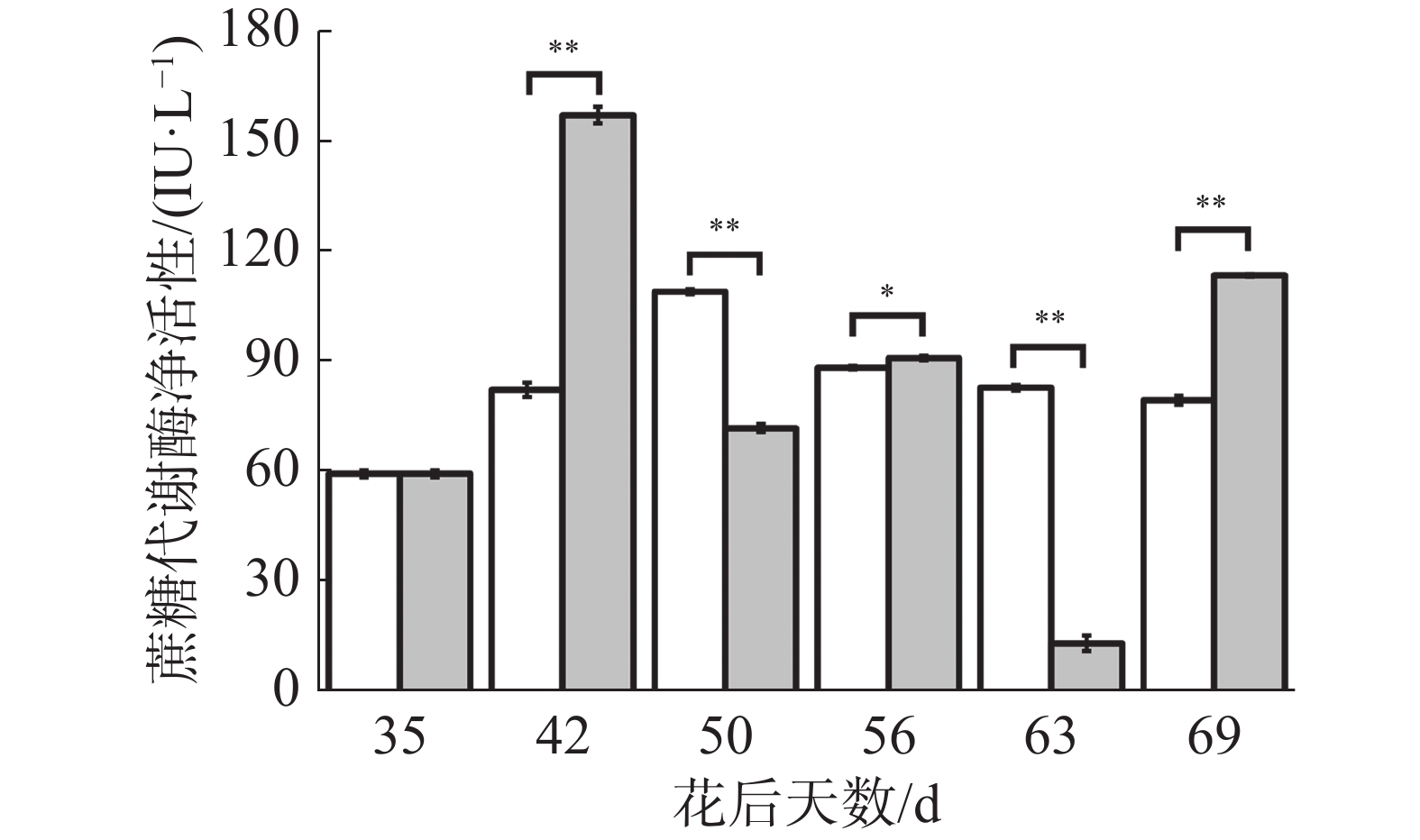
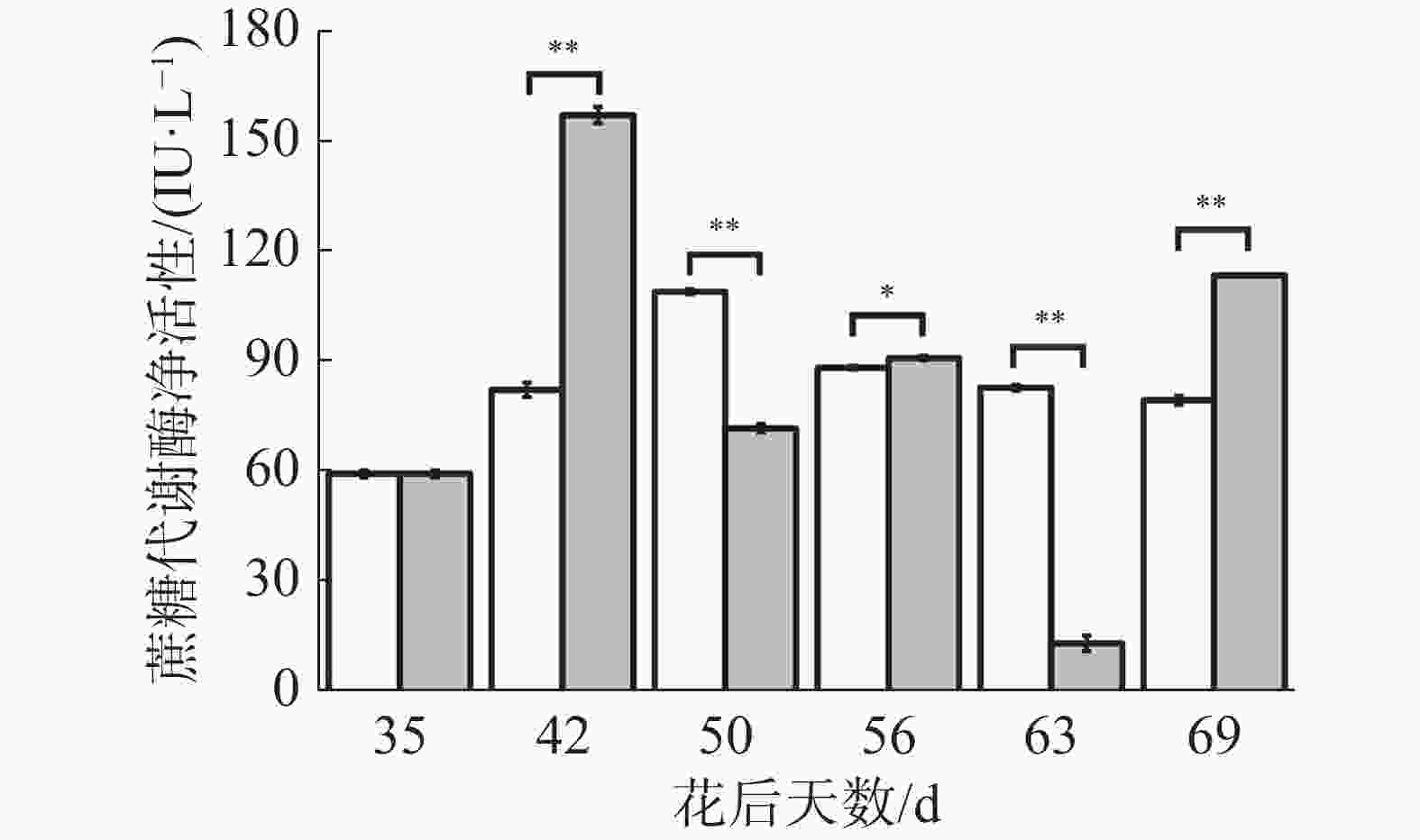
如图10所示,在花后35 d至50 d对照果实蔗糖代谢酶净活性不断上升,在花后50 d至69 d不断下降;在花后35 d至42 d处理果实蔗糖代谢酶净活性上升达到最大值,在花后42 d至69 d呈现下降−上升−下降−上升的变化趋势,其中在花后42、56、69 d处理均极显著或显著高于对照,在花后50、63 d处理均极显著低于对照。可见,处理对蔗糖代谢酶的作用很显著,在不同时期均改变了其活性大小,在“退糖”时处理显著提高其活性,这可能导致处理果实果糖、可溶性糖含量的上升。
-
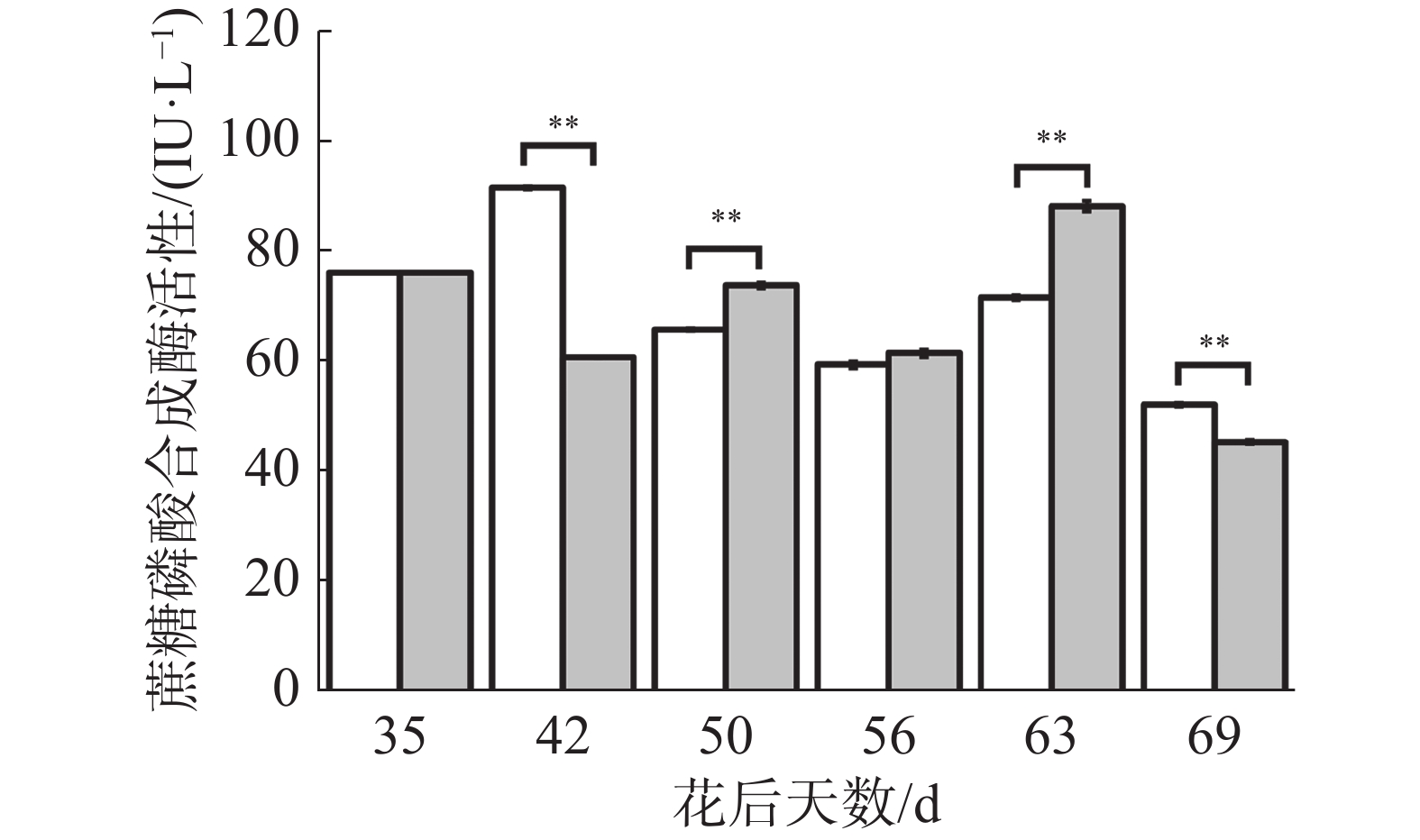
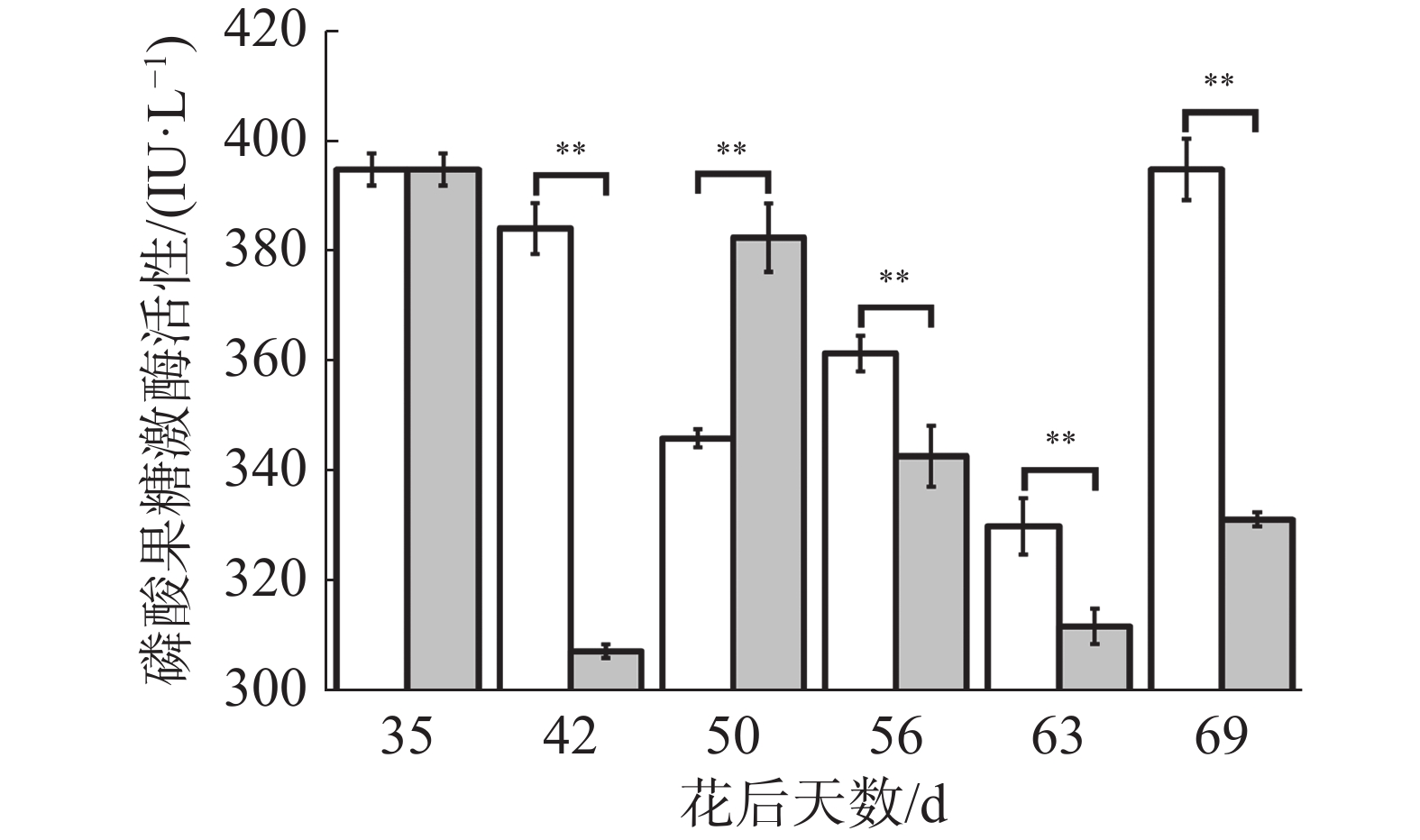
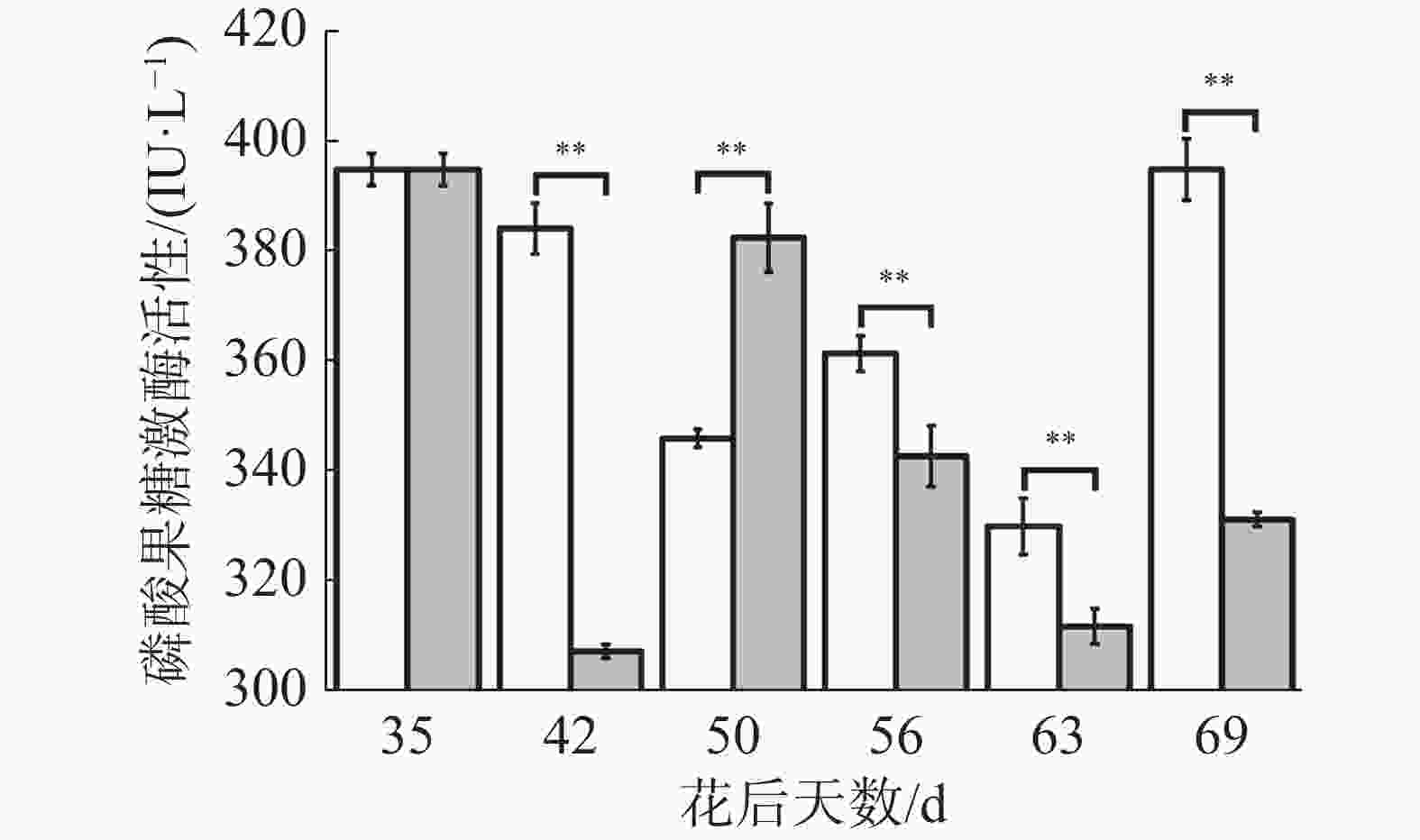
如图11所示,在花后35 d至50 d对照果实磷酸果糖激酶活性不断下降,处理果实先下降后上升,导致花后42 d处理极显著低于对照,花后50 d极显著高于对照;在花后50 d至花后69 d对照果实磷酸果糖激酶活性呈现上升-下降-上升的变化,处理呈现先不断下降最后上升的变化,导致花后56、63、69 d处理极显著低于对照。可见,处理有降低磷酸果糖激酶活性的趋势,这可能是处理解决“退糖”问题的关键。
-
钙是影响果实品质的重要元素之一,它能够维持细胞膜完整性,降低呼吸速率,延缓果实糖分的分解,保持果实硬度[24]。同时钙作为第二信使,参与调节植物的生长发育和对环境的适应[25]。有研究表明对番茄施用钙肥能够提高番茄的品质和产量[26]。也有研究表明施钙能提高花生的光合特性,从而实现增产[27]。果实中钙含量的增加有利于碳水化合物通过韧皮部运输到储存器官,从而可以有效地增加果实的糖含量[28]。叶片的光合效率也关系到果实糖含量,叶片中镁参与蛋白质的合成,35%的镁存在于叶绿体中,镁缺乏会导致叶绿素含量降低,减少植物中光合产物的积累,抑制碳水化合物的合成和运输[29],所以叶面喷施钙镁肥有可能促进叶绿体的形成导致光合作用加强,导致更多的光合同化物运送到果实中。本研究通过叶面喷施钙镁肥,果实果糖含量显著升高,从而提高了果实糖含量。前人也有相似的结果,在柑橘园施用石灰和镁提高了柑橘产量及品质,果实可溶性固形物含量提高[30],而石灰的主要成分就是钙[31]。
本研究发现在果实发育前期处理与对照果实己糖含量迅速升高,蔗糖代谢酶的净活性也快速升高;在花后69 d,处理显著地提高了中性转化酶活性,同时降低了酸性转化酶、蔗糖磷酸合成酶和蔗糖合成酶合成方向活性,从而提高了蔗糖代谢酶净活性,进而促进蔗糖的分解,导致果糖含量显著上升。蔗糖代谢酶净活性是这些酶综合作用的体现,通过比较分解与合成蔗糖的酶活性来判断蔗糖分解与合成的速率[32],一般而言己糖积累型果实有着更高的分解蔗糖的酶活性[33],上述结果也印证了这一点。葡萄糖是大多数植物首选的主要的碳和能量来源[34-35],它比果糖更易进入果实的代谢过程[36],这可能是处理果实果糖含量显著的升高而葡萄糖含量无显著变化的原因。前人研究表明低温降低了土豆块茎磷酸果糖激酶的活性导致糖酵解途径被抑制,使磷酸己糖积累,最终促进糖含量的上升[37]。本研究叶面钙镁肥处理使果实磷酸果糖激酶活性在“退糖”期显著降低,从而抑制了糖酵解途径,导致可溶性糖含量的上升。
总之,本研究通过叶面喷施钙镁肥提高中性转化酶活性、降低蔗糖磷酸合成酶和蔗糖合成酶合成活性来提高蔗糖代谢酶净活性,促进蔗糖的分解,而叶面钙镁肥可能促进叶片的光合作用导致更多的光合产物进入果实,使得处理与对照果实蔗糖含量最终无显著变化,同时降低磷酸果糖激酶活性抑制糖酵解途径,从而引起果糖和可溶性糖积累,进而解决了‘妃子笑’荔枝成熟期“退糖”的问题。
致谢:热带作物新品种选育教育部工程研究中心对本研究给予了大力支持。
Effect of calcium and magnesium foliar fertilizer on sugar contents and sugar metabolizing enzyme activities in 'Feizixiao' litchi pulp
DOI: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230033
- Received Date: 2023-03-10
- Accepted Date: 2023-05-11
- Rev Recd Date: 2023-05-03
- Available Online: 2023-12-07
- Publish Date: 2024-03-25
-
Key words:
- calcium and magnesium fertilizer /
- litchi /
- sugar /
- sucrose metabolizing enzyme
Abstract: In order to explore the reason why the "sugar receding" problem of 'Feizixiao' litchi fruit can be solved by the foliar nutrient of calcium and magnesium, the 16-year-old 'Feizixiao' litchi trees were taken as the experimental material, sprayed 0.3% CaCl2+0.3% MgCl2 mixed water solution on the leaf surface as the treatment, and sprayed water as the control, and the sugar contents and sugar metabolism enzyme activities of the fruit were determined. The results showed that fructose, glucose and sucrose accumulated rapidly in the early and middle stages of fruit growth and development, and the contents of fructose and glucose in the control fruit remained stable in the mature stage, while the contents of sucrose and soluble sugar decreased. The contents of fructose and total sugar in the fruit of the treatment were significantly higher than that of the control at 69 days after anthesis. The treatment significantly changed the activities of sugar metabolizing enzymes. At 69 days after anthesis, the treatment significantly increased the activities of neutral invertase and net activities of sucrose metabolizing enzymes, while the activities of acid invertase, sucrose phosphate synthase, sucrose synthase synthesis direction and phosphofructokinase significantly decreased. In summary, calcium and magnesium foliar fertilizer treatment enhances the net activities of sucrose metabolizing enzymes by increasing the activity of neutral invertase, reducing the activities of sucrose phosphate synthase and sucrose synthase synthesis, promoting sucrose decomposition, and reducing the activity of phosphofructokinase to inhibit glycolysis pathways, thereby causing the accumulation of fructose and soluble sugars, solving the problem of "sugar receding" during the mature stage of 'Feizixiao' litchi.
| Citation: | PENG Junjie, DU Jingjia, MA Wuqiang, CHEN Tiantian, SHUI Xian, ZHOU Kaibing. Effect of calcium and magnesium foliar fertilizer on sugar contents and sugar metabolizing enzyme activities in 'Feizixiao' litchi pulp[J]. Journal of Tropical Biology, 2024, 15(2): 217-223. doi: 10.15886/j.cnki.rdswxb.20230033 |









 DownLoad:
DownLoad: